Optimizing the Manufacturing Process Control of Si-Based Soft Magnetic Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The selection of Fe-Si-based SMC powders with varying Si contents and formulation of an experimental design considering major influencing process parameters.
- A microstructural analysis and property evaluation of the Fe-Si powders.
- Experimental fabrication of toroidal cores according to the established design, followed by an analysis of the effects of each major parameter on the magnetic and physical characteristics of resultant compacts.
- The identification of dominant factors using Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) analysis.
- A simulation-based analysis to assess internal stress and density deviation, with subsequent verification of the simulation reliability via a comparison with experimental data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fe-Si Material
2.1.1. Mechanical Properties of Fe-Si
2.1.2. Thermal Properties of Fe-Si
2.1.3. Chemical Composition and Crystal Structures of Fe-Si
2.1.4. Powder Morphology Analysis of Fe-Si
2.2. Experiment Methods
2.2.1. Coating Conditions and Insulation Composition
2.2.2. Experimental Factor Settings
2.2.3. Measurement Method
3. Powder Compaction Simulation
3.1. Yield Criteria for Porous Materials
3.2. Simulation Condition
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Results
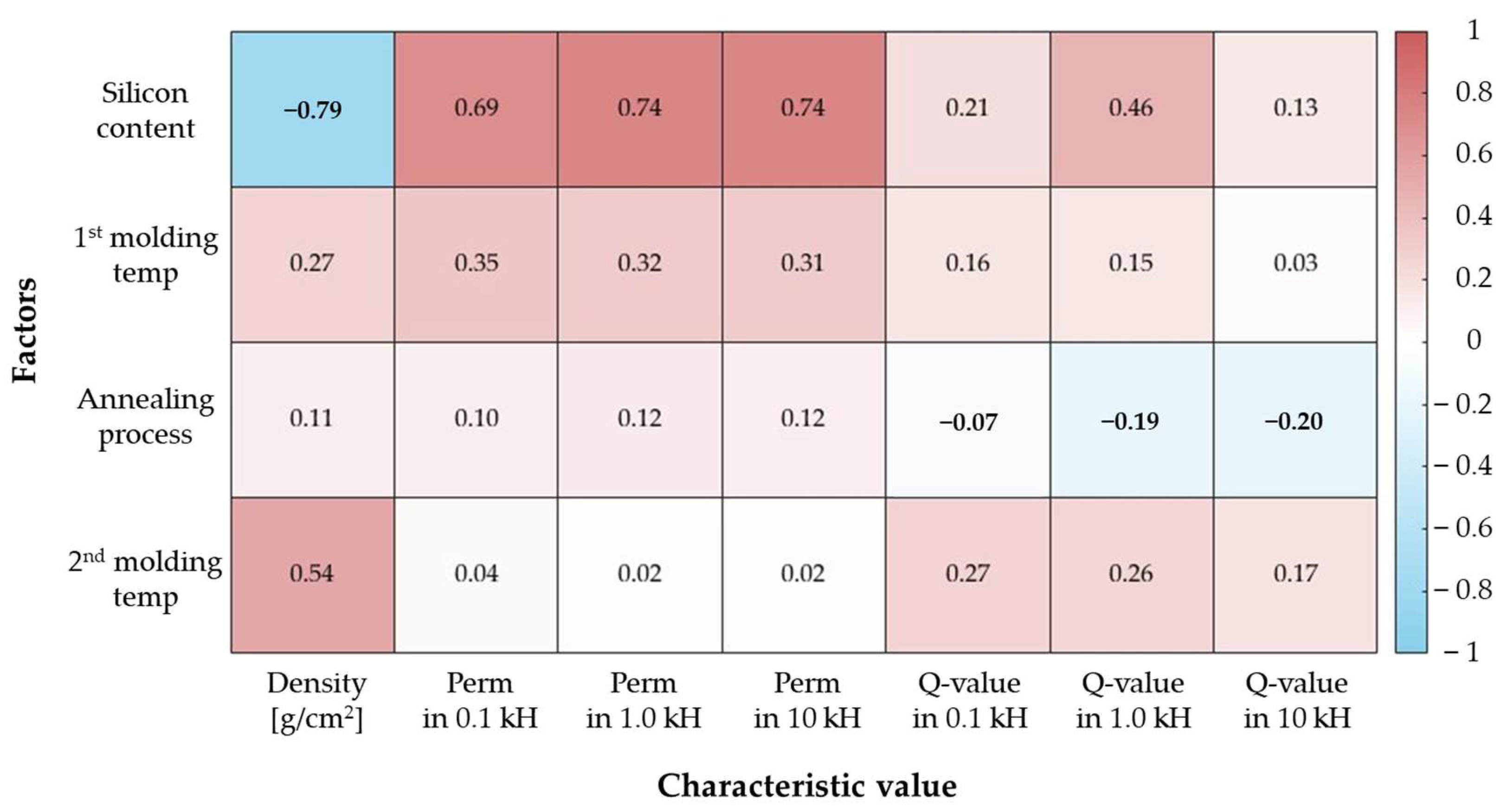
4.2. PCC Analysis
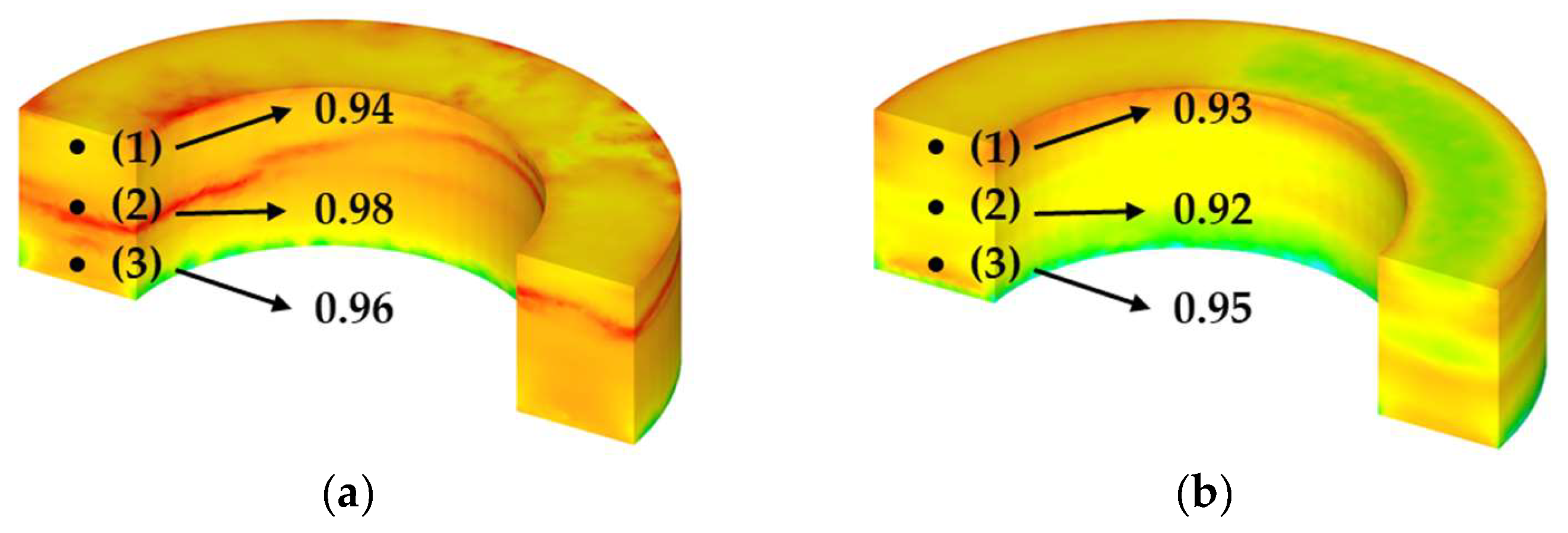
4.3. Simulation Result
4.4. Comparison Between Simulation and Bulk Prototype
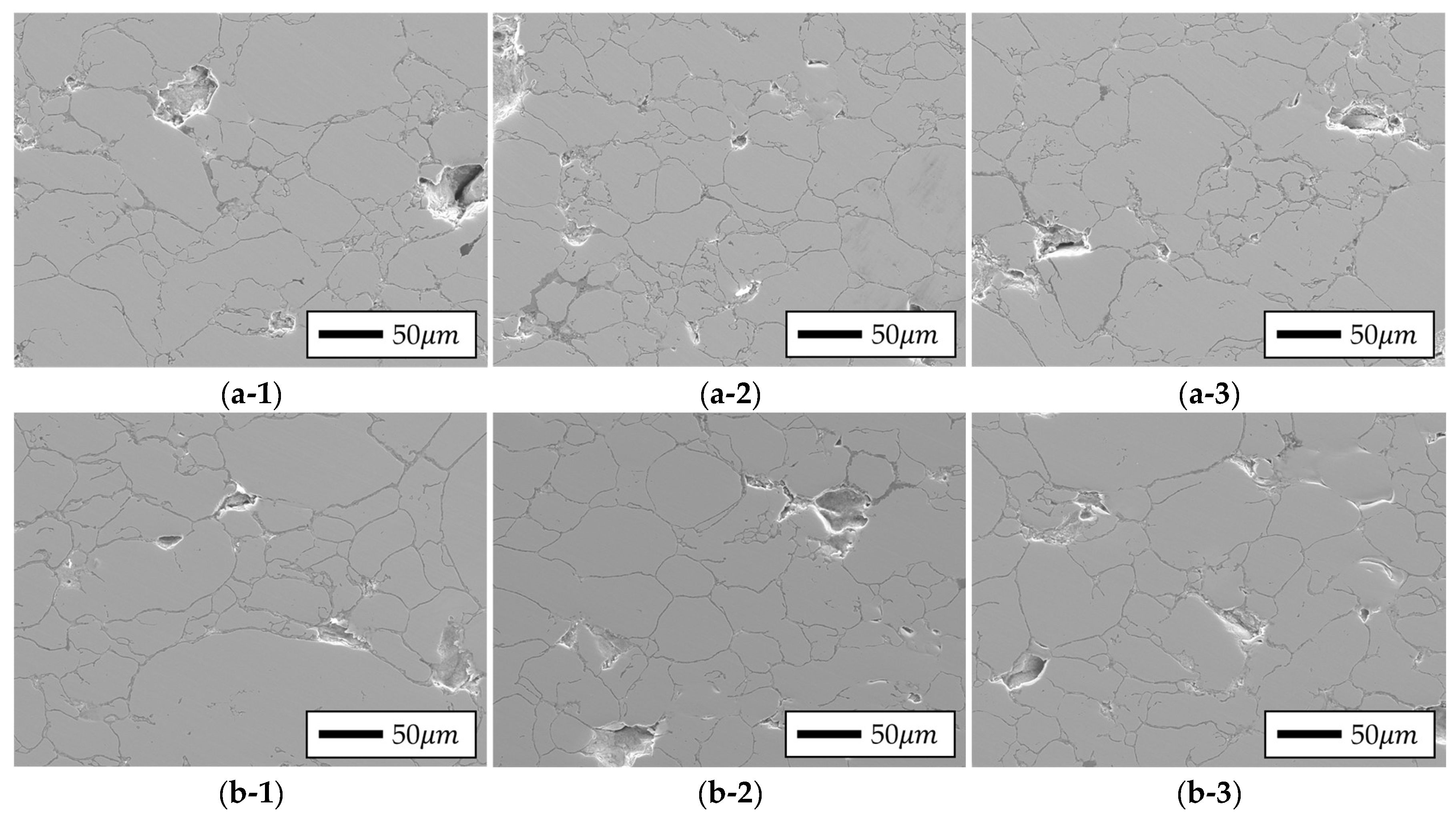
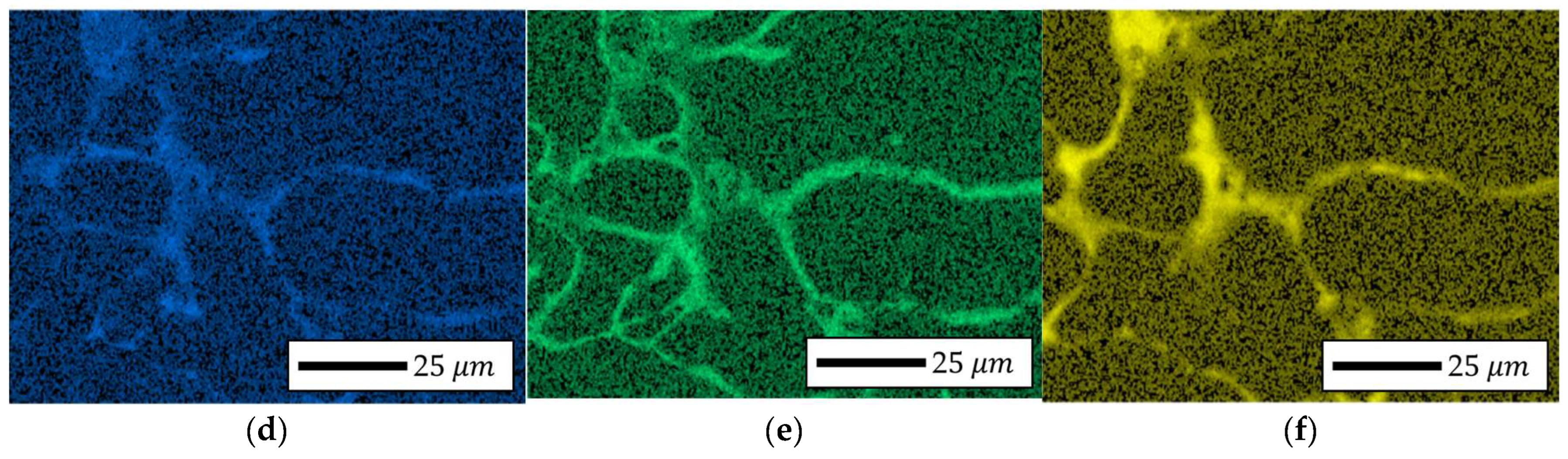
4.4.1. Bulk Morphology Analysis of Fe-Si
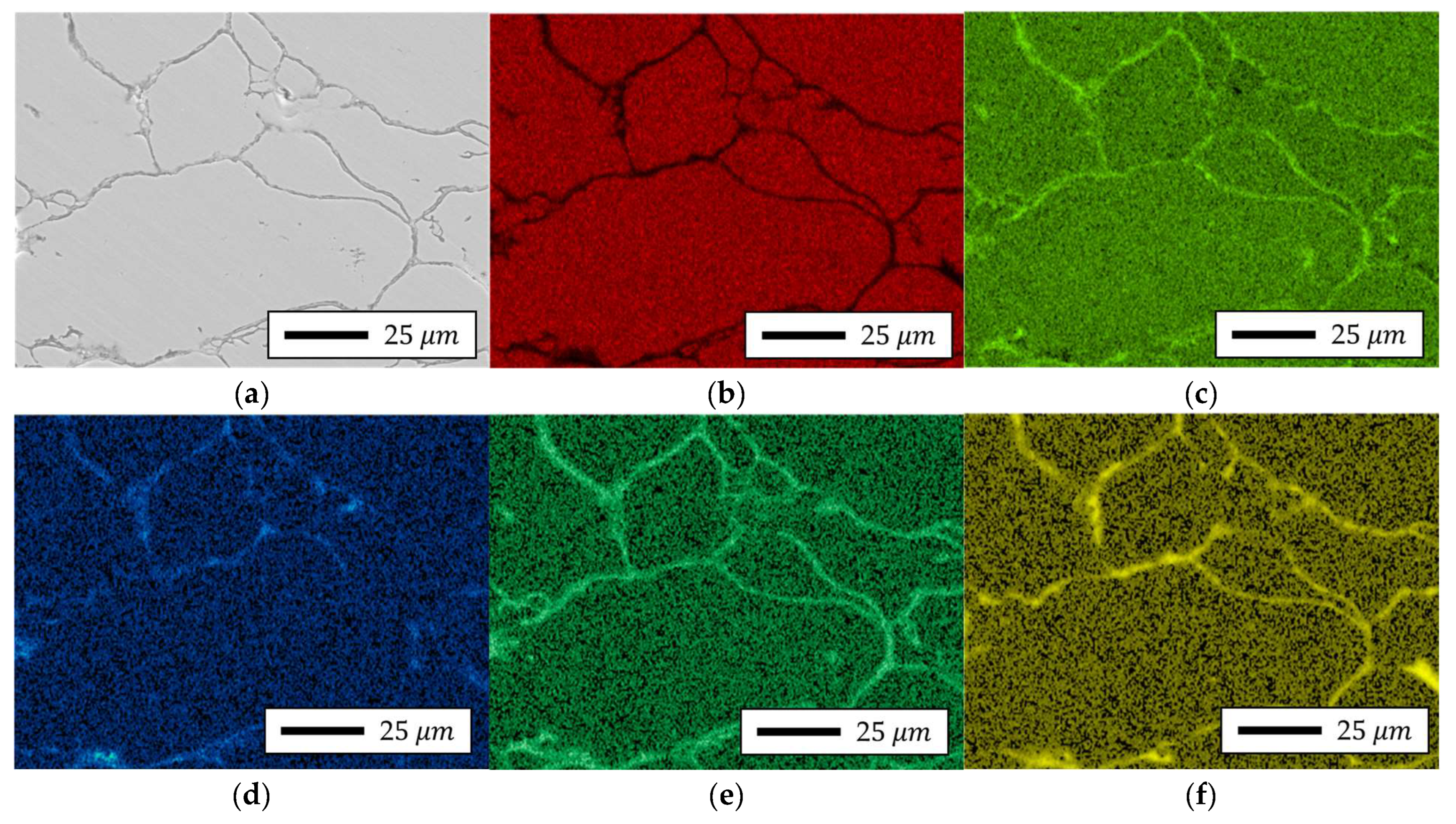
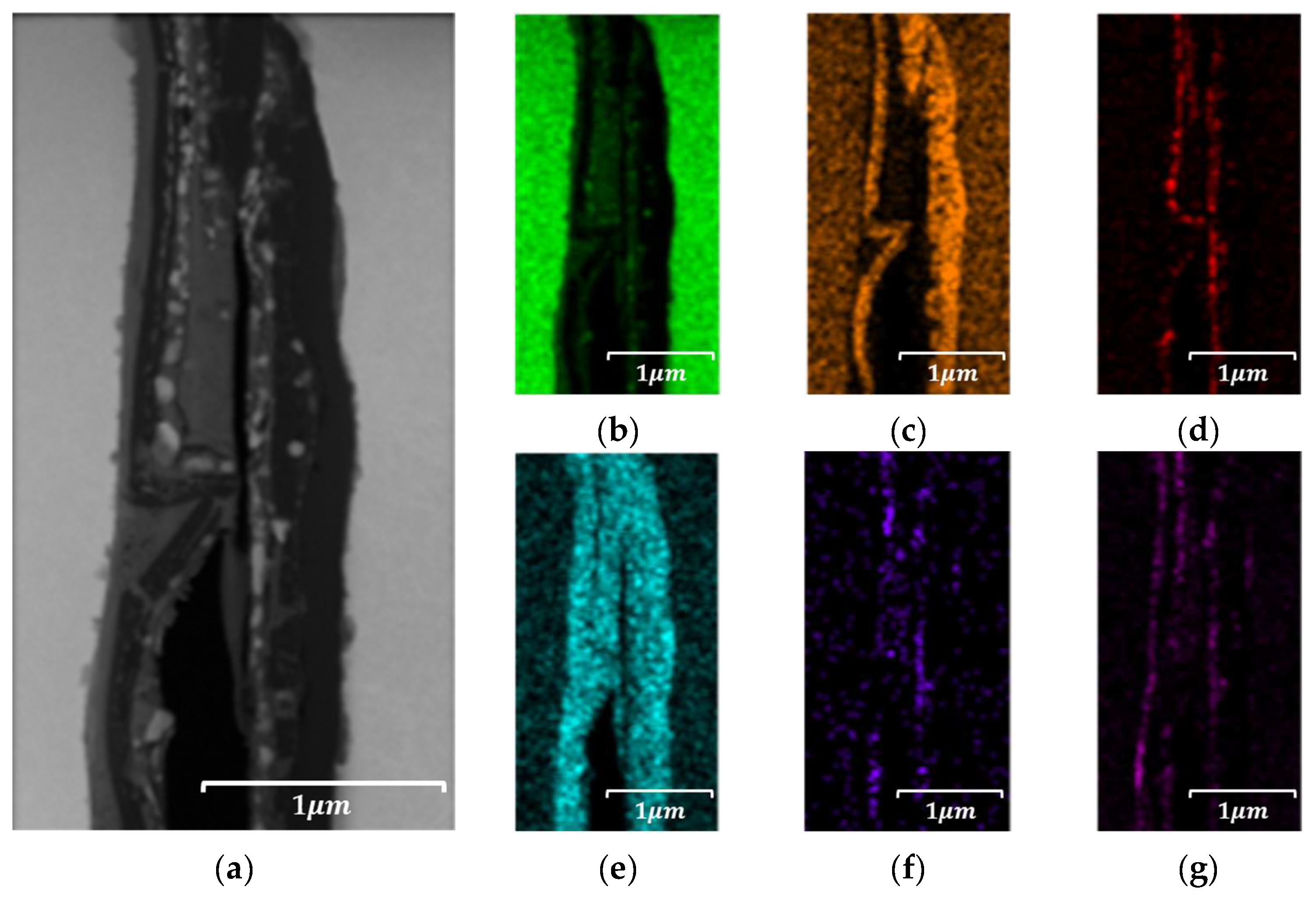
4.4.2. Localized Chemistry at Interfaces of Bulk Prototype
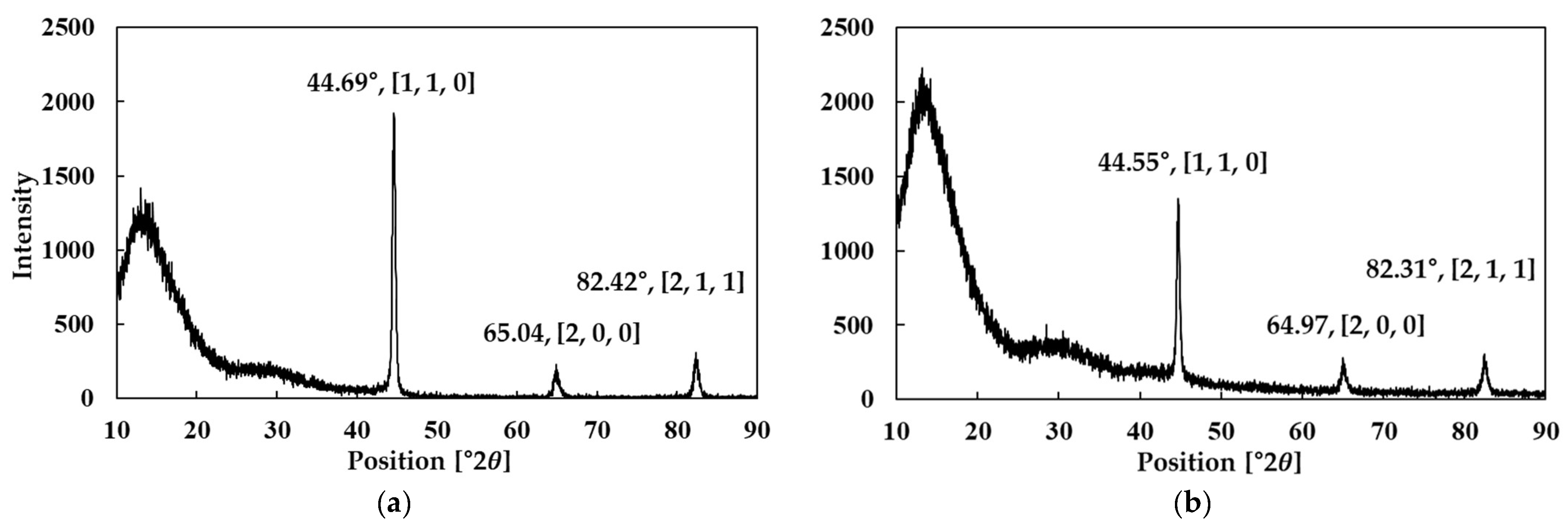
4.4.3. Crystal Structures of Bulk Prototype
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haghani, M.; Sprei, F.; Kazemzadeh, K.; Shahhoseini, Z.; Aghaei, J. Trends in electric vehicles research. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 123, 103881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Wu, X.; Zhou, M.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Y. Review and development of electric motor systems and electric powertrains for new energy vehicles. Automot. Innov. 2021, 4, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, N. Performance Analysis of Hybrid System. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2020, 8, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Atkinson, G.J. A review of soft magnetic composite materials and applications. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Valencia, Spain, 5–8 September 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.A. Advances on IPM Traction Motor Drives for Passenger Cars and High Speed Railway Trains. In Proceedings of the ASME/IEEE Joint Rail Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 23–26 March 2015; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2015; p. V001T08A005. [Google Scholar]
- Elgamli, E.; Anayi, F. Advancements in electrical steels: A comprehensive review of microstructure, loss analysis, magnetic properties, alloying elements, and the influence of coatings. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yuan, H.; Nie, M.; Guo, H.; Yu, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, R. Soft magnetic materials for power inductors: State of art and future development. Mater. Today Electron. 2023, 6, 100066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, L.; Franchini, F.; Pošković, E.; Actis Grande, M.; Bidulský, R. Effect of the temperature on the magnetic and energetic properties of soft magnetic composite materials. Energies 2021, 14, 4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Wu, P.; Qiao, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, T. Reduction of power loss in easy-plane FeSi soft magnetic composite under a weak bias magnetic field. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2024, 675, 415611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Z. Influence of soft magnetic properties of FeSiCr amorphous powder cores by the addition of FeSi powders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birčáková, Z.; Kollár, P.; Weidenfeller, B.; Füzer, J.; Bureš, R.; Fáberová, M. Iron Based Soft Magnetic Composite Material Prepared by Injection Molding. Powder Metall. Prog. 2021, 21, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y. Effects of nano-SiO2 on microstructure and magnetic properties of FeSi soft magnetic composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauda, M.; Füzer, J.; Füzerová, J.; Kollár, P.; Strečková, M.; Fáberová, M. Magnetic properties of soft magnetic FeSi composite powder cores. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2014, 126, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.; Xu, P.