Improvements in Wettability and Tribological Behavior of Zirconia Artificial Teeth Using Surface Micro-Textures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
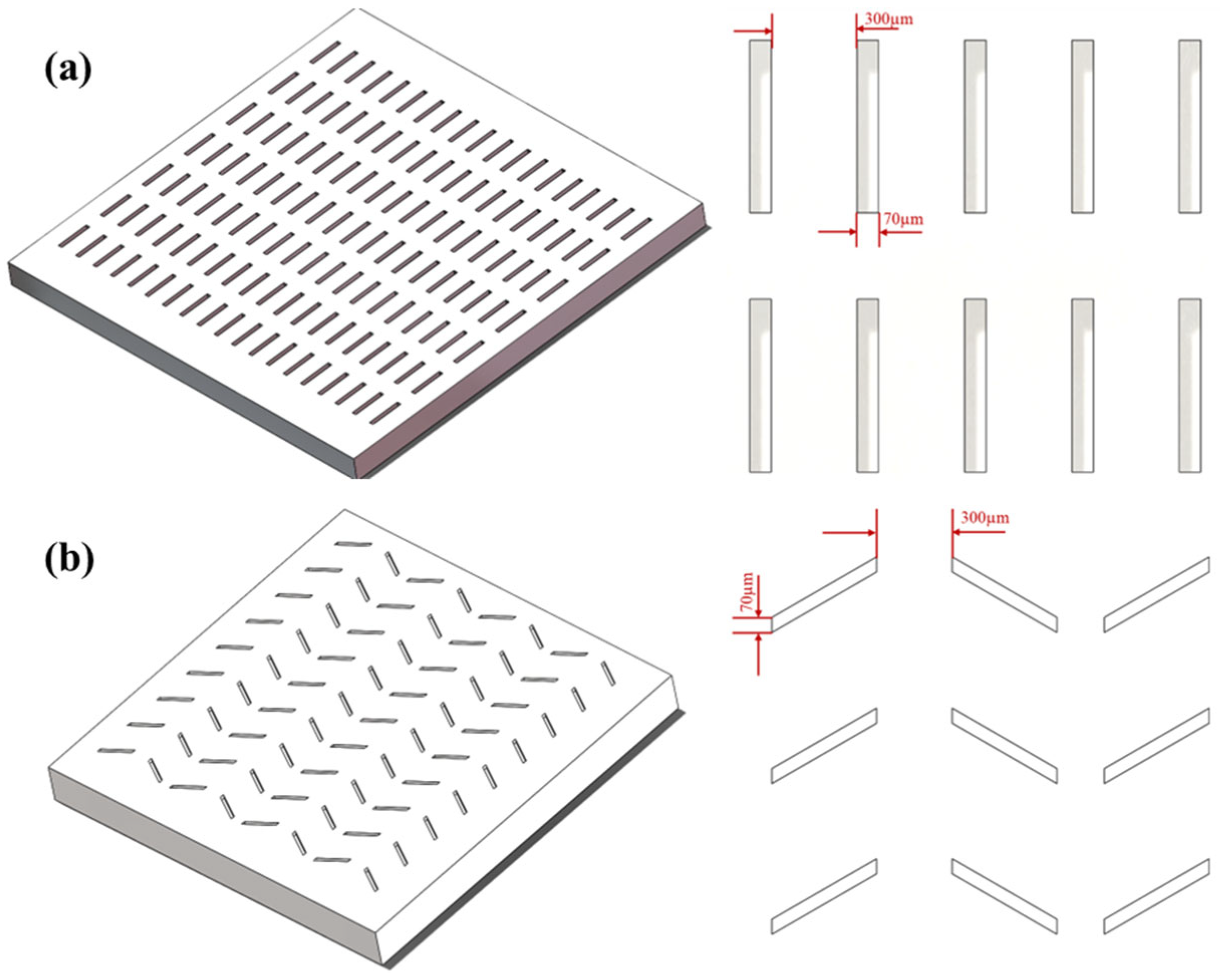
