Effect of Initial Position and Crystallographic Orientation on Grain Selection Procedure in Z-Form Selector for Ni-Based Single-Crystal Superalloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
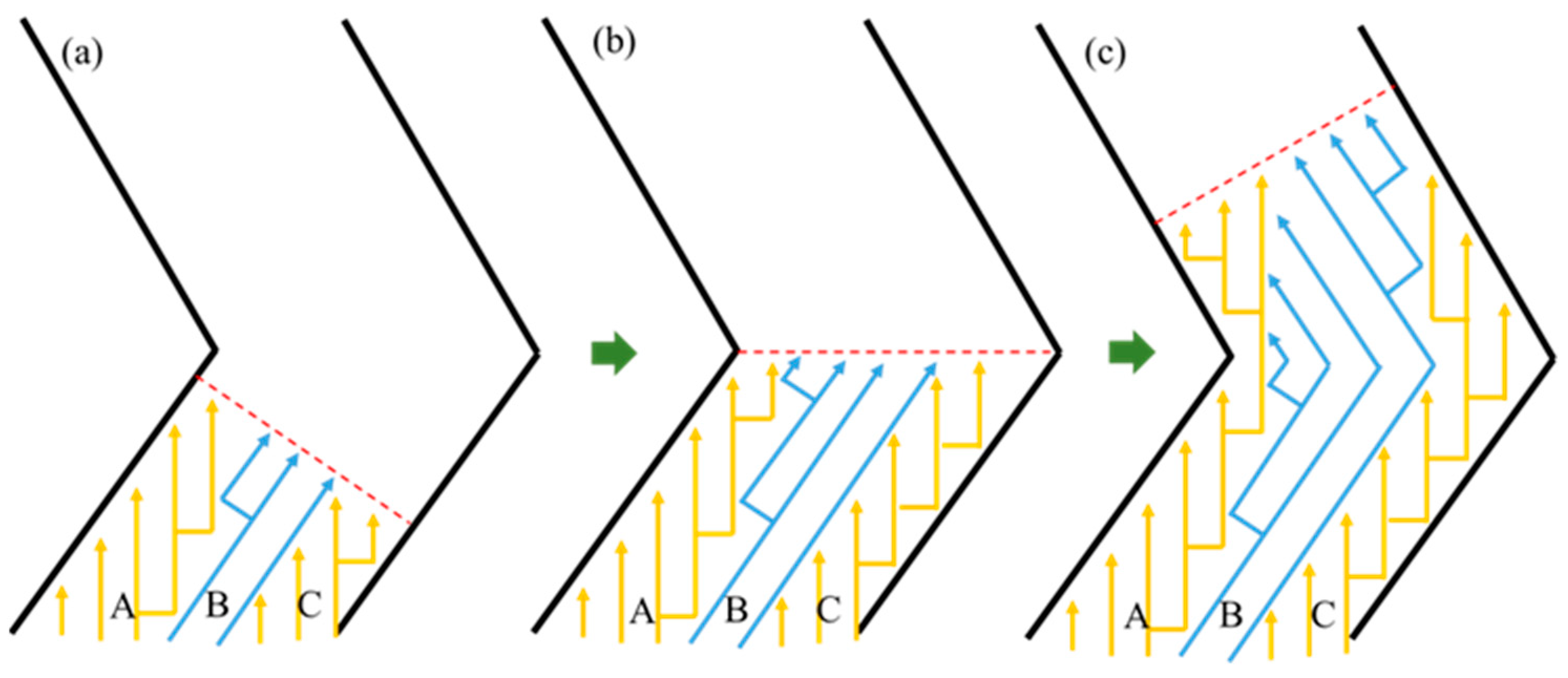
2. Materials and Methods
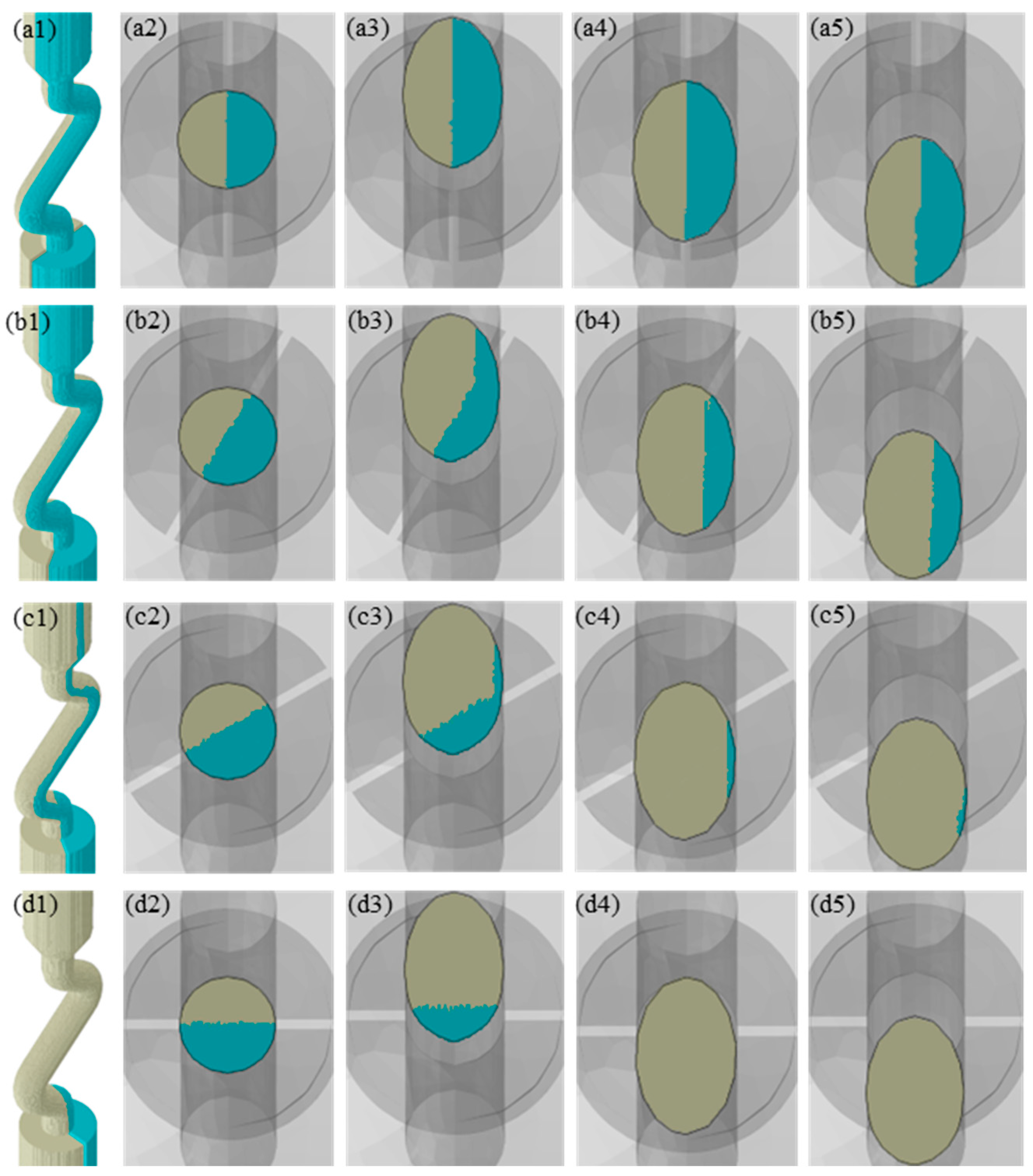
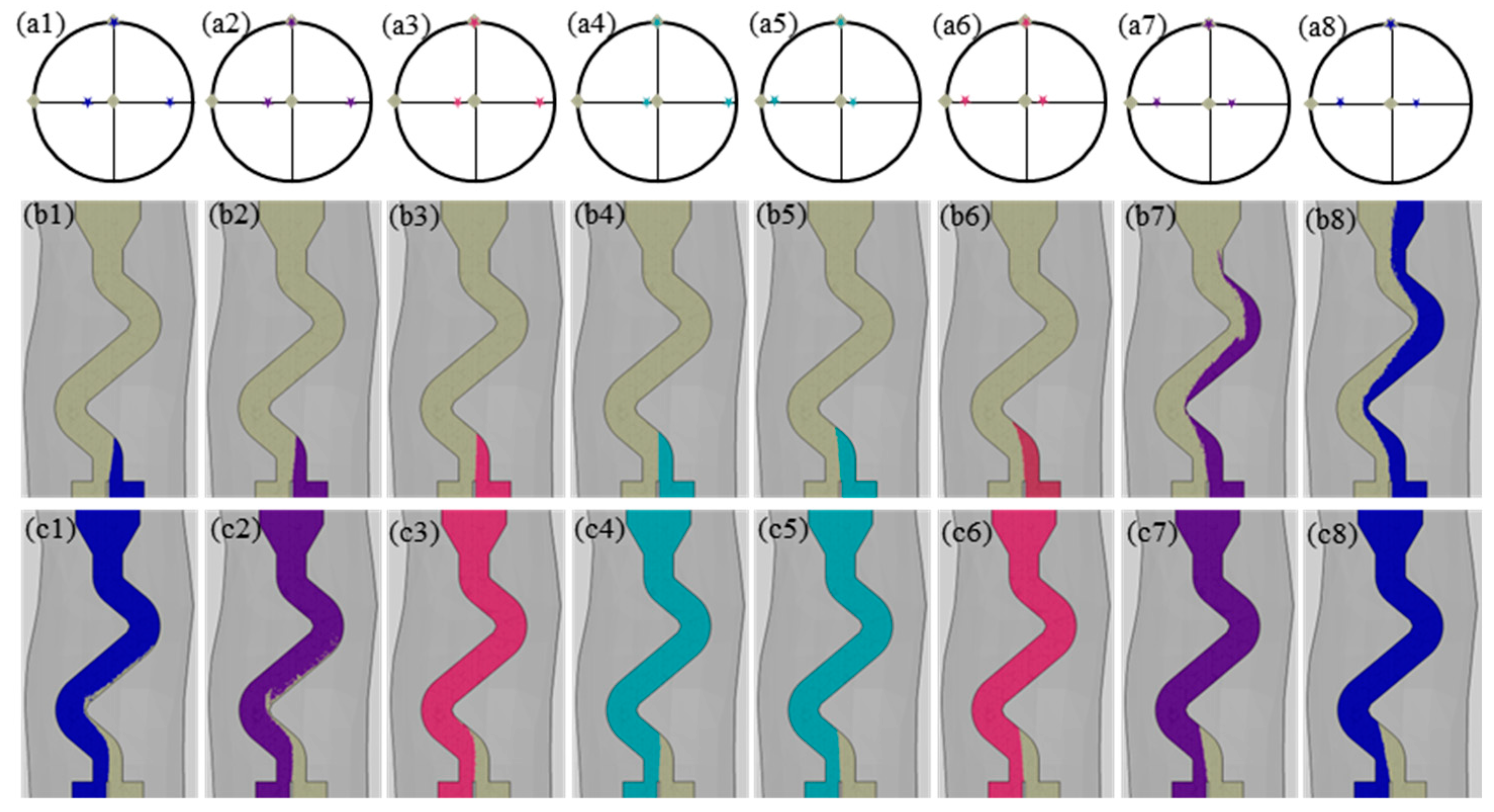
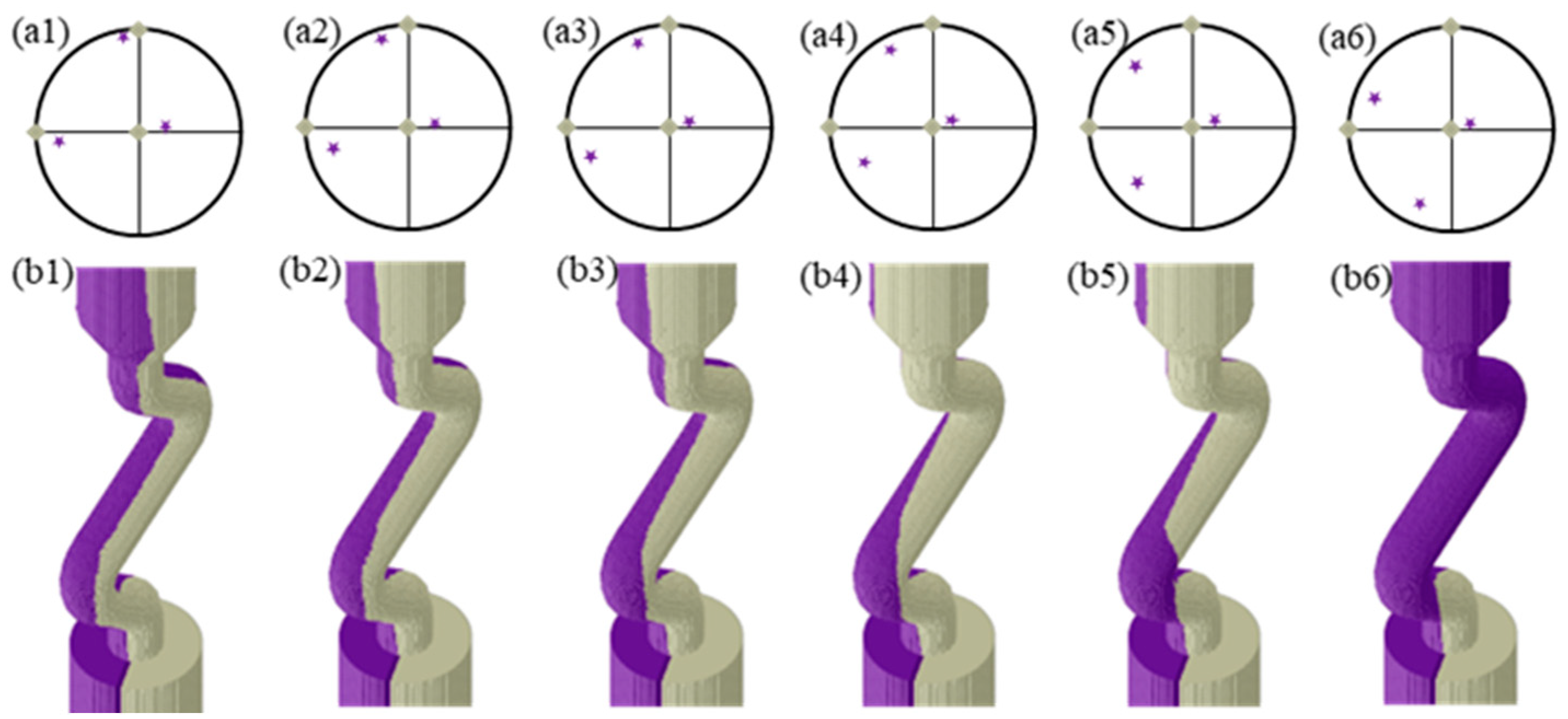
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reed, R.C. The Superalloys Fundamental and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Latief, F.H.; Kakehi, K. Effects of Re content and crystallographic orientation on creep behavior of aluminized Ni-base single crystal superalloys. Mater. Design. 2013, 49, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, P.; Cox, D.C.; Gandin, C.A.; Reed, R.C. Process modelling of grain selection during the solidification of single crystal superalloy castings. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2000, 280, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wu, W.P.; Chen, M.X.; Guo, Y.F. Molecular dynamics study of fatigue mechanical properties and microstructural evolution of Ni-based single crystal superalloys under cyclic loading. Comp. Mater. Sci. 2020, 185, 109954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higginbotham, G.J.S. From research to cost-effective directional solidification and single-crystal production-an integrated approach. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1986, 2, 442–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Hu, S.; Huo, M.; Sun, D.