Research on Creep Deformation of Dissimilar FSWed T-Joints Under Different Ultrasonic Vibration Modes: Experiment, Constitutive Model, and Simulation Verification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. UVCAT Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
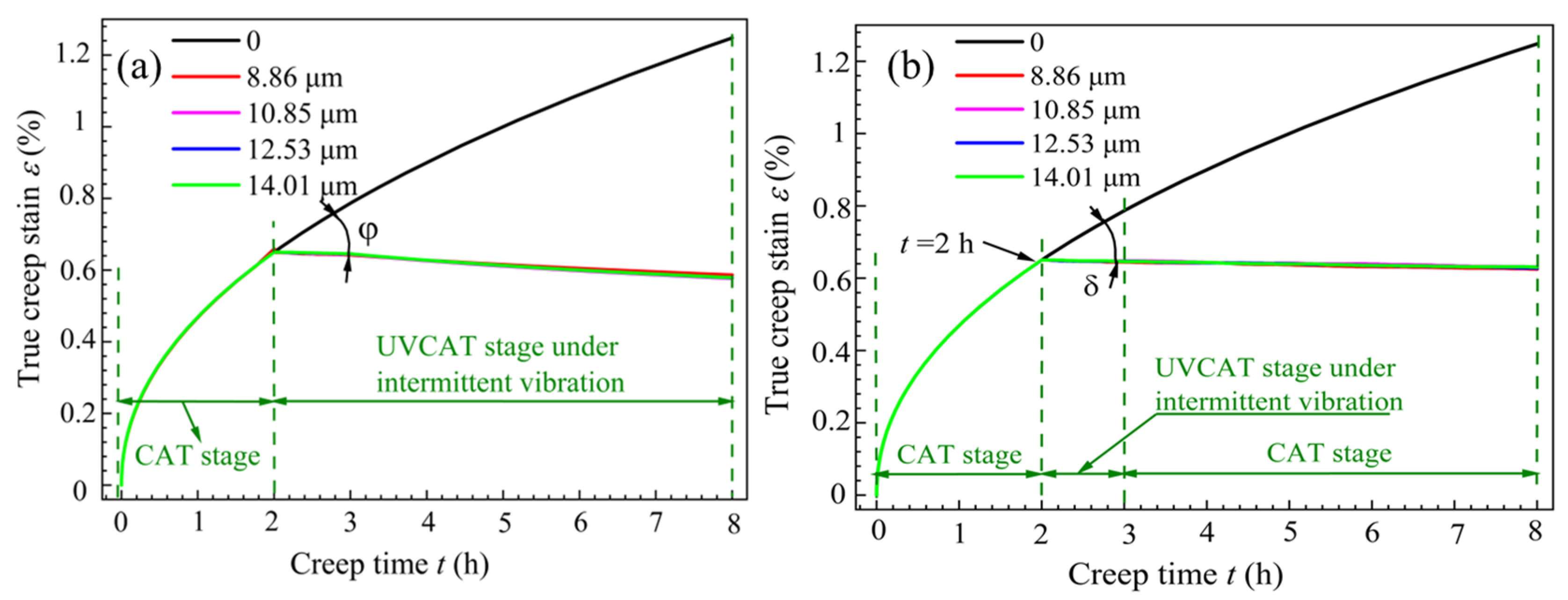
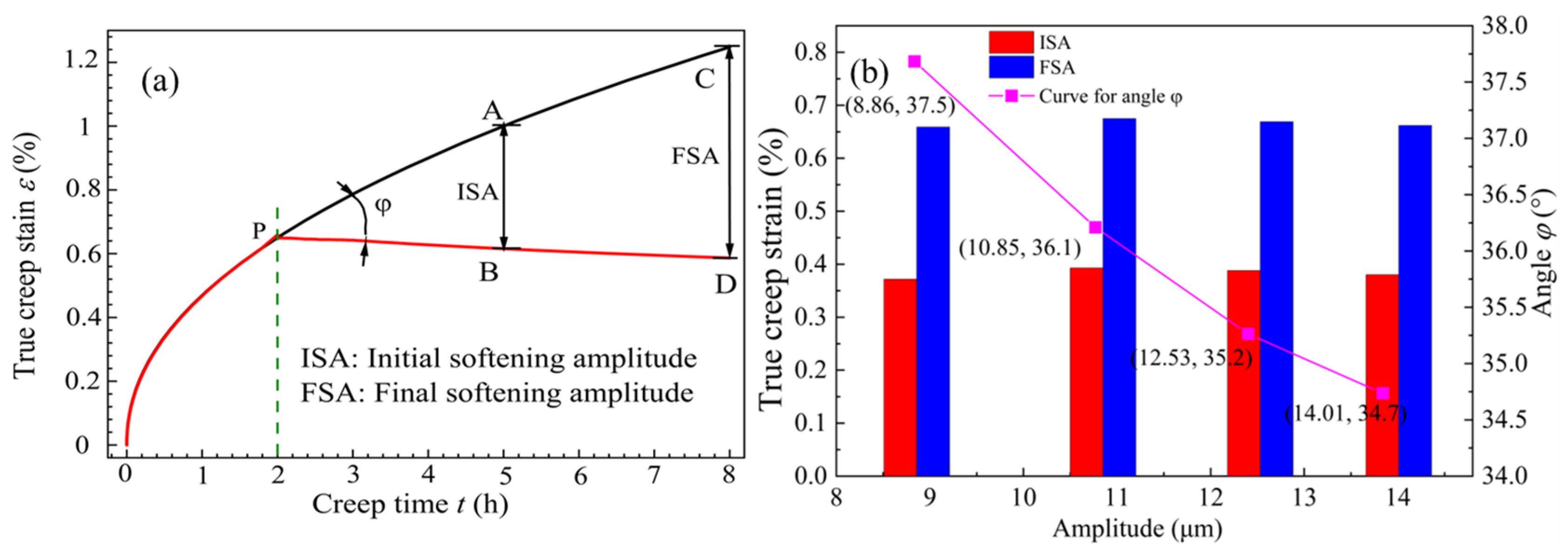
3.1. Creep Aging Process Parameters
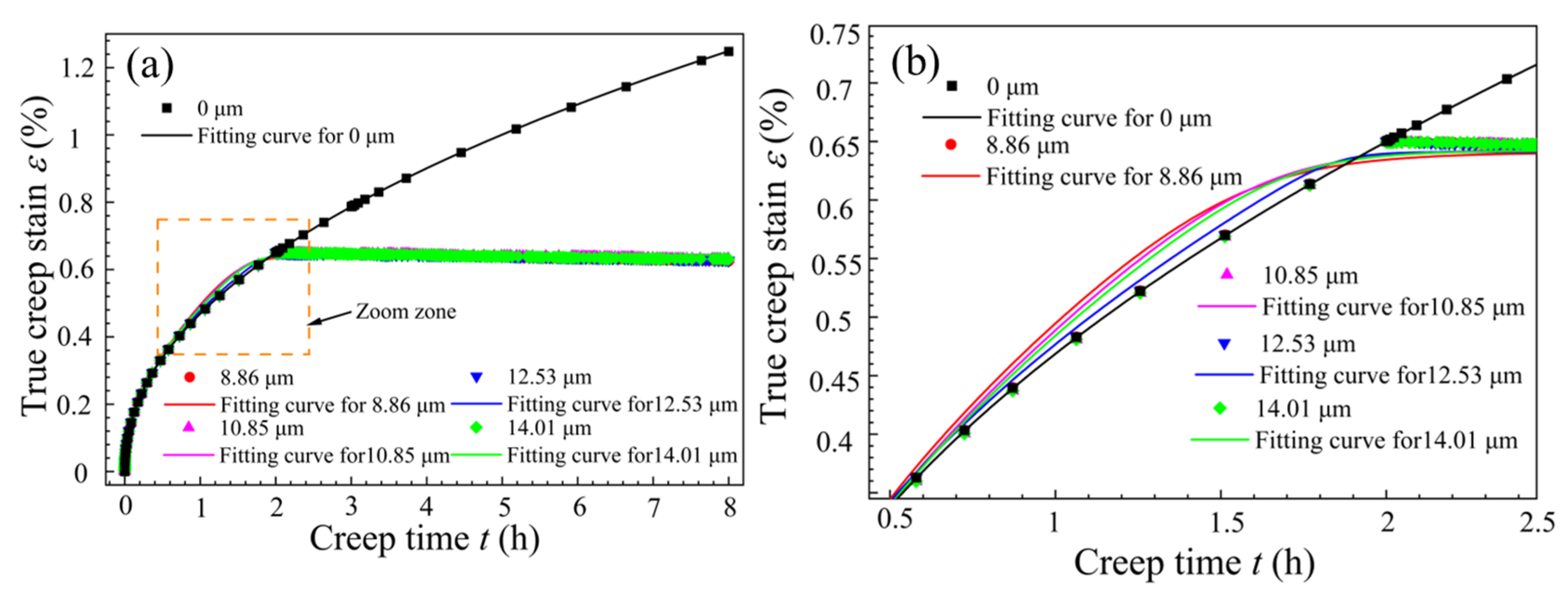
3.2. Creep Behavior Under Different Vibration Modes
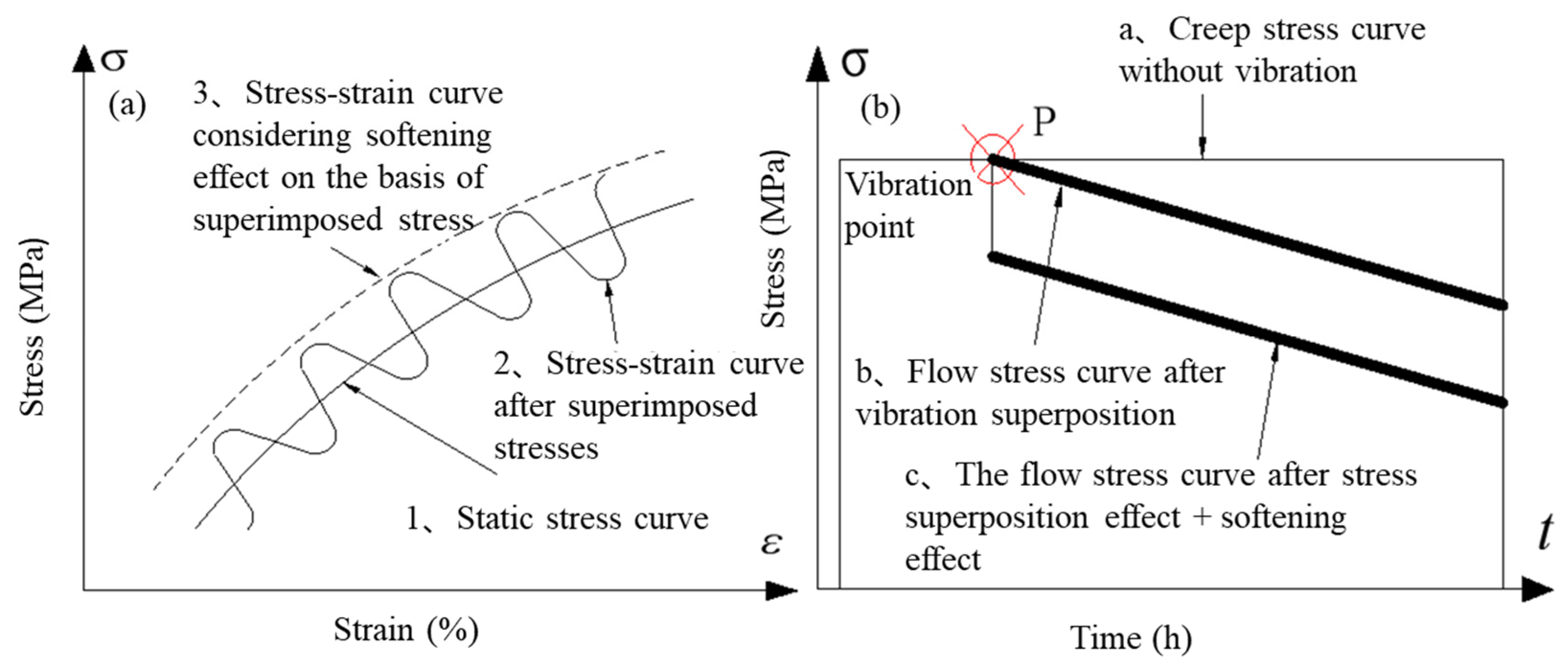
3.3. Constitutive Model
4. Finite Element Validation
- (1)
- Loading phase: the left end of the specimen is fully constrained and stationary, the right end is linearly loaded in the X direction, nonlinear analysis is turned off, and the conventional tensile time without vibration is 1 s.
- (2)
- CAT phase: the left end of the specimen remains stationary, the right end undergoes constant loading in the X direction, nonlinear analysis is enabled, and the time for the non-vibration CAT is set to 2 h.
- (3)
- UVCAT phase: the left end of the specimen remains stationary, while both a sine displacement function and a constant load are applied at the right end, with a vibration duration of 1 h.
- (4)
- CAT phase: the left end of the specimen remains stationary, and the right end continues to receive constant load in the X direction, with a non-vibration CAT applied for 5 h.
- (5)
- Unloading phase: the left end of the specimen remains stationary, the right end is linearly unloaded in the X direction, the temperature load is reduced to 25 °C, and the time for the non-vibration CAT is 1 s.
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Under non-vibration conditions during the CAT experiments, the optimal creep processing parameters for the T-joint were 155 °C, 130 MPa, and 8 h.
