Estimation of Several Wood Biomass Calorific Values from Their Proximate Analysis Based on Artificial Neural Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
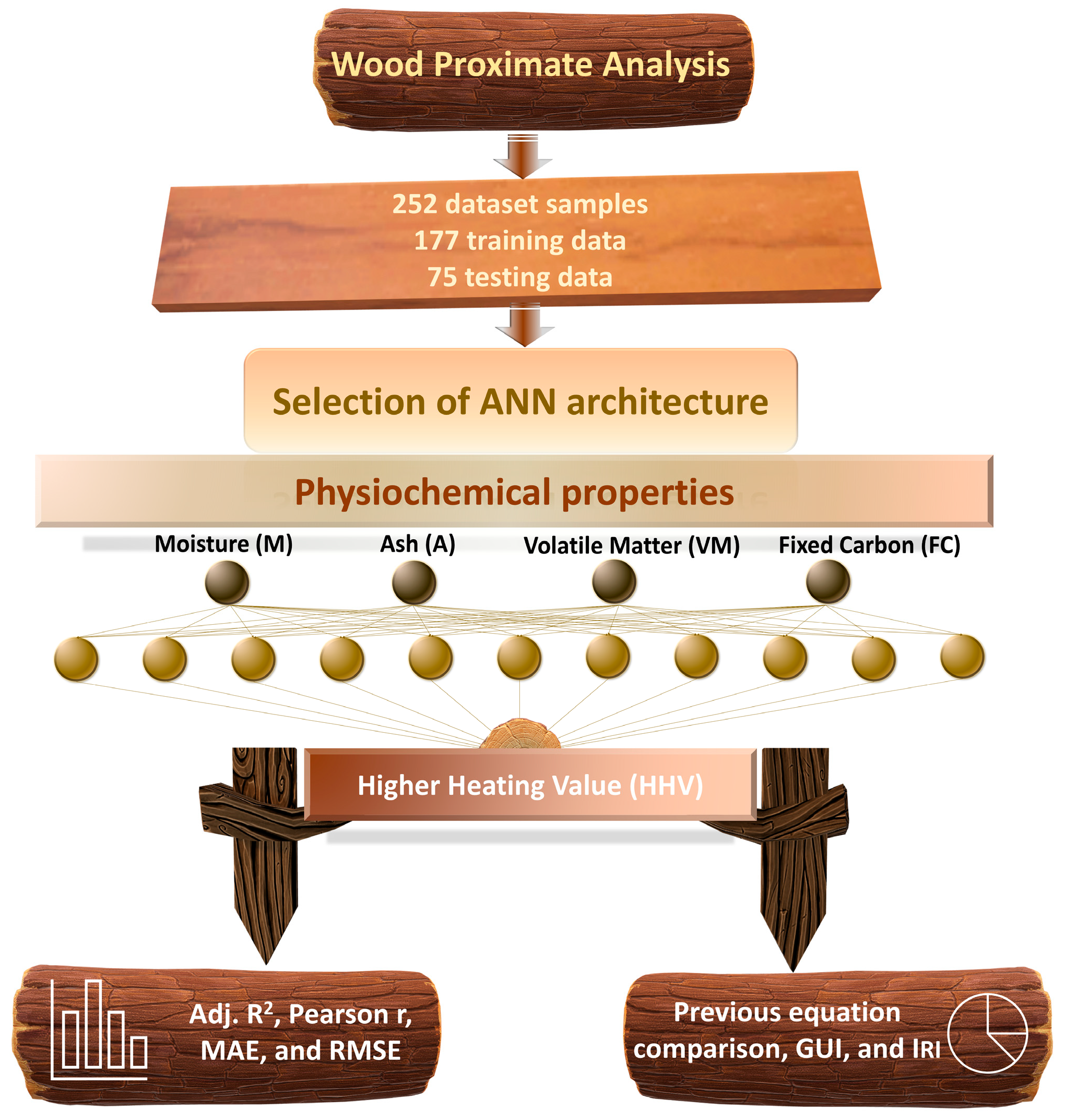
2. Materials and Methods
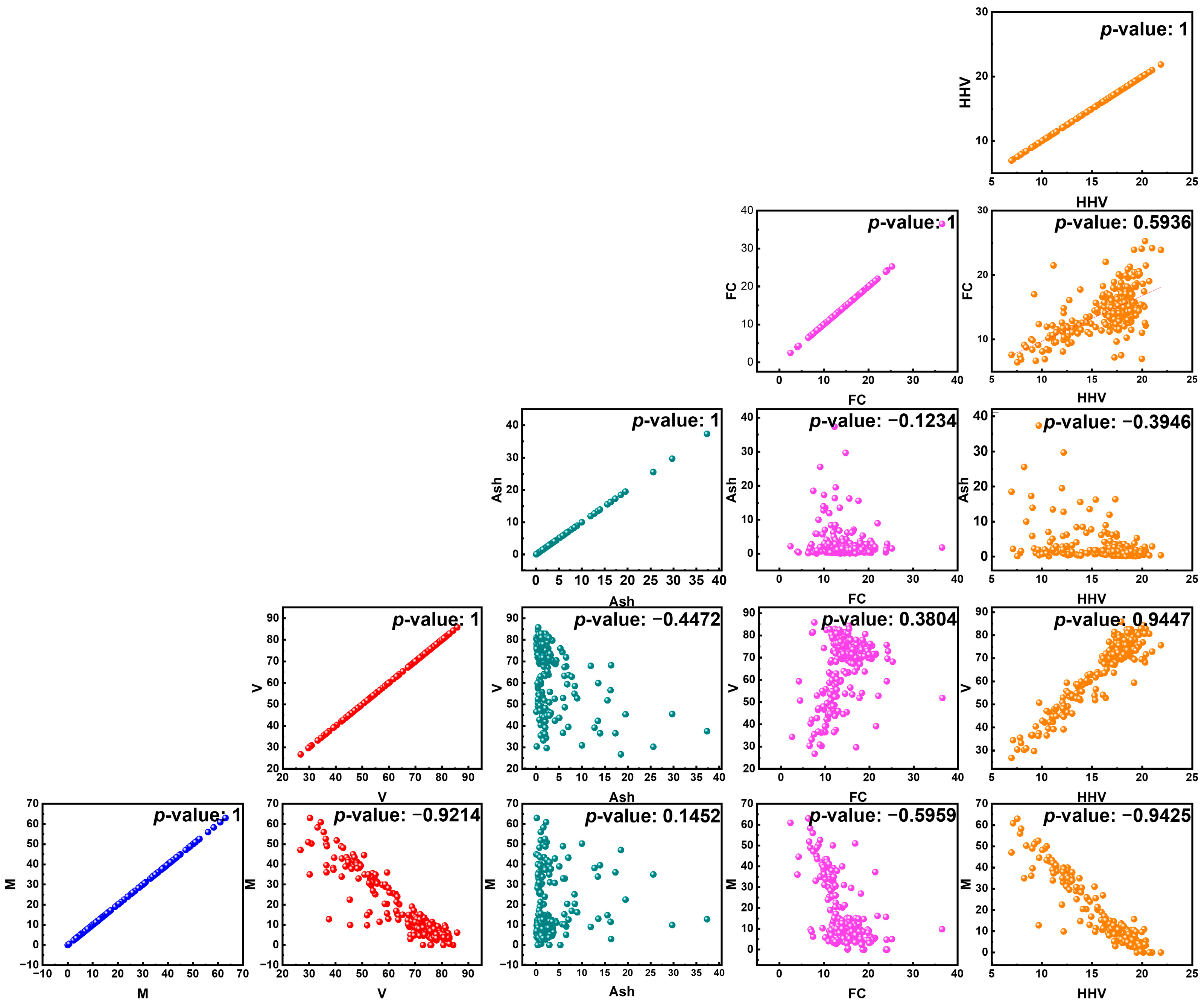
2.1. Data Collection
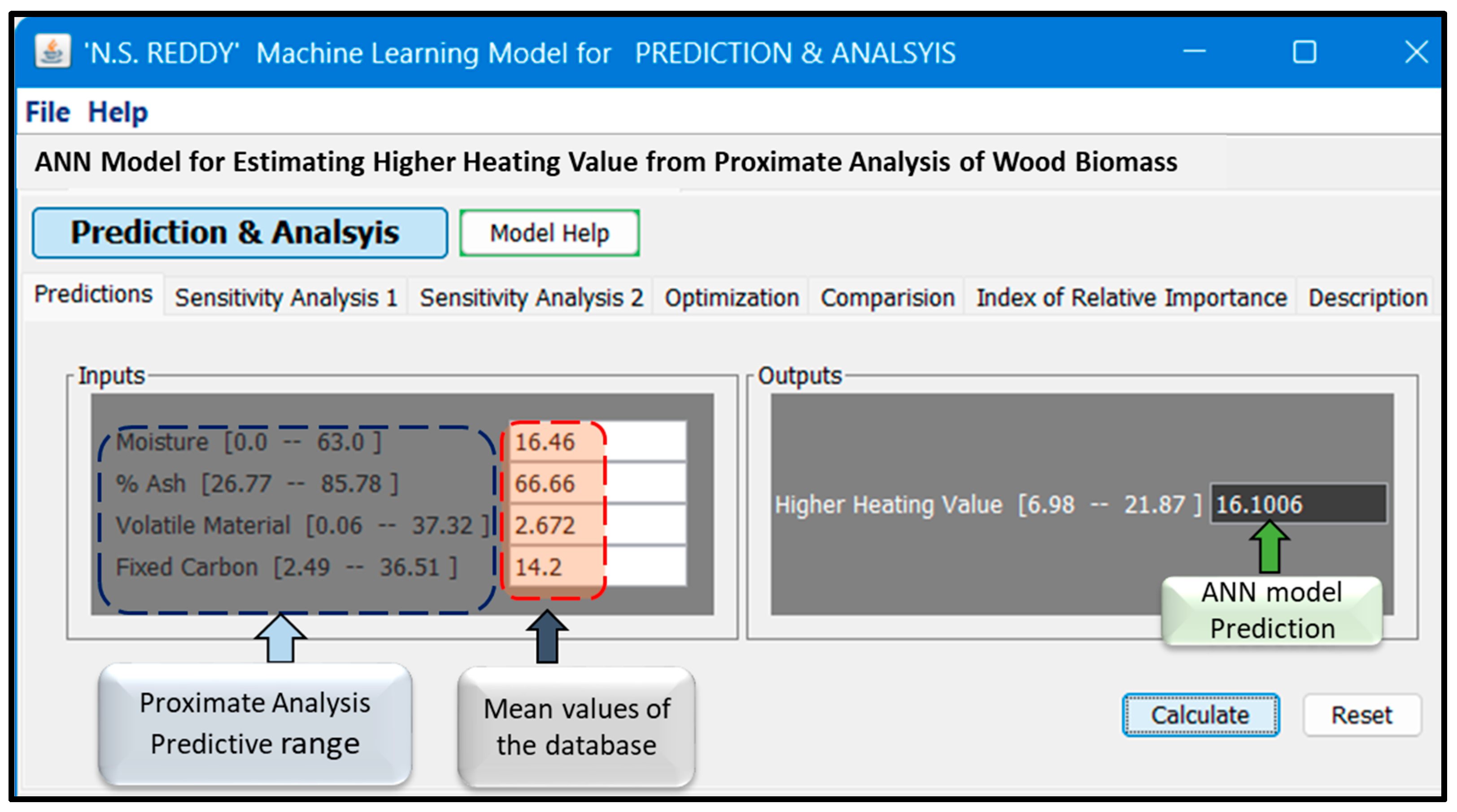
2.2. Development of GUI-Based ANN Model and Evaluation Procedure
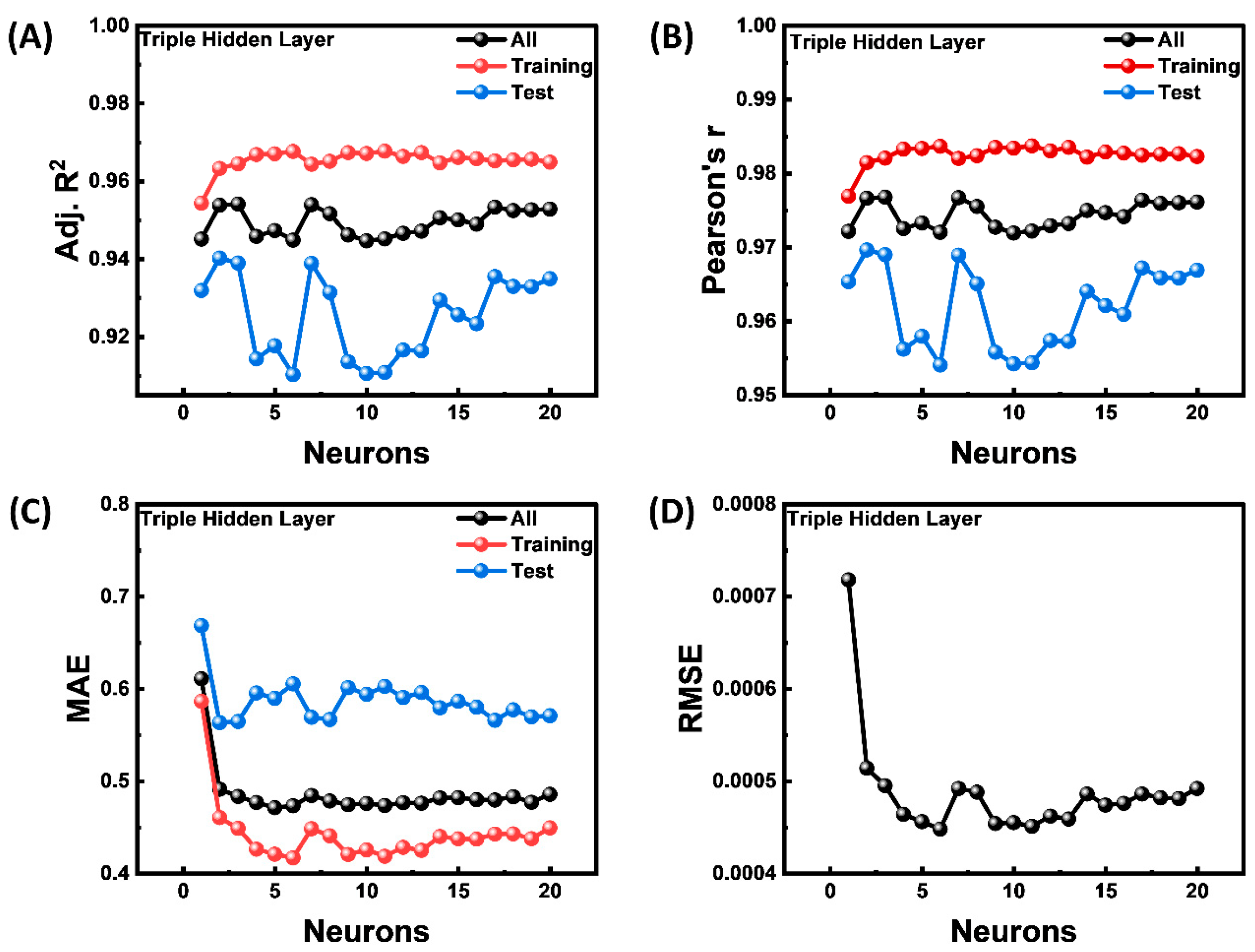
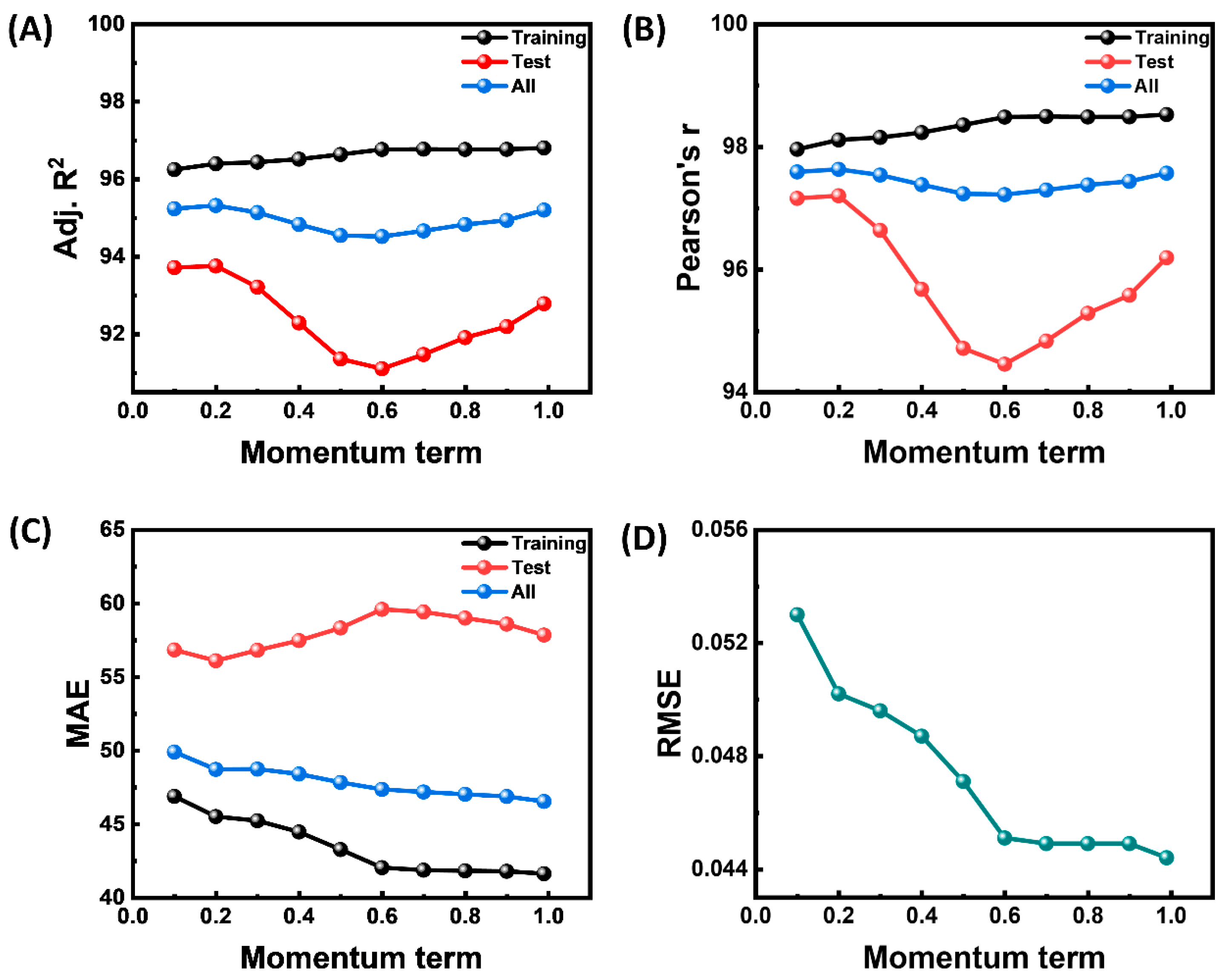
3. Results
3.1. Neural Network Architecture Optimization
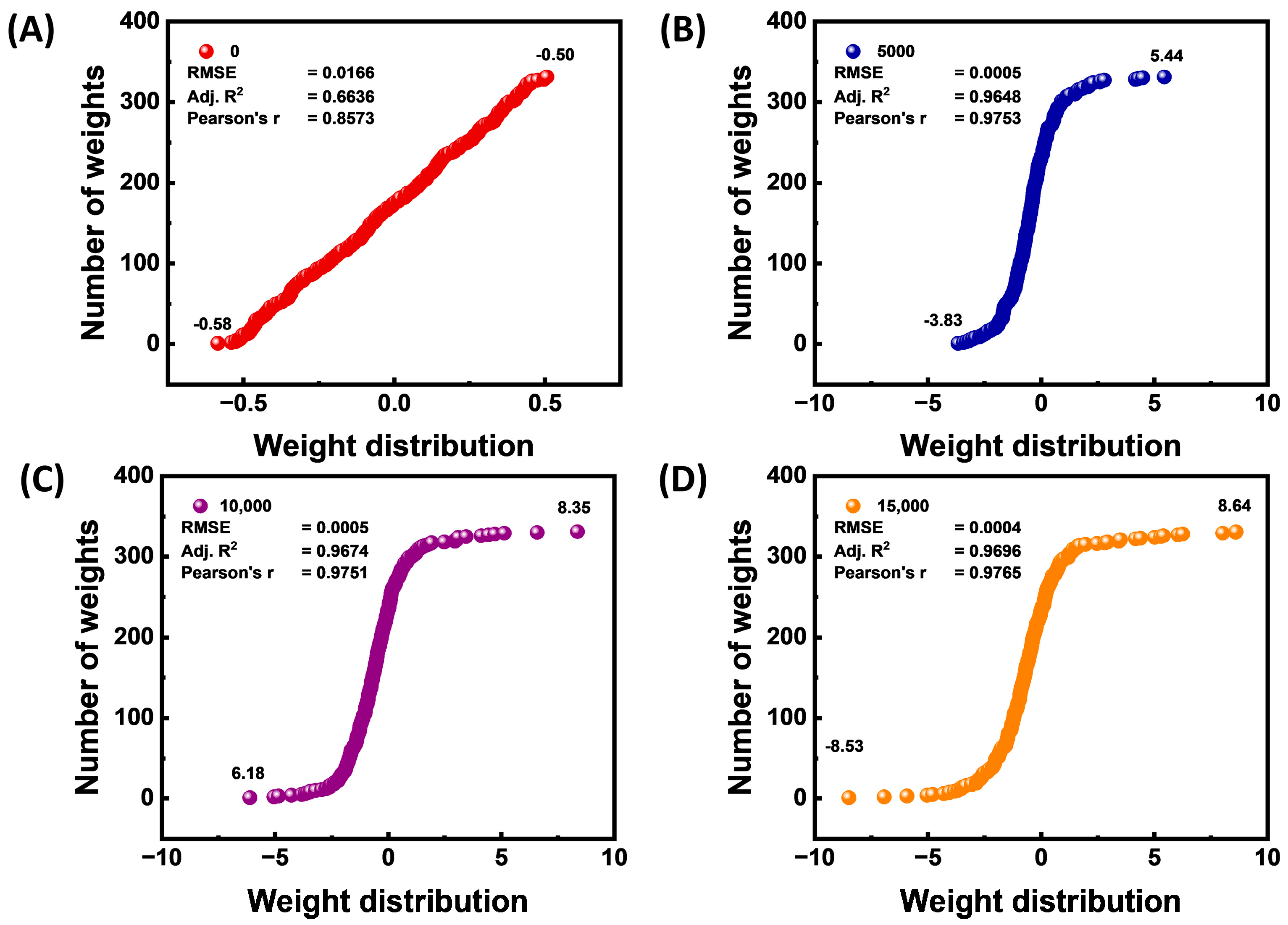
3.2. Transformations of Synaptic Weights
3.3. Index of Relative Performance
3.4. Creation of Virtual Biomass HHV System
3.5. Comparison of ANN Model Predictions for Biomass HHV with Experimental Results from the Literature and Proximate Analysis Data
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Past Research
4.2. Research Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daskin, M.; Erdogan, A.; Güleç, F.; Okolie, J.A. Generalizability of empirical correlations for predicting higher heating values of biomass. Energy Source Part A 2024, 46, 5434–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, S.A.; Ranjbar, S.F.; Jahromi, D.R. Applying feature selection and machine learning techniques to estimate the biomass higher heating value. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvidsson, M.; Morandin, M.; Harvey, S. Biomass gasification-based syngas production for a conventional oxo synthesis plant-greenhouse gas emission balances and economic evaluation. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, P.O.; Metari, S.; Arroyo-Mora, J.P.; Fagan, M.E.; Kalacska, M. Application of Machine Learning for Aboveground Biomass Modeling in Tropical and Temperate Forests from Airborne Hyperspectral Imagery. Forests 2025, 16, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, E.; Anttila, P.; Hakala, K.; Luostarinen, S.; Lehtoranta, S.; Merilehto, K.; Lehtinen, H.; Maharjan, A.; Mäntylä, V.; Niemeläinen, O.; et al. An open web-based GIS service for biomass data in Finland. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 176, 105972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skodras, G.; GrammelisO, P.; Basinas, P.; Kakaras, E.; Sakellaropoulos, G. Pyrolysis and combustion characteristics of biomass and waste-derived feedstock. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capareda, S.C. 1—Comprehensive biomass characterization in preparation for conversion. In Sustainable Biochar for Water and Wastewater Treatment; Mohan, D., Pittman, C.U., Mlsna, T.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.P.; Teixeira, S.; Teixeira, J.C. Characterization of the physicochemical and thermal properties of different forest residues. Biomass Bioenergy 2023, 175, 106870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, A.M.; Adeleke, A.A.; Nzerem, P.; Ikubanni, P.P.; Ayuba, S.; Rasheed, H.A.; Gimba, A.; Okafor, I.; Okolie, J.A.; Paramasivam, P. Comprehensive Characterization of Some Selected Biomass for Bioenergy Production. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 43771–43791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, A.; Noushabadi, A.S.; Raji, M.; Razmi, A.; Ceylan, S.; Mohammadi, A.H. Estimation of biomass higher heating value (HHV) based on the proximate analysis: Smart modeling and correlation. Fuel 2019, 257, 115931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, S.; Aghbashlo, M.; Tabatabaei, M. Biomass higher heating value (HHV) modeling on the basis of proximate analysis using iterative network-based fuzzy partial least squares coupled with principle component analysis (PCA-INFPLS). Fuel 2018, 222, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzun, H.; Yildiz, Z.; Goldfarb, J.L.; Ceylan, S. Improved prediction of higher heating value of biomass using an artificial neural network model based on proximate analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ma, Y.K.; Zhu, X.F. Effect of quantitative heat transfer performance on the separation and enrichment of bio-oil components during the selective condensation of biomass pyrolysis vapors. Fuel Process. Technol. 