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Hu, F.; Su, H.; Liu, W.; Zou, Z.; Wang, J. Dependence of core loss on magnetization state under DC bias field for soft magnetic composites based on FeSiAl/FeSi powders. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2024, 37, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellsén, A.-C.; Ye, Z. Novel Iron-Based FeSi Mixes for Inductor Applications. Höganäs AB Technical Paper. Available online: https://www.hoganas.com/globalassets/downloads/technical-papers/smc/worldpm_2018_novel20iron20based20fesi20mixes20for20inductor20applictions_hellsen.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- Foster, L.; Rajagopalan, R.; Altaf, N.U.H.; Randall, C. Production of Soft Magnetic Composites Using Cold Sintering Technique for Metals. In TMS Annual Meeting & Exhibition; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Xu, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, T.; Li, G.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X. Effects of heat treatment and compaction pressure on the microstructure and magnetic properties of core-shell structured FeSiBNbCu/SiO2 soft magnetic composites. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 923, 166394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Li, K.; Xu, J.; Lu, K.; Zeng, D. Reduction of core loss for FeSi soft magnetic composites prepared using atomic layer deposition-based coating and high-temperature annealing. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 909, 164655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Vargas, B.R.; Stornelli, G.; Folgarait, P.; Ridolfi, M.R.; Miranda Pérez, A.F.; Di Schino, A. Recent advances in additive manufacturing of soft magnetic materials: A review. Materials 2023, 16, 5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, I.; Hosseini, H.M.; Kianvash, A. The correlations between processing parameters and magnetic properties of an iron–resin soft magnetic composite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 305, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Duan, N.; Wang, S.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J. A stress-dependent magnetic hysteresis model for soft magnetic composite materials. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2016, 26, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, R.