- (2)
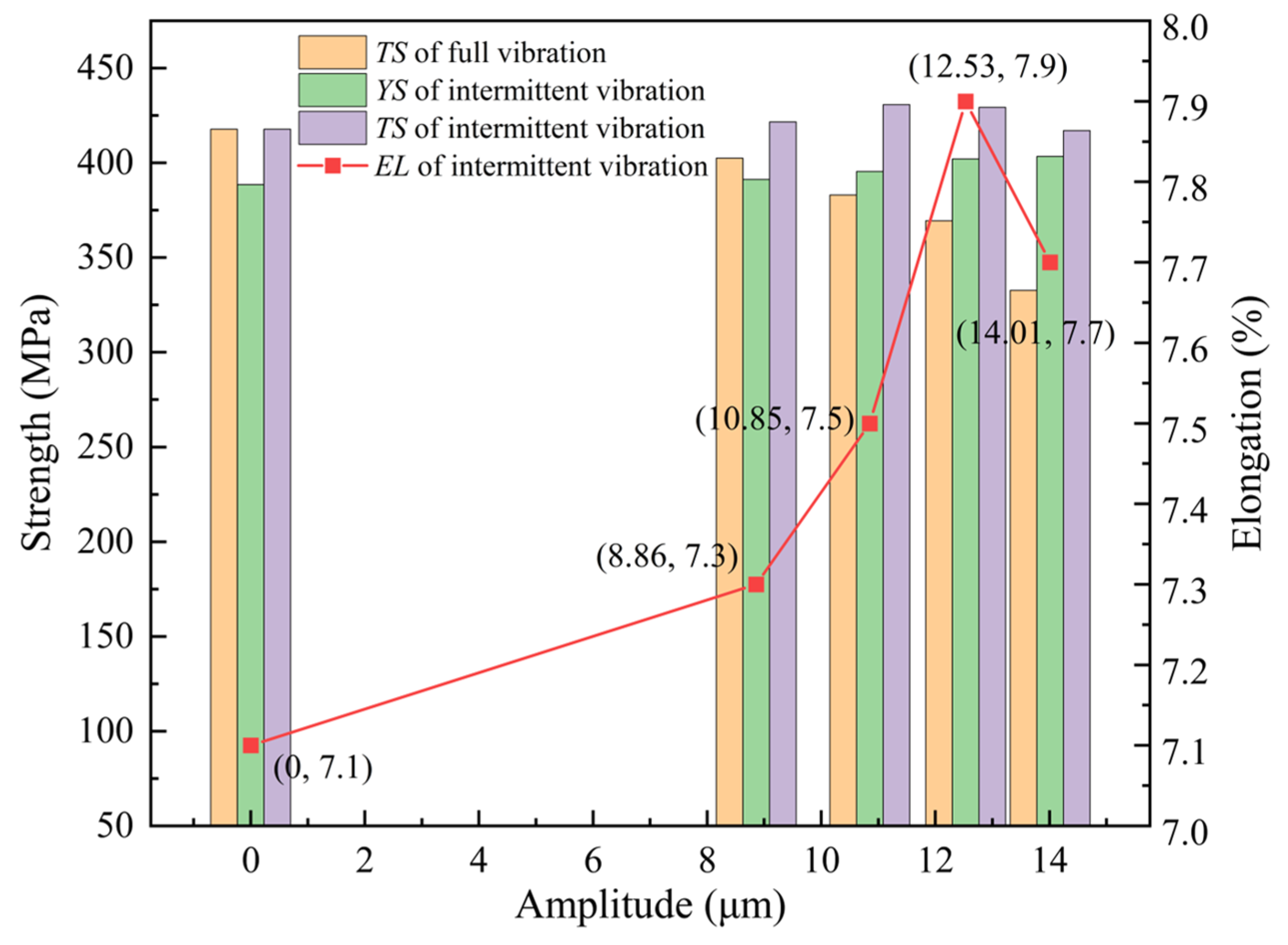
- The UVCAT experiments revealed that at the same amplitude, the creep limit for intermittent vibration was 64.7‰ to 97.2‰ larger than that for continuous vibration. Furthermore, compared to the TS of the CAT specimen under continuous vibration, the specimens under intermittent vibration significantly outperformed them. It was further found that under prolonged or large amplitude vibrations, the material exhibits a hardening effect. Whereas, under short-duration, low-amplitude, intermittent vibrations, the joint material showed a softening effect with sufficient release of residual stress. The optimal composite mechanical properties of the material occur at an amplitude of 12.53 μm, with the YS, TS, and EL being 402.1 MPa, 429.3 MPa, and 7.9%, respectively.
- (3)
- Based on the analysis of the UVCAT experiments, a creep aging constitutive model incorporating the mechanisms of superposition and acoustic softening effects was established. The fit to the experimental results yielded an error of 4.2%, which is less than 5%, satisfying engineering practical needs and confirming the accuracy of the model.
