On Predicting Optimal Structural Topologies in the Presence of Random Loads
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Concepts
2.1. Problem Formulation
2.2. Topology Optimization Algorithm
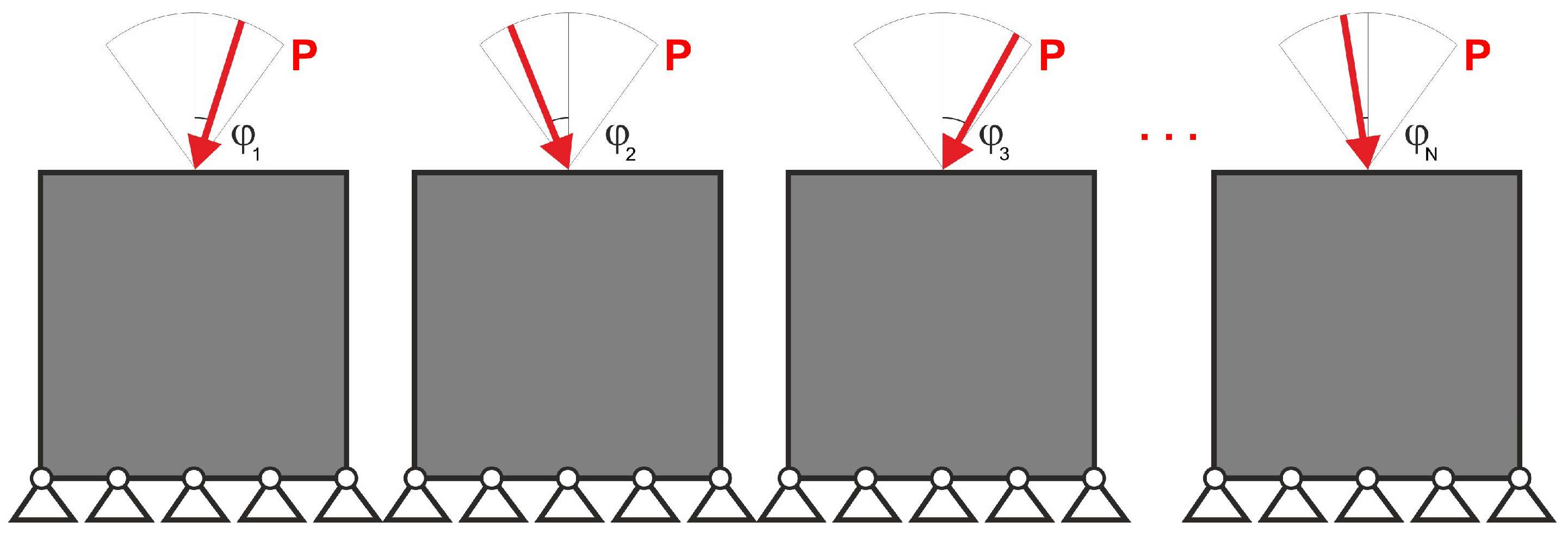
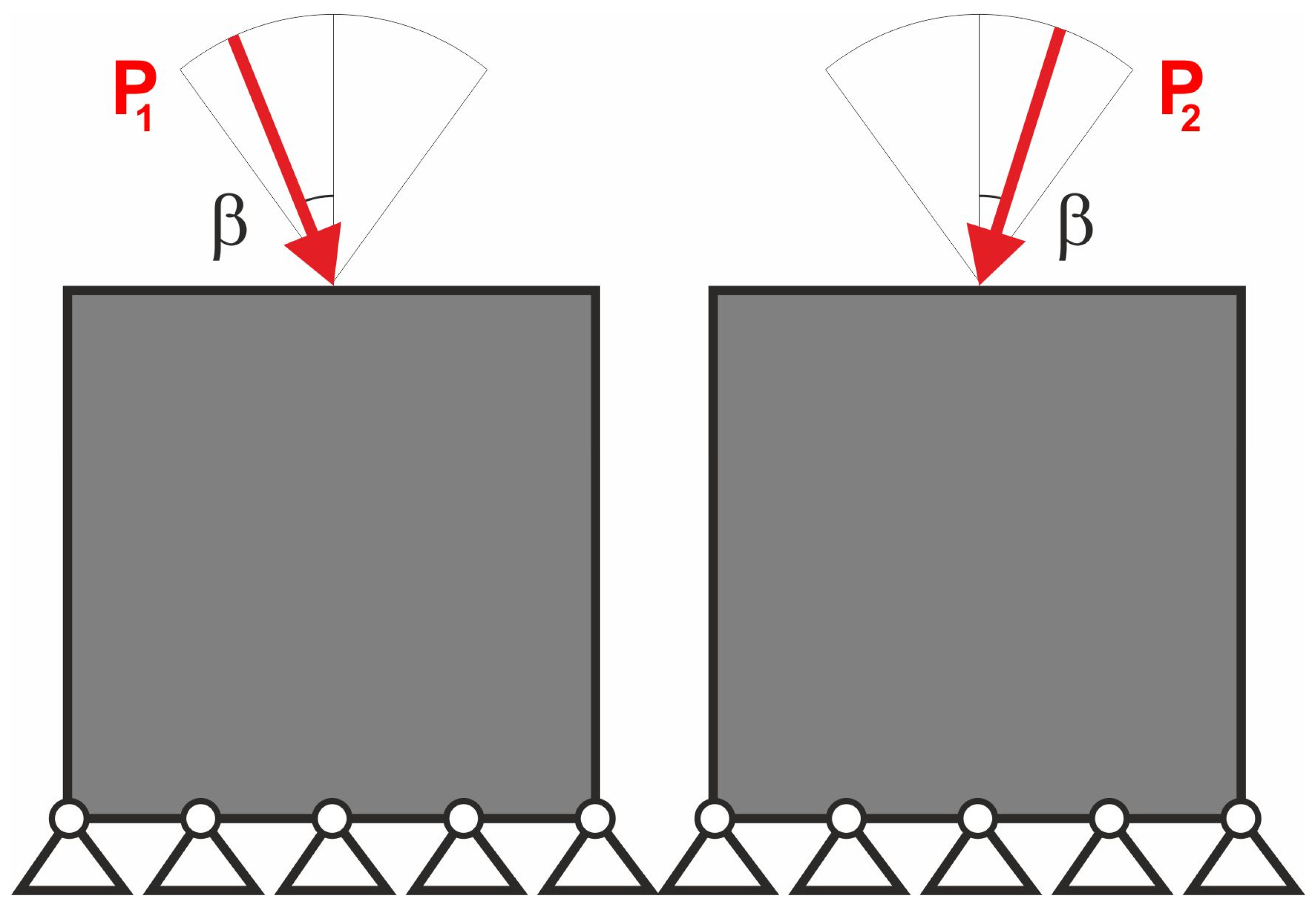
2.3. Multiple Load Case in Topology Optimization and the Concept of the Paper
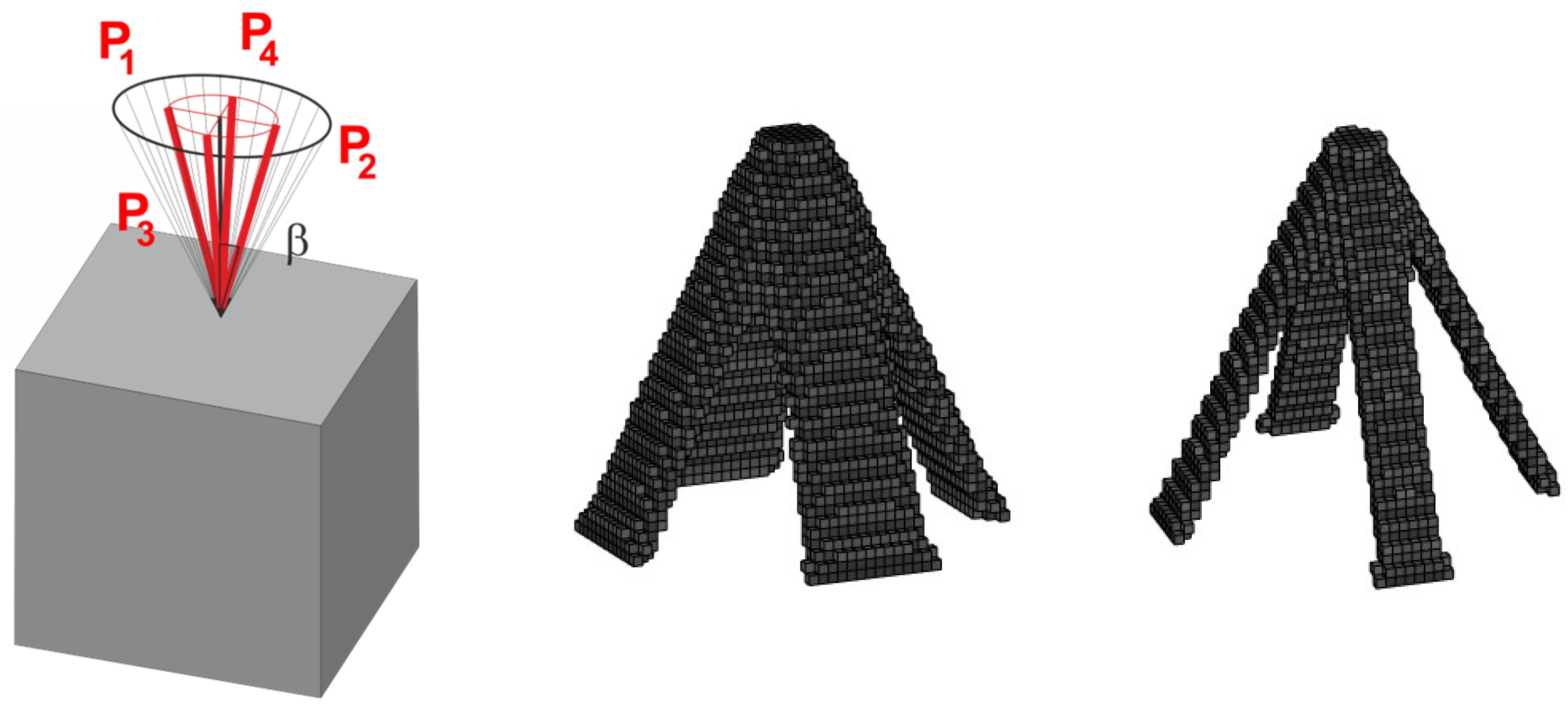
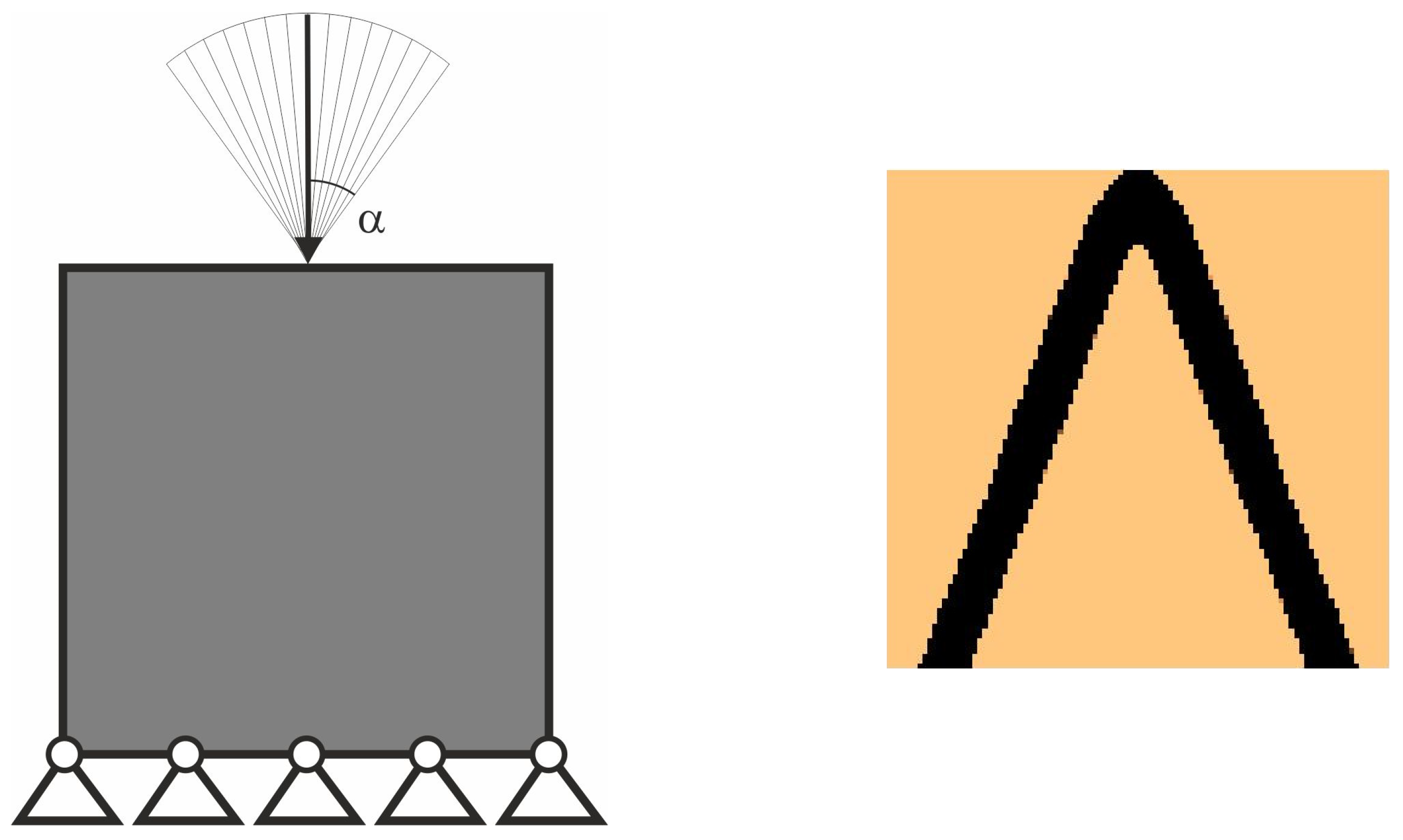
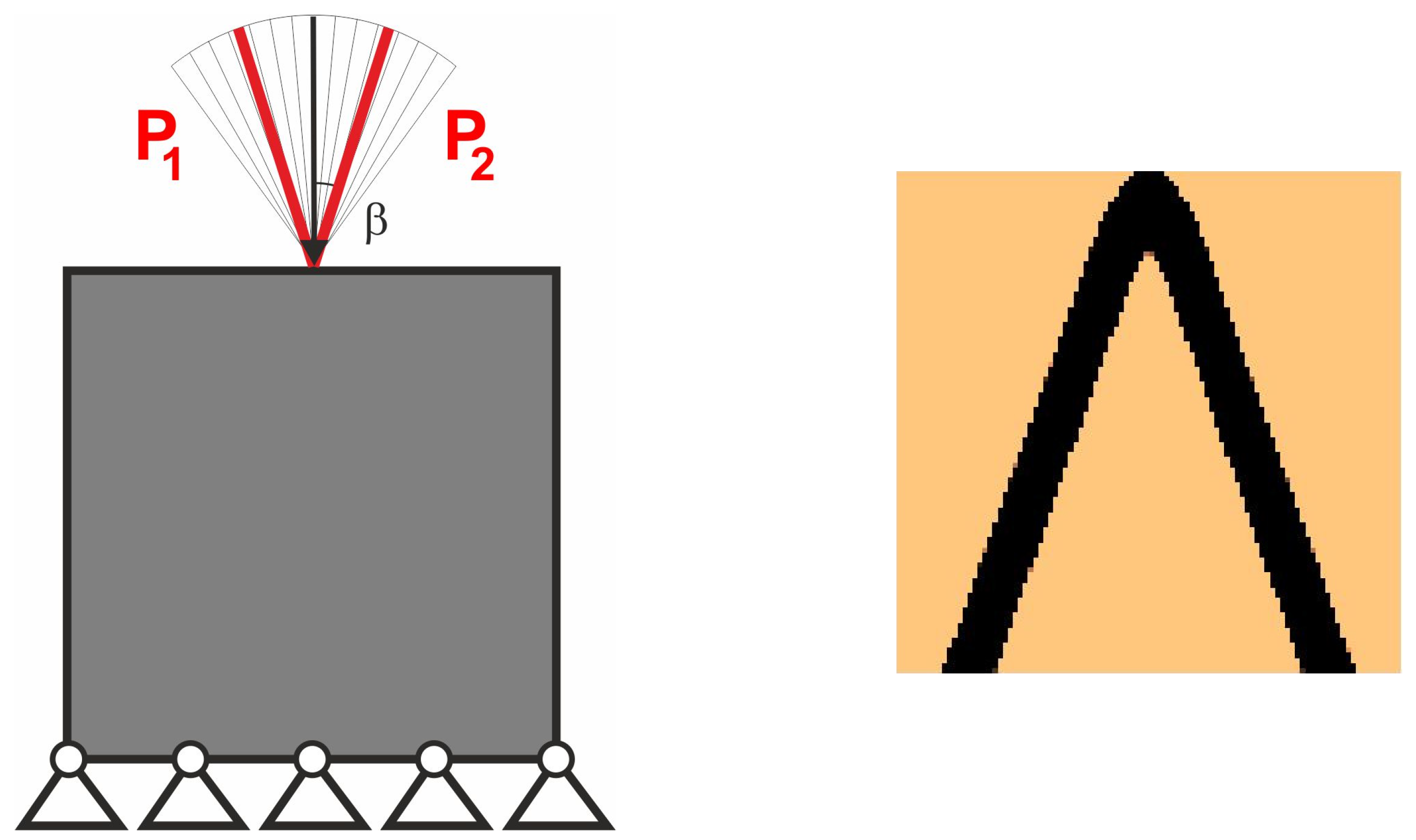
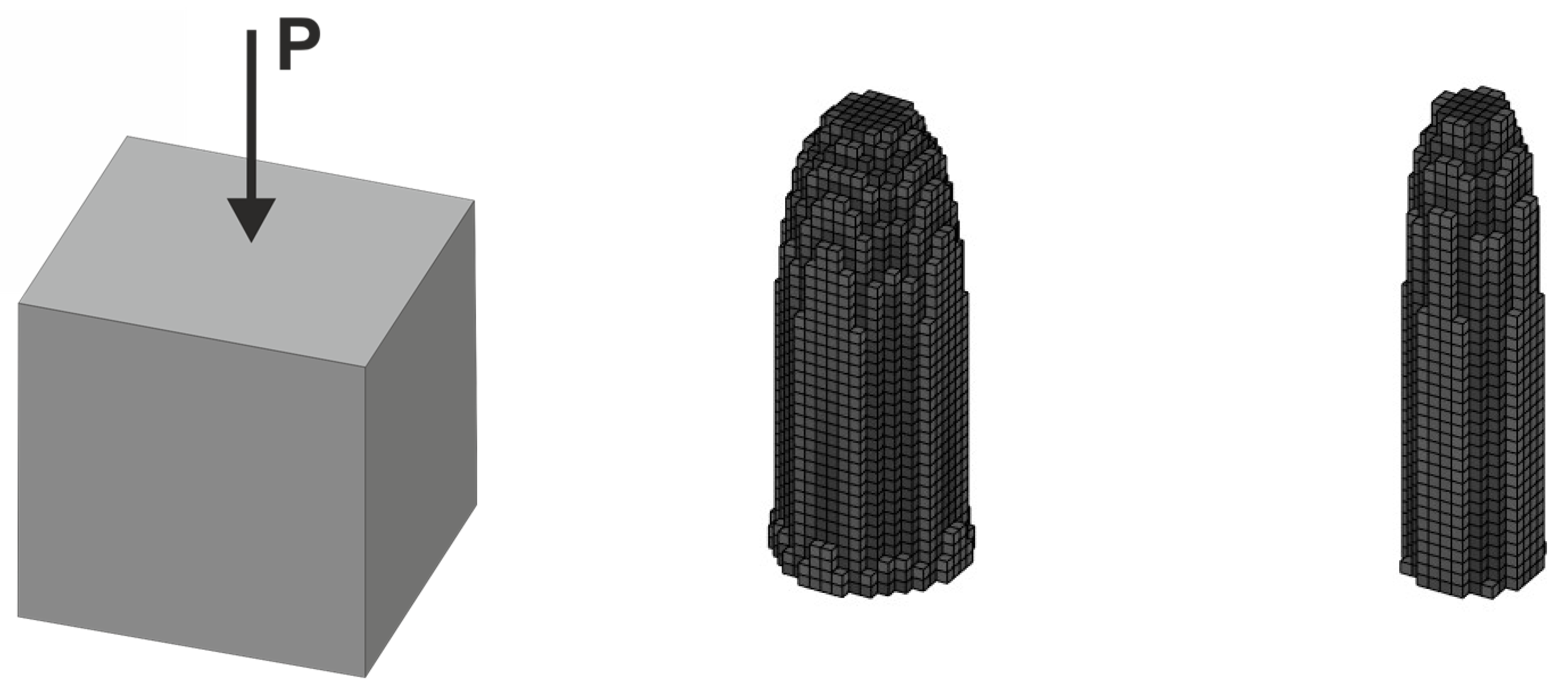
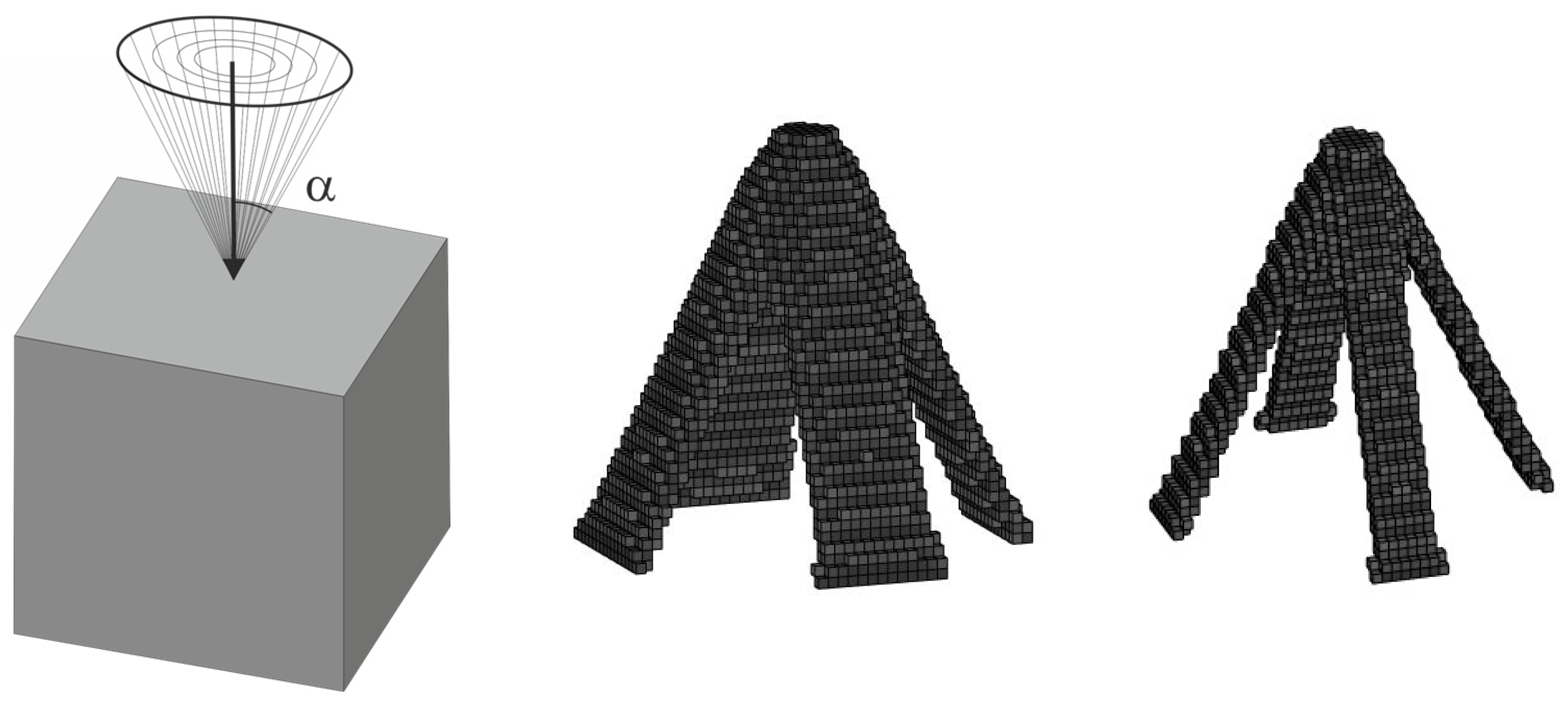
2.4. Equivalent Load Scheme (ELS) and Its Implementation
3. Results and Discussion
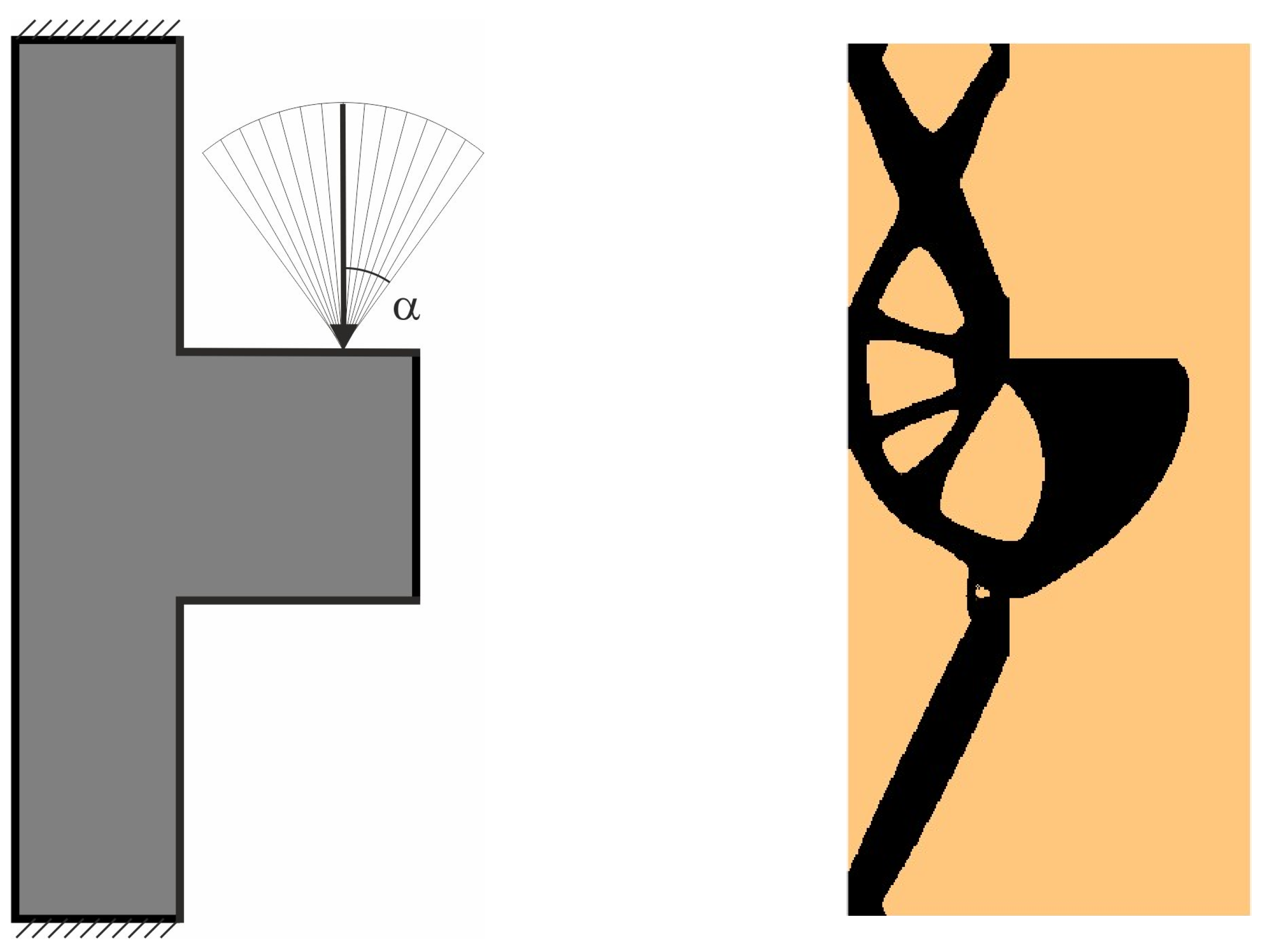
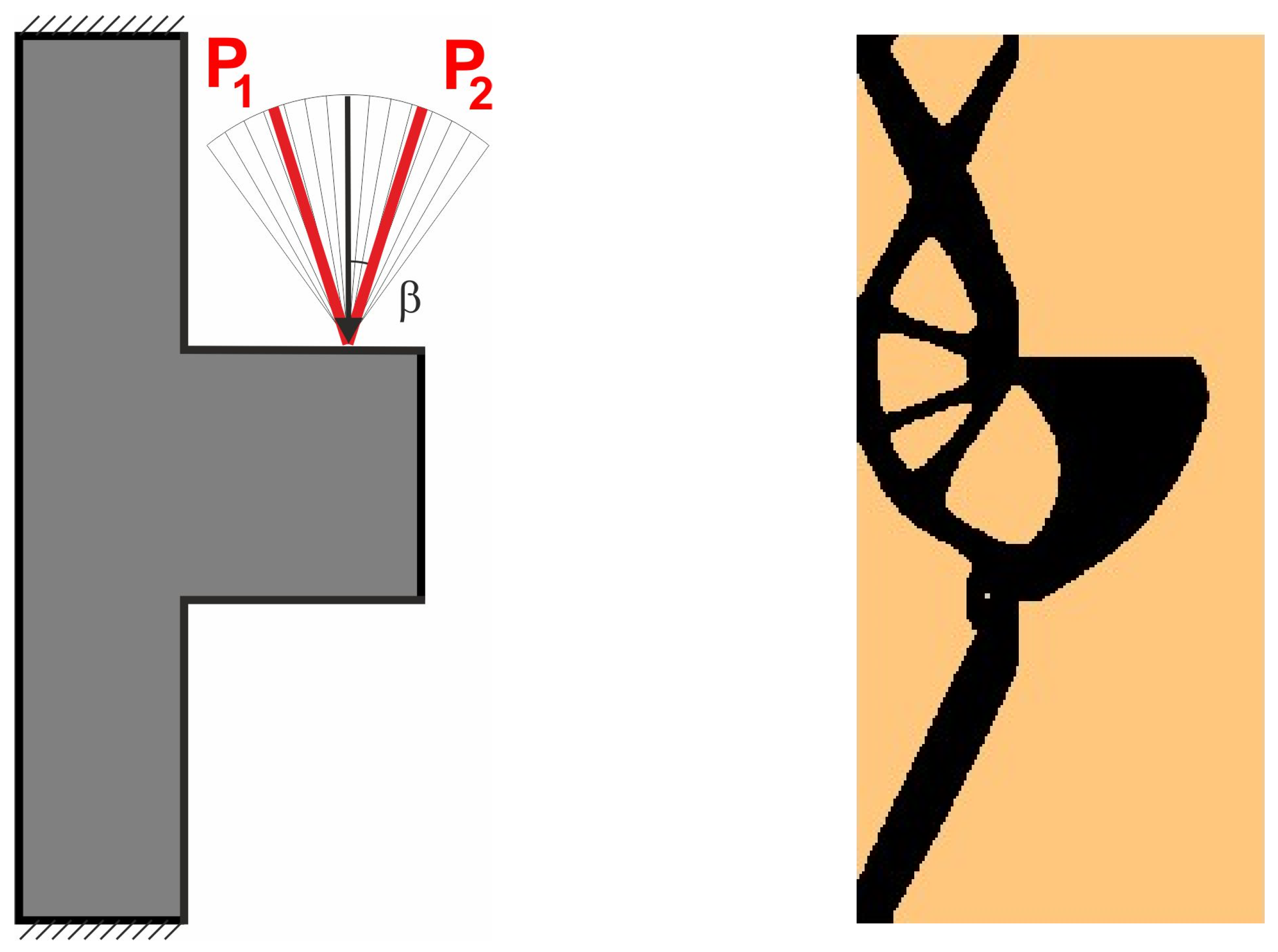
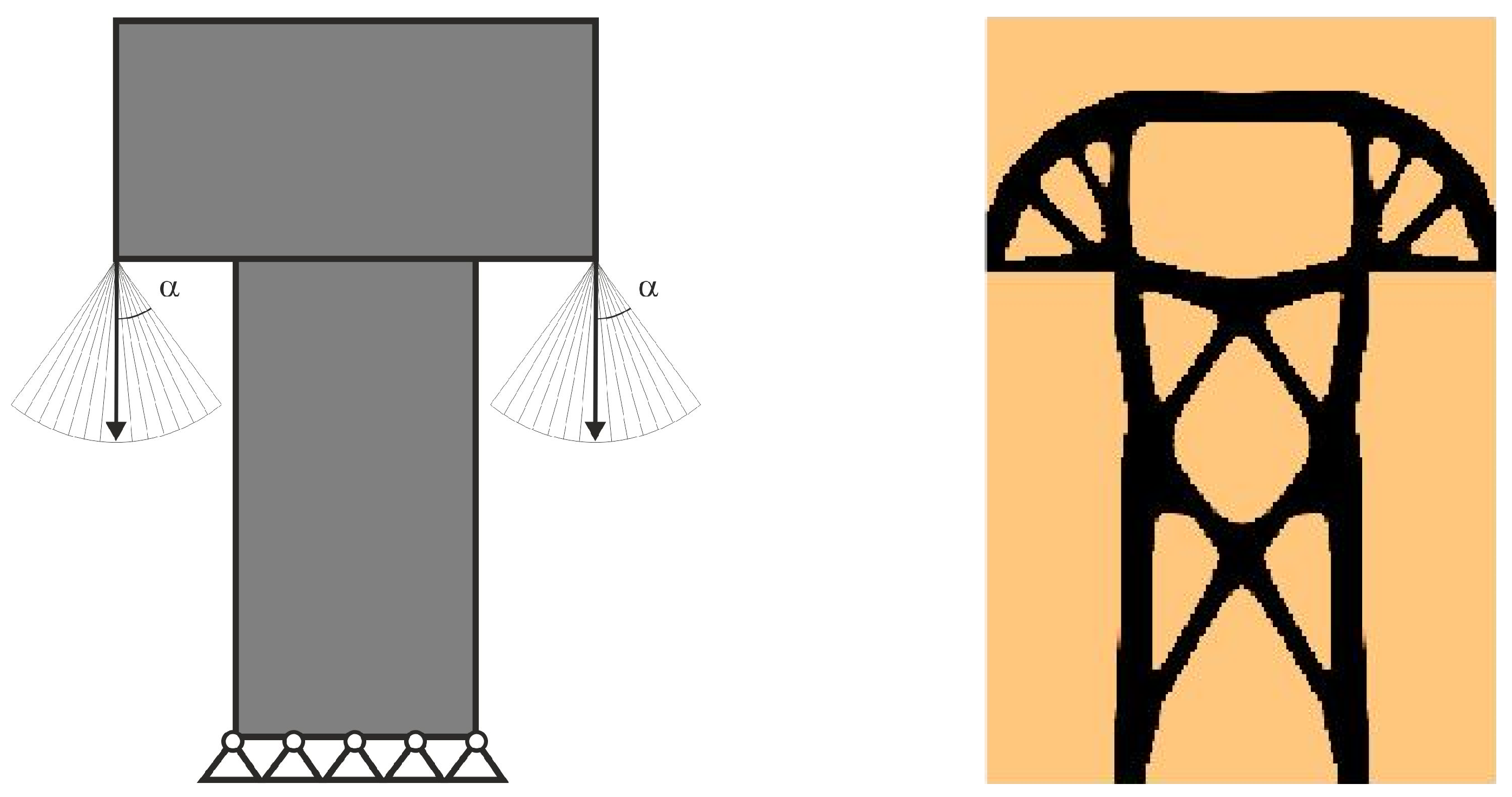
3.1. Generation of Plane Topologies Under Loads Applied at Random Angles
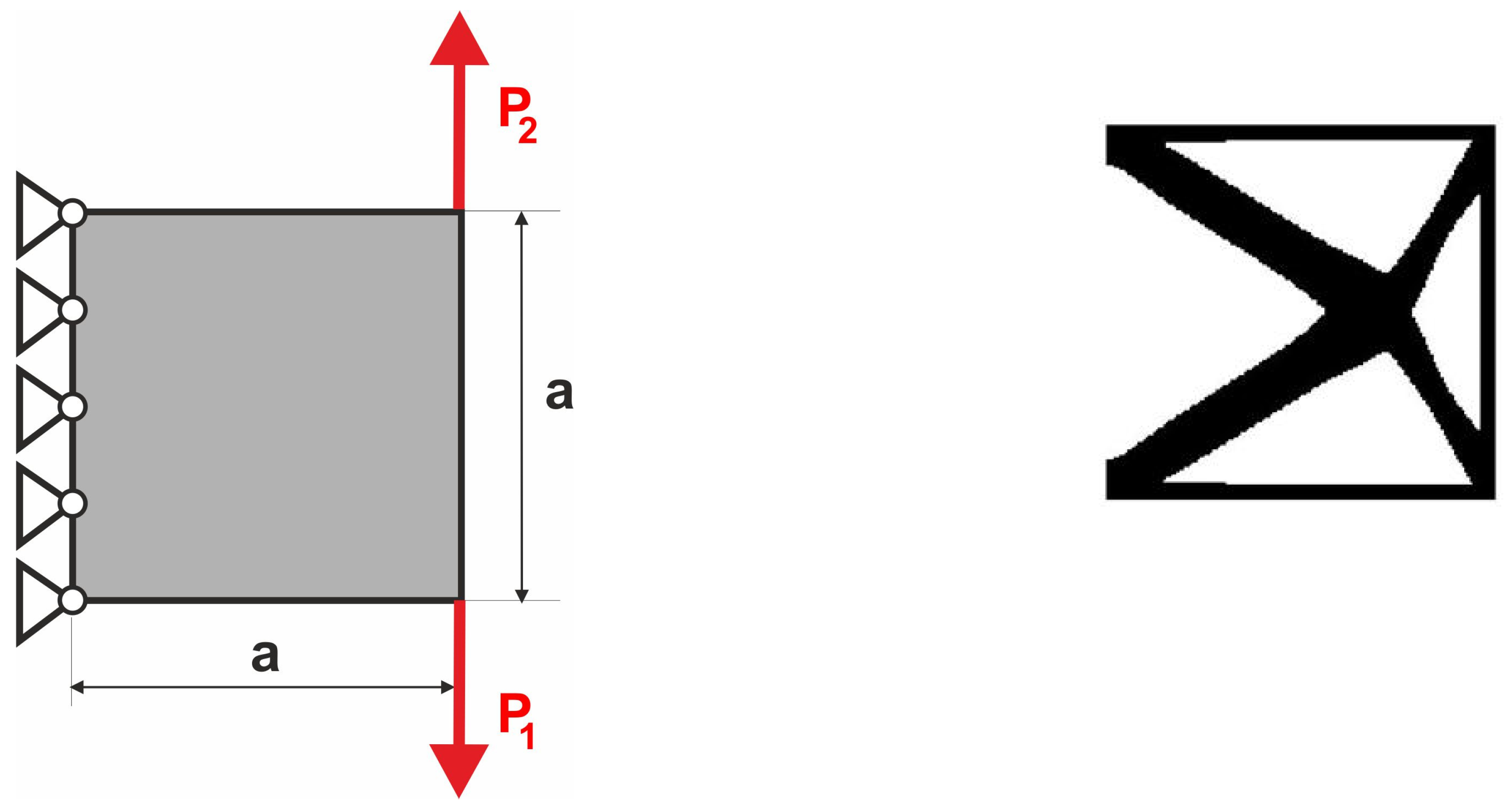
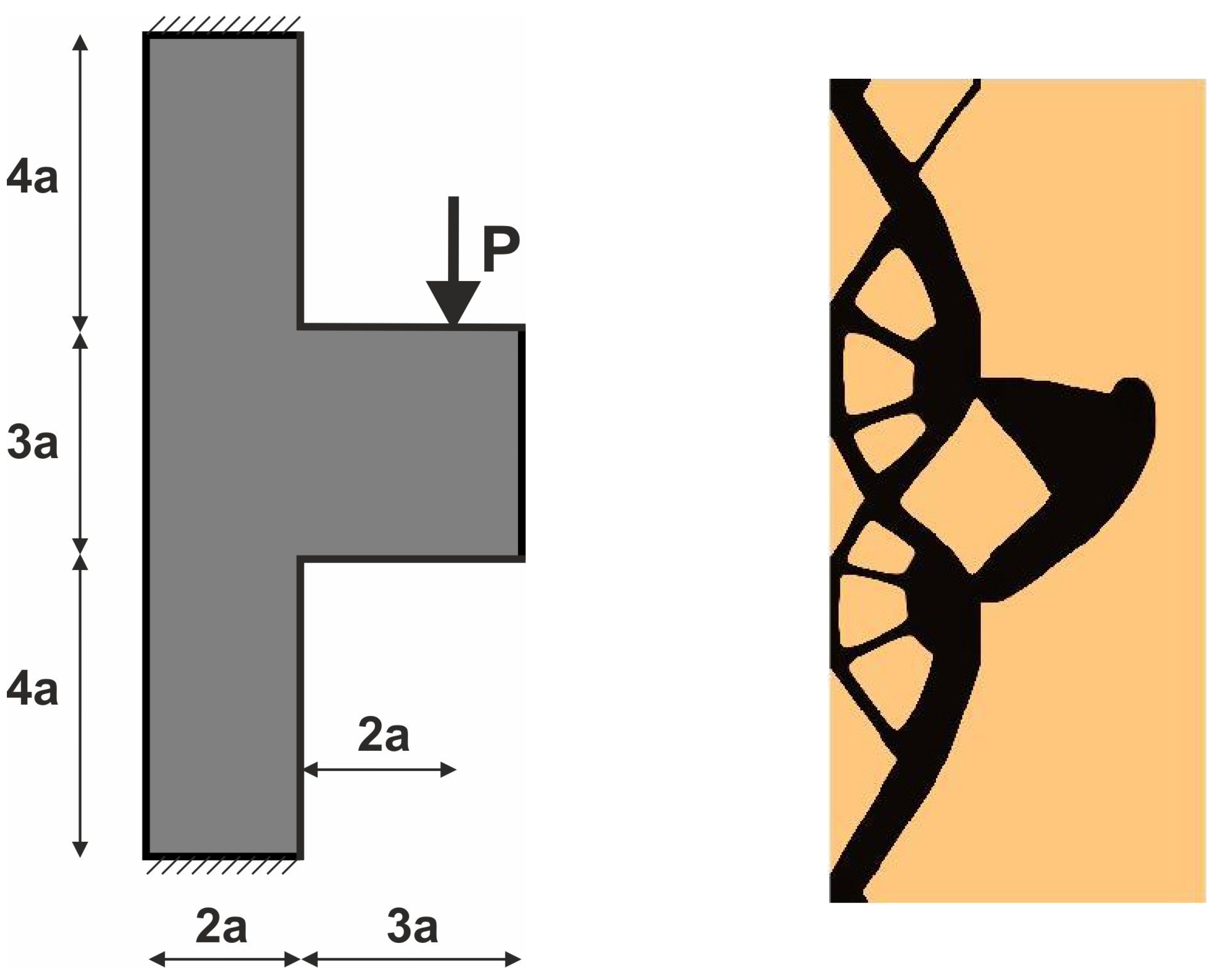
3.1.1. Plane Structure 1
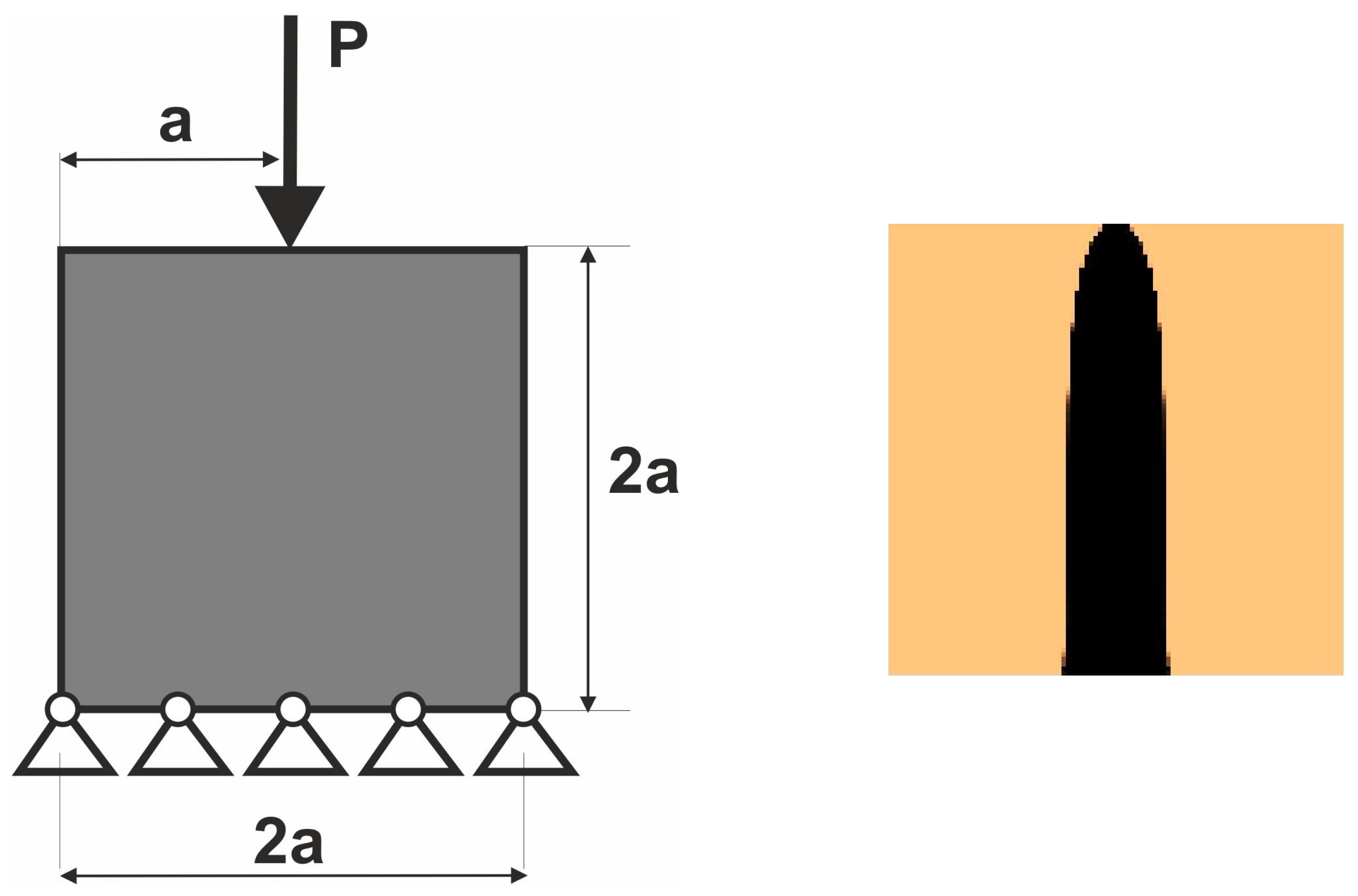
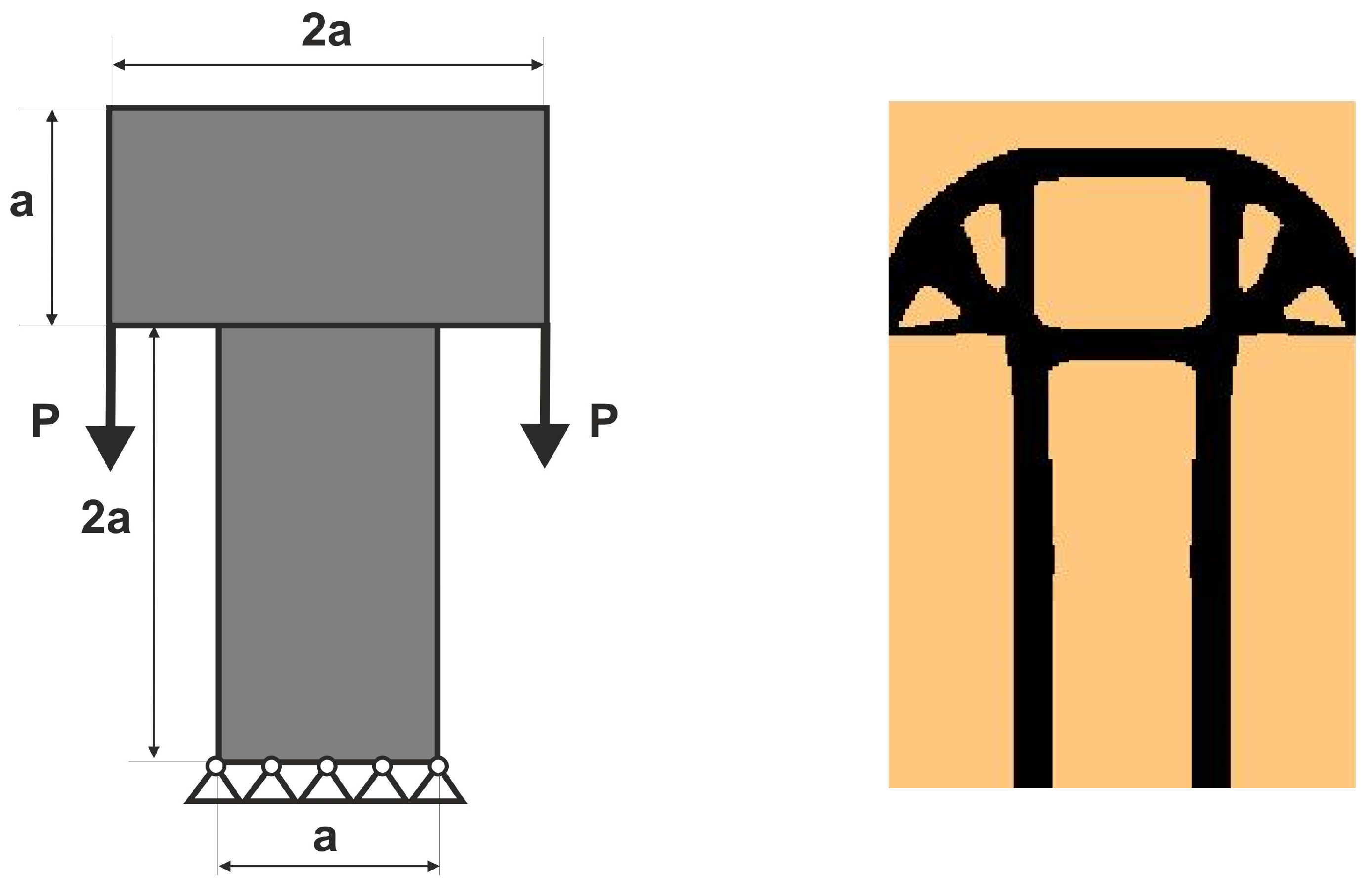
3.1.2. Plane Structure 2
3.1.3. Plane Structure 3
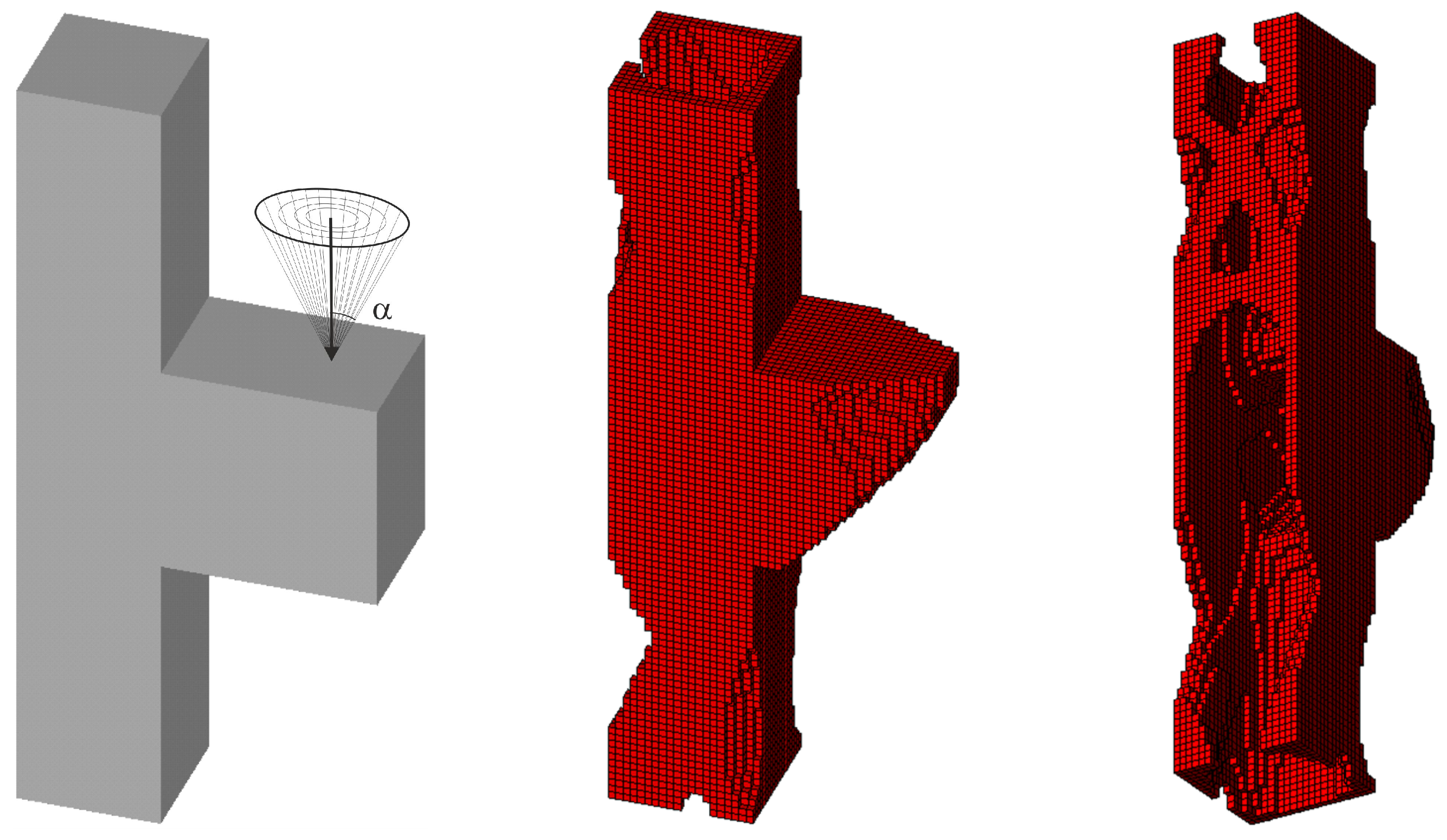
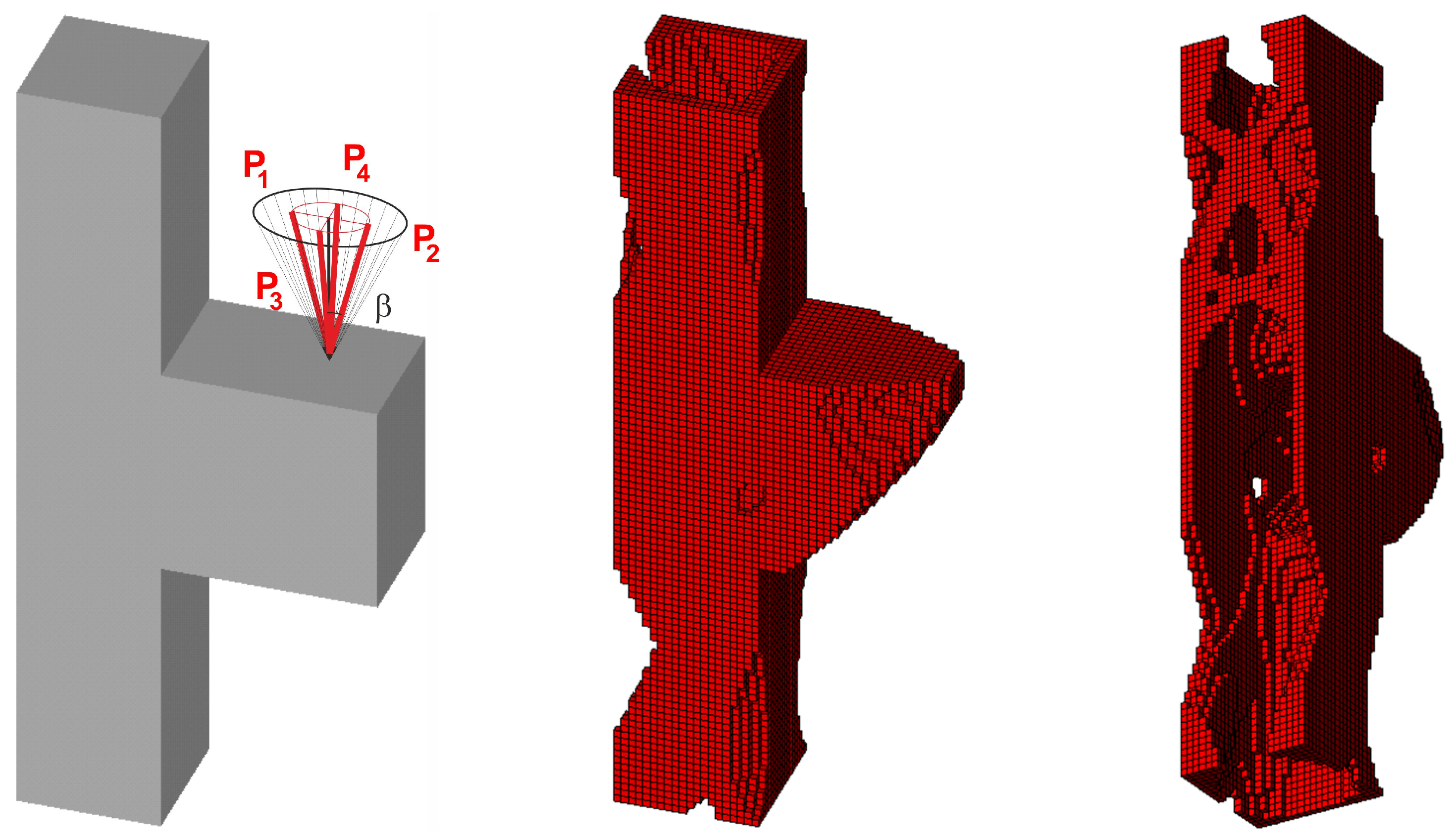
3.2. Generation of Spatial Topologies Under Loads Applied at Random Angles
3.2.1. Spatial Structure 1
3.2.2. Spatial Structure 2
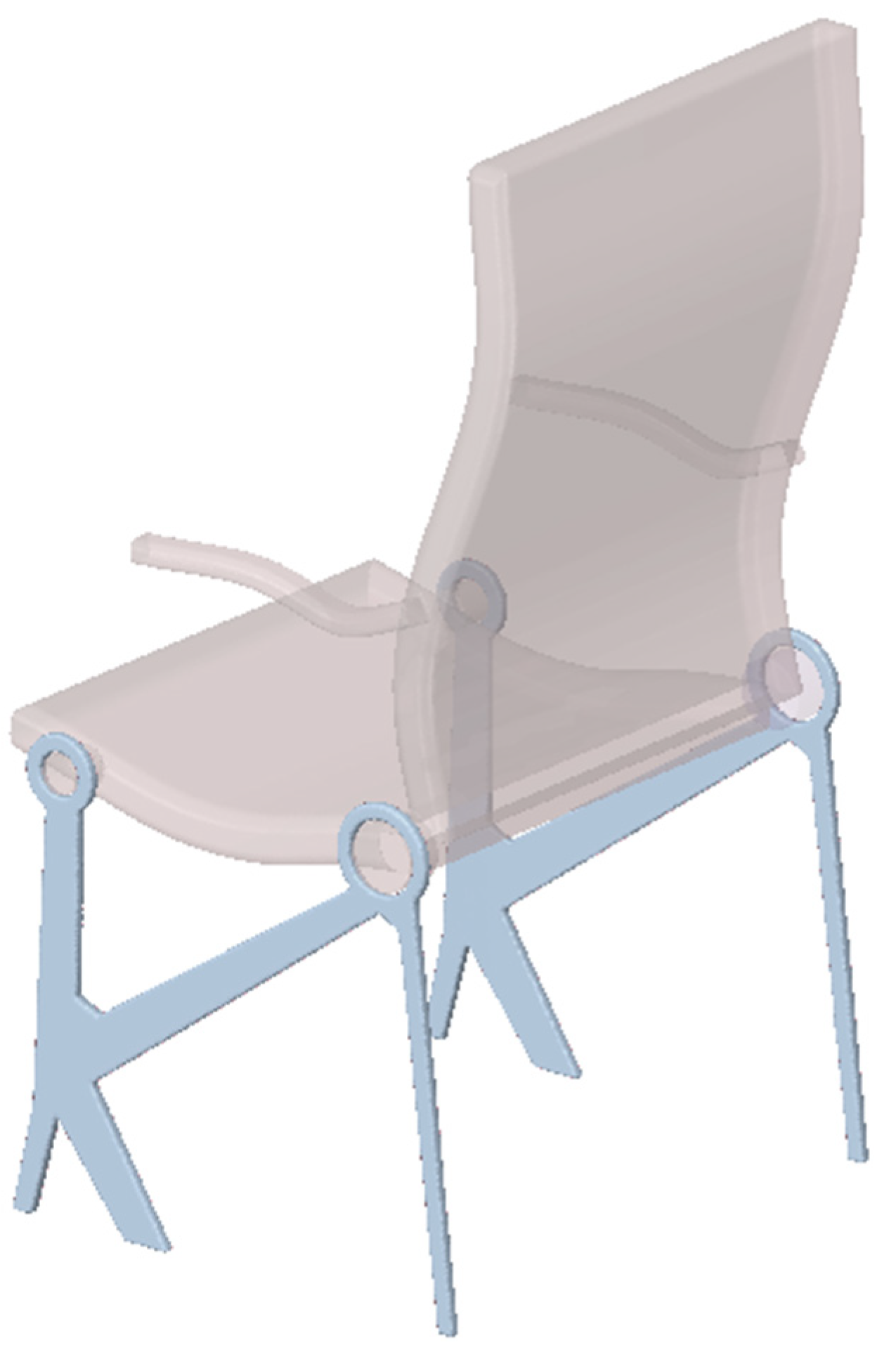
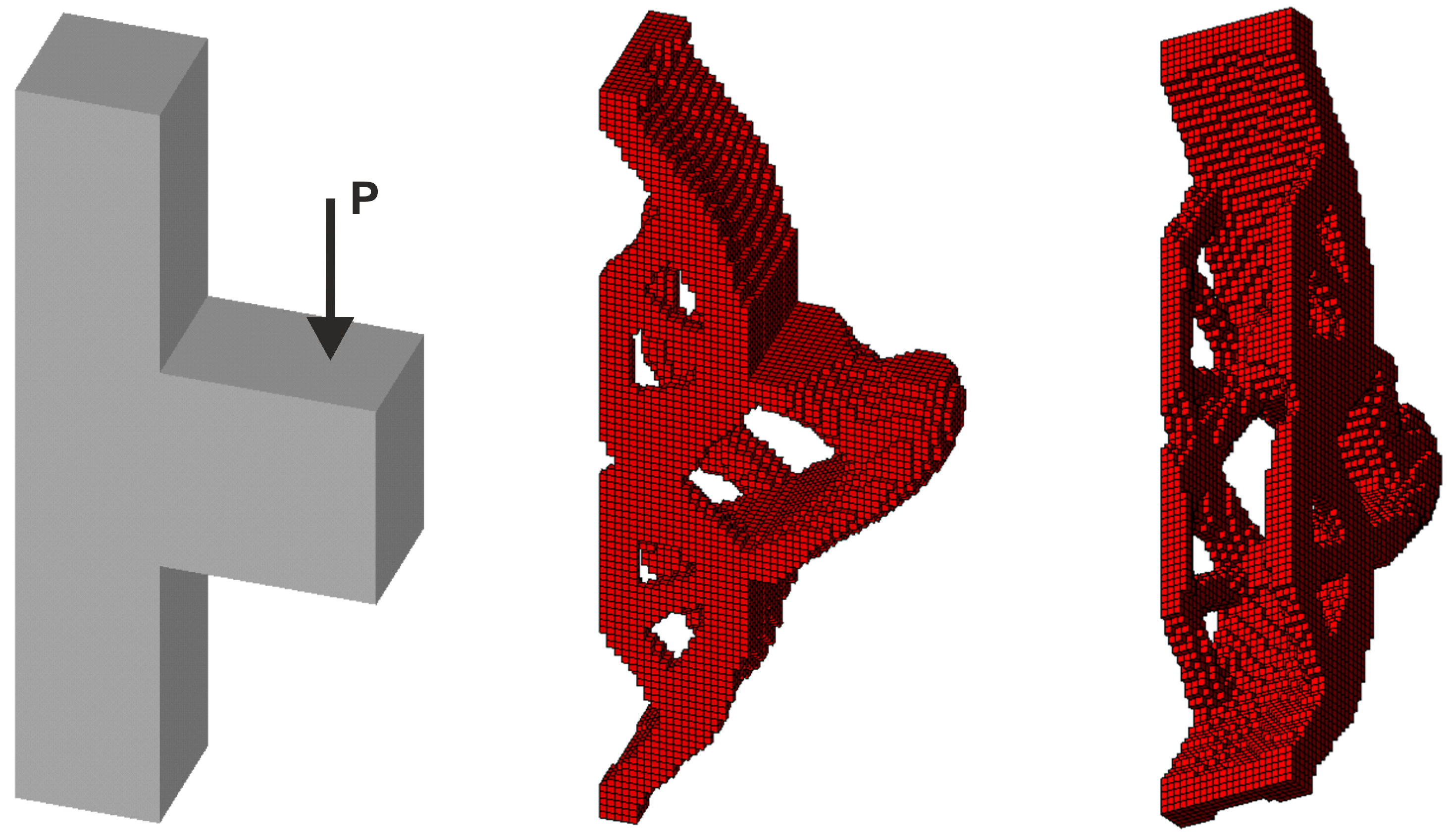
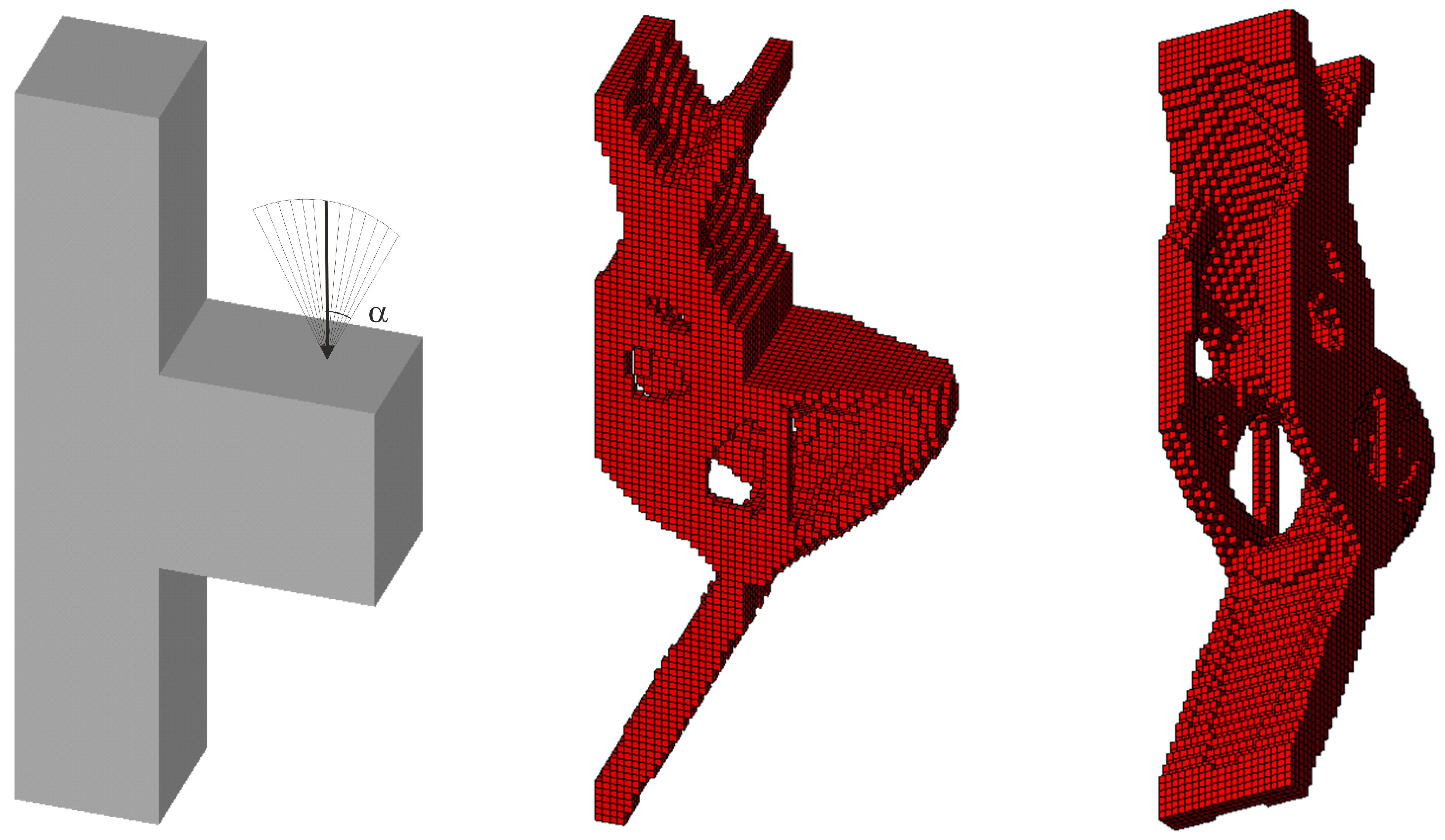
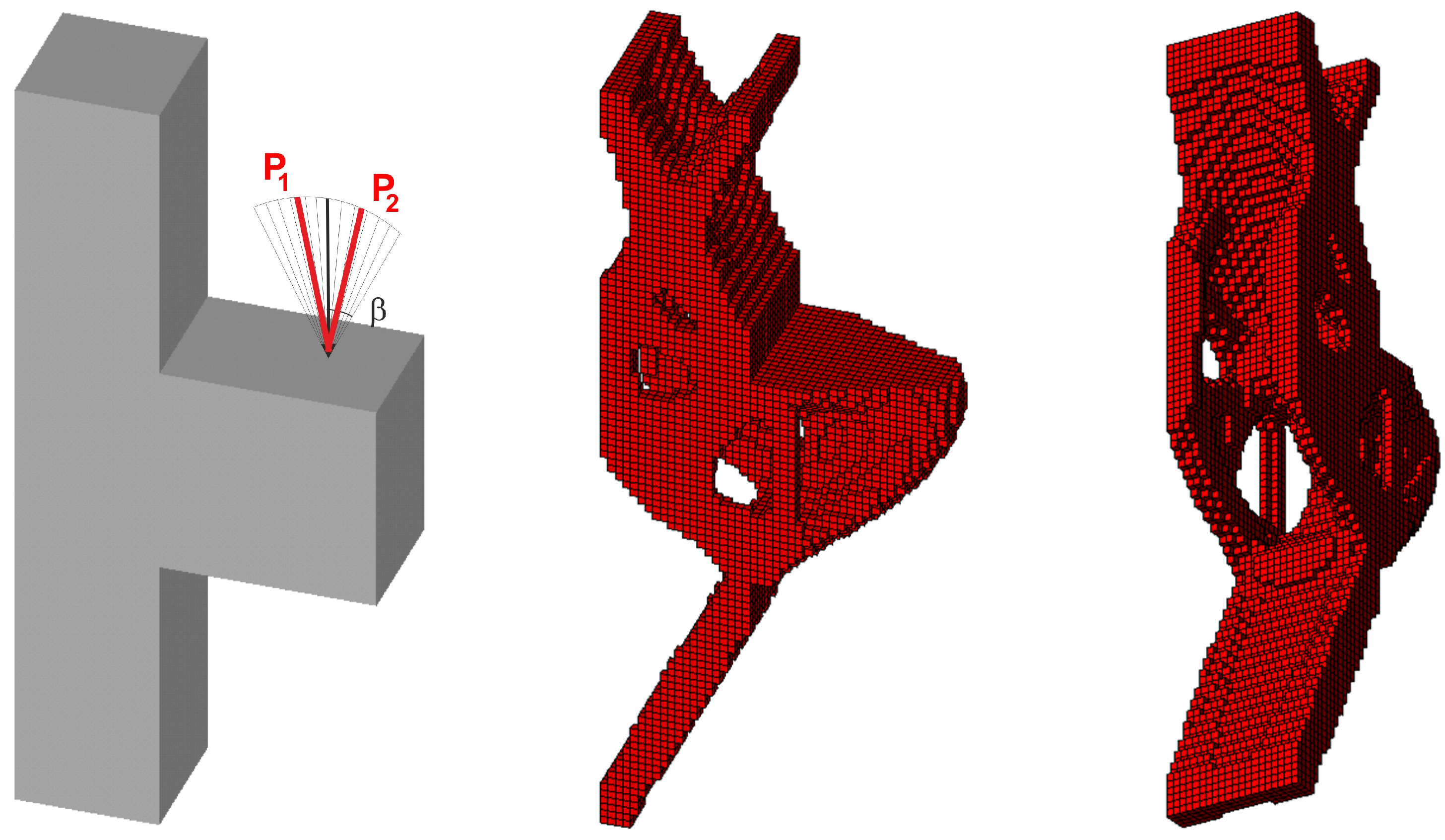
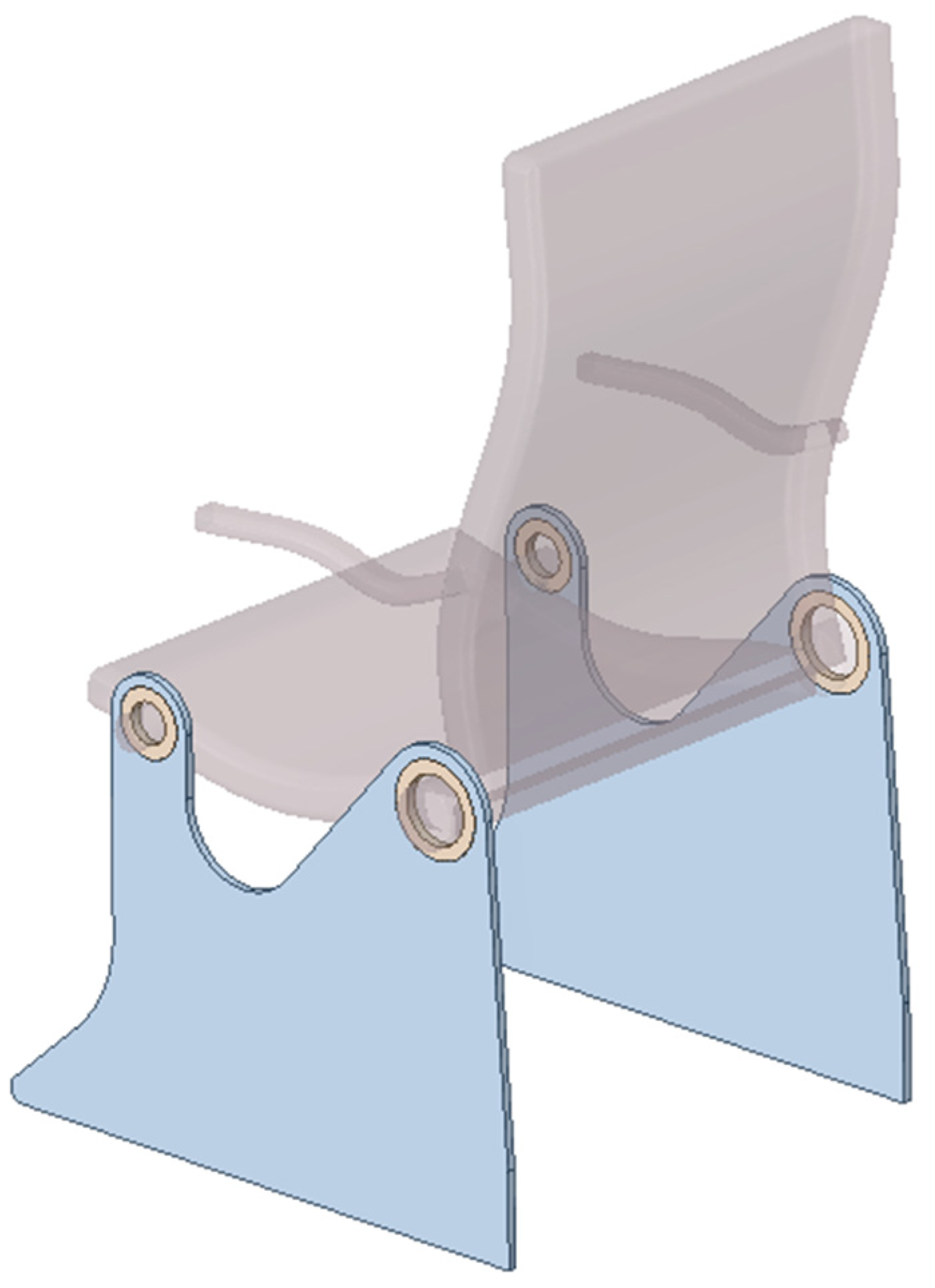
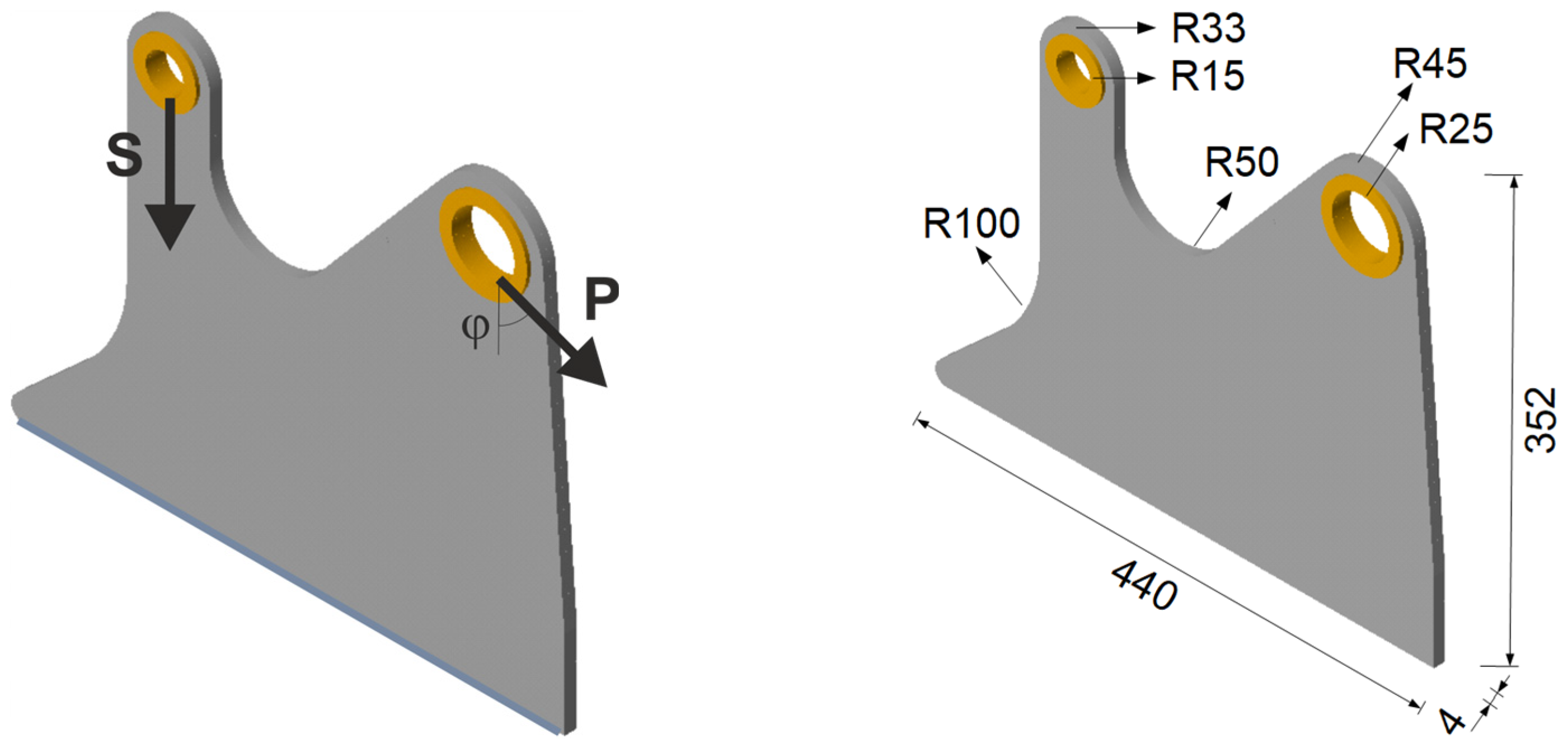
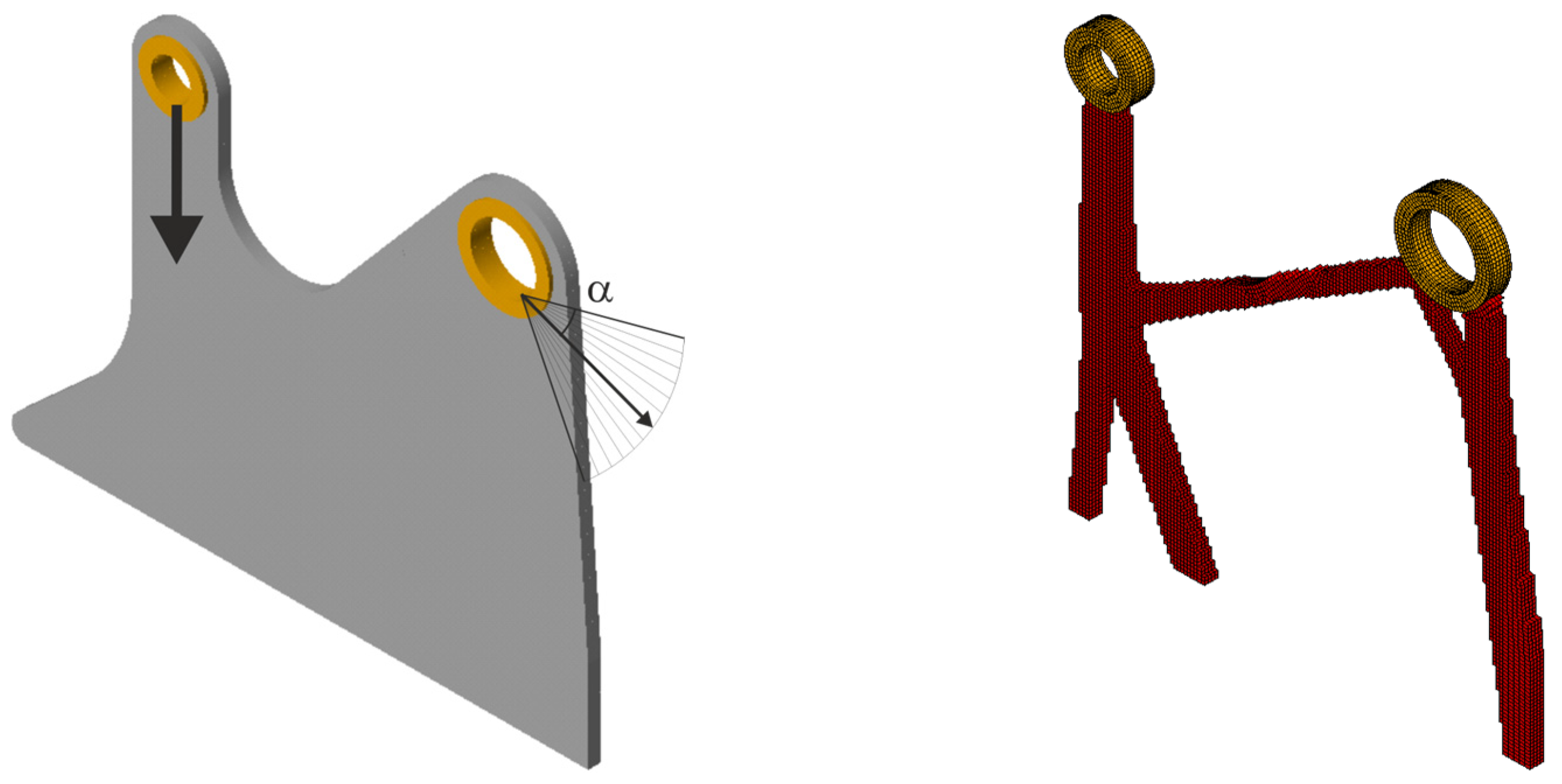
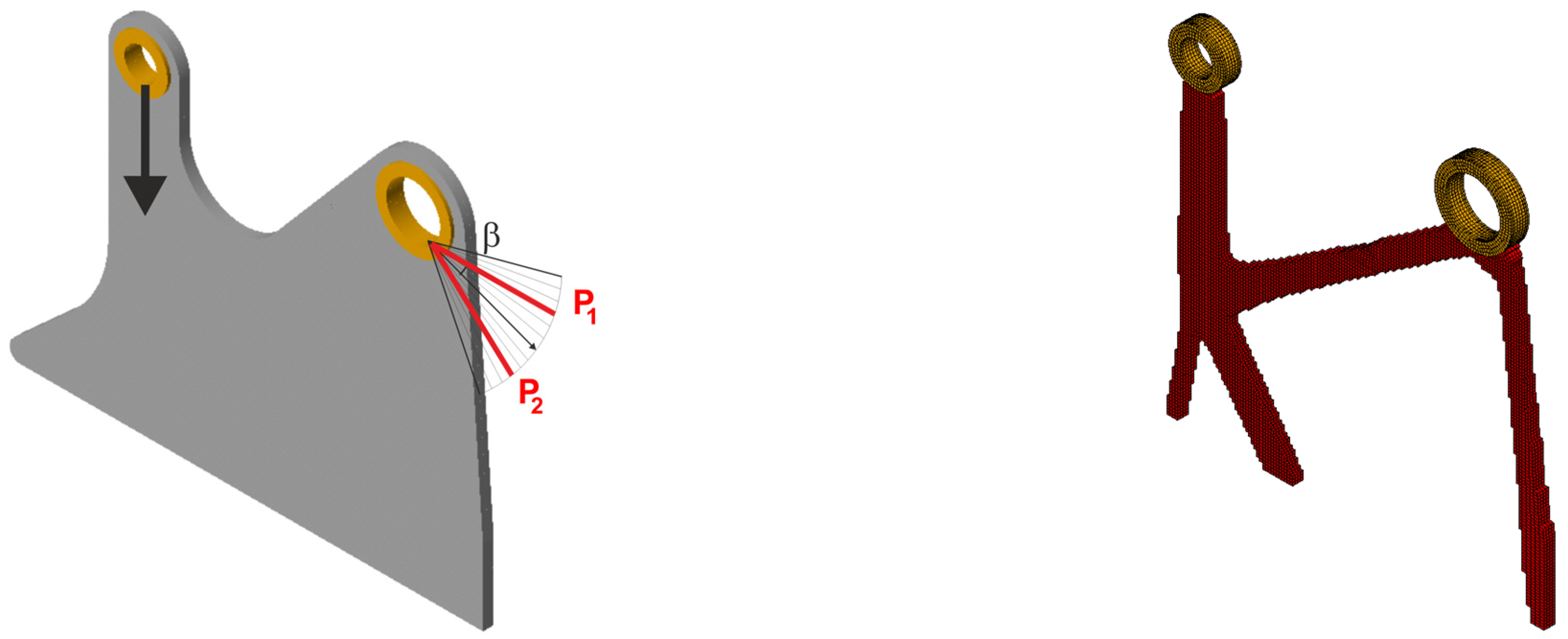
