Effect of Ti Doping of Al0.7CoCrFeNi-Based High Entropy Alloys on Their Erosion Resistance by Solid Particles
Abstract
1. Introduction
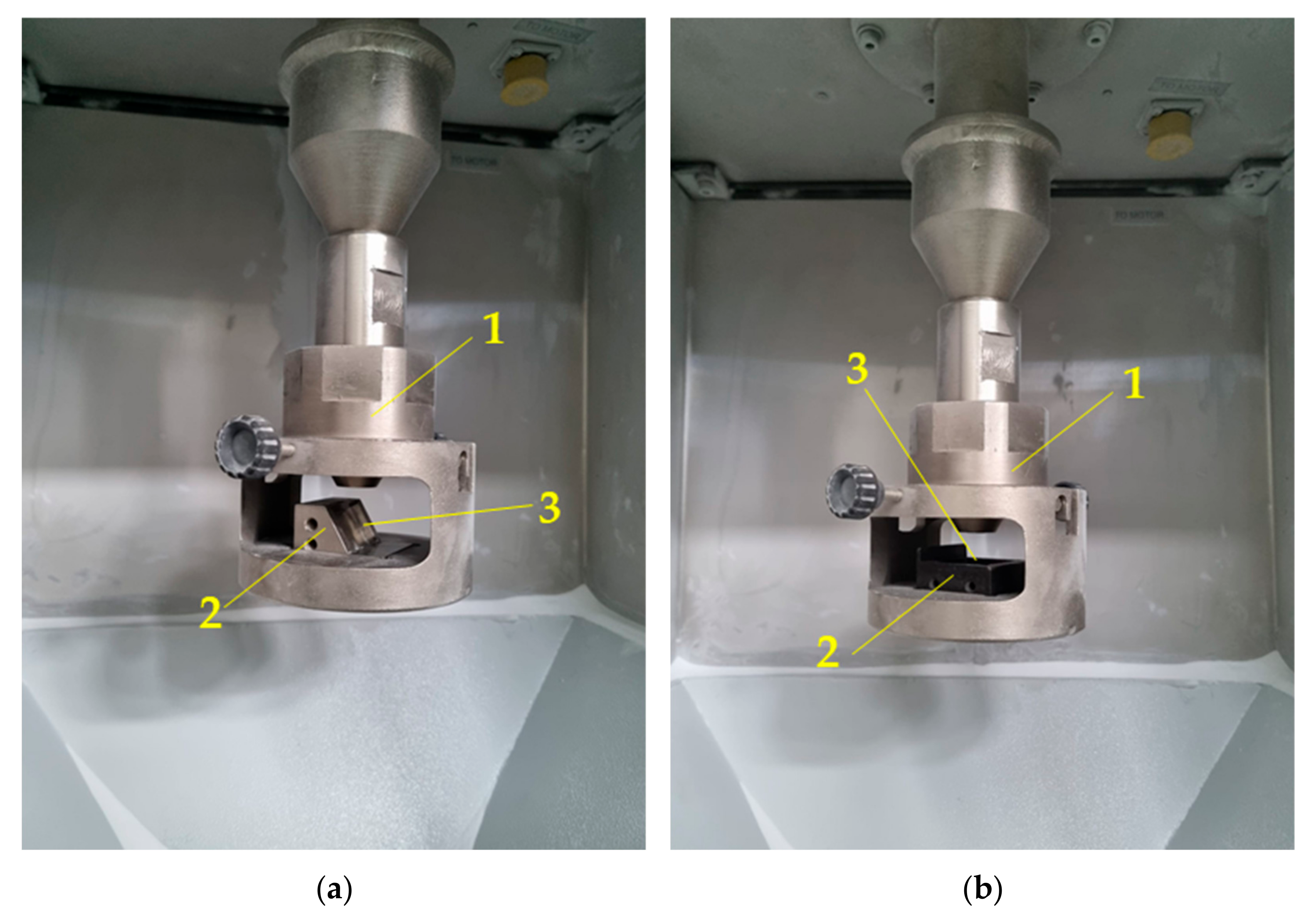
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Materials in the As-Cast Conditions
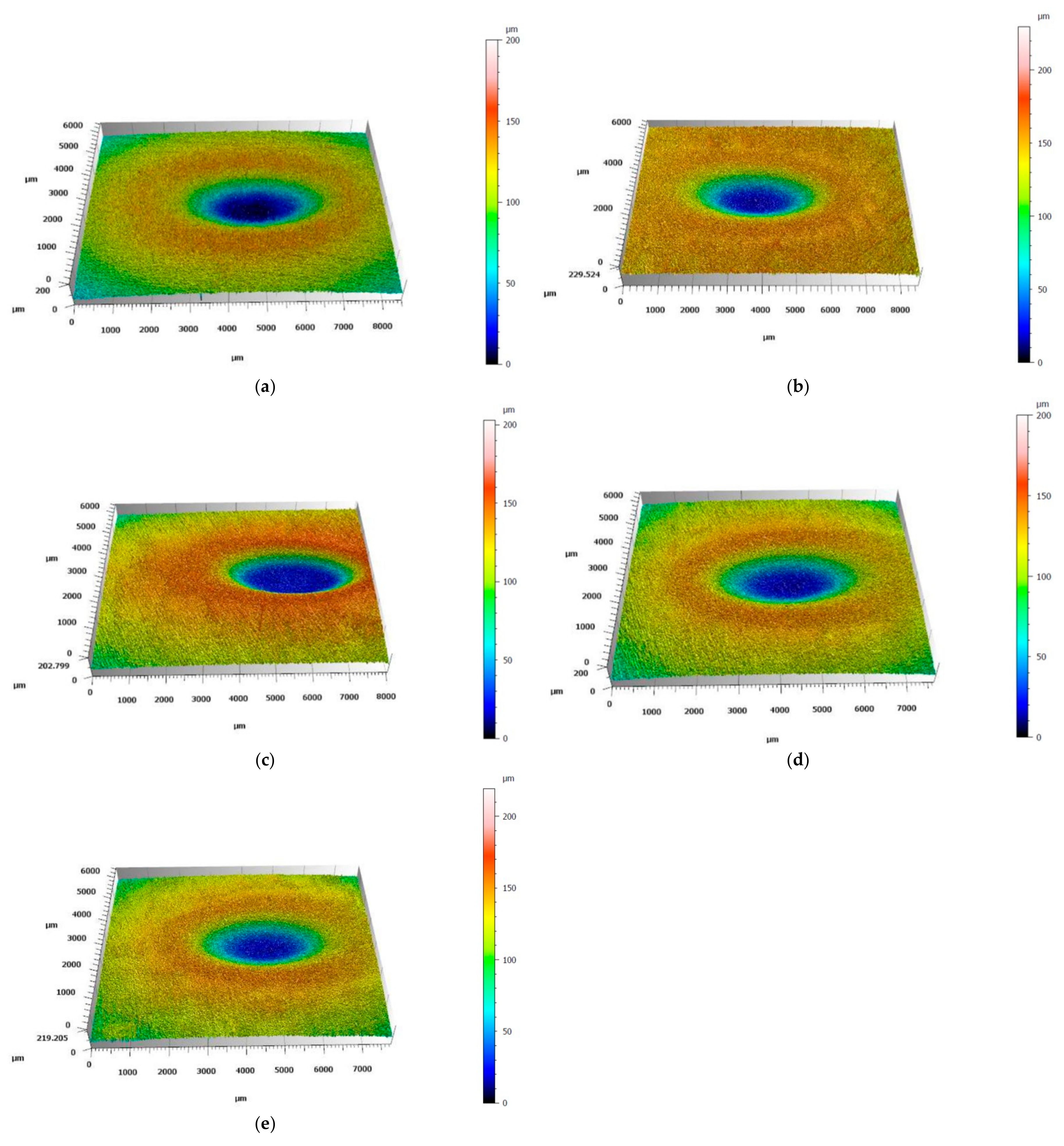
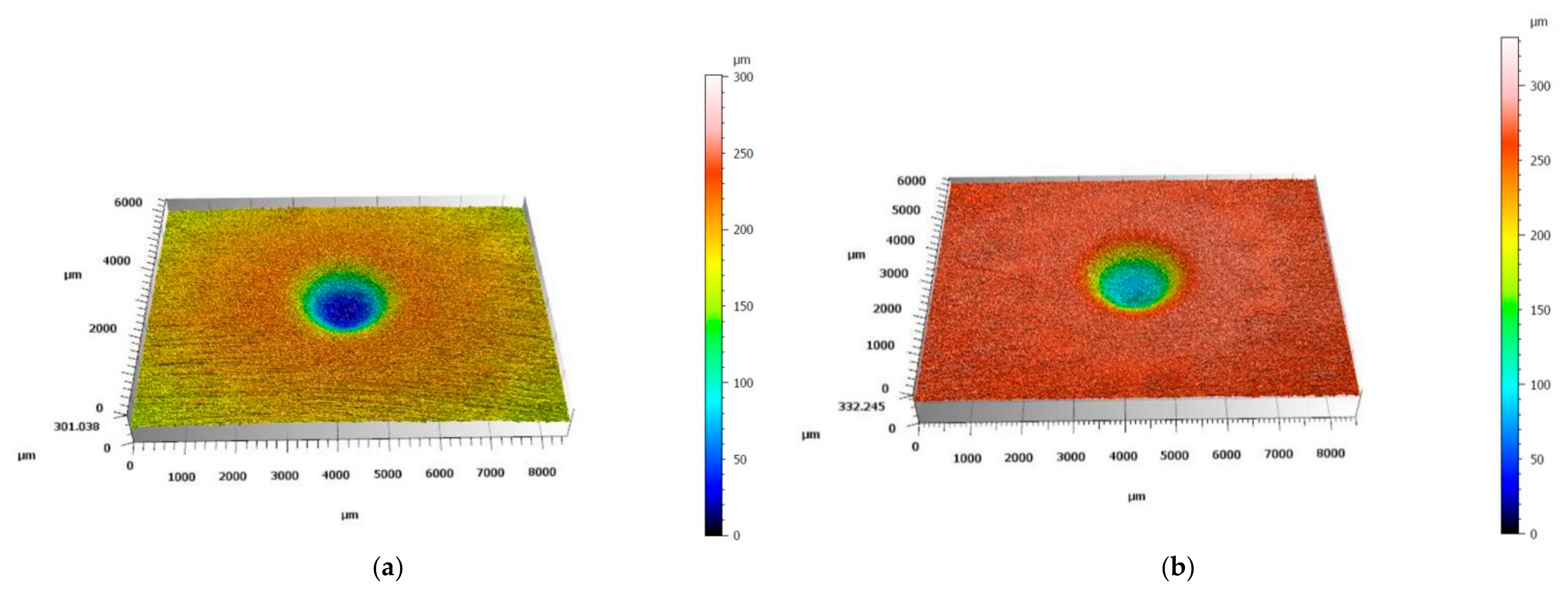
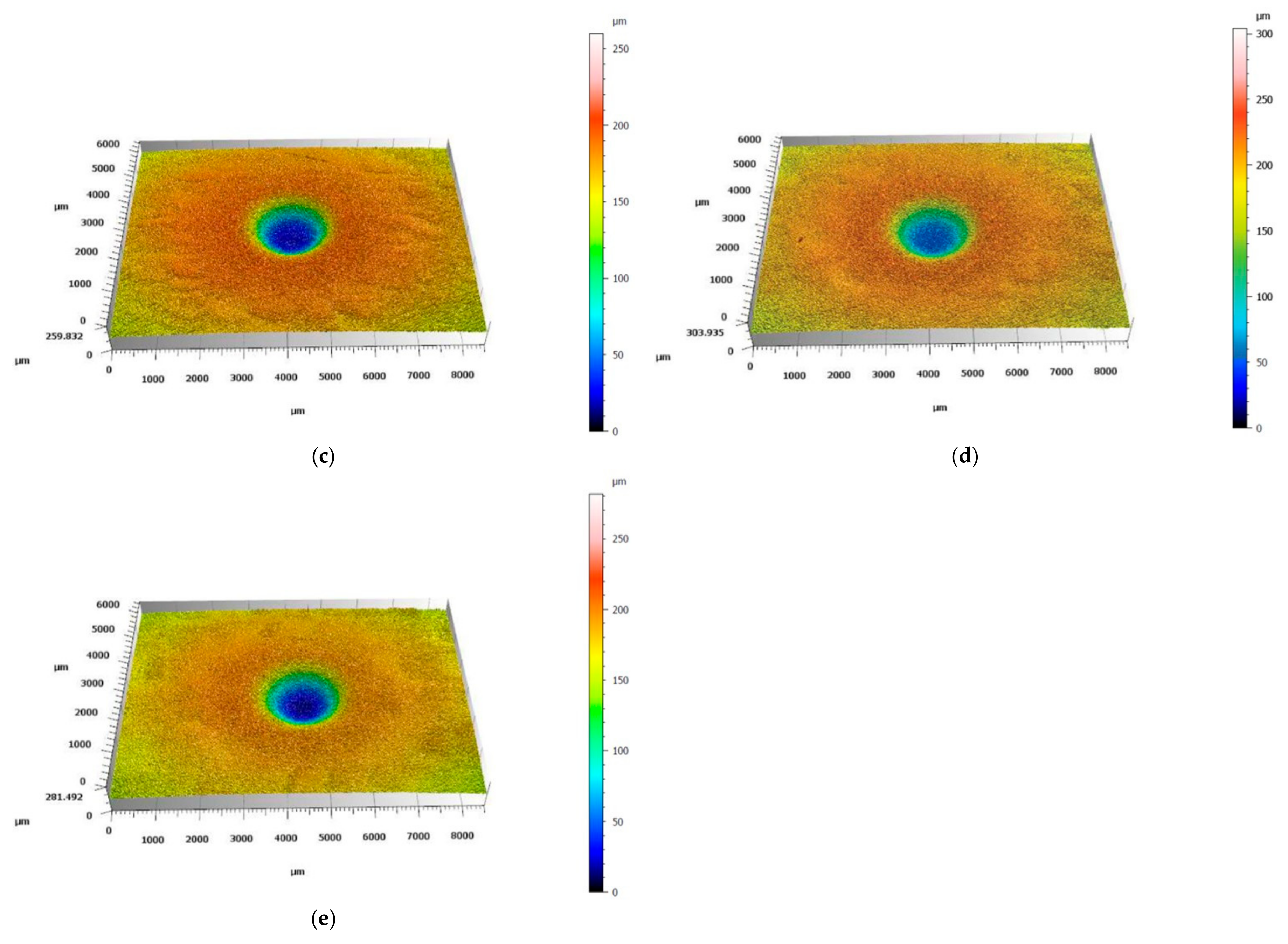