2023, 243, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, C.; Azevedo, J.L.T. Estimating the higher heating value of biomass fuels from basic analysis data. Biomass Bioenergy 2005, 28, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; Pizarro, C.; Lavín, A.G.; Bueno, J.L. Spanish biofuels heating value estimation. Part I: Ultimate analysis data. Fuel 2014, 117, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; Pizarro, C.; Lavín, A.G.; Bueno, J.L. Spanish biofuels heating value estimation. Part II: Proximate analysis data. Fuel 2014, 117, 1139–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; Pizarro, C.; Lavín, A.G.; Bueno, J.L. Biomass proximate analysis using thermogravimetry. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez-Martí, B.; Gaibor-Chávez, J.; Niño-Ruiz, Z.; Cortés-Rojas, E. Development of biomass fast proximate analysis by thermogravimetric scale. Renew. Energy 2018, 126, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandic, I.; Pezo, L.; Bilandzija, N.; Peter, A.; Suric, J.; Voca, N. Comparison of Different Machine Learning Models for Modelling the Higher Heating Value of Biomass. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaka, H.; Insel, M.A.; Yucel, O.; Sadikoglu, H. A comparison of machine learning algorithms for estimation of higher heating values of biomass and fossil fuels from ultimate analysis. Fuel 2022, 320, 123971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afolabi, I.C.; Epelle, E.I.; Gunes, B.; Güleç, F.; Okolie, J.A. Data-Driven Machine Learning Approach for Predicting the Higher Heating Value of Different Biomass Classes. Clean. Technol. 2022, 4, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandić, I.; Pezo, L.; Voća, N.; Matin, A. Biomass Higher Heating Value Estimation: A Comparative Analysis of Machine Learning Models. Energies 2024, 17, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, G.; Lu, K.; Li, C. Comparison of Artificial Neural Networks and kinetic inverse modeling to predict biomass pyrolysis behavior. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 169, 105802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odufuwa, O.Y.; Tartibu, L.K.; Kusakana, K. Artificial neural network modelling for predicting efficiency and emissions in mini-diesel engines: Key performance indicators and environmental impact analysis. Fuel 2025, 387, 134294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiodun, O.I.; Jantan, A.; Omolara, A.E.; Dada, K.V.; Mohamed, N.A.; Arshad, H. State-of-the-art in artificial neural network applications: A survey. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, H.R.; Galelli, S.; Razavi, S.; Castelletti, A.; Rizzoli, A.; Athanasiadis, I.N.; Sànchez-Marrè, M.; Acutis, M.; Wu, W.; Humphrey, G.B. Exploding the myths: An introduction to artificial neural networks for prediction and forecasting. Environ. Model. Softw. 2023, 167, 105776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.S.; Narayana, P.L.; Maurya, A.K.; Paturi, U.M.R.; Sung, J.; Ahn, H.J.; Cho, K.K.; Reddy, N.S. Modeling capacitance of carbon-based supercapacitors by artificial neural networks. J. Energy Storage 2023, 72, 108537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, S.; Aghbashlo, M.; Tabatabaei, M.; Mehrpooya, M. Estimation of biomass higher heating value (HHV) based on the proximate analysis by using iterative neural network-adapted partial least squares (INNPLS). Energy 2017, 138, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veza, I.; Irianto; Panchal, H.; Paristiawan, P.A.; Idris, M.; Fattah, I.M.R.; Putra, N.R.; Silambarasan, R. Improved prediction accuracy of biomass heating value using proximate analysis with various ANN training algorithms. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technologies Energy Research Centre of The Netherlands. Database for the Physico-Chemical Composition of (Treated) Lignocellulosic Biomass, Micro- and Macroalgae, Various Feedstocks for Biogas Production and Biochar. Available online: https://phyllis.nl/ (accessed on 4 March 2025).