- (4)
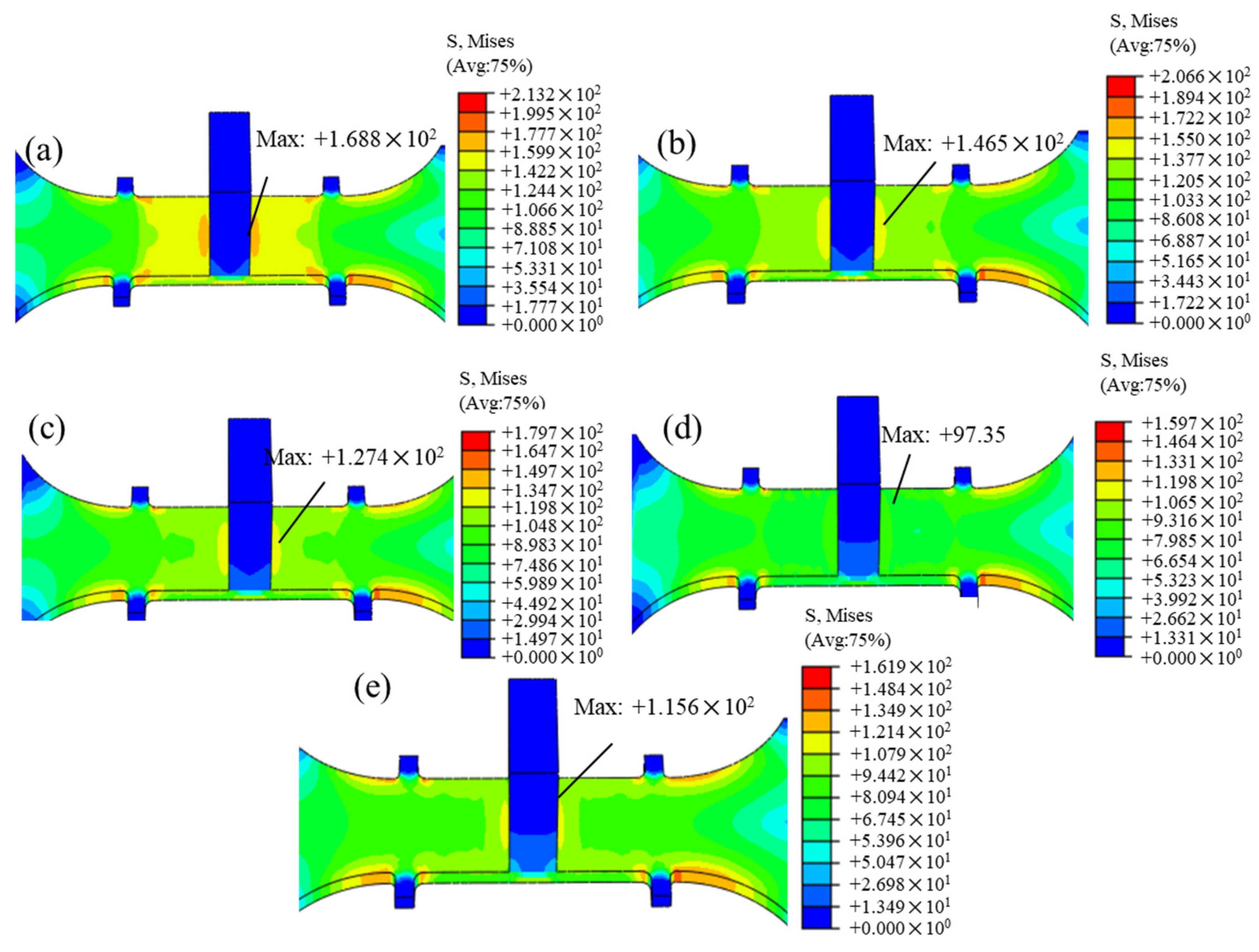
- The simulation results indicated that an amplitude of 12.53 μm, while reducing the generation of creep strain in the CAT specimens, led to a more thorough elimination of residual stress, with a more uniform distribution at 97.35 MPa. Moreover, the finite element calculated creep strain matched the experimental results well, with a maximum error of 3.8 × 10⁻4, further demonstrating that the creep constitutive model can effectively predict the creep behavior of T-joint materials during the UVCAT process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, M.; Wang, Y.; Malik, A.; Nazeer, F.; Yasin, G.; Khan, W.; Ahmad, T.; Zhang, H. Microstructure characterization of 7055-T6, 6061-T6511 and 7A52-T6 Al alloys subjected to ballistic impact against heavy tungsten alloy projectile. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2019, 19, 1484–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, T.; Wahid, M.A.; Alam, N.; Mehta, Y.; Siddiquee, A.N. Friction stir welding: A sustainable manufacturing process. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 46, 6558–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badkoobeh, F.; Mostaan, H.; Rafiei, M.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Berto, F. Friction stir welding/processing of Mg-based alloys: A critical review on advancements and challenges. Materials 2021, 14, 6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, D.Q.; Cao, Z.Q.; Cao, Y.J.; Huo, L.B.; Li, W.Y. Thermal fields in dissimilar 7055 Al and 2197 Al-Li alloy FSW T-joints: Numerical simulation and experimental verification. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 103, 3495–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhang, M.; Farahani, M.; Nazari, M. Experimental Correlation Between Microstructure, Residual Stresses and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Welded 2024-T6 Aluminum Alloys. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, T.; Schroepfer, D.; Rhode, M. Residual stresses in a high-and a medium-entropy alloy due to TIG and friction stir welding. J. Manuf. Mater. Process 2022, 6, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, M.C. Autoclave age forming large aluminum aircraft panels. J. Mech. Work. Technol. 1989, 20, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Xie, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, Y. Investigation on Creep Deformation and Age Strengthening Behavior of 304 Stainless Steel under High Stress Levels. Materials 2024, 17, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Shi, Z.; Rong, Q.; Bai, X.; Zeng, Y.; Lin, J. Experimental and numerical investigations on buckling behaviour of stiffened panel during creep age forming. Thin Wall Struct. 