3.2.3. Spatial Structure 3: Engineering Design
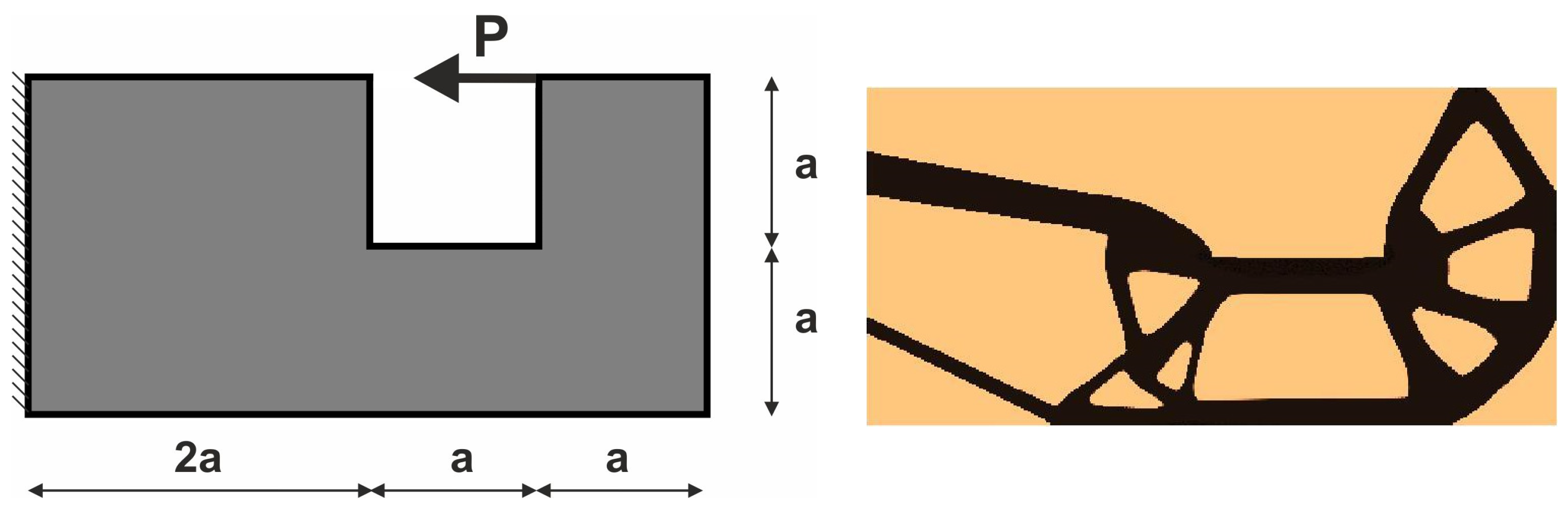
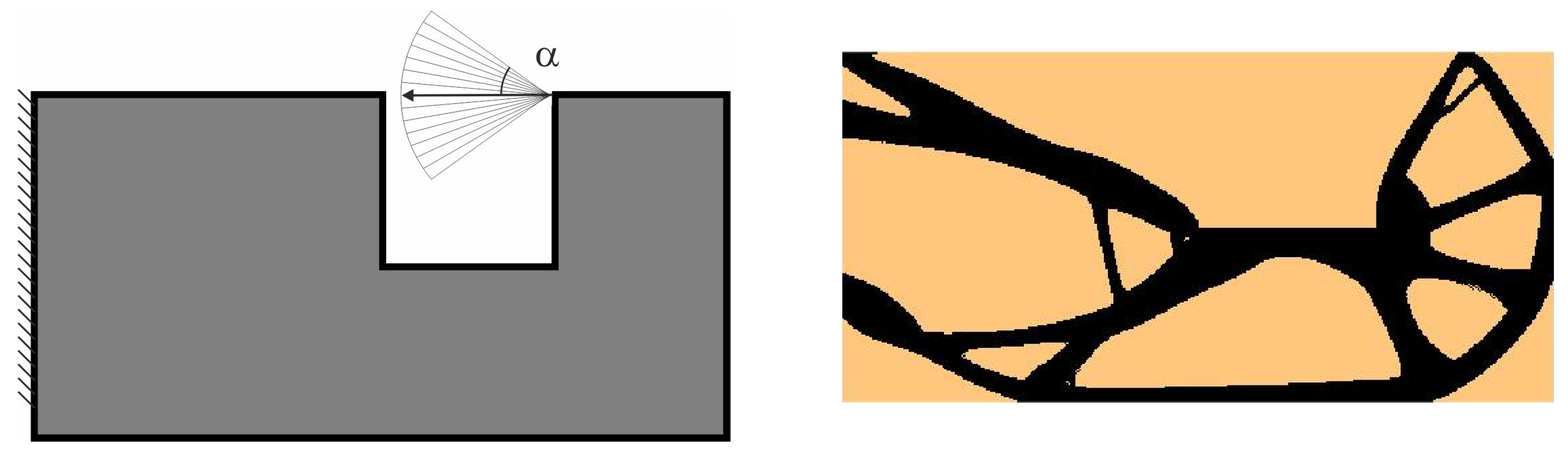
3.3. Illustration of the ELS Concept Versatility
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bendsoe, M.B.; Kikuchi, N. Generating optimal topologies in optimal design using a homogenization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1988, 71, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsoe, M.P. Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 1989, 1, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, H.; Dong, J.; Yue, W.; Xia, H. Topology Optimization: A Review for Structural Designs Under Statics Problems. Materials 2024, 17, 5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, T.P.; Bernardo, L.F.A.; Andrade, J.M.A. Topology Optimisation in Structural Steel Design for Additive Manufacturing. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logo, J.; Ismail, H. Milestones in the 150-year history of topology optimization: A review. Comput. Assist. Methods Eng. Sci. 2020, 27, 97–132. [Google Scholar]
- Eschenauer, H.A.; Olhoff, N. Topology optimization of continuum structures: A review. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2001, 54, 331–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csebfalvi, A. Robust topology optimization: A new algorithm for volume-constrained expected compliance minimization with probabilistic loading directions using exact analytical objective and gradient. Period. Polytech.-Civ. Eng. 2017, 61, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Frutos, J.; Herrero-Pérez, D. Evolutionary topology optimization of continuum structures under uncertainty using sensitivity analysis and smooth boundary representation. Comput. Struct. 