The Physical and Mechanical Properties of Arundo donax (L.) Reeds Affect Their Acoustic Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microscopic Observations
2.2. Sample Density ρ
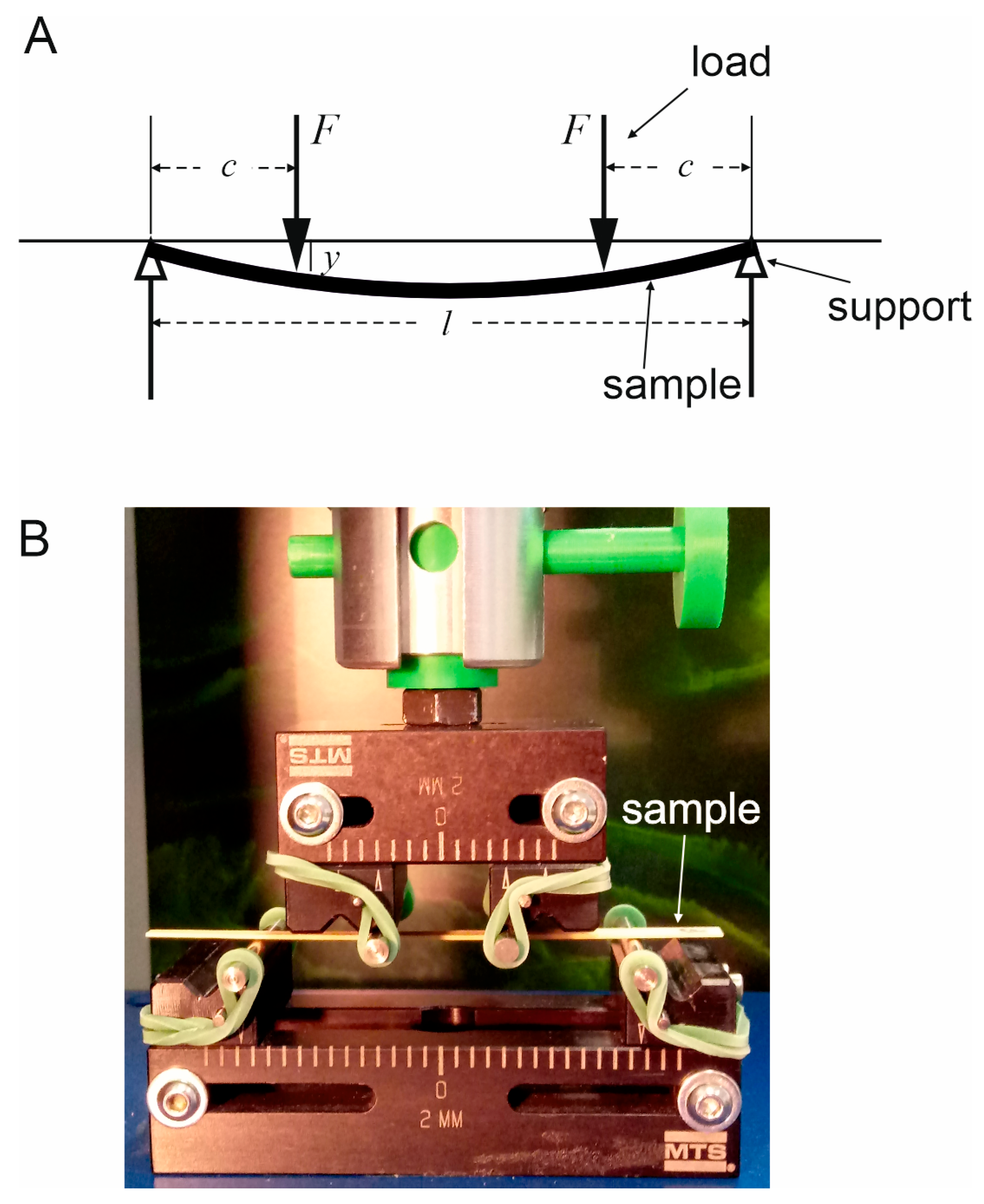
2.3. Young’s Modulus E
2.4. Statistical Analysis of the Measured Traits
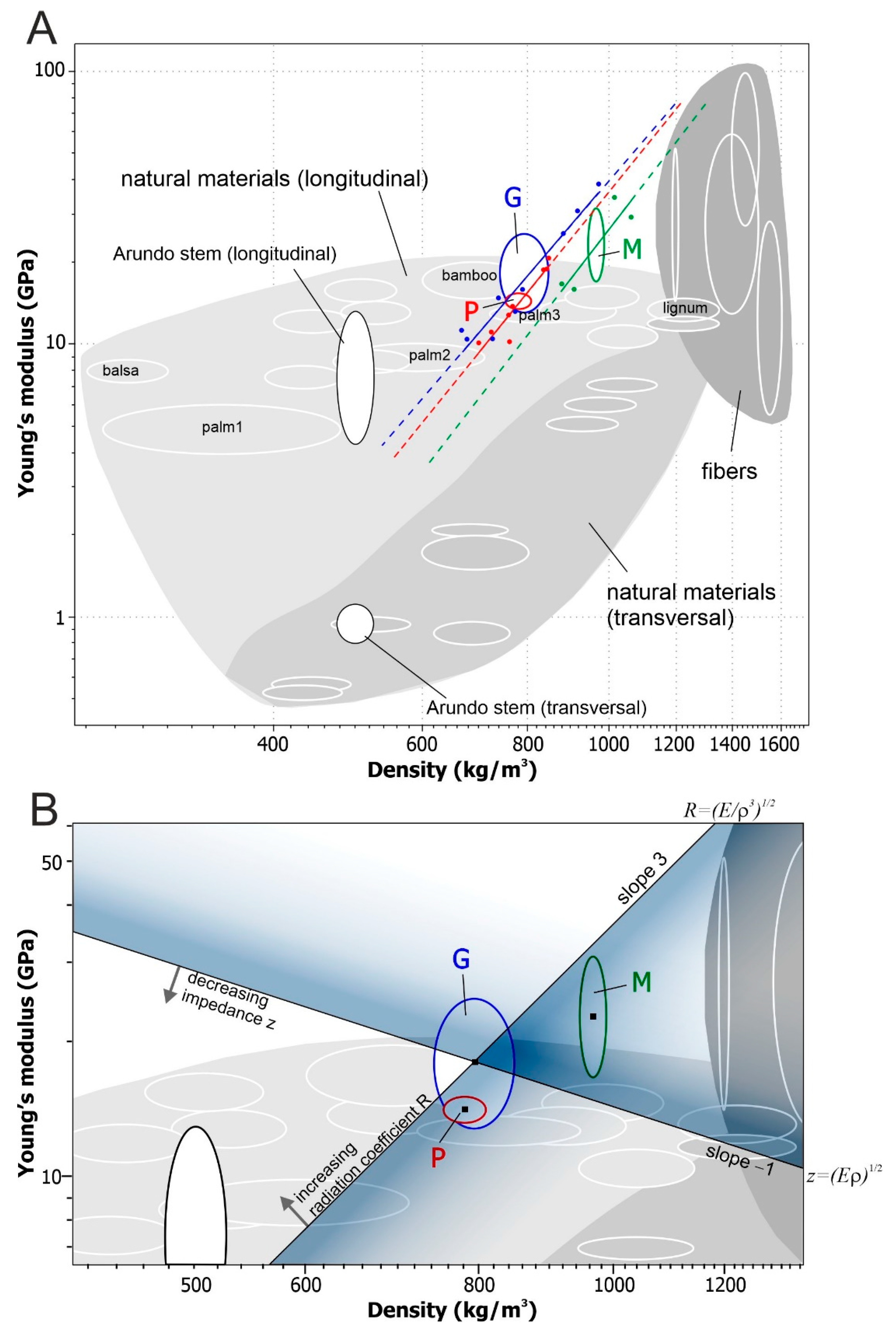
2.5. Material Property Chart and Acoustical Parameters
3. Results
3.1. Anatomy
3.2. Physical and Mechanical Properties
3.3. Reed Samples’ Position on the Material Property Chart
4. Discussion
4.1. Reed Samples
4.2. Density and Young’s Modulus Gradient
4.3. From Measurements to Model
4.4. Properties of Unprepared Arundo Stems Versus Properties of Reed Samples
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SD | Standard deviation |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| (I), (II), (III) | Three concentric bands formed by cells of different tissues, visible in cross-section through the Arundo internode: (I) an outermost thin ring of the hard waxy epidermis and outer cortical cells, (II) a slightly thicker sclerenchymatous ring including small vascular bundles, and (III) a thick inner cortex with parenchyma cells and vascular bundles encircled by sclerified fiber sheaths |
| G, P, M | Three different commercial brands of Arundo donax used in the experiments |
| ds | The thickness of the sclerenchyma layer, referring to band (II) in the cross-sectional view of the stem |
| h | Specimen thickness measured along the radius of the stem |
| b | Specimen width measured in the circumferential direction |
| L | Specimen length measured in the longitudinal direction |
| V | Specimen volume calculated using the formula V = b·h·L |
| A | The total cross-sectional area of the specimen with a porous structure |
| As | The solid cross-sectional area of the specimen with a porous structure |
| WF | Cell-wall fraction calculated as the ratio of As to A |
| m | Specimen mass |
| ρ | The overall density of the specimen calculated using the formula ρ = m/V |
| ρs | The density of the cell walls = solid density |
| F | The load applied in the mechanical test |
| c | The distance between the loading pin and the supporting pin in the mechanical test |
| l | The distance between supports in the mechanical test |
| y | Specimen deflection measured in the mechanical test |
| E | Young’s modulus calculated using the formula |
| NG, NP, NM | Number of specimens of particular Arundo brands used in density measurements and mechanical tests |
| hmin, hmax | Minimal and maximal thickness of the specimens of particular brands |
| ρav | Average density, mean of the function ρ(h) |
| Eav | Average Young’s modulus, mean of the function E(h) |
