Mitigating Environmental Impact Through the Use of Rice Husk Ash in Sustainable Concrete: Experimental Study, Numerical Modelling, and Optimisation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methodology
3. Data-Based Modelling and Optimisation
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
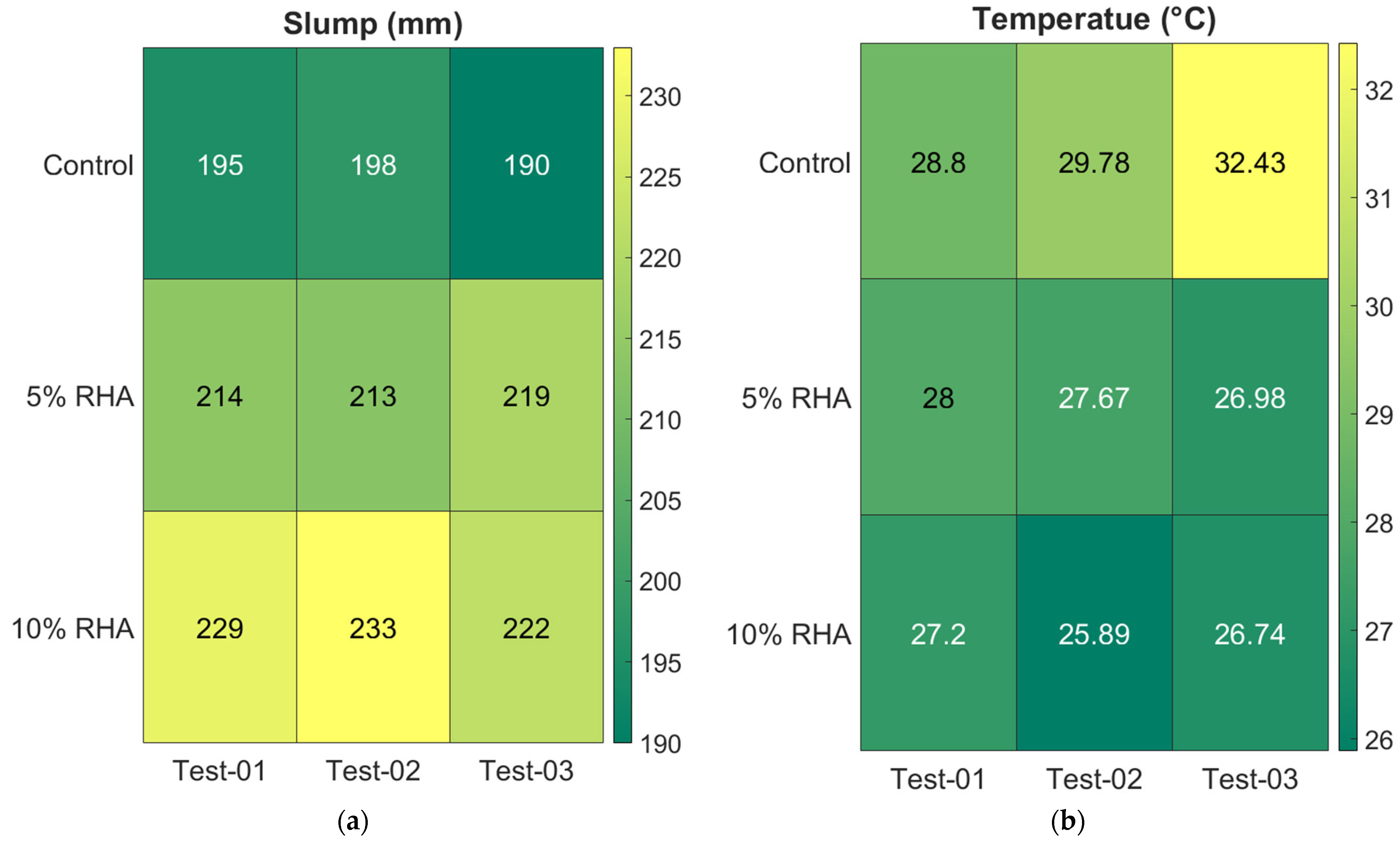
4.1. Fresh Properties of Concrete Mixes
4.2. Mechanical Properties
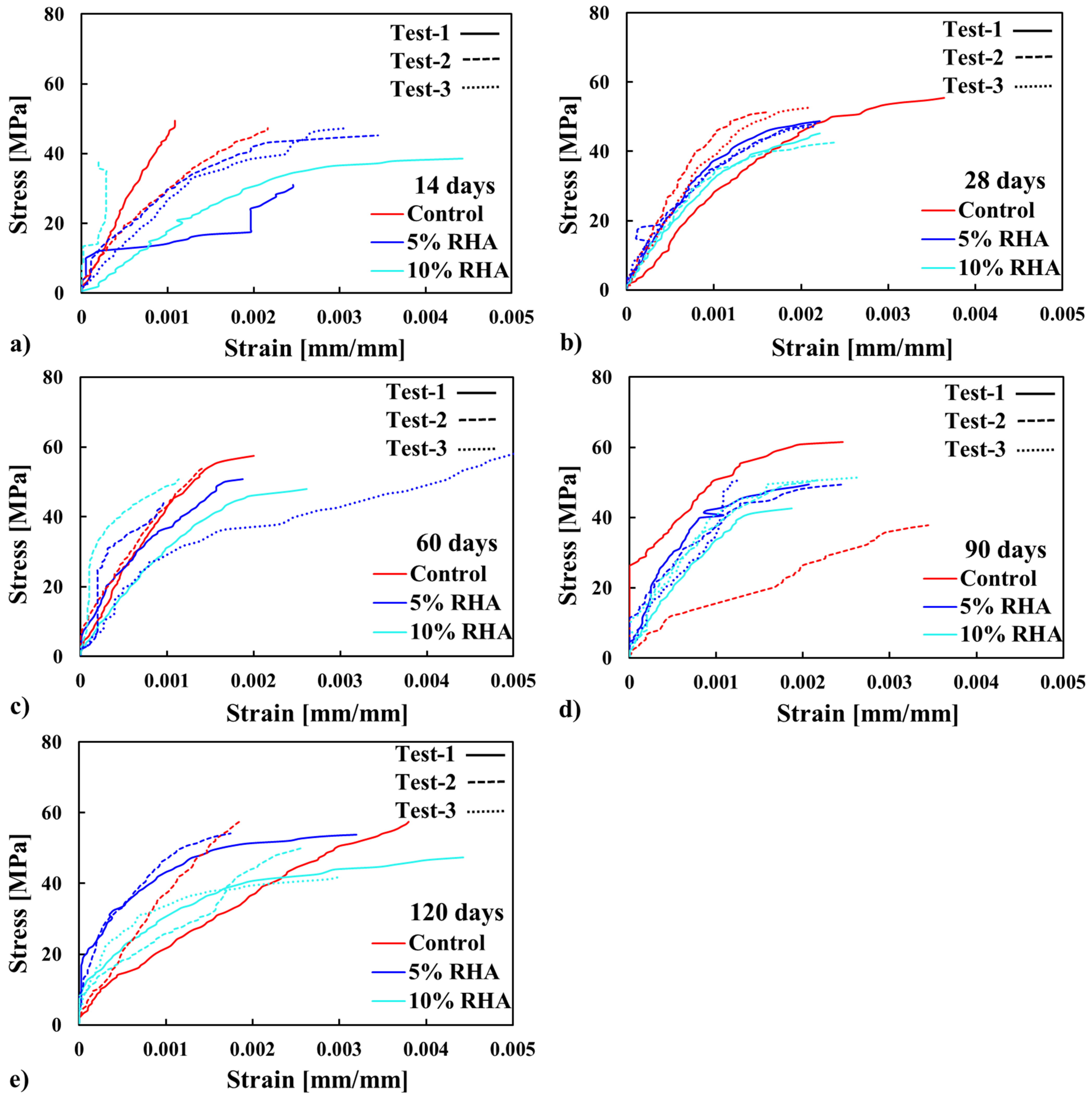
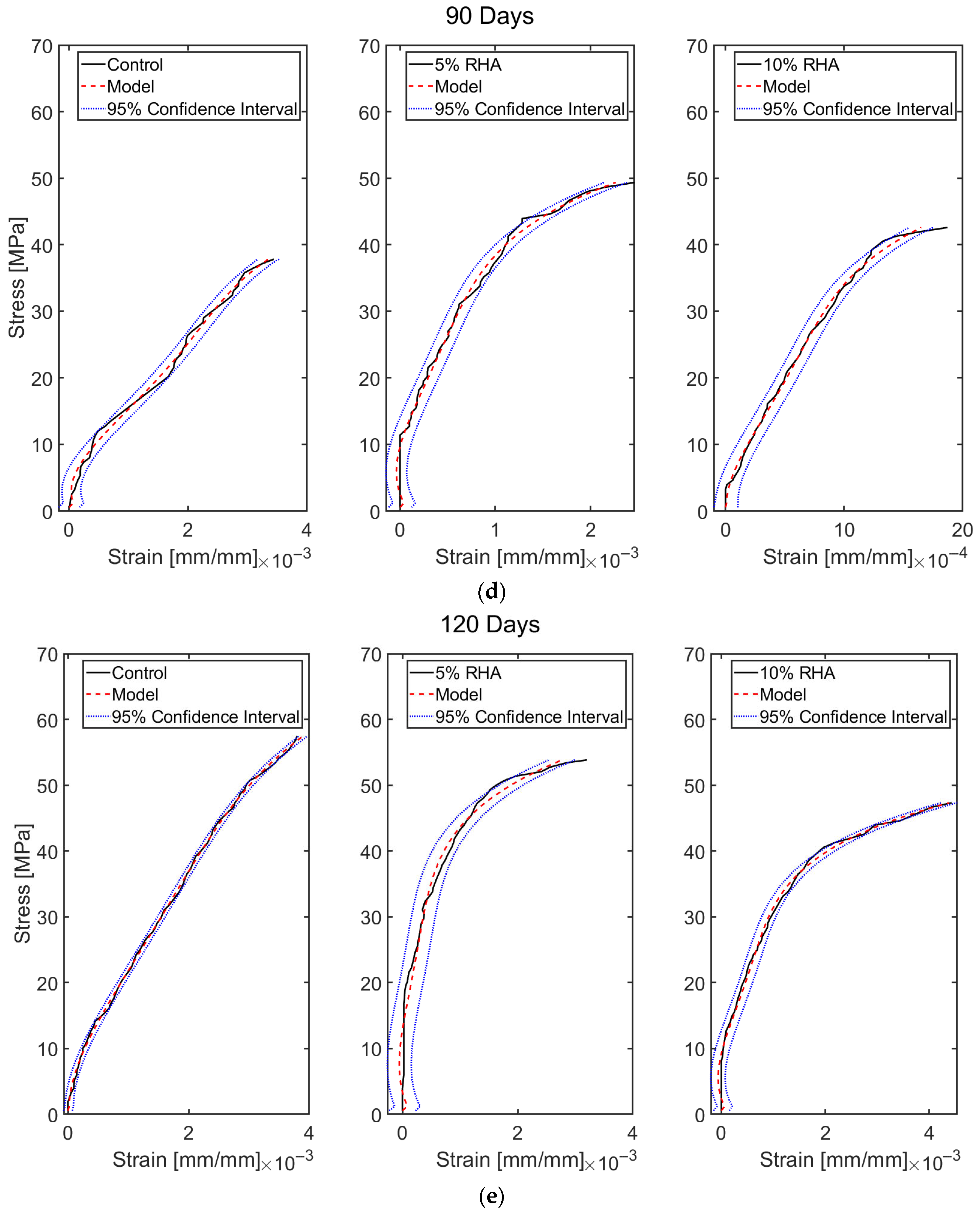
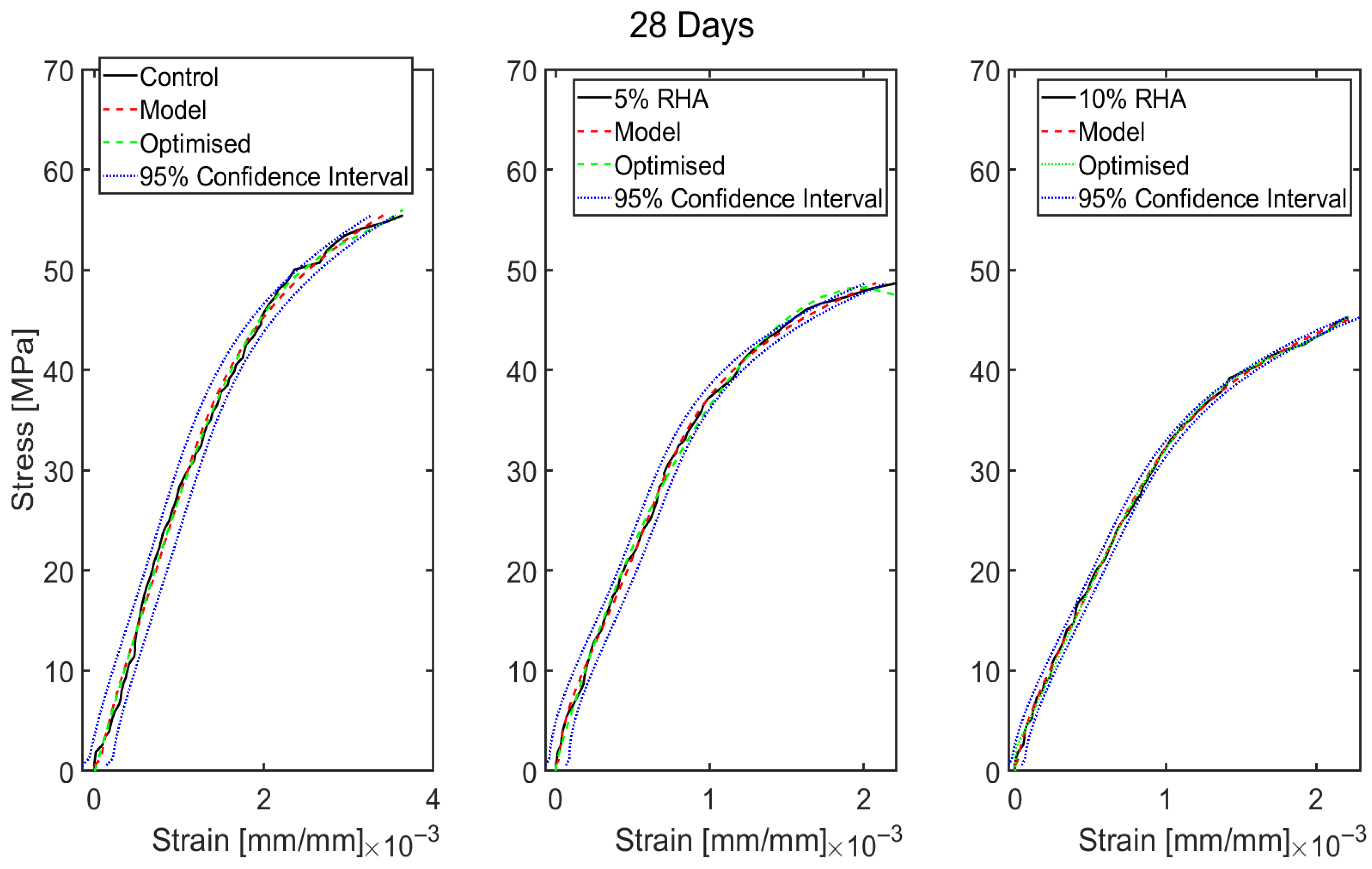
4.2.1. Stress–Strain Profile of Concrete Mixes
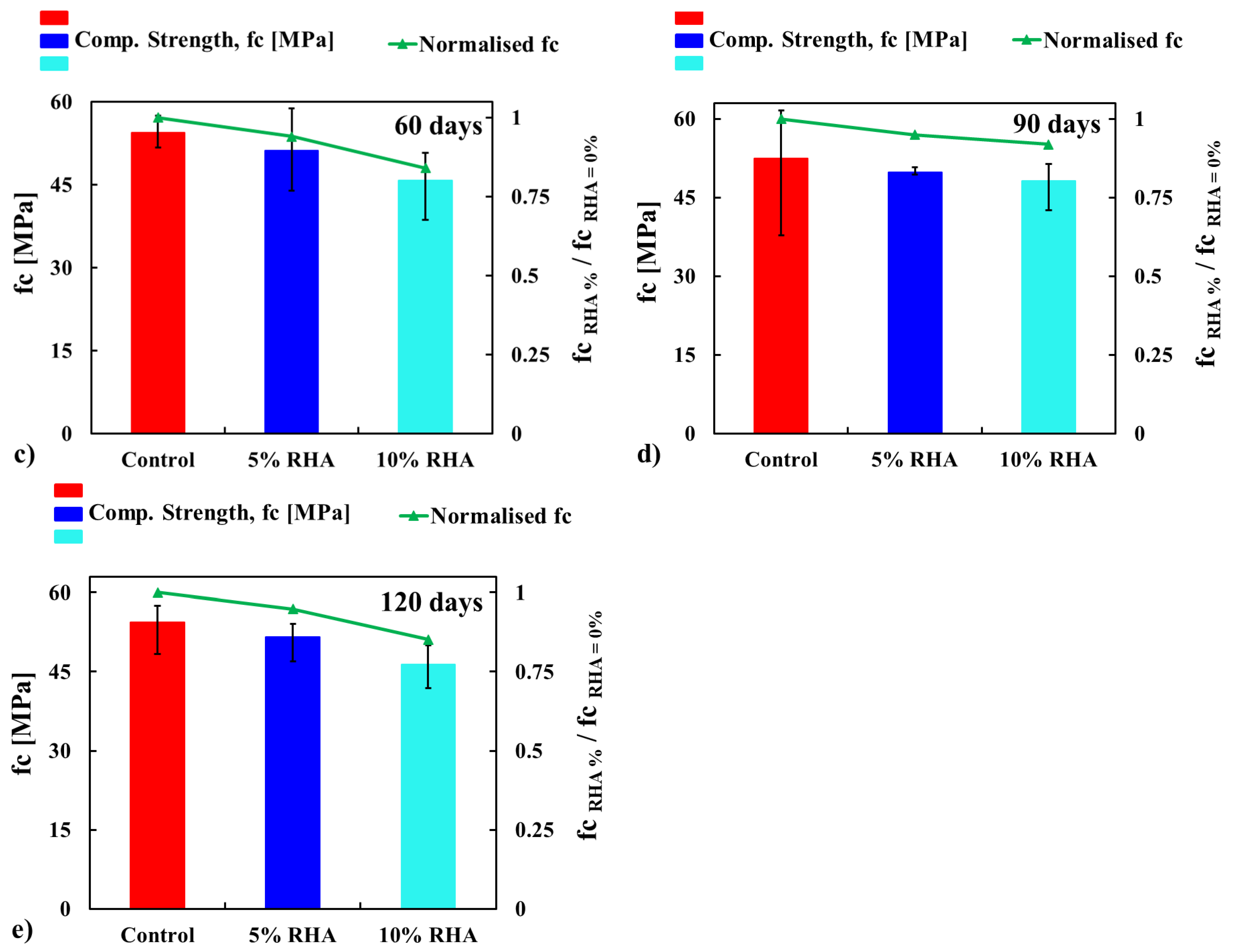
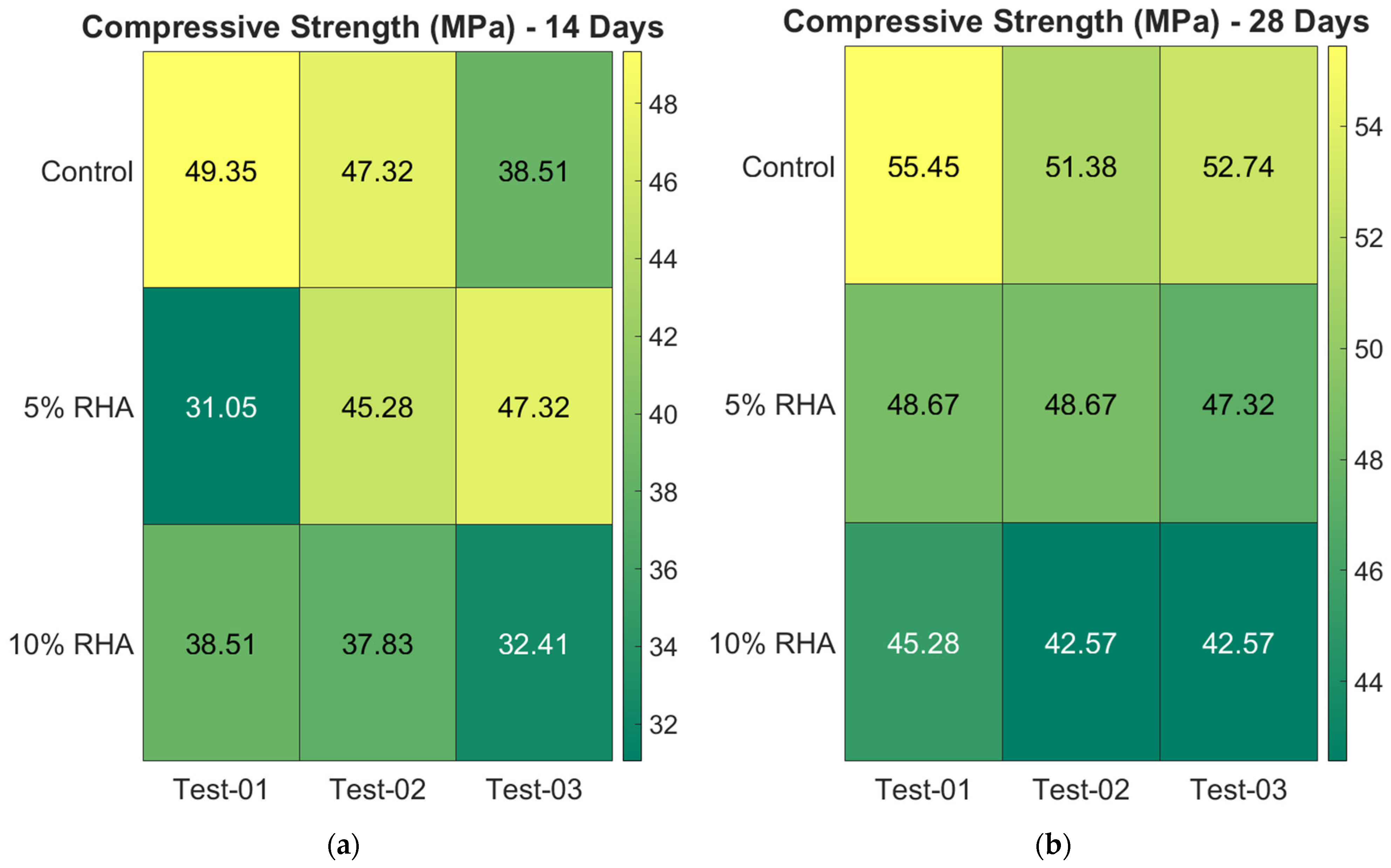
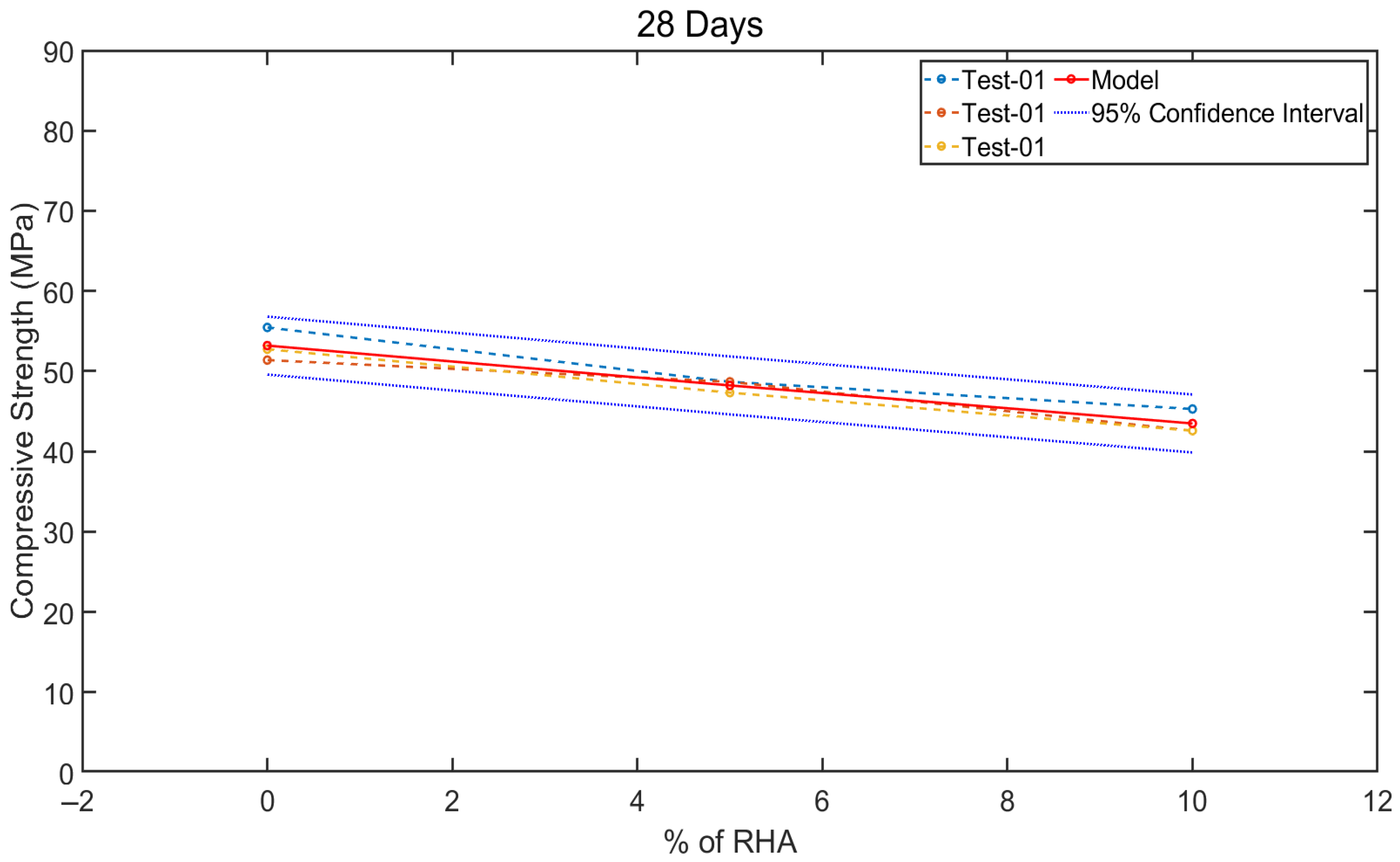
4.2.2. Compressive Strength of Concrete Mixes
5. Data-Based Model Results
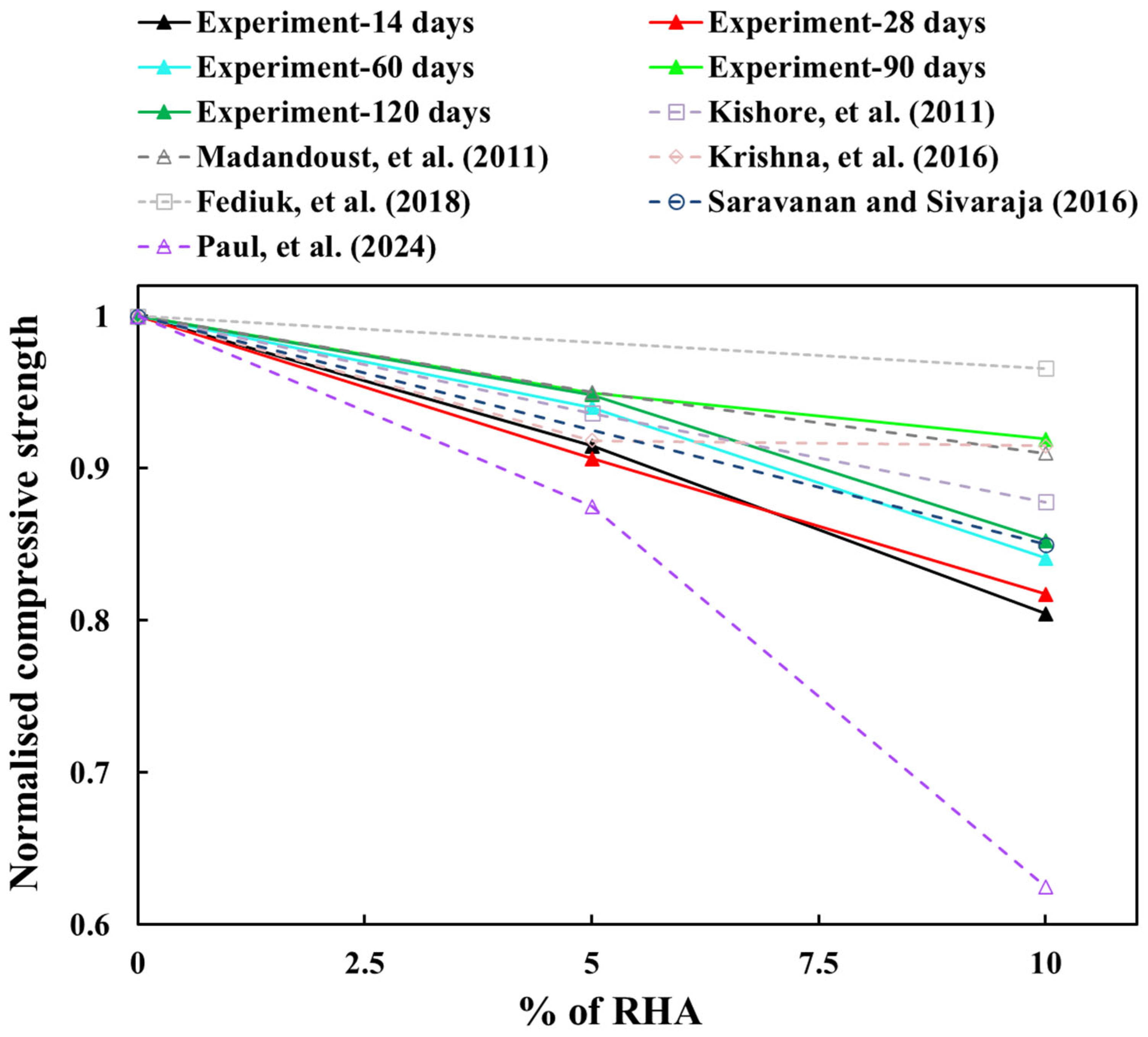
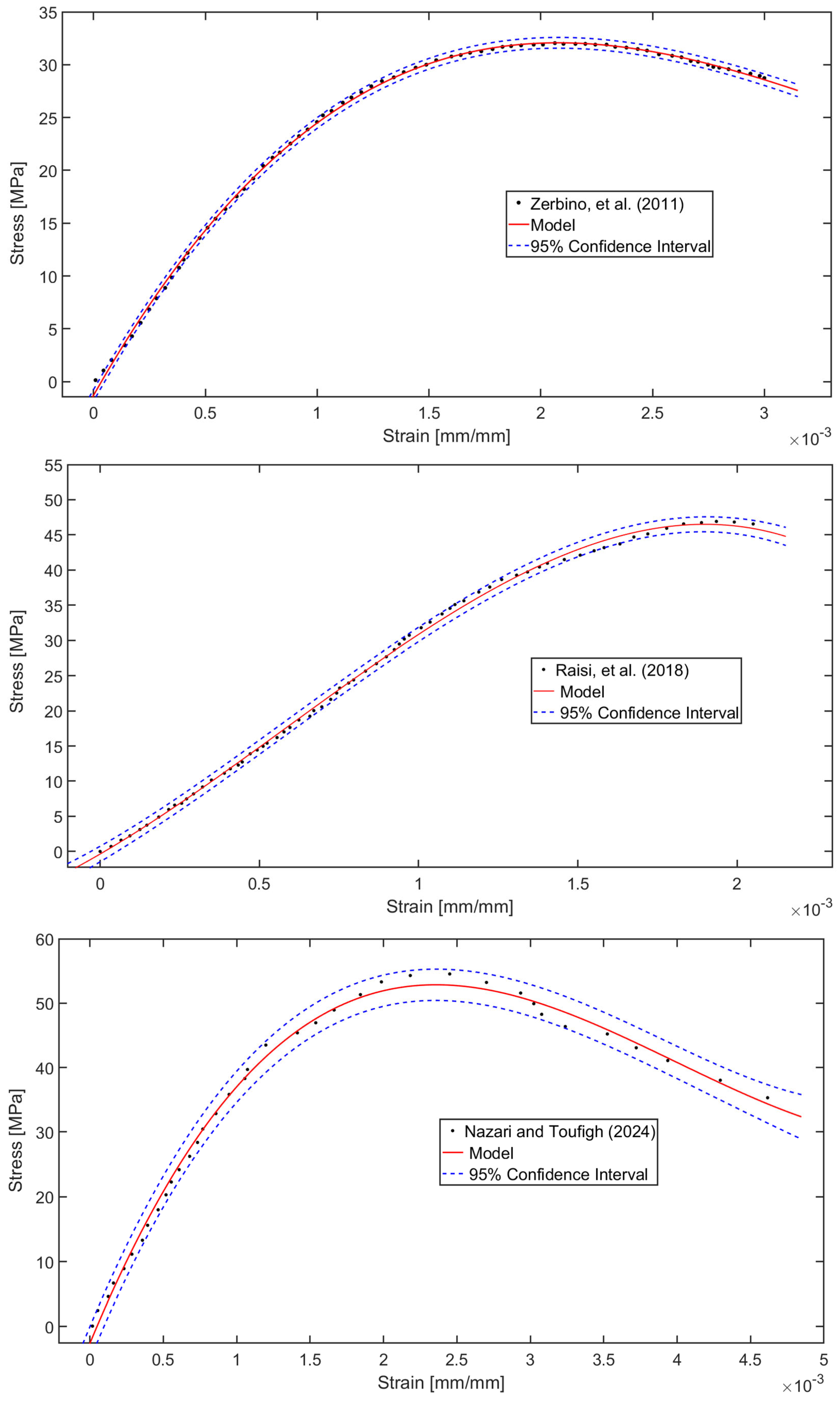
6. Data-Based Model Validation with Literature Findings
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aitcin, P.-C. Cements of yesterday and today: Concrete of tomorrow. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Romer, M.; Tschudin, M.; Bolio, H. Sustainable cement production—Present; future. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.K.; Monteiro, P.J.M. Concrete Microstructure; Properties; Materials; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.weforum.org/stories/2024/08/how-cement-and-concrete-companies-can-contribute-to-a-nature-positive-economy/ (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Schiller, G.; Roscher, J. Impact of urbanisation on construction material consumption: A global analysis. J. Ind. Ecol. 2023, 27, 1021–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.weforum.org/stories/2024/09/cement-production-sustainable-concrete-co2-emissions/ (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- Millera, S.A.; John, V.M.; Pacca, S.A.; Horvath, A. Carbon dioxide reduction potential in the global cement industry by 2050. