Optimization of the Sintering Densification, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Oxidation Resistance of Tib2–Tic–Sic Composite Ceramics via a Two-Step Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
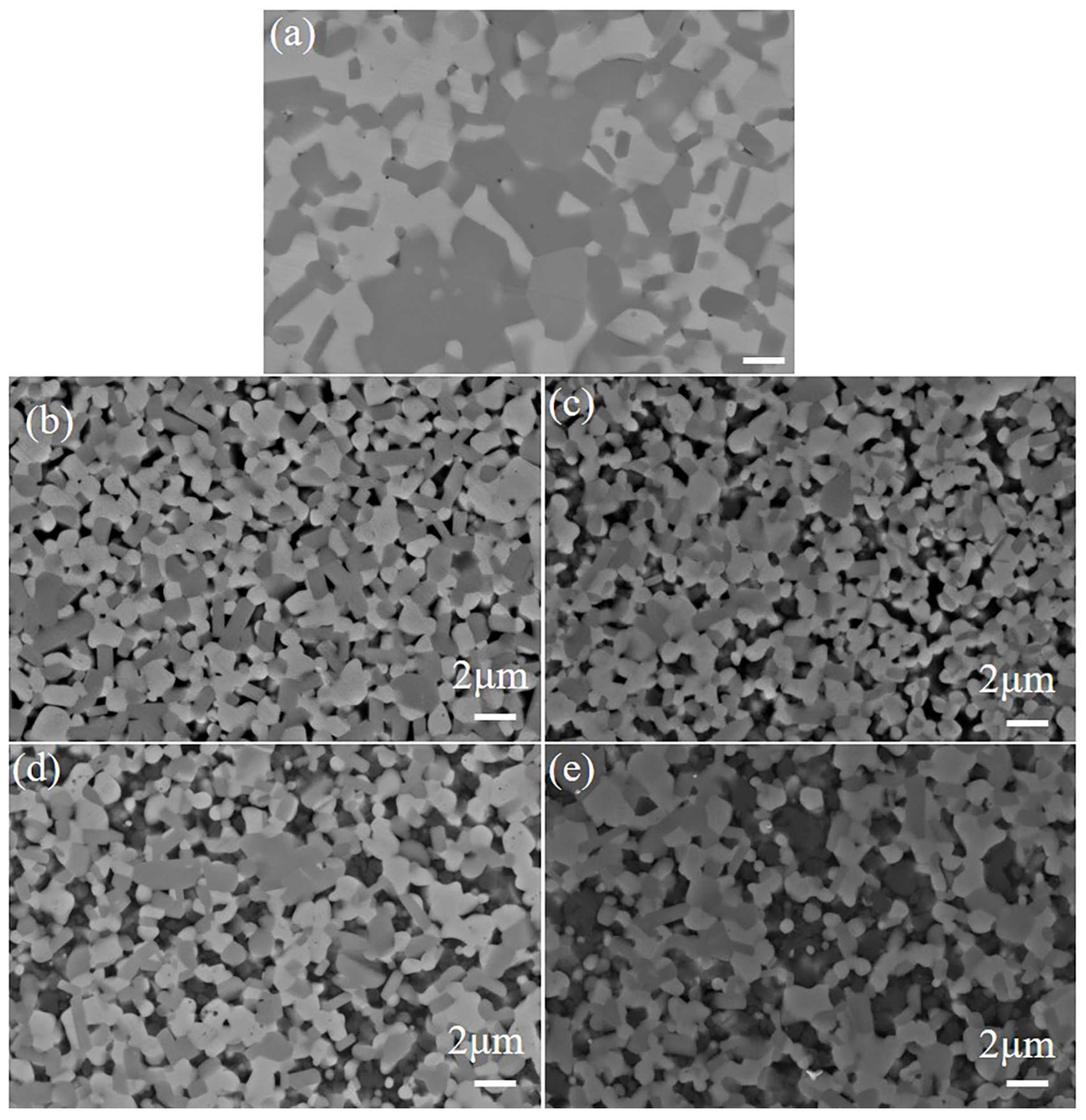
3.1. Sintering Densification
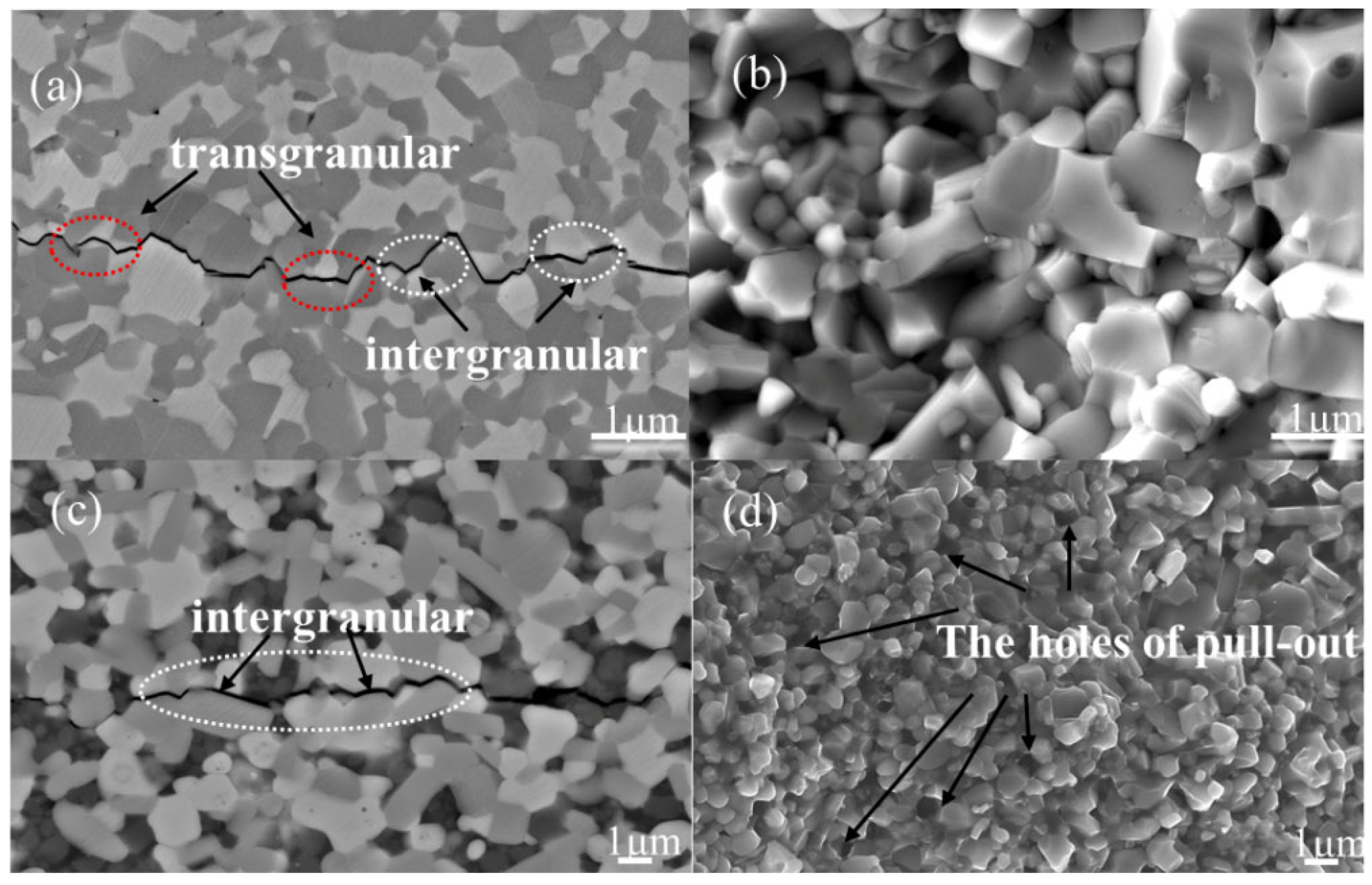
3.2. The Impact of SiC Content on TiB2–TiC–SiC Ceramics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Bi, J.; Liang, G.; Qiao, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liang, S.; Rong, J.; Che, C.; Yuan, J.; et al. Preparation and investigation of mechanical and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of TiC–TiB2/Si3N4 composites. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 107, 5810–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyev, D.S.; Kochetkov, R.A.; Seplyarskii, B.S. Study of Patterns and Mechanisms of Combustion of a Powdered and Granulated Ti–C–B System. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2024, 18, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yin, B.; Shang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J. Preparation and characterization of novel TiB2-12(Fe-Co-Cr-Ni) cermets and their corrosion resistance in molten