2018, 205, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maute, K. Topology Optimization under Uncertainty. In Topology Optimization in Structural and Continuum Mechanics. CISM International Centre for Mechanical Sciences; Rozvany, G.I.N., Lewiński, T., Eds.; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2014; Volume 549. [Google Scholar]
- De, S.; Hampton, J.; Maute, K.; Doostan, A. Topology optimization under uncertainty using a stochastic gradient-based approach. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2020, 62, 2255–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; He, X.; Jing, H. Topology optimization of bridges under random traffic loading using stochastic reduced-order models. Probabilist. Eng. Mech. 2024, 75, 103583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Dang, K.; Yang, W.; Ding, Y.; Xie, P. An efficient approach to reliability-based topology optimization for the structural lightweight design of planar continuum structures. J. Mech. 2021, 37, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauzowski, P.; Blachowski, B.; Logo, J. Topology optimization of elasto-plastic structures under reability constraints: A first order approach. Comput. Struct. 2021, 243, 106406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, H.G.; Sendhoff, B. Robust optimization—A comprehensive survey. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2007, 196, 3190–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalpour, M.; Tootkaboni, M. An efficient approach to reliability-based topology optimization for continua under material uncertainty. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2016, 53, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gea, H.C. Robust topology optimization under multiple independent unknown-but-bounded loads. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2018, 329, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Xinyu, G. A level set reliability-based topology optimization (LS-RBTO) method considering sensitivity mapping and multi-source interval uncertainties. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 419, 116587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Gu, K. Efficient reliability-based concurrent topology optimization method under PID-driven sequential decoupling framework. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 203, 112117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Topology design of multi-scale thermo-elastic structures considering performance reduction and disturbance based on interval models. Appl. Math. Model. 2025, 146, 116167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inou, N.; Shimotai, N.; Uesugi, T. A cellular automaton generating topological structures. In Proceedings of the 2nd European Conference on Smart Structures and Materials, Glasgow, UK, 12–14 October 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tovar, A.; Patel, M.N.; Niebur, G.L.; Sen, M.; Renaud, J.E. Topology Optimization Using a Hybrid Cellular Automaton Method With Local Control Rules. J. Mech. Des. 2006, 128, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajs-Zielińska, K.; Bochenek, B. Topology algorithm built as an automaton with flexible rules. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. 2021, 69, e138813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, B.; Tajs-Zielinska, K. Cellular Automaton Mimicking Colliding Bodies for Topology Optimization. Materials 2022, 15, 8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, Q.; Feng, F.; Chen, X.; Lv, X.; Lin, X.; Fu, T. Topology optimization design of three-dimensional multi-material and multi-body structure based on irregular cellular hybrid cellular automata method. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, E.; Toyoda, T. Structural design using cellular automata. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2000, 19, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajs-Zielińska, K.; Bochenek, B. CARMA—Cellular Automata with Refined Mesh Adaptation—The Easy Way of Generation of Structural Topologies. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Xu, G.; Kou, L.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, X. A hybrid cellular automata-based topology optimization method for incompressible fluid flow channels. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2025, 104, 102867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, D.C.; Chen, J.H.; Cui, X.Y.; Li, G.Y. Design of materials using hybrid cellular automata. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2017, 56, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Cuy, A.; Begambre-Carrillo, O.; Villalba-Morales, J.D. Topology optimization of steel slotted dampers with the hybrid cellular automata technique. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2025, 206, 103921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, J.; Tan, H.; Renaud, J.; Tovar, A. Two-material optimization of plate armor for blast mitigation using hybrid cellular automata. Eng. Optim. 2012, 44, 985–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Kang, B.S.; Renaud, J.E.; Tovar, A. Crashworthiness Design Using Topology Optimization. J. Mech. Des. 2009, 131, 061013-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duddeck, F.; Hunkeler, S.; Lozano, P.; Wehrle, E.; Zeng, D. Topology Optimization for Crashworthiness of Thin-Walled Structures Under Axial Impact Using Hybrid Cellular Automata. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2016, 54, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrousheh, M.; Marzbanrad, J.; Gohlich, D. Topology optimization of energy absorbers under crashworthiness using modified hybrid cellular automata (MHCA) algorithm. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2019, 60, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulig, N.; Nutwell, E.; Menze, L.S.; Detwiler, D. Preference-based topology optimization for vehicle concept design with concurrent static and crash load cases. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2018, 57, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.S.; Tovar, A.; Penninger, C.L.; Renaud, J.E. Strain-based topology optimization for crashworthiness using hybrid cellular automata. Int. J. Crashworth. 2011, 13, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Da, D.; Loh, C.