Comparison of Ignition Process and Thermodynamic Conditions of TC4 and TC17 Alloys Under High-Speed Rubbing Ignition
Abstract
1. Introduction
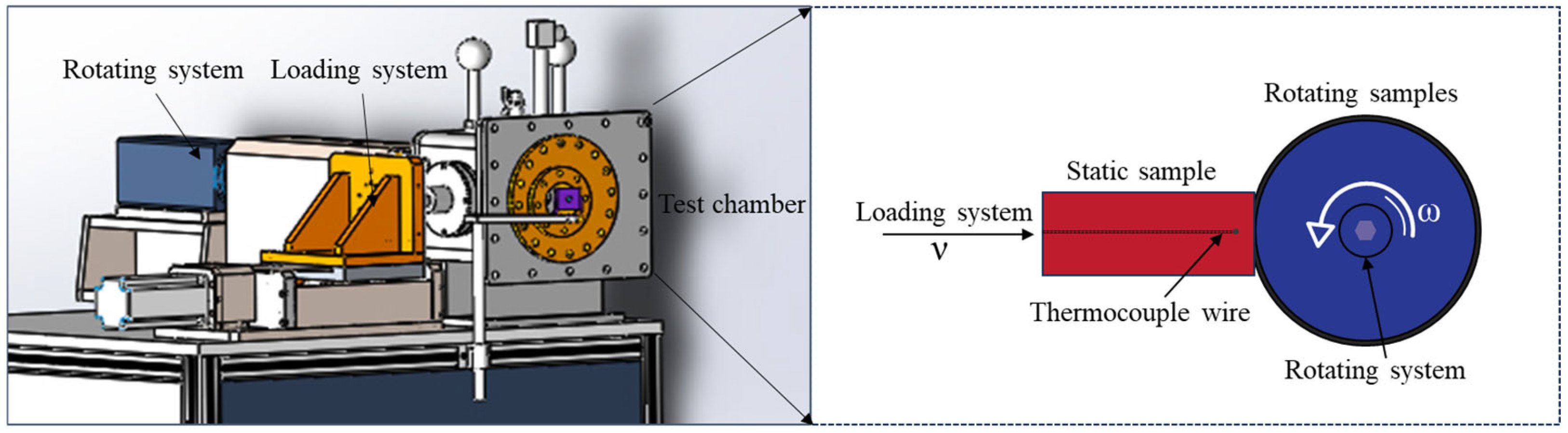
2. Experimental Details
Experimental Material
3. Results
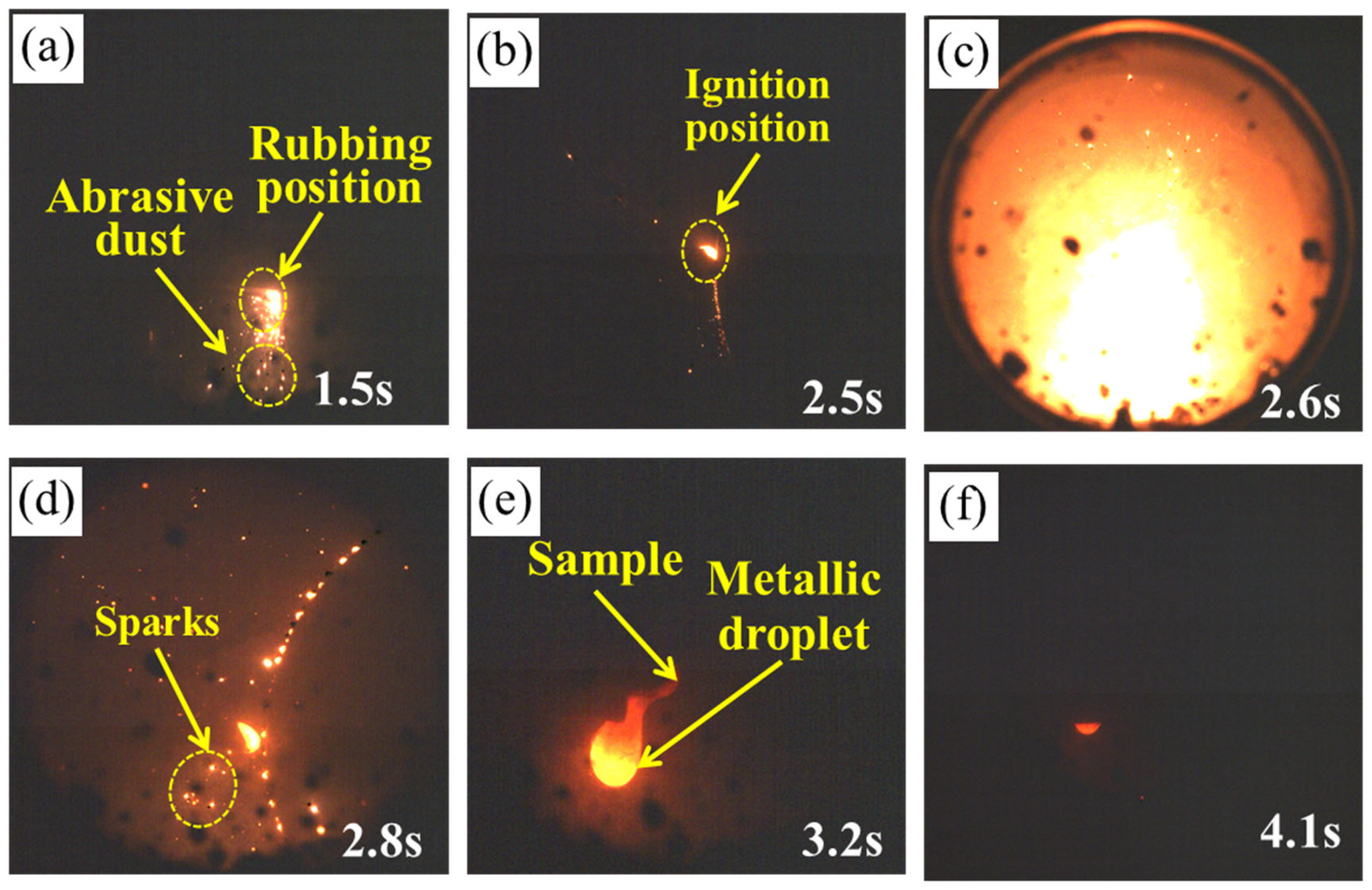