aluminum. Corros. Sci. 2021, 190, 109643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Xue, F.; Yang, H.; Li, G.; Luo, F.; Ruan, J. Effects of TiB2 particle size on the microstructure and mechanical properties of TiB2-based composites. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xiang, D.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Z. In situ synthesis of TiC cermet by spark plasma reaction sintering. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 661, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coban, O.; Bugdayci, M.; Baslayici, S.; Acma, M.E. Combustion Synthesis of B4C–TiB2 Nanocomposite Powder: Effect of Mg Particle Size on SHS and Optimization of Acid Leaching Process. J. Superhard Mater. 2023, 45, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T. Synthesis and sintering of TiC-TiB2 composite powders. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Huang, L.; An, Q.; Jiang, S.; Ma, X. Insights into arc–assisted self–propagating high temperature synthesis of TiB2–TiC ceramic coating via wire–arc deposition. J. Eur. Ceram Soc. 2020, 40, 4381–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhao, G.; Mao, P.; Hao, X.; Li, L.; He, N. Improved machinability of TiB2–TiC ceramic composites via laser-induced oxidation assisted micro-milling. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 11514–11525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cymerman, K.; Oleszak, D.; Rosinski, M.; Michalski, A. Structure and mechanical properties of TiB2/TiC—Ni composites fabricated by pulse plasma sintering method. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 1795–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Su, J. Effect of Ni content on mechanical property and oxidation resistance of porous TiB2-TiC ceramics fabricated by pressureless sintering. Ceram. Int. 2024, 51, 9301–9311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Chang, S.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Shen, H. Competitive reaction behavior and formation mechanism of reactively spark plasma sintered TiB2-TiC composite ceramics with tunable compositions. Ceram. Int. 2024, 51, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozień, D.; Graboś, A.; Nieroda, P.; Stępień, J.; Pasiut, K.; Gancarz, P.; Czekaj, I.; Ziąbka, M.; Banaś, W.; Żurowski, R.; et al. Spark plasma sintered TiB2-SiC UHTC derived from B4C and stoichiometric intermetallic phases from Ti-Si system. