Tailoring Mechanical Properties of Al-Cr-Cu-Fe-Mn-Ni Complex Concentrated Alloys Prepared Using Pressureless Sintering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Thermodynamic Calculations
2.2. Sample Preparation
3. Results and Discussion
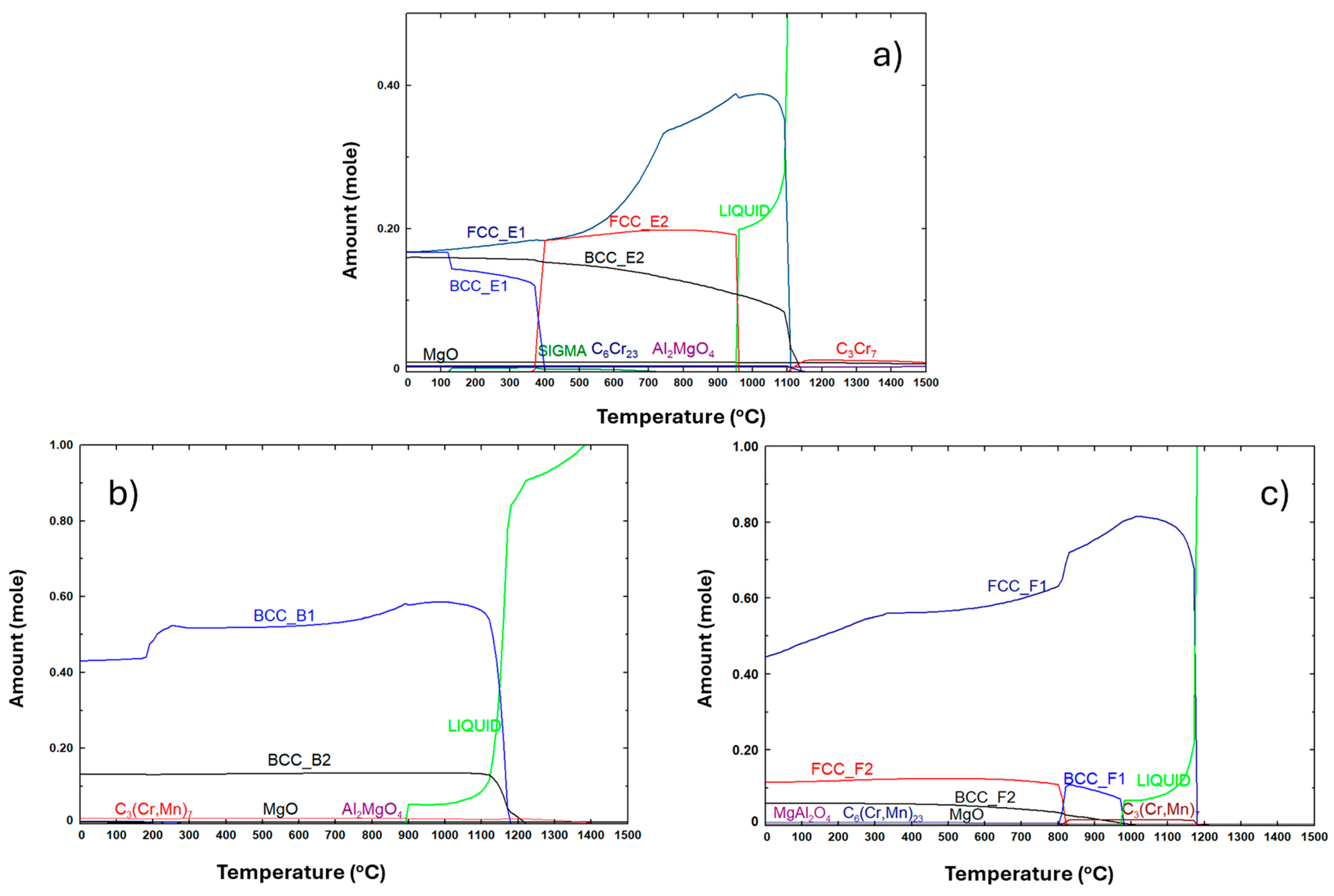