2.1. Zirconia Artificial Teeth Ceramic Specimens and Surface Texture Processing
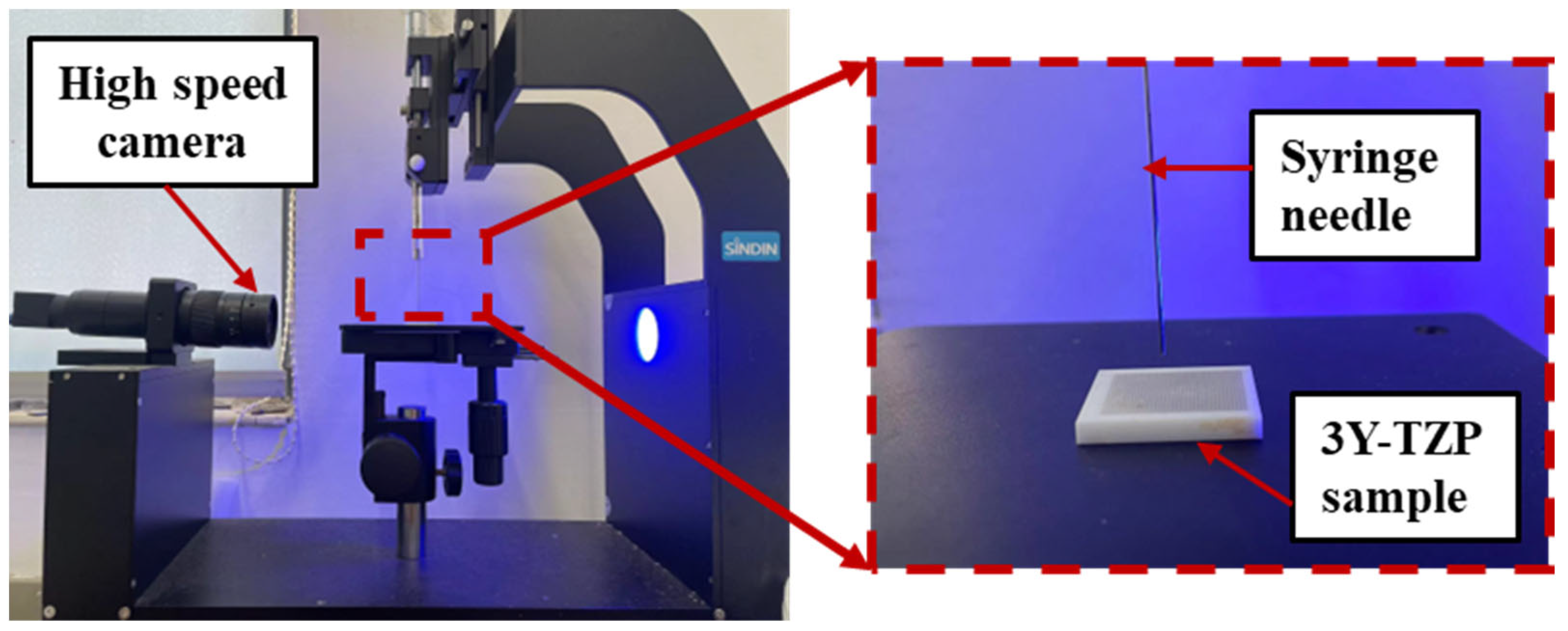
2.2. Wettability Test
2.3. Friction Test
3. Results and Discussion
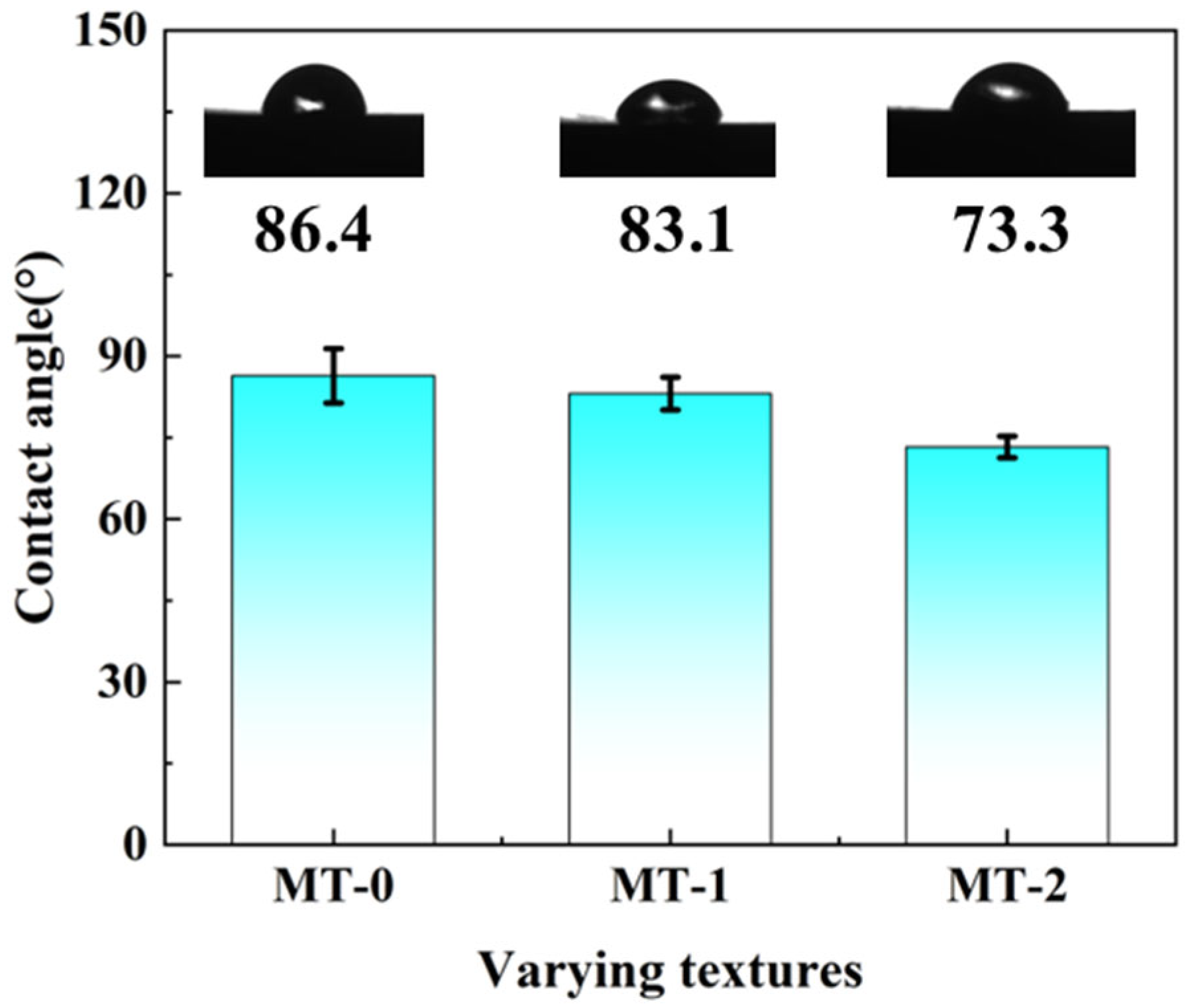
