In Situ Constructing Highly Aligned Ribbon-like PHBV Lamellae in PBAT: Towards Strong, Ductile and High-Barrier PBAT/PHBV Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
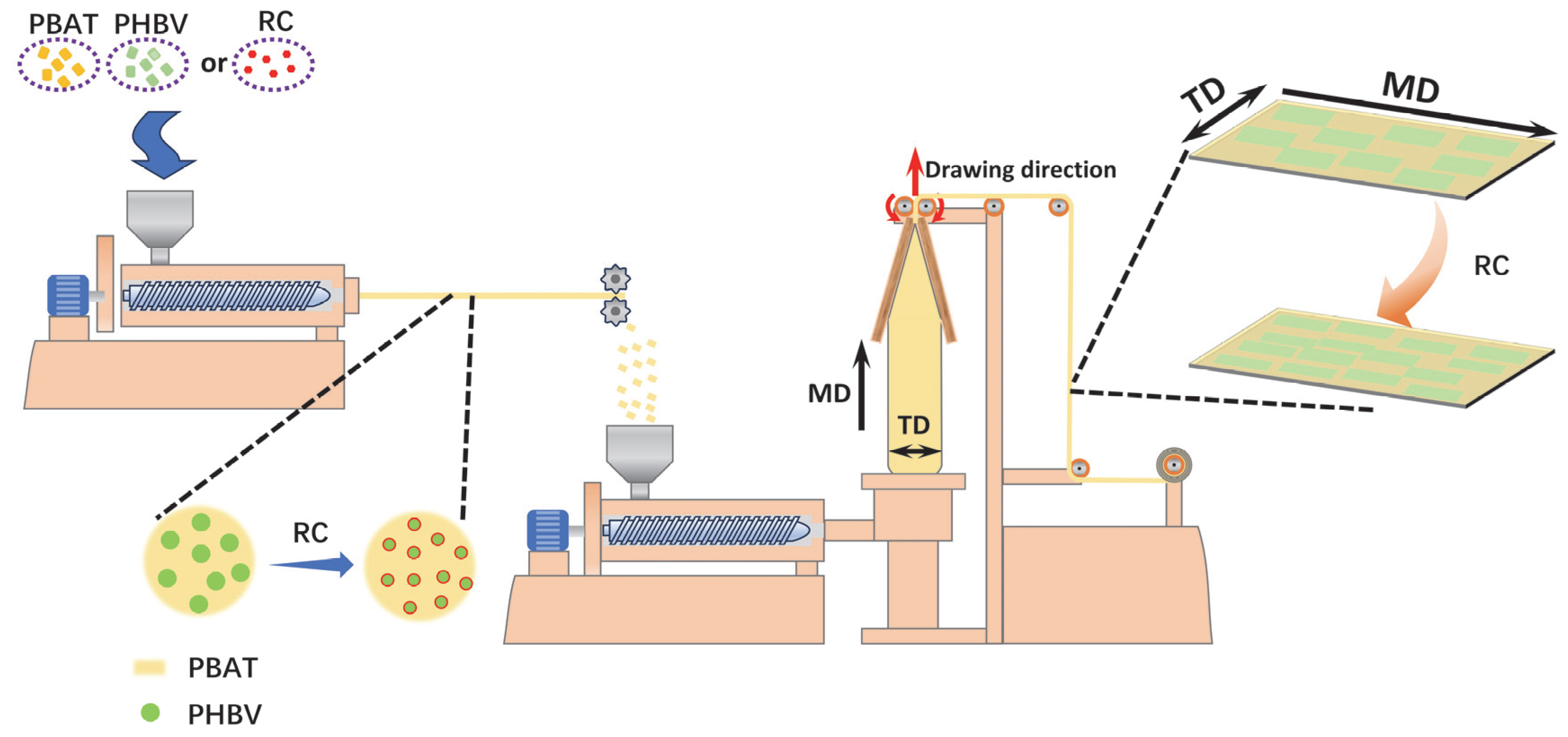
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Infrared Spectroscopy Characterization
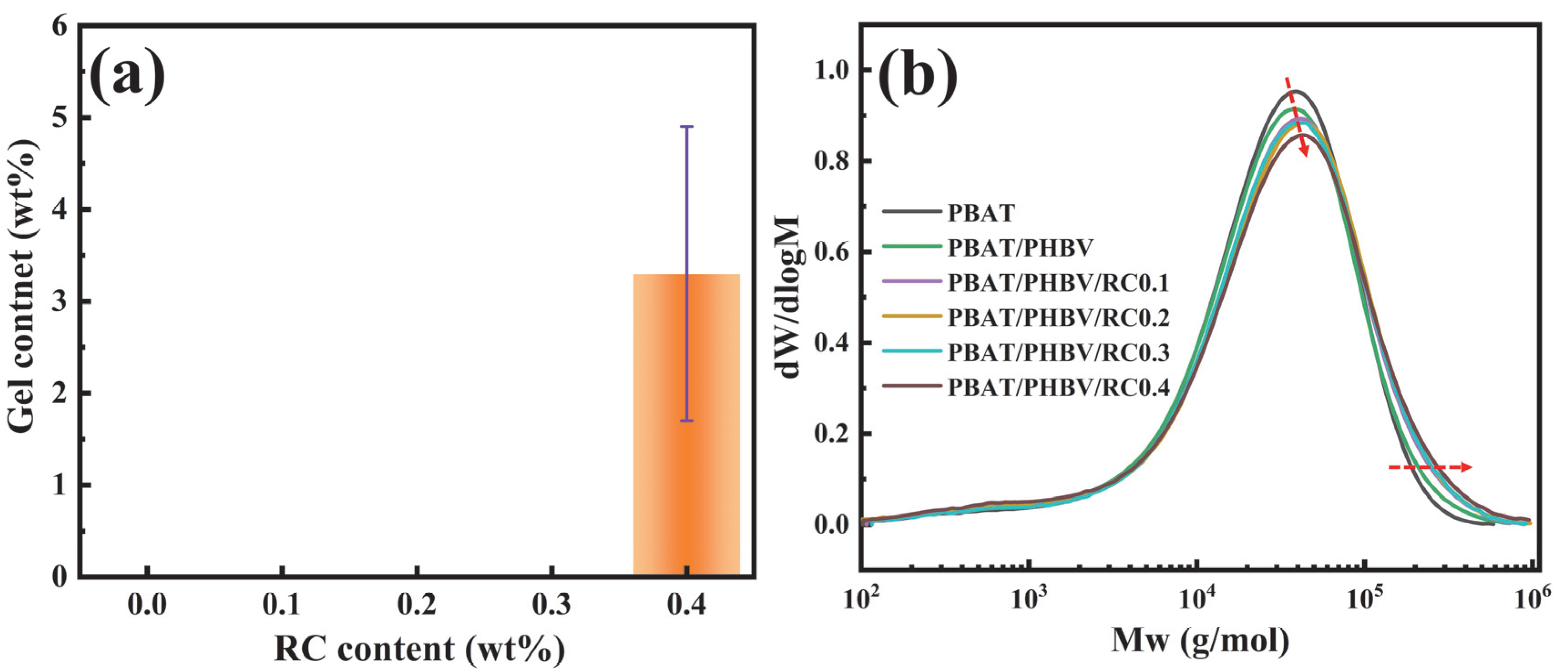
2.4. Gel Permeation Chromatography Characterization
2.5. Gel Content Characterization
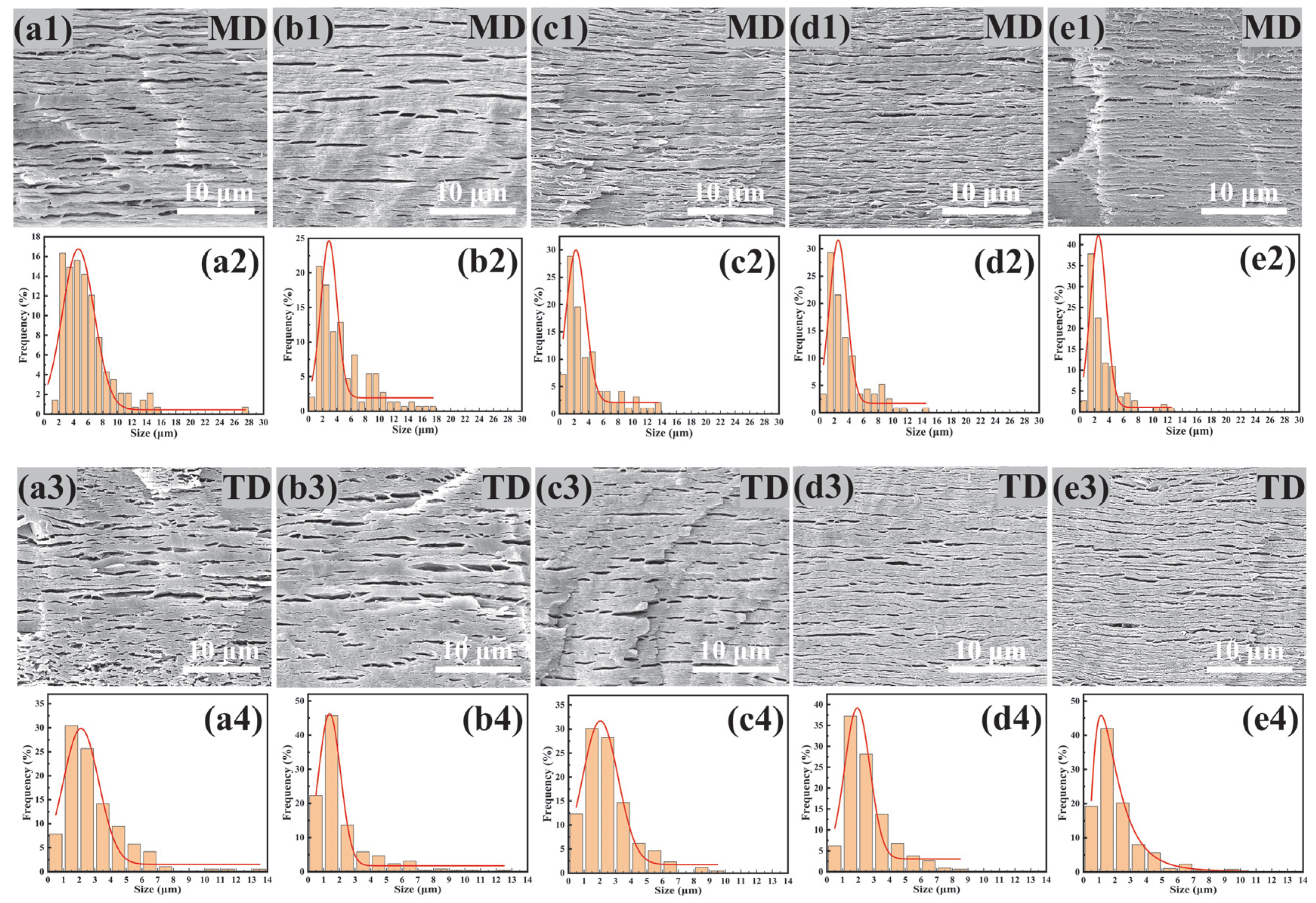
2.6. Morphology Characterization
2.7. Rheological Property Characterization
2.8. Thermal Property Characterization
2.9. Mechanical Performance Characterization
2.10. Barrier Performance Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
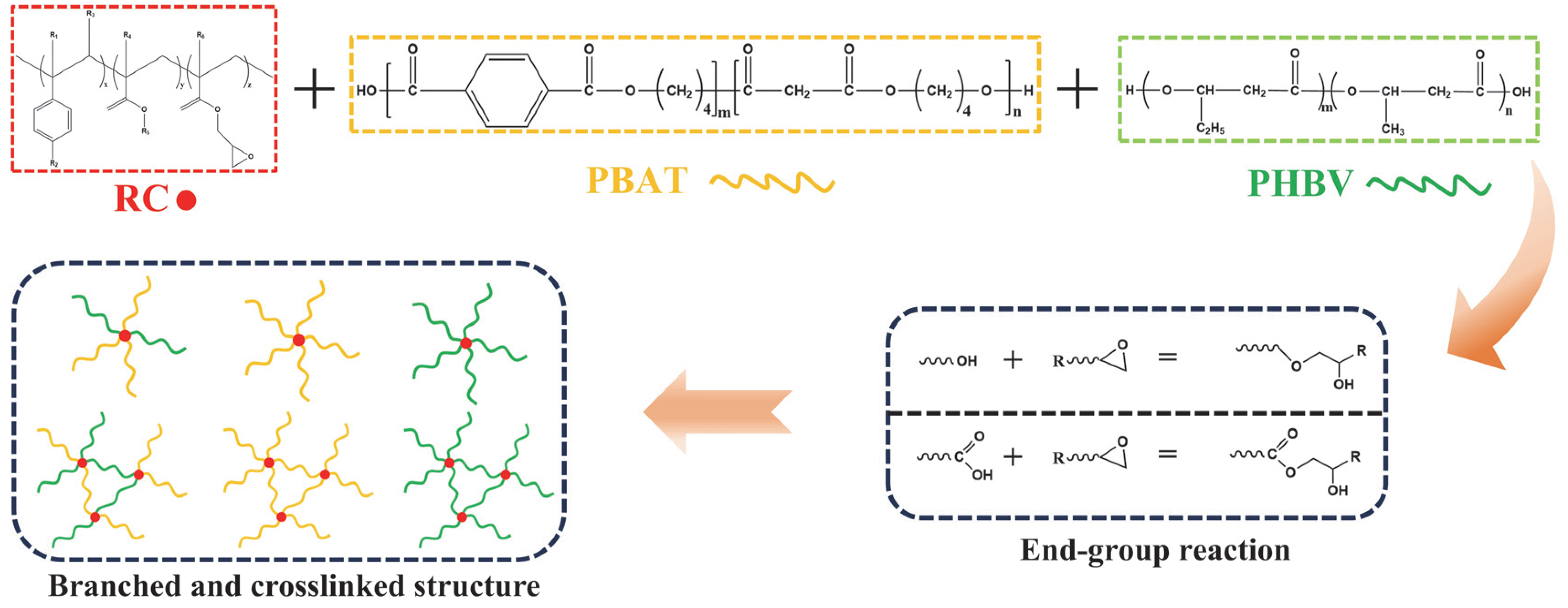
3.1. Compatibilization of PBAT/PHBV Blends
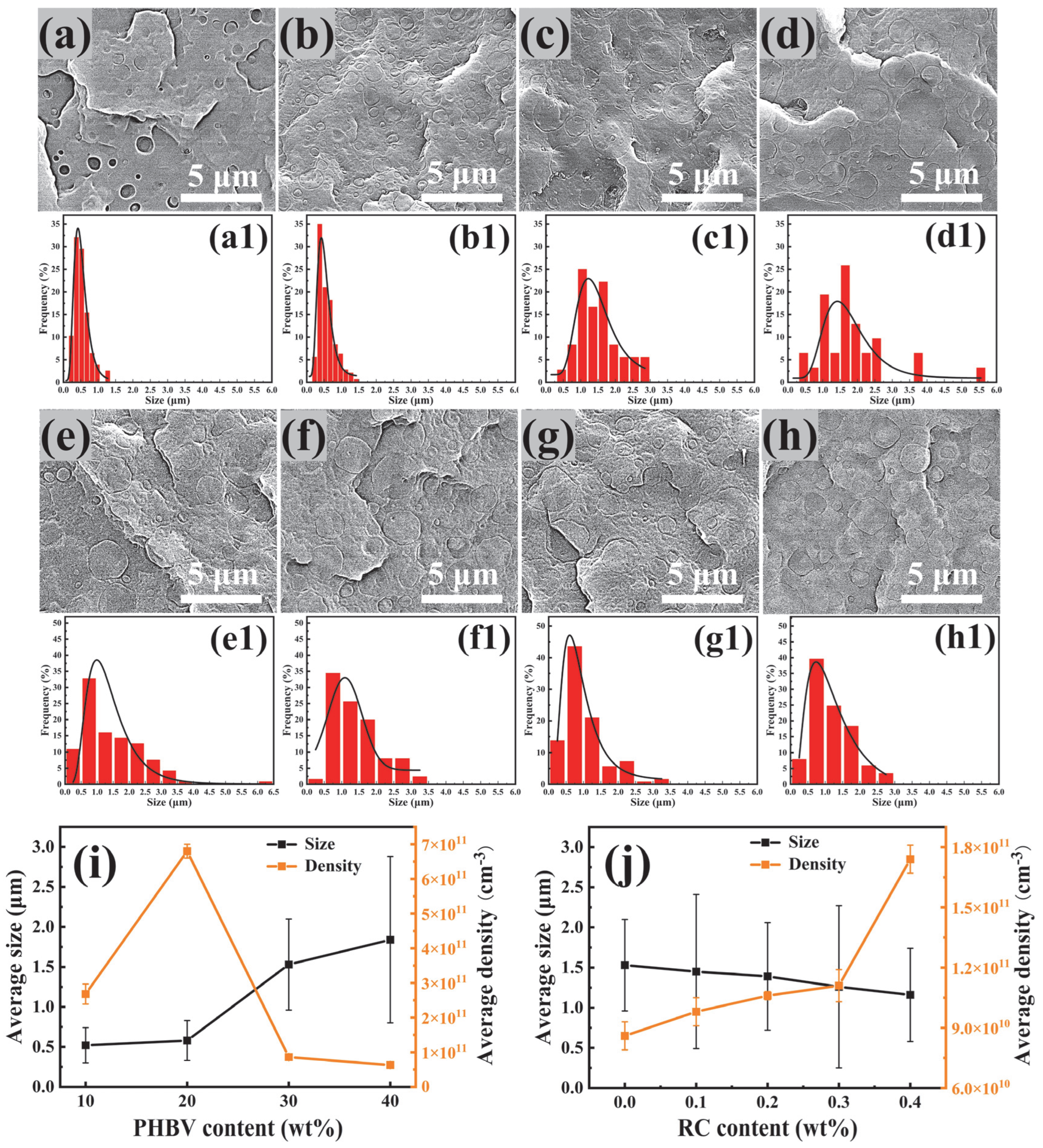
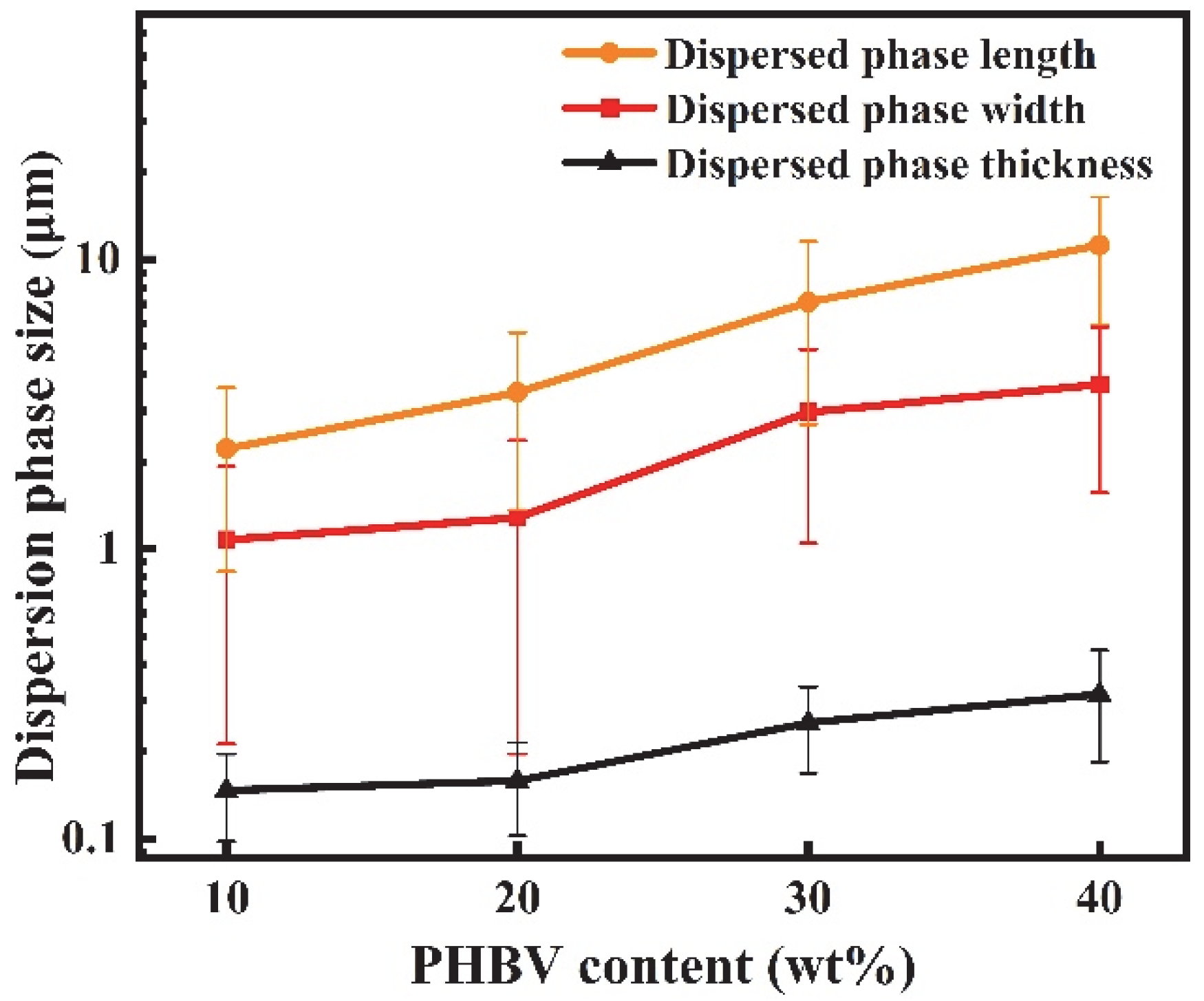
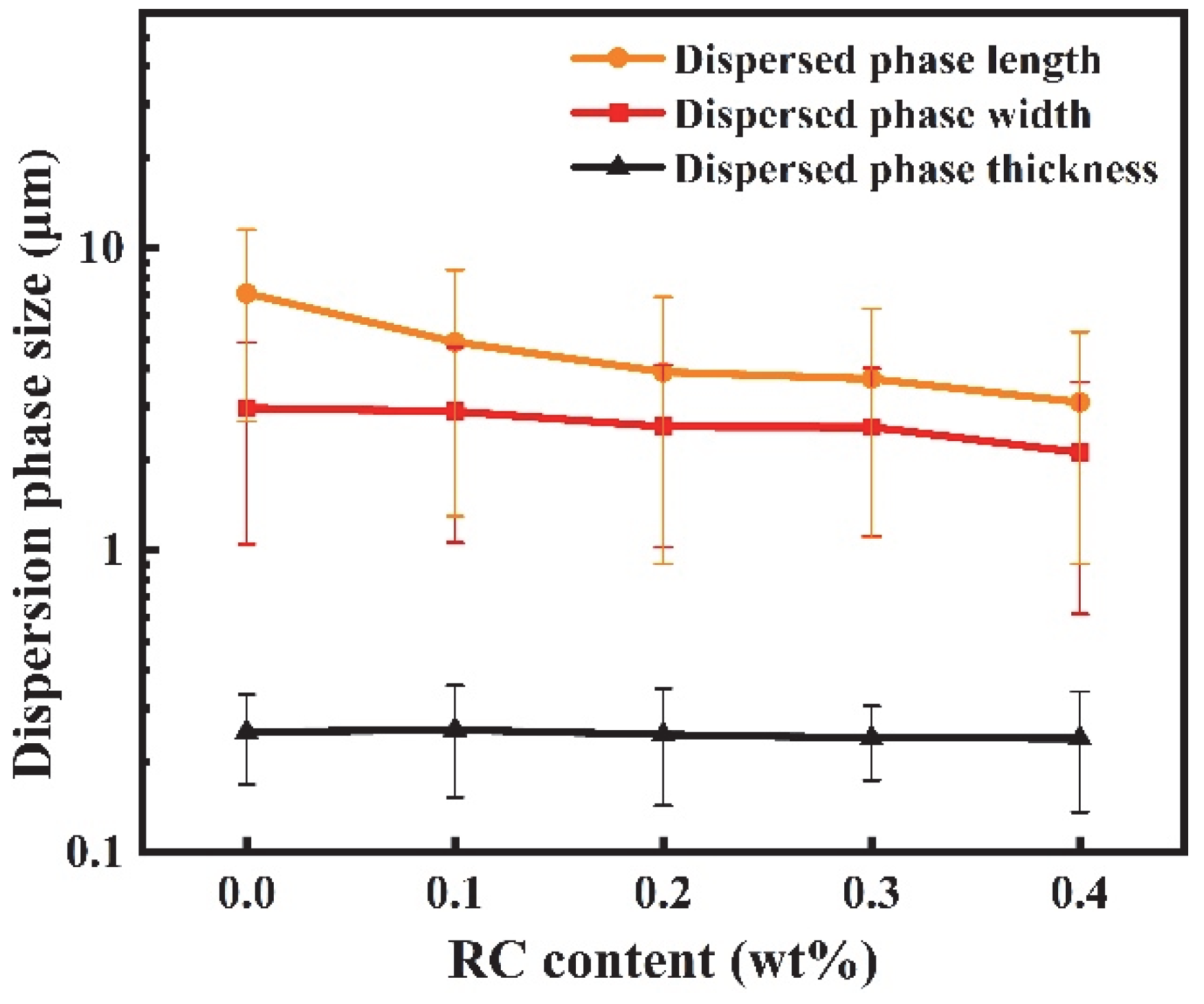
3.2. Morphology of PBAT/PHBV and PBAT/PHBV/RC Blends
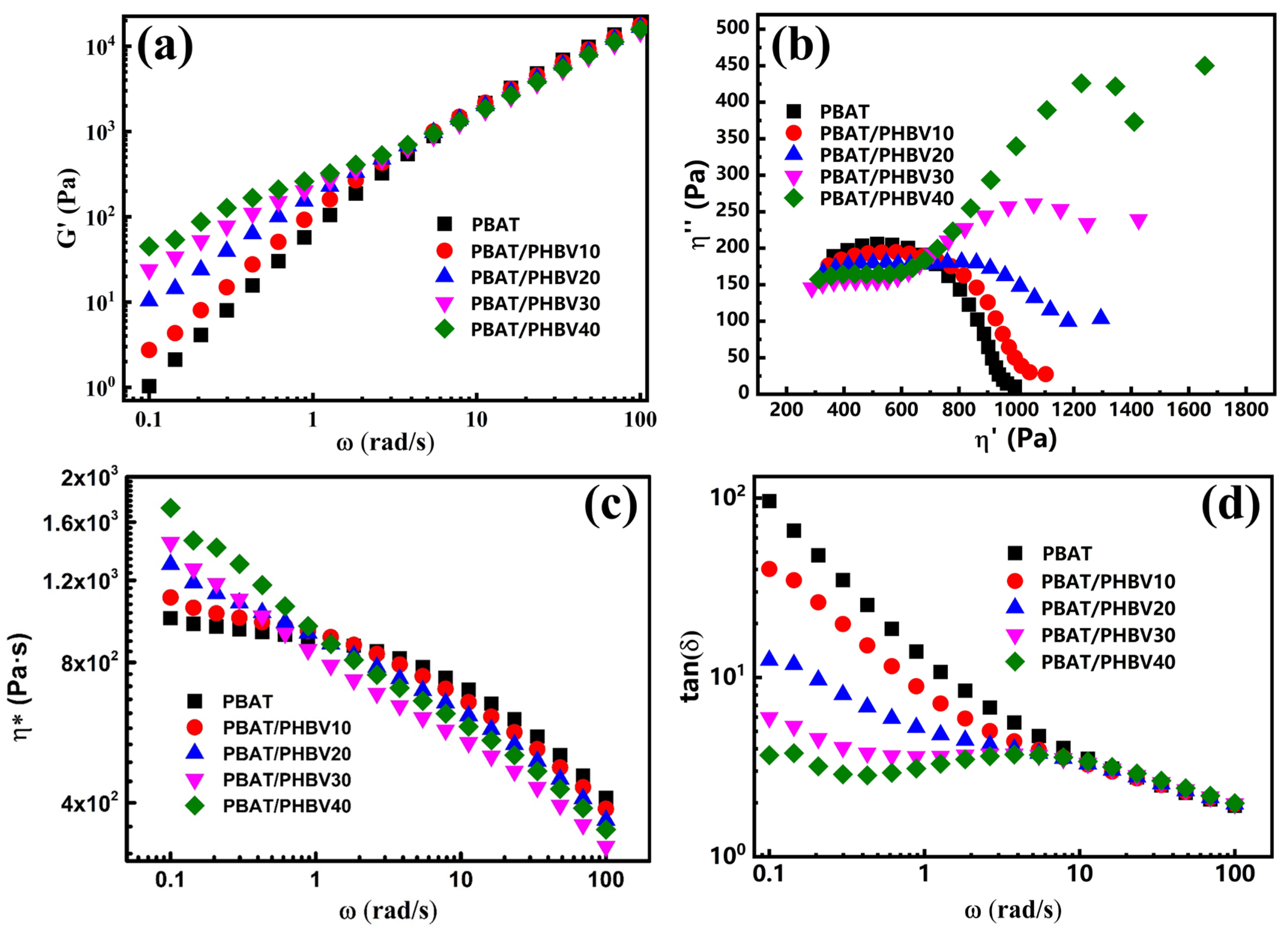
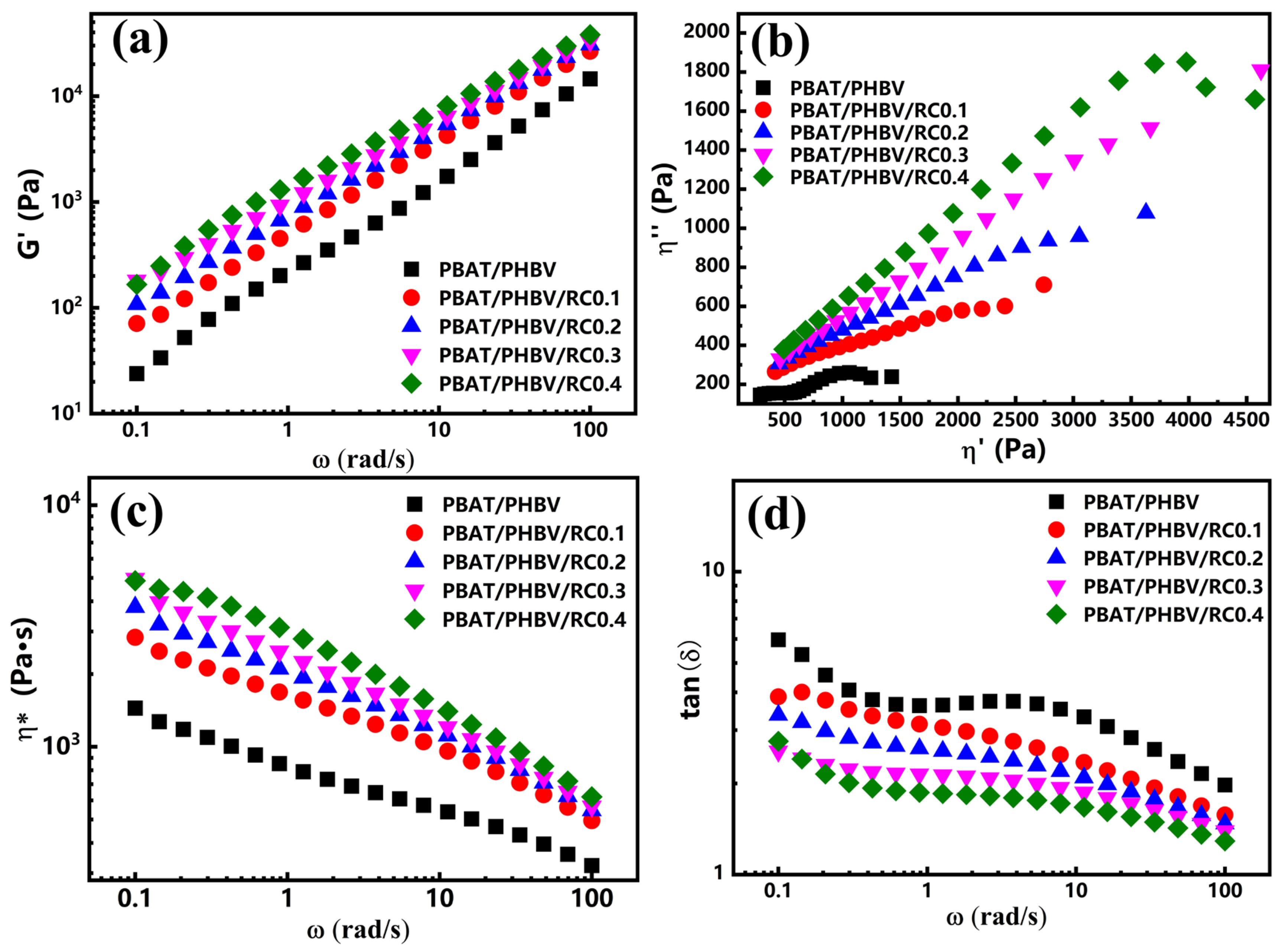
3.3. Rheological Behavior of PBAT/PHBV and PBAT/PHBV/RC Blends
3.4. Crystallization Behavior of PBAT/PHBV and PBAT/PHBV/RC Blends
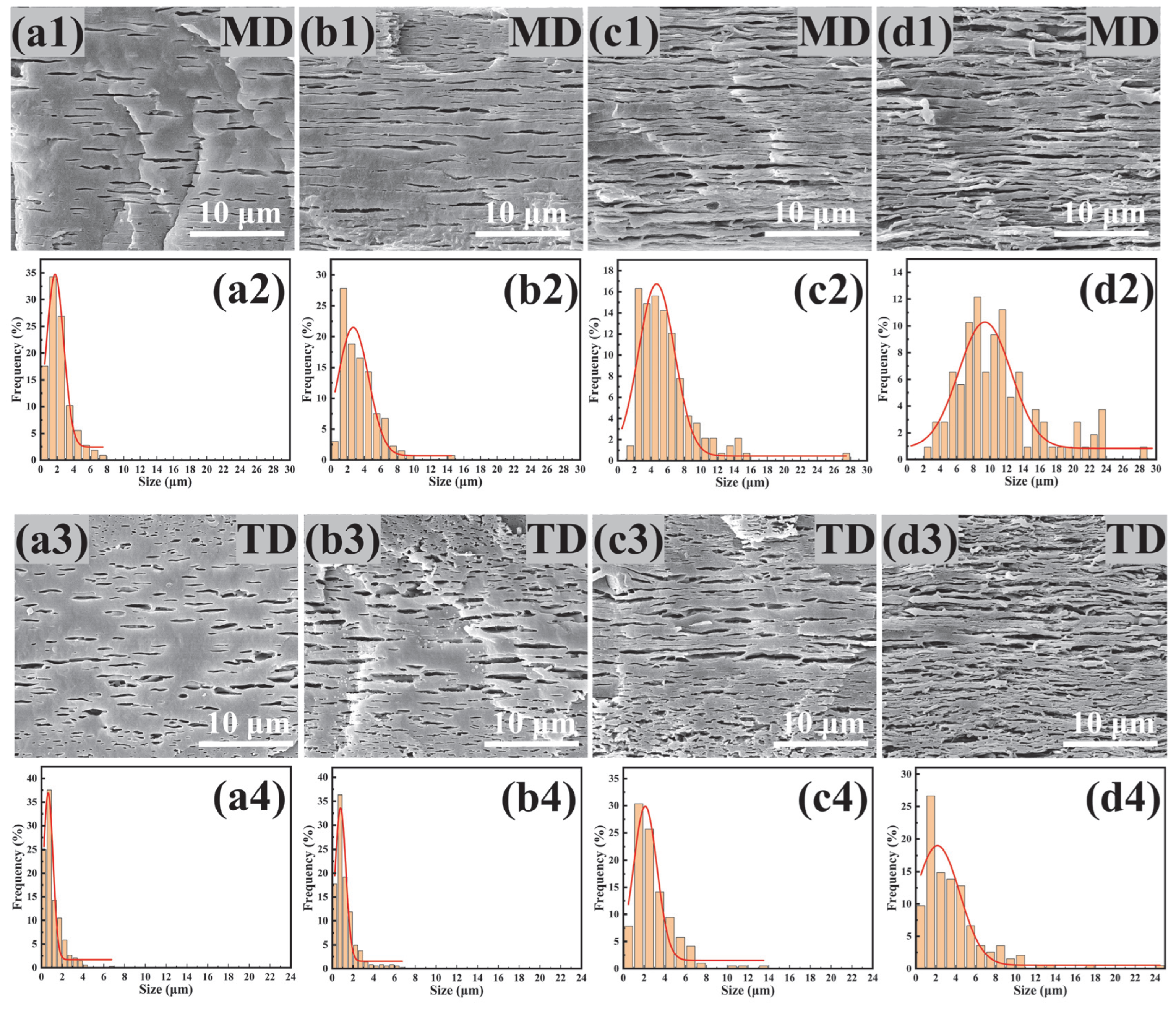
3.5. Morphology of PBAT/PHBV and PBAT/PHBV/RC Films
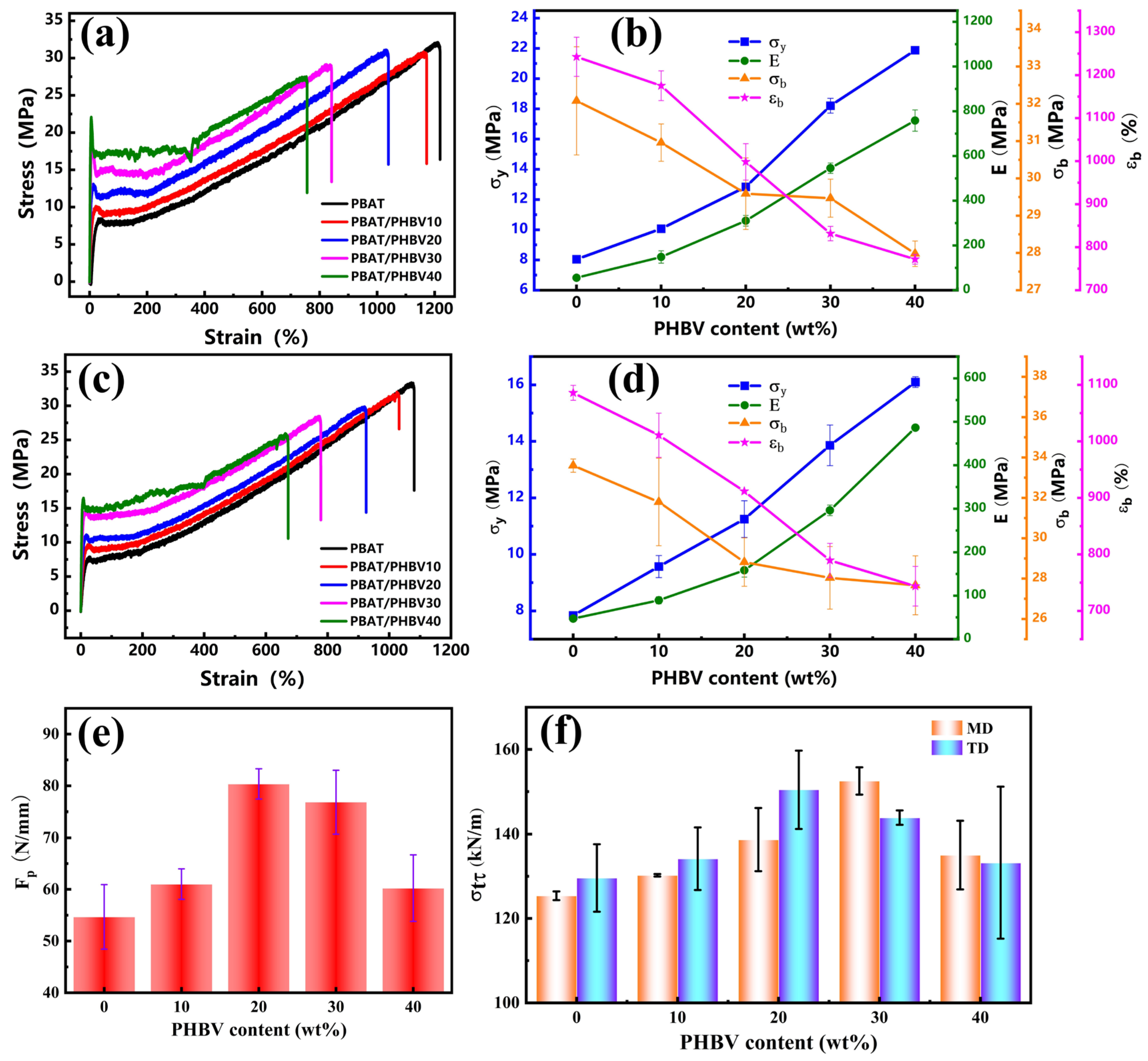
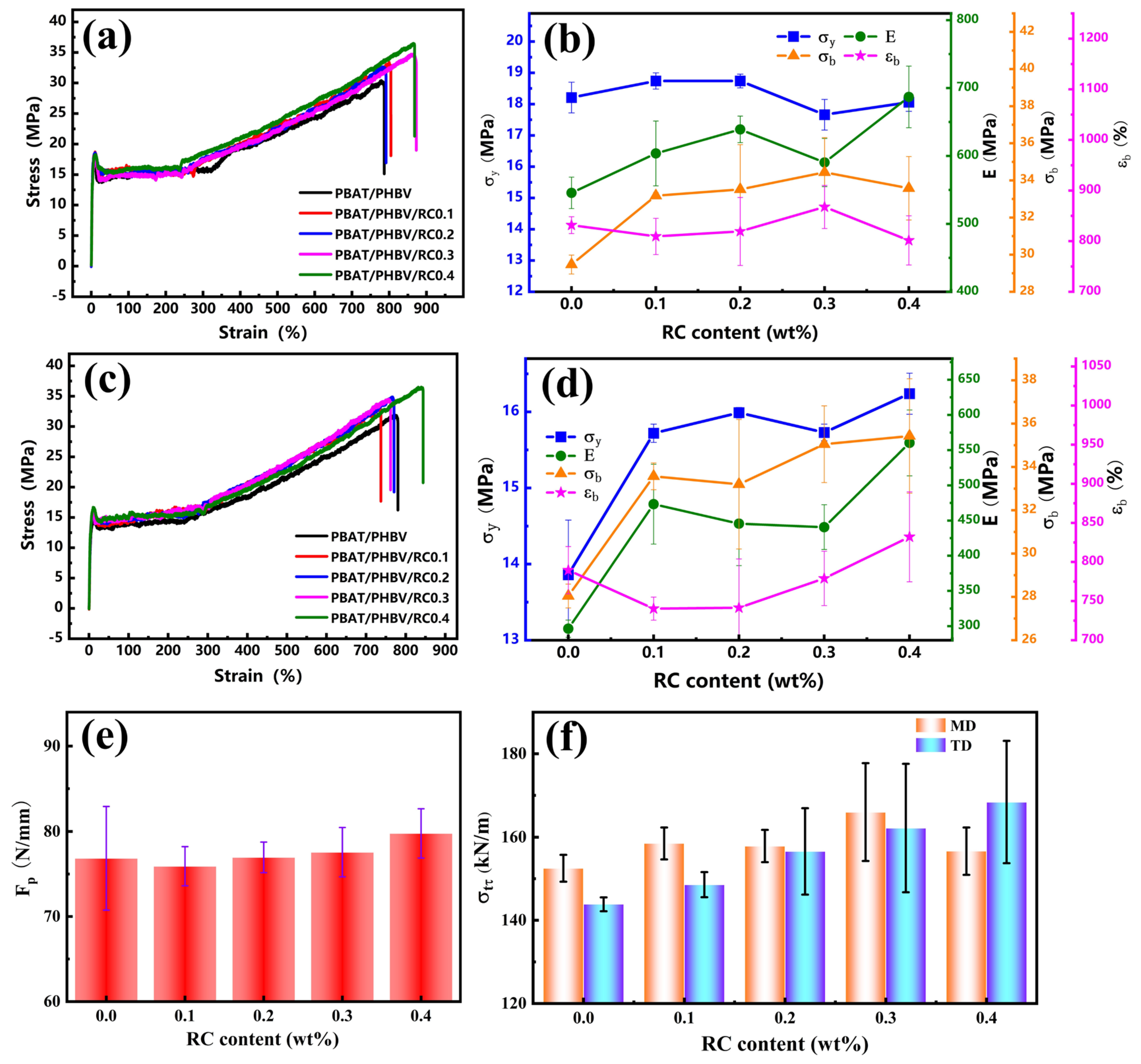
3.6. Mechanical Property of PBAT/PHBV and PBAT/PHBV/RC Blend Films
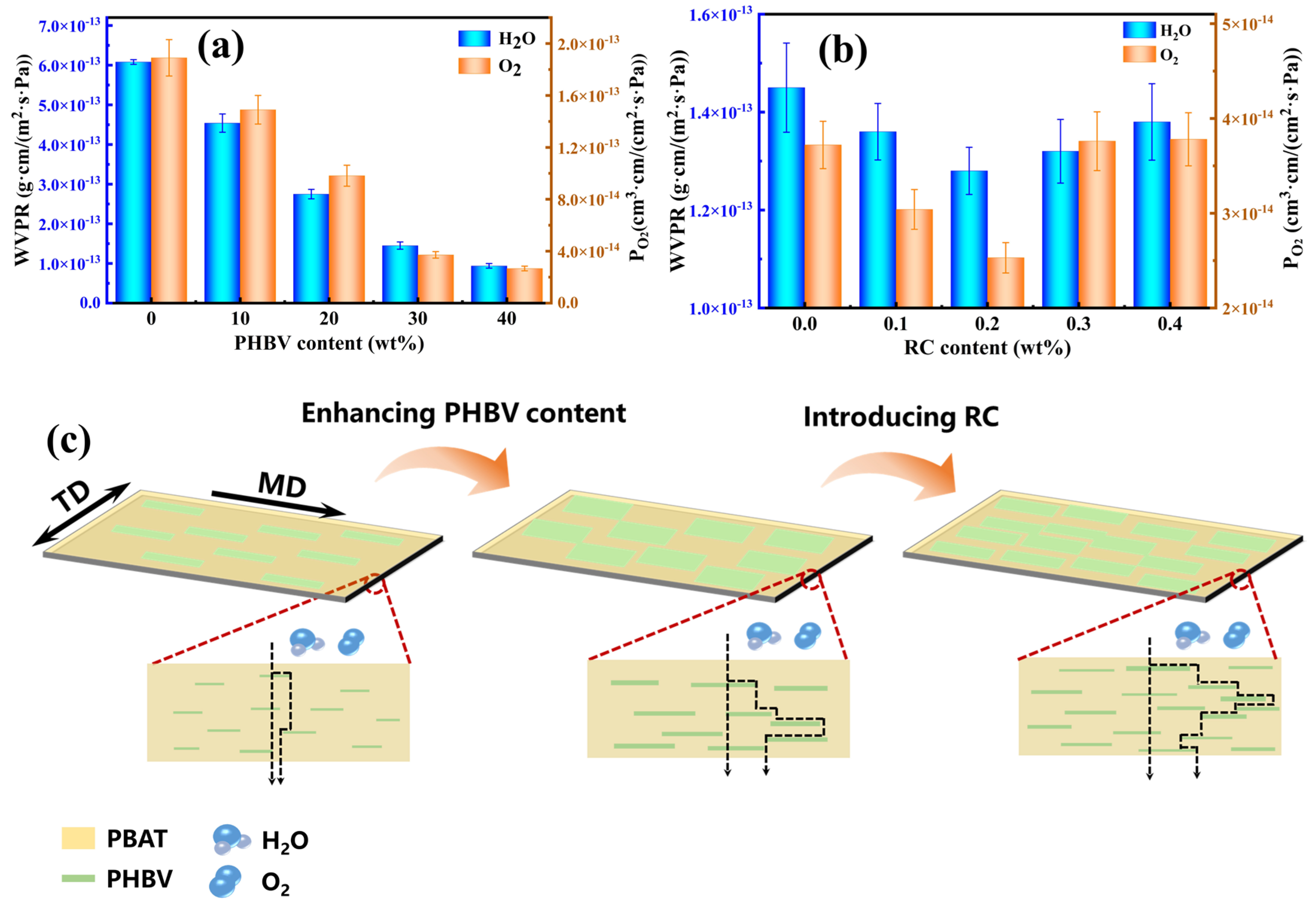
3.7. Barrier Performance of PBAT/PHBV and PBAT/PHBV/RC Blend Films
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blessing, E.; Amar, K.M.; Phil, D.; Mohini, S.; Atul, B.; Mike, T.; Loong-Tak, L.; Manjusri, M. Poly (Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) (PBAT)-Based Biocomposites: A Comprehensive Review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2024, 39, 2400179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Salem, K.S.; Hubbe, M.A.; Pal, L. Advances in barrier coatings and film technologies for achieving sustainable packaging of food products-a review. Trends. Food. Sci. Tech. 2021, 115, 461–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.G.; Sergio, J.C.; Misael, S.G.; Paloma, B. Current