| z | The acoustic impedance of the material z = (Eρ)1/2 |
| R | Radiation coefficient R = (E/ρ3)1/2 |
| p | Probability in statistical tests |
| r2 | Coefficient of determination |
| sc | Sclerenchyma |
| pa | Parenchyma |
| vb | Vascular bundle |
References
- Boldt-Neurohr, K.M. The physical properties and the anatomy of Arundo donax: Reed cane. Double Reed 2010, 33, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Spatz, H.-C.; Beismann, H.; Brüchert, F.; Emanns, A.; Speck, T. Biomechanics of the giant reed Arundo donax. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 1997, 352, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolesik, P.; Mills, A.; Sedgley, M. Anatomical characteristics affecting the musical performance of clarinet reeds made from Arundo donax L. (Gramineae). Ann. Bot. 1998, 81, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegst, U.G.K. Bending efficiency through property gradients in bamboo, palm, and wood-based composites. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. 2011, 4, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüggeberg, M.; Burgert, I.; Speck, T. Structural and mechanical design of tissue interfaces in the giant reed Arundo donax. J. R. Soc. Interface 2010, 7, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, C.E.; Jeronimidis, G.; Pretlove, A.J.; Barnett, J.R. Anatomical factors affecting the quality of oboe reeds made from Arundo donax L. In Recent Advances in Wood Anatomy; Donaldson, L.A., Smith, A.P., Butterfield, B.G., Whitehouse, L.T., Eds.; Forest Research Institute: Rotarua, New Zealand, 1996; pp. 308–315. [Google Scholar]
- Kampragkou, P.; Dabekaussen, M.; Kamperidou, V.; Stefanidou, M. Bio-additives in lime-based mortars: An investigation of the morphology performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 474, 141177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molari, L.; Coppolino, F.S.; García, J.J. Arundo donax: A widespread plant with great potential as sustainable structural material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Molari, L.; Valdrè, J.; Garcia, J.J. Multilevel analysis of six species of Phyllostachys bamboo and Arundo donax: Preliminary survey on Italian grown stands. Wood Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 1025–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadonte, D. The Clarinet Reed: An Introduction to Its Biology, Chemistry, and Physics. Ph. D. Thesis, Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki, M.; Nobuchi, T.; Nakafushi, Y.; Nose, M.; Shibata, M.; Li, P.; Shiojiri, M. Structural observations and biomechanical measurements of clarinet reeds made from Arundo donax. Microsc. Res. Techniq. 