Study on Microstructure and Properties of K-TIG Welded Joint of 95 mm Ti-6Al-4V Thick Plate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Welding Method
2.3. Microstructure and Performance Testing Method
3. Results and Discussion
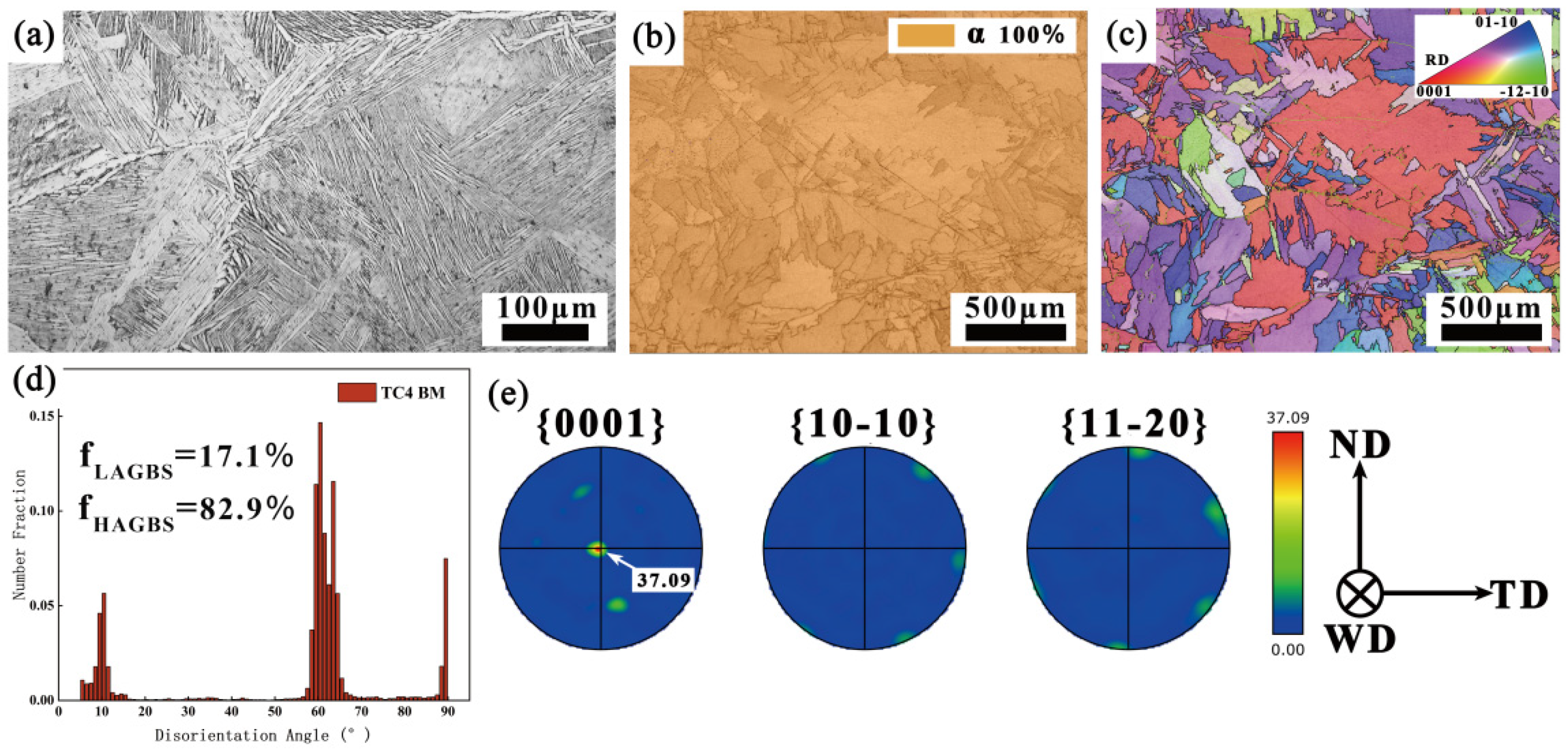
3.1. Microstructure Morphology of the Welded Joint