3.1. Thermodynamic Calculations
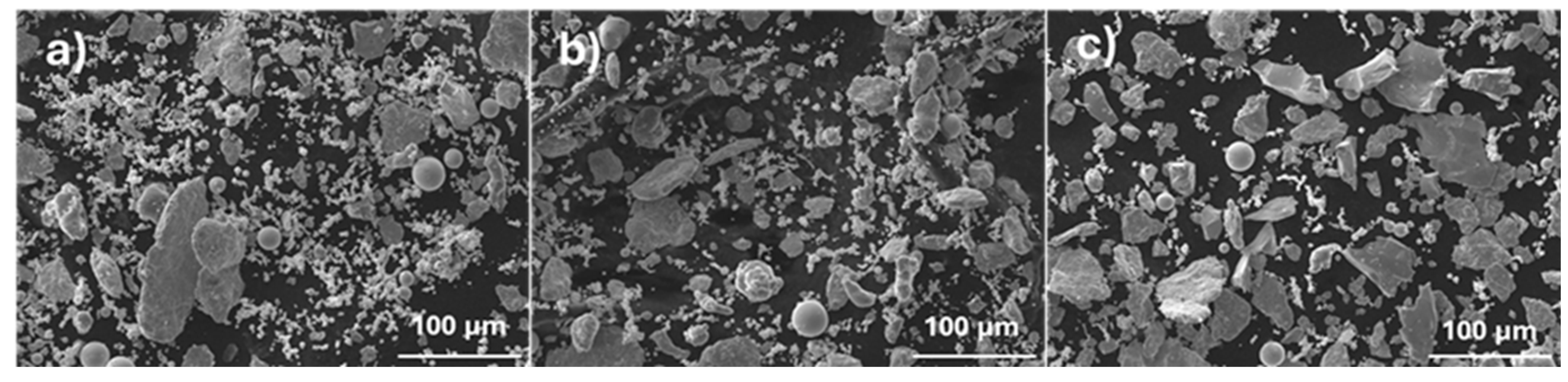
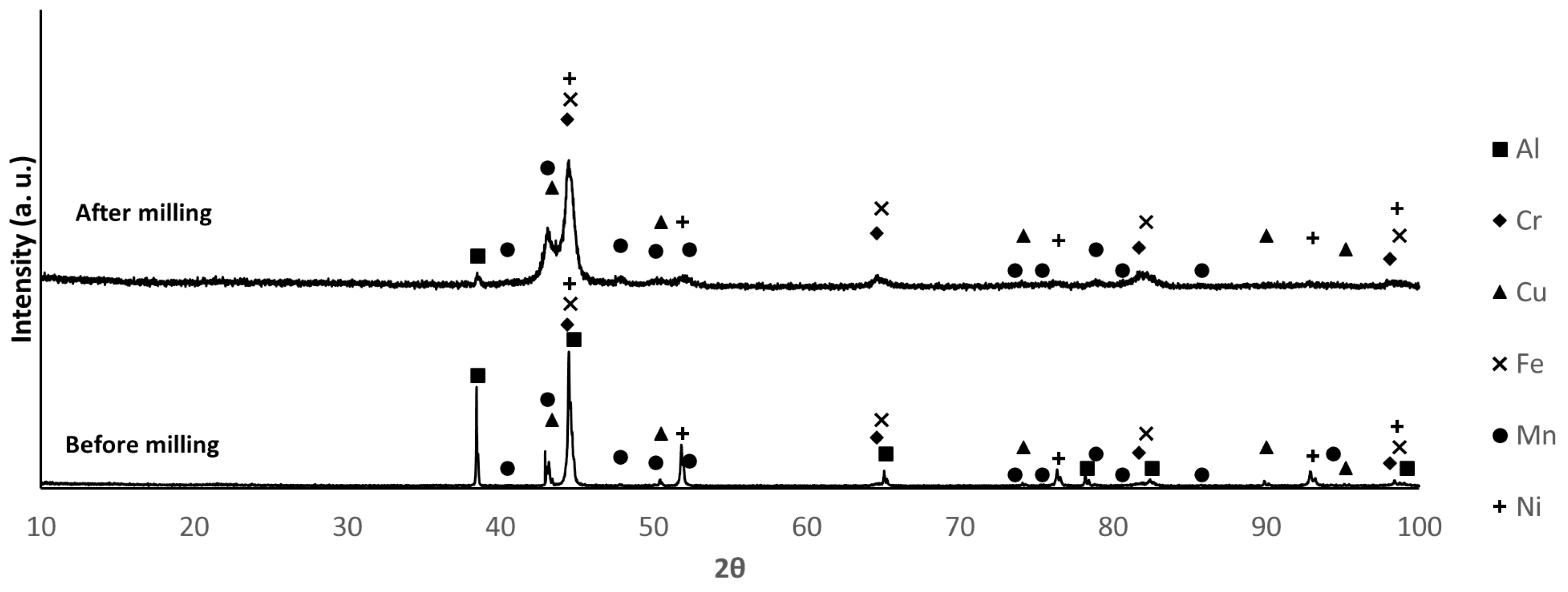
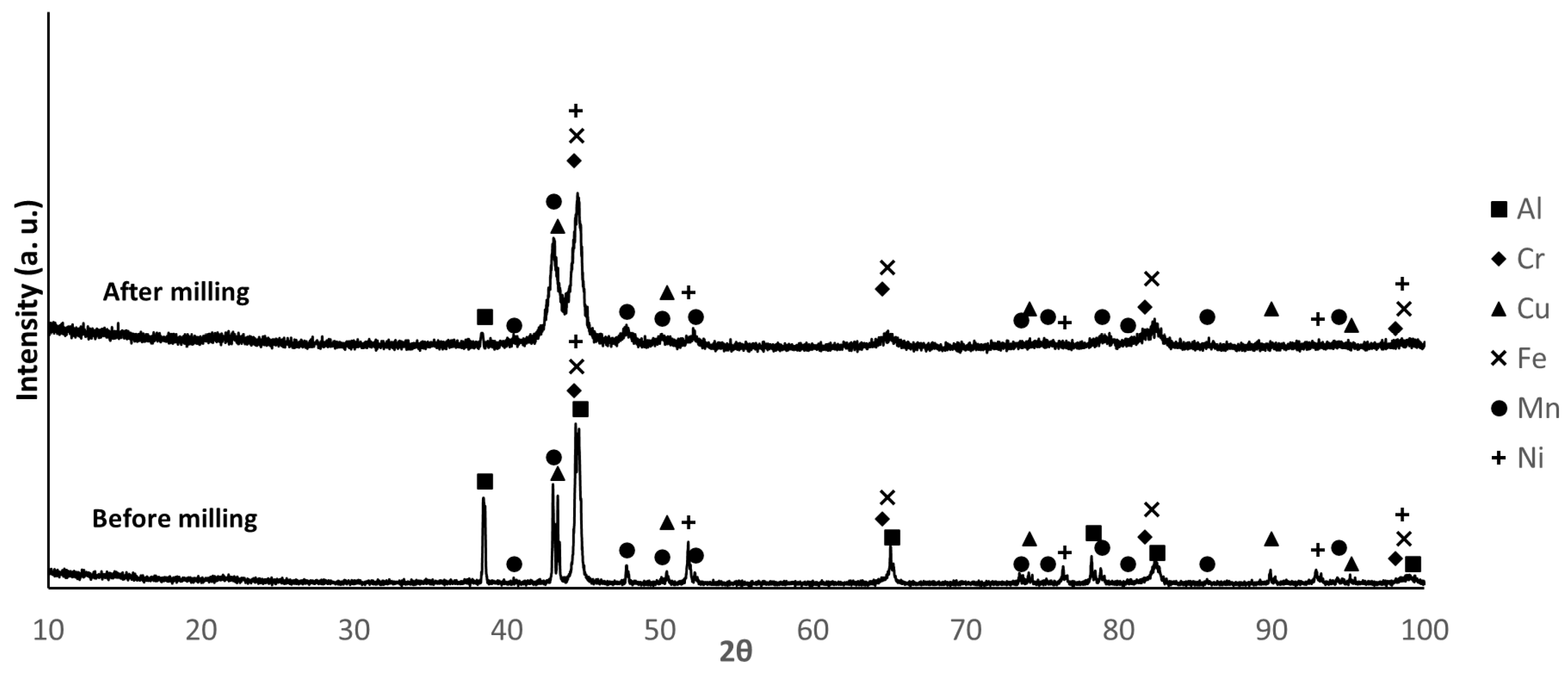
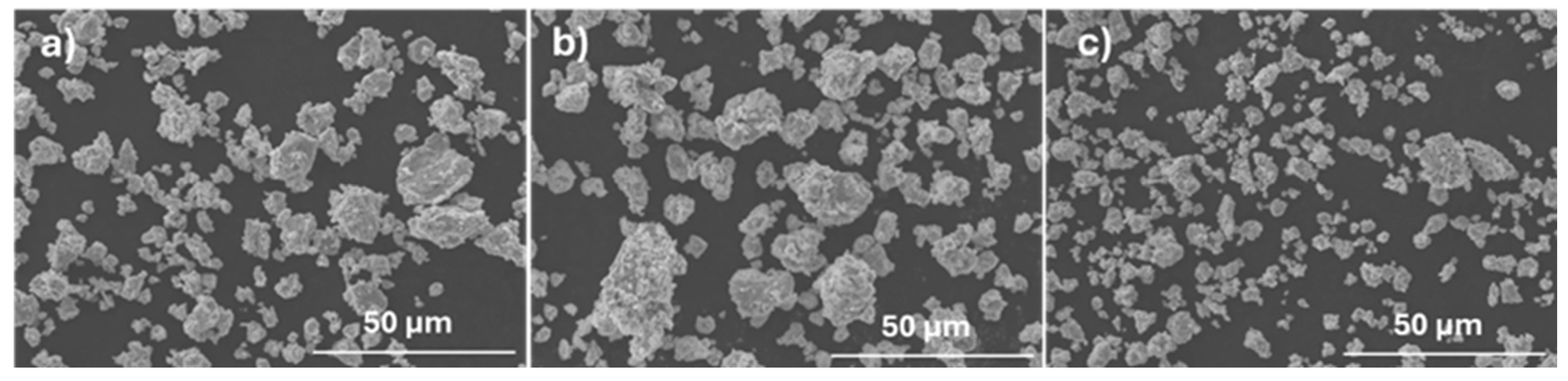
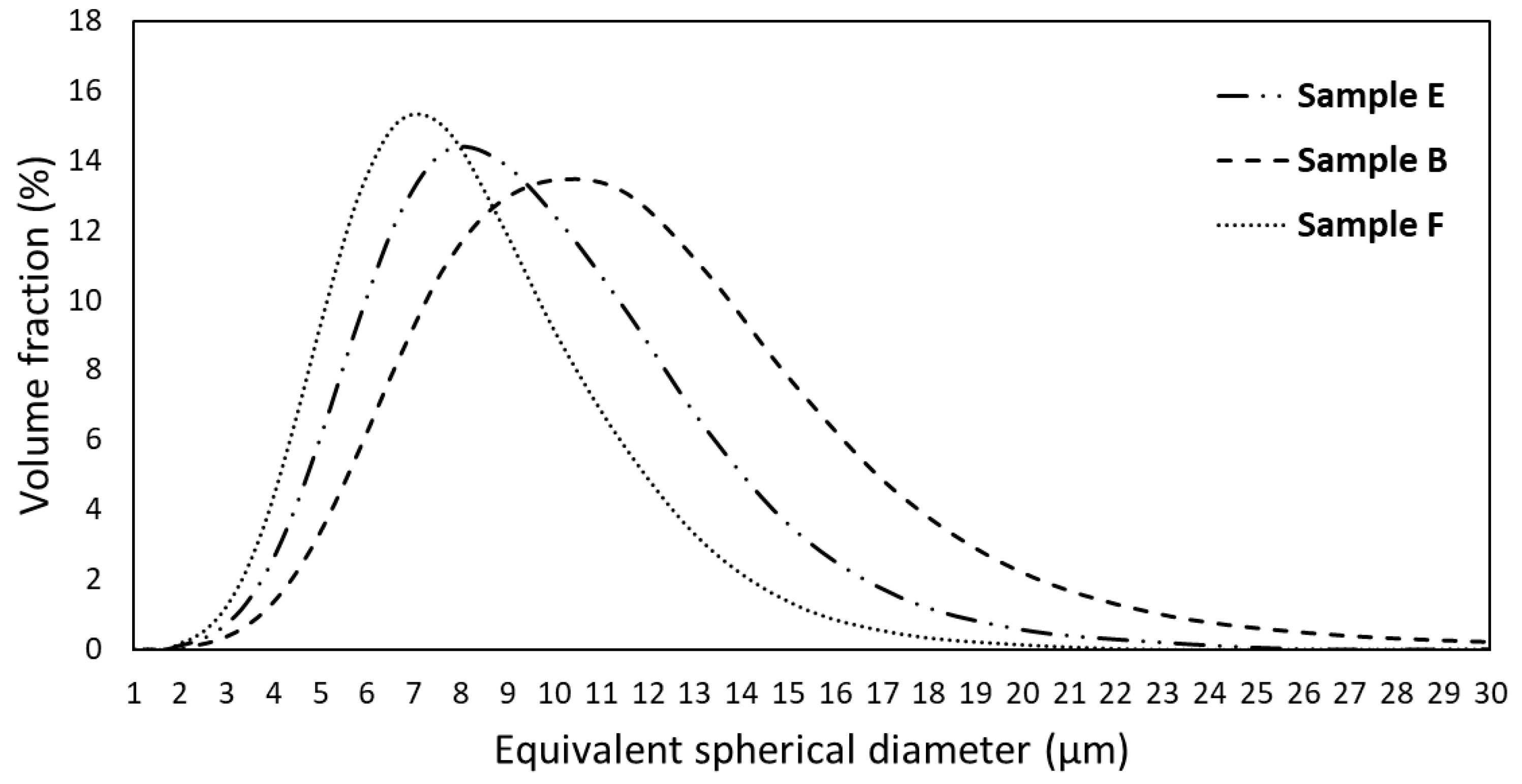
3.2. Powder Characterization
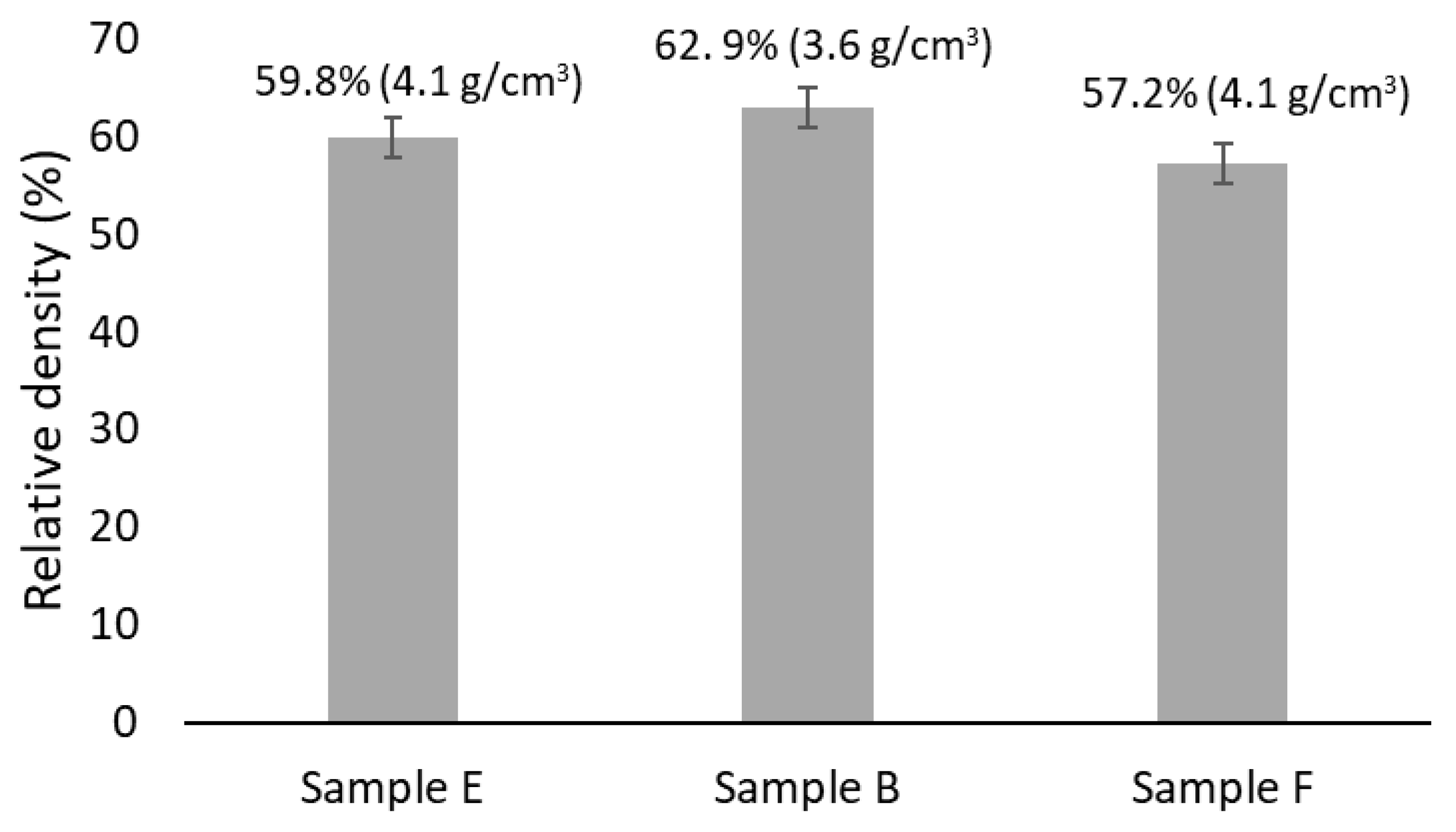