2022, 172, 108940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhong, J.; Zhan, L.H.; Wang, P.; Ruan, X.P.; Wu, H.Q.; Xu, Y.Q.; Ma, B.L.; Liu, C.H.; Zeng, Q.Q.; et al. Effect of pre-aging on creep aging properties and microstructure evolution of 2195 Al–Li alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 21, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ye, L.; Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, Q. The effects of temperature on the creep-aging behavior and mechanical properties of AA2050-T34 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 796, 164992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.P.; Zhan, L.H.; Liu, C.H.; Yang, J.S.; Chen, K.L.; Huang, Z.B. Strong stress-level ependence of creep-ageing behavior in Al-Cu-Li alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 802, 140381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y. Effects of creep aging upon Al-Cu-Li alloy: Strength, toughness and microstructure. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 764, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-L.; Wang, Z.-J.; Zhai, W.-D.; Cheng, Z.-N.; Li, F.-Y.; Li, X.-Q. The influence of ultrasonic vibration on parts properties during incremental sheet forming. Adv. Manuf. 2021, 9, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.B.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, S.Y.; Hu, J.C.; Li, K.Q.; Zhao, B. Residual Stresses in Ultrasonic-Assisted Laser Sintered Grinding Diamond Materials. Strength. Mater. 2019, 51, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, X.; Liu, H.; Liaw, P.K.; Ma, J.; Shen, J. Ultrasonic-vibration-enhanced plasticity of an entropic alloy at room temperature. Acta Mater. 2022, 225, 117569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Bi, R. Acoustic residual softening and microstructure evolution of T2 copper foil in ultrasonic vibration assisted micro-tension. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 841, 143044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, F.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Shi, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Lin, J. An investigation of creep age forming of AA7B04 stiffened plates: Experiment and FE modelling. J. Manuf. Process 2019, 37, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Liu, Z.; Pang, S.; Meng, T.; Zhi, Y.T.; Xu, Y.L.; Xiao, L.; Li, R.F. Investigation of tensile creep behavior of Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy based on creep constitutive model. Mat. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 805, 140567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhan, L.-H.; Huang, M.-H.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, C.; Hu, L.-B.; Hu, Z.-G.; Liu, D.-B. A unified constitutive model for multiphase precipitation and multi-stage creep ageing behavior of Al-Li-S4 alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. 2021, 31, 1217–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Ma, P.; Yang, J.; Zhan, L.; Huang, M. Strong in-plane anisotropy of creep ageing behavior in largely pre-deformed Al-Cu alloy: Experiments and constitutive modeling. Int. J. Plasticit 2022, 152, 103245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.Q.; Ma, G.L.; Deng, Z.H.; Xia, G.F.; Luo, J.J.; Wang, H.B. Research on the improved Graham model for aluminum-based alloy stiffened panel under the whole creep aging process. Chin. J. Appl. Mech. 2018, 35, 894–899. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Z.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.