2017, 80, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledet, D.A. Oboe Reed Style: Theory and Practice; Indiana University Press: Bloomington, IN, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wegst, U.G.K.; Ashby, M.F. The mechanical efficiency of natural materials. Philos. Mag. 2004, 84, 2167–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.J. The hierarchical structure and mechanics of plant materials. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 2749–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niklas, K.J. Plant Biomechanics: An Engineering Approach to Plant Form and Function; The University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA; London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Evert, R.F. Esau’s Plant Anatomy: Meristems, Cells, and Tissues of the Plant Body: Their Structure, Function, and Development, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ashby, M.F.; Shercliff, H.; Cebon, D. Materials: Engineering, Science, Processing and Design, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, L.J.; Ashby, M.F.; Harley, B.A. Cellular Materials in Nature and Medicine; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pelanconi, M.; Ortona, A. Nature-inspired, ultra-lightweight structures with gyroid cores produced by additive manufacturing and reinforced by unidirectional carbon fiber ribs. Materials 2019, 12, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegst, U.G.K. Wood for sound. Am. J. Bot. 2006, 93, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegst, U.G.K. Bamboo and wood in musical instruments. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2008, 38, 323–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spatz, H.-C.; Beismann, H.; Emanns, A.; Speck, T. Mechanical anisotropy and inhomogeneity in the tissue comprising the hollow stem of the giant reed Arundo donax. Biomimetics 1995, 3, 141–155. [Google Scholar]
- Speck, O.; Speck, T.; Spatz, H.-C. Arundo donax as a damped harmonic oscillator. BIONA-Rep. 2000, 14, 143–147. [Google Scholar]
- Timoshenko, S. Strength of Materials, 2nd ed.; D. Van Nostrand Company, Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada; New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Korn, G.A.; Korn, T.M. Mean-value theorems. Values of indeterminate forms. Weierstrass’s approximation theorems. In Mathematical Handbook for Scientists and Engineers; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1961; pp. 