3.1.1. Macroscopic Morphology
3.1.2. Microscopic Morphology
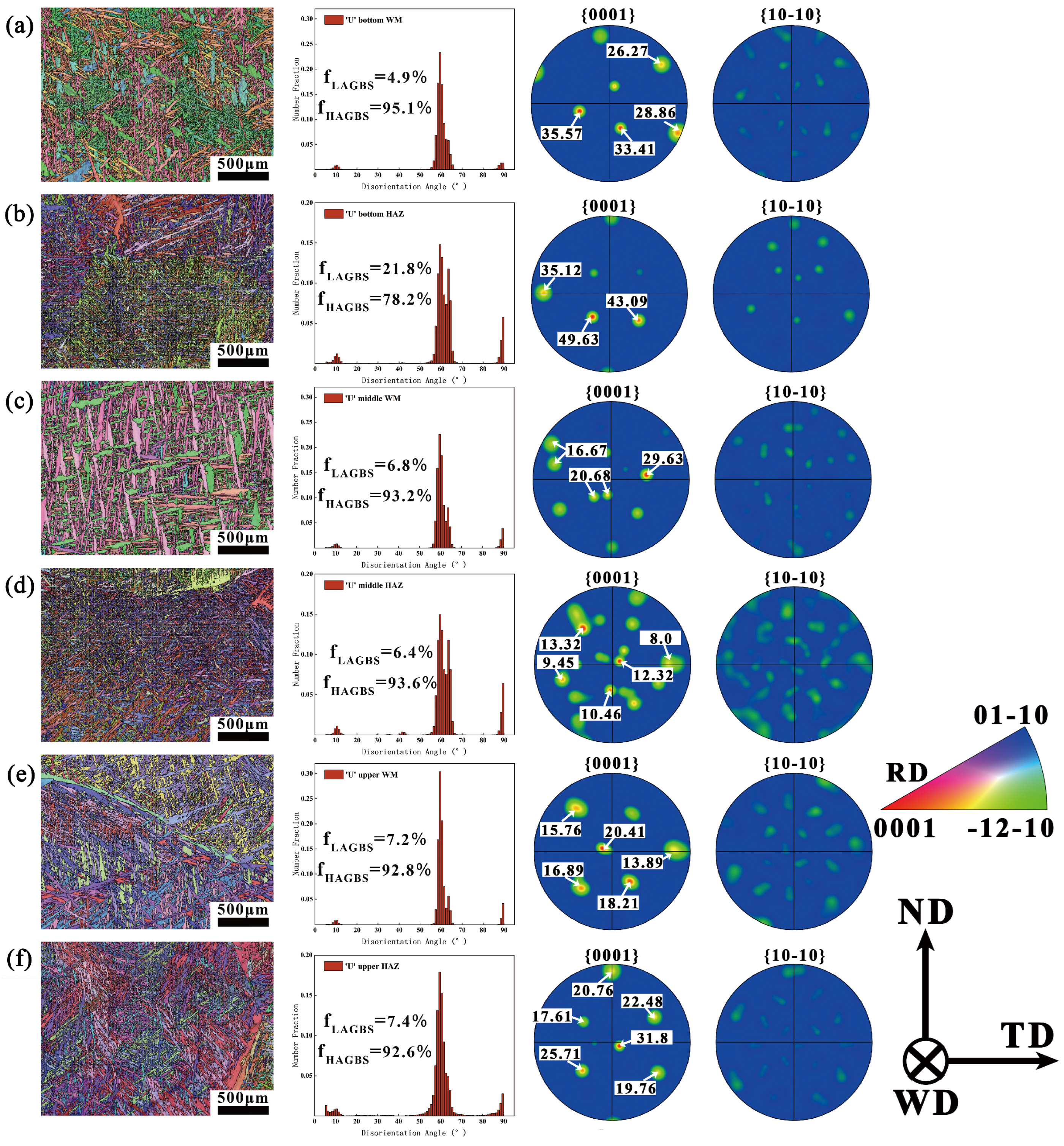
3.2. Grain Orientation and Distribution Analysis
3.3. Mechanical Properties of the Welded Joint