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J. High density Fe-based soft magnetic composites with nice magnetic properties prepared by warm compaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 947, 169460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Luo, F.; Shang, Y.; Duan, Z. Influence of Polytetrafluoroethylene Content, Compaction Pressure, and Annealing Treatment on the Magnetic Properties of Iron-Based Soft Magnetic Composites. Molecules 2024, 29, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Cao, Y.; Yu, R.H. Preparation and magnetic properties of novel hybrid magnetic powder cores. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18 (Suppl. 4), S4-610–S4-614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E209; Standard Practice for Compression Tests of Metallic Materials at Elevated Temperatures with Conventional or Rapid Heating Rates and Strain Rates. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017. Available online: https://www.astm.org/e0209-00.html (accessed on 16 August 2017).
- Kim, J.; Lee, S. Study on compressibility according to mixing ratio and milling time of Fe-6.5 wt.% Si. Materials 2024, 17, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KS-L-1604; Fine Ceramics—Determination of Thermal Diffusivity, Specific Heat Capacity, and Thermal Conductivity of Monolithic Ceramics by Laser Flash Method. Korean Agency for Technology and Standards: Eumseong-gun, Republic of Korea, 2022.
- ASTM E228; Standard Test Method for Linear Thermal Expansion of Solid Materials with a Push-Rod Dilatometer. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.astm.org/e0228-22.html (accessed on 9 January 2023).
- Buschow, K.V.; Van Engen, P.G.; Jongebreur, R. Magneto-optical properties of metallic ferromagnetic materials. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1983, 38, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-K.; Kim, G.H.; Choi, G.B.; Jeong, I.B. Magnetic properties and workability of Fe-Si alloy powder cores. J. Magn. 2008, 13, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Ahn, J.; Choi, M.; Lee, D.; Kim, J. Magnetic properties of Fe-1.5 wt% Si high-frequency powder cores. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 125340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Peng, K.; Zou, L. The improved magnetic properties of FeSi powders cores composed with different size particles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Zang, J.A.; Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Cheng, Y. Differences in the magnetic properties of Finemet/FeSi soft magnetic composites prepared with epoxy resin/nano-oxide composite coating layers. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 110177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; Xu, P.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zou, Z.; Su, H. Hot-compacted Fe–Si soft magnetic composite with low loss at low frequency. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Cheng, D.; Yu, H.; Liu, Z. Process optimization and magnetic properties of soft magnetic composite cores based on phosphated and mixed resin coated Fe powders. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 501, 166455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, F.; Qu, X.; Xie, C.; Zhang, L. Magnetic properties of iron-based soft magnetic composites prepared by utilizing polyimide insulating layer. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 486, 165287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Chen, F.; Zhang, P.; Qu, X.; Fan, E. Enhanced magnetic properties of iron-based soft magnetic composites with phosphate-polyimide insulating layer. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 813, 152205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Wang, L.; Dong, W.; Chen, C.; Li, Z.; Rehman, S.U.; Zou, H. MoS2 composite FeSiCr soft magnetic alloy materials and their wave-absorbing properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1010, 177835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yin, Y.; Tong, B.; Zhang, G. Tribological properties of MoS2 powder-lubricated interface. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2021, 73, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Feng, S.; Kan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Chi, S.P.; Sun, W. The preparation and magnetic properties of FeSiCr/MoS2 soft magnetic composites. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 0659d1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davletbaev, K.; Chougule, S.S.; Min, J.; Ko, K.; Kim, Y.; Choi, H.; Choi, Y.; Chavan, A.A.; Pak, B.; Rakhmonov, I.U.; et al. Effect of heat treatment on structure of carbon shell-encapsulated Pt nanoparticles for fuel cells. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Hendrikx, R.W.A.; Sloof, W.G. Prediction of oxide phases formed upon internal oxidation of advanced high-strength steels. Oxid. Met. 2018, 89, 531–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.