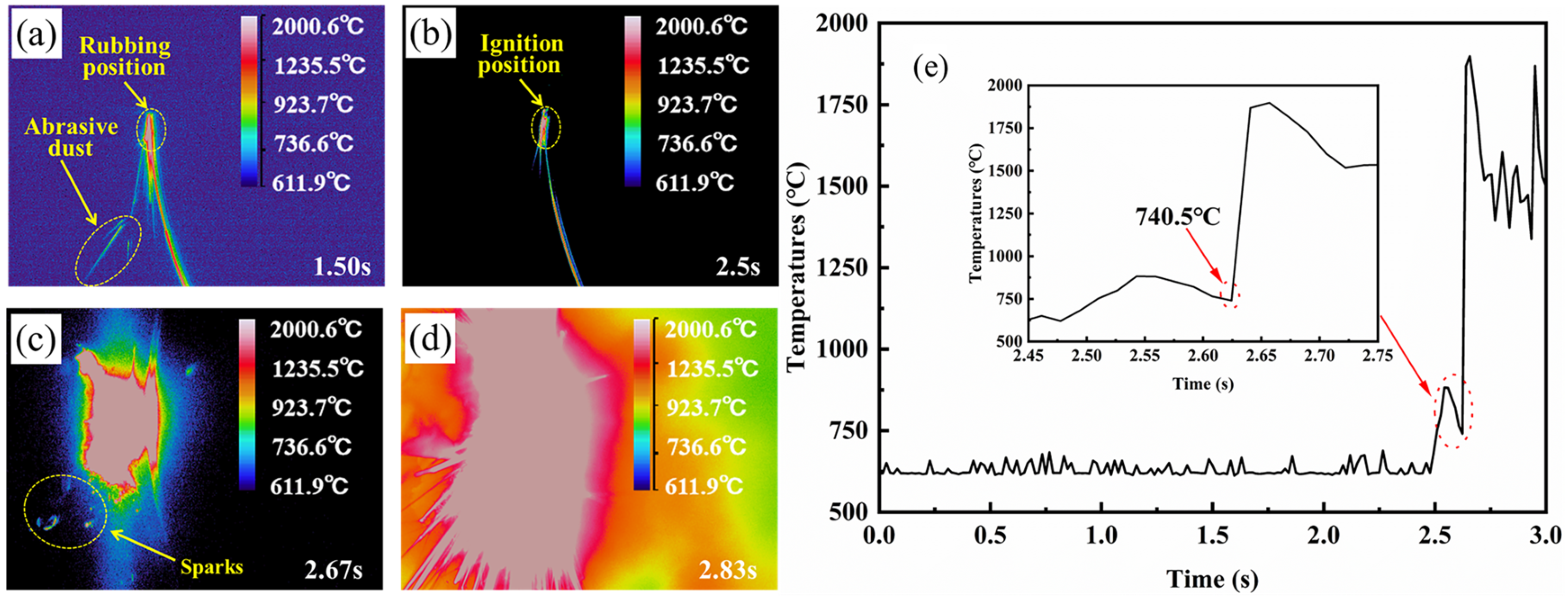
3.1. High-Speed Rubbing Ignition Process and Combustion Behavior
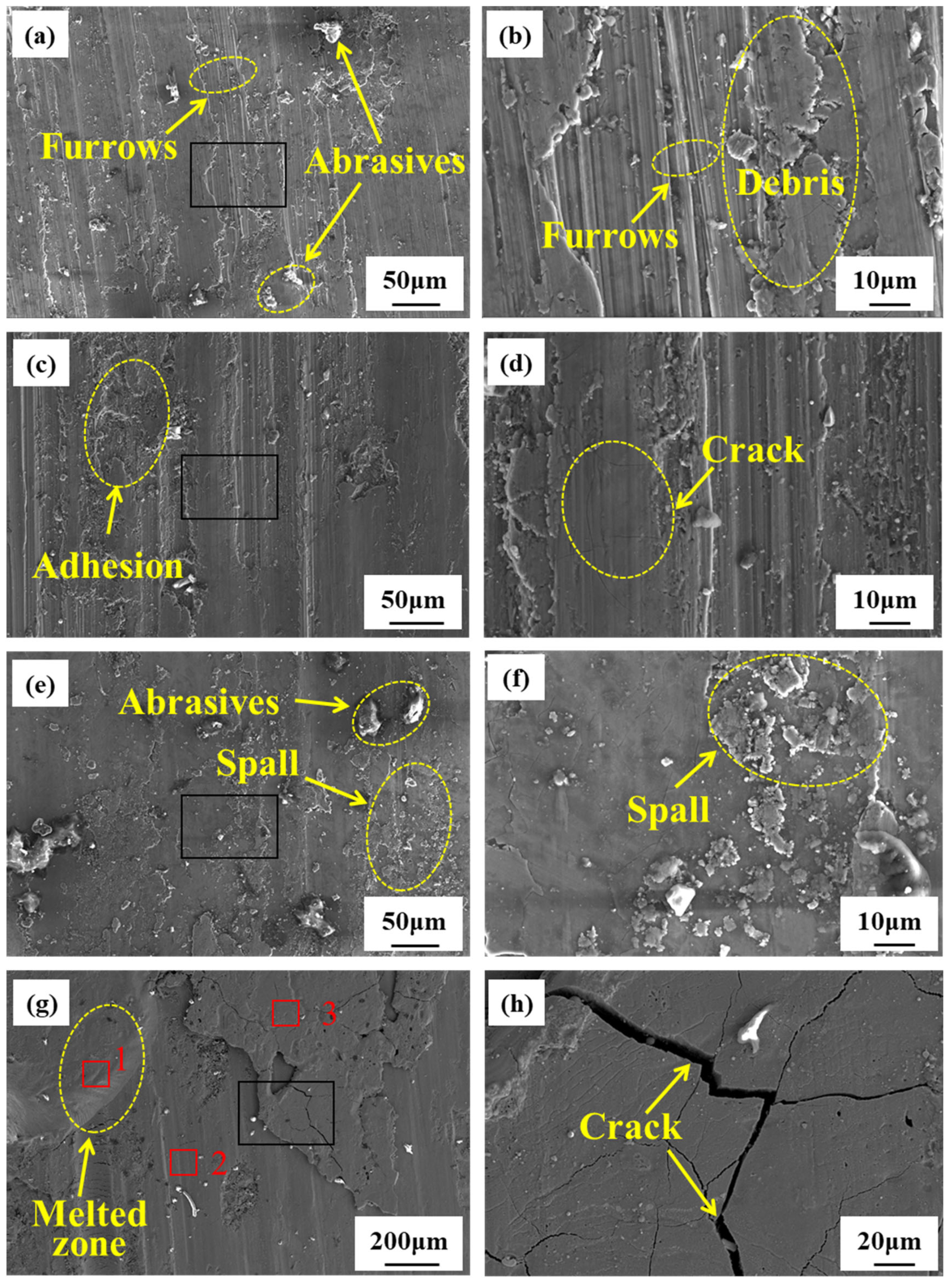
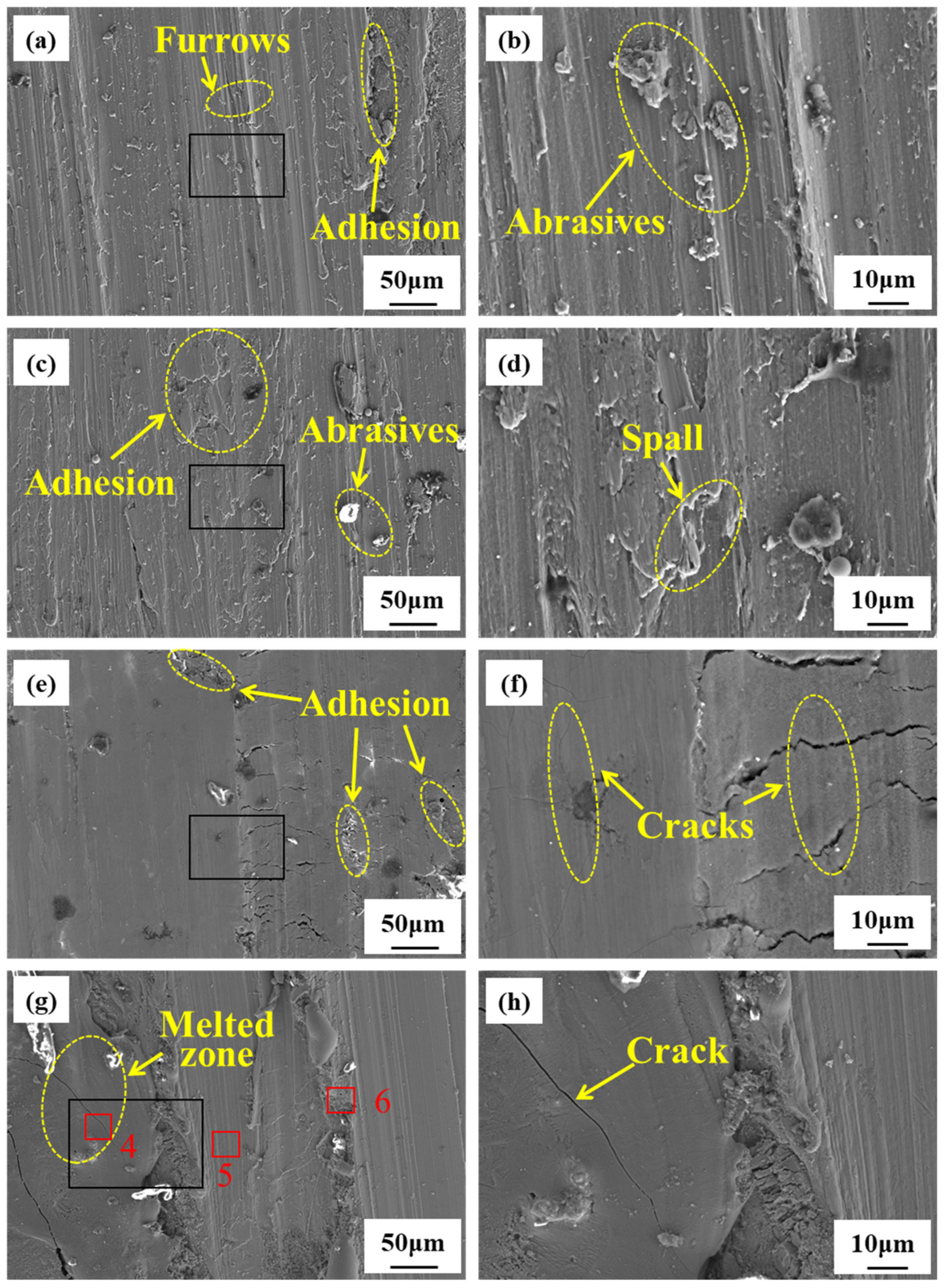
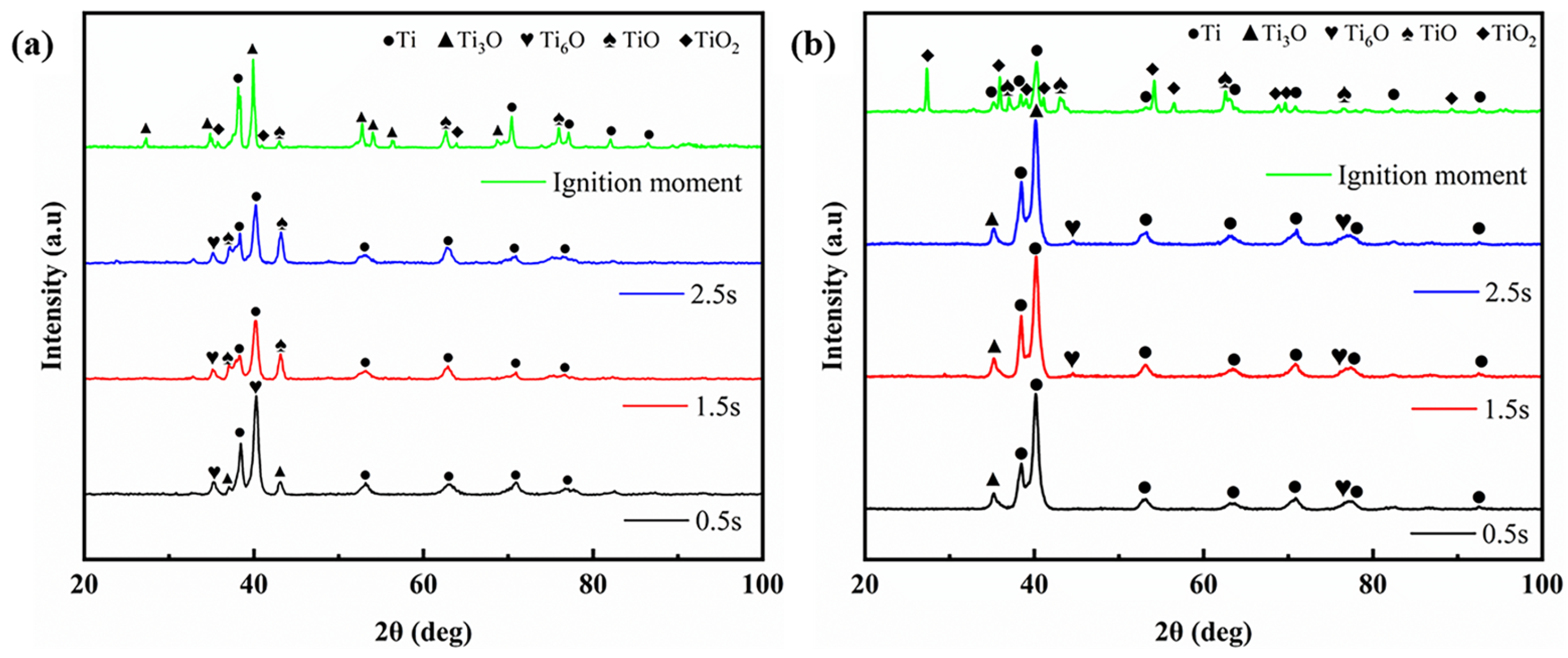
3.2. Microstructure and Composition During Rubbing Ignition Process
