Metallurgy, Properties and Applications of Superaustenitic Stainless Steels—SASSs
Highlights
- Insight into a class of materials that represents a market niche alternative to Ni and Ti alloys.
- Insight into chemical composition and related critical issues like segregation, precipitation of second phases.
- Analysis of physical, mechanical, and corrosion resistance properties of superaustenitic stainless steels.
- Market overview of superustenitic stainless steels with applications and perspectives.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Chemistry and Related Features
2.1. Chemical Composition and Microstructure
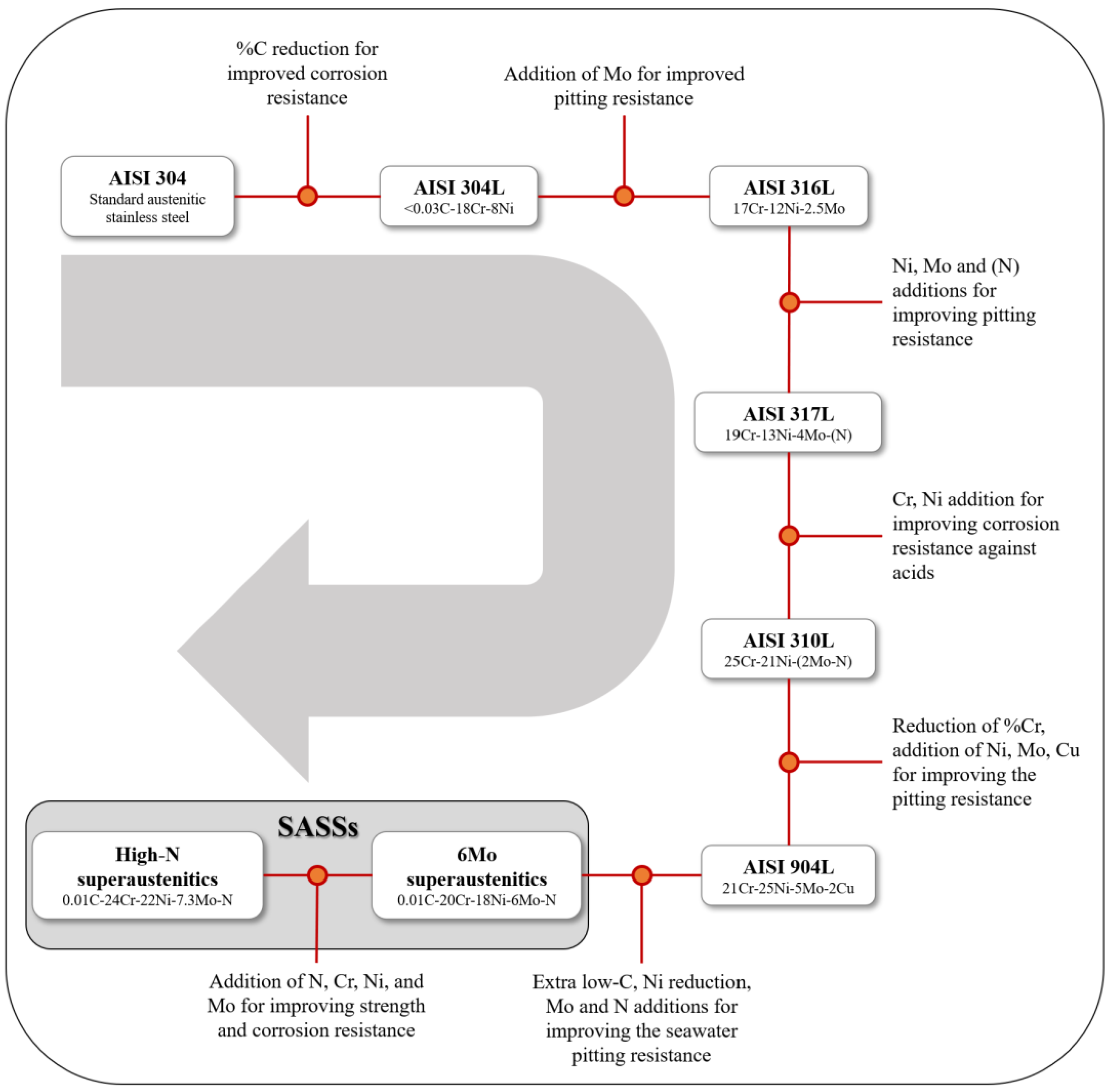
| Group | Most Common Name | UNS | C max | Cr | Ni | Mo | Mn | N | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard austenitics | AISI 304 | S30400 | 0.08 | 18.0–20.0 | 8.0–10.5 | - | 2.0 | - | - |
| High-performance austenitics | AISI 904L | N08904 | 0.02 | 19.0–23.0 | 23.0–28.0 | 4.0–5.0 | 2.0 | - | Cu = 1.0–2.0 |
| 6Mo superaustenitics | 20Mo-6 | N08026 | 0.03 | 22.0–26.0 | 33.0–37.0 | 5.0–6.7 | - | 0.1–0.16 | Cu = 2.0–4.0 |
| NAS 254N | S32053 | 0.03 | 23.0 | 25.0 | 5.5 | - | 0.2 | - | |
| 25-6Mo | N08926 | 0.02 | 19.0–21.0 | 24.0–26.0 | 6.0–7.0 | 1.0 | 0.15–0.25 | Cu = 0.5–1.5 | |
| Uranus SB8 | N08932 | 0.02 | 24.0–26.0 | 24.0–26.0 | 4.7–5.7 | - | 0.17–0.25 | Cu = 1.0–2.0 | |
| 254SMO | S31254 | 0.02 | 19.5–20.5 | 17.5–18.5 | 6.0–6.5 | 1.0 | 0.18–0.22 | Cu = 0.5–1.0 | |
| Nicrofer 3127 hMo | N08031 | 0.02 | 26.0–28.0 | 30.0–32.0 | 6.0–7.0 | - | 0.15–0.25 | Cu = 1.0–1.4 | |
| AL-6XN® | N08367 | 0.03 | 20.0–22.0 | 23.5–25.5 | 6.0–7.0 | - | 0.18–0.25 | Cu = 0.75 | |
