Optimization of Properties of Calcium Hexaluminate-Based Insulating Castables with Calcium Aluminate Cement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation Method
2.3. Characterization and Testing
3. Results
3.1. Phase Composition
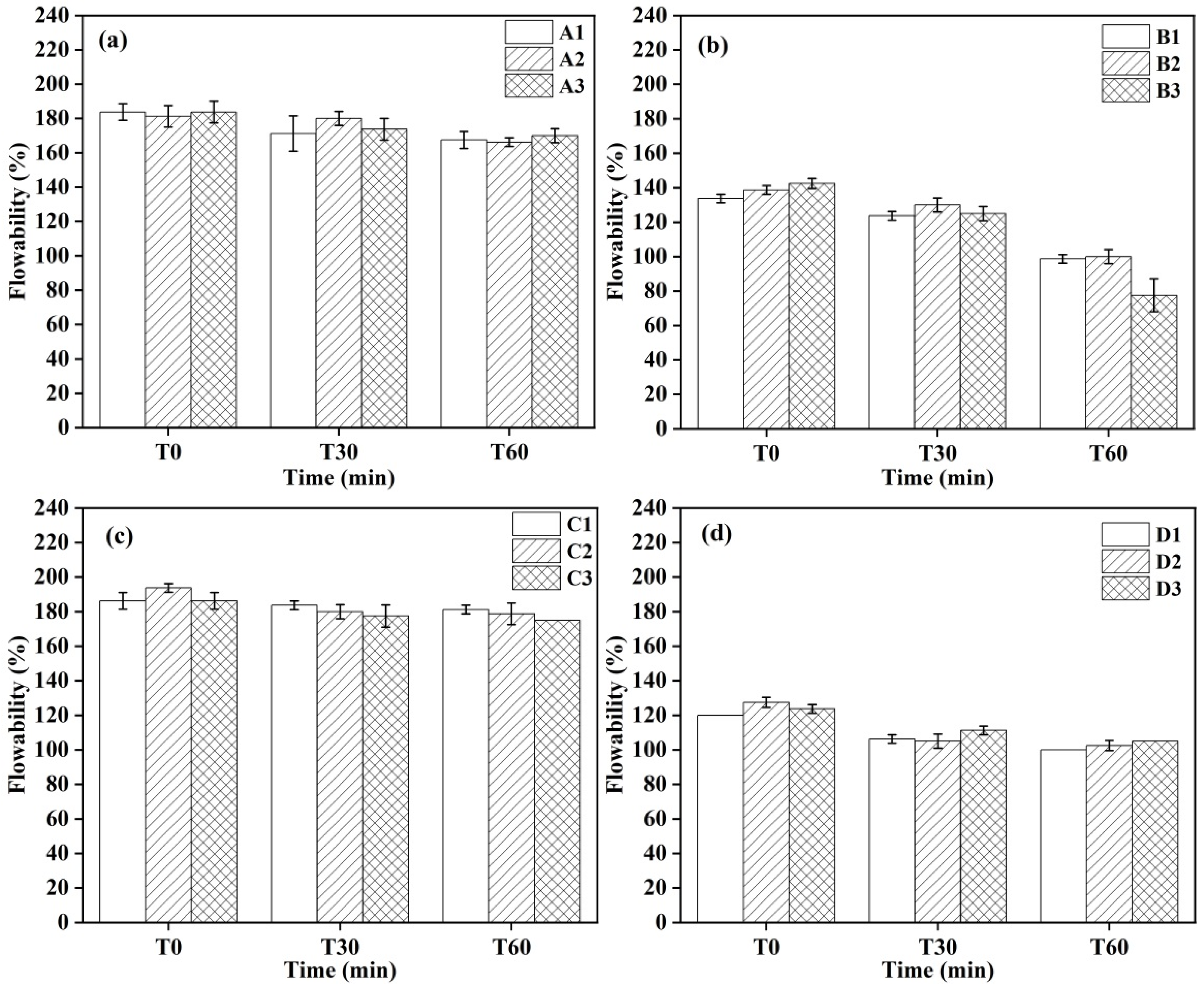
3.2. Flowability
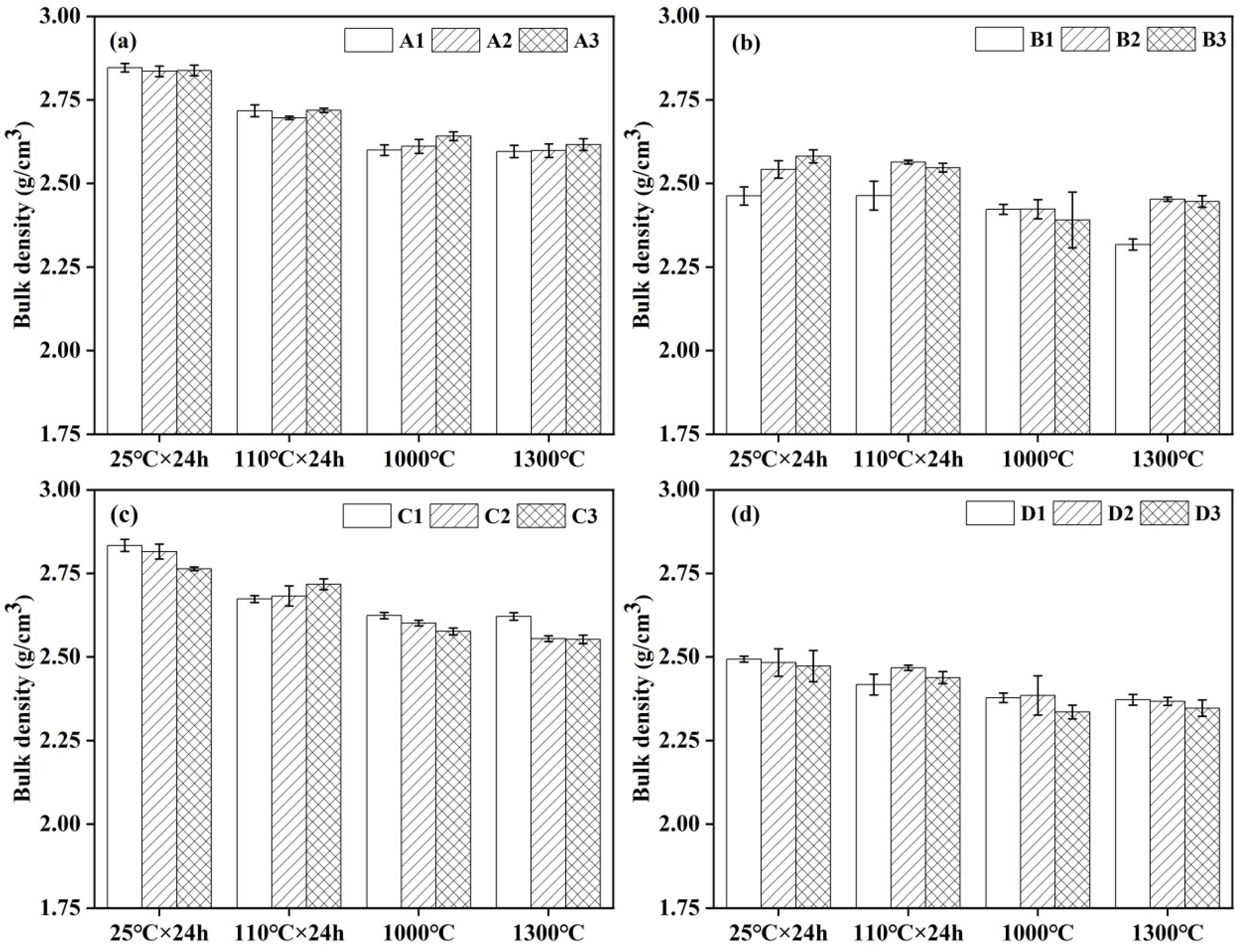
3.3. Bulk Density and Apparent Porosity
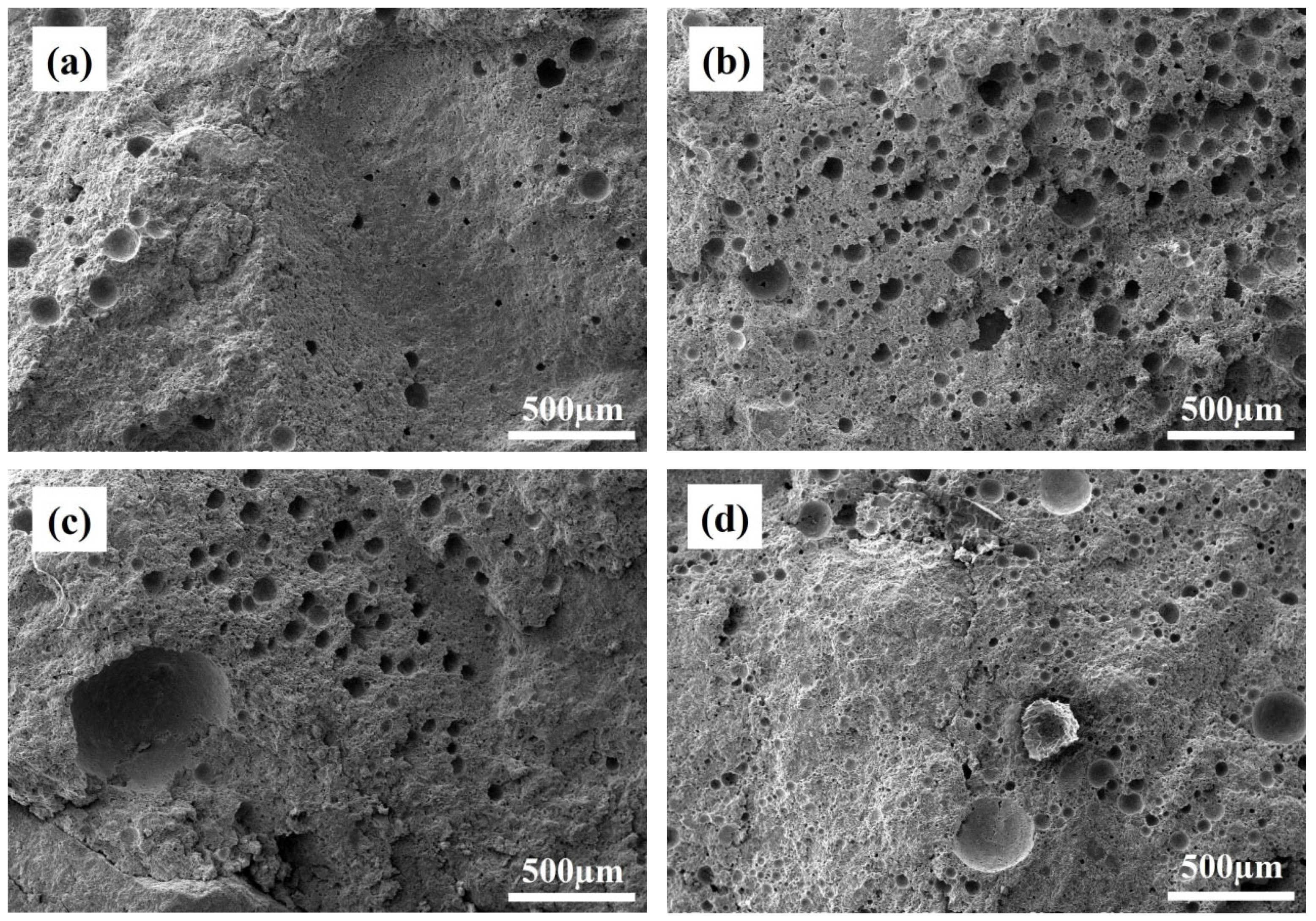
3.4. Microstructure
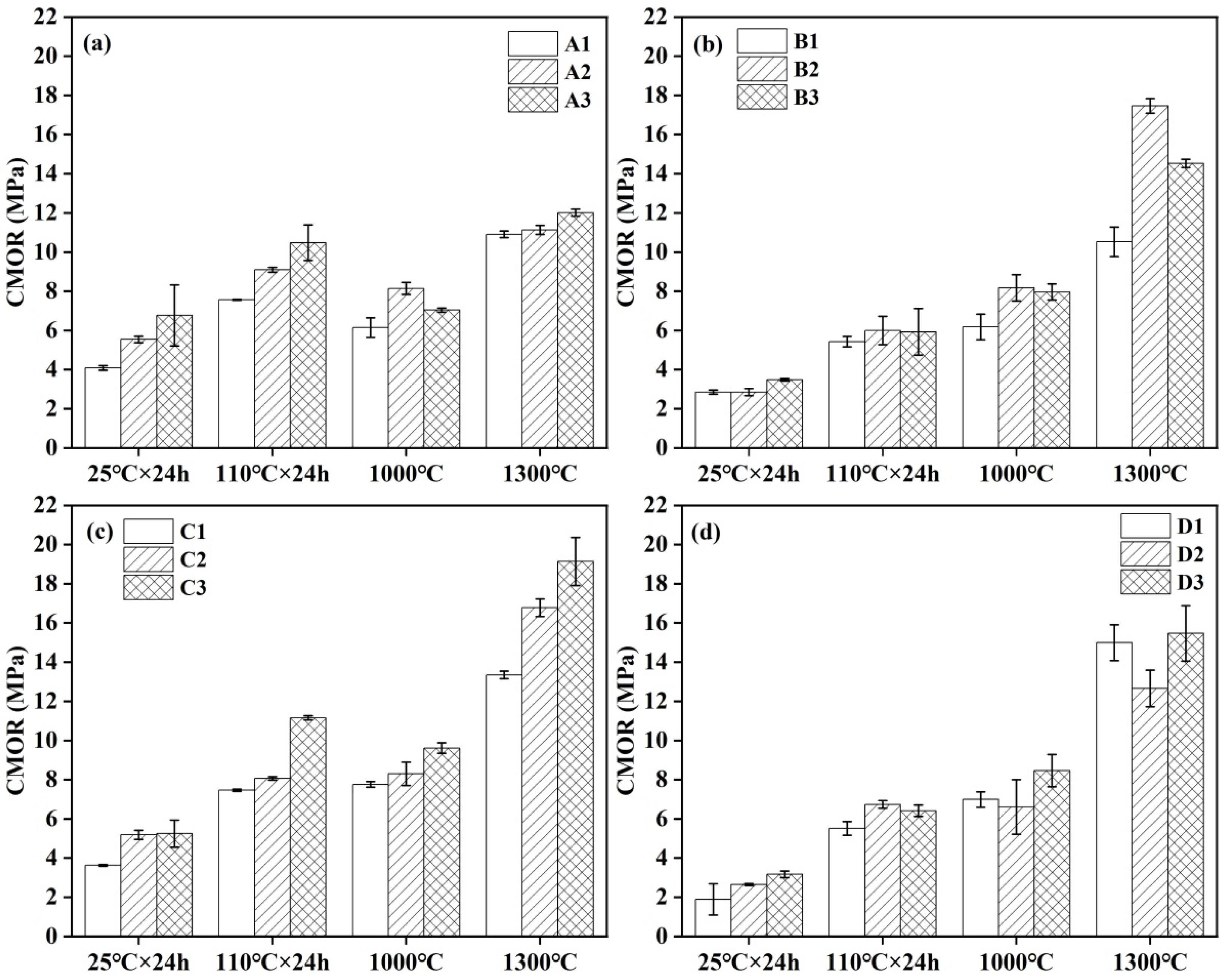
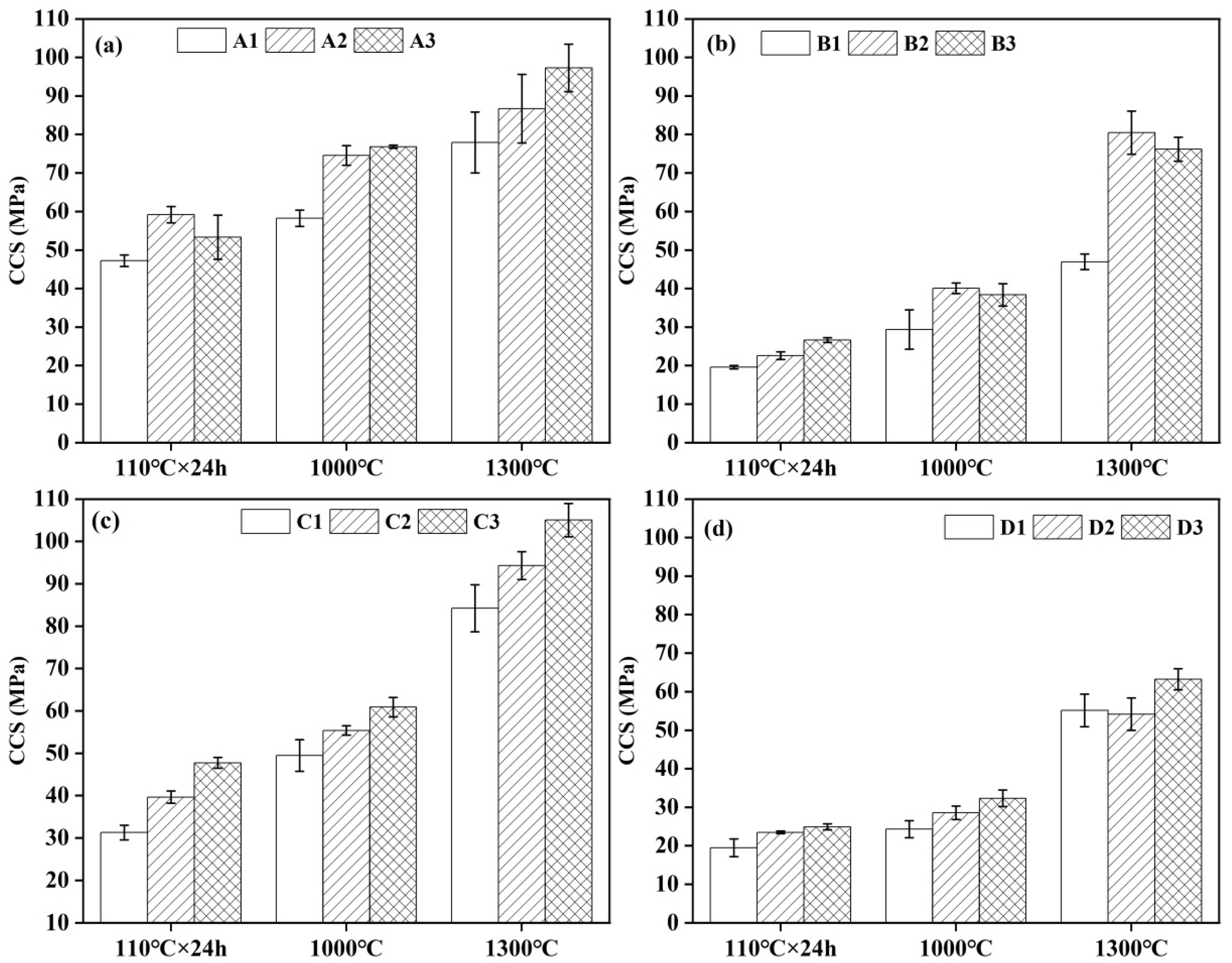
3.5. Strength
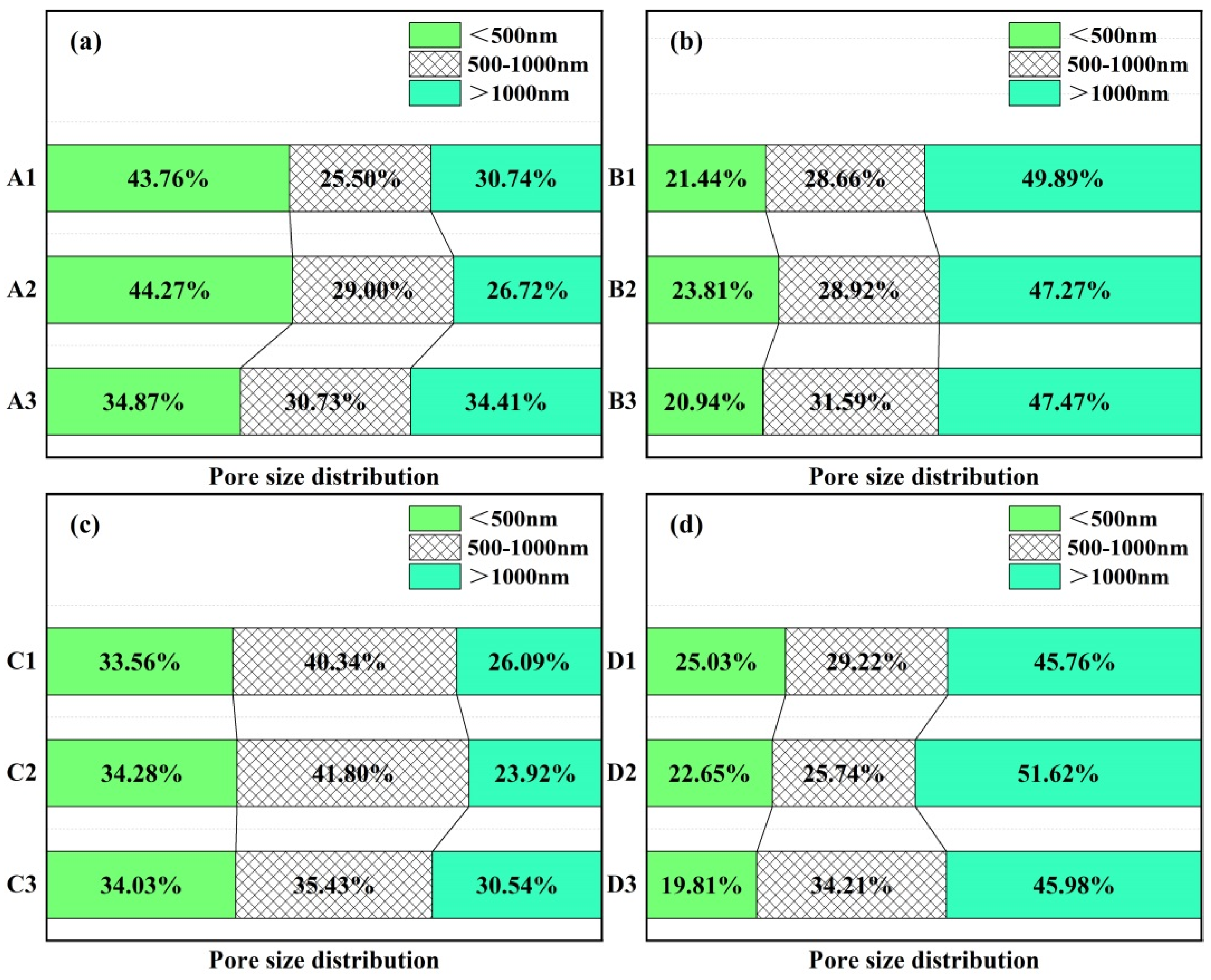
3.6. Pore Size Distribution
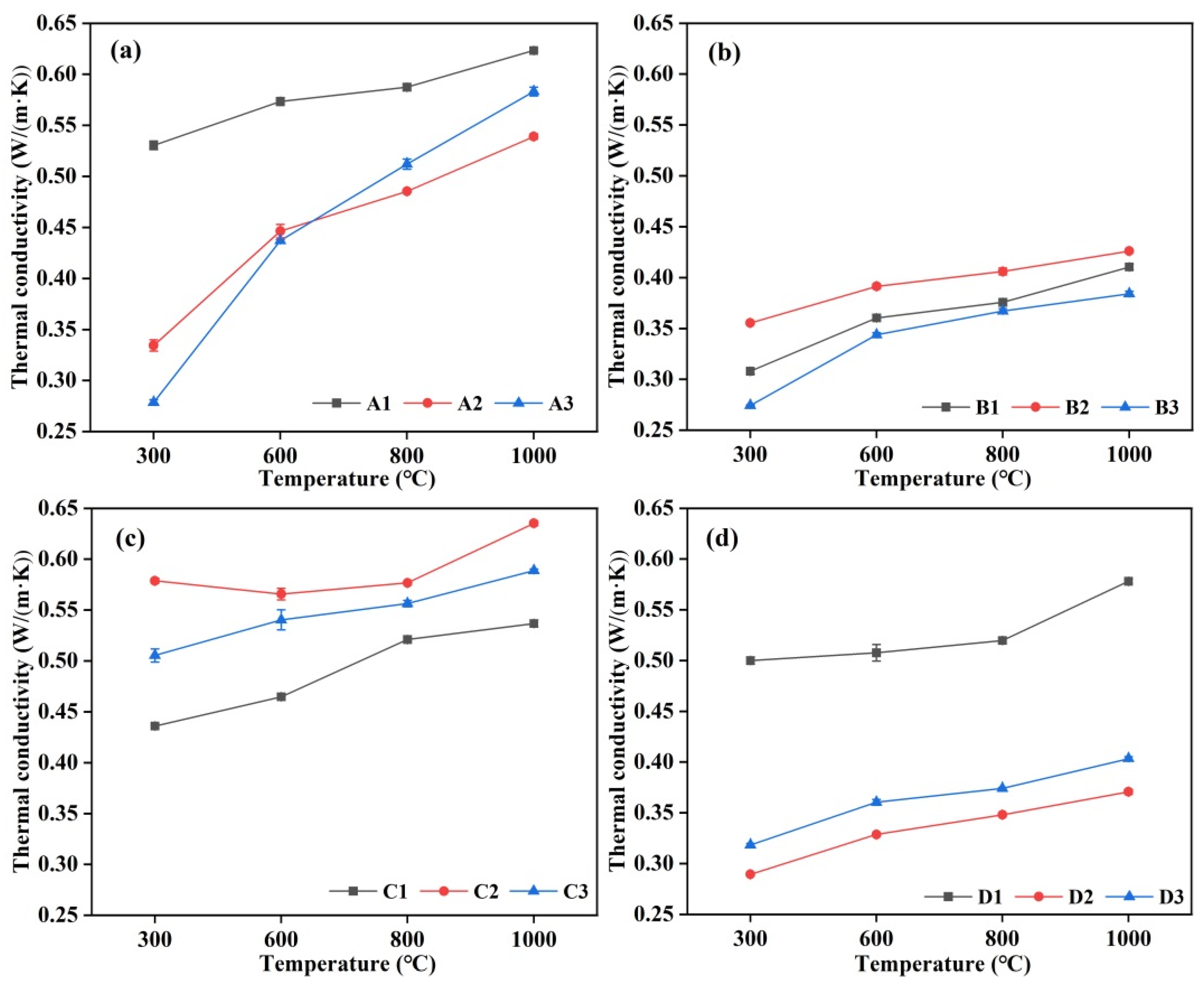
3.7. Thermal Conductivity
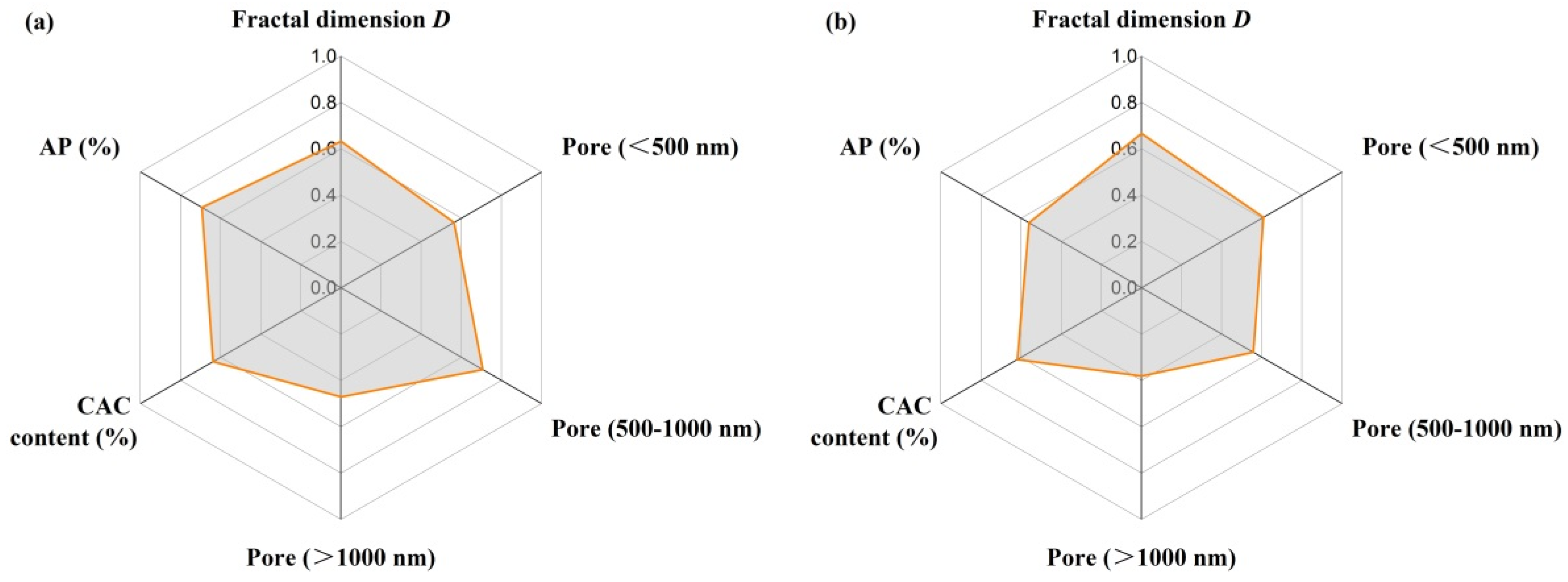
3.8. Grey Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uehara, T.; Kurihara, T. Transition of refractory technologies for furnaces and recent insulating technologies. Nippon Steel Tech. Rep. 2020, 125, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.Y.; Wang, E.H.; Hou, X.M.; Kang, J.Y.; Yang, T.; Liang, T.X.; Bei, G. Preparation of Zr4+ doped calcium hexaaluminate with improved slag penetration resistance. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 104, 4854–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, B.; Jia, Y.; Chen, J.; Feng, J.; Ren, B.; Yin, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gong, D. Slag resistance mechanism of CaO·6Al2O3 refractory and its effect on inclusions of aluminum deoxidized steel. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2022, 19, 3323–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, B.A.; Pena, P.; de Aza, A.H.; Sainz, M.A.; Caballero, A. Corrosion mechanism of polycrystalline corundum and calcium hexaluminate by calcium silicate slags. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2008, 29, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, A.P.; Consoni, L.B.; Pagliosa, C.; Aneziris, C.G.; Pandolfelli, V.C. Sintering effect of calcium carbonate in high-alumina refractory castables. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 10486–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Ding, D.; Xiao, G.; Lei, C.; Luo, J.; Chen, J.; Zang, Y. Preparation of Al2O3@CaCO3 aggregates and its effects on the thermal shock resistance of Al2O3-MgO castables. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2021, 18, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomão, R.; Ferreira, V.L.; de Oliveira, I.R.; Souza, A.D.; Correr, W.R. Mechanism of pore generation in calcium hexaluminate (CA6) ceramics formed in situ from calcined alumina and calcium carbonate aggregates. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 36, 4225–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Chan, H.M.; Soni, K.K. Control of calcium hexaluminate grain morphology in in-situ toughened ceramic composites. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 3223–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sako, E.; Braulio, M.; Zinngrebe, E.; Laan, S.R.V.D.; Pandolfelli, V.C. In-depth microstructural evolution analyses of cement-bonded spinel refractory castables: Novel insights regarding spinel and CA6 formation. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiraprabha, K.; Kosuke, O.; Kouichiro, W.; Takeshi, S. Control of hexagonal plate-like microstructure of in-situ calcium hexaluminate in monolithic refractories. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2018, 6, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.C.; Yan, S.; Li, W.; Jia, Q. Effect of adding calcium hexaaluminate particles on the properties of corundum-spinel castables. Refractories 2015, 49, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.T.; Wang, Z.Q.; Qin, S.M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhou, W.Z. Development and application of new generation of calcium hexaaluminate castables. Refractories 2024, 58, 53–56. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, T.; Wang, Q.; Li, B. Effects of cement content on the microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of cement-bonded corundum castables. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 4634–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piippo, A.; Ruotanen, K.; Visuri, V.-V.; Poutiainen, N.; Heikkinen, E.-P. Experimental study on the effect of calcium aluminate cement addition on the drying and physical properties of refractory castables containing colloidal silica. Materials 2024, 17, 5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sarkar, R. Alumina-spinel castable for steel ladles: An overview. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2023, 20, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.E.; Vieira, W.; Zhang, S.; Ahai, K.G.; Sarpoolaky, H.; Parr, C. Castable refractory concretes. Metall. Rev. 2013, 46, 145–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, P.; Li, X.; Zhu, B. Effect of micro-spinel powders addition on the microstructure and properties of alumina refractory castables. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 2989–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, N.Y.; Zaki, Z.I.; Elkader, O.H.A. Chemical activation of calcium aluminate cement composites cured at elevated temperature. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2012, 34, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Zhu, L.; Shang, X.; Ding, D.; Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Ye, G. Effect of particle size of calcium aluminate cement on volumetric stability and thermal shock resistance of CAC-bonded castables. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 772, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonovič, V.; Kerienė, J.; Boris, R.; Aleknevičius, M. The effect of temperature on the formation of the hydrated calcium aluminate cement structure. Procedia Eng. 2013, 57, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukrainczyk, N.; Matusinovic, T.; Kurajica, S.; Zimmermann, B.; Sipusic, J. Dehydration of a layered double hydroxide-C2AH8. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 464, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, F.A.; Innocentini, M.D.; Miranda, M.F.; Valenzuela, F.A.; Pandolfelli, V.C. Drying behavior of hydratable alumina-bonded refractory castables. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 24, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Luo, W.; Xia, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhao, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Yuan, W. Convenient preparation of calcium hexaluminate based castables with low thermal conductivity and sufficient strength. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2024, 21, 2818–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YB/T 5202.1-2003; Preparation of Specimen for Unshaped Refractories Part 1: Refractory Castables. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 401–406.