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snellings, R.; Suraneni, P.; Skibsted, J. Future and emerging supplementary cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 171, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Zou, D.; Long, X.; Miah, M.J.; Li, Y. Strength recovery of thermally damaged high-performance concrete subjected to post-fire carbonation curing. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 143, 105273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babafemi, A.J.; Knobel, H.; Kolawole, J.T.; Oyebanjo, O.M.; Bukalo, N.N.; Paul, S.C.; Miah, M.J. Performance of Selected South African Kaolinitic Clays for Limestone Calcined Clay Cement. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, M.J.; Huaping, R.; Paul, S.C.; Babafemi, A.J.; Li, Y. Long-term strength and durability performance of eco-friendly concrete with supplementary cementitious materials. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2023, 8, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juenger, M.C.G.; Siddique, R. Recent advances in understanding the role of supplementary cementitious materials in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Scrivener, K.; Hooton, R.D. Supplementary cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, M.A.M.; Brooks, J.J.; Kabir, S.; Rivard, P. Influence of supplementary cementitious materials on engineering properties of high strength concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2639–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lollini, F.; Redaelli, E.; Bertolini, L. A study on the applicability of the efficiency factor of supplementary cementitious materials to durability properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, A.; Basheer, P.A.M.; Nanukuttan, S.V.; Khan, Q.U.Z. Mechanical and durability properties of high performance concretes containing supplementary cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholampour, A.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Performance of sustainable concretes containing very high volume Class-F fly ash and ground granulated blast furnace slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Sun, W.; Wu, X.; Gao, B. The properties of the self-compacting concrete with fly ash and ground granulated blast furnace slag mineral admixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 95, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, Strength development of concretes with ordinary Portland cement, slag or fly ash cured at different temperatures. Mater. Struct. 