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Orientation controlling of Ni-based single-crystal superalloy by a novel method: Grain selection assisted by un-melted reused seed. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, W.; Dai, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yin, F.; Wang, X. Orientation control for nickel-based single crystal superalloys: Grain selection method assisted by directional columnar grains. Materials 2022, 15, 4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Geng, X.Q.; Zhang, X.L.; Liu, G.H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.D.; Guo, J.J. Effect of competitive crystal growth on microstructural characteristics of directionally solidified nickel-based single crystal superalloy. China Foundry 2022, 19, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X. A new mechanism of grain selection in spiral selector: The competitive growth between the entrance grains. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 33, 4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esaka, H.; Tamura, M.; Shinozuka, K. Analysis of yield rate in single crystal casting process using an engineering simulation model. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Q. Simulation and experimental studies on grain selection and structure design of the spiral selector for casting single crystal Ni-based superalloy. Materials 2017, 10, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zeng, L.; Xia, M.; Ren, N.; Li, J. Substrate stimulating technique for Ni-based single crystal superalloy preparation during direction solidification. Mater. Des. 2022, 224, 111334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zeng, L.; Ren, N.; Xia, M.; Li, J. A comprehensive understanding of grain selection in spiral grain selector during directional solidification. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 102, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.J.; Lee, H.; Yun, D.W.; Jeong, H.W.; Yoo, Y.S.; Seo, S.M.; Lee, J.H. Analysis of a Single Crystal Solidification Process of an Ni-based Superalloy using a CAFE Model. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2023, 61, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, F.; Ma, D. A Study of Grain Selection in Two-Dimensional (2D) Grain Selectors during the Investment Casting of Single-Crystal Superalloy. Materials 2023, 16, 4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.M.; Kim, I.S.; Lee, J.H.; Jo, C.Y.; Miyahara, H.; Ogi, K. Grain structure and texture evolutions during single crystal casting of the Ni-base superalloy CMSX-4. Met. Mater. Int. 2009, 15, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeliga, D.; Kubiak, K.; Burbelko, A.; Motyka, M.; Sieniawski, J. Modeling of Directional Solidification of Columnar Grain Structure in CMSX-4 Nickel-Based Superalloy Castings. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, L.; Gao, S.; Zhao, X.; Huang, T.; Zhang, J.; Fu, H. Simulation of grain selection during single crystal casting of a Ni-base superalloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, N.