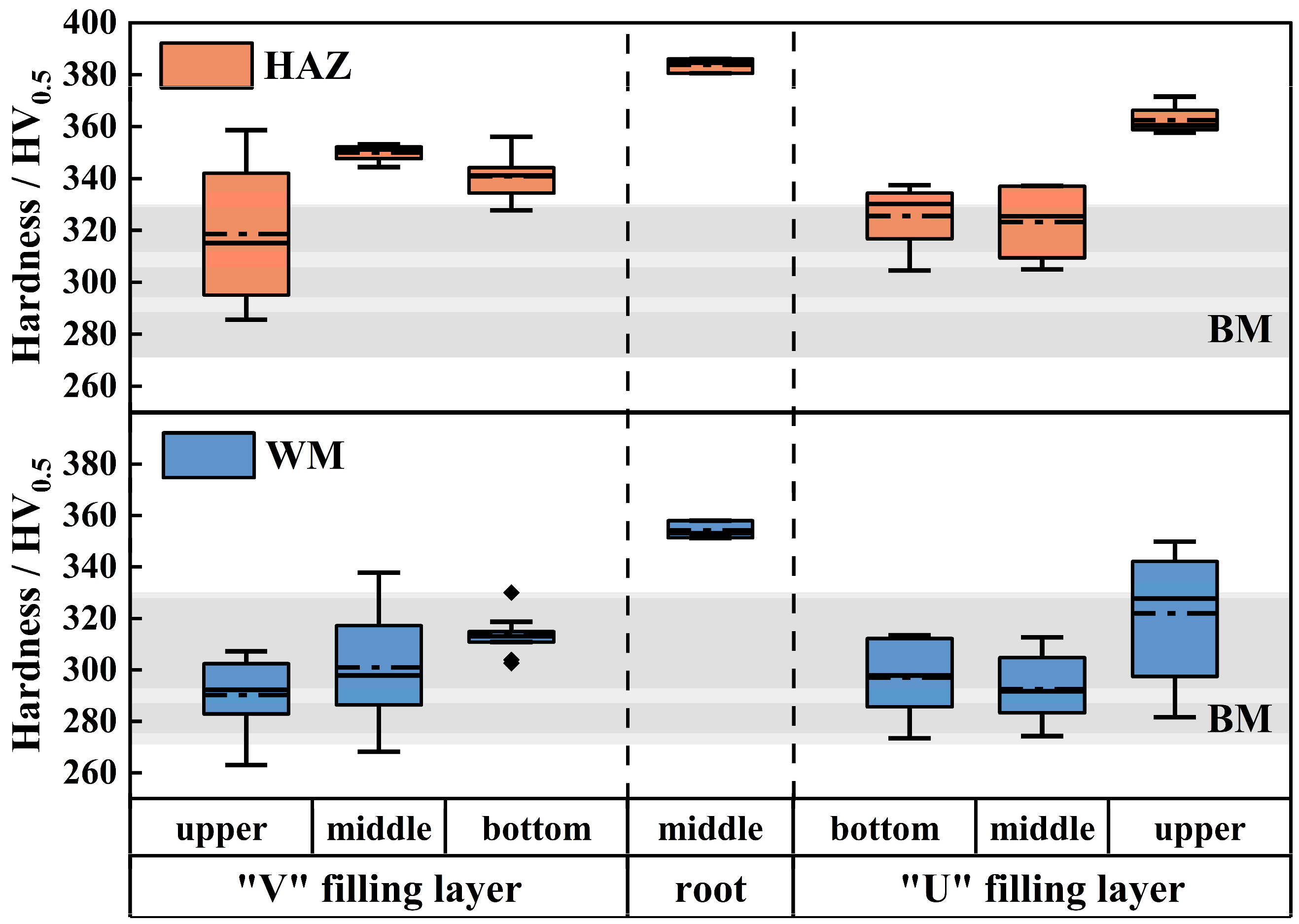
3.3.1. Microhardness
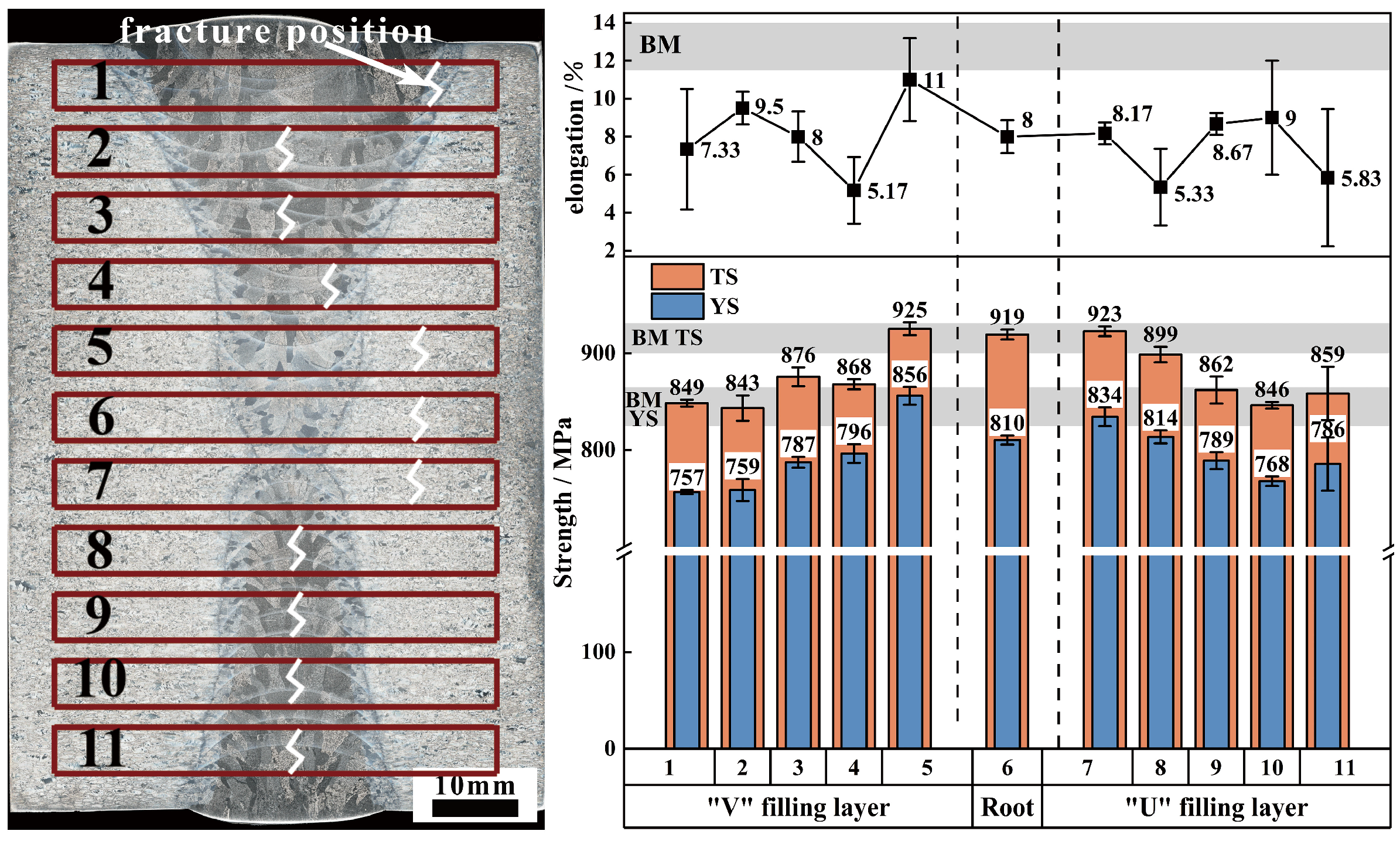
3.3.2. Tensile Property
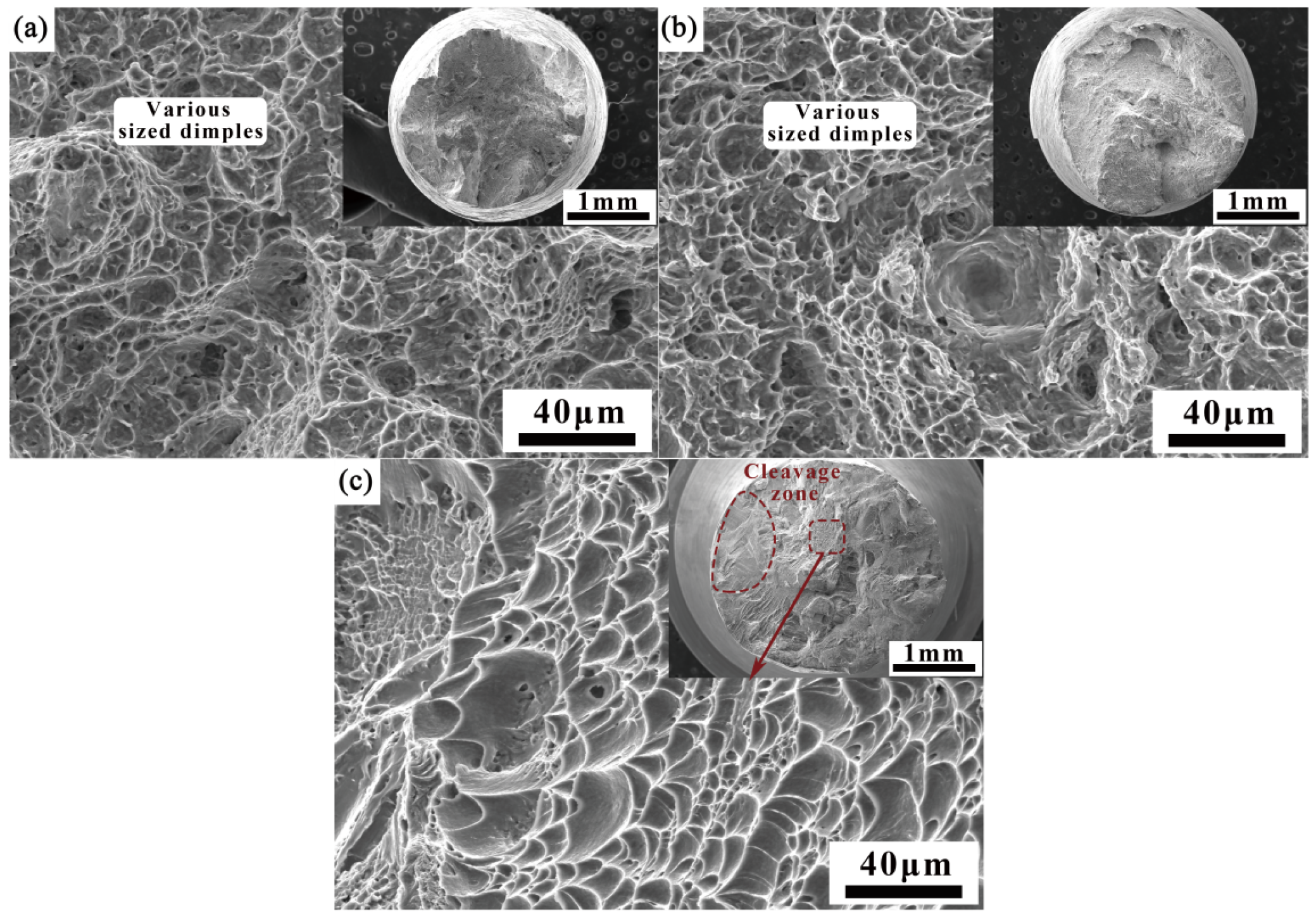