2002, 35, 536–540. [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Tian, Q.; Miao, J.; Liu, J. Early-age hydration and mechanical properties of high volume slag and fly ash concrete at different curing temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.; Martirena, F.; Bishnoi, S.; Maity, S. Calcined clay limestone cements (LC3). Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endale, S.A.; Taffese, W.Z.; Vo, D.-H.; Yehualaw, M.D. Rice Husk Ash in Concrete. Sustainability 2023, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeh, B.A.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Alaskar, A. Recycling of rice husk waste for a sustainable concrete: A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 312, 127734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amran, M.; Fediuk, R.; Murali, G.; Vatin, N.; Karelina, M.; Krishna, T.O.R.S.; Sahoo, A.K.; Das, S.K.; Mishra, J. Rice Husk Ash-Based Concrete Composites: A Critical Review of Their Properties and Applications. Crystals 2021, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, N.V.; Ye, G.; van Breugel, K.; Fraaij, A.L.A.; Dai, B.D. The study of using rice husk ash to produce ultra high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 2030–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensale, G.R. Strength development of concrete with rice-husk ash. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2006, 28, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-H.; Malhotra, V.M. High-Performance Concrete Incorporating Rice Husk Ash as a Supplementary Cementing Material. ACI Mater. J. 1996, 93, 629–636. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, D.; Siddique, R.; Kunal. Strength, permeability and microstructure of self-compacting concrete containing rice husk ash. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 130, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, R.; Bhikshma, V.; Prakash, P.J. Study on Strength Characteristics of High Strength Rice Husk Ash Concrete. Procedia Eng. 2011, 14, 2666–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madandoust, R.; Ranjbar, M.M.; Moghadam, H.A.; Mousavi, S.Y. Mechanical properties and durability assessment of rice husk ash concrete. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 110, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbino, R.; Giaccio, G.; Isaia, G.C. Concrete incorporating rice-husk ash without processing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Jabbar, A.; Ahmad, I.; Khan, W.; Khan, A.N.; Mirza, J. Reduction in environmental problems using rice-husk ash in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, N.K.; Sandeep, S.; Mini, K.M. Study on concrete with partial replacement of cement by rice husk ash. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 149, 012109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fediuk, R.S.; Lesovik, V.S.; Svintsov, A.P.; Mochalov, A.V.; Kulichkov, S.V.; Stoyushko, N.Y.; Gladkova, N.A.; Timokhin, R.A. Self-compacting concrete using pretreatmented rice husk ash. Mag. Civ. Eng. 2018, 3, 66–76. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, M.M.; Sivaraja, M. Mechanical Behavior of Concrete Modified by Replacement of Cement by Rice Husk Ash. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2016, 59, e161072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Xu, J. Compression behavior and permeability of concrete composed of glass sand and rice husk ash. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.C.; Basit, M.A.; Hasan, N.M.S.; Islam, M.S. Sustainable cement mortar production using rice husk and eggshell powder: A study of strength, electrical resistivity, and microstructure. Smart Constr. Sustain. Cities 2024, 2, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, M.J.; Miah, M.S.; Hasan, N.M.S.; Sobuz, M.H.R.; Li, Y. Role of recycled crushed clay bricks as fine aggregates in enhancing the performance of ferrocement-strengthened RC beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 478, 141412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Cuenca, E.; Ferrara, L. Optimised data-driven method to study the self-healing and durability of ultra-high performance concrete. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 143, 110043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffese, W.Z.; Hilloulin; Zaccardi, Y.V.; Marani, A.; Nehdi, M.L.; Hanif, M.U.; Kamath, M.; Nunes, S.; von Greve-Dierfeld, S.; Kanellopoulos, A. Machine learning in concrete durability: Challenges and pathways identified by RILEM TC 315-DCS towards enhanced predictive models. Mater. Struct. 2025, 58, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, M.J.; Miah, M.S.; Alam, W.B.; Monte, F.L.; Ye, L. Strengthening of RC beams by ferrocement made with unconventional concrete. Mag. Civ. Eng. 2019, 89, 94–105. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C136/C136M-14; Standard Test Method for Sieve Analysis of Fine and Coarse Aggregates. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014.
- ASTM C33M-18; Standard Specification for Concrete Aggregates. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Farooque, K.N.; Zaman, M.; Halim, E.; Islam, S.; Hossain, M.; Mollah, Y.A.; Mahmood, A.J. Characterisation and Utilisation of Rice Husk Ash (RHA) from Rice Mill of Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2009, 44, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM C39/C39M-18; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Cylindrical Concrete Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Miah, M.S.; Lienhart, W. Data-Based Prognosis and Monitoring of Civil Infrastructures. In European Workshop on Structural Health Monitoring. EWSHM 2022; Rizzo, P., Milazzo, A., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 254, pp. 1007–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J. Local Polynomial Modelling and Its Applications: From Linear Regression to Nonlinear Regression. In Monographs on Statistics and Applied Probability; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-0-412-98321-4. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, B.; Hastie, T.; Johnstone, I.; Tibshirani, R. Least Angle Regression. Ann. Statistics. 2004, 32, 407–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GeeksforGeeks. Linear Regression in Machine Learning. Archived From the Original on 2024-10-04. 2025. Available online: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/ml-linear-regression/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Stigler, S.M. Gergonne’s 1815 paper on the design and analysis of polynomial regression experiments. Hist. Math. 1974, 1, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steel, R.G.D.; Torrie, J.H. Principles and Procedures of Statistics with Special Reference to the Biological Sciences; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Glantz, S.A.; Slinker, B.K. Primer of Applied Regression and Analysis of Variance; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Du, D.Z.; Pardalos, P.M.; Wu, W. History of Optimisation. In Encyclopedia of Optimization; Floudas, C., Pardalos, P., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 1538–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Powell, M.D. On Search Directions for Minimization Algorithms. Math. Program. 1973, 4, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinnon, K.M. Convergence of the Nelder–Mead simplex method to a non-stationary point. SIAM J. Optim. 1999, 9, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolda, T.G.; Lewis, R.M.; Torczon, V. Optimisation by direct search: New perspectives on some classical and modern methods. SIAM Rev. 2003, 45, 385–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, M.S.; Chatzi, E.N.; Weber, F. Semi-active control of structural systems with uncertainties using an unscented Kalman filter. In Research and Applications in Structural Engineering, Mechanics and Computation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lagarias, J.C.; Reeds, J.A.; Wright, M.H.; Wright, P.E. Convergence Properties of the Nelder-Mead Simplex Method in Low Dimensions. SIAM J. Optim. 1998, 9, 112–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, M.J.; Miah, M.S.; Uddin, M.; Suzaudoula, M. Optimisation of mechanical properties of high performance concrete made with fly ash and blast furnace slag. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Advances in Civil Engineering (ICACE 2018), Penang, Malaysia, 19 December 2018; pp. 502–507. [Google Scholar]