3.1. Wettability Analysis
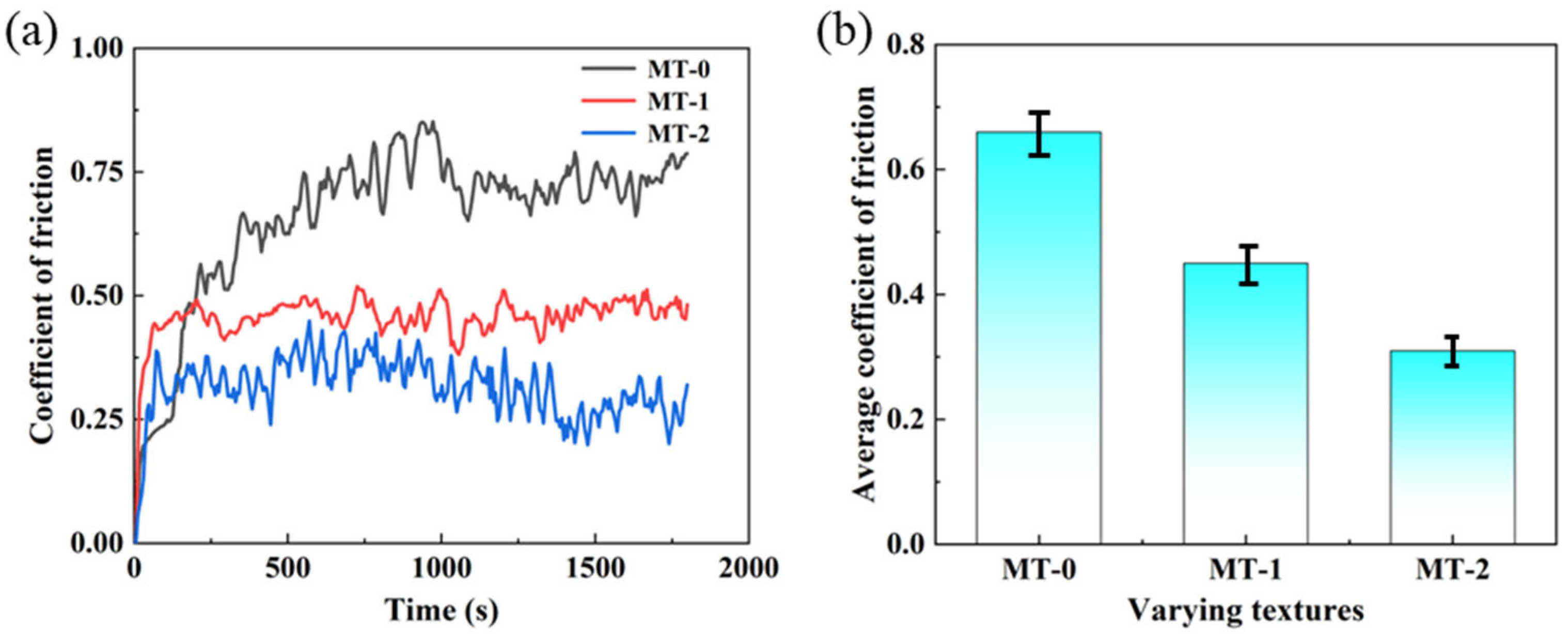
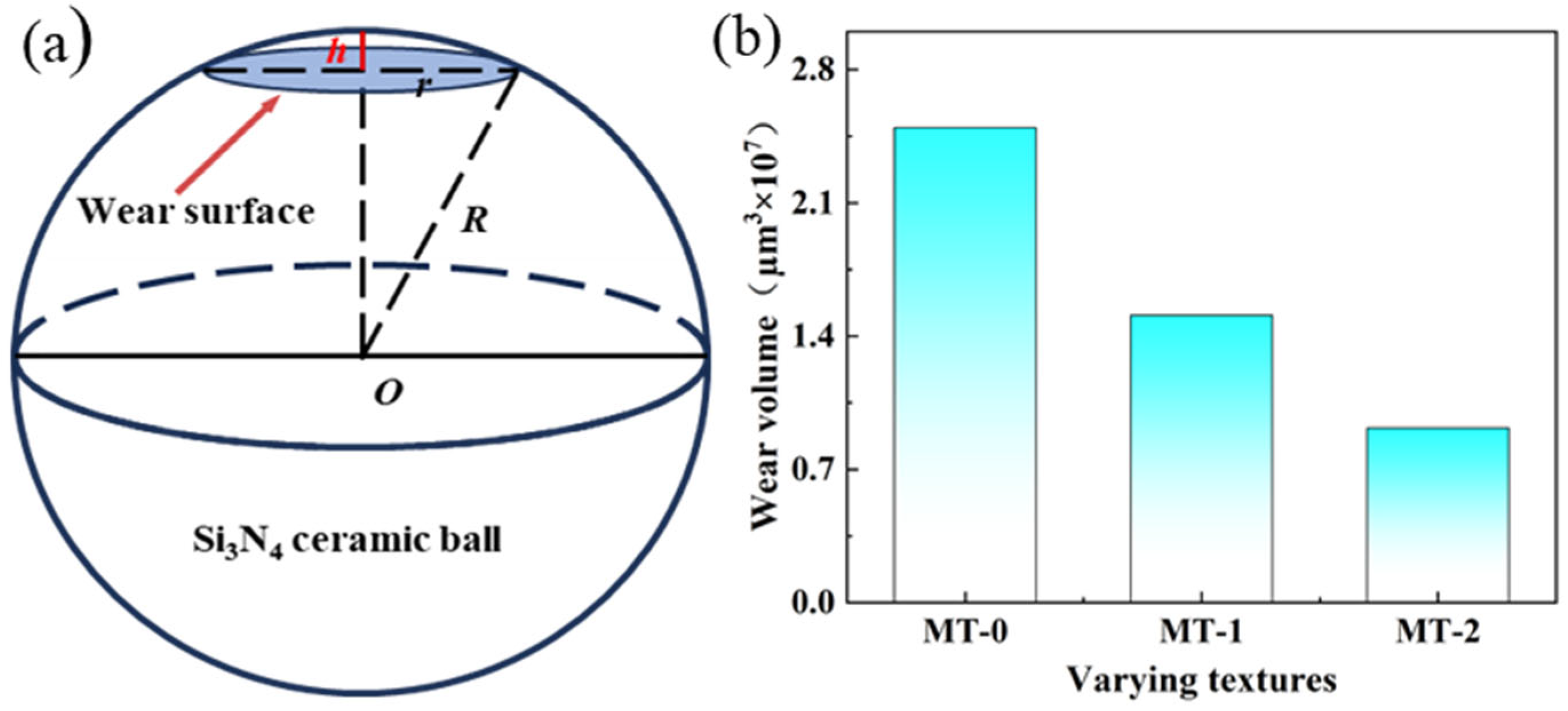
3.2. Friction and Wear Performance Analysis
3.2.1. Effects of Texture on Frictional Properties of Zirconia Artificial Teeth