-S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, C.W.; Son, H.T. Densification and Magnetic Properties of Fe Powder Compacts According to Heat-Treatment Conditions. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2023, 68, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Ou, C.; Pan, Q.; He, B.; Zhang, B.; Zeng, S. Influence of Phosphorization Process and Heat Treatment on the Magnetic Properties of Pure Iron Soft Magnetic Composite Materials. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2024, 34(5), 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, Y.; Li, G.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. Effect of annealing treatment on the magnetic properties with wide temperature range of co-doped FeSi soft magnetic composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2023, 567, 170343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, X. Deduction of a porosity-dependent yield criterion and its geometrical description for porous materials. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2014, 89, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternero, F.; Rosa, L.G.; Urban, P.; Montes, J.M.; Cuevas, F.G. Influence of the total porosity on the properties of sintered materials—A review. Metals 2021, 11, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staf, H.; Olsson, E.; Lindskog, P.; Larsson, P.L. Determination of the frictional behavior at compaction of powder materials consisting of spray-dried granules. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Tan, J.; Du, J.; Zhang, N. Investigation on the friction mechanism and its relation to the force chains during powder compaction. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 89, 124602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapovichev, A.V.; Khaimovich, A.I.; Erisov, Y.A.; Ryazanov, M.V. Investigation of Soft Magnetic Material Fe-6.5Si Fracture Obtained by Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2022, 15, 8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Li, G.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Sun, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, D.; Dong, Z. Characterization of the Fe-6. 5wt%Si Strip with Rapid Cooling Coupling Deep Supercooled Solidification. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25412–25420. [Google Scholar]