trends in biopolymers for food packaging: A review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1225371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bian, H.; Meng, X.; Yuan, J.; Ding, J.; Li, W.; Xu, J.; Guo, B. Synthesis of Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) with Branched Monomer for Biodegradable Copolyesters with Enhanced rocessability and Rheological Properties. ACS Omega 2025, 10, 14258–14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, J. Enhanced degradation and gas barrier of PBAT through composition design of aliphatic units. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2022, 195, 109795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, J.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, H.; Li, L. Preservation of soy protein-based meat analogues by using PLA/PBAT antimicrobial packaging film. Food Chem. 2022, 380, 132022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Xie, D.; Yang, C. Effects of a PLA/PBAT biodegradable film mulch as a replacement of polyethylene film and their residues on crop and soil environment. Agr. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Ghosh, T.; Zhang, W.; Rhim, J.W. Recent progress in pbat-based films and food packaging applications: A mini-review. Food Chem. 2024, 437, 137822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Wu, L.; Li, B.G. Sulfonated biodegradable PBAT copolyesters with improved gas barrier properties and excellent water dispersibility: From synthesis to structure-property. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2020, 182, 109391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Du, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, T.; Xu, J.; Yu, H.; Guo, B. Effects of Different Isomers of Thiophenedicarboxylic Acids on the Synthesis and Properties of Thiophene-Based Sustainable Polyesters. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 6652–6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, B.; Shang, Z.; Yu, L.; Wei, C.; Wei, Z.; Sang, L.; Li, Y. High-barrier poly(butylene succinate-co-terephthalate) blend with poly(lactic acid) as biodegradable food packaging films. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 7250–7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S. Compatibilization, processing and characterization of poly(butylene adipate terephthalate)/polylactide (PBAT/PLA) blends. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 025308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Z.; Weng, Y. In situ formation of microfibrillar PBAT in PGA films: An effective way to robust barrier and mechanical properties for fully biodegradable packaging films. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 21280–21290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Lai, L.; Wu, L.; Steven, J.S.; Wang, W. Enhancement of water vapor barrier properties of biodegradable poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) films with highly oriented organomontmorillonite. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6654–6662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J.; Wang, W.; Hou, H. Starch/poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) blown antimicrobial films based on ε-polylysine hydrochloride and different nanomontmorillonites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Wang, S.; Lia, J.; Liu, P.; Wu, L.; Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Steven, J.S.; Wang, W. Stiffening, strengthening, and toughening of biodegradable poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) with a low nanoinclusion usage. Carbohyd. Polym. 2020, 247, 116687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyeri, K.; Hyeonyeol, J.; Lee, M.; Park, S.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.; Oh, D.X.; Koo, J.; et al. Enhanced mechanical properties of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/cellulose nanocrystal nanocomposites obtained by in situ polymerization. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Han, Y.; Rong, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, Y. Interfacial Engineering with Rigid Nanoplatelets in Immiscible Polymer Blends: Interface Strengthening and Interfacial Curvature Controlling. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 11016–11027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Yang, S.; Feng, J. High-reactive silica nanosheets as compatibilizers for immiscible PLLA/PBAT polymer blends. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 236, 109979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alias, A.R.; Khairul, W.M.; Sarbon, N.M. Emerging materials and technologies of multi-layer film for food packaging application: A review. Food Control 2022, 136, 108875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Hong, W.; Yu, G.; Du, Q.; Guo, S.; Li, C. Preparation and improving mechanism of PBAT/PPC-based micro-layer biodegradable mulch film with excellent water resistance and mechanical properties. Polymer 2024, 291, 126614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Development of multilayer films based on PLA/PBAT and sodium alginate for active packaging. J. Food Saf. 2024, 44, e13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jiang, C.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Liang, F.; Yang, Z. Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(butylene succinate) (PLA/PBS) layered composite gas barrier membranes by anisotropic janus nanosheets compartibilizers. ACS Macro Lett. 2022, 11, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Zhang, C.; Weng, Y. Improvement of the gas barrier properties of PLA/OMMT films by regulating the interlayer spacing of OMMT and the crystallinity of PLA. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 18675–18684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivan, P.; Lucas, C.; Roey, N.; Yiftach, N.; Dalia, L.; Jaime, G.; Oren, R. Graphene-induced enhancement of water vapor barrier in polymer nanocomposites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 134, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Antonio, E.C.; Sanjay, B.T.; Jaya, K.; Francesco, B.; Athanassia, A. Graphene morphology effect on the gas barrier, mechanical and thermal properties of thermoplastic polyurethane. Compos. Sci. Tech. 2020, 200, 108461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lan, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Q.; Gong, P.; Chul, B.P.; Li, G. Microcellular foams simultaneous reinforcing and toughening strategy of combining nano-fibrillation network and supercritical solid-state foaming. Polymer 2022, 252, 124928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, A.; Dong, G.