3.2.2. Effects of Different Parameters on Friction Characteristics of Zirconia Artificial Teeth
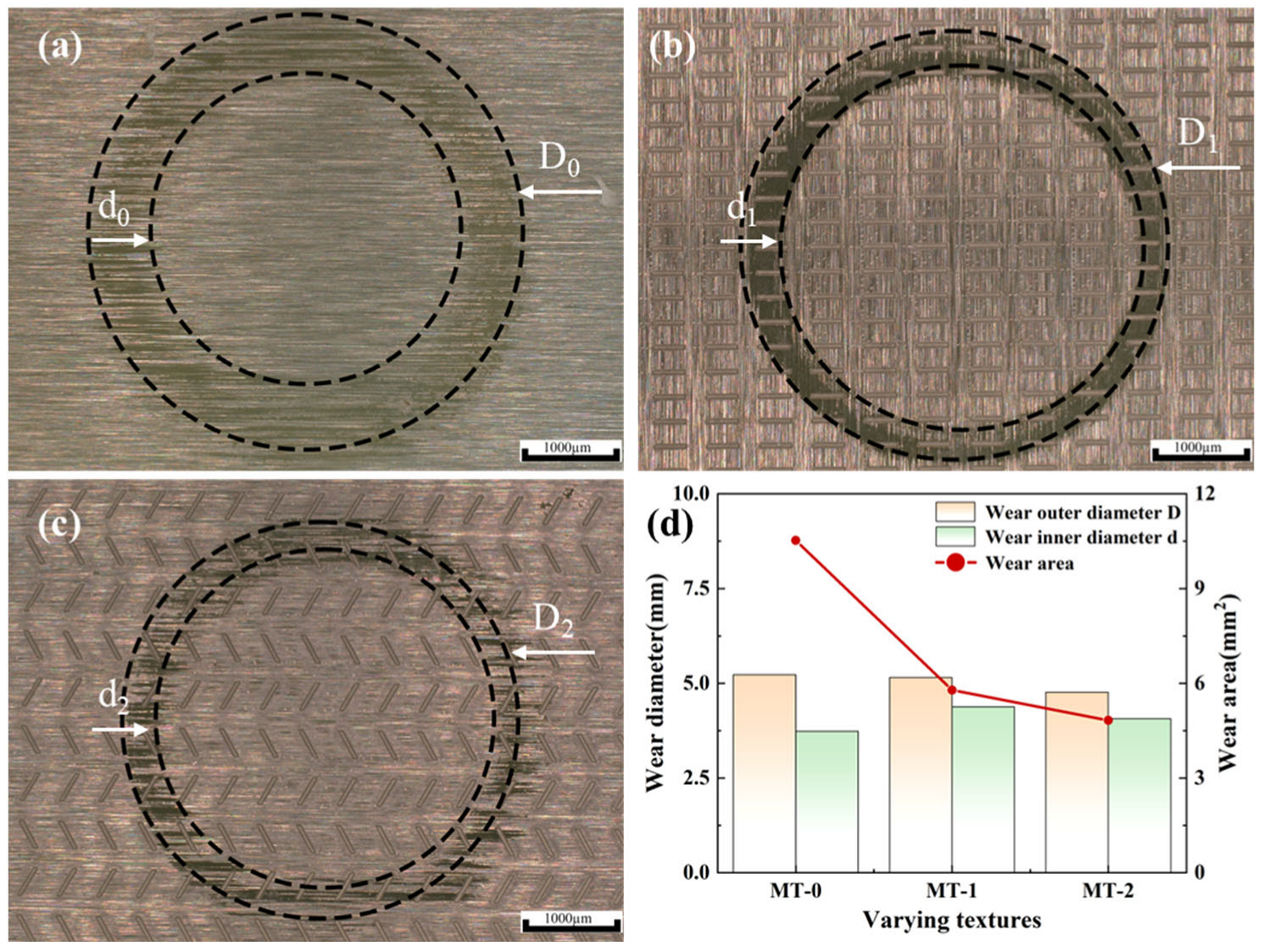
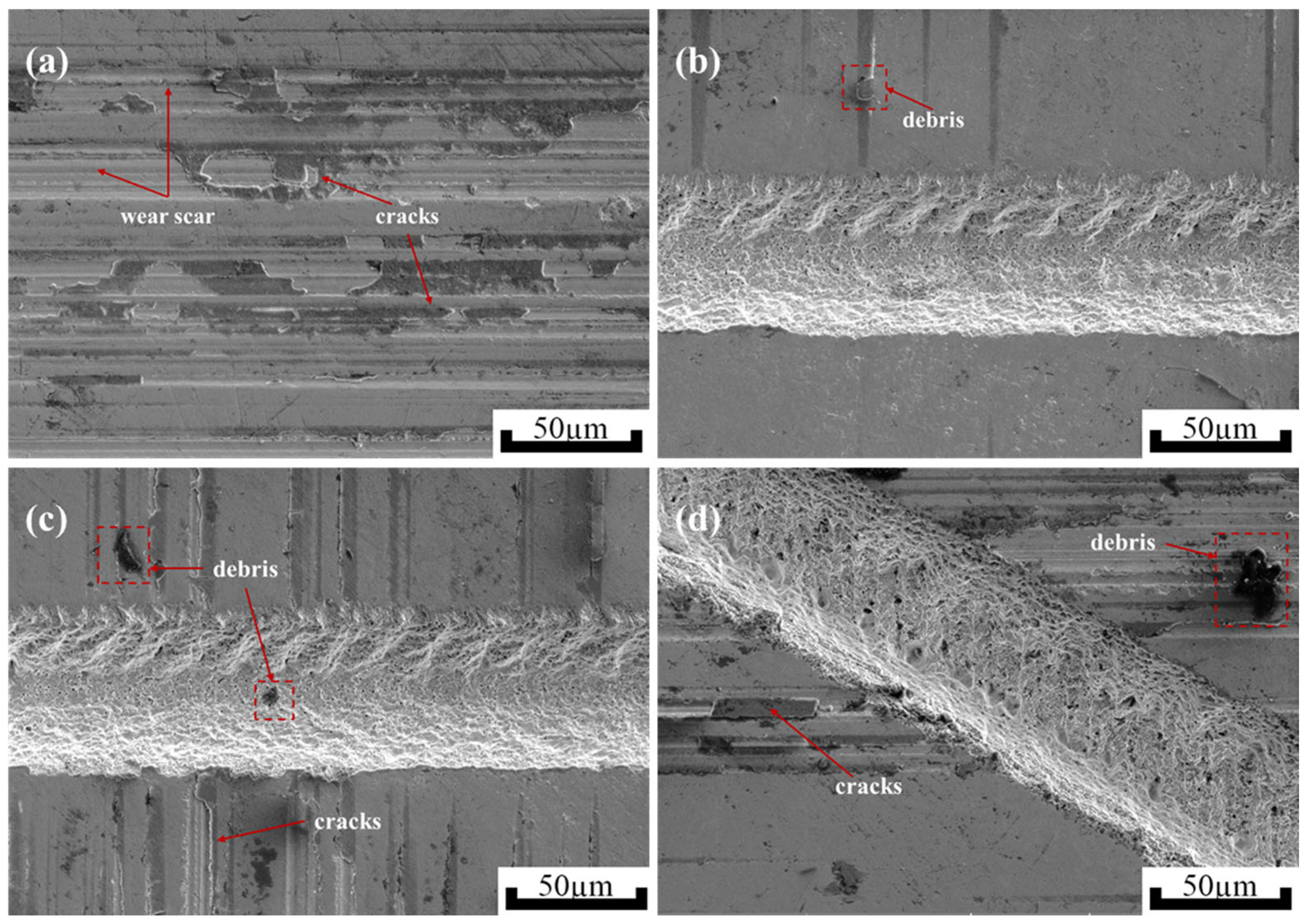
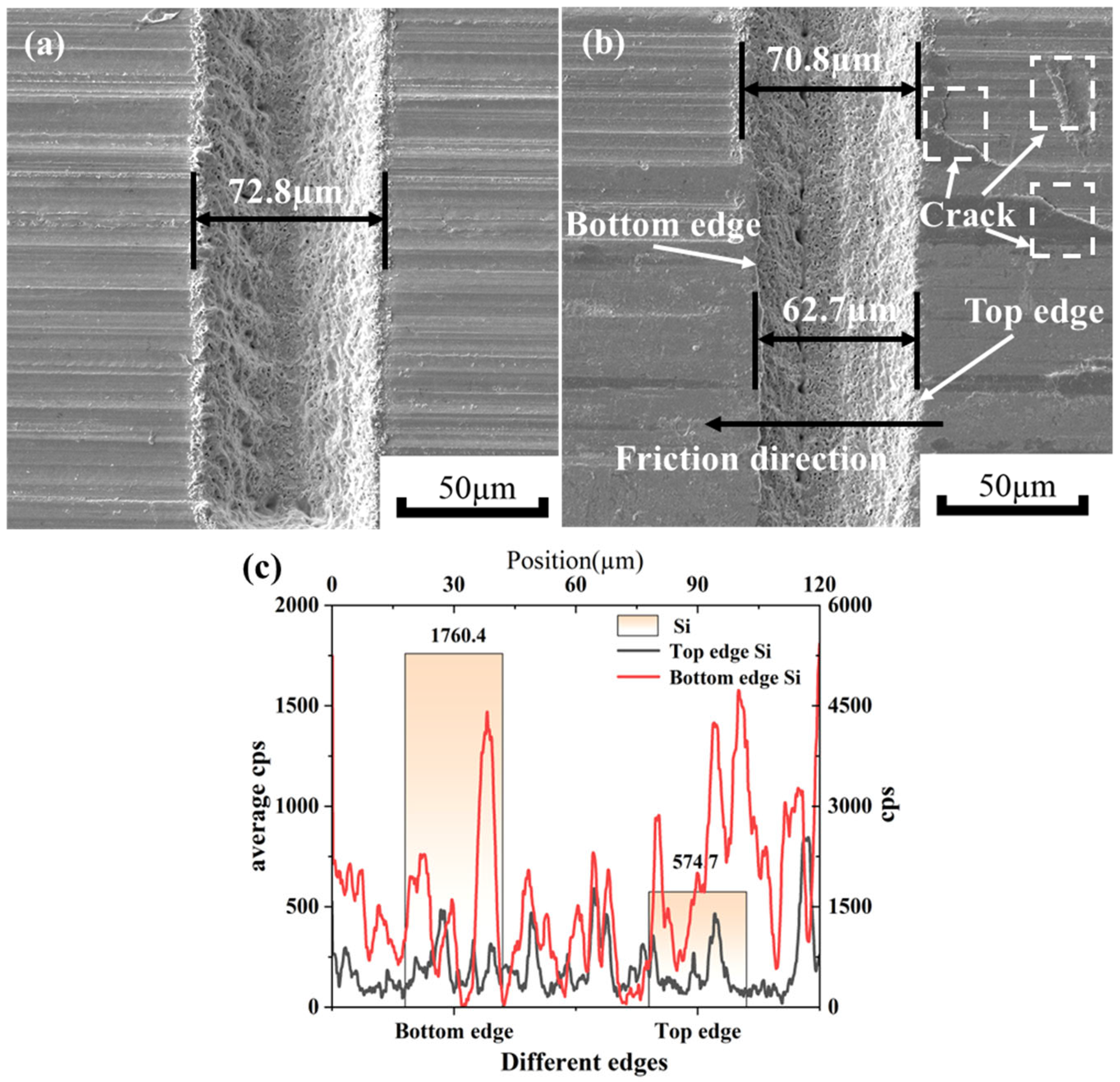