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 44, 5401–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalčíková, A.; Tatarko, P.; Sedlák, R.; Medveď, D.; Chlup, Z.; Múdra, E.; Dusza, J. Mechanical and tribological properties of TiB2-SiC and TiB2-SiC-GNPs ceramic composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 4860–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-H.; Delbari, S.A.; Namini, A.S.; Ahmadi, Z.; Van Le, Q.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Asl, M.S.; Mohammadi, M. Microstructural evolution of TiB2–SiC composites empowered with Si3N4, BN or TiN: A comparative study. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asl, M.S.; Ahmadi, Z.; Namini, A.S.; Babapoor, A.; Motallebzadeh, A. Spark plasma sintering of TiC–SiCw ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 19808–19821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntuyi, S.D.; Johnson, O.T.; Shongwe, M.B. Spark Plasma Sintering of Ceramic Matrix Composite of ZrB2 and TiB2: Microstructure, Densification, and Mechanical Properties–A Review. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 27, 2146–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, D.C.; Zhao, J.; Chen, T.; Song, H.L.; Ru, H.Q. Microstructure and Properties of SiC/TiB2 Composites Fabricated via Pressureless Sintering. J. Shenyang Ligong Univ. 2023, 42, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, M.; Pazhouhanfar, Y.; Delbari, S.A.; Shaddel, S.; Namini, A.S.; Asl, M.S. Influence of TiB2 content on the properties of TiC–SiCw composites. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 7403–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.Q.; Zhu, S.Z.; Liu, L.; Ma, Z.; Gao, L.H. Influence of Adding TiB2 on Structure and Mechanical Properties of SiC–Based Composite Ceramics. J. China. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 45, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Huang, C.; He, N.; Liu, H.; Zou, B. Microstructure and mechanical properties at room and elevated temperatures of reactively hot pressed TiB2–TiC–SiC composite ceramic tool materials. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 5353–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of TiB2-TiC-SiC ceramics joint brazed using Ti-Ni composite foils. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 3380–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z. Joining TiB2–TiC–SiC composite to Ta with a Ti/Ni/Ti interlayer: Interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 64, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.S.S.; Prasad, K.; Patnaik, L. Effect of SiC and TiC Reinforcements on the Mechanical Properties of ZrB2–SiC–TiC Hybrid Composite Fabricated Through Spark Plasma Sintering. Silicon 2023, 15, 3339–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.-Q.; Zhu, D.-G.; Jiang, X.-S.; Sun, H.-L.; Xia, Z.-H. Research on Microstructures and Properties of in-situ Synthesis of TiB2-TiC0.8-SiC Multiphase Ceramics. J. Inorg. Mater. 2013, 28, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, J.; Chandra, S.; Das, S.J. Oxidation behaviour of silicon carbide–a review. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2014, 38, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
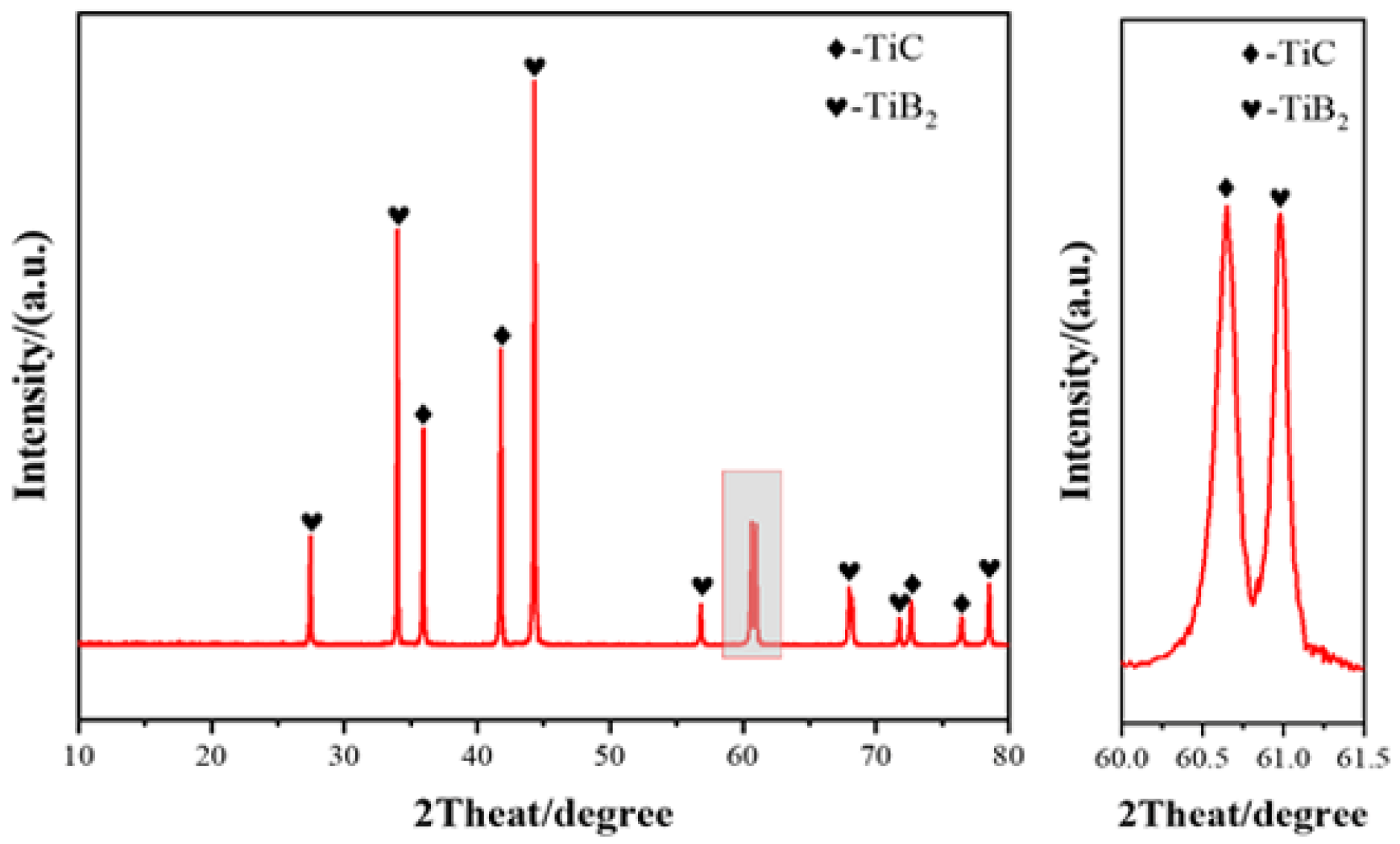
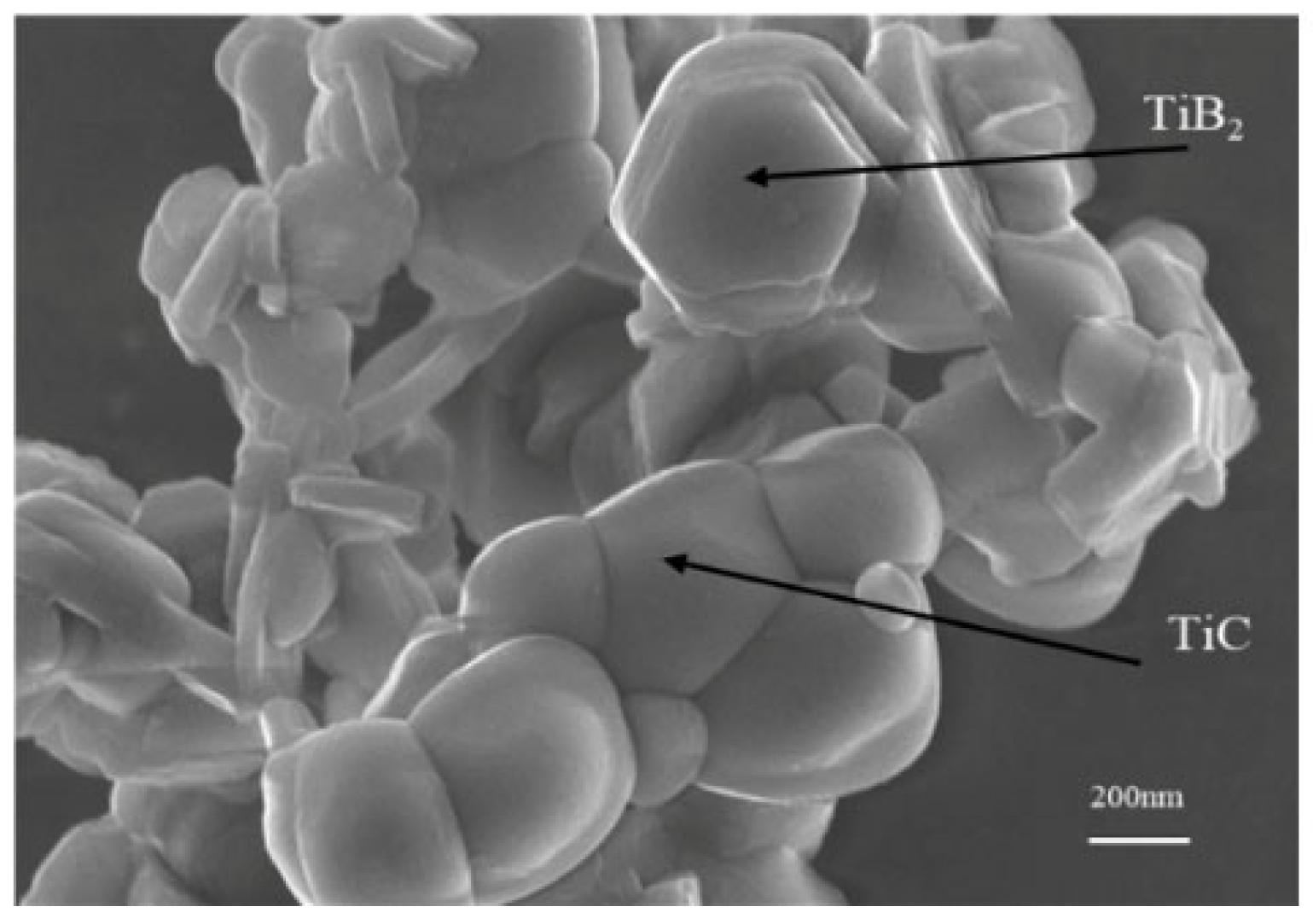

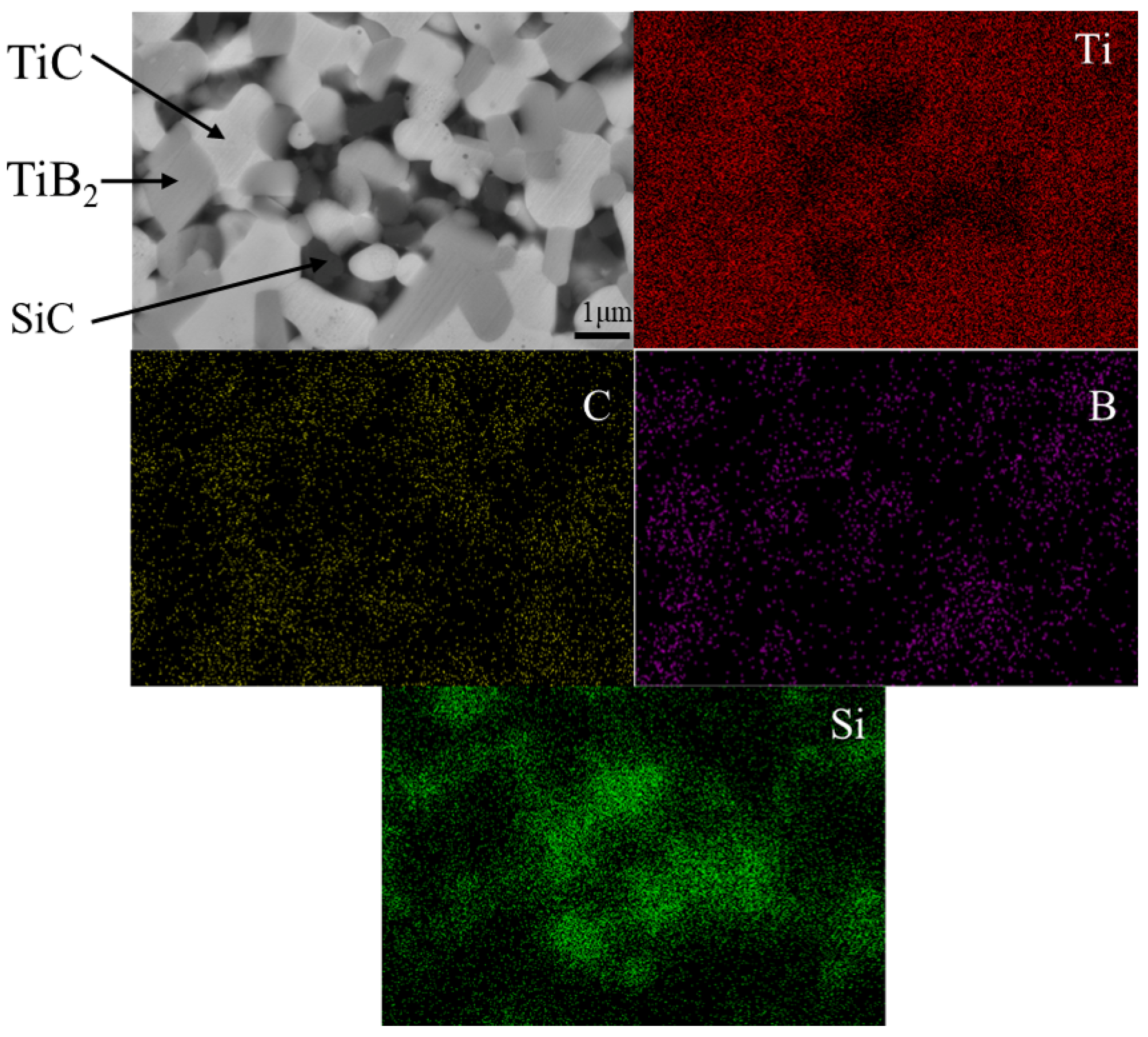

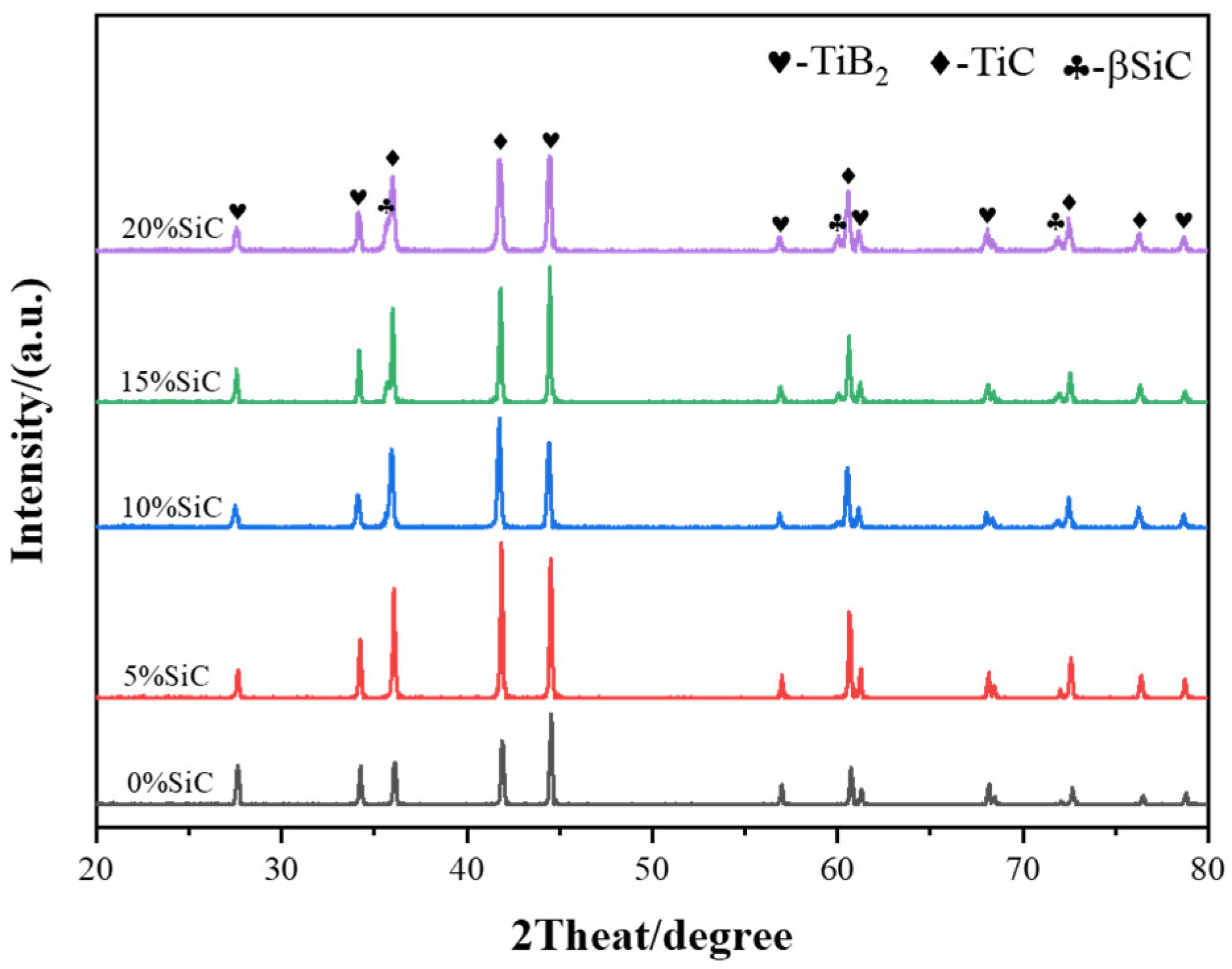


| Sample | Sintering Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Pressure (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15% SiC–1800 | 1800 | 10 min | 40 Mpa |
| 15% SiC–1850 | 1850 | 10 min | 40 Mpa |
| 15% SiC–1900 | 1900 | 10 min | 40 Mpa |
| 15% SiC–1950 | 1950 | 10 min | 40 Mpa |