3.3. Sample Characterization After Sintering
4. Conclusions
- -
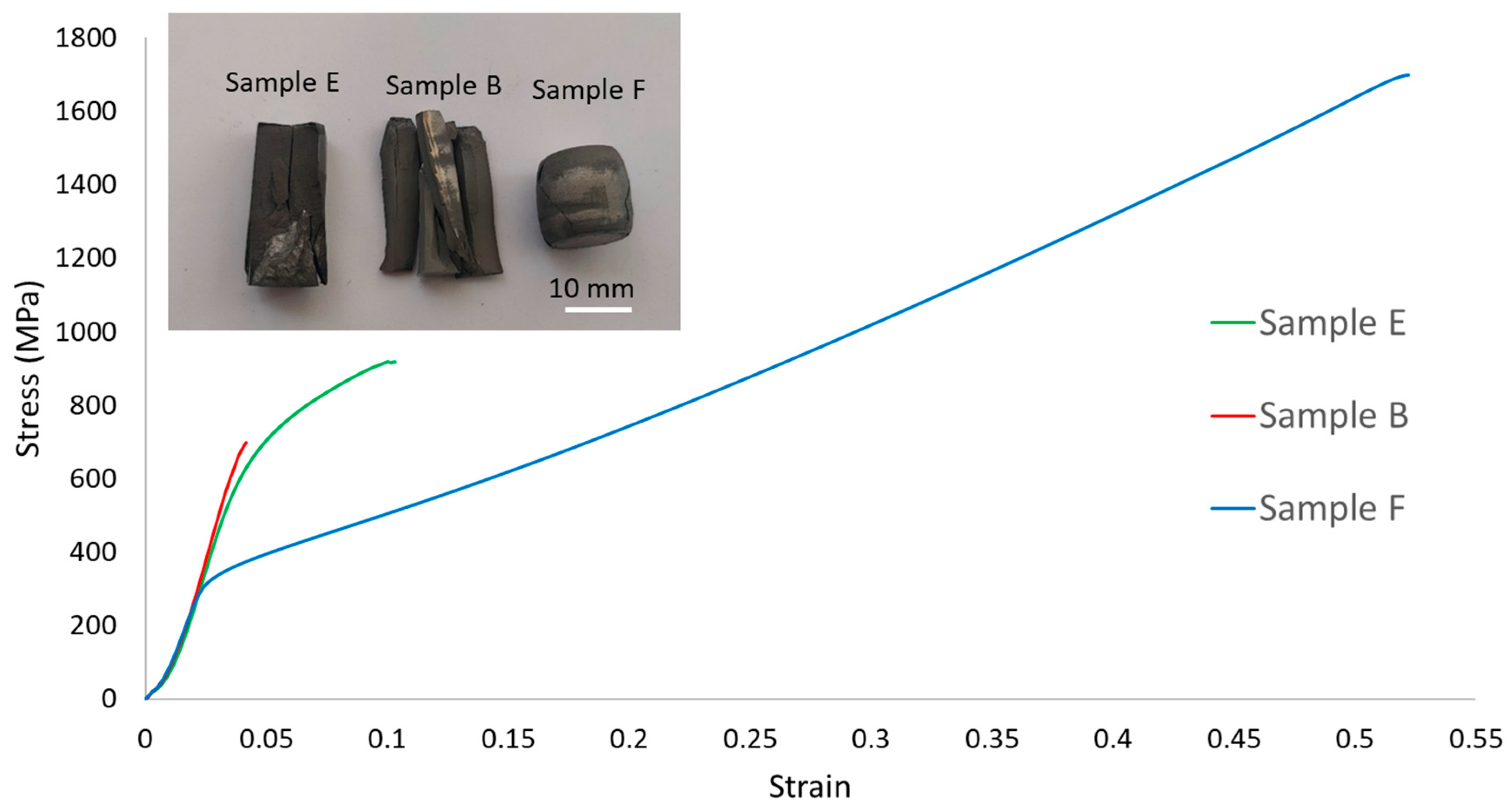
- Samples B showed the highest yield stress (approximately 700 MPa) and hardness (367 HV2) values but almost no ductility, failing shortly after the elastic domain.