| High-N superaustenitics | Uranus B66 | S31266 | 0.03 | 23.0–25.0 | 21.0–24.0 | 5.0–7.0 | 3.0 | 0.35–0.6 | Cu = 0.5–3.0 W = 1.0–3.0 |
| 654SMO | S32654 | 0.02 | 24.0–26.0 | 21.0–23.0 | 7.0–8.0 | 2.0–4.0 | 0.45–0.55 | Cu = 0.3–0.6 | |
| Nirosta® 4565S | S34565 | 0.03 | 23.0–26.0 | 16.0–19.0 | 3.5–5.0 | 3.5–6.5 | 0.4–0.6 | Nb < 0.15 |
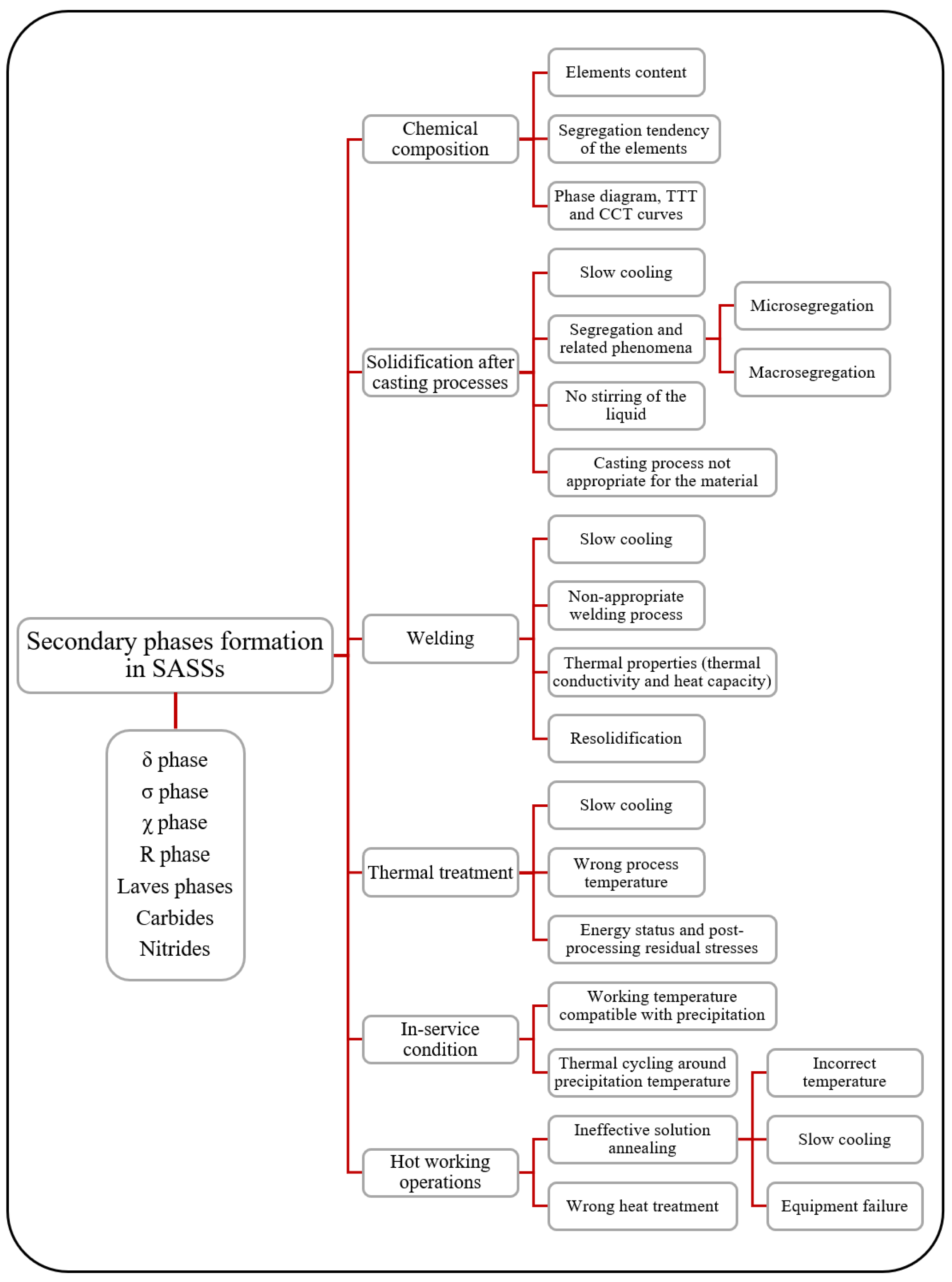
2.2. Secondary Phases
3. Properties of SASSs
3.1. Physical Properties
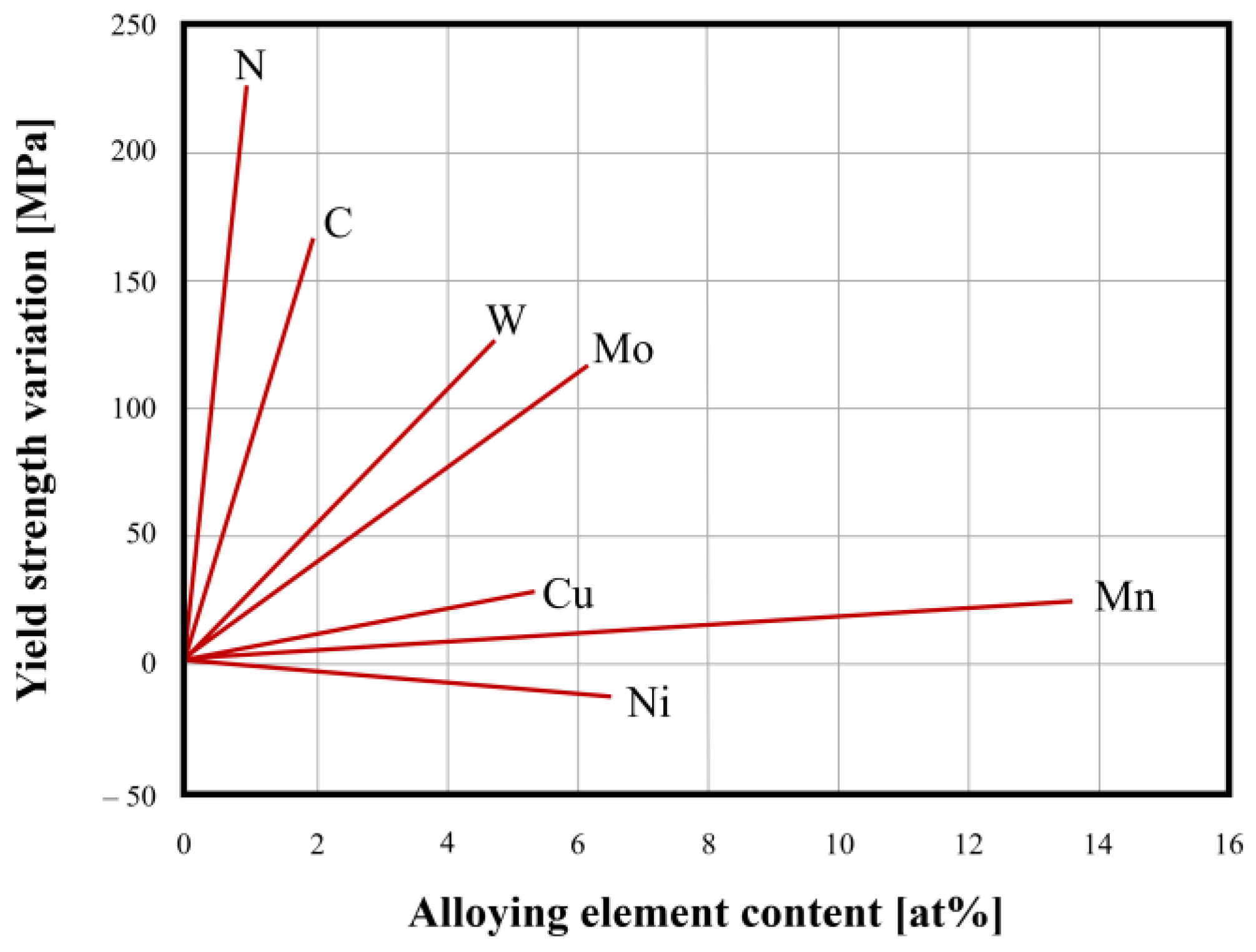
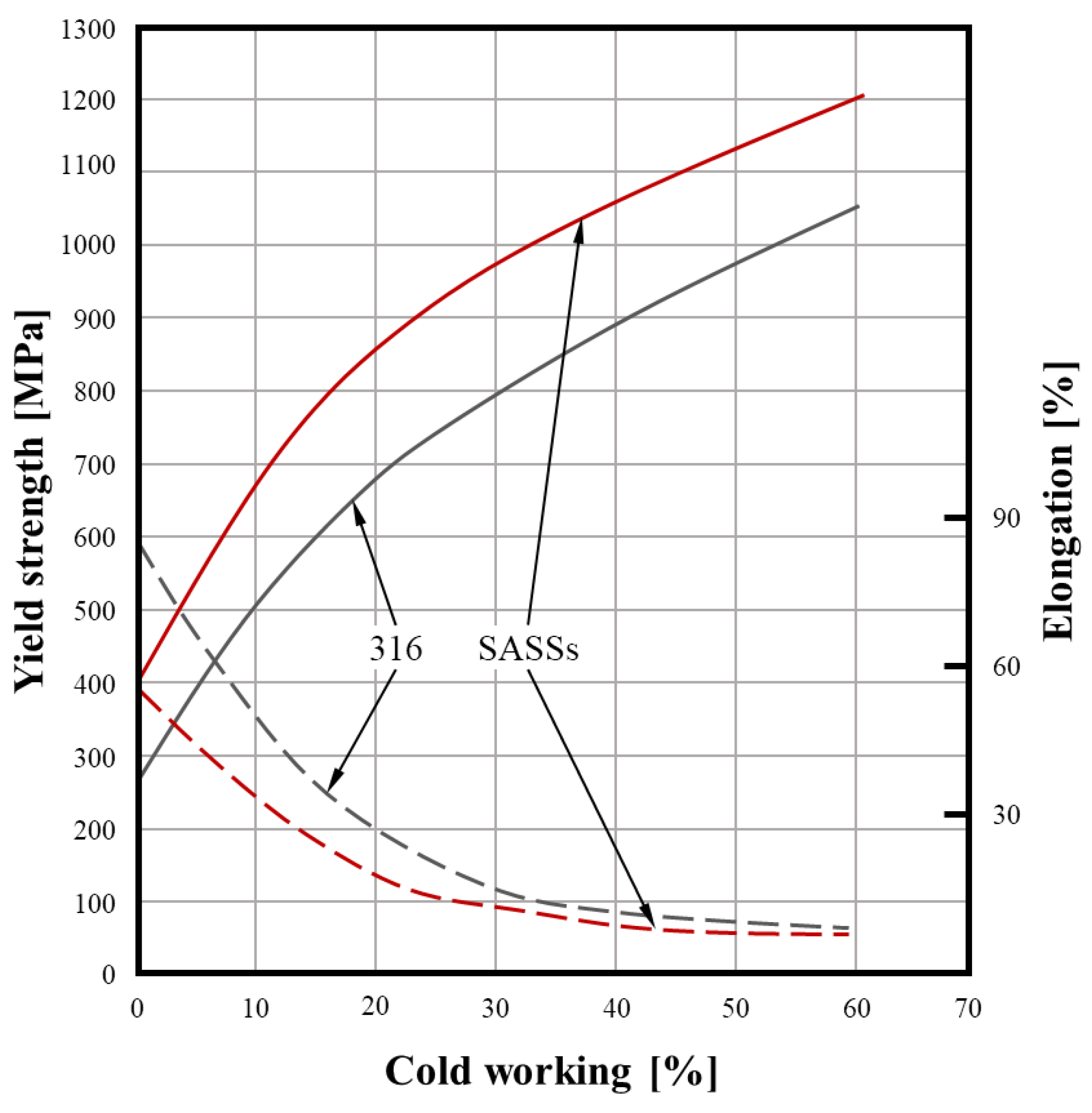
3.2. Mechanical Properties
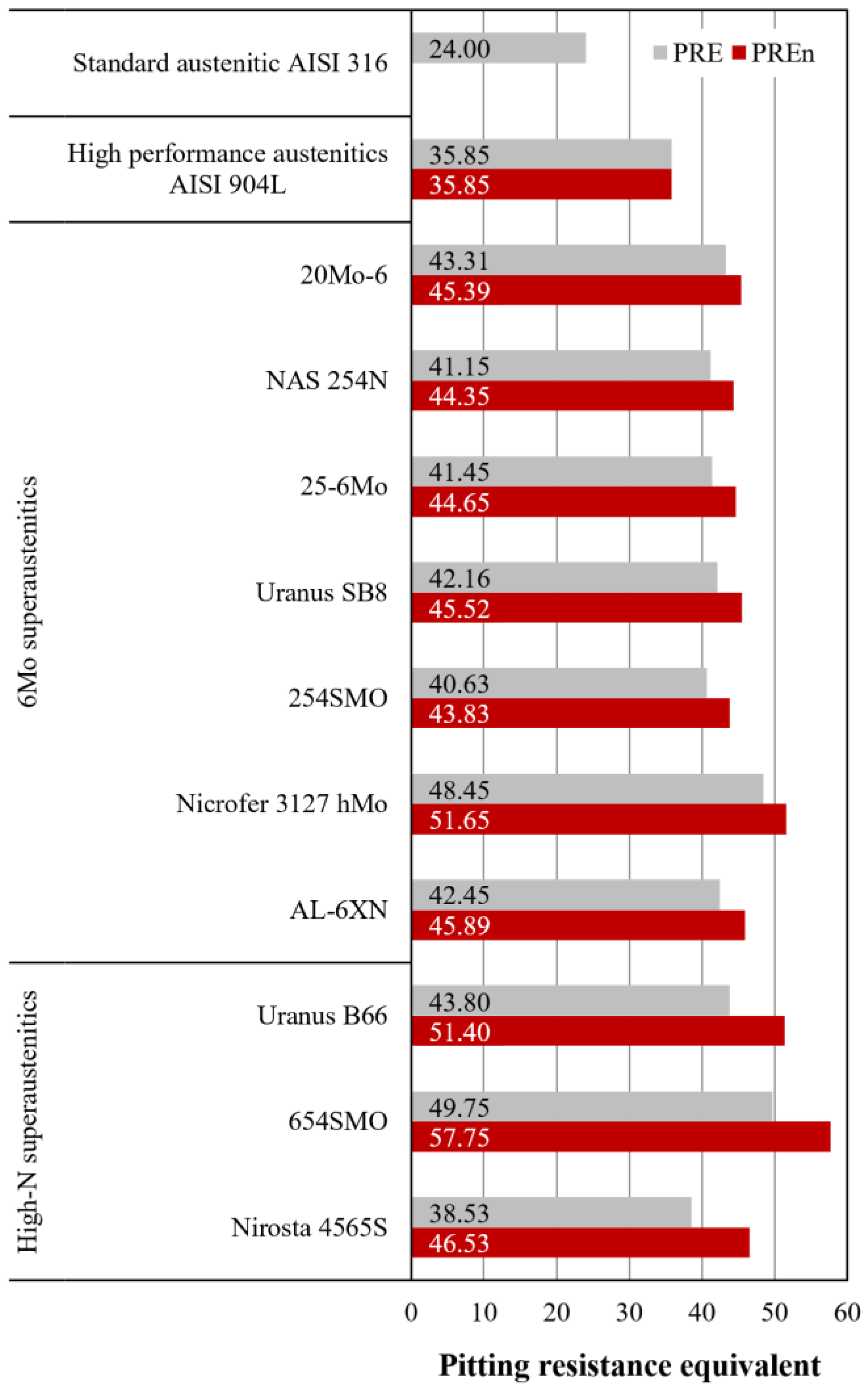
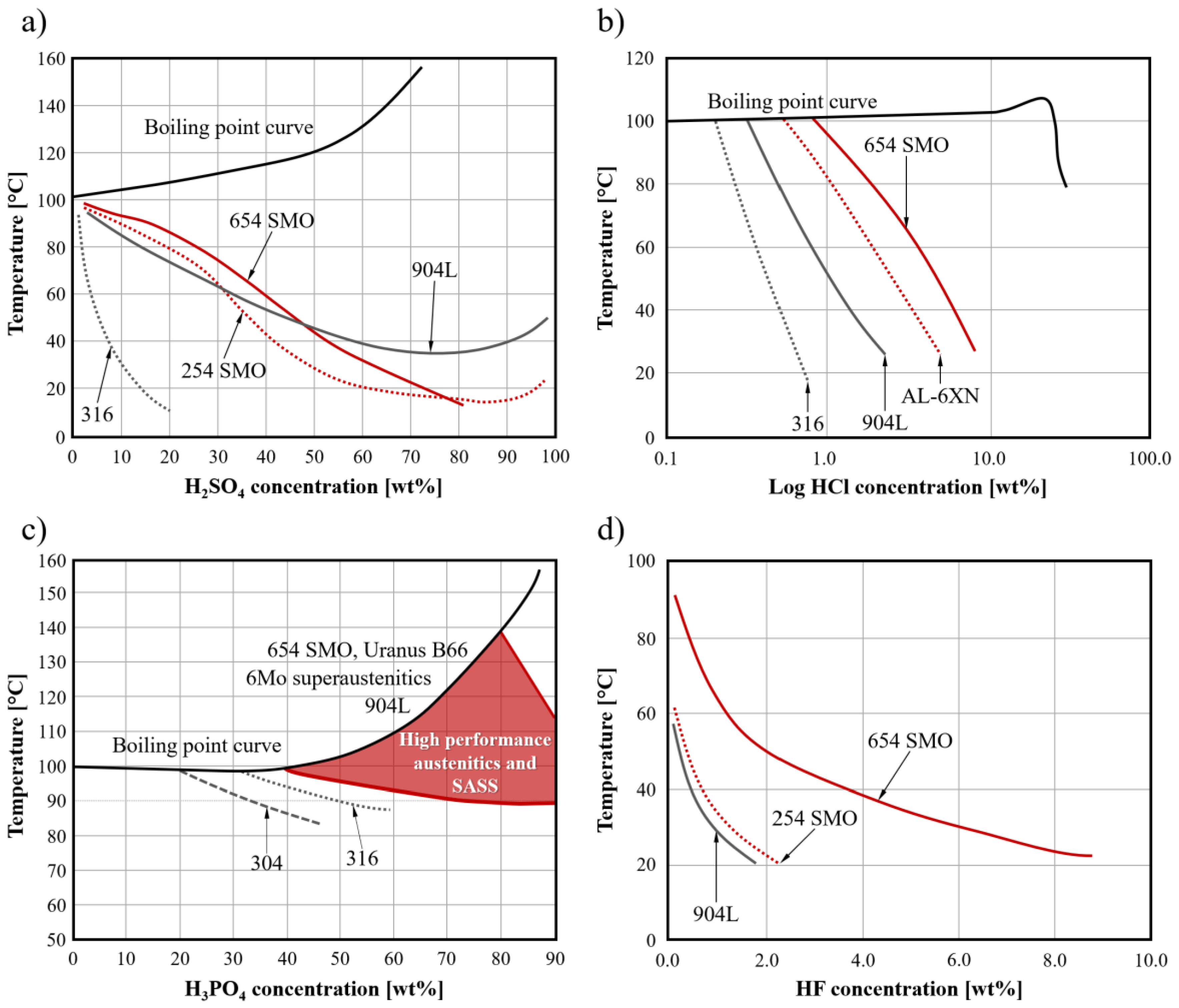
3.3. Corrosion Resistance
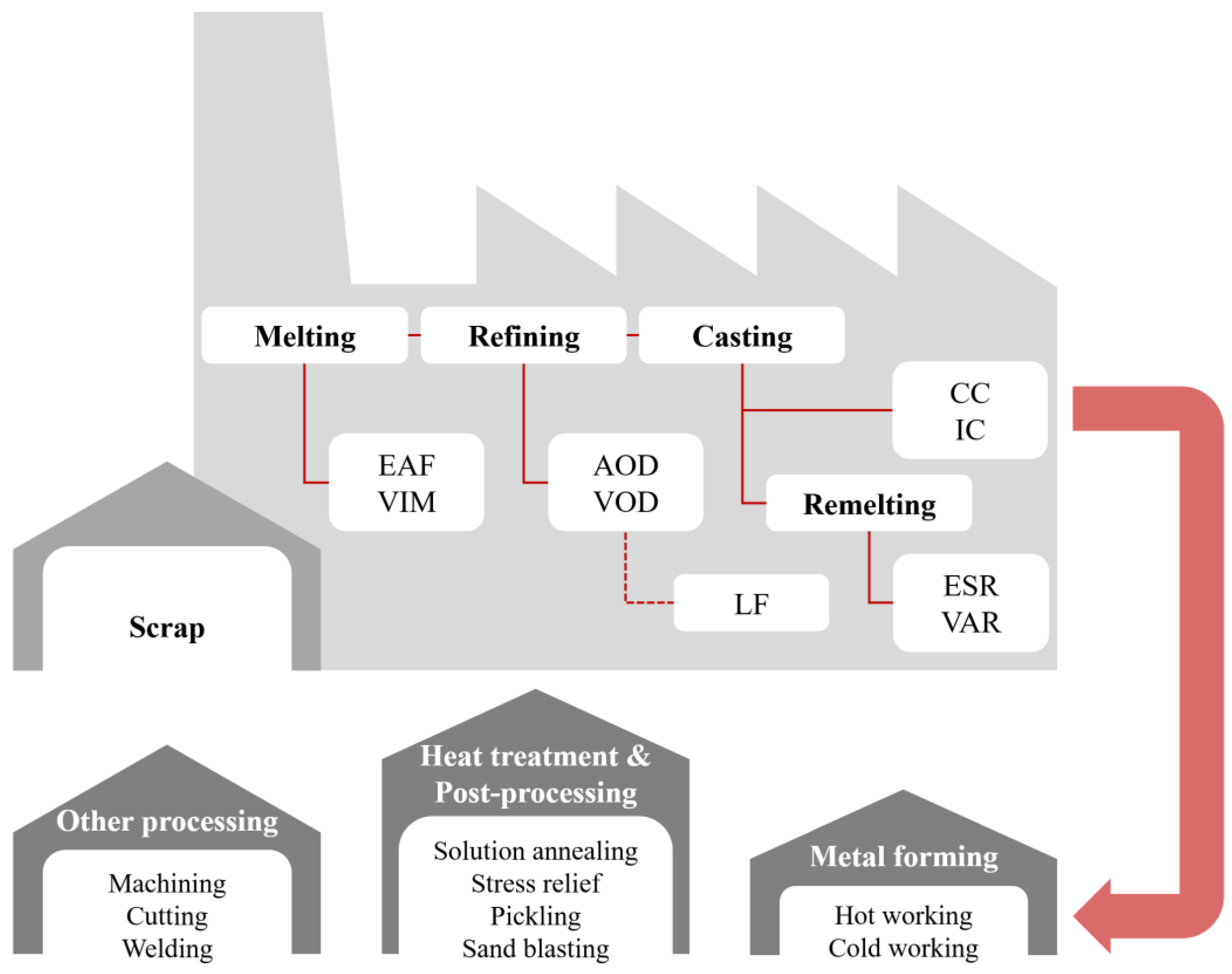
4. Manufacturing, Processing and Applications
4.1. Melting, Refining and Casting
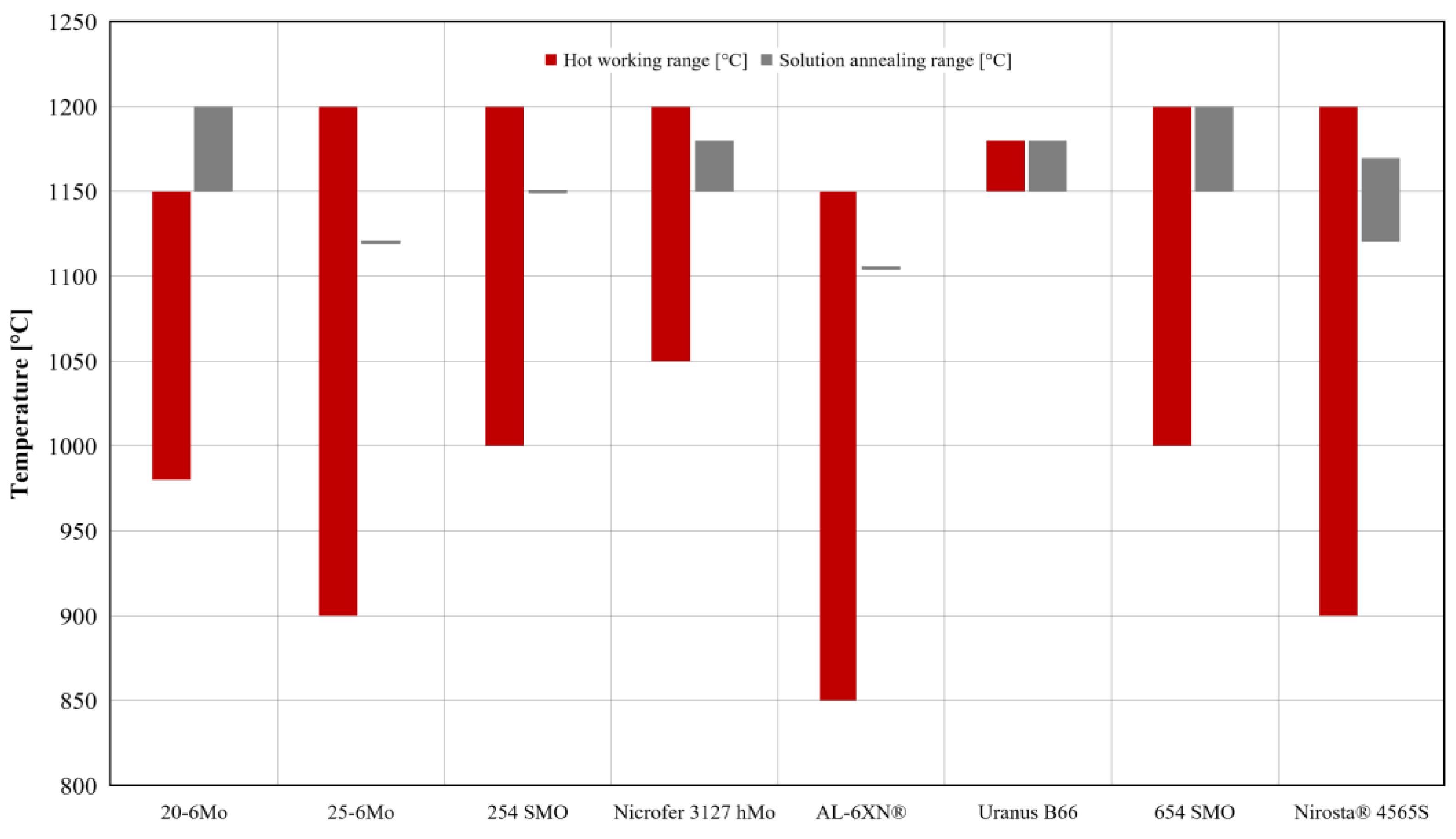
4.2. Metal Forming and Heat Treating
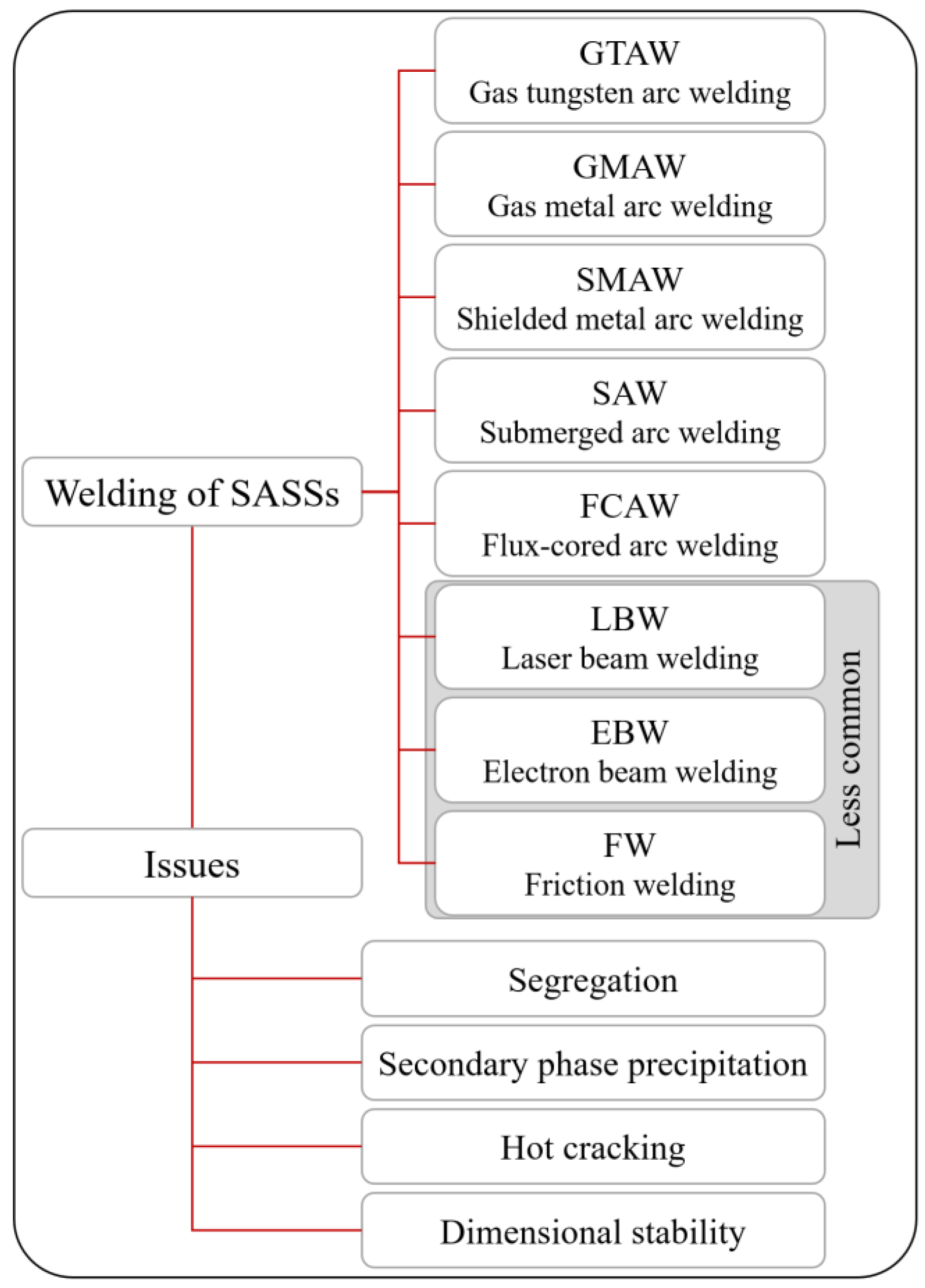
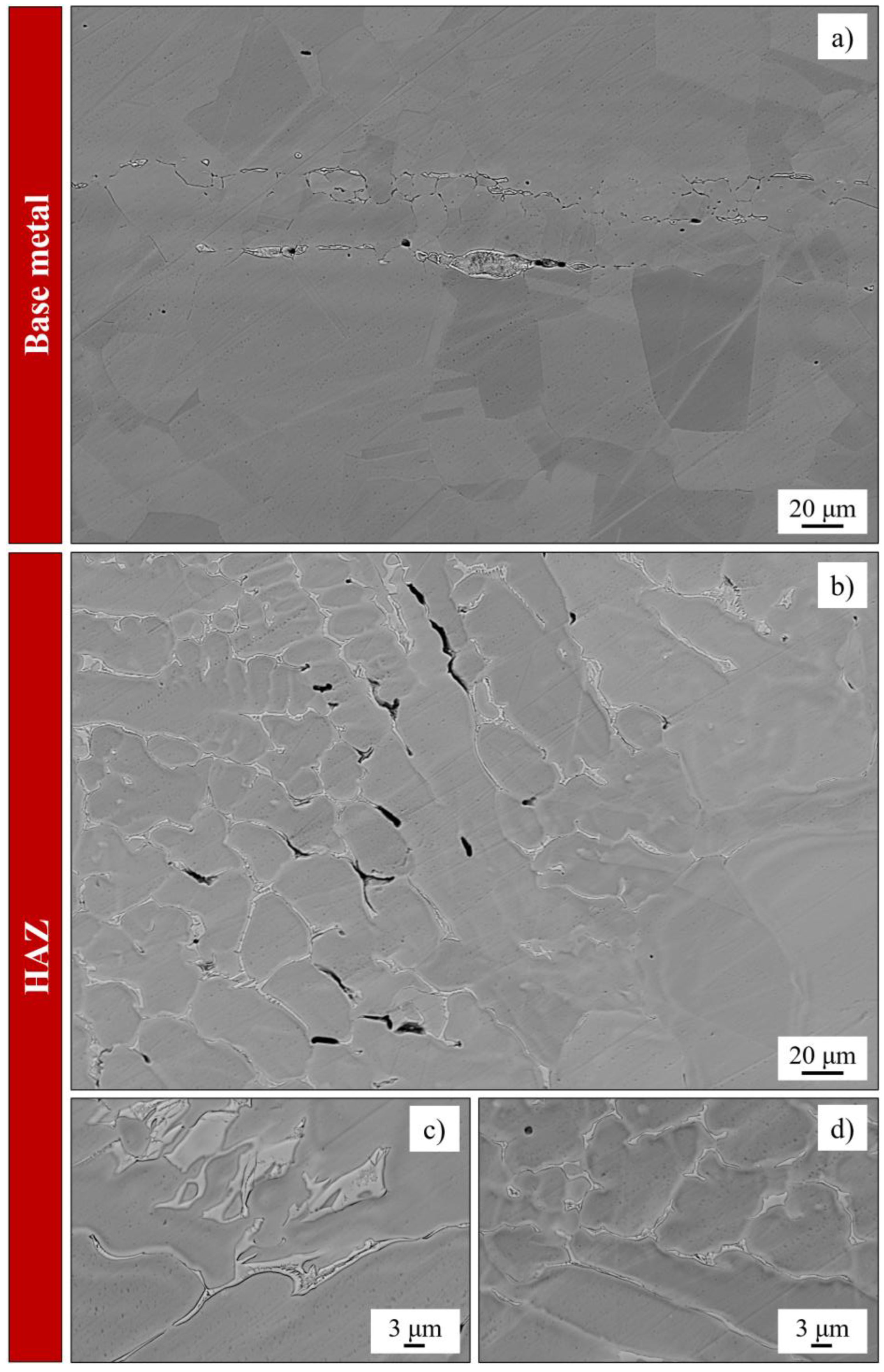
4.3. Welding
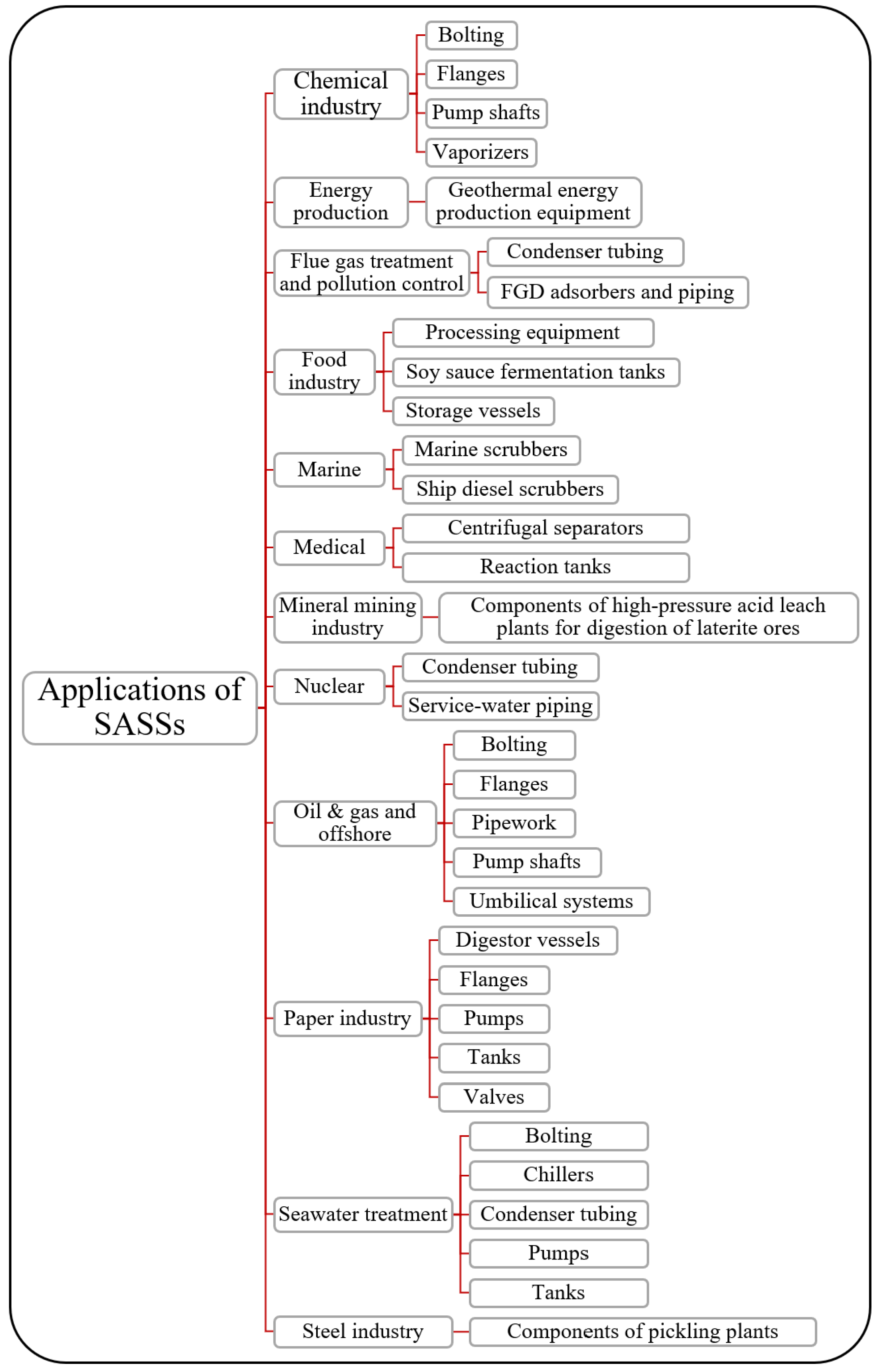
4.4. Market Share and Applications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ASM International. ASM Specialty Handbook: Stainless Steels; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Burt, V. Corrosion in the Petrochemical Industry; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Malandruccolo, A. Superaustenitic Stainless Steels: A Comprehensive Overview; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bonollo, F.; Tiziani, A.; Tovo, R.; Volpone, L.M. Superaustenitic Stainless Steels: The Microstructure and Fatigue Strength of Welded Joints. Weld. Int. 2004, 18, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, J. The Alloy Tree: A Guide to Low-Alloy Steels, Stainless Steels and Nickel-base Alloys; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 79–91. [Google Scholar]