- Sadan, M.K.; Ahn, H.-J.; Chauhan, G.S.; Reddy, N.S. Quantitative estimation of poly(methyl methacrylate) nano-fiber membrane diameter by artificial neural networks. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 74, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippmann, R. An introduction to computing with neural nets. IEEE ASSP Mag. 1987, 4, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.R.S.; Premasudha, M.; Panigrahi, B.B.; Cho, K.K.; Reddy, N.G.S. Modeling constituent-property relationship of polyvinylchloride composites by neural networks. Polym. Compos. 2020, 41, 3208–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugavel, A.B.; Ellappan, V.; Mahendran, A.; Subramanian, M.; Lakshmanan, R.; Mazzara, M. A Novel Ensemble Based Reduced Overfitting Model with Convolutional Neural Network for Traffic Sign Recognition System. Electronics 2023, 12, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhi, A.; Knapic, S.; Främling, K. Explainable Agents for Less Bias in Human-Agent Decision Making. In Proceedings of the Explainable, Transparent Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems: Second International Workshop, EXTRAAMAS 2020, Auckland, New Zealand, 9–13 May 2020; Revised Selected Papers, Auckland, New Zealand, 2020. pp. 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, K.; Dwivedi, P. Decoding the black box: LIME-assisted understanding of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) in classification of social media tweets. Soc. Netw. Anal. Min. 2024, 14, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.S.; Mazhar, S.S.; Mazhar, K.; AlSaleh, D.A.; Mazhar, A. Model-agnostic explainable artificial intelligence methods in finance: A systematic review, recent developments, limitations, challenges and future directions. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2025, 58, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Saravia, R.C.; Lizcano-Prada, J.O.; Bohórquez-Ballesteros, L.A.; Angarita-Martínez, J.D.; Duarte-Castillo, A.E.; Candela-Becerra, L.J.; Uribe-Rodríguez, A. Designing a hydrogen supply chain from biomass, solar, and wind energy integrated with carbon dioxide enhanced oil recovery operations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 99, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, Z.; Du, L.; Miao, F.; Liu, L. Prediction of product yields and heating value of bio-oil from biomass fast pyrolysis: Explainable predictive modeling and evaluation. Energy 2025, 324, 136087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, F.; Girard, A.; Krotki, M.; Ordoñez, J. Modelling and simulation of the wood biomass supply from the sustainable management of natural forests. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 124487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.Y. Prediction of higher heating values of biomass from proximate and ultimate analyses. Fuel 2011, 90, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, L.; González, F. Study of the physical and chemical properties of lignocellulosic residues with a view to the production of fuels. Fuel 1991, 70, 947–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, A.K.; Jain, R.; Banerjee, P.; Barnwal, J.P. Development of a new proximate analysis based correlation to predict calorific value of coal. Fuel 2008, 87, 3077–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, T.; Marquez, F.; Rodriguez-Mirasol, J.; Rodriguez, J.J. Predicting heating values of lignocellulosics and carbonaceous materials from proximate analysis. Fuel 2001, 80, 1567–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbaş, A. Calculation of higher heating values of biomass fuels. Fuel 1997, 76, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimuk, Y.; Antonava, Z.; Krouk, V.; Korsakova, A.; Kursevich, V. Prediction of higher heating value (HHV) based on the structural composition for biomass. Fuel 2021, 299, 120860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noushabadi, A.S.; Dashti, A.; Ahmadijokani, F.; Hu, J.; Mohammadi, A.H. Estimation of higher heating values (HHVs) of biomass fuels based on ultimate analysis using machine learning techniques and improved equation. Renew. Energy 2021, 179, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güleç, F.; Pekaslan, D.; Williams, O.; Lester, E. Predictability of higher heating value of biomass feedstocks via proximate and ultimate analyses—A comprehensive study of artificial neural network applications. Fuel 2022, 320, 123944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghel, B.; Yahya, S.I.; Rezaei, A.; Alobaid, F. A Dynamic Recurrent Neural Network for Predicting Higher Heating Value of Biomass. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, J.; Channiwala, S.A.; Ghosal, G.K. A correlation for calculating HHV from proximate analysis of solid fuels. Fuel 2005, 84, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaya, A.V. Proximate analysis based multiple regression models for higher heating value estimation of low rank coals. Fuel Process. Technol. 2009, 90, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thipkhunthod, P.; Meeyoo, V.; Rangsunvigit, P.; Kitiyanan, B.; Siemanond, K.; Rirksomboon, T. Predicting the heating value of sewage sludges in Thailand from proximate and ultimate analyses. Fuel 2005, 84, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callejón-Ferre, A.J.; Velázquez-Martí, B.; López-Martínez, J.A.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Greenhouse crop residues: Energy potential and models for the prediction of their higher heating value. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A.; Dincer, K. Modeling Higher Heating Values of Lignites. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2008, 30, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.F.; Lin, C.J.; Chyan, J.M.; Chen, I.M.; Chang, J.E. Multiple regression models for the lower heating value of municipal solid waste in Taiwan. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wen, S. Proximate analysis based prediction of gross calorific value of coals: A comparison of support vector machine, alternating conditional expectation and artificial neural network. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 129, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathiravale, S.; Muhd Yunus, M.N.; Sopian, K.; Samsuddin, A.H.; Rahman, R.A. Modeling the heating value of Municipal Solid Waste. Fuel 2003, 82, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



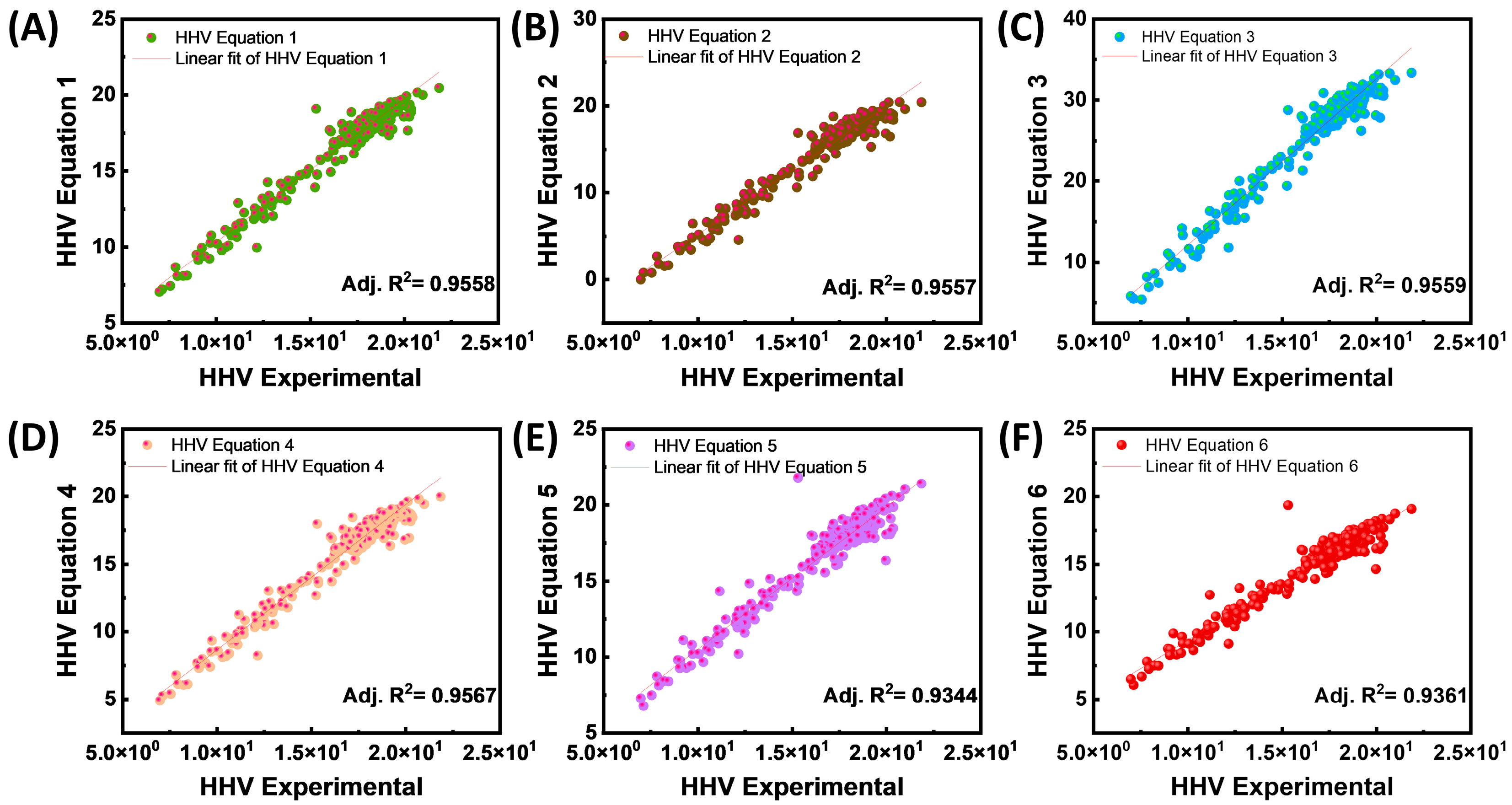

| Equation Number | Equations | Units | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | HHV = 0.1905 × VM + 0.2521 × FC | (MJ/kg) | [39] |
| (2) | HHV = −10.81408 + 0.3133 × (VM + FC) | (MJ/kg) | [40] |
| (3) | HHV = 0.03 × Ash − 0.11 × M + 0.33 × VM + 0.35 × FC | (MJ/kg) | [41] |
| (4) | HHV = 3.0368 + 0.2218 × VM + 0.2601 × FC | (MJ/kg) | [14] |
| (5) | HHV = 0.3543 × FC + 0.1708 × VM | (MJ/kg) | [42] |
| (6) | HHV = 0.312 × FC + 0.1534 × VM | (MJ/kg) | [43] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Devara, I.K.G.; Lestari, W.A.; Paturi, U.M.R.; Park, J.H.; Reddy, N.G.S. Estimation of Several Wood Biomass Calorific Values from Their Proximate Analysis Based on Artificial Neural Networks. Materials 2025, 18, 3264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143264
Devara IKG, Lestari WA, Paturi UMR, Park JH, Reddy NGS. Estimation of Several Wood Biomass Calorific Values from Their Proximate Analysis Based on Artificial Neural Networks. Materials. 2025; 18(14):3264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143264
Chicago/Turabian StyleDevara, I Ketut Gary, Windy Ayu Lestari, Uma Maheshwera Reddy Paturi, Jun Hong Park, and Nagireddy Gari Subba Reddy. 2025. "Estimation of Several Wood Biomass Calorific Values from Their Proximate Analysis Based on Artificial Neural Networks" Materials 18, no. 14: 3264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143264
APA StyleDevara, I. K. G., Lestari, W. A., Paturi, U. M. R., Park, J. H., & Reddy, N. G. S. (2025). Estimation of Several Wood Biomass Calorific Values from Their Proximate Analysis Based on Artificial Neural Networks. Materials, 18(14), 3264. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18143264