- -
- In contrast, samples F exhibited the lowest yield stress (approximately 300 MPa) and hardness (211 HV2) values but the highest ductility, reaching a plastic strain of around 0.43.
- -
- Samples E, containing both BCC and FCC phases, showed yield stress (650 MPa), hardness (357 HV2) and maximum plastic strain (0.05) values between those exhibited by samples B and F.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCAs | Complex Concentrated alloys |
| BCC | Body-centred cubic |
| FCC | Face-centred cubic |
| MADS | Mesh Adaptive Direct Search |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission Electron Microscopy |
| EBSD | Electron Backscatter Diffraction |
| EDS | Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy |
References
- Gao, M.C.; Yeh, J.W.; Liaw, P.K.; Zhang, Y. High-Entropy Alloys-Fundamentals and Applications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–115. [Google Scholar]
- Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. A critical review of high entropy alloys and related concepts. Acta Mater. 2017, 122, 448–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsse, S.; Miracle, D.B.; Senkov, O.N. Mapping the world of complex concentrated alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 135, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsse, S.; Couzinié, J.; Miracle, D.B. From high-entropy alloys to complex concentrated alloys. C. R. Phys. 2018, 19, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Tsai, C.W.; Tung, C.C.; Yeh, J.W.; Shun, T.T.; Yang, C.C.; Chen, S.K. Effect of the substitution of Co by Mn in Al-Cr-Cu-Fe-Co-Ni high-entropy alloys. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat. 2006, 31, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soare, V.; Mitrica, D.; Constantin, I.; Popescu, G.; Csaki, I.; Tarcolea, M.; Carcea, I. The Mechanical and corrosion behaviors of as-cast and re-melted AlCrCuFeMnNi multi-component high-entropy alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2015, 46, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.; Lopes, A. Microstructural characterization of AlCrCuFeMnNi complex concentrated alloy prepared by pressureless sintering. Materials 2024, 17, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.; Simões, P.; Lopes, A. Hot uniaxial pressing and pressureless sintering of AlCrCuFeMnNi complex concentrated alloy—A comparative study. Materials 2024, 17, 5457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, T.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Hui, X. Microstructure, mechanical properties, and oxidation behavior of AlxCr0.4CuFe0.4MnNi high entropy alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2017, 19, 1600726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Huang, M.; Li, H.; Hong, L.; Yang, S. Effect of Al content on microstructure and mechanical properties of as-cast AlxFeMnNiCrCu0.5 high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 832, 142495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Liu, W.H.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Nieh, T.G.; Lu, Z.P. Effects of Al addition on structural evolution and tensile properties of the FeCoNiCrMn high-entropy alloy system. Acta Mater. 2014, 62, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.H.; Wang, L.; Si, J.J.; Wu, Y.D.; Hui, X.D. Affordable FeCrNiMnCu high entropy alloys with excellent comprehensive tensile properties. Intermetallics 2016, 77, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrica, D.; Olaru, M.T.; Dragut, V.; Predescu, C.; Berbecaru, A.; Ghita, M.; Carcea, I.; Burada, M.; Dumitrescu, D.; Serban, B.A.; et al. Influence of composition and as-cast structure on the mechanical properties of selected high entropy alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 242, 122555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murty, B.S.; Yeh, J.W.; Ranganathan, S. High-Entropy Alloys; Elsevier Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, A.; Suhane, A. Mechanically alloyed high entropy alloys: Existing challenges and opportunities. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 2431–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Kumar, S.; Mallick, A. Light weight MnTiAlNiFe high-entropy alloy (LWHEA) fabricated by powder metallurgy process: Mechanical, microstructure, and tribological properties. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Alam, S.N.; Ray, B.C. Fundamentals of Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS): An Ideal Processing Technique for Fabrication of Metal Matrix Nanocomposites; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez, M.; Fernández, A.; Menéndez, J.L.; Torrecillas, R.; Kessel, H.U.; Hennicke, J.; Kirchner, R.; Kessel, T. Challenges and Opportunities for Spark Plasma Sintering: A Key Technology Form a New Generation of Materials; INTECH Open Access Publisher: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Dong, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Q. Sintering, microstructure, and mechanical properties of TiTaNbZrHf high-entropy alloys prepared by cold isostatic pressing and pressure-less sintering of hydrides. Materials 2023, 16, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuan, Z.; Fan, Z.; Shuanglin, C.; Weisheng, C. Computational thermodynamics aided high-entropy alloy design. JOM 2012, 64, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xie, L.; Wang, W.Y.; Liaw, P.; Zhang, Y. High-throughput calculations for high-entropy alloys: A brief review. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazuddin; Gurao, N.P.; Krishanu, B. In the quest of single phase multi-component multiprincipal high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 697, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimen, E.G.; Christian, R.; Sébastien, L.D.; Charles, A.; Arthur, D.P. Calculating all local minima on liquidus surfaces using the FactSage software and databases and the mesh adaptive direct search algorithm. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2011, 43, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheribi, A.E.; Audet, C.; Digabel, S.L.; Bélisle, E.; Bale, C.W.; Pelton, A.D. Calculating optimal conditions for alloy and process design using thermodynamic and property databases, the FactSage software and the mesh adaptive direct search algorithm. Calphad 2012, 36, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheribi, A.E.; Pelton, A.D.; Bélisle, E.; Digabel, S.L.; Harvey, J.P. On the prediction of low-cost high entropy alloys using new thermodynamic multi-objective criteria. Acta Mater. 2018, 161, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, C.W.; Bélisle, E.; Chartrand, P.; Decterov, S.A.; Eriksson, G.; Gheribi, A.E.; Hack, K.; Jung, I.H.; Kang, Y.B.; Melançon, J.; et al. FactSage Thermochemical Software and Databases, 2010–2016. Calphad 2016, 54, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powder Diffraction File (PDF) Database 2024; International Centre for Diffraction Data: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2024.
