Sustainable Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Hard Disks: Grinding NdFeB Magnets and Financial and Environmental Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
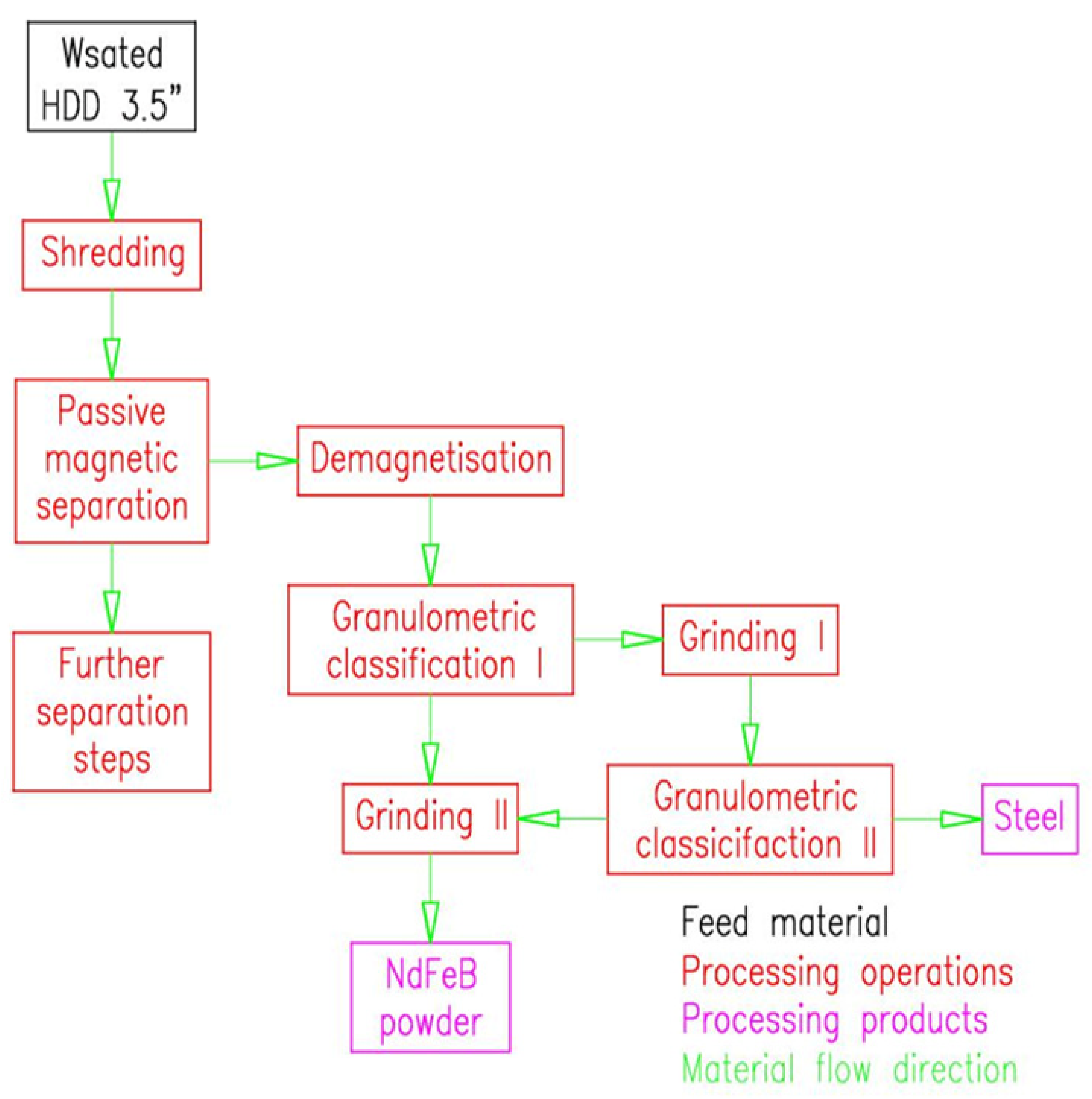
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Methods for Grinding
2.3. Methods for Financial and Environmental Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Grinding of Neodymium Alloy
| Particle Diameters | Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Test 4 | Test 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d10, μm | 9.07 | 7.85 | 7.92 | 7.57 | 6.76 |
| d50, μm | 23.70 | 20.19 | 20.68 | 20.55 | 19.51 |
| d90, μm | 178.35 | 37.80 | 37.53 | 37.25 | 36.37 |
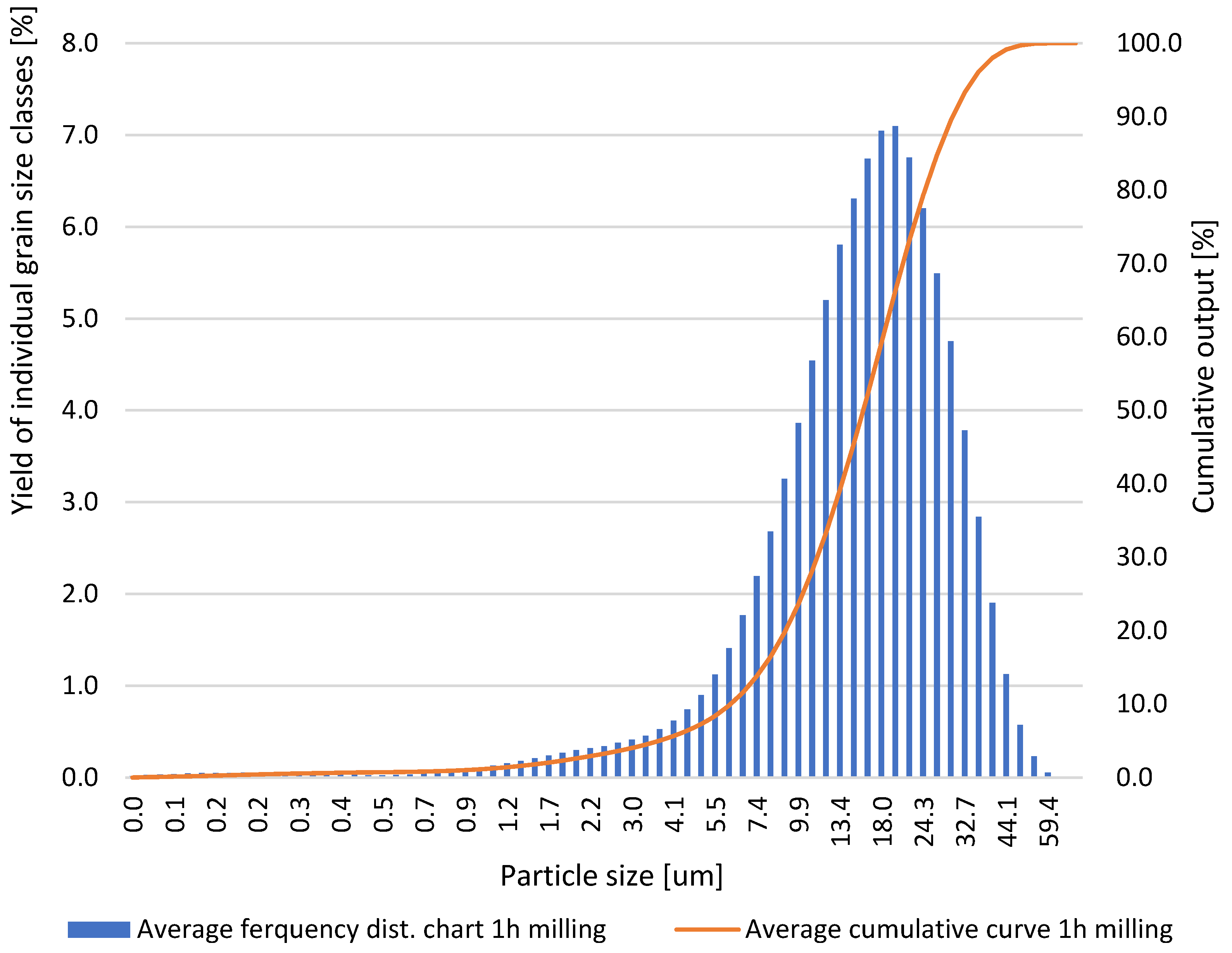
| Particle Diameters | Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Test 4 | Test 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d10, μm | 6.50 | 6.29 | 6.55 | 6.51 | 6.26 |
| d50, μm | 17.18 | 16.13 | 16.69 | 16.57 | 16.51 |
| d90, μm | 32.71 | 31.02 | 31.18 | 31.02 | 31.66 |

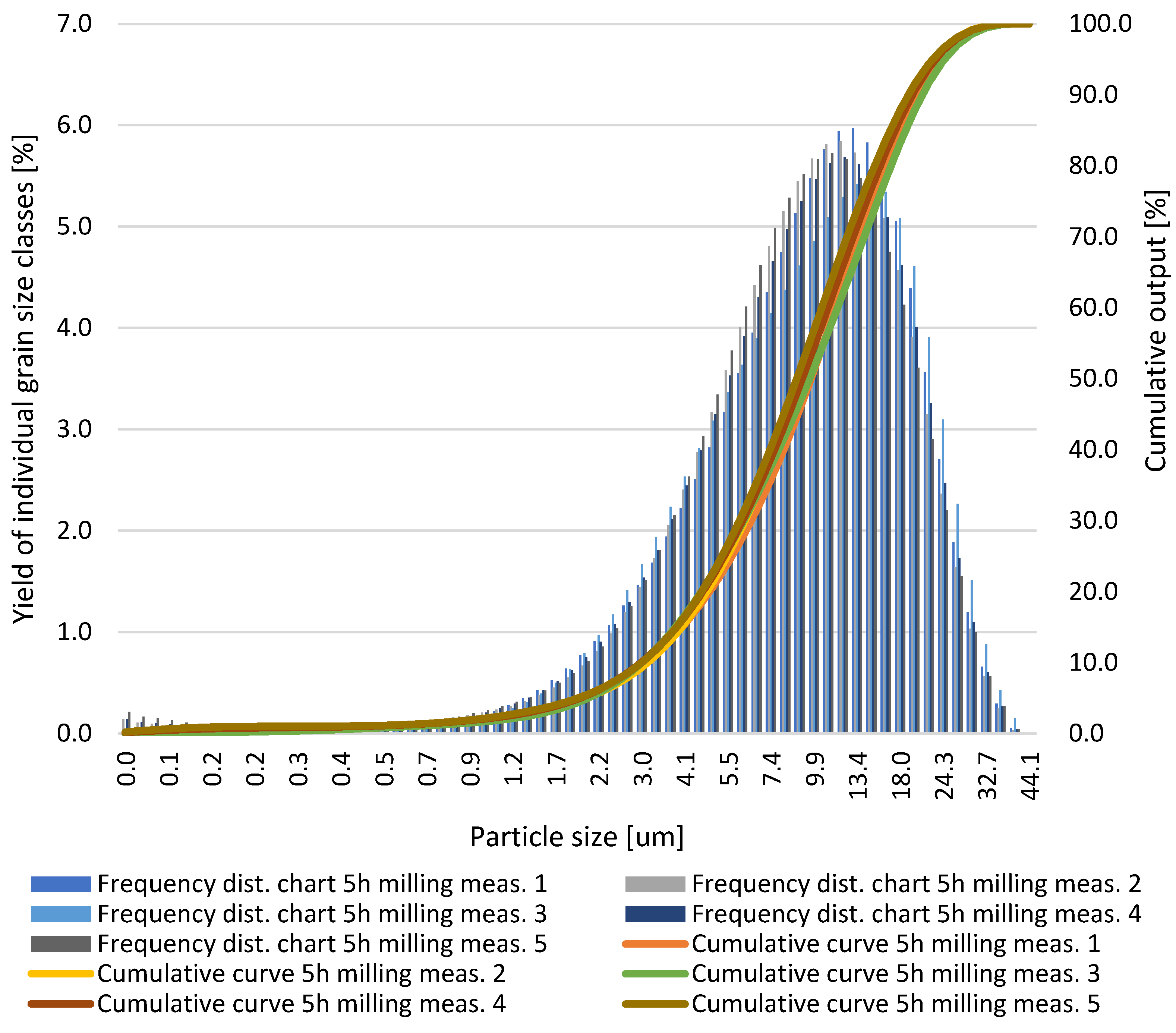
| Particle Diameters | Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Test 4 | Test 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d10, μm | 3.24 | 3.29 | 3.17 | 3.15 | 3.16 |
| d50, μm | 10.22 | 9.63 | 10.12 | 9.62 | 9.25 |
| d90, μm | 21.12 | 20.41 | 22.16 | 20.64 | 20.10 |

| Particle Diameters | Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Test 4 | Test 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d10, μm | 2.73 | 2.63 | 2.56 | 2.49 | 2.46 |
| d50, μm | 8.10 | 7.74 | 7.78 | 7.52 | 7.55 |
| d90, μm | 19.61 | 17.74 | 16.73 | 16.90 | 17.06 |
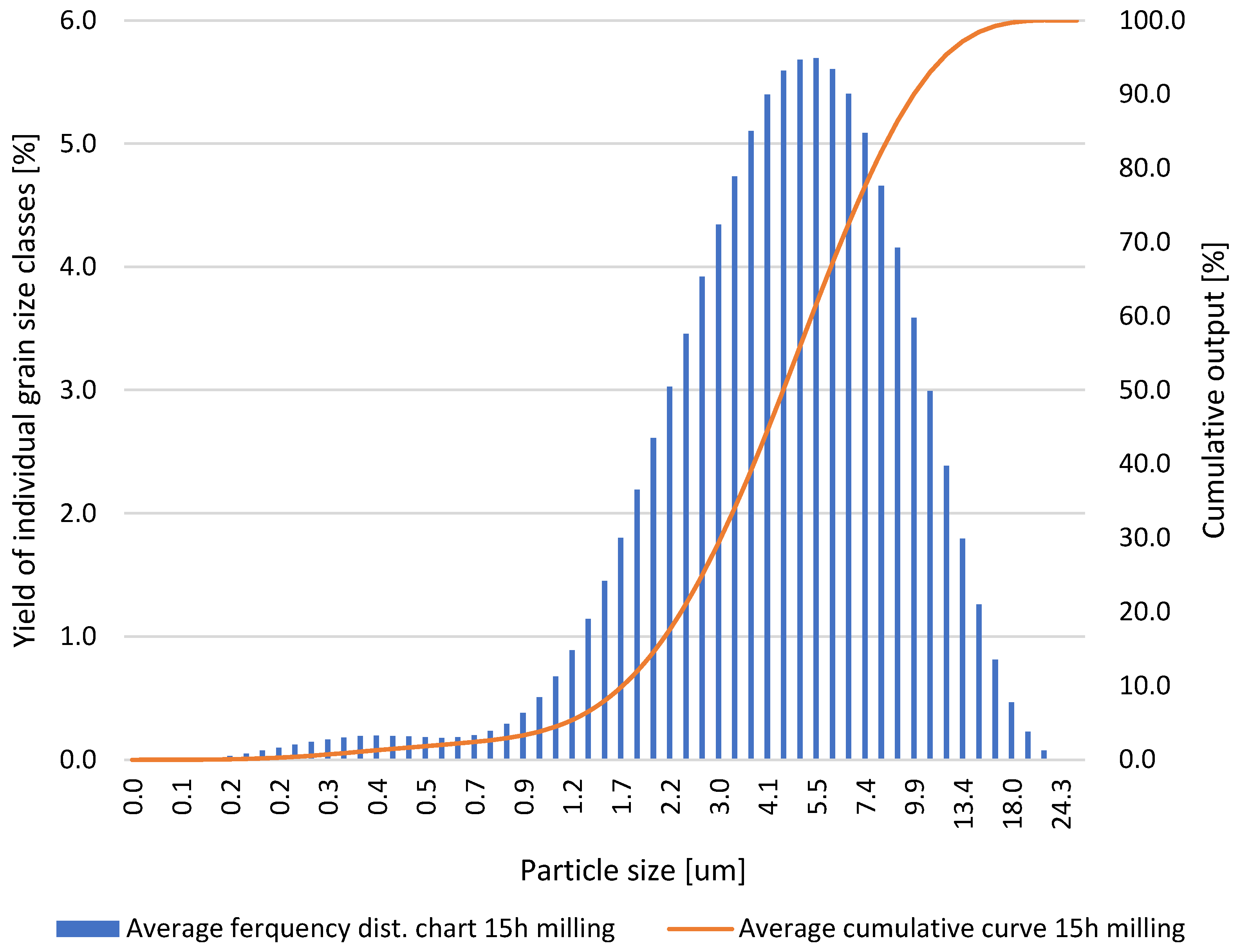
