Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Fe67.6-Pd32-In0.4 (at.%) Shape Memory Melt-Spun Ribbons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
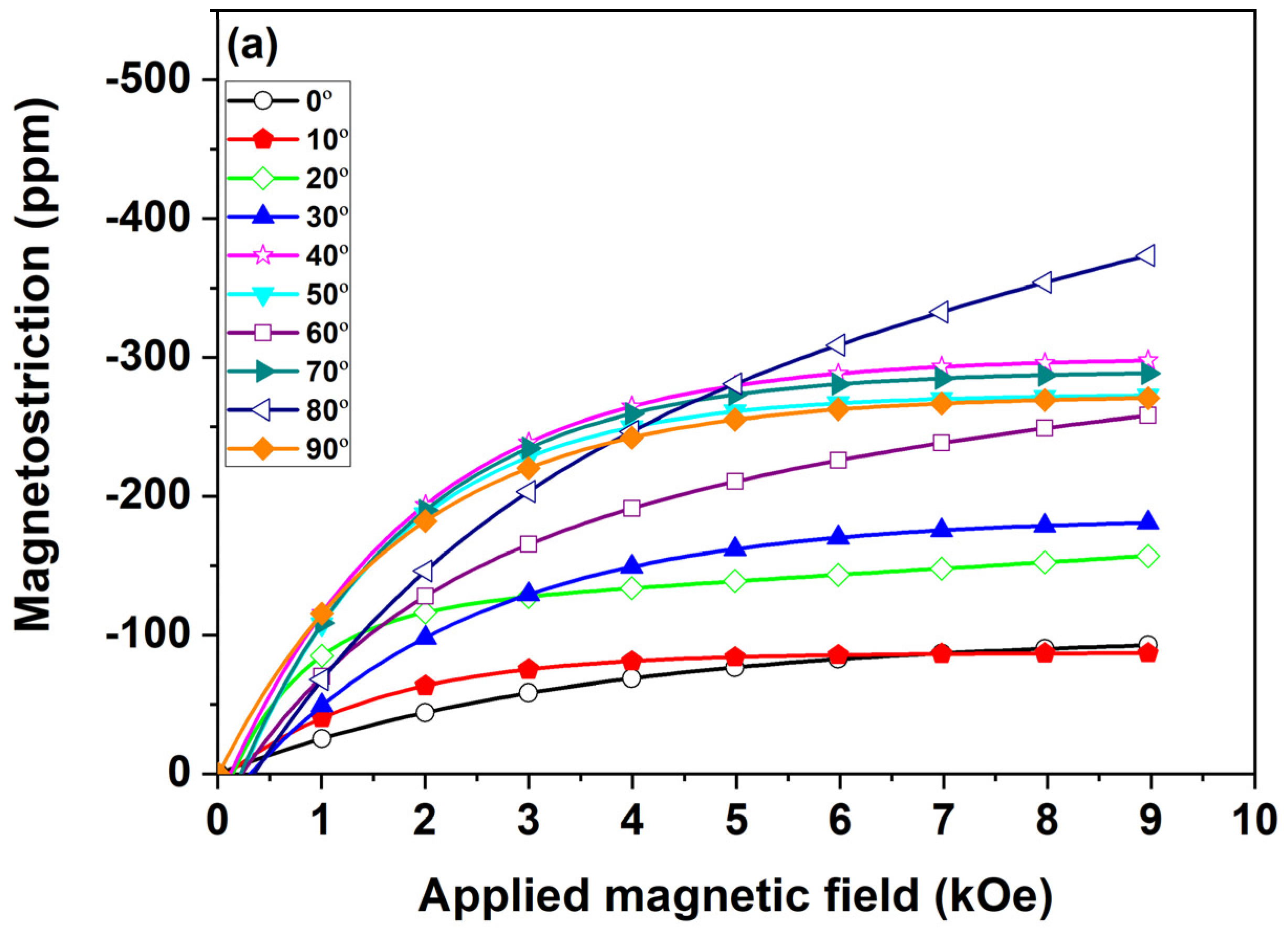
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ullakko, K.; Huang, J.K.; Kantner, C.; O’handley, R.C.; Kokorin, V.V. Large magnetic-field-induced strains in Ni2MnGa single crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 1966–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heczko, O.; Sozinov, A.; Ullakko, K. Giant field-induced reversible strain in magnetic shape memory NiMnGa alloy. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2000, 36, 3266–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozinov, A.; Likhachev, A.A.; Lanska, N.; Ullakko, K. Giant magnetic-field-induced strain in NiMnGa seven-layered martensitic phase. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 1746–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heczko, O. Magnetic shape memory effect and highly mobile twin boundaries. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 1559–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zink, M.; Mayr, S.G. Ferromagnetic shape memory alloys: Synthesis, characterisation and biocompatibility of Fe–Pd for mechanical coupling to cells. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 1579–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunge, A.; Chiriac, A.; Sofronie, M.; Crăciunescu, I.; Porav, A.S.; Turcu, R. Anticoagulant Properties of Coated Fe-Pd Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Ribbons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadaki, T.; Otsuka, K.; Shimizu, K. Shape memory alloys. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1988, 18, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohmura, T.; Oshima, R.; Fujita, F.E. Thermoelastic FCC-FCT Martensitic Transformation in Fe-Pd Alloy. Scripta Met. 1980, 14, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T. Significant elastocaloric effect in a Fe-31.2 Pd (at.%) single crystal. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 161914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakeshita, T.; Ullakko, K. Giant magnetostriction in ferromagnetic shape-memory alloys. MRS Bull. 2002, 27, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vokoun, D.; Hu, C.T.; Kafka, V. Magnetic properties of annealed Fe–29.9 at% Pd ribbons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2003, 264, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, Y.; Hagood, N.W.; Kimura, H.; Watanabe, T. Shape memory effect and magnetostriction in rapidly solidified Fe-29.6 at% Pd alloy. Mater. Trans. JIM 1998, 39, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yasuda, H.Y.; Komoto, N.; Ueda, M.; Umakoshi, Y. Microstructure control for developing Fe–Pd ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2002, 3, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Hiraga, K.; Oshima, R. Origin of Tetragonality of BCT Martensite in Substitutional Fe–Pd (–Ni) Disordered Alloys. Mater. Trans. JIM 1992, 33, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cui, J.; Shield, T.W.; James, R.D. Phase transformation and magnetic anisotropy of an iron–palladium ferromagnetic shape-memory alloy. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Nojiri, T.; Ohtsuka, H.; Umemoto, M. Effect of Co and Ni on martensitic transformation and magnetic properties in Fe-Pd ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Mater. Trans. 2003, 44, 2499–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vokoun, D.; Wang, Y.W.; Goryczka, T.; Hu, C.T. Magnetostrictive and shape memory properties of Fe–Pd alloys with Co and Pt additions. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, S261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alarcos, V.; Recarte, V.; Pérez-Landazábal, J.I.; Gómez-Polo, C.; Chernenko, V.A.; González, M.A. Reversible and irreversible martensitic transformations in Fe-Pd and Fe-Pd-Co alloys. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2008, 158, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, R.A.; Willoughby, S.D.; Ramirez, A.; MacLaren, J.M.; Cui, J.; Pan, Q.; James, R.D. Electronic and structural properties of Fe 3 Pd–Pt ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 7818–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Tagawa, T.; Taya, M. Martensitic transformation in Pd-rich Fe–Pd–Pt alloy. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gruner, M.E.; Hamann, S.; Brunken, H.; Ludwig, A.; Entel, P. Compositional trends and magnetic excitations in binary and ternary Fe–Pd–X magnetic shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 577, S333–S337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alarcos, V.; Recarte, V.; Pérez-Landazábal, J.I.; González, M.A.; Rodríguez-Velamazán, J.A. Effect of Mn addition on the structural and magnetic properties of Fe–Pd ferromagnetic shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 4224–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lee, H.T. Grain size refinement and magnetostriction of ferromagnetic shape memory Fe–Pd–Rh alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lee, H.T. Magnetostriction and magnetic structure in annealed recrystallization of strain-forged ferromagnetic shape memory Fe–Pd–Rh alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 09D312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, S.; Gruner, M.E.; Irsen, S.; Buschbeck, J.; Bechtold, C.; Kock, I.; Mayr, S.G.; Savan, A.; Thienhaus, S.; Quandt, E.; et al. The ferromagnetic shape memory system Fe–Pd–Cu. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 5949–5961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vokoun, D.; Hu, C.T.; Lo, Y.H.; Lančok, A.; Heczko, O. Transformation properties of Fe70-Pd30-XInX shape memory melt-spun ribbons. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, S845–S848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofronie, M.; Popescu, B.; Enculescu, M. Structural, magnetic and magnetostrictive properties of the ternary iron–palladium–silicon ferromagnetic shape memory ribbons. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofronie, M.; Tolea, F.; Tolea, M.; Popescu, B.; Valeanu, M. Magnetic and magnetostrictive properties of the ternary Fe67. 5Pd30. 5Ga2 ferromagnetic shape memory ribbons. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2020, 142, 109446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Sato, R.; Tatetsu, Y.; Takahata, R.; Yamazoe, S.; Yamauchi, M.; Inagaki, Y.; Horibe, Y.; Kudo, M.; Toriyama, T.; et al. Inter-element miscibility driven stabilization of ordered pseudo-binary alloy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, C. Immiscible behaviour in the iron-indium system. Int. J. Mater. Res. 1967, 58, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Sutou, Y.; Omori, T.; Oikawa, K.; Ishida, K.; Yoshikawa, A.; Umetsu, R.Y.; Kainuma, R. Pd–In–Fe shape memory alloy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 261906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Zhao, D.; Sun, W.; Wei, Z. Microstructure, martensitic transformation and elastocaloric effect in Pd-In-Fe polycrystalline shape memory alloys. Intermetallics 2018, 100, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.T.; Goryczka, T.; Vokoun, D. Effects of the spinning wheel velocity on the microstructure of Fe–Pd shape memory melt-spun ribbons. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Iijima, T.; He, G.; Takahashi, T.; Oikawa, K.; Furuya, Y. Properties of sputter-deposited Fe–Pd thin films. Smart Mater. 2001, 4234, 284–291. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, S.; Inoue, K.; Koterazawa, K.; Mizuuchi, K. Shape memory behavior of Fe–Pd alloy thin films prepared by dc magnetron sputtering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 339, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Ghorbani, M.; Dolati, A. Electrochemical investigation of electrodeposited Fe–Pd alloy thin films. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 56, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Nath, A.; Roy, S.S. Additive manufacturing of multi-functional biomaterials for bioimplants: A review. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 1136, p. 012016. [Google Scholar]