- German, R.M.; Suri, P.; Park, S.J. Review: Liquid phase sintering. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Ronghui, P.; Hanbing, C.; Yulong, R.; Jun, T. Optimization of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloys Through Multiple Remelting and Heat Treatment Cycles. Metals 2025, 15, 234. [Google Scholar]
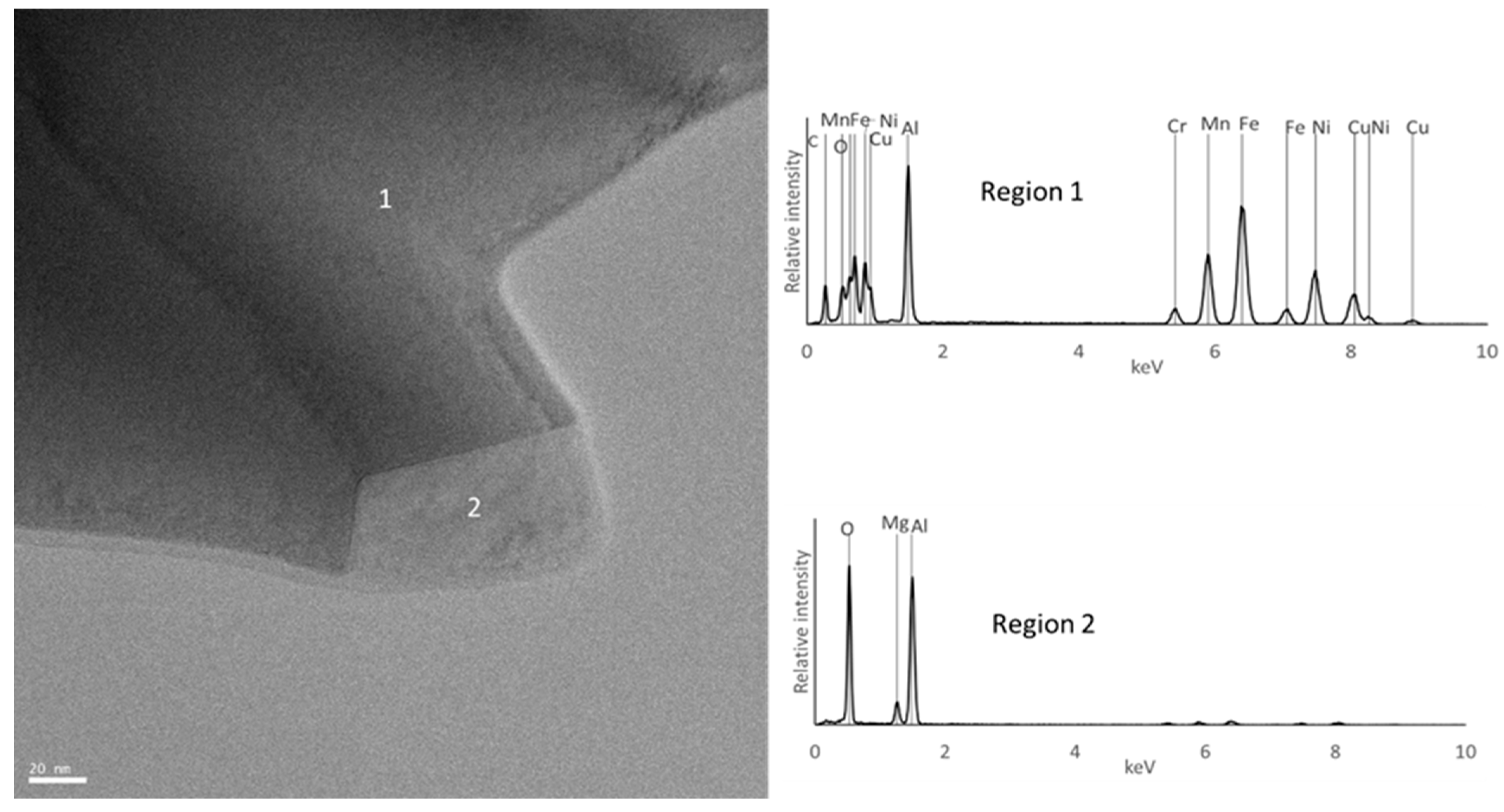
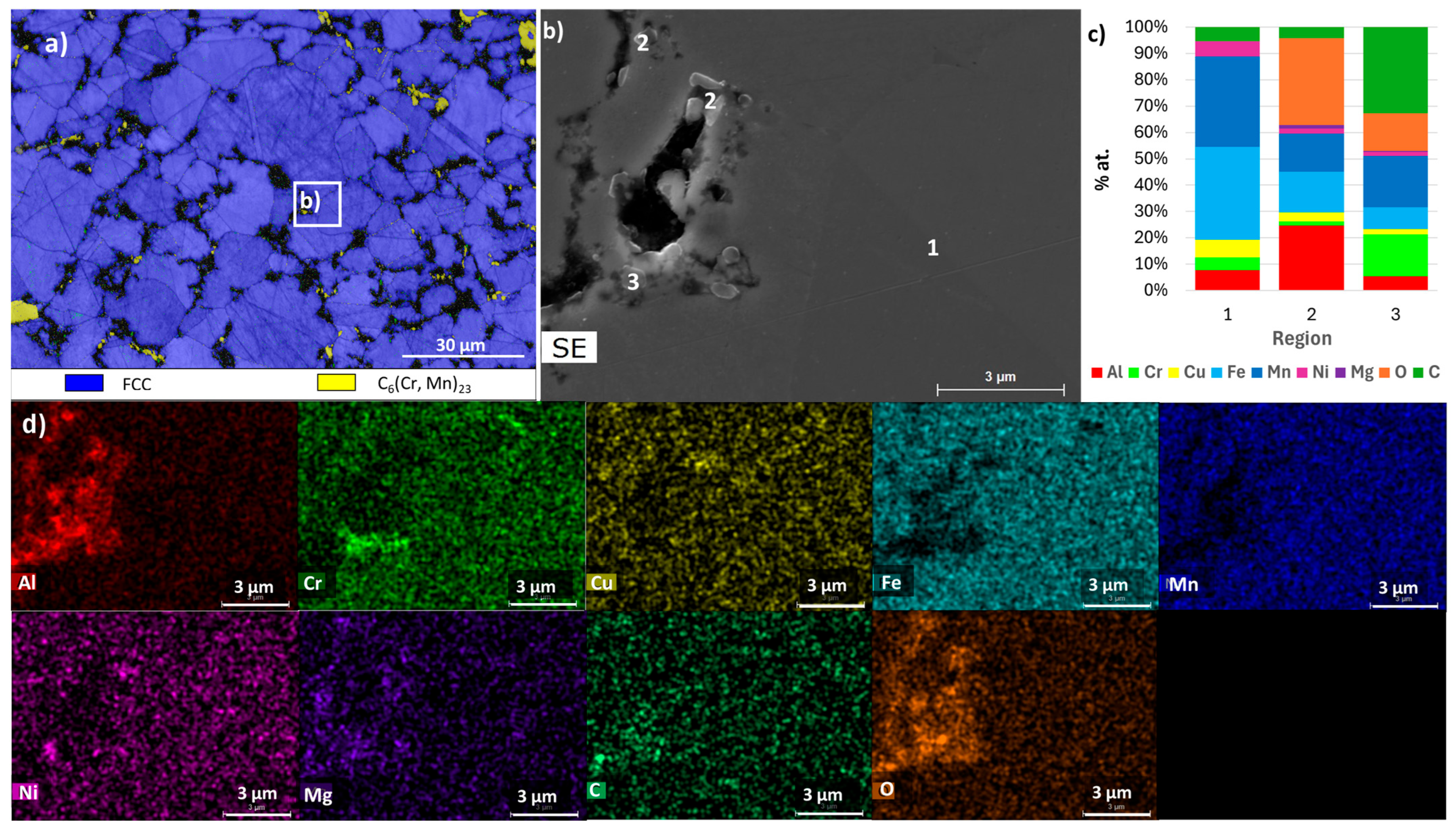
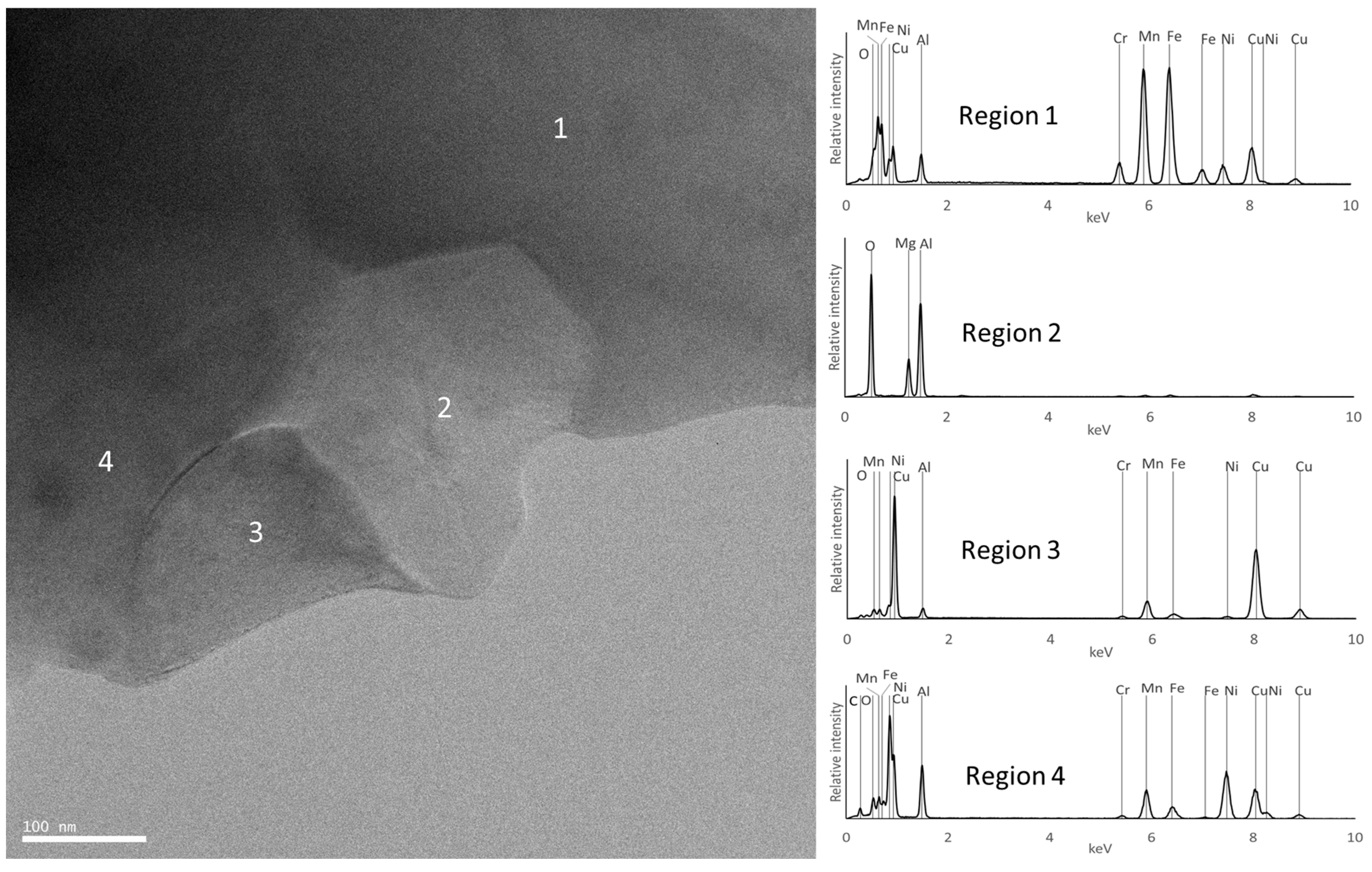
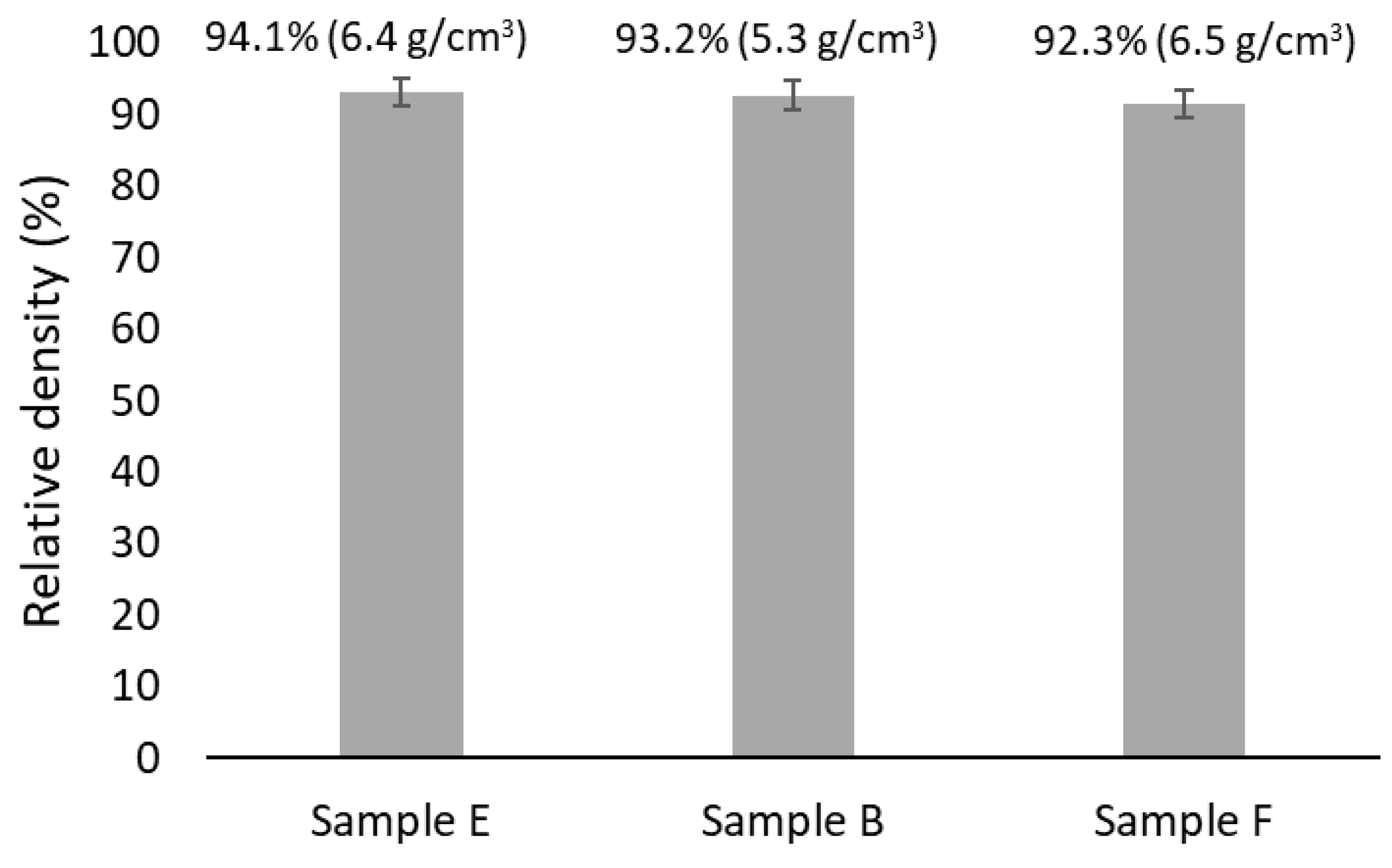
| Composition | Al | Cr | Cu | Fe | Mn | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 16.6 | 16.6 | 16.6 | 16.6 | 16.6 | 16.6 |
| B | 35.0 | 5.0 | 7.5 | 25.0 | 15.0 | 12.5 |
| F | 10.6 | 5.0 | 10.7 | 32.9 | 35.0 | 5.8 |
| Composition | Phases Predicted by Thermodynamic Calculations (at 25 °C) | Phases Identified by | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XRD | EBSD | SEM-EDS | TEM-EDS | ||
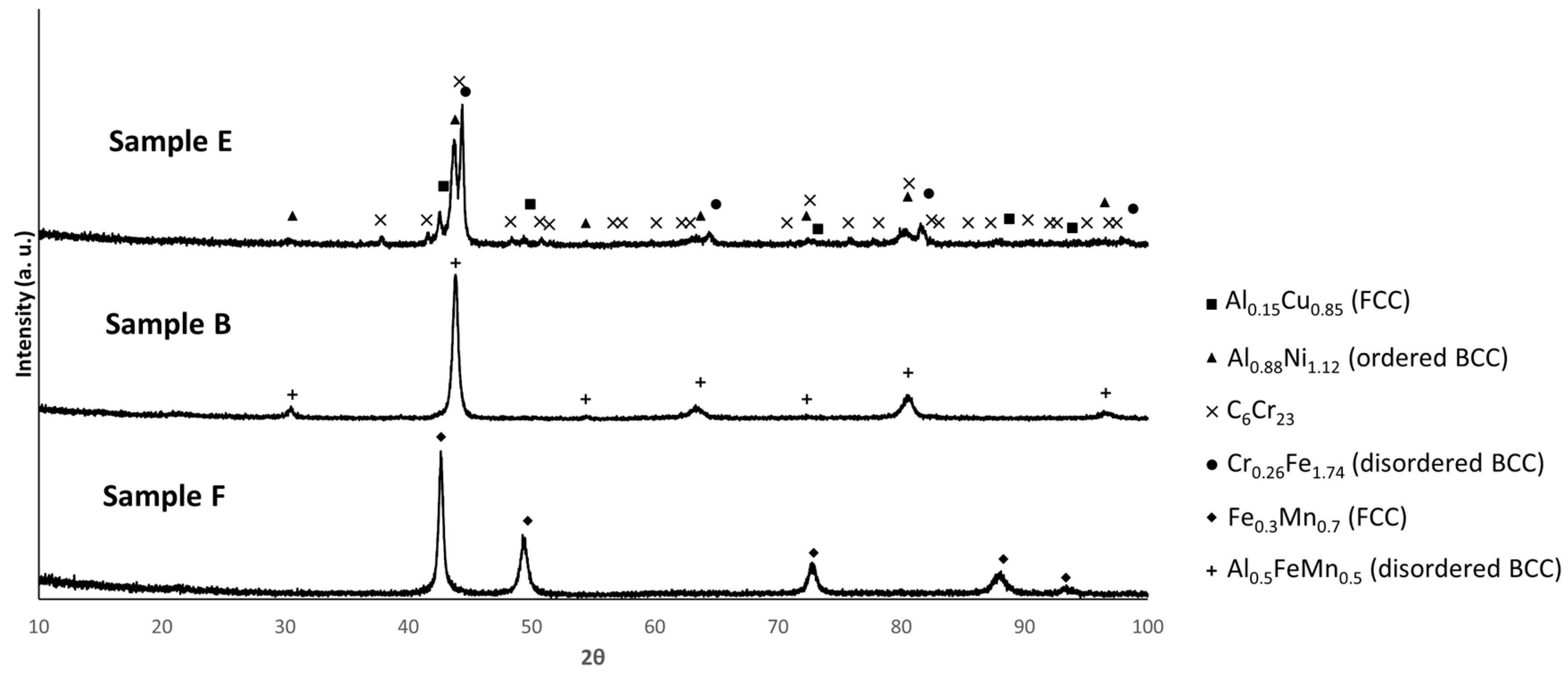