| Particle Diameters | Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Test 4 | Test 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d10, μm | 1.78 | 1.77 | 1.76 | 1.76 | 1.74 |
| d50, μm | 4.58 | 4.67 | 4.69 | 4.79 | 4.78 |
| d90, μm | 10.06 | 10.39 | 10.46 | 10.72 | 10.57 |
3.2. Economic and Environmental Aspects of Neodymium Alloy Production
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



References
- Friebe, P.; Suponik, T.; Nuckowski, P.M. Research on Hard Drives in the Context of the Construction of Shredding Knives in the Recovery of Rare Earth Elements. In Global Challenges for a Sustainable Society; Benítez-Andrades, J.A., García-Llamas, P., Taboada, Á., Estévez-Mauriz, L., Baelo, R., Eds.; Springer Proceedings in Earth and Environmental Sciences; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 86–97. ISBN 978-3-031-25839-8. [Google Scholar]
- Friebe, P. Przegląd literatury dotyczącej odzysku sproszkowanej mieszaniny stopu NdFeB z ZSEiE. In KOMEKO Konferencja Naukowo-Techniczna Przemysł Przyjazny dla Środowiska; KOMAG Institute of Mining Technology: Gliwice, Poland, 2023; pp. 61–67. ISBN 978-83-65593-32-0. [Google Scholar]
- Friebe, P. Development of a Prototype Shredder for WEEE Equipped with NdFeB Magnets. Min. Mach. 2023, 41, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-T.; Petavratzi, E.; Zils, M.; Einarsson, S.; Morasae, E.K.; Lysaght, O.; Hopkinson, P. Mapping the Flows and Stocks of Permanent Magnets Rare Earth Elements for Powering a Circular Economy in the UK. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 47, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, P.C. Rare Earth Elements and Permanent Magnets (Invited). J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 07A721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- München, D.D.; Veit, H.M. Neodymium as the Main Feature of Permanent Magnets from Hard Disk Drives (HDDs). Waste Manag. 2017, 61, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collocott, S.; Dunlop; Gwan, P.; Kalan, B.; Lovatt, H.; Wu, W.; Watterson, P. Applications of Rare-Earth Permanent Magnets in Electrical Machines: From Motors for Niche Applications to Hybrid Electric Vehicles; University of Technology: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Shewane, P.P.G.; Singh, A.; Gite, M.; Narkhede, A. An Overview of Neodymium Magnets over Normal Magnets for the Generation of Energy. Int. J. Recent Innov. Trends Comput. Commun. 2014, 2, 4056–4059. [Google Scholar]
- Heim, J.W.; Vander Wal, R.L. NdFeB Permanent Magnet Uses, Projected Growth Rates and Nd Plus Dy Demands across End-Use Sectors through 2050: A Review. Minerals 2023, 13, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Ge, J. Global Wind Power Development Leads to High Demand for Neodymium Praseodymium (NdPr): A Scenario Analysis Based on Market and Technology Development from 2019 to 2040. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, K.; Ouyang, X.; Sen, B.; Liu, L.; Dai, T.; Liu, G. Tracking Three Decades of Global Neodymium Stocks and Flows with a Trade-Linked Multiregional Material Flow Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 11807–11817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koese, M.; Parzer, M.; Sprecher, B.; Kleijn, R. Self-Sufficiency of the European Union in Critical Raw Materials for E-Mobility. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 212, 108009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal Filho, W.L.; Kotter, R.; Özuyar, P.G.; Abubakar, I.R.; Eustachio, J.H.P.P.; Matandirotya, N.R. Understanding Rare Earth Elements as Critical Raw Materials. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- München, D.D.; Stein, R.T.; Veit, H.M. Rare Earth Elements Recycling Potential Estimate Based on End-of-Life NdFeB Permanent Magnets from Mobile Phones and Hard Disk Drives in Brazil. Minerals 2021, 11, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, M. An Overview of NdFeB Magnets Recycling Technologies. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2024, 46, 100884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramprasad, C.; Gwenzi, W.; Chaukura, N.; Izyan Wan Azelee, N.; Upamali Rajapaksha, A.; Naushad, M.; Rangabhashiyam, S. Strategies and Options for the Sustainable Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Electrical and Electronic Waste. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 135992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Afiuny, P.; McIntyre, T.; Yih, Y.; Sutherland, J.W. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of NdFeB Magnets: Virgin Production versus Magnet-to-Magnet Recycling. Procedia CIRP 2016, 48, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Afiuny, P.; Dove, S.; Furlan, G.; Zakotnik, M.; Yih, Y.; Sutherland, J.W. Life Cycle Assessment of Neodymium-Iron-Boron Magnet-to-Magnet Recycling for Electric Vehicle Motors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 3796–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omodara, L.; Pitkäaho, S.; Turpeinen, E.