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Ashby, M.F. Materials Selection in Mechanical Design; Butterworth–Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Cintura, E.; Faria, P.; Molari, L.; Barbaresi, L.; D’Orazio, D.; Nunes, L. Characterization of an Arundo donax-based composite: A solution to improve indoor comfort. Ind. Crop Prod. 2024, 208, 117756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, A.E. Viscoelasticity of the giant reed material Arundo donax. Wood Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Maraldi, M.; Molari, L. Grading bamboo through four-point bending tests. A report on six species of Italian bamboo. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isnard, S.; Rowe, N.P.; Speck, T. Growth habit and mechanical architecture of the sand dune-adapted climber Clematis flammula var. maritima L. Ann. Bot. 2003, 91, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]



| Brand | ρ ± SD | CV | E ± SD | CV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | 792.5 ± 100.1 a | 0.13 | 19.6 ± 9.8 a | 0.50 |
| P | 778.9 ± 52.4 a | 0.07 | 15.0 ± 4.1 b | 0.27 |
| M | 963.3 ± 74.4 b | 0.08 | 24.8 ± 8.2 c | 0.33 |
| ρ(h) = ρ0hn | E(h) = E0hn | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brand | ρ0 | n | E0 | n |
| G | 572 ± 22 | −0.44 ± 0.05 | 4.6 ± 0.7 | −1.82 ± 0.16 |
| P | 633 ± 21 | −0.36 ± 0.06 | 6.1 ± 0.4 | −1.53 ± 0.10 |
| M | 736 ± 28 | −0.35 ± 0.05 | 9.2 ± 4.8 | −1.28 ± 0.59 |
| Brand | hmin ± Δhmin [mm] | hmax ± Δhmax [mm] | Average Density ρav ± Δρav [kg/m3] | Average Young’s Modulus Eav ± ΔEav [GPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | 0.326 ± 0.005 | 0.661 ± 0.026 | 792 ± 53 | 19 ± 6 |
| P | 0.453 ± 0.029 | 0.692 ± 0.026 | 779 ± 35 | 15 ± 1 |
| M | 0.363 ± 0.012 | 0.594 ± 0.025 | 965 ± 21 | 24 ± 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karczewski, J.; Potocka, I.; De Tullio, M.C.; Szymanowska-Pułka, J. The Physical and Mechanical Properties of Arundo donax (L.) Reeds Affect Their Acoustic Quality. Materials 2025, 18, 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122759
Karczewski J, Potocka I, De Tullio MC, Szymanowska-Pułka J. The Physical and Mechanical Properties of Arundo donax (L.) Reeds Affect Their Acoustic Quality. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122759
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarczewski, Jerzy, Izabela Potocka, Mario C. De Tullio, and Joanna Szymanowska-Pułka. 2025. "The Physical and Mechanical Properties of Arundo donax (L.) Reeds Affect Their Acoustic Quality" Materials 18, no. 12: 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122759
APA StyleKarczewski, J., Potocka, I., De Tullio, M. C., & Szymanowska-Pułka, J. (2025). The Physical and Mechanical Properties of Arundo donax (L.) Reeds Affect Their Acoustic Quality. Materials, 18(12), 2759. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122759