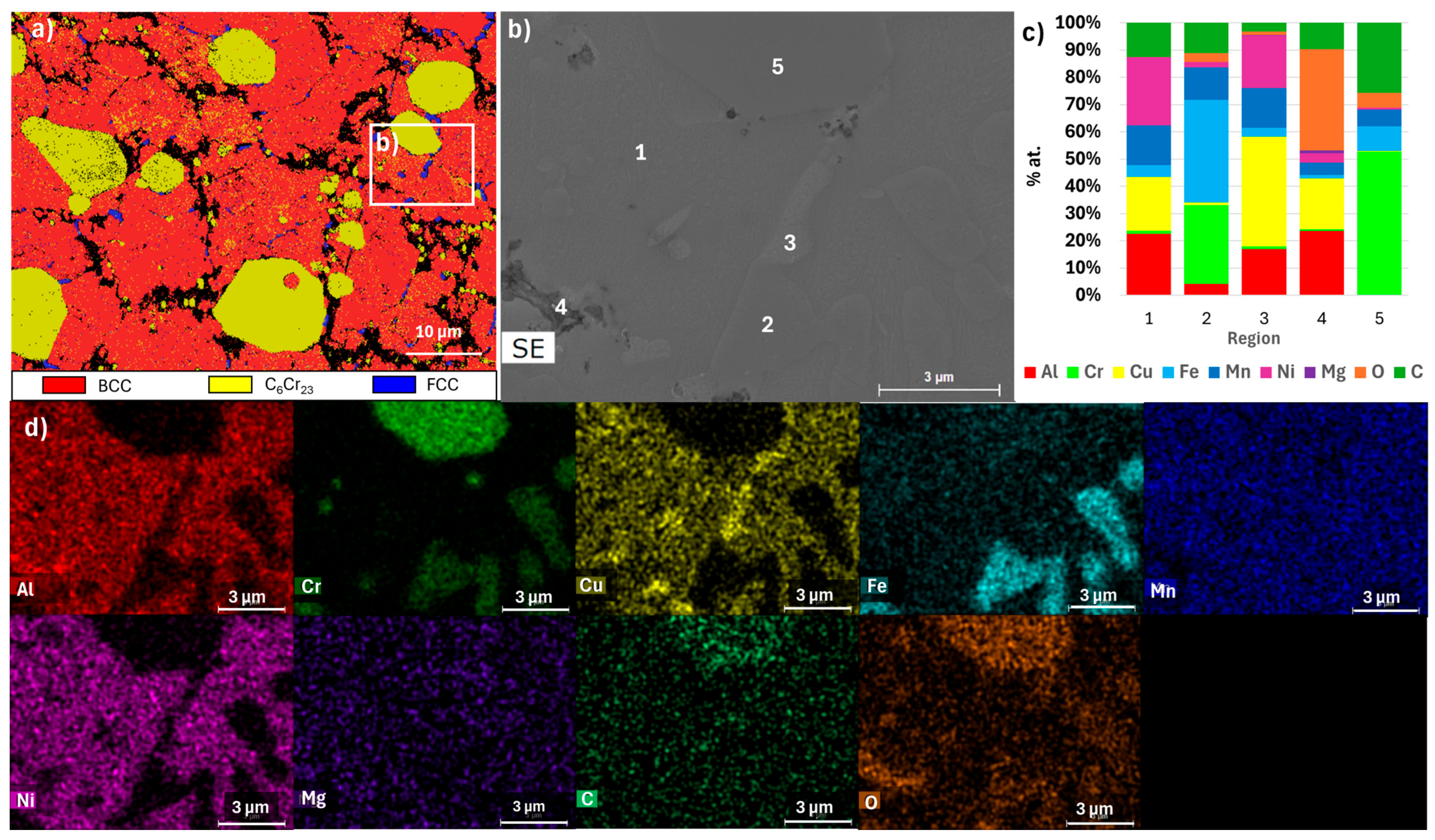
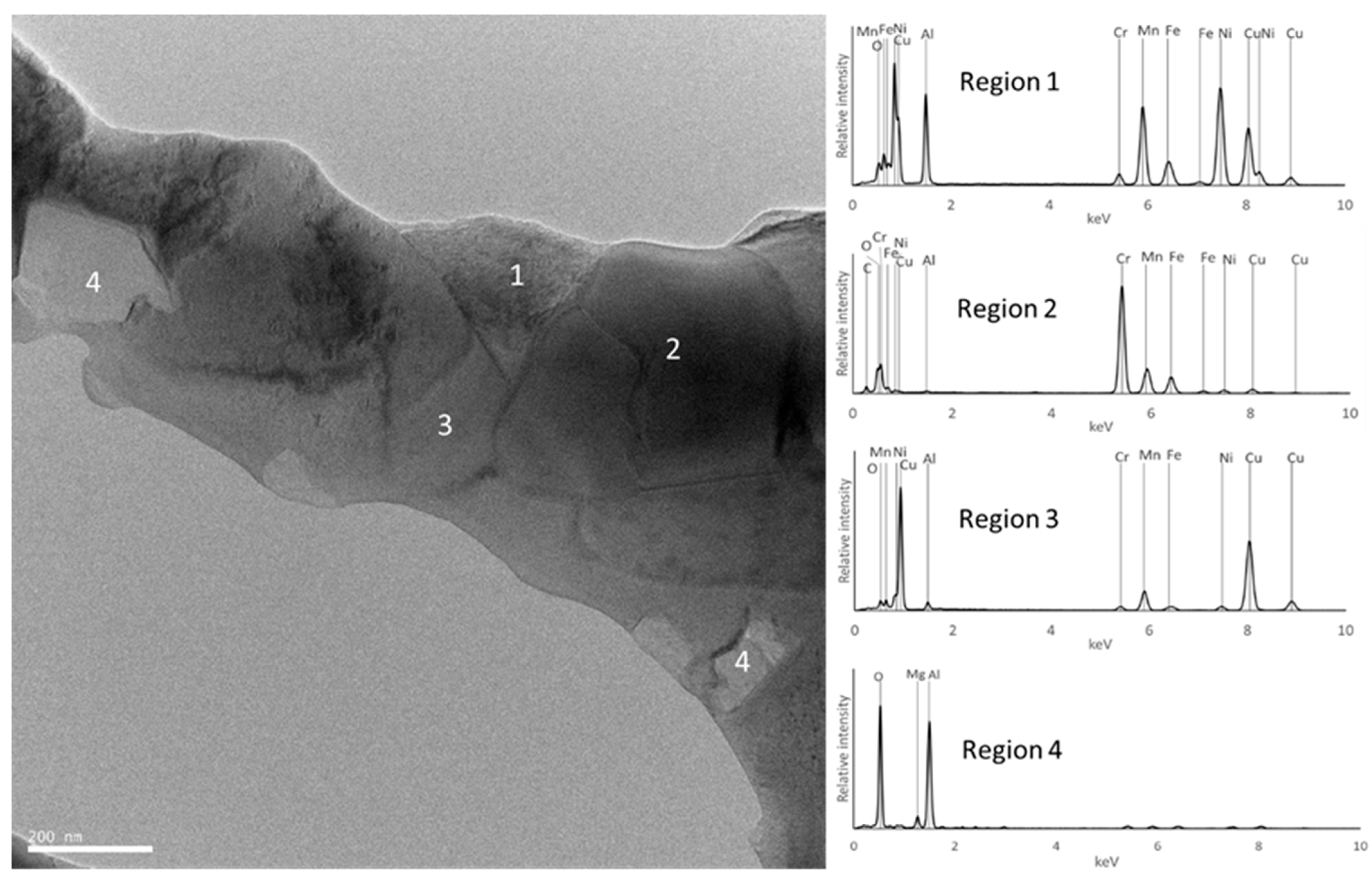
| E | FCC_E1 rich in Cu and Al | Al0.15 Cu0.85 (FCC) | FCC | Region 3 | Region 3 |
| BCC_E1 rich in Fe, Mn, Al and Cr | Cr0.26Fe1.74 (disordered BCC) | BCC | Region 2 | Region 2 | |
| BCC_E2 rich in Al and Ni | Al0.88Ni1.12 (ordered BCC) | BCC | Region 1 | Region 1 | |
| C6Cr23 | C6Cr23 | C6Cr23 | Region 5 | Not detected | |
| Sigma | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | |
| MgO | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | |
| Al2MgO4 | Not detected | Not detected | Consistent with composition of region 4 | Region 4 | |
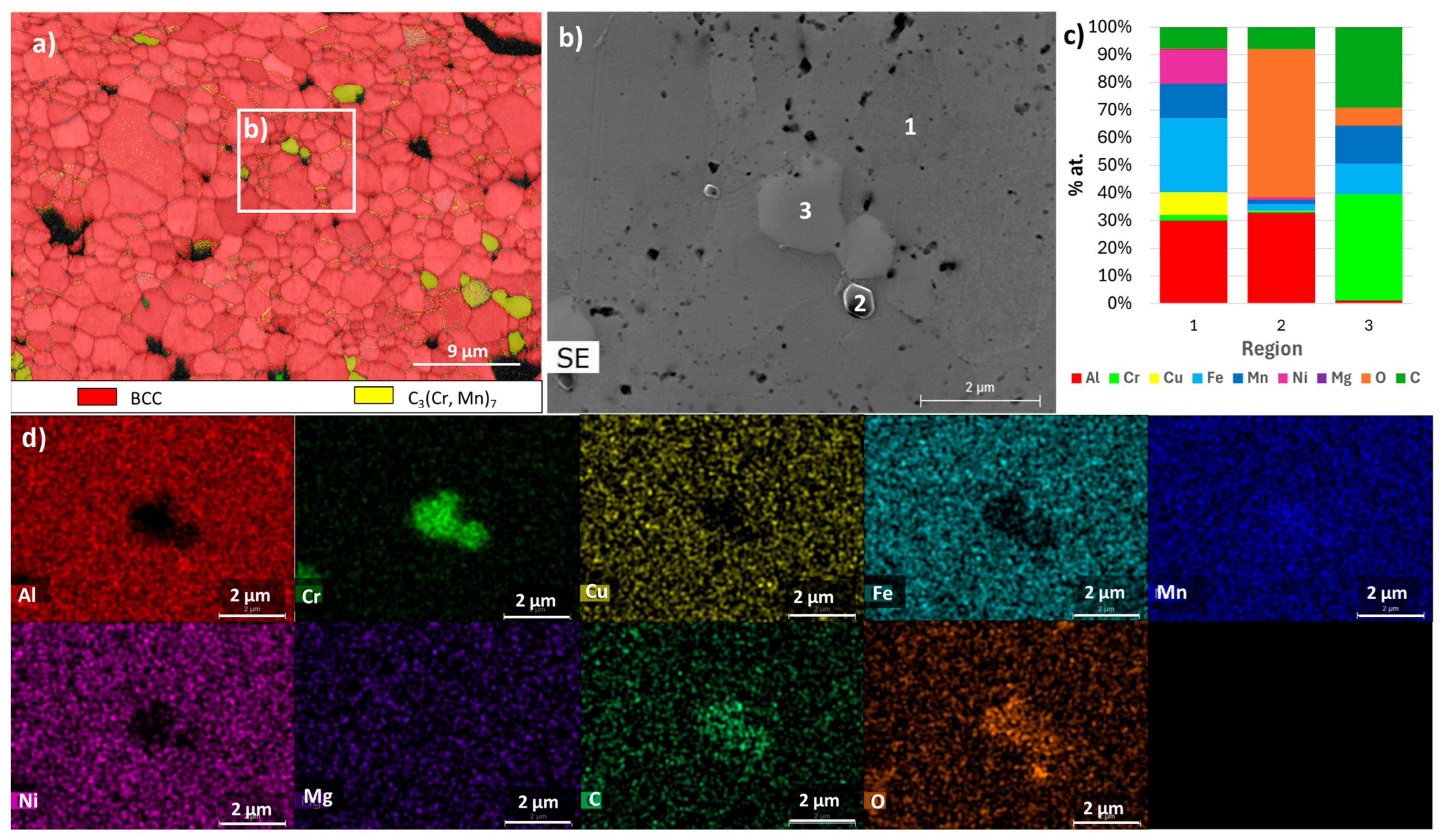
| B | BCC_B1 rich in Al, Fe and Mn | Al0.5FeMn0.5 (disordered BCC) | BCC | Region 1 | Region 1 |
| BCC_B2 rich in Al and Ni | Not detected | BCC | Not detected | Not detected | |
| C3(Cr,Mn)7 | Not detected | C3(Cr,Mn)7 | Consistent with composition of region 3 | Not detected | |