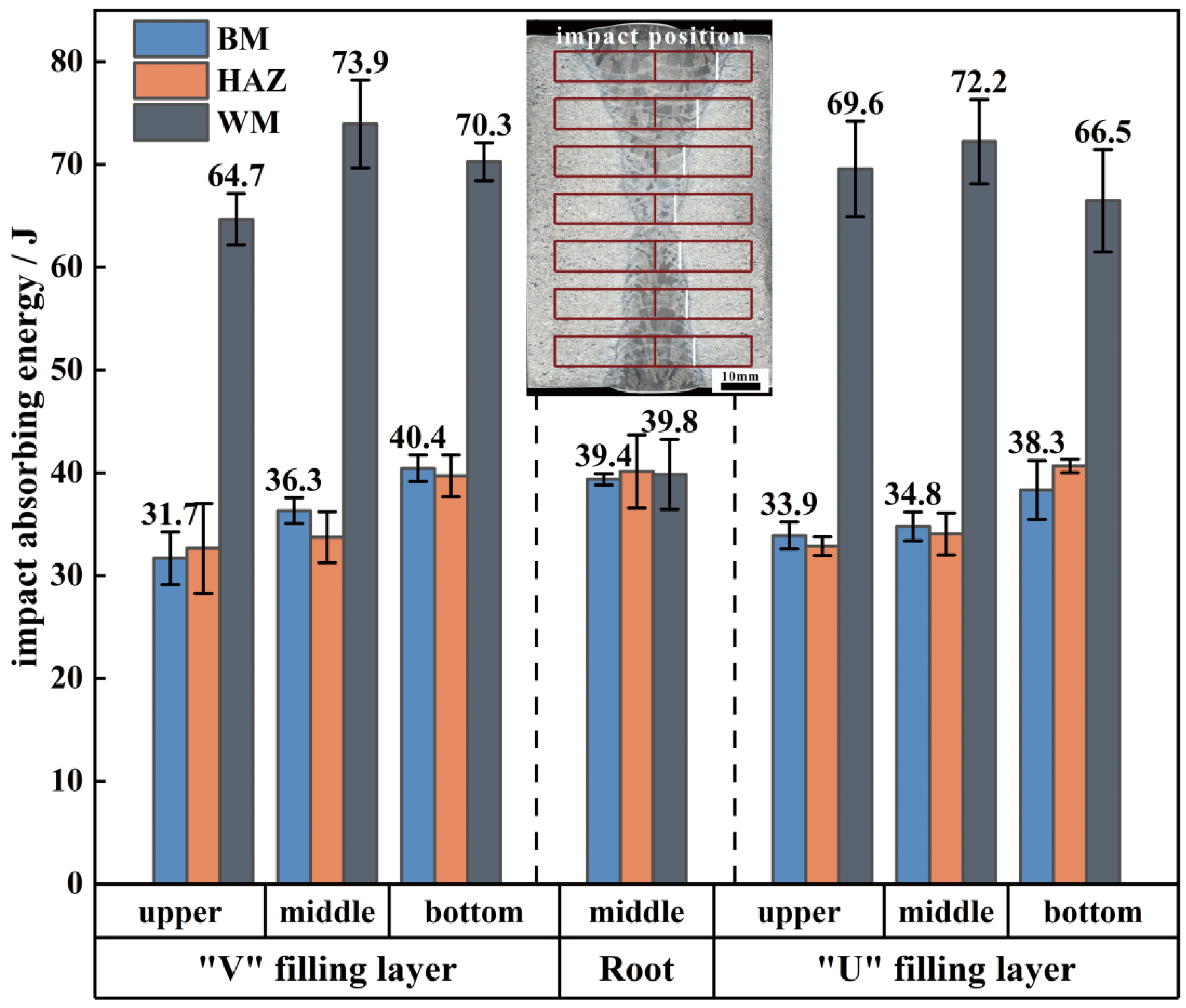
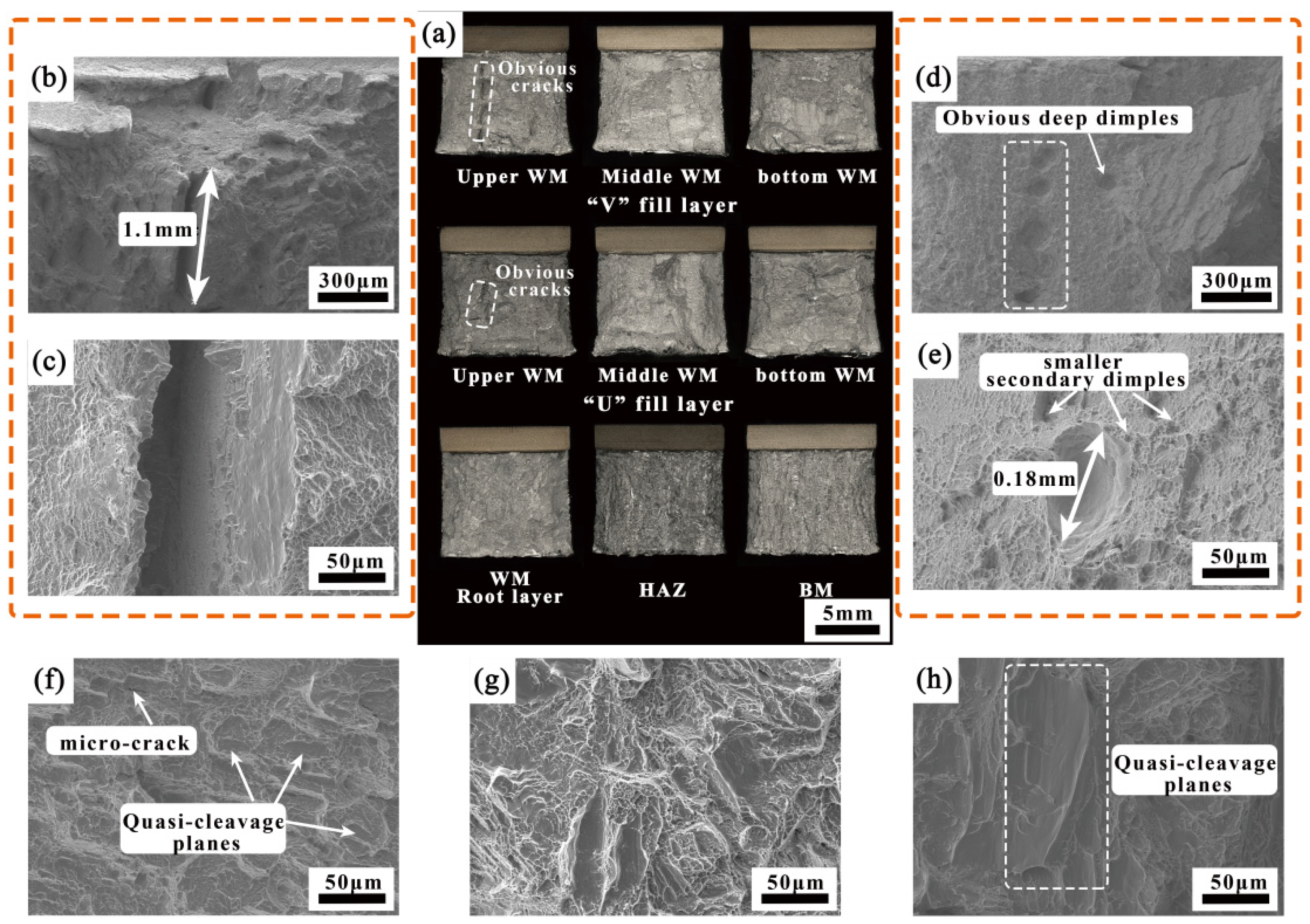
3.3.3. Impact Property
4. Conclusions
- The mechanical arc oscillation K-TIG hot-wire filling welding technology is successfully applied to weld 95 mm-thick Ti-6Al-4V alloy workpieces, demonstrating high welding efficiency and good joint properties.