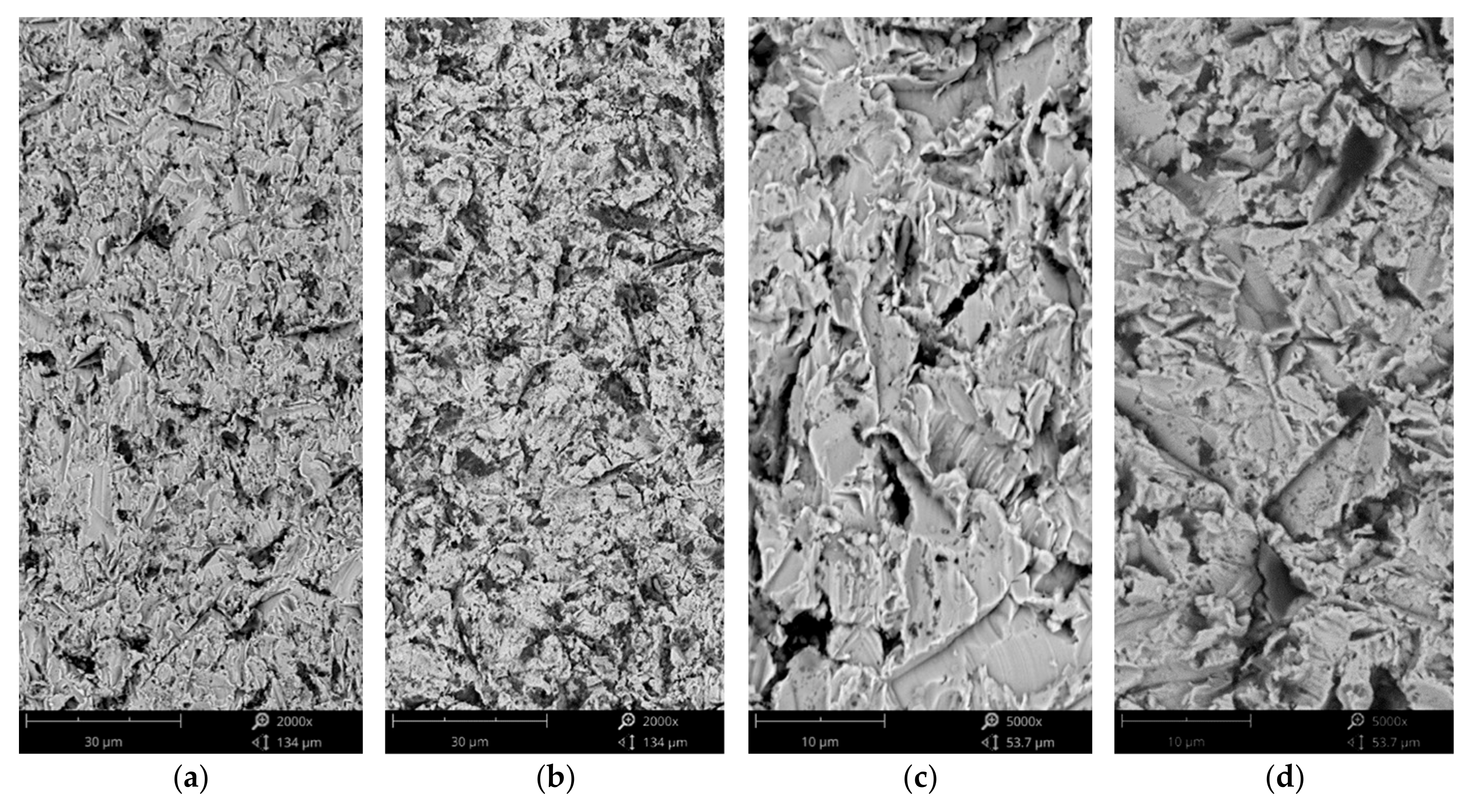
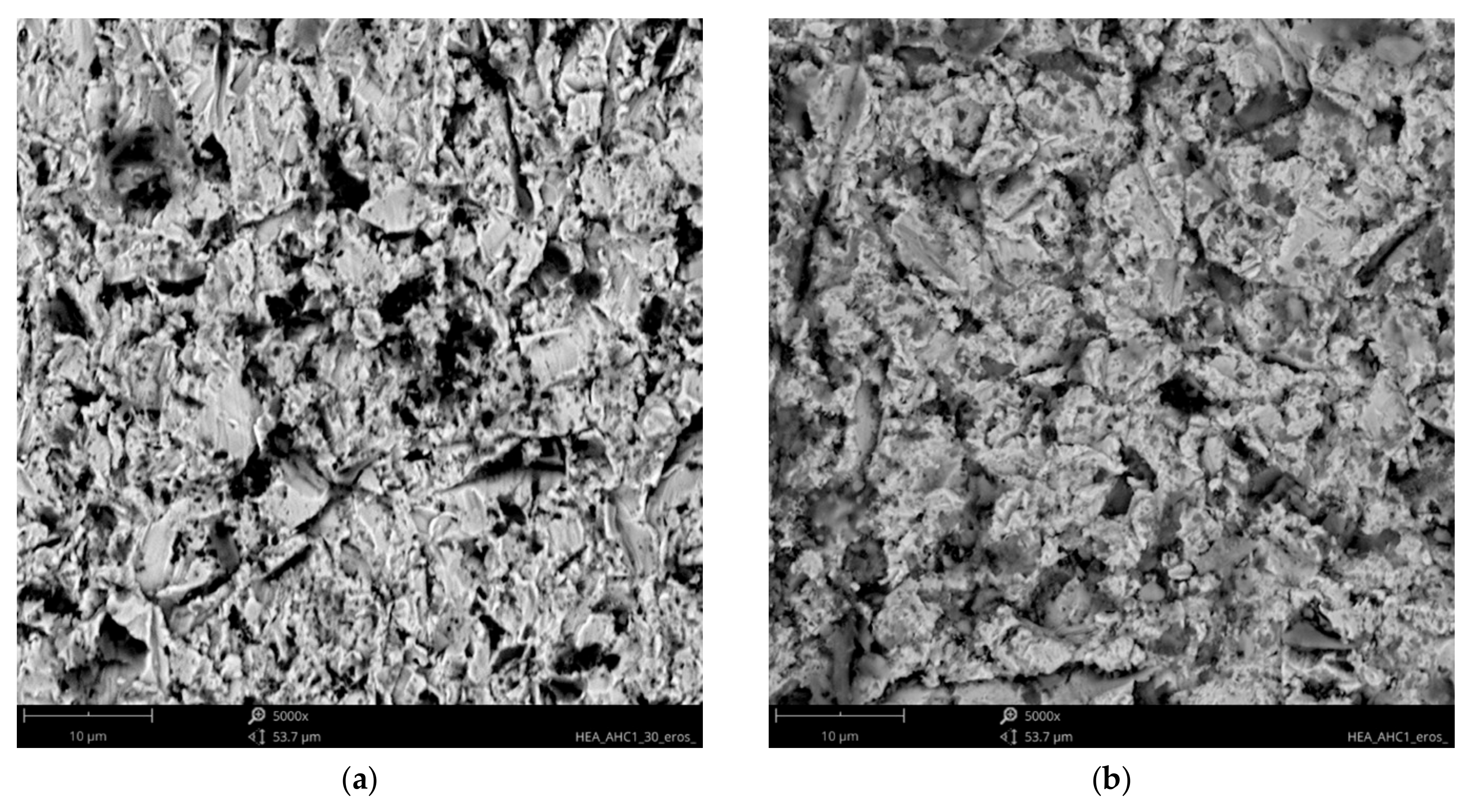
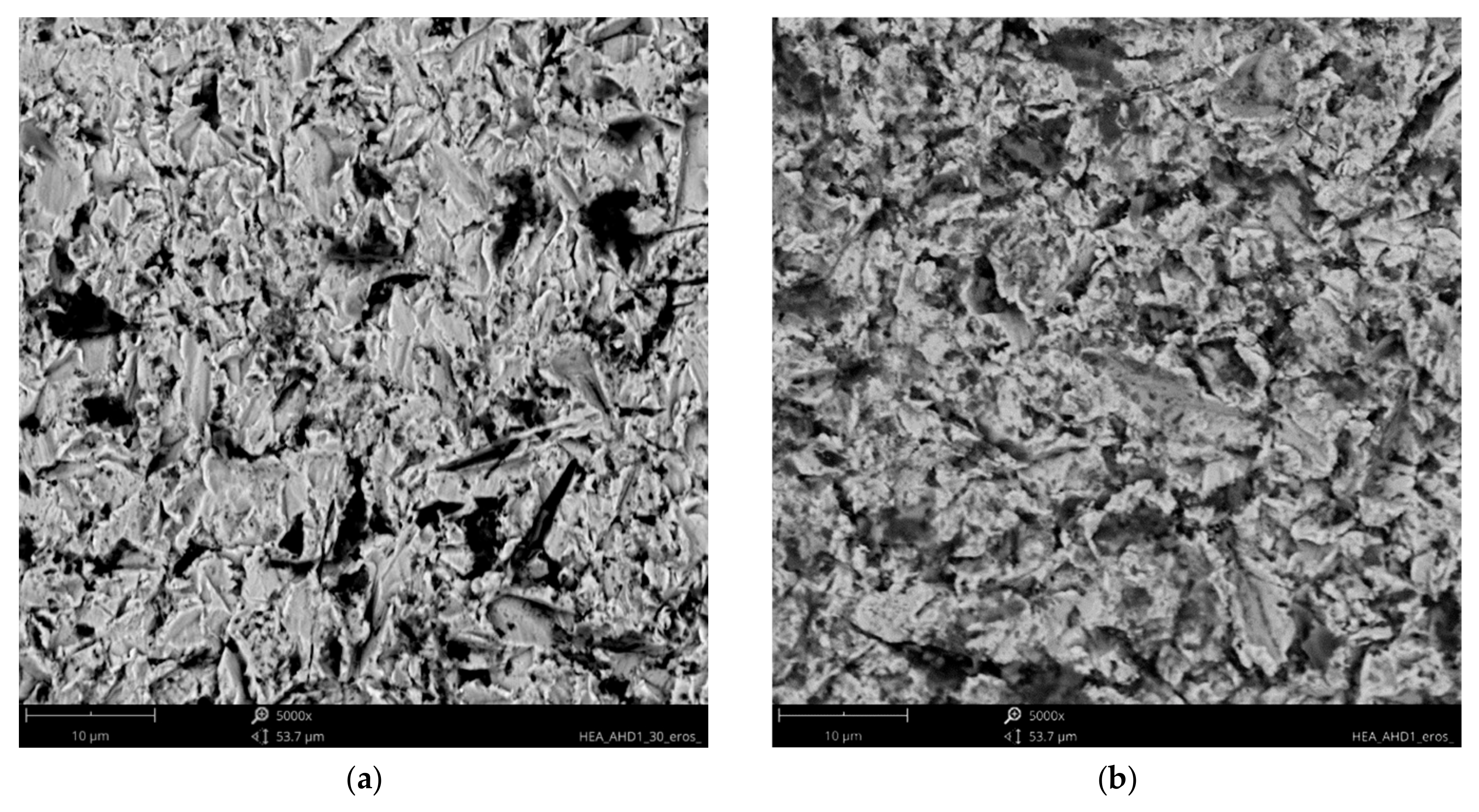
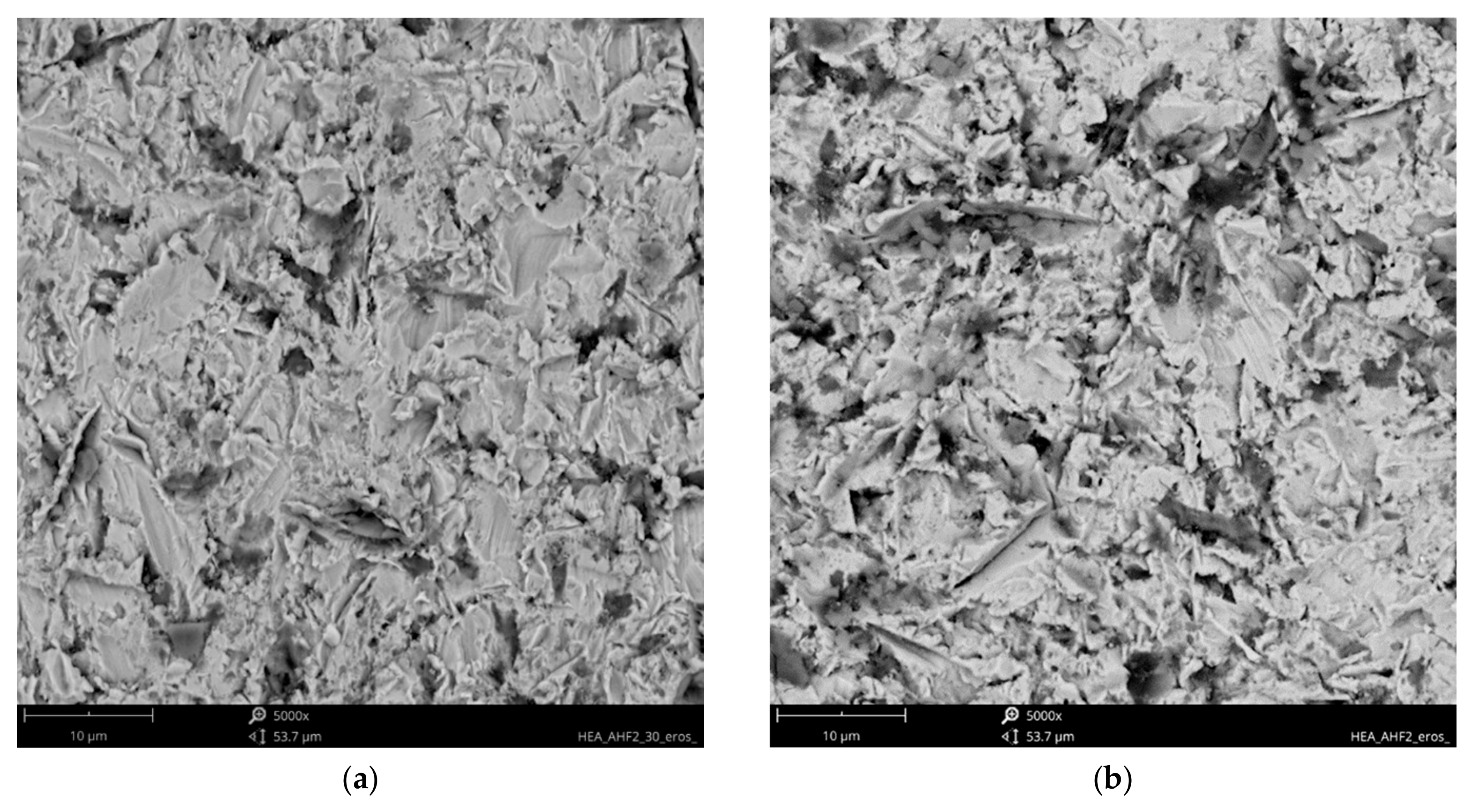
3.2. Solid Particle Erosion Tests
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
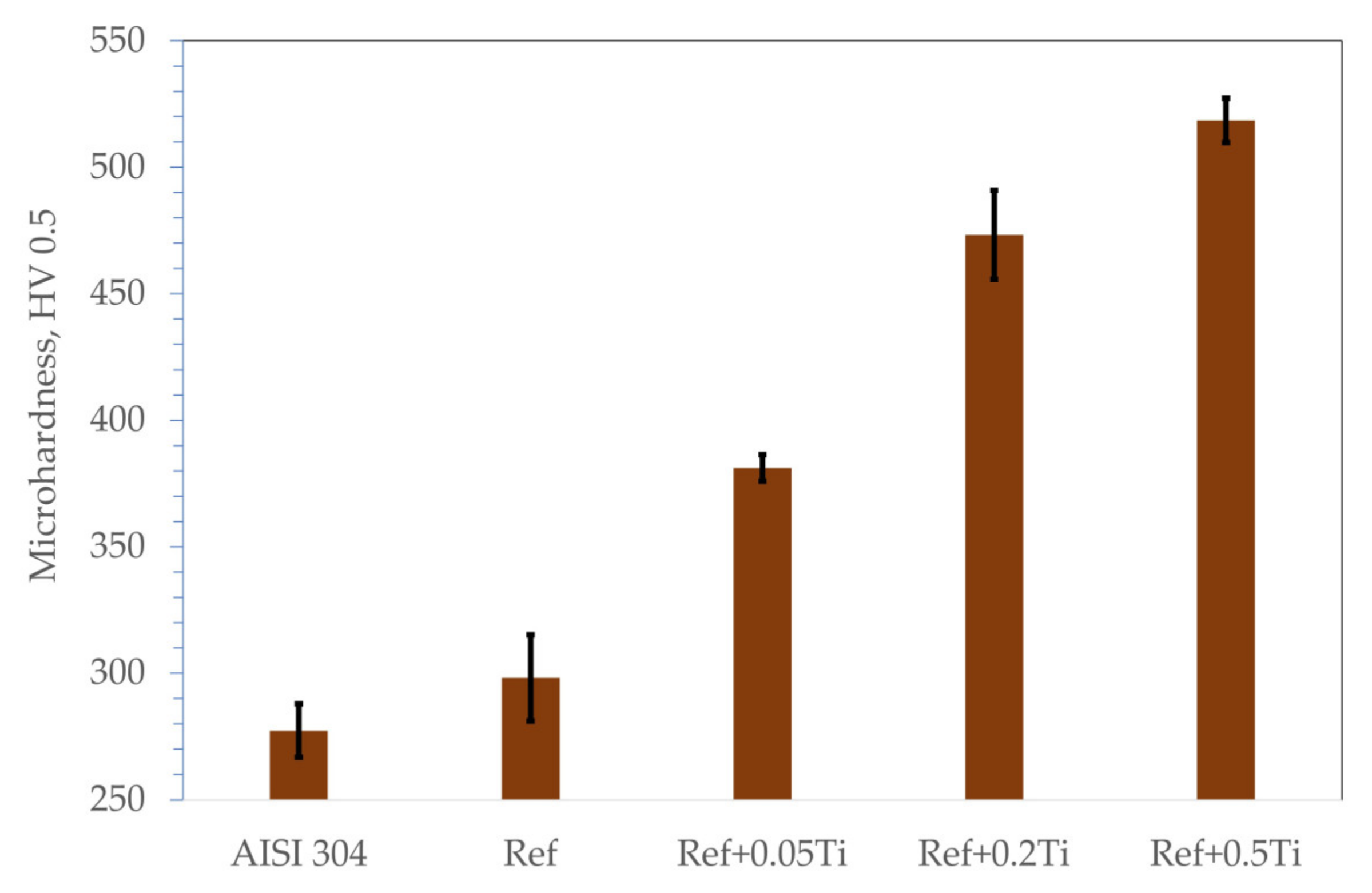
- The studied Ref. (Al0.7CoCrFeNi) HEA exhibits higher hardness and erosion resistance compared with the state-of-the-art stainless steel AISI 304. As a reason for such a phenomenon, a combination of an HEA multiphase microstructure is claimed.
- Alloying with Ti results in a further increase in hardness and the erosion resistance of the studied HEA. The resistance to the erosion of solid particles of Al0.7CoCrFeNi can be improved by adding titanium Al0.7CoCrFeNiTix. The increase in titanium corresponds well to the improvement in the erosion resistance of the Al0.7CoCrFeNiTix alloys.
- Higher erosion rates were observed for tests conducted at 30 degrees rather than 90 degrees, which is the effect of the dominance of ductile erosion mechanisms.
- Detailed erosion mechanisms review the grooving, ploughing, and fatigue resulting in the spallation of the material. In the case of the hardest, the surface cracks were noted.