- Panaligan, T.R.L.; Lee, A.K.S.; Petareal, C.J.; Tadena, J.R. Synthesis, Characterization, and Utilization of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia Crassipes) Magnetic Biochar for Nitrate Removal from Simulated Wastewater. Key Eng. Mater. 2024, 980, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bures, R.; Milyutin, V.A.; Faberova, M.; Bircakova, Z.; Kollar, P.; Fuzer, J. The first experimentally obtained dataset on processing parameters and properties of soft magnetic composites. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Feng, S.; Shao, G.; Yuan, W.; Sun, K.; Li, X.; Fan, R. Influence of the annealing process on magnetic performance of iron based soft magnetic composites. Eng. Sci. 2020, 11, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



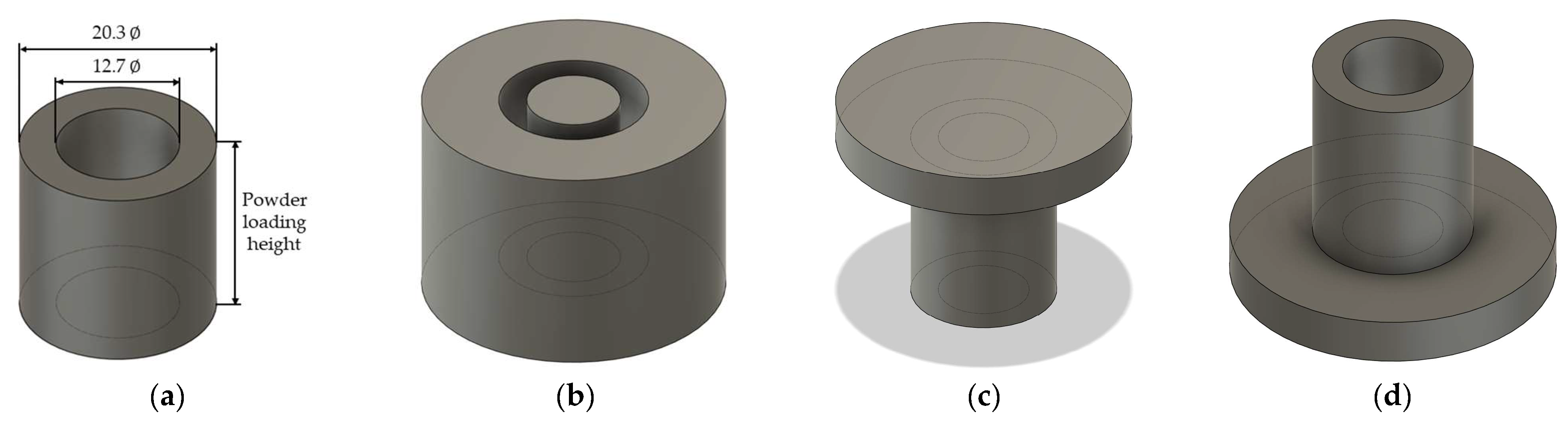
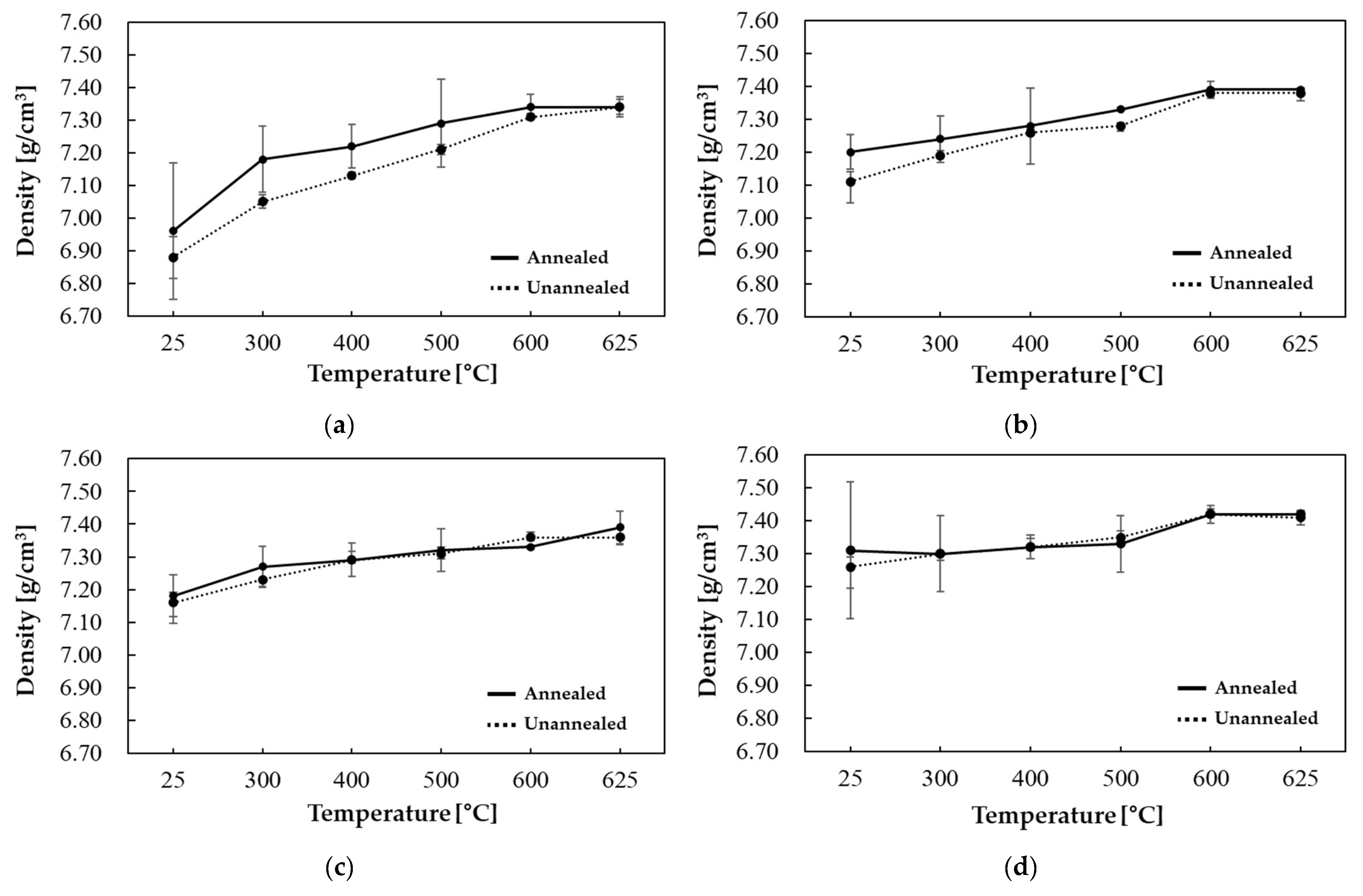

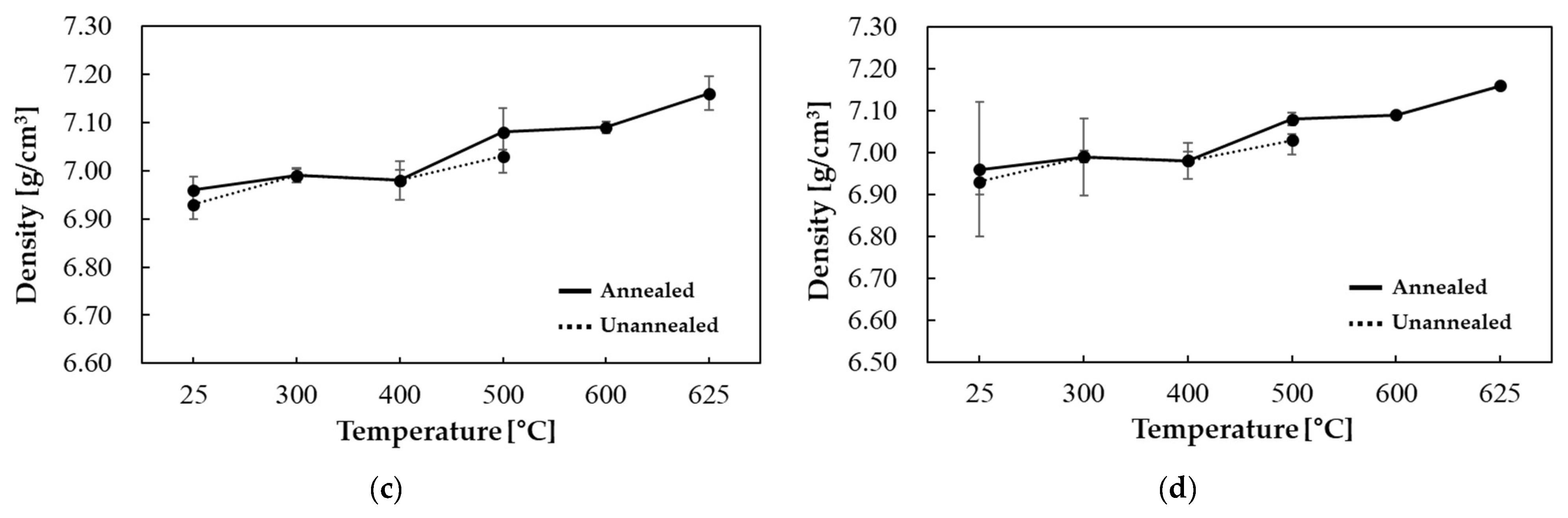
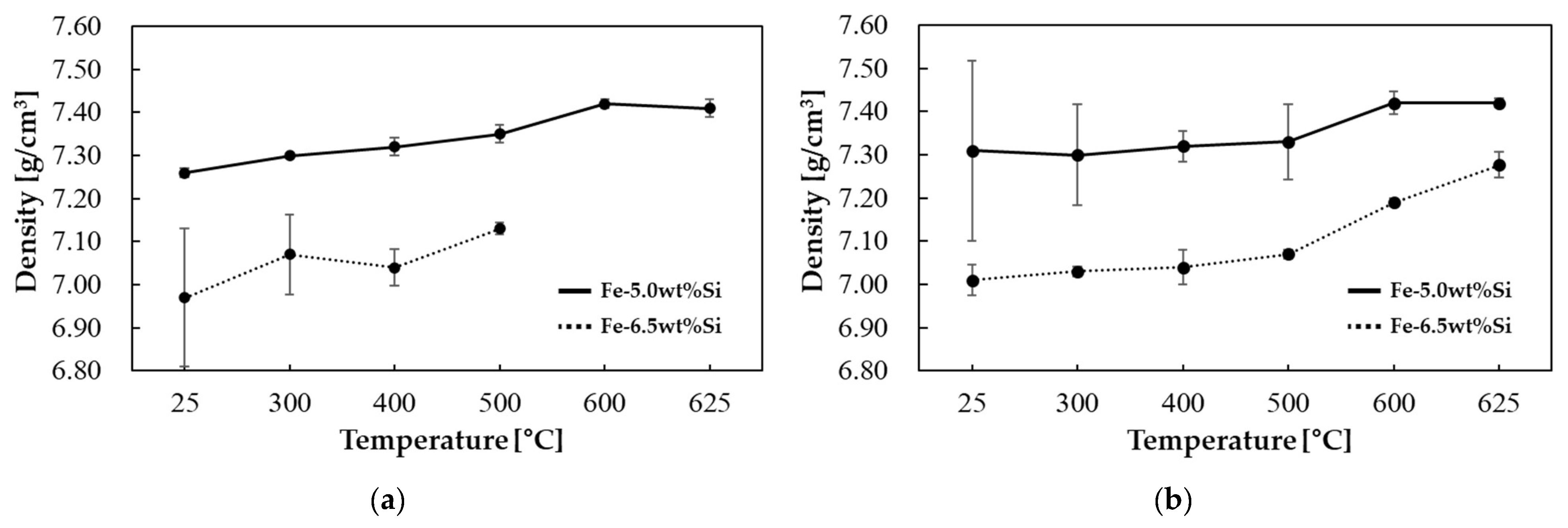






| Temperature (°C) | Thermal Diffusivity (mm2/s) | Specific Heat (J/gK) | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 5.38 | 0.45 | 17.7 |
| 100 | 5.56 | 0.47 | 19.0 |
| 200 | 5.66 | 0.52 | 21.4 |
| 300 | 5.58 | 0.54 | 21.9 |
| 400 | 5.33 | 0.57 | 22.2 |
| 500 | 4.91 | 0.58 | 20.8 |
| 600 | 4.61 | 0.63 | 21.0 |
| 700 | 3.81 | 0.70 | 19.4 |
| 800 | 2.79 | 0.74 | 15.0 |
| 900 | 4.03 | 0.77 | 22.7 |
| Temperature (°C) | Thermal Diffusivity (mm2/s) | Specific Heat (J/gK) | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 4.20 | 0.45 | 14.2 |
| 100 | 4.34 | 0.54 | 17.6 |
| 200 | 4.50 | 0.57 | 19.0 |
| 300 | 4.59 | 0.58 | 20.0 |
| 400 | 4.60 | 0.60 | 20.6 |
| 500 | 4.51 | 0.64 | 21.6 |
| 600 | 4.21 | 0.91 | 28.6 |
| 700 | 3.76 | 1.07 | 30.2 |
| 800 | 4.17 | 0.97 | 30.4 |
| 900 | 4.51 | 0.93 | 31.3 |
| Temperature (°C) | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (1e-6/K) | |
|---|---|---|
| Fe-5.0 wt.%Si | Fe-6.5 wt.%Si | |
| 100 | 11.25 | 11.27 |
| 200 | 11.94 | 11.90 |
| 300 | 12.50 | 12.61 |
| 400 | 12.91 | 13.07 |
| 500 | 13.25 | 13.54 |
| 600 | 13.58 | 14.18 |
| 700 | 13.79 | 14.68 |
| 800 | 13.97 | 15.03 |
| 900 | 14.24 | 15.32 |
| Element | Fe | Si | O |
|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 94.85 | 5.02 | 0.13 |
| Element | Fe | Si | O |
|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 93.62 | 6.54 | 0.16 |
| Si Content | 5.0 wt.% | 6.5 wt.% |
|---|---|---|
| average particle size of powder | 79.136 | 99.804 |
| Composition | H3PO4 | PI | MoS2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wt.% | 1.0 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| Factor | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | Level 5 | Level 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si content [wt.%] | 5.0 | 6.5 | ||||