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Fu, H. Grain selection during casting Ni-base, single-crystal superalloys with spiral grain selector. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 3767–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, F.; Ma, D. Grain orientation optimization of two-dimensional grain selector during directional solidification of Ni-based superalloys. Materials 2020, 13, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Dong, H.; D’souza, N.; Gebelin, J.C.; Reed, R. Grain selection in spiral selectors during investment casting of single-crystal components: Part II. Numerical modeling. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 3439–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Lu, Q.; Li, J.; Jin, T.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z. Modes of grain selection in spiral selector during directional solidification of nickel-base superalloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2012, 28, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, D.; Chalmers, U.B. The origin of the preferred orientation in the columnar zone of ingots. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 1959, 215, 447–457. [Google Scholar]
- Gandin, C.A.; Rappaz, M. A coupled finite element-cellular automaton model for the prediction of dendritic grain structures in solidification processes. Acta Metall. Mater. 1994, 42, 2233–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Volek, A.; Green, N. Mechanism of competitive grain growth in directional solidification of a nickel-base superalloy. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 2631–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, T.; Ohno, M.; Shimokawabe, T.; Aoki, T. Two-dimensional phase-field simulations of dendrite competitive growth during the directional solidification of a binary alloy bicrystal. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Takaki, T.; Sakane, S.; Ohno, M.; Shibuta, Y.; Mohri, T. Overgrowth behavior at converging grain boundaries during competitive grain growth: A two-dimensional phase-field study. Int. J. Heat Mass. Tran. 2020, 160, 120196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, A.; Guillemot, G.; Tourret, D.; Karma, A.; Gandin, C.A. Growth competition between columnar dendritic grains—Cellular automaton versus phase field modeling. Acta Mater. 2018, 155, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.L.; Li, Z.L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Q.Y.; Liu, B.C. Numerical Simulation and Experimental Study on Grain Selection of DD6 Superalloy in Spiral Grain Selector by Directional Solidification. Rare Metal. Mat. Eng. 2017, 46, 1856–1861. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaei, M.; Kermanpur, A.; Sadeghi, F. Effects of withdrawal rate and starter block size on crystal orientation of a single crystal Ni-based superalloy. J. Cryst. Growth 2018, 485, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, F.; Kermanpur, A.; Norouzi, E. Optimizing Grain Selection Design in the Single-Crystal Solidification of Ni-Based Superalloys. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2018, 53, 1800108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.W.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.F. Effect of Withdrawal Rate of Spiral Selector on Grain Selection Behavior and Grain Orientation Evolution. Rare Metal. Mat. Eng. 2021, 50, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.; Yuan, L.; Lee, P.; Pollock, T. Simulation of diffusion-limited lateral growth of dendrites during solidification via liquid metal cooling. Acta Mater. 2014, 69, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
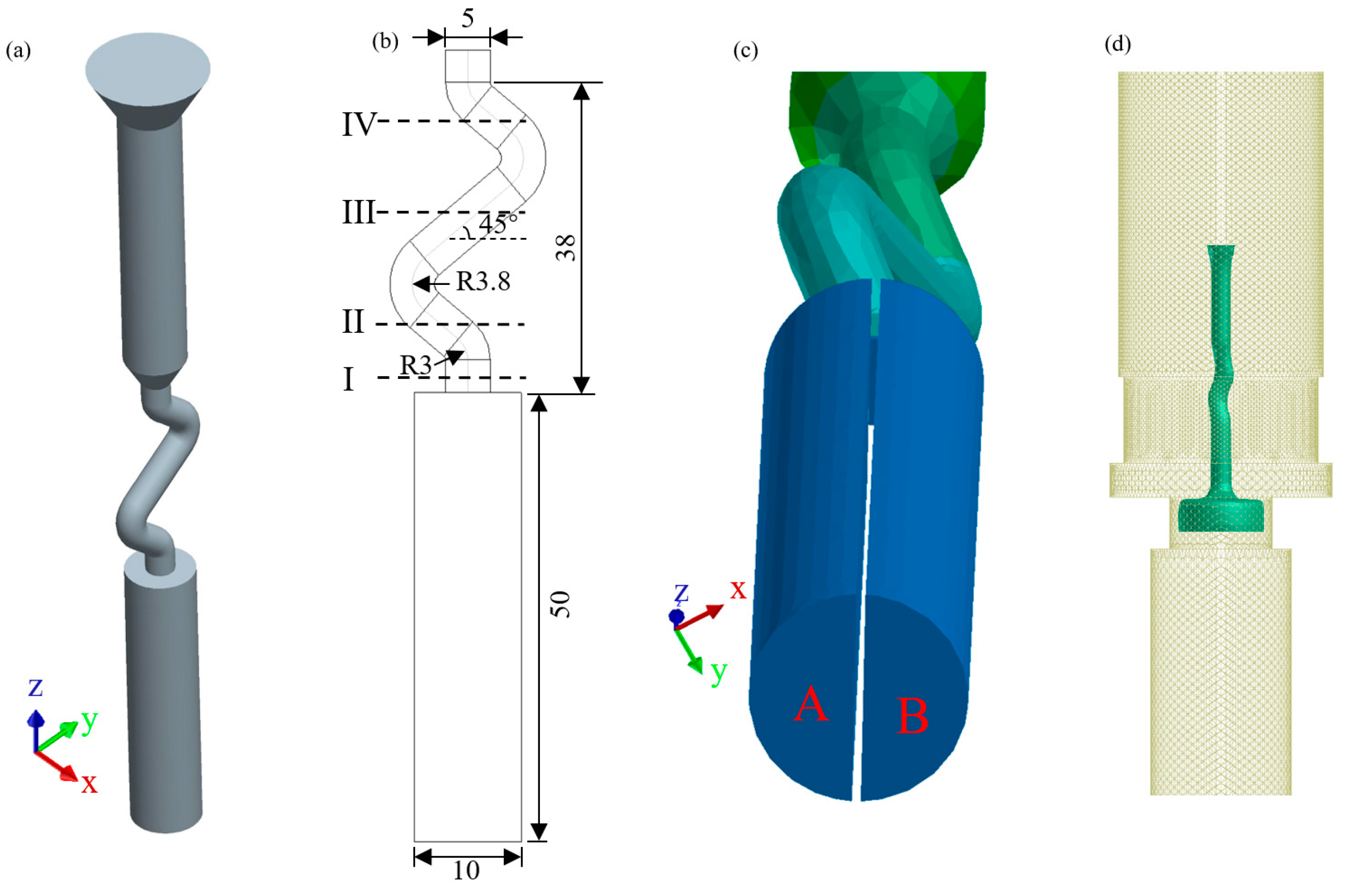
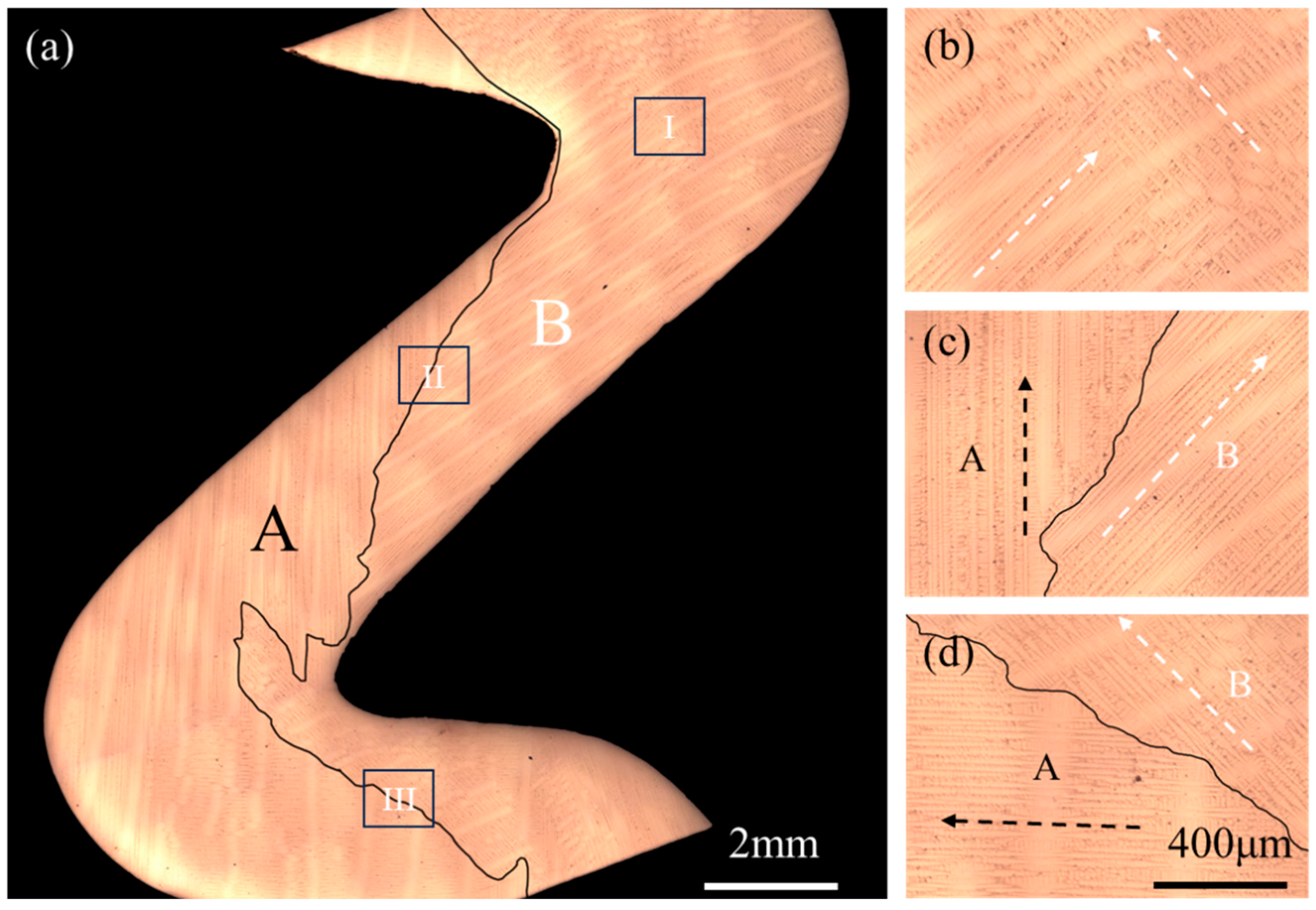
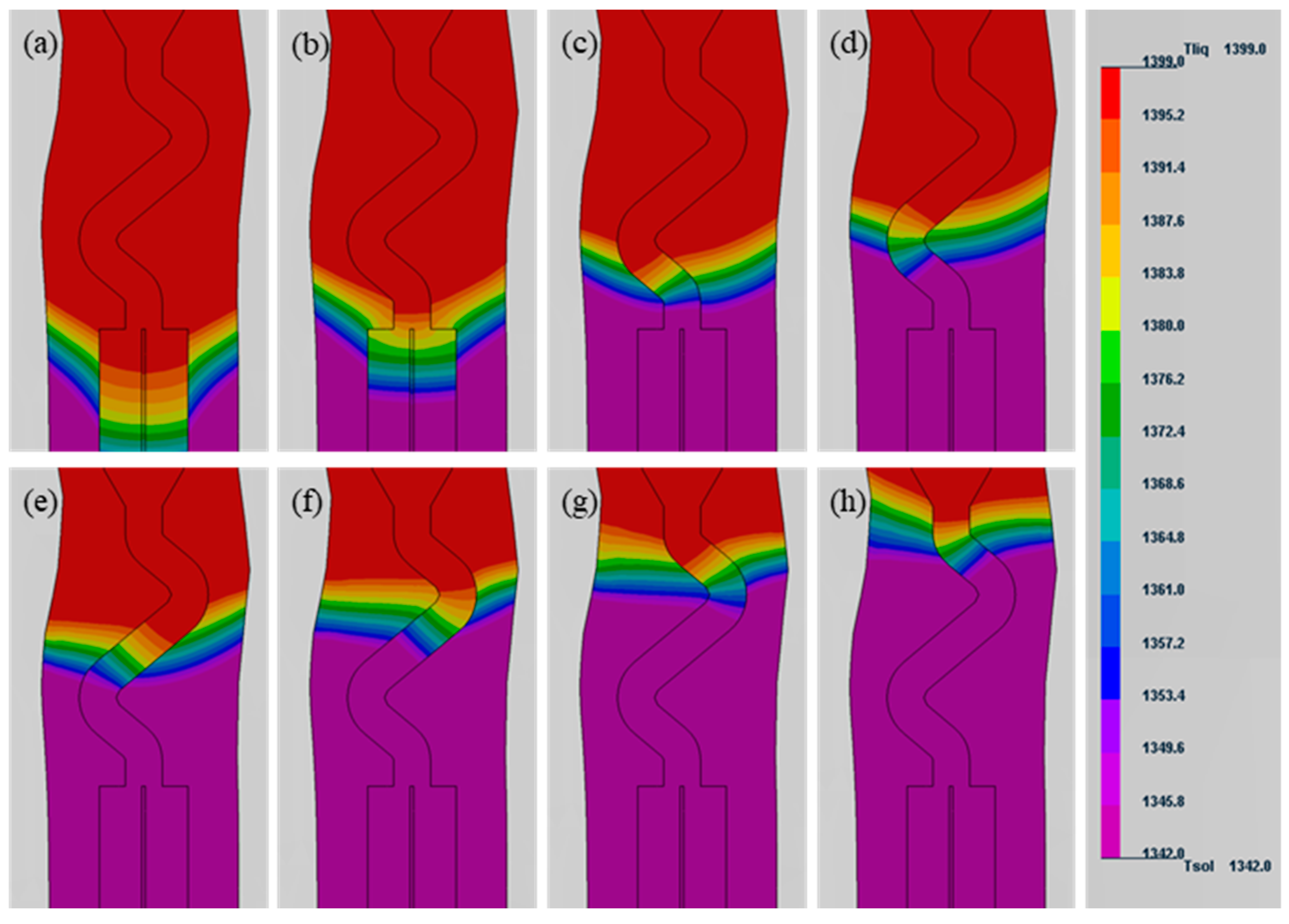
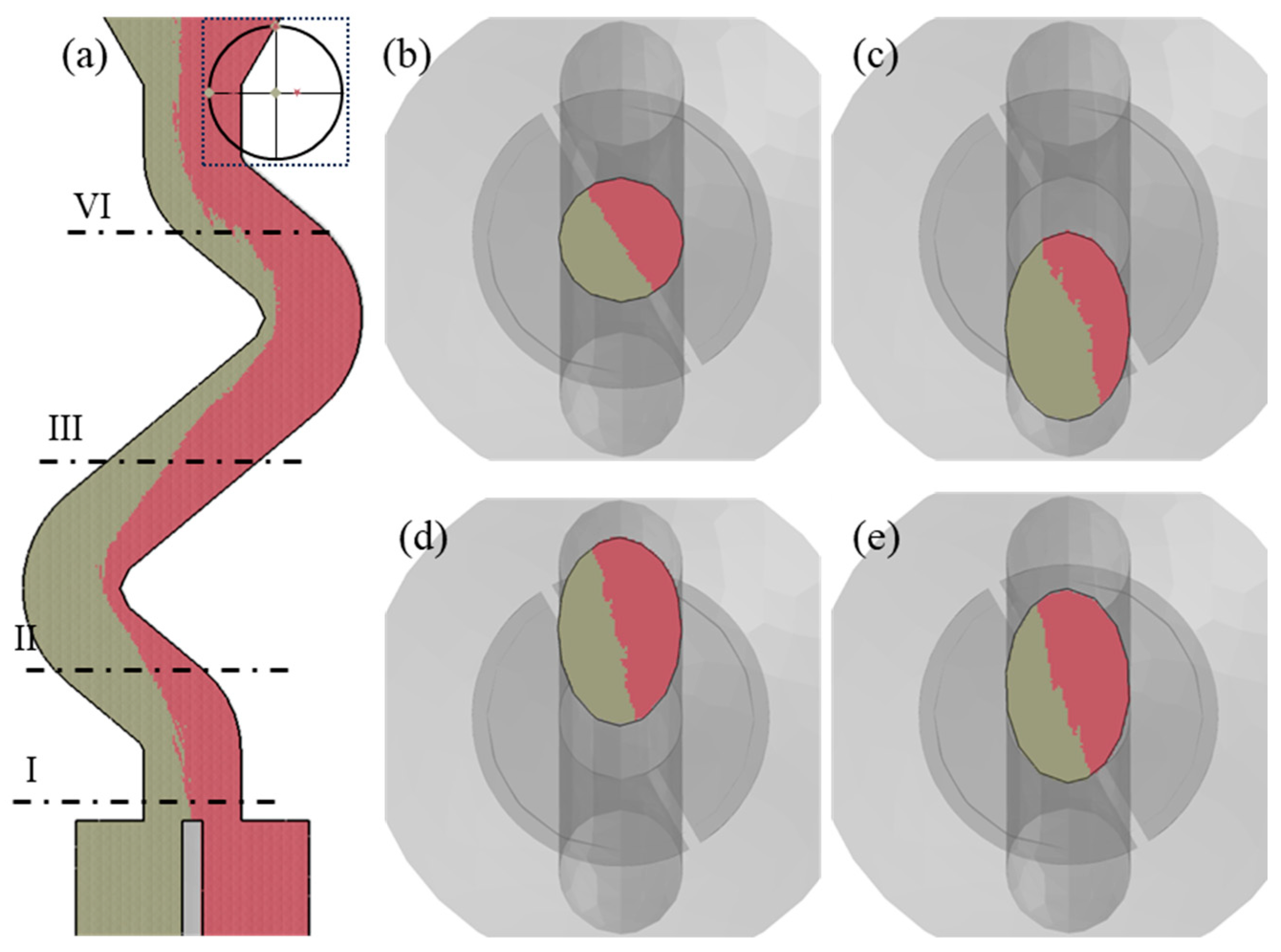

| Initial condition | |
| Melting temperature of DD33 superalloy | 1550 °C |
| Mold temperature | 1550 °C |
| Chill-plate temperature | 40 °C |
| Boundary condition | |
| Heater temperature | 1550 °C |
| Emissivity | 0.8 |
| Cooler temperature | 40 °C |
| Interface heat transfer coefficients | |
| Alloy melt and ceramic shell mold | 200–1900 W (m2 K)−1 |
| Alloy melt and water-cooled chill plate | 1000 W (m2 K)−1 |
| Ceramic shell mold and water-cooled chill plate | 50 W (m2 K)−1 |
| Alloy properties | |
| Specific heat | 358–773 KJ/kg/K |
| Latent heat | 277.4 KJ/kg |