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, G. Microcellular injection molded lightweight and tough poly (l-lactic acid)/in-situ polytetrafluoroethylene nanocomposite foams with enhanced surface quality and thermally-insulating performance. Int. J. Biological Macromol. 2022, 215, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhong, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Preparation of antishrinkage and high strength poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) microcellular foam via in situ fibrillation of polylactide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 282, 136782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, A.; Eunse, C.; Eric, S.K.; Ali, R.; Adel, R.K.; Chul, B.P.; Patrick, C.L. Nanofibrillated polymer systems: Design, application, and current state of the art. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2021, 113, 101346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lun, H.M.; Kim, S.; Chang, E.; Park, C.B.; Lee, P.C. Recent progress in micro-/nano-fibrillar reinforced polymeric composite foams. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 926–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Tan, A.; Chen, C.; Li, L.; Ge, L.; Wang, L.; Razaad, I.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Mo, Y.; et al. Start a Research on Biopolymer Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): A Review. Polymers 2014, 6, 706–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeld, W.M.; Manjusri, M.; Amar, K.M. Review of recent advances in the biodegradability of polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) bioplastics and their composites. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 5519–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Mi, J.; Du, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C. Effect of the crystallization of modified polybutylene terephthalate on its foaming using supercritical CO2: Transition from microcellular to nanocellular foam. J. Supercrit. Fluid. 