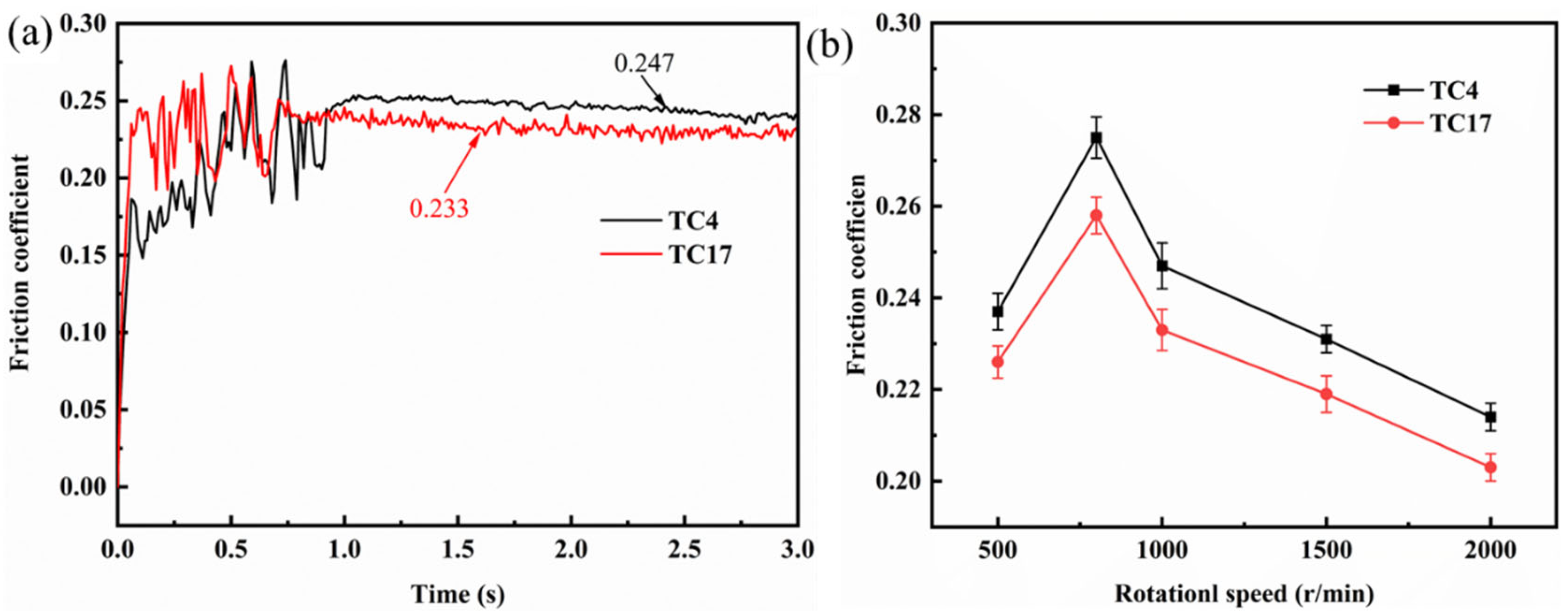
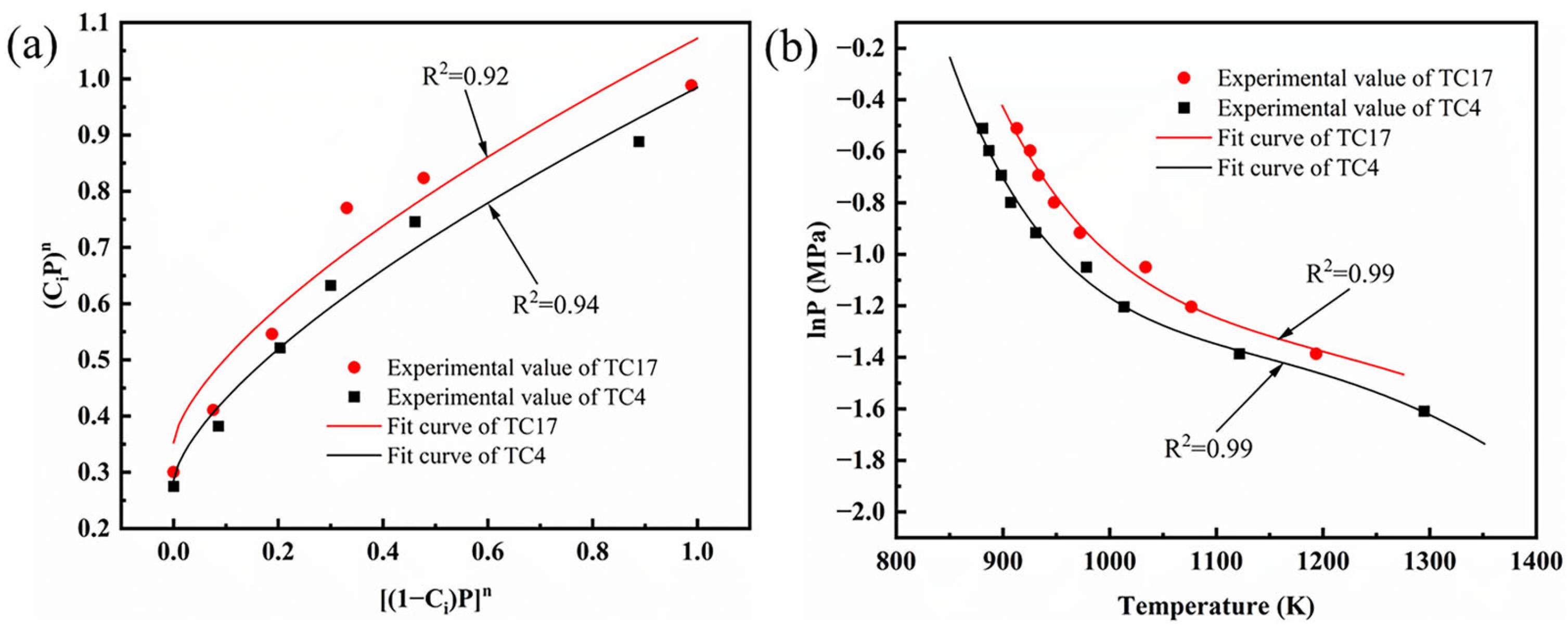
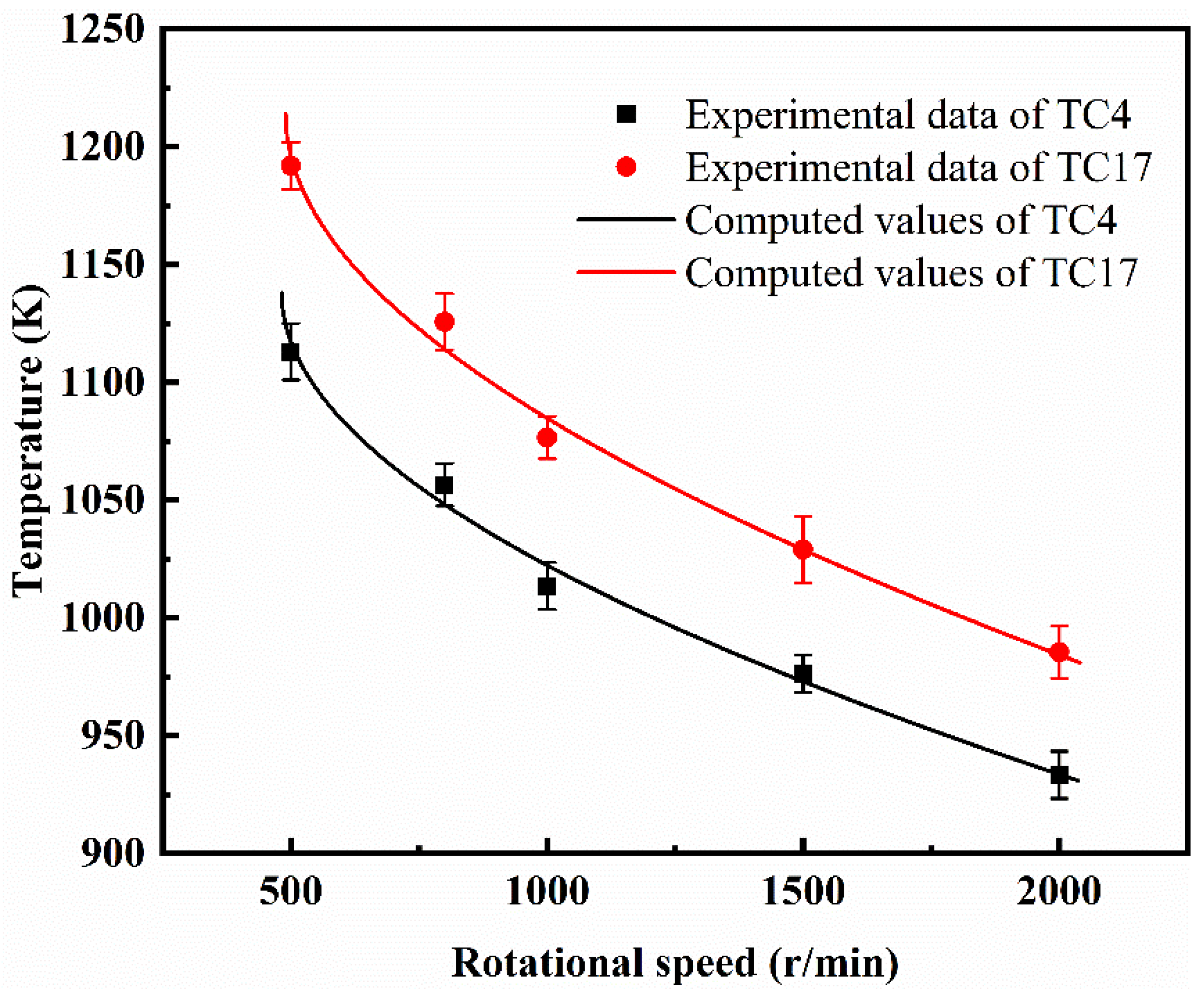
3.3. Critical Ignition Conditions of TC4 and TC17 Alloys
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparative Analysis of Ignition Process
4.2. Thermodynamic Analysis of High-Speed Rubbing Ignition
Determination of the Reaction Order and Adsorption Coefficient
- The determination of the activation energy and pre-exponential factor
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- At the moment of ignition due to rubbing, both titanium alloys demonstrated a rapid increase in temperature, emitting a bright white light and generating intense heat. The critical pressure and ignition temperature for rub-induced ignition increased with larger sample sizes, while they decreased with higher rotational speeds, oxygen pressure, and oxygen concentration. Under the same test conditions, the critical pressure and ignition temperature for the rub-induced ignition of the TC17 alloy were both higher than those of the TC4 alloy.