- Under the engagement strengthening effect, the strength of the welded joint can reach more than 92.6% and the elongation is 40~70% of the BM. The hardness of the root weld is approximately 351.3–386.1 HV5, while the hardness of the filler metal weld ranges from 263 to 337 HV0.5, and the hardness of the heat-affected zone lies between 285 and 371.6 HV0.5. The significant difference in hardness between the filler and root welds is likely due to the inherently lower hardness of the filler material.
- The WM microstructure primarily consists of various forms of α phases and fine α+β structures. The HAZ is characterized by interlaced acicular α phase and a small amount of massive α phase. The α phase disperses in a relatively wide, multidirectional pattern.
- The impact of multi-cycle thermal effects on texture types and strength varies with different welding currents. In high-current filling welding, multi-cycle thermal effects can effectively increase the diversity of texture types in the HAZ while weakening the texture strength.
- The joint exhibits excellent impact property, with the impact absorption energy of the filling weld seam ranging from 64.7 to 73.9 J, approximately twice that of the BM. The impact toughness in other areas is comparable to that of the BM, with no noticeable weak spots. The contribution of the engagement strengthening effect in TIG thick-plate welding to the impact toughness of the filling layers should not be overlooked.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, A.; Zhang, J.; Gao, C.; Hu, R.; Pang, S. Effects of groove constraint space on plasma characteristics during Laser-MIG hybrid welding of Titanium alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 48, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhan, X.; Gao, Z.; Yan, T.; Zhou, Z. Microstructure and stress distribution of TC4 titanium alloy joint using laser-multi-pass-narrow-gap welding. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 108, 3725–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Fan, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, R.; Li, B.; Jiang, P.; Xue, X.; Kou, H.; Li, J. Deciphering the role of macrozones in the microstructure globularization and tensile fracture: Insights from a new developed marine engineering titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 917, 147396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Jia, J.-L.; Zhang, L.-J.; Zhuang, M.-X.; Wu, J.-H. Fatigue inhomogeneity of 140 mm thick TC4 titanium alloy double-sided electron beam welded joints. Int. J. Fatigue 2022, 165, 107214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragatheswaran, T.; Rajakumar, S.; Balasubramanian, V. Optimization of the weld characteristics of plasma-arc welded titanium alloy joints: An experimental study. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2022, 37, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auwal, S.T.; Ramesh, S.; Yusof, F.; Manladan, S.M. A review on laser beam welding of titanium alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 1071–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, A.B. Gas tungsten arc welding of α + β titanium alloys: A review. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 25, 309–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Zhang, L.-J.; Zhuang, M.-X.; Bai, L.; Na, S.-J. Narrow-gap laser welding with beam wobbling and filler wire and microstructural performance of joints of thick TC4 titanium alloy plates. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 152, 108089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Miao, J.; Chang, C.; Chang, Y. Research status of insufficient sidewalls penetration in narrow gap TIG welding of thick metal plates. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 134, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jia, Z.; Yue, J.; Liu, H.; Li, L. Arc interruption phenomena and internal causes in narrow gap P-GMAW. Weld. World 2020, 64, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Miao, J.; Xu, X.; Chang, Y. Study on Arc Behavior and Weld Formation of Magnetically Controlled Narrow Gap TIG Welding. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2025, 26, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davim, J.P. Welding Technology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, T.; Liu, W. Microstructure, texture, and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V joints by K-TIG welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 37, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, S.; Cui, S.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, T.; Luo, Z. Experimental investigation of focusing cathode region by cooling tungsten. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 138, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, T.; Lv, Z.; Luo, Z. Focusing cathode tip characteristics in cooling tungsten. Energy 2019, 167, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X. Cathode-arc-anode behavior in cooling-induced cathode-focusing GTA system: A unified numerical model. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 199, 123484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Liu, Z.M.; Zhao, X.C.; Lv, Z.Y.; Fan, X.G. Cathode-focused high-current arc: Heat source development with stable keyhole in stationary welding. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 143, 118475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, F. Study on microstructure, mechanical and corrosion behavior of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy by Keyhole gas tungsten arc welding. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathabai, S.; Jarvis, B.L.; Barton, K.J. Comparison of keyhole and conventional gas tungsten arc welds in commercially pure titanium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 299, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermingham, M.J.; McDonald, S.D.; Dargusch, M.S.; StJohn, D.H. Grain-refinement mechanisms in titanium alloys. J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbarasan, N.; Narein, N.; Jerome, S. Influence of Mechanical Arc Oscillation on the Microstructural and Mechanical Properties of Inconel 718 Welds. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2019, 72, 1541–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ault, J.; Pillers, J.; Veeck, S. The GTAW of Ti-6Al-4V castings and its effect on microstructural and mechanical properties. JOM 2005, 57, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.; Rack, H.J. Phase transformations during cooling in α+β titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 243, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.L.; Qian, M.; Tang, H.P.; Yan, M.; Wang, J.; StJohn, D.H. Massive transformation in Ti–6Al–4V additively manufactured by selective electron beam melting. Acta Mater. 2016, 104, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Wang, Y.; He, S.; Zhang, C.; Jing, X. Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of TIG weld joint made by forged Ti–4Al–2V alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 821, 141604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, P.; Cao, Z.; Hai, M.; Qiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of K-TIG welded dissimilar joints between TC4 and TA17 titanium alloys. Mater. Charact. 2023, 196, 112644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Sun, Y.; Kato, H.; Nakata, K. Investigation of welding parameter dependent microstructure and mechanical properties in friction stir welded pure Ti joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 3386–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoghue, J.; Antonysamy, A.A.; Martina, F.; Colegrove, P.A.; Williams, S.W.; Prangnell, P.B. The effectiveness of combining rolling deformation with Wire–Arc Additive Manufacture on β-grain refinement and texture modification in Ti–6Al–4V. Mater. Charact. 2016, 114, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.D.; Fang, H.Y.; Liu, X.S.; Meng, Q.G. Influence of a welding sequence on the welding residual stress of a thick plate. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2005, 13, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Chew, K.G. Effect of welding on impact toughness of butt-joints in a titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 347, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Liao, Z.; Li, W.; Cui, Y.; Yu, W.; Lv, Y. Investigating the impact toughness properties and influential factors of titanium alloy joints. Mater. Charact. 2024, 218, 114465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, C.R.; Choudhury, A. Failure Analysis of Engineering Materials; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.H.; Cao, R. Micromechanism of Cleavage Fracture of Metals: A Comprehensive Microphysical Model for Cleavage Cracking in Metals, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Butterworth-Heinemann: Boston, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]






| Material | Al | V | Fe | O | C | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base material | 6.08 | 3.82 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.034 | bal. |
| Filling metal | 5.96 | 2.78 | 0.015 | 0.043 | 0.005 | bal. |
| Material | UTS/MPa | YS/MPa | Elongation/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base material | 900~931 | 825~865 | 11.5~14 |
| Filler metal | 826 | 677 | 13.8 |
| Current (A) | Weld Speed (mm/min) | Wire Feed Speed (mm/min) | Weave Speed (mm/min) | Amplitude (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root weld | 600 | 200 | —— | —— | —— |
| Filling weld | 220~320 | 130 | 2000~6000 | 100~130 | 3~6 |
| Sample Number | Sample State | UTS/MPa | YS/MPa | Elongation/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #4 | As-welded | 868 | 796 | 5.17 |
| Annealing | 873 | 799 | 7.5 | |
| #8 | As-welded | 899 | 814 | 5.33 |
| Annealing | 901 | 831 | 6.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Y.; Hui, S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, X.; Ye, W.; Wang, Z. Study on Microstructure and Properties of K-TIG Welded Joint of 95 mm Ti-6Al-4V Thick Plate. Materials 2025, 18, 3848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163848
Gong Y, Hui S, Yu Y, Zhang Z, Ye X, Ye W, Wang Z. Study on Microstructure and Properties of K-TIG Welded Joint of 95 mm Ti-6Al-4V Thick Plate. Materials. 2025; 18(16):3848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163848
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Yinqing, Songxiao Hui, Yang Yu, Zhihao Zhang, Xiongyue Ye, Wenjun Ye, and Zhongliang Wang. 2025. "Study on Microstructure and Properties of K-TIG Welded Joint of 95 mm Ti-6Al-4V Thick Plate" Materials 18, no. 16: 3848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163848
APA StyleGong, Y., Hui, S., Yu, Y., Zhang, Z., Ye, X., Ye, W., & Wang, Z. (2025). Study on Microstructure and Properties of K-TIG Welded Joint of 95 mm Ti-6Al-4V Thick Plate. Materials, 18(16), 3848. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163848