- GB/T 4513.4-2017; Monolithic (Unshaped) Refractory Products―Part 4: Determination of Consistency of Castables. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB/T 5072-2008; Refractories―Determination of Cold Compressive Strength. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 59–68.
- GB/T 3001-2017; Refractory Products―Determination of modulus of rupture at ambient temperature. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- GB/T 2997-2015; Test Method for Bulk Density, Apparent Porosity and True Porosity of Dense Shaped Refractory Products. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- GB/T 5988-2022; Refractory Products―Determination of Permanent Change in Dimensions on Heating. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- YB/T 4130-2005; Refractory Materials―Determination of Thermal Conductivity. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 365–371.
- Ren, B.; Zheng, S.; Ping, L.; Wang, M.; Dai, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, S.; Wu, X. Re-calibrating the mercury-intrusion-porosimetry-measured pore size distribution of coals: A novel method for calculating the matrix compression coefficient. Processes 2024, 12, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Ding, D.; Xiao, G.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Kang, J.; Chong, X.; Lei, C.; Luo, J.; Zheng, X. Gas permeability of alumina-spinel refractory castables bonded with hydratable magnesium carboxylate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 106, 7618–7631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jin, M.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S. Pore structure and fractal analysis of the influence of fly ash and silica fume on the mechanical property and abrasion resistance of concrete. Fractals 2021, 29, 2140003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Grey correlation analysis between strength of slag cement and particle fractions of slag powder. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2007, 29, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Li, R.; Hu, M.; Zou, L. Determination of low-temperature crack control parameter of binding asphalt materials based on gray correlation analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 217, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Gr, Y.; Feng, D. The influence of shrinkage-reducing agent solution properties on shrinkage of cementitious composite using grey correlation analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F. Research on the identification coefficient of relational grade for grey system. Syst. Eng.-Theory Pract. 1997, 17, 50–55. [Google Scholar]




| Raw Materials | Recipe Numbers | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | C1 | C2 | C3 | D1 | D2 | D3 | ||
| CA6 | <5 mm | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 |
| <0.074 mm | 20 | 19 | 18 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 20 | 19 | 18 | |
| Alumina bubbles (0.5–0.2 mm) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| Calcined alumina (D50 = 5 μm) | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | |
| Reactive alumina (D50 = 1.5 μm) | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | |
| Calcium aluminate cement (Secar71) | 8 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
| Dispersant (WSM-M) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| Air-entraining agent (AEA2066) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | |
| Foam stabilizer (MT 400 PFV) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | |
| Water addition | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.8 | 10.8 | 10.8 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.8 | 10.8 | 10.8 | |
| Sample | A1 | A2 | A3 | B1 | B2 | B3 | C1 | C2 | C3 | D1 | D2 | D3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fractal dimensions | 2.820 | 2.805 | 2.800 | 2.713 | 2.829 | 2.816 | 2.844 | 2.847 | 2.875 | 2.775 | 2.734 | 2.784 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, Y.; Ding, C.; Luo, W.; Yang, H.; Yuan, W. Optimization of Properties of Calcium Hexaluminate-Based Insulating Castables with Calcium Aluminate Cement. Materials 2025, 18, 2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102354
Xia Y, Ding C, Luo W, Yang H, Yuan W. Optimization of Properties of Calcium Hexaluminate-Based Insulating Castables with Calcium Aluminate Cement. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102354
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Yufeng, Cuijiao Ding, Wei Luo, Haizhen Yang, and Wenjie Yuan. 2025. "Optimization of Properties of Calcium Hexaluminate-Based Insulating Castables with Calcium Aluminate Cement" Materials 18, no. 10: 2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102354
APA StyleXia, Y., Ding, C., Luo, W., Yang, H., & Yuan, W. (2025). Optimization of Properties of Calcium Hexaluminate-Based Insulating Castables with Calcium Aluminate Cement. Materials, 18(10), 2354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102354