- (2)
- During the rubbing ignition process, the initial stage was primarily characterized by abrasive and adhesive wear. As the duration of rubbing increased, the material on the rubbing surface began to peel away, creating conditions conducive to ignition. At the moment of ignition, significant peeling occurred, along with visible cracks and molten structures, leading to the generation of a substantial amount of titanium oxide on the rubbing surface.
- (3)
- The reaction order, absorption coefficient, and activation energy of the Frank-Kamenetskii model for the TC4 and TC17 alloys were determined. The ignition temperature of the TC4 and TC17 alloys at different speeds was predicted with a relative error of within 2.06%, indicating that the Frank-Kamenetskii model can be applied to describe the critical ignition conditions of bulk metals under frictional conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Standard symbol | Nomenclature | Dimension |
| δ | Frank-Kamenetskii parameter | - |
| E | activation energy | kJ·mol−1 |
| l | sample length | m |
| λ | thermal conductivity | W·m−1 K−1 |
| R | universal gas constant | J·mol−1·K−1 |
| T | temperature | K |
| q | heat of reaction per unit mass | MJ·kg−1 |
| k | pre-exponent | kg·m−2·s−1 |
| α | adsorption coefficient | MPa−n |
| Ci | oxygen concentration | - |
| n | reaction order | - |
| P | critical total pressure | MPa |
| P0 | atmospheric pressure | MPa |
| δcr | Frank-Kameneskii parameters under critical conditions | - |
| N(α) | critical value of δ without energy input | - |
| H | gas heat transfer coefficient | W·m−2·K−1 |
| r | rotor disk radius | m |
| ω | rotational speed | r/min |
| μ | frictional coefficient | |
| N | load | N |
| η | heat transfer coefficient | |
| α1 | heat distribution coefficient | |
| d | sample thickness | m |
| b | sample width | m |
References
- Huang, Z.H.; Qu, H.L.; Deng, C.; Yang, J.C. Development and application of titanium and titanium alloys for aviation. Mater. Rep. 2011, 25, 102–107. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Yu, J.; Zhong, Y.; Gu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, W.; Yan, J.; Ge, Y.; Yin, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. Influence of scanning on nano crystalline β-Ti alloys fabricated by selective laser melting and their applications in biomedical science. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, Y.; Faller, K.; Fox, S.P. Newly developed titanium alloy sheets for the exhaust systems of motorcycles and automobiles. JOM 2004, 56, 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littman, F.E.; Church, F.M.; Kinderman, E.M. A study of metal ignitions I. The spontaneous ignition of titanium. J. Less Common Met. 1961, 3, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, R.R. An overview on the use of titanium in the aerospace industry. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 213, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xie, G.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, J.; Hao, Z.; Lu, W.; Liu, X. Combustion behaviour and mechanism of TC4 and TC11 alloys. Corros. Sci. 2020, 168, 108564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Xie, G.L.; Li, H.Y.; Lu, W.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Huang, J. Combustion behavior and mechanism of Ti14 titanium alloy. Materials 2020, 13, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Huang, J. A review on combustion behavior and mechanism of Ti alloys for advanced aero-engine. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 960, 170584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, G.; Li, H.; Xiong, J.; Yu, J.; He, G.; Huang, J. Combustion Mechanism of Alloying Elements Cr in Ti-Cr-V Alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolobov, V.I. Mechanism of Self-Ignition of Titanium Alloys in Oxygen. Combust. Explos. Shock. Waves 2002, 38, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolobov, V.I. Possible Mechanism of Autoignition of Titanium Alloys in Oxygen. Combust. Explos. Shock. Waves 2003, 39, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolobov, V.I.; Podlevskikh, N.A. Mechanism of metal ignition due to fracture. Combust. Explos. Shock. Waves 2007, 43, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaikin, B.I.; Bloshenko, V.N.; Merzhanov, A.G. On the ignition of metal particles. Combust. Explos. Shock. Waves 1970, 6, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisova, Y.A.; Sklyarov, N.M. Fireproof titanium alloys. Phys. Metallogr. 1993, 6, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.Y.; Mi, G.B.; Li, P.J.; Huang, X.; Cao, C.X. Theoretical study on ignition of titanium alloy under high temperature friction condition. Acta Phys. Sin. 2020, 69, 216101–216112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Acosta, M.A.; Martines-Arano, H.; Soto-Ruvalcaba, L.; Martínez-González, C.L.; Martínez-Gutiérrez, H.; Torres-Torres, C. Fractional thermal transport and twisted light induced by an optical two-wave mixing in single-wall carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2020, 147, 106136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, G.; Huang, X.; Cai, J.; Li, S.; Cao, J.; Cao, C. Fireproof Property and Its Mechanism of A New High Temperature Titanium Alloy. In Proceedings of the 13th World Conference on Titanium; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, G.B.; Cao, C.X. Ignition Resistance Performance and Its Mechanism of TC17 Titanium Alloy for Aero-Engine. J. Aeronaut. Mater. 2014, 34, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Mi, G.; Li, P.; Huang, X.; Cao, C. Theoretical calculation of characteristics on titanium fire in aero-engine. J. Aeronaut. Mater. 