- Nelder, J.A.; Mead, R. A simplex method for function minimization. Comput. J. 1965, 7, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, M.S.; Werner, L. Performance Comparison of Derivative-Free Optimization Methods, Proceedings of International Structural Engineering and Construction; ISEC Press: Fargo, ND, USA, 2024; Volume 11, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Miah, M.S.; Chatzi, E.N.; Dertimanis, V.K.; Weber, F. Nonlinear modeling of a rotational MR damper via an enhanced Bouc–Wen model. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Shao, C.; Ma, C.; Chen, M.; Bai, J. Effect of different superplasticisers on the mechanism, workability, and microstructure of biomass-activated grouts. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 373, 130857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Cong, P.; Hao, H.; Zhao, Q.; Mei, L.; Zhang, A.; Han, Z.; Hu, M. Improving workability and mechanical properties of one-part waste brick power based-binders with superplasticisers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 335, 127535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisi, E.M.; Amiri, J.V.; Davoodi, M.R. Mechanical performance of self-compacting concrete incorporating rice husk ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 177, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari, A.; Toufigh, V. Effects of elevated temperatures and re-curing on concrete containing rice husk ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 439, 137277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
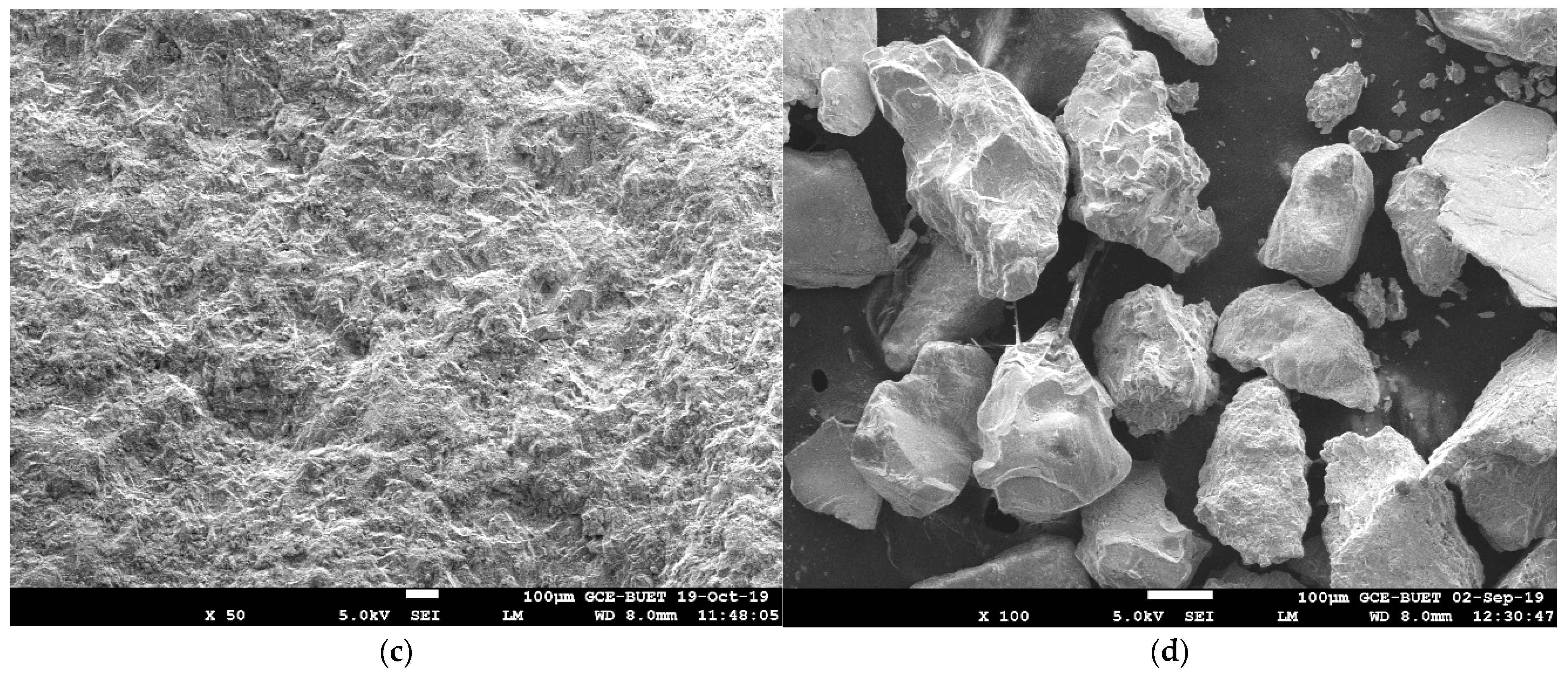









| Properties | Unit | NCS | NS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific gravity (SSD) | - | 2.73 | 2.54 |
| Unit weight (SSD) | kg/3 | 1550 | 1530 |
| Absorption capacity | % | 1.00 | 3.10 |