- McCafferty, E. Introduction to Corrosion Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 293–294. [Google Scholar]
- Marin, R.; Combeau, H.; Zollinger, J.; Dehmas, M.; Rouat, B.; Lamontagne, A.; Loukachenko, N.; Lhenry-Robert, L. σ-Phase Formation in Super Austenitic Stainless Steel During Directional Solidification and Subsequent Phase Transformations. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2020, 51, 3526–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, R.; Combeau, H.; Zollinger, J.; Dehmas, M.; Rouat, B.; Lamontagne, A.; Cardinaux, D.; Lhenry-Robert, L. Solidification Path and Phase Transformation in Super-Austenitic Stainless Steel UNS S31254. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 529, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, Y.; Lee, C.; Hong, S. Precipitation Behavior of the Sigma Phase with Ni and Mn Content Variations in Superaustenitic Stainless Steel Weld Metal. Mater. Charact. 2018, 144, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N.; Scott Chumbley, L.; Gleeson, B. Phase Transformations in Cast Superaustenitic Stainless Steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2009, 18, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoukis, T.; Papadopoulou, E.G.; Zormalia, S.; Kokkonidis, P.; Fourlaris, G. Precipitation Sequence in Cold Deformed Superaustenitic Stainless Steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoukis, T.; Redjaïmia, A.; Fourlaris, G. Characterization of Precipitation Sequence in Superaustenitic Stainless Steels. Solid State Phenom. 2011, 172–174, 493–498. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsoukis, T.; Redjaïmia, A.; Fourlaris, G. Phase Transformations and Mechanical Properties in Heat Treated Superaustenitic Stainless Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 561, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, M.; Kroupa, A.; Sopoušek, J.; Vřešt’ál, J.; Miodownik, P. Phase changes in superaustenitic steels after long-term annealing. Z. Met. 2004, 95, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar]
- Callister, W.D.; Rethwisch, D.G. Materials Science and Engineering—An Introduction, 10th ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; p. G–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Su, X.P. Predicting the Density of Molten Alloys using Computational Thermodynamics. Calphad 2020, 68, 101690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Han, P. Effect of Nitrogen on the Corrosion Resistance of 6Mo Super Austenitic Stainless Steel. Metals 2024, 14, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Meguid, E.; Abd El Latif, A. Critical Pitting Temperature for Type 254 SMO Stainless Steel in Chloride Solutions. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, L.J.; Cavalcante, A.L.S.N.; Vieira, R.C.A.; de Lima-Neto, P.; da Silva, M.J.G. Pitting Corrosion Resistance of Austenitic and Super Austenitic Stainless Steels in Aqueous Medium of NaCl and H2SO4. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 31, 1755–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.-K.; Kim, S.-J. Electrochemical Properties of Super Austenite Stainless Steel with Temperature in a Green Death Solution. Coatings 2023, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 15324:2000; Corrosion of Metals and Alloys—Evaluation of Stress Corrosion Cracking by the Drop Evaporation Test. International Organization of Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.