- As the main reason for the increase in hardness and the stabilization of the resistance to the erosion of BCC, the suppression of α-FCC and the occurrence of Ni3Ti phases by Ti are identified. Solid solution and precipitation strengthening mechanisms by the addition of Ti were identified.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HEAs | high entropy alloys |
| BCC | Body Centered Cubic |
| FCC | Face Centered Cubic |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| SEM | scanning electron microscopy |
| BSEs | Backscattered Electrons |
| EDS | Electron Diffraction Spectroscopy |
References
- Rizzo, A.; Goel, S.; Luisa Grilli, M.; Iglesias, R.; Jaworska, L.; Lapkovskis, V.; Novak, P.; Postolnyi, B.O.; Valerini, D. The Critical Raw Materials in Cutting Tools for Machining Applications: A Review. Materials 2020, 13, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Guo, S.; Yu, P.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, J. A Review on Leading-Edge Erosion Morphology and Performance Degradation of Aero-Engine Fan and Compressor Blades. Energies 2023, 16, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, P.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, Y. Research on high-temperature friction and wear performances of Stellite 12 laser cladding layer against coated boron steels. Wear 2023, 520–521, 204665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejrani, E.; Sebold, D.; Nowak, W.J.; Mauer, G.; Naumenko, D.; Vassen, R.; Quadakkers, W.J. Isothermal and cyclic oxidation behavior of free standing MCrAlY coatings manufacturesd by high-velocity atmospheric plasma spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 313, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, W.; Naumenko, D.; Mor, G.; Mor, F.; Mack, D.E.; Vassen, R.; Singheiser, L.; Quadakkers, W.J. Effect of processing parameters on MCrAlY bondcoat roughness and lifetime of APS-TBC systems. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 260, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, R.; Wessel, E.; Nowak, W.J.; Naumenko, D.; Quadakkers, W.J. Predicting Effect of Base Alloy Composition on Oxidation-Induced Degradation of an MCrAlY Coating. JOM 2018, 70, 1520–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, W.J.; Ochał, K.; Wierzba, P.; Gancarczyk, K.; Wierzba, B. Effect of Substrate Roughness on Oxidation Resistance of an Aluminized Ni-Base Superalloy. Metals 2019, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, W.J.; Hader, B.; Ochał, K.; Wierzba, B. Increase in Oxidation Resistance of MAR M-509 via LA-CVD Aluminizing. Coatings 2021, 11, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W.; Chen, S.-K.; Lin, S.-J.; Gan, J.-Y.; Chin, T.-S.; Shun, T.-T.; Tsau, C.-H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.-W. Recent Progress in High Entropy Alloys. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mater. 2006, 31, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Liu, Y.; Yu, T.; Wang, D.; Leng, X.; Wang, K.; Liu, L.; Pan, J.; Yao, S.; Chen, Z. Review on wear resistance of laser cladding high-entropy alloy coatings. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 911–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; XI, S.; Sun, C. Microstructure and properties of laser cladding and CoCr2.5FeNi2Tix high-entropy alloy composite coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 152986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.J.; Tian, Q.W.; Yin, K.X.; Niu, S.Q.; Wu, M.H.; Wang, W.W.; Wang, Y.N.; Huang, J.C. Effect of Fe on microstructure and properties of AlCoCrFexNi (x = 1.5, 2.5) high entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. Intermetallics 2020, 119, 106722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, T.; Xiao, M.; Shen, Y. Effect of iron content on microstructure and properties of FexNi2Co2CrTiNb high-entropy alloy coating. Optik 2020, 204, 164168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Xi, S.; Mao, P.; Wang, C. Microstructure and wear behavior of mechanically alloyed powder AlxMo0.5NbFeTiMn2 high entropy alloy coating formed by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol 2020, 401, 126244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Liu, C. Microstructure and properties of Al2CrFeCoCuTiNix high-entropy alloys prepared by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 553, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarewicz, M.; Gradzka-Dahlke, M.; Nowak, W.J.; Gradzik, A.; Szala, M.; Walczak, M. Effect of Vanadium Addition on the Wear Resistance of Al0.7CoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy. Materials 2024, 17, 6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Diao, G.; Tang, Y.; Chen, K.; Lin, K.; He, A.; Fraser, D.; Li, J.; Chung, R.; Li, Q.Y.; et al. Effects of rare-earth element yttrium (Y) on the solid-particle erosion resistance of AlCrFeNi medium-entropy alloy at ambient and elevated temperatures. Front. Coat. Dye. Interface Eng. 2025, 3, 1598207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Haché, M.J.; Cheng, C.; Lyu, T.; Liu, Z.; Papini, M.; Zou, Y. Solid-particle erosion of a dual-phase AlCoFeNi2 high-entropy alloy. Wear 2023, 528–529, 204971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, B.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, C.; Niu, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Investigation on solid particles erosion resistance of laser cladded CoCrFeNiTi high entropy alloy coating. Intermetallics 2021, 131, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, B.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J.; Shen, Y.; Huang, L.; Qin, X.; Wu, Y.; Pu, K. High-temperature solid particle erosion characteristics and damage mechanism of AlxCoCrFeNiSi high-entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding. Intermetallics 2023, 159, 107939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, R.B.; Ngan, S.; McDonald, A. Dry abrasive wear and solid particle erosion assessments of high entropy alloy coatings fabricated by cold spraying. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Nair, R.B.; McDonald, A. Effect of tungsten and vanadium additions on the dry abrasive wear and solid particle erosion of flame-sprayed AlCoCrFeMo high entropy alloy coatings. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 114, 106245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, P.; Sun, H.; Li, T.; Qin, C. Effects of Elements on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AlCoCrFeNiTi High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2023, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarewicz, M.; Grądzka-Dahlke, M. Review of Recent Research on AlCoCrFeNi High-Entropy Alloy. Metals 2021, 11, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Han, Z.; Zhang, G.; Kostka, A. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Al0.7CoCrFeNi high-entropy-alloy prepared by directional solidification. Intermetallics 2018, 93, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarewicz, M.; Grądzka-Dahlke, M.; Rećko, K.; Łępicka, M.; Czajkowska, K. Investigation of the Structure and Corrosion Resistance of novel High-Entropy Alloys for Potential Biomedical Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Gan, C. Phase change and Mechanical Behaviors of TixCoCrFeNiCu1-yAly High Entropy Alloys. J. ASTM Int. 2010, 7, JAI102527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, K.; Xu, Z.; Li, D.Y. Effect of Ti addition on the sliding wear behavior of AlCrFeCoNi high-entropy alloy. Wear 2020, 462–463, 203493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, G.L. Solid solution alloys of AlCoCrFeNiTix with excellent room-temperature mechanical properties. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 181904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, L.; Ni, Z.; Qiao, D.; Zhang, Q.; Sui, H. Effect of Nb on microstructure and properties of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 high entropy alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 290, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Phase selection of BCC/B2 phases for the improvement of tensile behaviors in FeNiCrAl medium entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 916, 165382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisl, S.; Landefeld, A.; Van Steenberge, N.; Chang, Y.; Schnitzer, R. The role of alloying elements in NiAl and Ni3Ti strengthened Co-free maraging steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 861, 144313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, T.; Li, R.; Lin, S.; Xie, Z.; Li, L.; Cristino, V.; Xu, R.; Liu, B. Comparative study on microstructures and mechanical properties of ultra ductility single-phase Nb40Ti40Ta20 refractory medium entropy alloy by selective laser melting and vacuum arc melting. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 942, 169065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon Nava, J.G.; Stott, F.H.; Stack, M.M. The effect of substrate hardness on the erosion-corrosion resistance of materials in low-velocity conditions. Corros. Sci. 1993, 35, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, J.; Toor, I.H.; Ahmed, W.H.; Gasem, Z.M.; Habib, M.A.; Ben-Mansour, R.; Badr, H.M. Evaluating the Effect of Hardness on Erosion Characteristics of Aluminum and Steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform 2014, 23, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- G-76-18; Standard Test Method for Conducting Erosion Tests by Solid Particle Impingement Using Gas Jets. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Noble, N.; Radhika, N.; Sathishkumar, M.; Basak, A.K. Slurry Erosion Behaviour of AlCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloy Coating Prepared by Atmospheric Plasma Spraying. Trans. IMF 2024, 102, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wu, Y.; Hong, S.; Cheng, J.; Zhu, S.; Chen, Y. Erosion Behavior and Mechanism of the HVOF-Sprayed (AlCoCrFeNi)x/(WC-10Co)1-x Composite Coatings at Different Slurry Sand Concentrations. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 110, 106011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, A.; Ji, X.; Jiang, J.; Bao, Y. Slurry Erosion Behavior of AlxCoCrFeNiTi0.5 High-Entropy Alloy Coatings Fabricated by Laser Cladding. Metals 2018, 8, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahr, K.-H.Z. Microstructure and Wear of Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1987; ISBN 978-0-08-087574-3. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, P.; Kumar, P.; Virdi, R.L. Investigation of Solid Particle Erosion Behaviour of SS-304 under Different Conditions. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 48, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna-Camacho, J.R.; Marí, C.; Calderó, J.; Juá, G.; Chagoya-Ramí, J.A.; Ramí, P.; Sá, S.M. Solid Particle Erosion of AISI304 SSCaused by Alumina Particles. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 2024, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hejwowski, T.; Szala, M. Wear-Fatigue Study of Carbon Steels. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2021, 15, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayyagari, A.; Hasannaeimi, V.; Grewal, H.S.; Arora, H.; Mukherjee, S. Corrosion, Erosion and Wear Behavior of Complex Concentrated Alloys: A Review. Metals 2018, 8, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
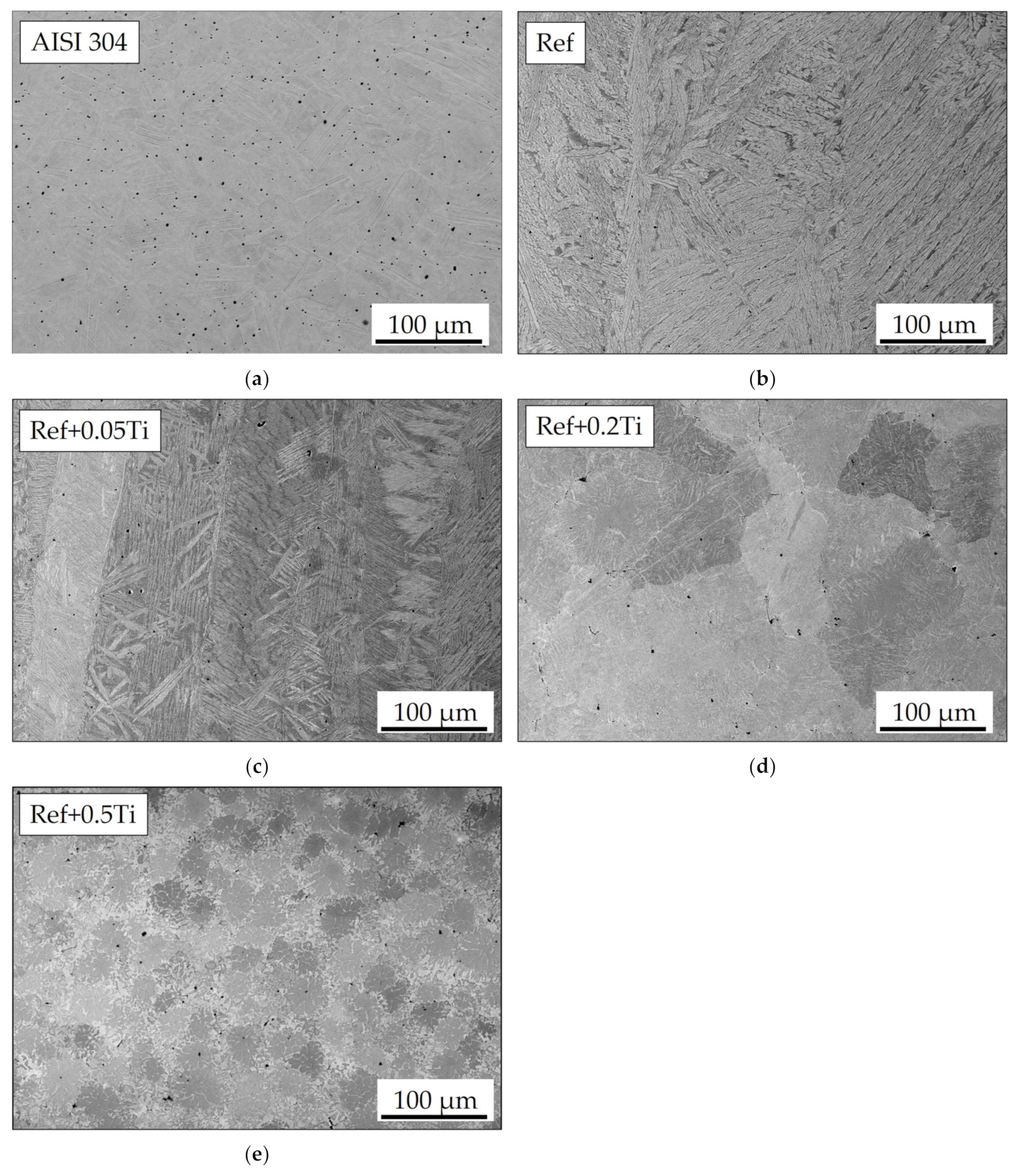

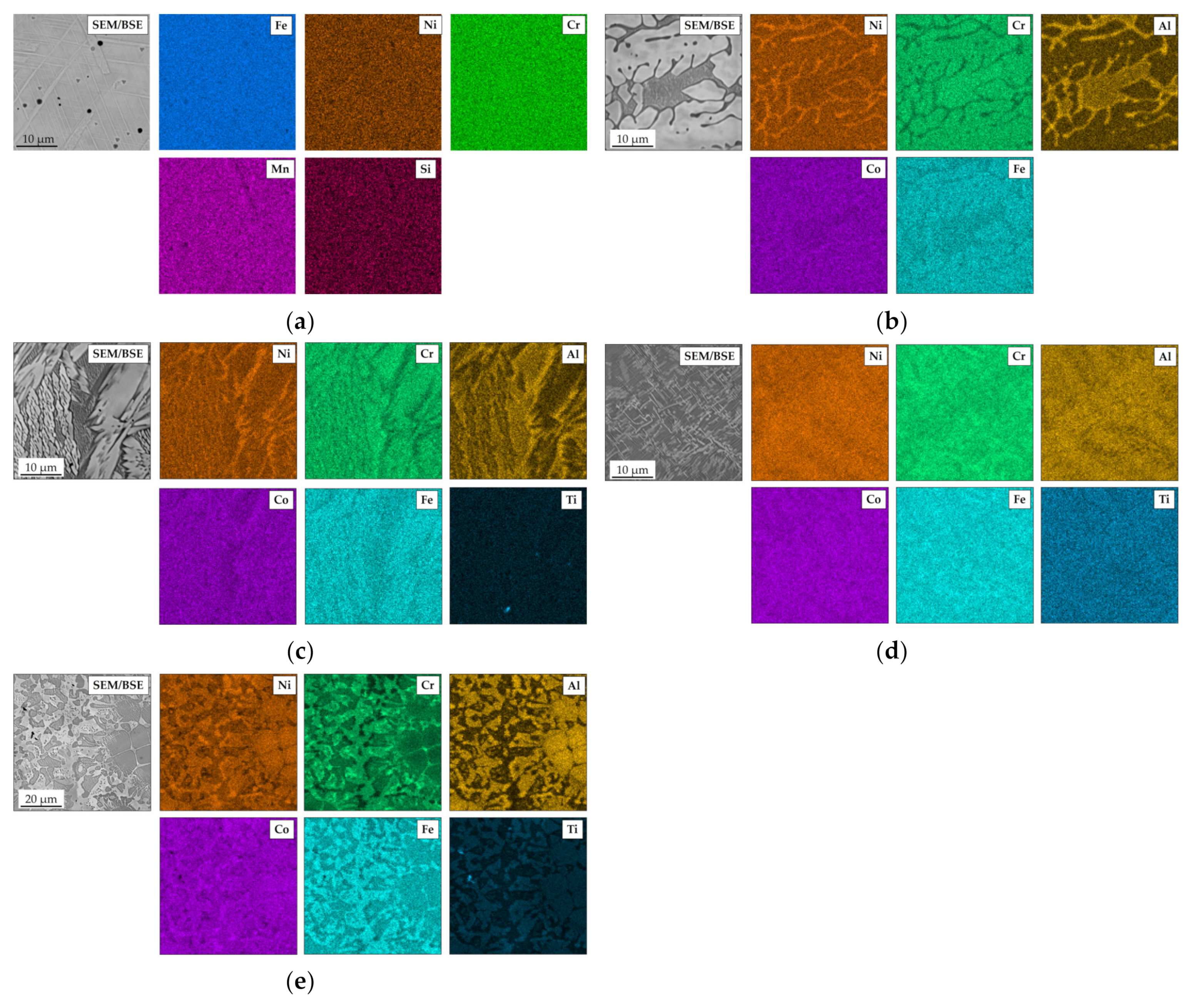

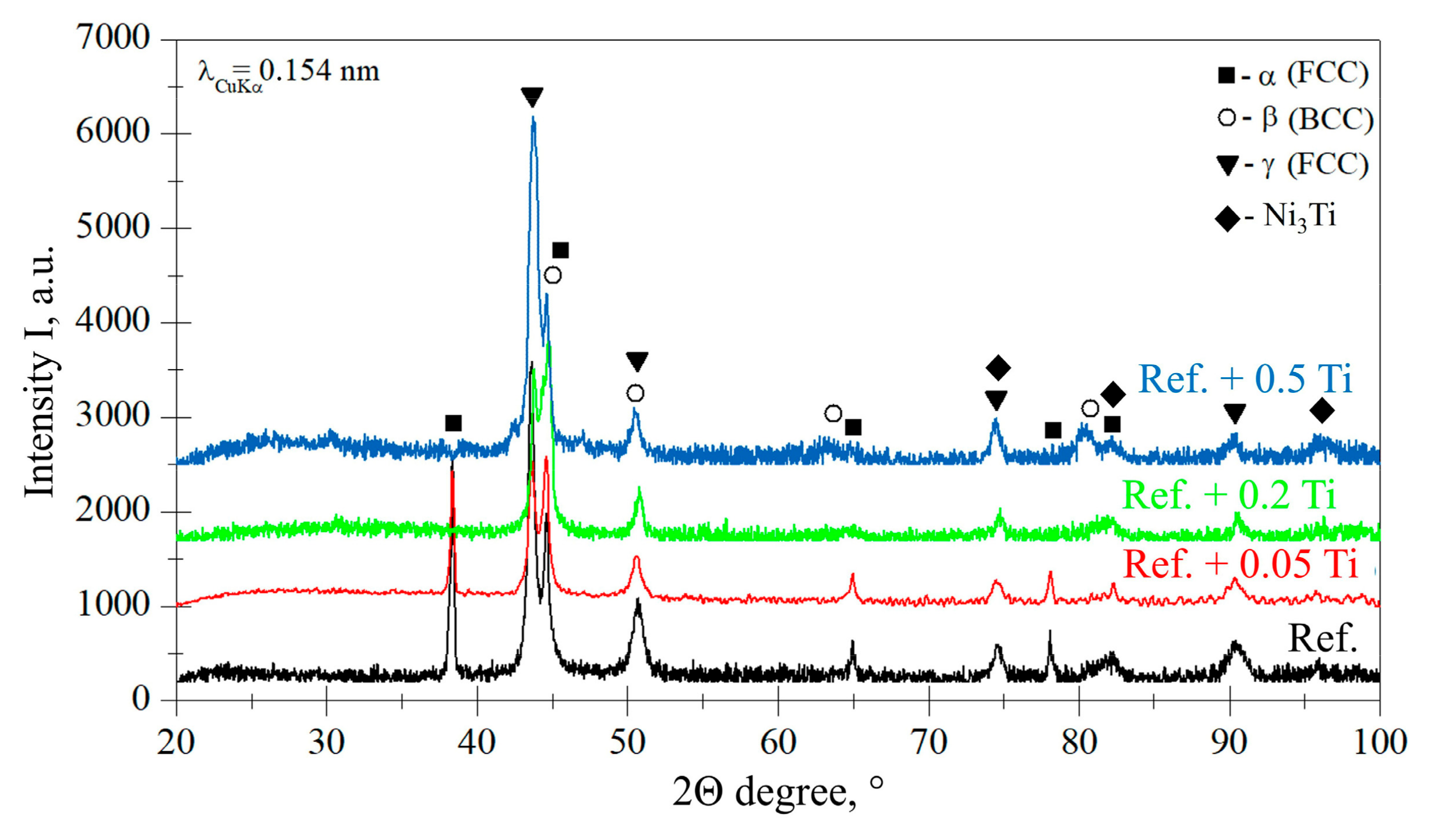
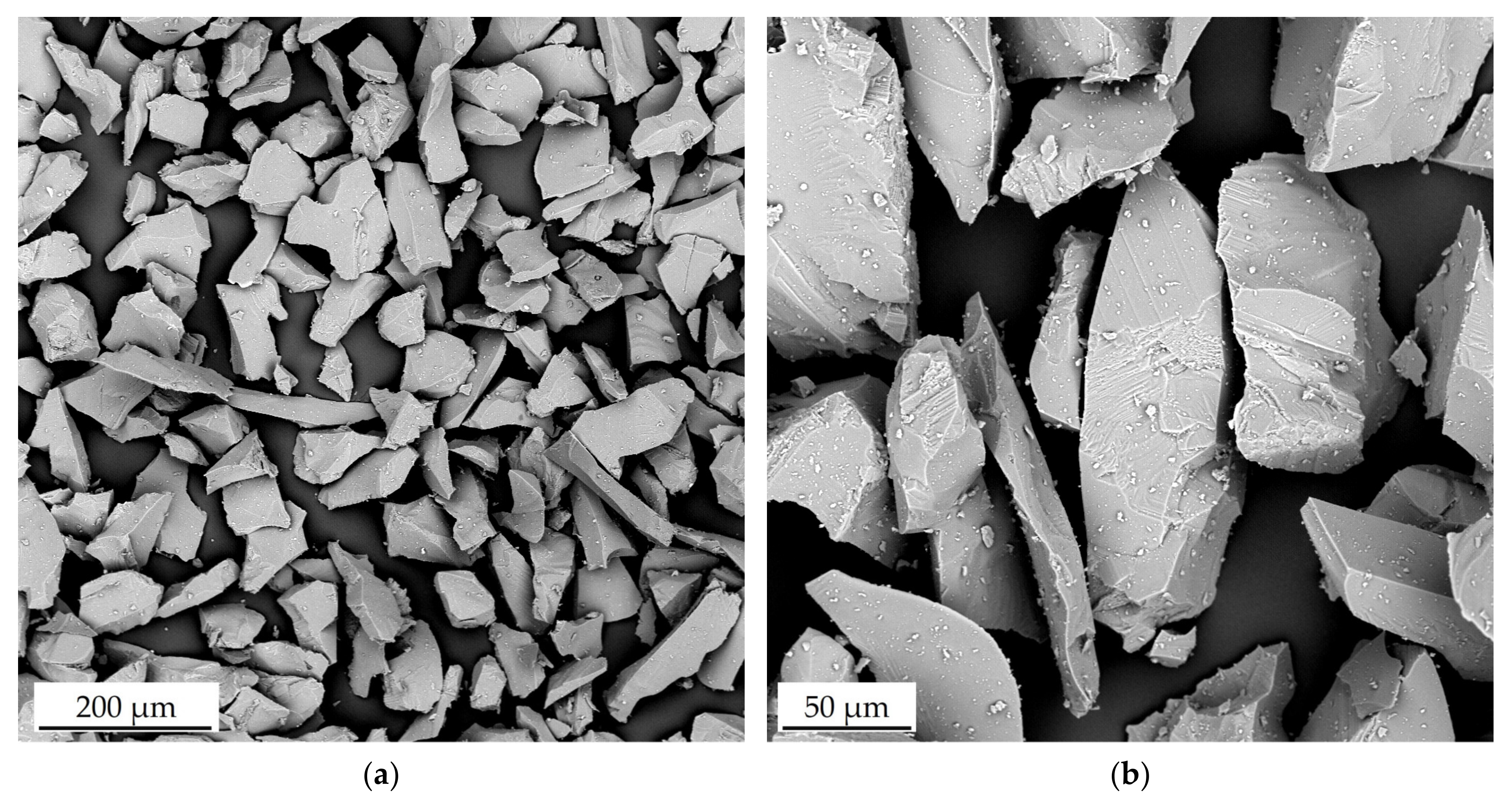
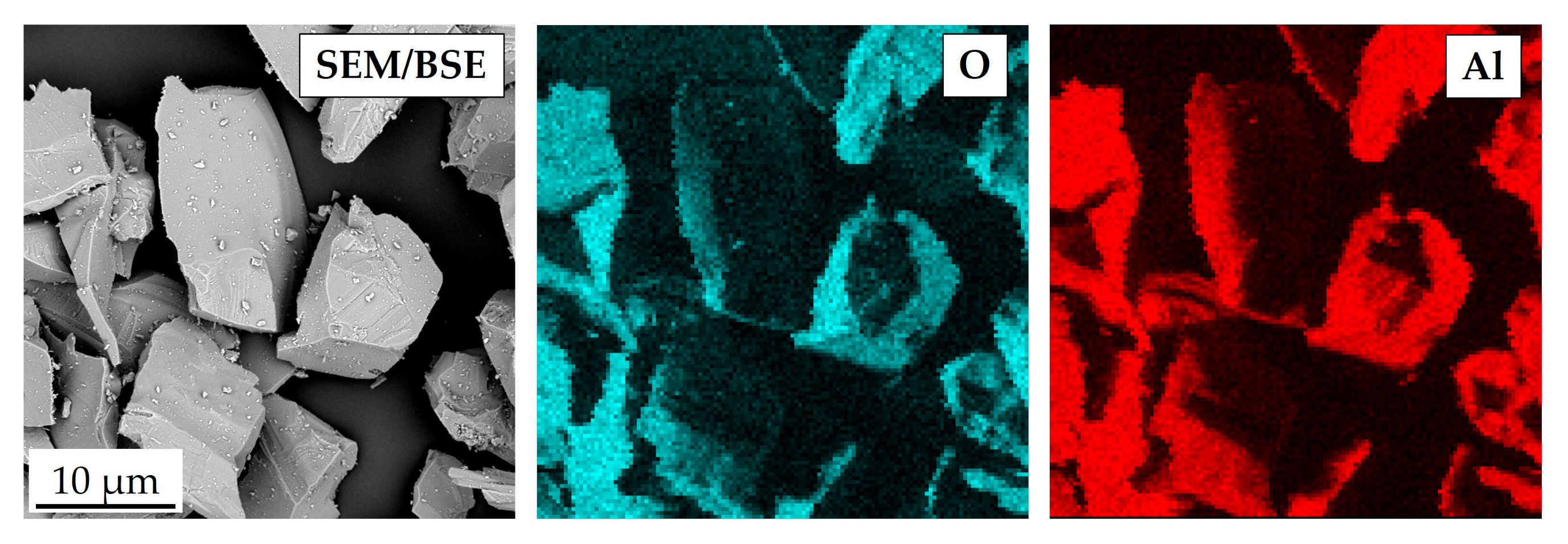
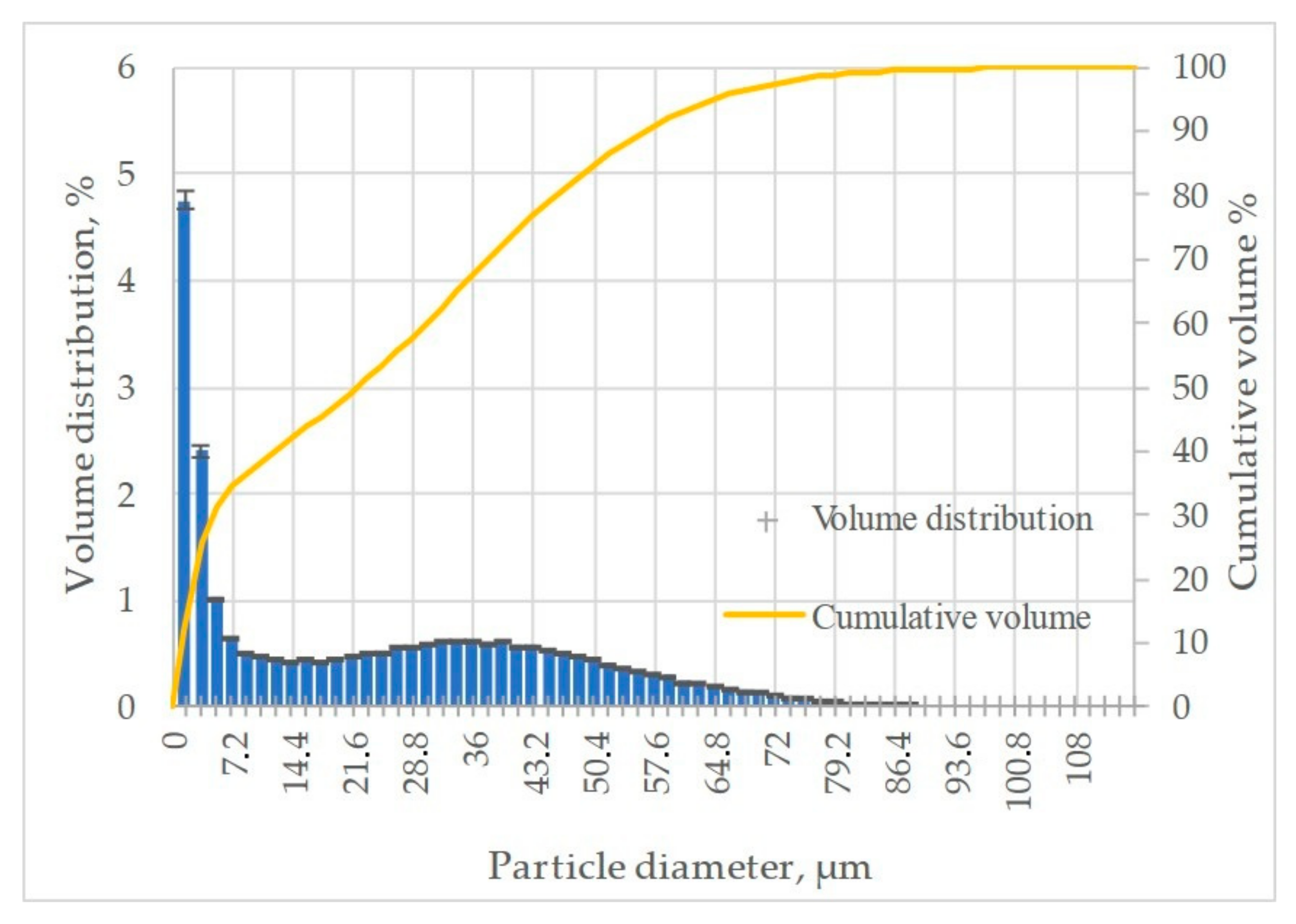
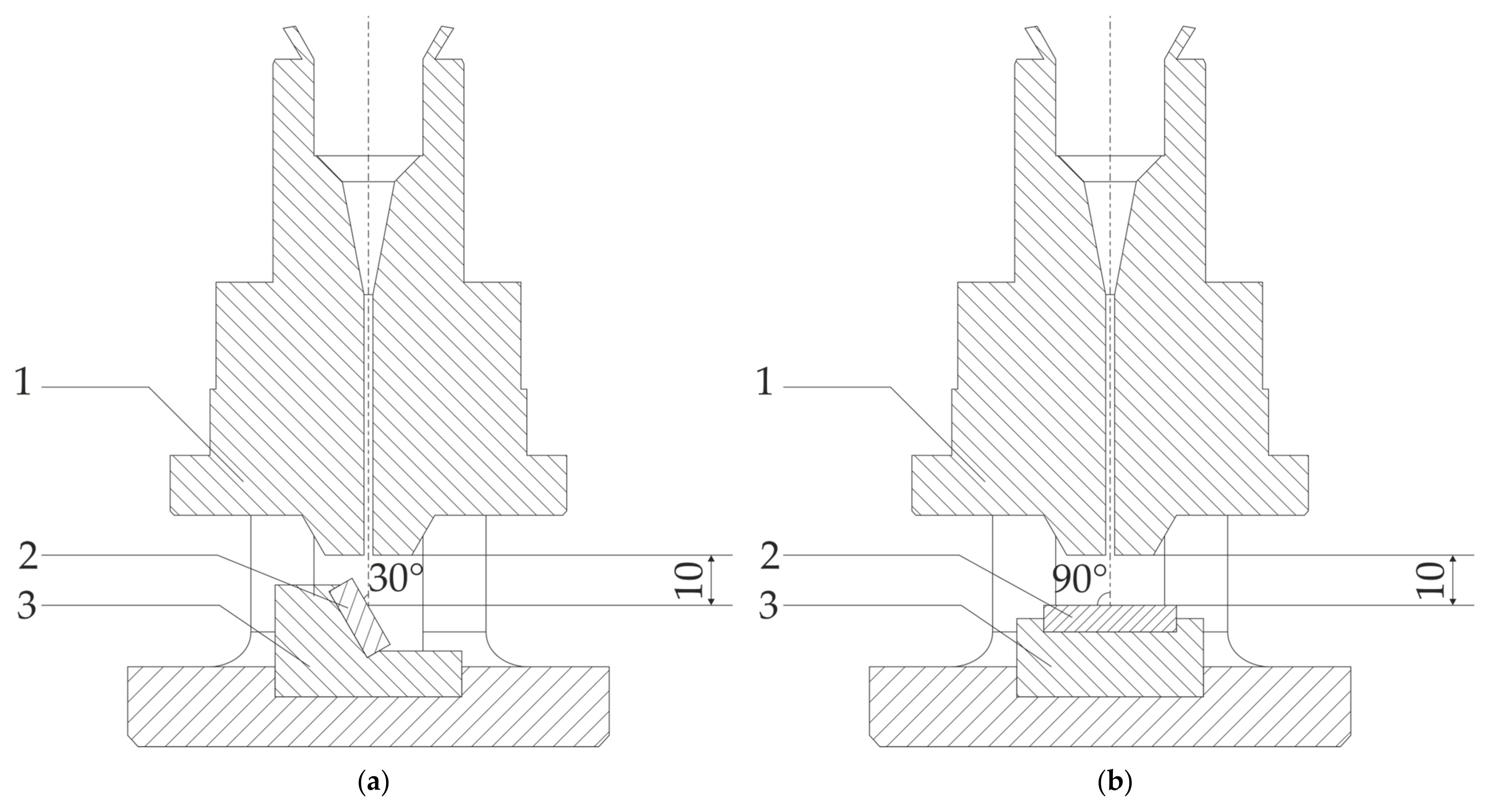



| Element | Ni | Cr | Fe | Si | Mn | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content in wt.% | 9.25 | 18 | Bal. | 1 | 2 | 0.035 |
| Elements | Ni | Co | Cr | Al | Fe | Ti | HEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration in at. % | 21.3 | 21.3 | 21.3 | 14.9 | 21.3 | 0.00 | Ref. |
| 21.0 | 21.0 | 21.0 | 14.7 | 21.0 | 1.0 | Ref.+0.05Ti | |
| 20.4 | 20.4 | 20.4 | 14.3 | 20.4 | 4.1 | Ref.+0.2Ti | |
| 19.2 | 19.2 | 19.2 | 13.5 | 19.2 | 9.6 | Ref.+0.5Ti |
| Elements | Ni | Co | Cr | Al | Fe | Ti | HEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration in at. % | 21.4 | 21.1 | 22.1 | 13.5 | 21.9 | 0.0 | Ref. |
| 21.3 | 19.8 | 22.5 | 13.2 | 21.9 | 1.3 | Ref.+0.05Ti | |
| 20.8 | 19.1 | 21.6 | 12.8 | 21.3 | 4.5 | Ref.+0.2Ti | |
| 18.6 | 21.5 | 19.1 | 11.8 | 19.0 | 10.0 | Ref.+0.5Ti |
| Point | Element Concentration C, at. % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Co | Cr | Fe | Ni | Ti | |
| A | 15.0 | 19.9 | 23.9 | 20.7 | 20.5 | 0.0 |
| B | 11.1 | 21.4 | 22.7 | 22.4 | 22.4 | 0.0 |
| C | 14.6 | 18.9 | 23.1 | 20.7 | 21.1 | 1.5 |
| D | 12.2 | 20.4 | 22.0 | 22.3 | 22.0 | 1.1 |
| E | 9.8 | 19.9 | 22.3 | 22.7 | 20.7 | 4.6 |
| F | 12.6 | 18.8 | 19.6 | 19.9 | 21.3 | 7.9 |
| G | 16.3 | 21.8 | 14.9 | 16.1 | 20.7 | 10.2 |
| H | 6.1 | 18.4 | 33.9 | 25.4 | 11.2 | 5.0 |
| I | 6.8 | 22.4 | 23.9 | 24.7 | 16.4 | 6.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nowak, W.J.; Kubaszek, T.; Gradzik, A.; Grądzka-Dahlke, M.; Perkowski, D.; Tokarewicz, M.; Walczak, M.; Szala, M. Effect of Ti Doping of Al0.7CoCrFeNi-Based High Entropy Alloys on Their Erosion Resistance by Solid Particles. Materials 2025, 18, 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143328
Nowak WJ, Kubaszek T, Gradzik A, Grądzka-Dahlke M, Perkowski D, Tokarewicz M, Walczak M, Szala M. Effect of Ti Doping of Al0.7CoCrFeNi-Based High Entropy Alloys on Their Erosion Resistance by Solid Particles. Materials. 2025; 18(14):3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143328
Chicago/Turabian StyleNowak, Wojciech J., Tadeusz Kubaszek, Andrzej Gradzik, Małgorzata Grądzka-Dahlke, Dariusz Perkowski, Marzena Tokarewicz, Mariusz Walczak, and Mirosław Szala. 2025. "Effect of Ti Doping of Al0.7CoCrFeNi-Based High Entropy Alloys on Their Erosion Resistance by Solid Particles" Materials 18, no. 14: 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143328
APA StyleNowak, W. J., Kubaszek, T., Gradzik, A., Grądzka-Dahlke, M., Perkowski, D., Tokarewicz, M., Walczak, M., & Szala, M. (2025). Effect of Ti Doping of Al0.7CoCrFeNi-Based High Entropy Alloys on Their Erosion Resistance by Solid Particles. Materials, 18(14), 3328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143328