2021, 41, 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, B.F. Critical Behaviour in Chemically Reacting Systems III—An Analytical Criterion for Insensitivity. Combust. Flame 1975, 24, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.H. On the thermal conduction equation for self-heating materials with surface cooling. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1958, 54, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, B.F. Unified Theory of Explosions, Cool Flames and Two Stage Ignitions. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1969, 65, 1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, B.F. Spontaneous Combustion and Self-Heating. In SFPE Handbook of Fire Protection Engineering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 20, pp. 604–632. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Torrent, J.; Ramírez-Gómez, A.; Querol-Aragón, E.; Grima-Olmedo, C.; Medic-Pejic, L. Determination of the risk of selfignition of coals and biomass materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Restuccia, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Z.; Huang, X.; Fang, J.; Rein, G. Experimental Study of Self-heating Ignition of Lithium-Ion Batteries During Storage: Effect of the Number of Cells. Fire Technol. 2020, 56, 2649–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Dou, C.; Jiao, Y.; Li, J.; He, G.; Song, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, C. A Theoretical Description of the Ignition Conditions for TC17 Alloy in Oxygen-Enriched Atmospheres. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2023, 196, 3559–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GJB2218A-2018; Specification of Titanium and Titanium Alloy Bars and Forging Stocks for Aircraft. State Administeration of Science, Technology and Industry for National Defense: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Dou, C.; Jin, P.; He, G.; Song, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, C. A Comparative Study on the Mathematic Models for the Ignition of Titanium Alloy in Oxygen-Enriched Environment. Metals 2022, 12, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straffelini, G.; Molinari, A. Mild Sliding Wear of Fe–0.2%C, Ti–6%Al–4%V and Al-7072: A Comparative Study. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 41, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Ding, H.Y.; Zhou, G.H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Xia, M.; Guo, X. Role of Fe2O3 in Dry Sliding Wear of a Titanium Alloy and Formation of Tribo-Layers. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2019, 48, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Xiao, G.; Li, S.; Chen, B.; Zhuo, X.; Zhang, J. Study of Surface Integrity of Titanium Alloy (TC4) by Belt Grinding to Achieve the Same Surface Roughness Range. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, A.; Straffelini, G.; Tesi, B.; Bacci, T. Dry sliding wear mechanisms of the Ti6Al4V alloy. Wear 1997, 208, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, P.; Mi, G.; Cao, J.; Huang, X.; He, L.; Li, P. Microstructure Characteristics after combustion and fireproof mechanism of TiAl-based alloys. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 16, 364–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, A.; Wake, G.C.; Gray, B.F. Friction and localized heat initiation of ignition: The asymmetrical slab and cylindrical annulus. Combust. Flame 1985, 61, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Alloy | Ti | Al | Zr | Mo | Si | V | Sn | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC4 | Bal. | 6 | - | - | - | 4 | - | - |
| TC17 | Bal. | 5 | 2 | 4 | - | - | 2 | 4 |
| Alloy | Room Temperature Mechanical Properties | High-Temperature Tensile Properties | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (Rm/MPa) | Elongation (%) | Reduction of Area (%) | Test Temperature(°C) | Tensile Strength (Rm/MPa) | |
| TC4 | 825 | 10 | 25 | 400 | 620 |
| TC17 | 1120 | 7 | 15 | 370 | 907 |
| Region | Ti | O | Al | Mo | Zr | V | Sn | Cr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 50.88 | 43.16 | 3.77 | 2.19 | ||||
| 2 | 74.72 | 19.26 | 2.83 | 3.19 | ||||
| 3 | 63.77 | 28.76 | 4.54 | 2.53 | ||||
| 4 | 52.18 | 41.95 | 2.69 | 0.38 | 1.31 | 0.66 | 0.82 | |
| 5 | 58.85 | 31.17 | 3.55 | 1.44 | 1.36 | 1.16 | 2.46 | |
| 6 | 54.12 | 35.76 | 3.56 | 1.9 | 1.48 | 1.13 | 2.07 |
| Alloy | n | α (MPa−n) | E (kJ/mol) | K (kg·m−3·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC4 | 0.68 | 2.45 | 97.18 | 160.15 |
| TC17 | 0.77 | 2.03 | 107.52 | 147.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zu, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, L.; Huang, J. Comparison of Ignition Process and Thermodynamic Conditions of TC4 and TC17 Alloys Under High-Speed Rubbing Ignition. Materials 2025, 18, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010016
Li Y, Li J, Zu Z, Wang C, Zhang Y, Shao L, Huang J. Comparison of Ignition Process and Thermodynamic Conditions of TC4 and TC17 Alloys Under High-Speed Rubbing Ignition. Materials. 2025; 18(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yajun, Jianjun Li, Zichong Zu, Congzhen Wang, Yuqi Zhang, Lei Shao, and Jinfeng Huang. 2025. "Comparison of Ignition Process and Thermodynamic Conditions of TC4 and TC17 Alloys Under High-Speed Rubbing Ignition" Materials 18, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010016
APA StyleLi, Y., Li, J., Zu, Z., Wang, C., Zhang, Y., Shao, L., & Huang, J. (2025). Comparison of Ignition Process and Thermodynamic Conditions of TC4 and TC17 Alloys Under High-Speed Rubbing Ignition. Materials, 18(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18010016