| MgO | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | |
| Al2MgO4 | Not detected | Not detected | Consistent with composition of region 2 | Region 2 | |
| F | FCC_F1 rich in Fe and Mn | Fe0.3Mn0.7 (FCC) | FCC | Region 1 | Region 1 |
| FCC_F2 rich in Cu | Not detected | FCC | Not detected | Region 3 | |
| BCC_F2 rich in Al and Ni | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | Region 4 | |
| C6(Cr,Mn)23 | Not detected | C3(Cr,Mn)7 | Consistent with composition of region 3 | Not detected | |
| MgO | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | Not detected | |
| Al2MgO4 | Not detected | Not detected | Consistent with composition of region 2 | Region 2 | |
| Samples | Dynamic Young’s Modulus (GPa) | Vickers Hardness (HV2) |
|---|---|---|
| E | 145 ± 1 | 357 ± 15 |
| B | 135 ± 4 | 367 ± 6 |
| F | 147 ± 4 | 211 ± 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, T.; Lopes, A. Tailoring Mechanical Properties of Al-Cr-Cu-Fe-Mn-Ni Complex Concentrated Alloys Prepared Using Pressureless Sintering. Materials 2025, 18, 4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174068
Silva T, Lopes A. Tailoring Mechanical Properties of Al-Cr-Cu-Fe-Mn-Ni Complex Concentrated Alloys Prepared Using Pressureless Sintering. Materials. 2025; 18(17):4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174068
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Tiago, and Augusto Lopes. 2025. "Tailoring Mechanical Properties of Al-Cr-Cu-Fe-Mn-Ni Complex Concentrated Alloys Prepared Using Pressureless Sintering" Materials 18, no. 17: 4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174068
APA StyleSilva, T., & Lopes, A. (2025). Tailoring Mechanical Properties of Al-Cr-Cu-Fe-Mn-Ni Complex Concentrated Alloys Prepared Using Pressureless Sintering. Materials, 18(17), 4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18174068