-L.; Saillard, P.; Said, R. FE simulation of asymmetric creep-ageing behaviour of AA2050 and its application to creep age forming. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 140, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Zhan, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, B.; Chen, K.; Ren, H. Anisotropy in creep-aging behavior of Al–Li alloy under different stress levels: Experimental and constitutive modeling. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 20, 3456–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Cao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, G. Effect of pre-stretching on microstructures and mechanical behaviors of creep-aged 7055 Al alloy and its constitutive modeling. Metals 2019, 9, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 2039—2012; Test Method for Uniaxial Tensile Creep of Metallic Materials. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Hutchinson, C.R. Fundamentals of Aluminum Metallurgy: Production, Processing and Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 422–467. [Google Scholar]
- Hisam, M.W.; Dar, A.A.; Elrasheed, M.O.; Khan, M.S.; Gera, R.; Azad, I. The Versatility of the Taguchi Method: Optimizing Experiments Across Diverse Disciplines. J. Stat. Theory Appl. 2024, 23, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.Q.; Hu, J.Y.; Tang, Z.W. A Special Device for Constant Temperature Vibration Creep Compound Aging Tensile. Patent CN201821367332.3, 12 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, M.; Yu, Y.; Xia, R.; Xu, J. A new creep constitutive relationship for high temperature alloys. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 194, 106207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalewski, Z.L.; Hayhurst, D.R.; Dyson, B.F. Mechanisms-based creep constitutive equations for an aluminum alloy. J. Strain Anal. Eng. 1994, 29, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semerenko, Y.O.; Natsik, V.D.; Tabachnikova, E.D.; Huang, Y.; Langdon, T.G. Mechanisms of Low-Temperature Dislocation Motion in High-Entropy Al0.5CoCrCuFeNi Alloy. Metals 2024, 14, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wen, B.C. Mechanism Analysis of Volume Effect in Metal Vibrational Plastic Machining. J. Net. Form. Eng. 1998, 16, 35–36, 47–48. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Li, W. Effect of pre-strain on creep aging behavior of 2524 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 691, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch, S.; Chauhan, S.S.; Kumar, V. A review on genetic algorithm: Past, present, and future. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 8091–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Bian, T.; Wu, C.; Gao, Y.; Lei, C. Advances and challenges on springback control for creep age forming of aluminum alloy. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2022, 35, 8–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
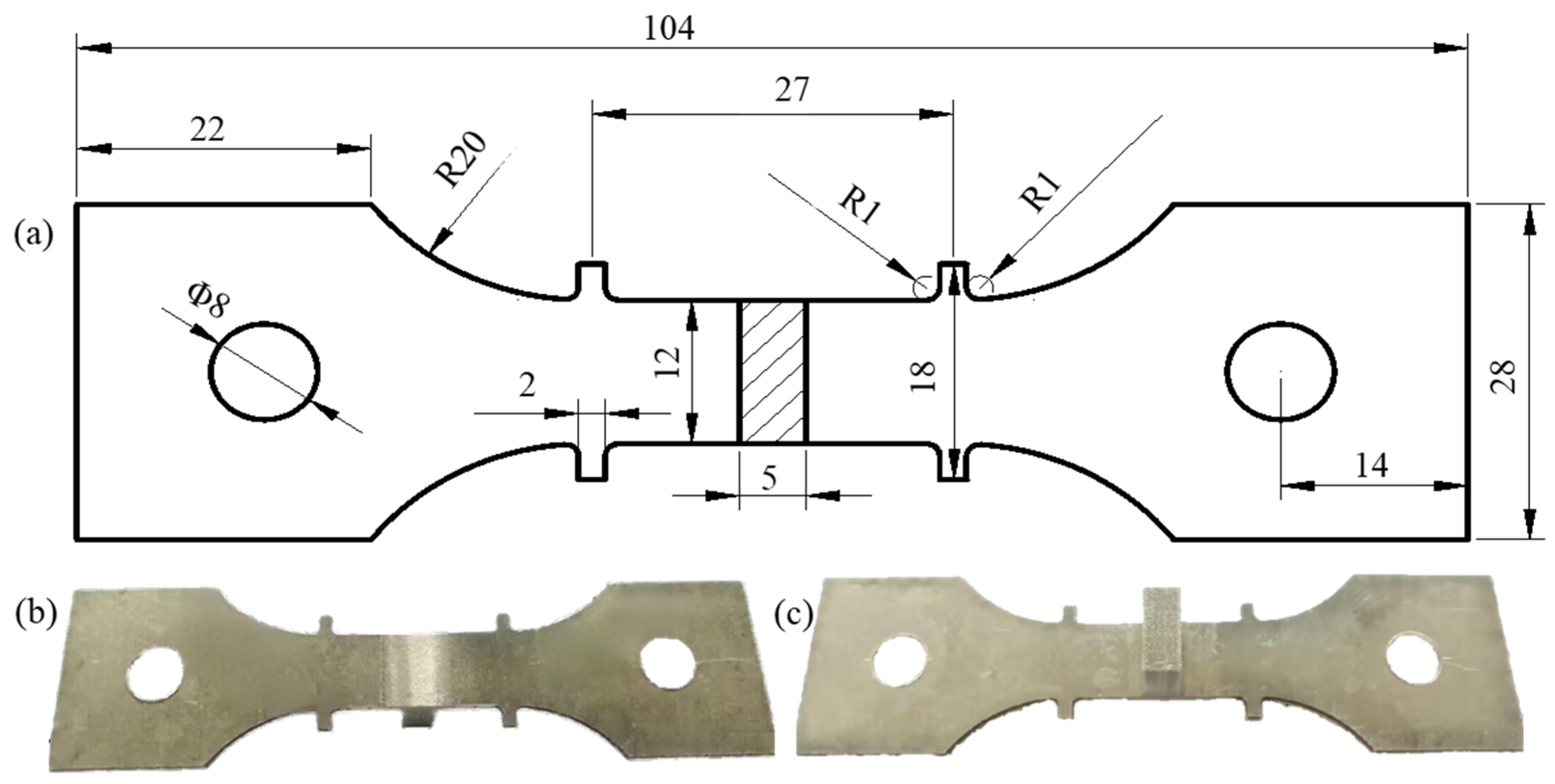






| 7055-T61 alloy | Zn | Mg | Cu | Zr | Fe | Mn | Si | Ti | Cr | Al |
| 7.9 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.06 | 0.001 | Bal. | |
| 2197-T8 alloy | Li | Cu | Ag | Mn | Mg | Zr | Fe | Si | Zn | Al |