| Thermal conductivity | 6.7–33.2 W/m/K |
| Density | 7.63–8.78 g/cm3 |
| Order Number | Angle between the thin Slice and the YOZ Plane (°) | Surface Nucleation (Single Crystal Type, Euler Angle) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bottom Surface of A | Bottom Surface of B | ||||||
| Φ1 (°) | Φ (°) | Φ2 (°) | Φ1 (°) | Φ (°) | Φ2 (°) | ||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| 2 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0 | |
| 4 | 5 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6 | 45 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 7 | 95 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 8 | 120 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 9 | 150 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 10 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 11 | 5 | 15 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 12 | 5 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 13 | 5 | 15 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 14 | 5 | 15 | 45 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 15 | 5 | 15 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 16 | 60 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| 17 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −20 | 0 |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −15 | 0 | |
| 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −10 | 0 | |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | −5 | 0 | |
| 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | |
| 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | |
| 23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 15 | 0 | |
| 24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 | 0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, Y.; Bao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J. Effect of Initial Position and Crystallographic Orientation on Grain Selection Procedure in Z-Form Selector for Ni-Based Single-Crystal Superalloy. Materials 2024, 17, 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081885
Guo Y, Bao J, Zhang X, Zhang M, Yang X, Zhang J. Effect of Initial Position and Crystallographic Orientation on Grain Selection Procedure in Z-Form Selector for Ni-Based Single-Crystal Superalloy. Materials. 2024; 17(8):1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081885
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Yuanyuan, Jun Bao, Xuanning Zhang, Mai Zhang, Xiqiong Yang, and Jian Zhang. 2024. "Effect of Initial Position and Crystallographic Orientation on Grain Selection Procedure in Z-Form Selector for Ni-Based Single-Crystal Superalloy" Materials 17, no. 8: 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081885
APA StyleGuo, Y., Bao, J., Zhang, X., Zhang, M., Yang, X., & Zhang, J. (2024). Effect of Initial Position and Crystallographic Orientation on Grain Selection Procedure in Z-Form Selector for Ni-Based Single-Crystal Superalloy. Materials, 17(8), 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17081885