| 1st forming temperature [°C] | RT | 300 | 400 | 500 | ||
| 2nd forming temperature [°C] | RT | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 625 |
| annealing process | Yes | No |
| Experimental Parameter | Value/Condition |
|---|---|
| forming pressure | 8 tons per square unit |
| 1st forming temperature | RT, 300 °C, 400 °C, 500 °C |
| 2nd forming temperature | RT, 300 °C, 400 °C, 500 °C, 600 °C, 625 °C |
| annealing temperature | 700 °C |
| annealing atmosphere | 10% H2 + 90% Ar |
| specimen shape | toroidal core |
| target specimen weight | 8 g |
| number of specimens per condition | 3 specimens |
| insulation coating composition | 1.0 wt.% H3PO4 + 0.5 wt.% PI + 1.0 wt.%MoS2 |
| Index | Density [g/ cm3] | Permeability in 0.1 kH | Permeability in 1.0 kH | Permeability in 10 kH | Q-Factor in 0.1 kH | Q-Factor in 1.0 kH | Q-Factor in 10 kH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | 87 | 87 | 87 | 87 | 87 | 87 | 87 |
| Min | 6.85 | 3.26 | 3.95 | 3.99 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 2.18 |
| Max | 7.42 | 99.92 | 125.15 | 126.33 | 0.04 | 0.51 | 7.18 |
| Silicon Content | Initial Relative Density | Powder Loading Height [mm] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.0 wt.% | 3.27 | 0.419 | 12.009 |
| 6.5 wt.% | 3.08 | 0.395 | 12.302 |
| Silicon Content | Average Relative Density | Average Effective Stress [MPa] | Average Hydrostatic Pressure [MPa] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5.0 wt.% | 0.95 | 220.25 | −356.13 |
| 6.5 wt.% | 0.93 | 301.12 | −396.99 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.; Lee, S. Optimizing the Manufacturing Process Control of Si-Based Soft Magnetic Composites. Materials 2025, 18, 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102321
Kang S, Lee S. Optimizing the Manufacturing Process Control of Si-Based Soft Magnetic Composites. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102321
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Seongsu, and Seonbong Lee. 2025. "Optimizing the Manufacturing Process Control of Si-Based Soft Magnetic Composites" Materials 18, no. 10: 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102321
APA StyleKang, S., & Lee, S. (2025). Optimizing the Manufacturing Process Control of Si-Based Soft Magnetic Composites. Materials, 18(10), 2321. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102321