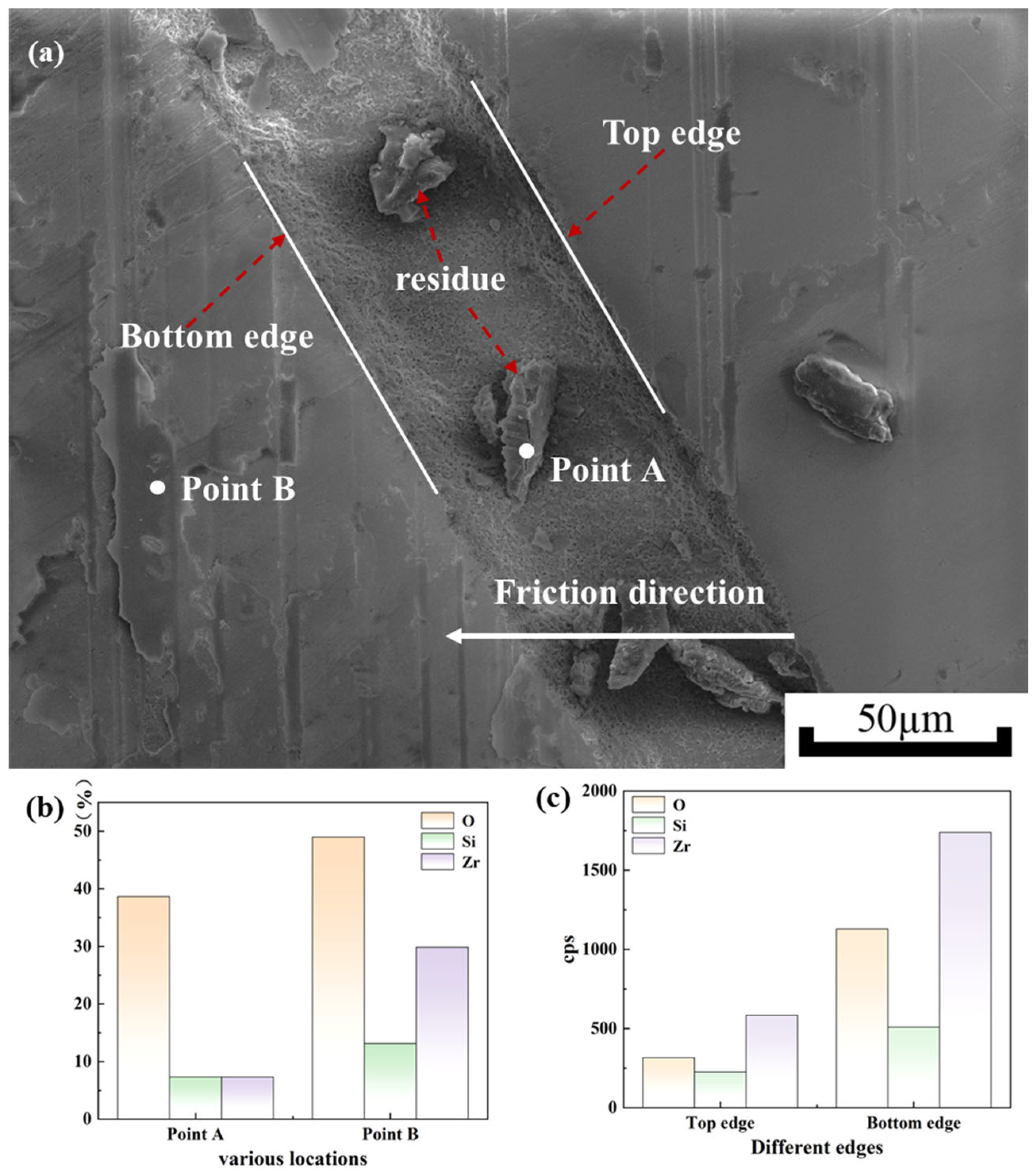
3.2.3. Surface Morphology Analysis of Zirconia Artificial Teeth
3.3. Mechanistic Analysis of Micro-Textures and Friction Performance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Zirconia artificial teeth with micro-textures exhibit better friction properties compared to MT-0. MT-2 has the best friction properties. The average coefficient of friction is the smallest at 0.34.