-M.; Saavalainen, P.; Oravisjärvi, K.; Keiski, R.L. Recycling and Substitution of Light Rare Earth Elements, Cerium, Lanthanum, Neodymium, and Praseodymium from End-of-Life Applications—A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, S.A.; Yunas, J.; Hashim, A.M. The Effects of Particle Sizes of Neodymium Iron Boron Microstructure on the Magnetic Characteristics. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Regional Symposium on Micro and Nanoelectronics (RSM), Langkawi, Malaysia, 28–30 August 2023; pp. 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu, R.K. Influence of Particle Size of Iron Powder on the Microstructure of Nd–Fe–B Alloy Powder Prepared by Reduction-Diffusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 346, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebe, P.; Suponik, T.; Nuckowski, P.M.; Matusiak, P.; Kowol, D. Sposób Odzysku Metali z Zużytych Dysków Twardych. The Patent Office of the Republic of Poland Patent Application: P.452083, 19 May 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y. A Study on Demagnetization Heat Treatment of Waste Neodymium Iron Boron (NdFeB) Magnets by Using Computer Simulation. PeerJ Mater. Sci. 2023, 5, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuiness, P.J.; Devlin, E.; Harris, I.R.; Rozendaal, E.; Ormerod, J. A Study of Nd-Fe-B Magnets Produced Using a Combination of Hydrogen Decrepitation and Jet Milling. J. Mater. Sci. 1989, 24, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shdiara, T.; Konomi, M.; Watanabe, S. Applications of the Hybrid Ion Milling Method to Neodymium Magnets. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 898–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczyk, M.; Cook, J.S.; Collocott, S.J. Application of High Energy Ball Milling to the Production of Magnetic Powders from NdFeB-Type Alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 1995, 217, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Wong, C.W.Y.; Li, C. Circular Economy Practices in the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Industry: A Systematic Review and Future Research Agendas. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, K.; Parajuly, K.; Wenzel, H. Tracking the Flow of Resources in Electronic Waste—The Case of End-of-Life Computer Hard Disk Drives. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12441–12449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueberschaar, M.; Rotter, V.S. Enabling the Recycling of Rare Earth Elements through Product Design and Trend Analyses of Hard Disk Drives. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2015, 17, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Zhu, N.; Zhu, W.; Liu, B.; Wu, P.; Dang, Z. Efficient Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Discarded NdFeB Magnets by Mechanical Activation Coupled with Acid Leaching. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 25532–25543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Loy, S.; Önal, M.A.R.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. Recovery of Valuable Metals from NdFeB Magnets by Mechanochemically Assisted Ferric Sulfate Leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 191, 105154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TRADING ECONOMICS. 20 Million Indicators from 196 Countries. Available online: https://tradingeconomics.com/ (accessed on 18 March 2025).