| Fineness modulus | - | 7.43 | 2.82 |
| Chemical Composition | OPC (%) | RHA (%) | NCS (%) | NS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | 5.03 | 0.30 | 11.81 | 4.55 |
| SiO2 | 21.47 | 91.3 | 50.32 | 84.56 |
| CaO | 65.01 | 0.21 | 12.32 | 0.85 |
| Fe2O3 | 3.76 | 0.12 | 13.44 | 4.15 |
| SO3 | 2.04 | 0.24 | 0.15 | - |
| MgO | 0.92 | 0.31 | 5.53 | 0.37 |
| K2O | - | 2.65 | 0.69 | 4.18 |
| TiO2 | - | 0.15 | 2.02 | 0.31 |
| P2O5 | - | - | 0.29 | 0.13 |
| Na2O | - | 1.52 | 3.11 | 0.82 |
| MnO | - | - | 0.17 | 0.04 |
| ZrO2 | - | - | - | - |
| SrO | - | - | 0.06 | 0.02 |
| Cr2O3 | - | - | 0.07 | - |
| Mix ID | OPC | RHA | NCS | NS | Water |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 500 | 0 | 974 | 745 | 175 |
| 5% RHA | 475 | 25 | 974 | 745 | 175 |
| 10% RHA | 450 | 50 | 974 | 745 | 175 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miah, M.J.; Miah, M.S.; Mughal, H.; Hasan, N.M.S. Mitigating Environmental Impact Through the Use of Rice Husk Ash in Sustainable Concrete: Experimental Study, Numerical Modelling, and Optimisation. Materials 2025, 18, 3298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143298
Miah MJ, Miah MS, Mughal H, Hasan NMS. Mitigating Environmental Impact Through the Use of Rice Husk Ash in Sustainable Concrete: Experimental Study, Numerical Modelling, and Optimisation. Materials. 2025; 18(14):3298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143298
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiah, Md Jihad, Mohammad Shamim Miah, Humera Mughal, and Noor Md. Sadiqul Hasan. 2025. "Mitigating Environmental Impact Through the Use of Rice Husk Ash in Sustainable Concrete: Experimental Study, Numerical Modelling, and Optimisation" Materials 18, no. 14: 3298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143298
APA StyleMiah, M. J., Miah, M. S., Mughal, H., & Hasan, N. M. S. (2025). Mitigating Environmental Impact Through the Use of Rice Husk Ash in Sustainable Concrete: Experimental Study, Numerical Modelling, and Optimisation. Materials, 18(14), 3298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143298