2022, 181, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Mi, J.; Du, Z.; Zhang, C. Evolution of cell morphology from sub-macroscale to nanoscale in modified thermoplastic polyether ester elastomer via supercritical CO2 foaming. J. Supercrit. Fluid. 2021, 175, 105186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.; Seong, S.B.; Nik, M.M.; Lee, J.H.; Park, C.B. Extensional Flow Resistance of 3D Fiber Networks in Plasticized Nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 6467–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Wu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y. Viscoelasticity and thermal stability of polylactide composites with various functionalized carbon nanotubes. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2008, 93, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, K.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Min, J. The effect of compatibilization on the properties and foaming behavior of poly(ethylene terephthalate)/poly(ethylene-octene) blends. Cell. Polym. 2017, 36, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X. Microcellular foaming behaviors of poly (lactic acid)/low-density polyethylene blends induced by compatibilization effect. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1721–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Mi, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, X. Multiple actions of poly(ethylene octene) grafted with glycidyl methacrylate on the performance of poly(lactic acid). RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 34418–34427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, L. Shrink-resistant poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) foam reinforced with crystalline poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) particles. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 7519–7527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Chen, Z. Effect of chain extension on the rheological property and thermal behaviour of poly(lactic acid) foams. Cell. Polym. 2013, 32, 343–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, K.; Ma, Z.; Xu, N.; Pang, S.; Pan, L. Biodegradable blends of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and polyglycolic acid with enhanced mechanical, rheological and barrier performances. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palai, B.; Mohanty, S.; Kumar, S. Synergistic effect of polylactic acid(PLA) and Poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) based sustainable, reactive, super toughened eco-composite blown films for flexible packaging applications. Polym. Test. 2020, 83, 106130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jia, D.; Sun, Z.; Zhou, S.; Dai, K.; Zhong, G.; Li, Z. Bioinspired nanolayered structure tuned by extensional stress: A scalable way to high-performance biodegradable polyesters. Small 2024, 20, 2402842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, P.; Haldar, D.; Sharma, C.; Chopra, J.; Chakrabortty, S.; Dilip, K.J. Innovations in poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and nanocomposites for sustainable food packaging via biochemical biorefinery platforms: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Biological Macromol. 2024, 283, 137574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Q.; Yin, C.; Li, X.; He, C. Linear relationship between lateral size of reduced graphene oxide (RGO) and water vapor barrier property in RGO/PEI composite membrane. J. Membrane Sci. 2023, 684, 121876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenbock-Fermor, A.; Rudov, A.A.; Gumerov, R.A.; Tsarkova, L.A.; BöKer, A.; MöLler, M.; Potemkin, I.I. Morphology-controlled kinetics of solvent uptake by block copolymer films in nonselective solvent vapors. Acs Macro Lett. 2014, 3, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binh, M.T.; Boon, P.C.; Tizazu, H.M. The barrier properties of sustainable multiphase and multicomponent packaging materials: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 133, 101071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
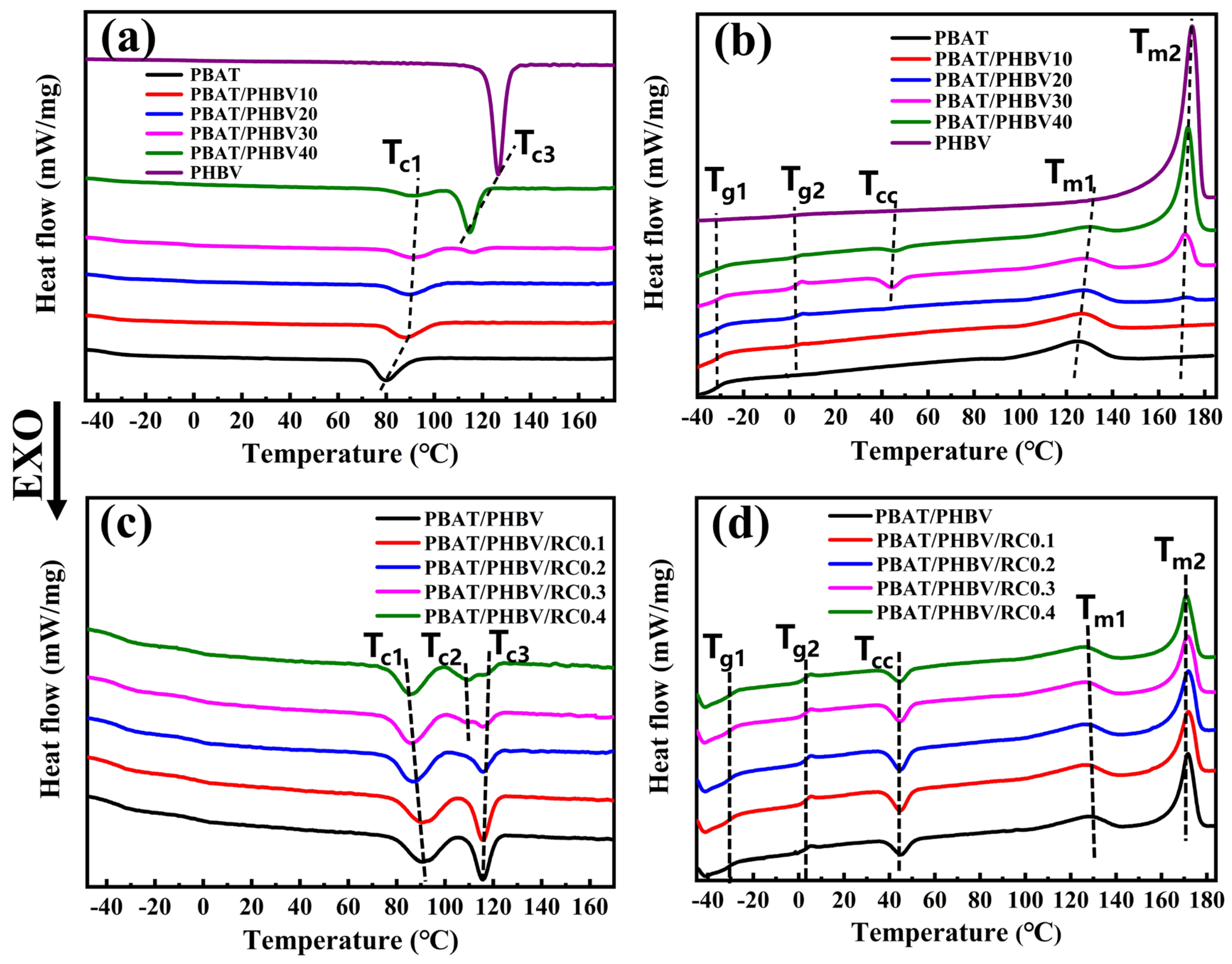