| Sample | TiB2 | TiC | SiC |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0% SiC | 44.25% | 55.5% | 0% |
| 5% SiC | 42.275% | 52.725% | 5% |
| 10% SiC | 40.05% | 49.95% | 10% |
| 15% SiC | 37.825% | 47.175% | 15% |
| 20% SiC | 35.6% | 44.4% | 20% |
| Temperature (°C) | Relative Density (%) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Vickers Hardness (GPa) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1800 | 96.54% | 359.51 ± 14.7 | 20.91 ± 0.51 | 4.98 ± 0.24 |
| 1850 | 97.08% | 374.16 ± 41.2 | 21.59 ± 0.73 | 5.01 ± 0.12 |
| 1900 | 98.76% | 435.98 ± 25.3 | 22.20 ± 0.43 | 5.71 ± 0.34 |
| 1950 | 98.08% | 432.64 ± 34.7 | 21.91 ± 0.62 | 5.06 ± 0.24 |
| Temperature (°C) | Relative Density (%) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Vickers Hardness (GPa) | Fracture Toughness (MPa·m1/2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% SiC | 98.56% | 509.44 ± 31.5 | 22.10 ± 0.36 | 4.16 ± 0.24 |
| 5% SiC | 97.49% | 247.76 ± 17.3 | 20.99 ± 0.45 | 4.20 ± 0.25 |
| 10% SiC | 97.99% | 410.90 ± 31.5 | 22.05 ± 0.63 | 4.55 ± 0.36 |
| 15% SiC | 98.76% | 435.98 ± 25.3 | 22.20 ± 0.43 | 5.71 ± 0.34 |
| 20% SiC | 98.10% | 417.14 ± 22.3 | 22.03 ± 0.47 | 5.42 ± 0.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, F.; Sun, W.; Lu, Y.; Ma, J.; Xu, S. Optimization of the Sintering Densification, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Oxidation Resistance of Tib2–Tic–Sic Composite Ceramics via a Two-Step Method. Materials 2025, 18, 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143297
Han F, Sun W, Lu Y, Ma J, Xu S. Optimization of the Sintering Densification, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Oxidation Resistance of Tib2–Tic–Sic Composite Ceramics via a Two-Step Method. Materials. 2025; 18(14):3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143297
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Fei, Wenzhou Sun, Youjun Lu, Junqing Ma, and Shidiao Xu. 2025. "Optimization of the Sintering Densification, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Oxidation Resistance of Tib2–Tic–Sic Composite Ceramics via a Two-Step Method" Materials 18, no. 14: 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143297
APA StyleHan, F., Sun, W., Lu, Y., Ma, J., & Xu, S. (2025). Optimization of the Sintering Densification, Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Oxidation Resistance of Tib2–Tic–Sic Composite Ceramics via a Two-Step Method. Materials, 18(14), 3297. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143297