- (2)
- Micro-textures improve the frictional properties of zirconia artificial teeth under different working conditions. The coefficient of friction increases as the pH of the lubricant increases. Moreover, as the load increases, the coefficient of friction first increases and then decreases, reaching its peak at 15 N. Additionally, zirconia artificial teeth demonstrate the optimal friction performance at a rotational speed of 200 r/min.
- (3)
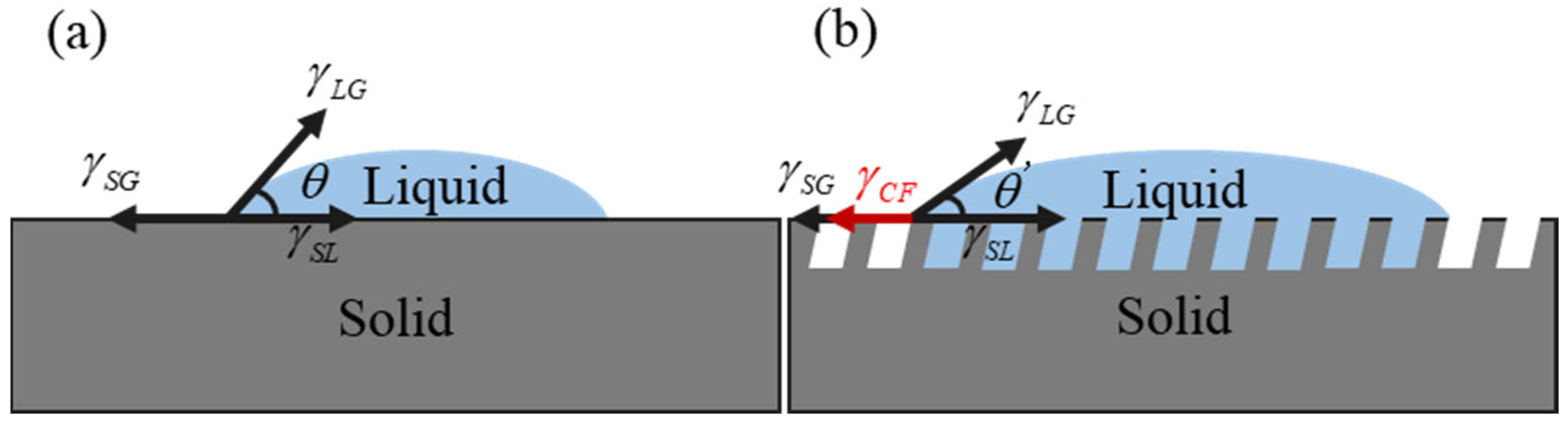
- Micro-textures reduce the coefficient of friction by storing debris and lubricant during friction. The bottom edge of the textured grooves acts as a cutting tool to cut debris adhering to the silicon nitride ceramic balls, preventing debris from scratching the surface. The surface contact angles of MT-1 and MT-2 are 83.1° and 73.3°, respectively, which are smaller than that of MT-0. The surfaces of zirconia ceramics are more hydrophilic due to the micro-textures. The hydrophilic surface forms a lubricating film on the ceramic surface, thus reducing the coefficient of friction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehta, S.; Loomans, B.; Banerji, S.; Bronkhorst, E.; Bartlett, D. An investigation into the impact of tooth wear on the oral health related quality of life amongst adult dental patients in the United Kingdom, Malta and Australia. J. Dent. 2020, 99, 103409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, P.d.O.; Faot, F.; Cury, A.A.D.B.; Garcia, R.C.M.R. Effect of dental wear, stabilization appliance and anterior tooth reconstruction on mandibular movements during speech. Braz. Dent. J. 2009, 19, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zheng, Y.; Bashandeh, K.; Shakil, A.; Jha, S.; Polycarpou, A.A. Review of dental tribology: Current status and challenges. Tribol. Int. 2022, 166, 107354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, F.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Vleugels, J.; Braem, A.; Castagne, S. Laser surface texturing of zirconia-based ceramics for dental applications: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 123, 112034. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, B.F.O.; Durães, L.; da Silva, E.A.B.; Costa, I.I.O.; Khomchenko, V.A.; Vezo, R.A.N.; Ramalho, A. Synthesis, Structural, and Mechanical Properties of Alumina–Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia Nanocomposites for Prospective Dental Ceramics. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2025, 272, 401843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhloufi, S.; Labjar, N.; Labjar, H.; Idrissi, M.S.; El Hajjaji, S. Electrochemical behavior and surface stability of dental zirconia ceramics in acidic environments. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 150, 106288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmiri, R.; Standard, O.C.; Hart, J.N.; Sorrell, C.C. Optical properties of zirconia ceramics for esthetic dental restorations: A systematic review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2018, 119, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lawn, B.R. Novel Zirconia Materials in Dentistry. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, Z. Wear behaviour of human teeth in dry and artificial saliva conditions. Wear 2001, 249, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhou, Z. Friction and wear behavior of human teeth under various wear conditions. Tribol. Int. 2007, 40, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Incau, E.; Couture, C.; Maureille, B. Human tooth wear in the past and the present: Tribological mechanisms, scoring systems, dental and skeletal compensations. Arch. Oral Biol. 2012, 57, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, P.; Carvalho, A.; Silva, F.S.; Gomes, J.R.; Carvalho, O.; Madeira, S. Comparative toothbrush abrasion resistance and surface analysis of different dental restorative materials. Tribol. Int. 2022, 175, 107799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Pinto, P.; Madeira, S.; Silva, F.S.; Carvalho, O.; Gomes, J.R. Tribological Characterization of Dental Restorative Materials. Biotribology 2020, 23, 100140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, M.S. Wear behavior of various dental restorative materials. Mater. Technol. 2019, 34, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hiyasat, A.S.; Saunders, W.P.; Sharkey, S.W.; Smith, G.M.; Gilmour, W.H. Investigation of human enamel wear against four dental ceramics and gold. J. Dent. 1998, 26, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijani, D.; Deladi, E.L.; Akchurin, A.; De Rooij, M.B.; Schipper, D.J. The influence of surface texturing on the frictional behaviour of parallel sliding lubricated surfaces under conditions of mixed lubrication. Lubricants 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niketh, S.; Samuel, G.L. Surface texturing for tribology enhancement and its application on drill tool for the sustainable machining of titanium alloy. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, J. Friction properties of groove texture on Cr12MoV surface. J. Cent. South Univ. 2017, 24, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yuan, Z.; Zheng, P.; He, Y.; Tang, M.; Wang, Y. Study on the wear performance of 304 stainless steel aerospace joint bearings. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2024, 12, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zheng, H. Comparison of the effect of typical patterns on friction and wear properties of chromium alloy prepared by laser surface texturing. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 106, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xing, Y.; Huang, P.; Liu, L. Tribological properties of dimple-textured titanium alloys under dry sliding contact. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 309, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugihara, T.; Kobayashi, R.; Enomoto, T. Direct observations of tribological behavior in cutting with textured cutting tools. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 168, 103726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Dai, J.; Yu, D.; Ji, M.; Chen, M. Biomimetic microtextured surfaces to improve tribological and antibacterial behaviors of 3Y-TZP ceramics. J. Mater. Res. Technol. JMRT 2023, 23, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Liu, L. Synergistic effect of surface textures and DLC coatings for enhancing friction and wear performances of Si3N4/TiC ceramic. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, C.; Jiang, L. Tribological behavior of CoCrMo artificial knee joint with symmetrically biomimetic textured surfaces on PEEK. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 157, 108774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyr, A.; Qiu, M.; Speltz, J.W.; Jacobsen, R.L.; Sanders, A.P.; Raeymaekers, B. A patterned microtexture to reduce friction and increase longevity of prosthetic hip joints. Wear 2014, 315, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, W.; Duan, R.; Meng, R.; Ge, D.; Li, X. Effect of texture parameters on cutting performance of flank-faced textured carbide tools in dry cutting of green Al2O3 ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 13205–13217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, J.; Wu, F.; Duan, R.; Zhang, X.; Hou, Y. Wear resistance of carbide tools with textured flank-face in dry cutting of green alumina ceramics. Wear 2017, 372–373, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubiak, K.J.; Wilson, M.C.T.; Mathia, T.G.; Carval, P. Wettability versus roughness of engineering surfaces. Wear 2011, 271, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yu, Y.; Hu, X.; Mo, X.; Zhou, W.; Dai, X.; Shan, L.; Yu, D. Study on the characteristics of the capillary wetting and flow in open rectangular microgrooves heat sink. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 143, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H. Effect of curved surfaces on the impacting nano-droplets and their shape control: A molecular dynamics simulation study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 454, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Element | ZrO2 | Y2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | TiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity contained (%) | ≥94 | 5.33 | 0.23 | 0.007 | 0.0012 |
| Physical Property | Value | Physical Property | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density/(kg/m3) | 6000 | Thermal conductivity/(W/(m·k)) | 2.5 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.23 | Durometer/HV | 1200 |
| Bending strength/MPa | 1000 | Compressive strength/MPa | 2100 |
| Young’s modulus/GPa | 210 | Rupture strength/MPa | 800 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Jia, F.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, N.; Wang, C.; Lin, Z. Improvements in Wettability and Tribological Behavior of Zirconia Artificial Teeth Using Surface Micro-Textures. Materials 2025, 18, 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133117
Liu Y, Wang G, Jia F, Jiang X, Jiang N, Wang C, Lin Z. Improvements in Wettability and Tribological Behavior of Zirconia Artificial Teeth Using Surface Micro-Textures. Materials. 2025; 18(13):3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133117
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yayun, Guangjie Wang, Fanshuo Jia, Xue Jiang, Ning Jiang, Chuanyang Wang, and Zhouzhou Lin. 2025. "Improvements in Wettability and Tribological Behavior of Zirconia Artificial Teeth Using Surface Micro-Textures" Materials 18, no. 13: 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133117
APA StyleLiu, Y., Wang, G., Jia, F., Jiang, X., Jiang, N., Wang, C., & Lin, Z. (2025). Improvements in Wettability and Tribological Behavior of Zirconia Artificial Teeth Using Surface Micro-Textures. Materials, 18(13), 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133117