- Steinsmo, U.; Drugli, J.M. Assessment of Susceptibility to Chloride Stress Corrosion Cracking of Highly Alloyed Stainless Steels Part 1: Dorp Evaporation Test Method. In Proceedings of the National Association of Corrosion Engineers (NACE) International Annual Conference and Corrosion Show, New Orleans, LA, USA, 9–14 March 1997. [Google Scholar]
- AMS International. ASM Handbook Volume 15—Casting; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Toulouevski, Y.; Zinurov, I. Innovation in Electric Arc Furnaces, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Cao, G.; Li, C.; Liu, Z. Influences of Cooling Rates on Solidification and Segregation Characteristics of Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo-N Super Austenitic Stainless Steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 275, 116326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Nie, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Z. Microstructural Bandings Evolution Behavior and their Effect on Microstructure and Mechanical Property of Superaustenitic Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Cao, G.; Li, C.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Gao, F. Solidification structures of Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo-N Super-Austenitic Stainless Steel processed by Twin-Roll Strip Casting and Ingot Casting and their Segregation Evolution Behaviors. ISIJ Int. 2018, 58, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straffelini, G. Ductility and Formability of Metals—A Metallurgical Engineering Perspective; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Masamura, T.; Seto, Y.; Tsuchiyama, T.; Kimura, K. Work-hardening Mechanism in High-Nitrogen Austenitic Stainless Steel. Mater. Trans. 