| Samples | Tg1 (°C) | Tg2 (°C) | Tc1 (°C) | Tc2 (°C) | Tc3 (°C) | Tcc (°C) | ΔHc1 (J/g) | ΔHc2 (J/g) | ΔHcc (J/g) | Tm1 (°C) | Tm2 (°C) | ΔHm1 (J/g) | ΔHm2 (J/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBAT | −30.9 | - | 79.9 | - | - | - | 16.2 | - | - | 124.5 | - | 15.9 | - |
| PBAT/PHBV10 | −30.3 | 1.6 | 88.3 | - | - | - | 12.9 | - | - | 126.2 | - | 12.1 | - |
| PBAT/PHBV20 | −30.6 | 1.7 | 89.4 | - | - | 42.5 | 10.6 | - | 0.2 | 127.6 | 172.0 | 9.6 | 0.6 |
| PBAT/PHBV30 | −30.3 | 1.7 | 90.8 | - | 115.5 | 44.3 | 8.2 | 6.4 | 2.4 | 128.1 | 171.7 | 4.9 | 12.3 |
| PBAT/PHBV40 | −30.1 | 1.8 | 91.3 | - | 114.7 | 45.2 | 5.2 | 19.3 | 0.8 | 130.0 | 172.7 | 2.7 | 22.3 |
| PHBV | - | 1.7 | - | - | 126.6 | - | - | 86.7 | - | - | 174.5 | - | 86.9 |
| PBAT/PHBV/RC0.1 | 30.4 | 1.7 | 87.4 | - | 115.4 | 44.4 | 8.4 | 5.8 | 3.5 | 126.9 | 171.9 | 4.9 | 12.7 |
| PBAT/PHBV/RC0.2 | 30.7 | 1.8 | 87.5 | - | 115.8 | 44.8 | 8.4 | 3.5 | 3.2 | 126.6 | 171.9 | 4.6 | 10.8 |
| PBAT/PHBV/RC0.3 | 30.6 | 1.7 | 85.6 | 109.0 | 115.5 | 45.1 | 8.3 | 3.0 | 2.7 | 126.4 | 171.4 | 4.5 | 10.0 |
| PBAT/PHBV/RC0.4 | 30.7 | 1.6 | 86.2 | 109.5 | 115.7 | 44.3 | 7.9 | 3.9 | 2.0 | 126.6 | 170.8 | 4.6 | 10.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Guo, B. In Situ Constructing Highly Aligned Ribbon-like PHBV Lamellae in PBAT: Towards Strong, Ductile and High-Barrier PBAT/PHBV Films. Materials 2025, 18, 3947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173947
Wang Y, Xu J, Guo B. In Situ Constructing Highly Aligned Ribbon-like PHBV Lamellae in PBAT: Towards Strong, Ductile and High-Barrier PBAT/PHBV Films. Materials. 2025; 18(17):3947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173947
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yaqiao, Jun Xu, and Baohua Guo. 2025. "In Situ Constructing Highly Aligned Ribbon-like PHBV Lamellae in PBAT: Towards Strong, Ductile and High-Barrier PBAT/PHBV Films" Materials 18, no. 17: 3947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173947
APA StyleWang, Y., Xu, J., & Guo, B. (2025). In Situ Constructing Highly Aligned Ribbon-like PHBV Lamellae in PBAT: Towards Strong, Ductile and High-Barrier PBAT/PHBV Films. Materials, 18(17), 3947. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173947