- SMM. Steel, Aluminum, Nickel, Rare Earth, New Energy, Copper Prices Charts and News-Shanghai Metals Market. Available online: https://www.metal.com/ (accessed on 25 April 2025).



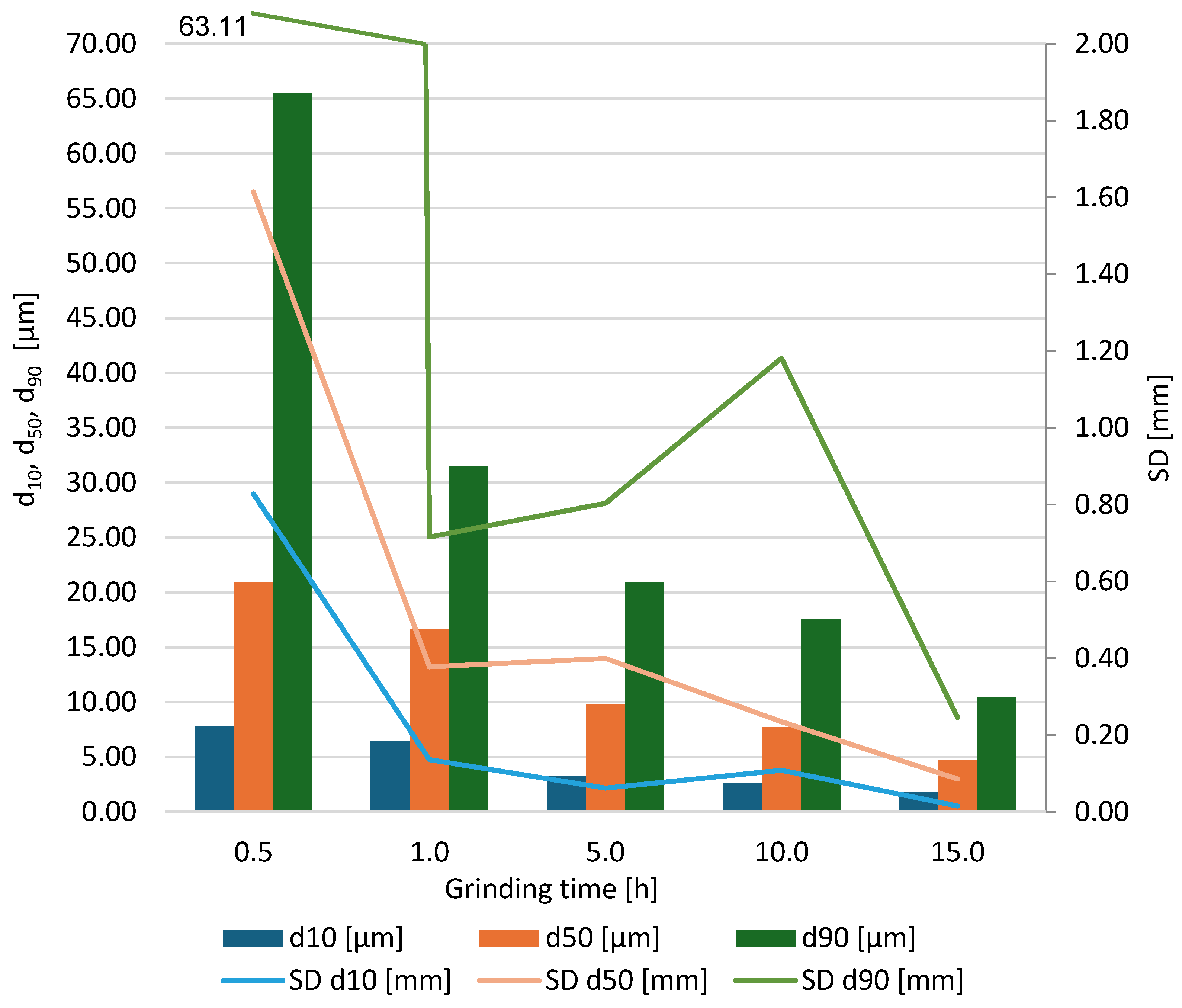
| Grinding Time [h] | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle Diameters | 0.5 | 1.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 | |||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| d10, μm | 7.83 | 0.83 | 6.42 | 0.14 | 3.20 | 0.06 | 2.57 | 0.11 | 1.76 | 0.02 |
| d50, μm | 20.9 | 1.61 | 16.6 | 0.38 | 9.77 | 0.40 | 7.74 | 0.23 | 4.70 | 0.09 |
| d90, μm | 65.4 | 63.11 | 31.5 | 0.72 | 20.8 | 0.80 | 17.6 | 1.18 | 10.44 | 0.25 |
| Grinding Time [h] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 1.0 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 | |
| U, - | 2.75 | 1.51 | 1.82 | 1.94 | 1.85 |
| S50, - | 34.9 | 43.9 | 74.7 | 94.3 | 155.3 |
| Mass of HDDs Collected per 1 Million Inhabitants of Southern Poland | Mass of Nd, Pr, and Dy in HDDs Collected per 1 Million Inhabitants in Southern Poland | Average Nd, Pr, and Dy Content in HDD per 1 Million Inhabitants in Southern Poland | Estimated Value of Nd, Pr, and Dy in HDDs per 1 Million Inhabitants of Southern Poland | Estimated Value Nd, Pr, and Dy in HDDs Collected in Poland in 2024 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t/year | kg/year | kg/year | USD/year | USD/year | ||
| 13.6 | 125.2 | Nd | Pr | Dy | 9607.04 | 360,264.00 |
| 99.3 | 15.0 | 10.9 | ||||
| Process | Device Operation Time for 1 kg of Feed for Each Process in kg/h | Nominal Power in kW | Energy Consumption in kWh/kg Feed | Energy Consumption in kWh/kg HDD | Duste Mission, g/m2 h | Noise Emission, dBA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shredding | 62.85 | 5.54 | 0.0880 | 0.0880 | 0.015 | 82.1 |