2020, 61, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, E.; Zheng, W.J.; Song, Z.G.; Xiang, J.Z.; Wei, X.P. Optimization of Hot Workability in Superaustenitic Stainless Steel 654SMO. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2014, 21, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, E.; Zheng, W.; Xiang, J.; Song, Z.; Feng, H.; Zhu, Y. Hot Working Characteristic of Superaustenitic Stainless Steel 254SMO. Acta Metall. Sin. 2014, 27, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Feng, H.; Han, P.; Dong, N.; Zhang, W.; Li, G.; Fan, G.; et al. A New Insight into High-Temperature Oxidation Mechanism of Super-Austenitic Stainless Steel S32654 in Air. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 686, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Applied Welding Engineering—Processes, Codes, and Standards, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 257–262. [Google Scholar]
- Gialanella, S.; Malandruccolo, A. Aerospace Alloys; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 321–330. [Google Scholar]
- Sunny, K.; Korra, N.N. A Systematic Review about Welding of Super Austenitic Stainless Steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 4378–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, S.; Karlsson, B. Precipitation Behavior in Heat Affected Zone of Welded Superaustenitic Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1999, 15, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perricone, M.; Anderson, T.D.; Robino, C.V.; DuPont, J.N.; Michael, J.R. Effect of Composition on the Formation of Sigma during Single-pass Welding of Mo-bearing Stainless Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2007, 38A, 1976–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, K.; Pak, S.H.; Ahn, S.K. Evaluation of Weld Metal Hot Cracking Susceptibility in Superaustenitic Stainless Steel. Met. Mater. Int. 2013, 19, 1267–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stainless Steel. Available online: https://www.eos.info/metal-solutions/metal-materials/stainless-steel (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Coranic, T.; Gaspar, S.; Pasko, J. Utilization of Optimization of Internal Topology in Manufacturing of Injection Moulds by the DMLS Technology. Appl. Sci. 2020, 11, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, M.F. Stainless Steels for Design Engineers; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2008; pp. 208–252. [Google Scholar]
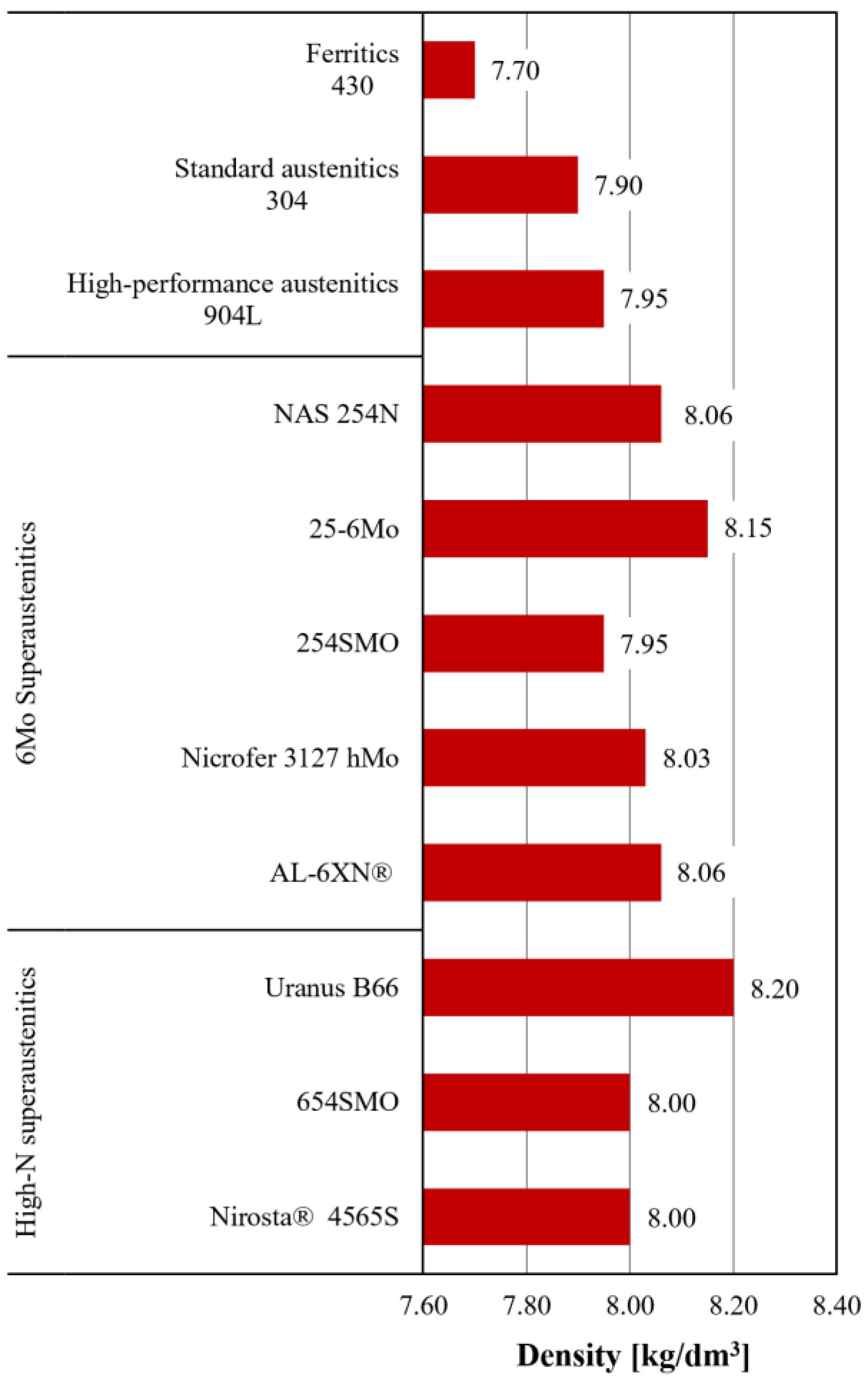

| Group | Most Common Name | Thermal Conductivity at 20 °C [W/(m · K)] | Specific Heat [J/(kg · K)] | Mean CTE at T = 20–200 °C [10−6 · K−1] | Mean CTE at T = 20–400 °C [10−6 · K−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferritics | AISI 430 | 25 | 460 | 10.0 | 10.5 |
| Standard Austenitics | AISI 304 | 15 | 500 | 16.5 | 17.5 |
| High-performance austenitics | AISI 904L | 12 | 461 | 16.1 | 16.9 |
| 6Mo superaustenitics | NAS 254N * | 11.9 | 457 | 15.2 | 15.8 |
| 25-6Mo | 12 | 461 | 16.1 | 16.9 | |
| 254 SMO | 14 | 498 | 17.0 | 18.0 | |
| Nicrofer 3127 hMo | 12 | 440 | 14.7 | 15.5 | |
| AL-6XN® ** | 13.7 | 461 | 15.3 | 16.0 | |