| 1.5 | 2.88 | 0.36 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.006 | Bal. |
| Materials | Transverse Tensile Strength/MPa | Longitudinal Tensile Strength/MPa | Elongation/% | Melting Point/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7055-T6 | 600 | 540 | 13 | 590 |
| 2197-T8 | 570 | 530 | 6 | 560 |
| No. | Creep Temperature/°C | Loading Stress/MPa | Creep Time/h | Combination |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 140 | 130 | 6 | A1B1C1 |
| 2 | 140 | 145 | 8 | A1B2C2 |
| 3 | 140 | 160 | 10 | A1B3C3 |
| 4 | 140 | 175 | 12 | A1B4C4 |
| 5 | 155 | 130 | 8 | A2B1C2 |
| 6 | 155 | 145 | 6 | A2B2C1 |
| 7 | 155 | 160 | 12 | A2B3C4 |
| 8 | 155 | 175 | 10 | A2B4C3 |
| 9 | 170 | 130 | 10 | A3B1C3 |
| 10 | 170 | 145 | 12 | A3B2C4 |
| 11 | 170 | 160 | 6 | A3B3C1 |
| 12 | 170 | 175 | 8 | A3B4C2 |
| 13 | 185 | 130 | 12 | A4B1C4 |
| 14 | 185 | 145 | 10 | A4B2C3 |
| 15 | 185 | 160 | 8 | A4B3C2 |
| 16 | 185 | 175 | 6 | A4B4C1 |
| No. | Frequency/KHz | Amplitude/µm | Tension Rate/mm·min−1 | Vibration Application Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | No |
| 2 | 20 | 8.86 | 1 | Continuous vibration of 2 h |
| 3 | 20 | 10.85 | 1 | |
| 4 | 20 | 12.53 | 1 | |
| 5 | 20 | 14.01 | 1 | |
| 6 | 20 | 8.86 | 1 | 2~3 h intermittent vibration |
| 7 | 20 | 10.85 | 1 | |
| 8 | 20 | 12.53 | 1 | |
| 9 | 20 | 14.01 | 1 |
| Parameter of Equation | Parameter Value | Parameter of Equation | Parameter Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1/h−1 | 3.166 × 10−10 | m0 | 2.650 × 10−11 |
| C2/MPa−1 | 8.742 × 10−2 | m1 | 2.307 |
| h/MPa | 1.483 × 105 | CΦ | 0.132 |
| σ0/MPa | 256.473 | CA | 18.304 |
| H* | 0.2716 | Φ* | 1.526 × 10−4 |
| n0 | 3.0175 | B | 0.0537 |
| n1 | 0.0327 | K(A) | 0.6835 |
| n2 | 2.1068 | k0 | 2.6783 |
| n3 | 1.3685 | k2 | 2.3595 |
| n4 | −23.671 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, T.; Han, Y.; Zuo, D.; Fu, H.; Feng, S.; Gao, C.; Li, W. Research on Creep Deformation of Dissimilar FSWed T-Joints Under Different Ultrasonic Vibration Modes: Experiment, Constitutive Model, and Simulation Verification. Materials 2025, 18, 2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102275
Ye T, Han Y, Zuo D, Fu H, Feng S, Gao C, Li W. Research on Creep Deformation of Dissimilar FSWed T-Joints Under Different Ultrasonic Vibration Modes: Experiment, Constitutive Model, and Simulation Verification. Materials. 2025; 18(10):2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102275
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Ti, Yanjie Han, Duquan Zuo, Haoran Fu, Shilin Feng, Chong Gao, and Wenya Li. 2025. "Research on Creep Deformation of Dissimilar FSWed T-Joints Under Different Ultrasonic Vibration Modes: Experiment, Constitutive Model, and Simulation Verification" Materials 18, no. 10: 2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102275
APA StyleYe, T., Han, Y., Zuo, D., Fu, H., Feng, S., Gao, C., & Li, W. (2025). Research on Creep Deformation of Dissimilar FSWed T-Joints Under Different Ultrasonic Vibration Modes: Experiment, Constitutive Model, and Simulation Verification. Materials, 18(10), 2275. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18102275