-L.; Zhao, H.; Yin, S.; Xu, J. Multiscale topology optimization for non-uniform microstructures with hybrid cellular automata. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2020, 62, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajs-Zielińska, K.; Bochenek, B. Cellular Automata Approach to Topology Optimization of Graded Multi-Material Structures. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajs-Zielińska, K. Topology Optimization of Periodic Structures Subject to Self-Weight Loading Using a Heuristic Method. Materials 2024, 17, 5652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Huang, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Xie, C.; Kong, D. A dynamic-static coupling topology optimization method based on hybrid cellular automata. Structures 2023, 50, 1573–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewiński, T.; Czarnecki, S.; Dzierżanowski, G.; Sokół, T. Topologyoptimization in structuralmechanics. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. 2013, 61, 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund, O. A 99 line topology optimization code written in MATLAB. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2001, 21, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsoe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. Topology Optimization: Theory, Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bendsoe, M.P. Optimization of Structural Topology, Shape, and Material; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Bochenek, B. An easy way for the generation of structural topologies under random loads using cellular automata. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2023, 20, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, S.W.K.; Lee, H.; Huh, M.; Kim, I.Y. Simultaneous isotropic and anisotropic multi-material topology optimization for conceptual-level design of aerospace components. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2021, 64, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivers, N.C.; Carrick, C.A.; Kim, I.Y. Design optimization of a business aircraft seat considering static and dynamic certification loading and manufacturability. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2020, 62, 3457–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Tovar, A. An efficient 3D topology optimization code written in Matlab. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2014, 50, 1175–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bochenek, B.; Tajs-Zielińska, K. On Predicting Optimal Structural Topologies in the Presence of Random Loads. Materials 2025, 18, 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122819
Bochenek B, Tajs-Zielińska K. On Predicting Optimal Structural Topologies in the Presence of Random Loads. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122819
Chicago/Turabian StyleBochenek, Bogdan, and Katarzyna Tajs-Zielińska. 2025. "On Predicting Optimal Structural Topologies in the Presence of Random Loads" Materials 18, no. 12: 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122819
APA StyleBochenek, B., & Tajs-Zielińska, K. (2025). On Predicting Optimal Structural Topologies in the Presence of Random Loads. Materials, 18(12), 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122819