| High-N superaustenitics | Uranus B66 *** | 12 | 450 | 15.0 | 16.0 |
| 654 SMO | 8.6 | 510 | 15.4 | 16.2 | |
| Nirosta® 4565S | 14.5 | 510 | 15.5 | 16.8 |
| Group | Most Common Name | UTS [MPa] | Yield Strength [MPa] | Elongation [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferritics | AISI 430 | 430 | 260 | 18 |
| Standard austenitics | AISI 304 | 520 | 200 | 45 |
| High-performance austenitics | AISI 904L | 530 | 230 | 35 |
| 6Mo superaustenitics | 25-6Mo | 650 | 295 | 35 |
| 254SMO | 650 | 300 | 35 | |
| Uranus SB8 | 550 | 250 | 35 | |
| Nicrofer 3127 hMo | 650 | 280 | 35 | |
| AL-6XN | 690 | 310 | 30 | |
| High-N superaustenitics | Uranus B66 | 750 | 420 | 35 |
| 654SMO | 750 | 430 | 35 | |
| Nirosta 4565S | 800 | 420 | 35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malandruccolo, A.; Menapace, C.; Giroletti, I. Metallurgy, Properties and Applications of Superaustenitic Stainless Steels—SASSs. Materials 2025, 18, 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133079
Malandruccolo A, Menapace C, Giroletti I. Metallurgy, Properties and Applications of Superaustenitic Stainless Steels—SASSs. Materials. 2025; 18(13):3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133079
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalandruccolo, Alessio, Cinzia Menapace, and Igor Giroletti. 2025. "Metallurgy, Properties and Applications of Superaustenitic Stainless Steels—SASSs" Materials 18, no. 13: 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133079
APA StyleMalandruccolo, A., Menapace, C., & Giroletti, I. (2025). Metallurgy, Properties and Applications of Superaustenitic Stainless Steels—SASSs. Materials, 18(13), 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18133079