| Passive magnetic separation | 93.36 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Demagnetisation | 0.18 | 2.0 | 5.8824 | 0.0857 | - | - |
| Granulometric classification I | 0.36 | 0.2 | 0.5348 | 0.0041 | 0.011 | 78.2 |
| Grinding I | 216.00 | 0.25 | 0.0075 | 0.000058 | 0.02 | 75.7 |
| Granulometric classification II | 0.36 | 0.2 | 0.5348 | 0.0041 | 0.01 | 77.7 |
| Grinding II | 0.008 | 1.0 | 100.00 | 0.7692 | - | 84.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Friebe, P.; Suponik, T.; Nuckowski, P.M.; Kremzer, M.; Baron, R.; Matusiak, P.; Kowol, D. Sustainable Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Hard Disks: Grinding NdFeB Magnets and Financial and Environmental Analysis. Materials 2025, 18, 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122697
Friebe P, Suponik T, Nuckowski PM, Kremzer M, Baron R, Matusiak P, Kowol D. Sustainable Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Hard Disks: Grinding NdFeB Magnets and Financial and Environmental Analysis. Materials. 2025; 18(12):2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122697
Chicago/Turabian StyleFriebe, Paweł, Tomasz Suponik, Paweł M. Nuckowski, Marek Kremzer, Rafał Baron, Piotr Matusiak, and Daniel Kowol. 2025. "Sustainable Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Hard Disks: Grinding NdFeB Magnets and Financial and Environmental Analysis" Materials 18, no. 12: 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122697
APA StyleFriebe, P., Suponik, T., Nuckowski, P. M., Kremzer, M., Baron, R., Matusiak, P., & Kowol, D. (2025). Sustainable Recovery of Rare Earth Elements from Hard Disks: Grinding NdFeB Magnets and Financial and Environmental Analysis. Materials, 18(12), 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18122697