- Bierwagen, O. Indium oxide—A transparent, wide-band gap semiconductor for (opto) electronic applications. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2015, 30, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhuo, Y.; Tu, W.; Li, Z.; Ma, X.; Pei, Y.; Wang, G. High mobility indium tin oxide thin film and its application at infrared wavelengths: Model and experiment. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 22123–22134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, T.; Lee, C.C.; Taya, M. Design of FePd spring actuators. In Center for Intelligent Materials and Systems; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hasbi, M.Y.; Mabruri, E.; Yudanto, S.D.; Ridlo, F.M.; Adjiantoro, B.; Irawan, D.; Astawa, I.G.P.; Rido, M.R.; Romijarso, T.B.; Roberto, R.; et al. Opportunities and Challenges of Fe-Based Shape Memory Alloys for Biomedical Applications–Short Review; AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2024; Volume 3003. [Google Scholar]
- Budhani, R.C.; Goel, T.C.; Chopra, K.L. Melt-spinning technique for preparation of metallic glasses. Bull. Mater. Sci. 1982, 4, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimp, M.A.; Vedula, K. Effect of boron on the tensile properties of B2 FeAl. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1986, 78, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Yamada, H.; Adachi, K. A new low temperature phase (fct) of Fe–Pd invar. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1980, 48, 2161–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Oshima, R.; Fujita, F.E. Martensitic transformation in the Fe–Pd alloy system. Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met. 1984, 25, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, H.; Noda, Y.; Yamada, Y. A spatially modulated structure during the martensitic fcc-fct transformation in fe–pd alloy. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1988, 57, 3668–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heczko, O.; Svec, P.; Janickovic, D.; Ullakko, K. Magnetic properties of Ni-Mn-Ga ribbon prepared by rapid solidification. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2002, 38, 2841–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flitcraft, E.; De Vecchis, P.R.; Kuprienko, A.; Chmielus, M.; Fink, C. Effect of rapid solidification and post-processing on microstructure, magnetic and structural transition temperatures and magnetic properties in Ni50Mn29Ga21 magnetic shape-memory alloy. Acta Mater. 2023, 260, 119325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
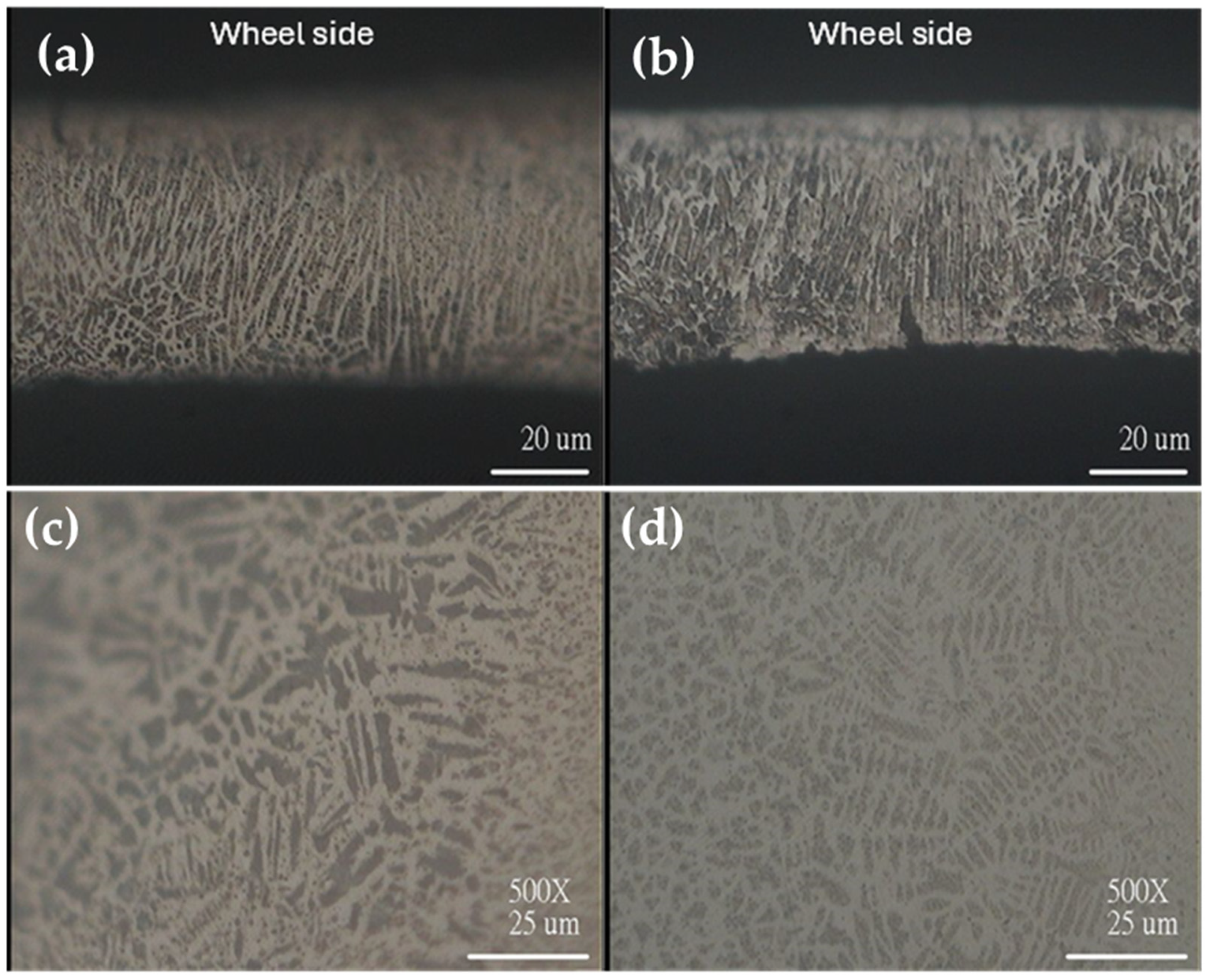


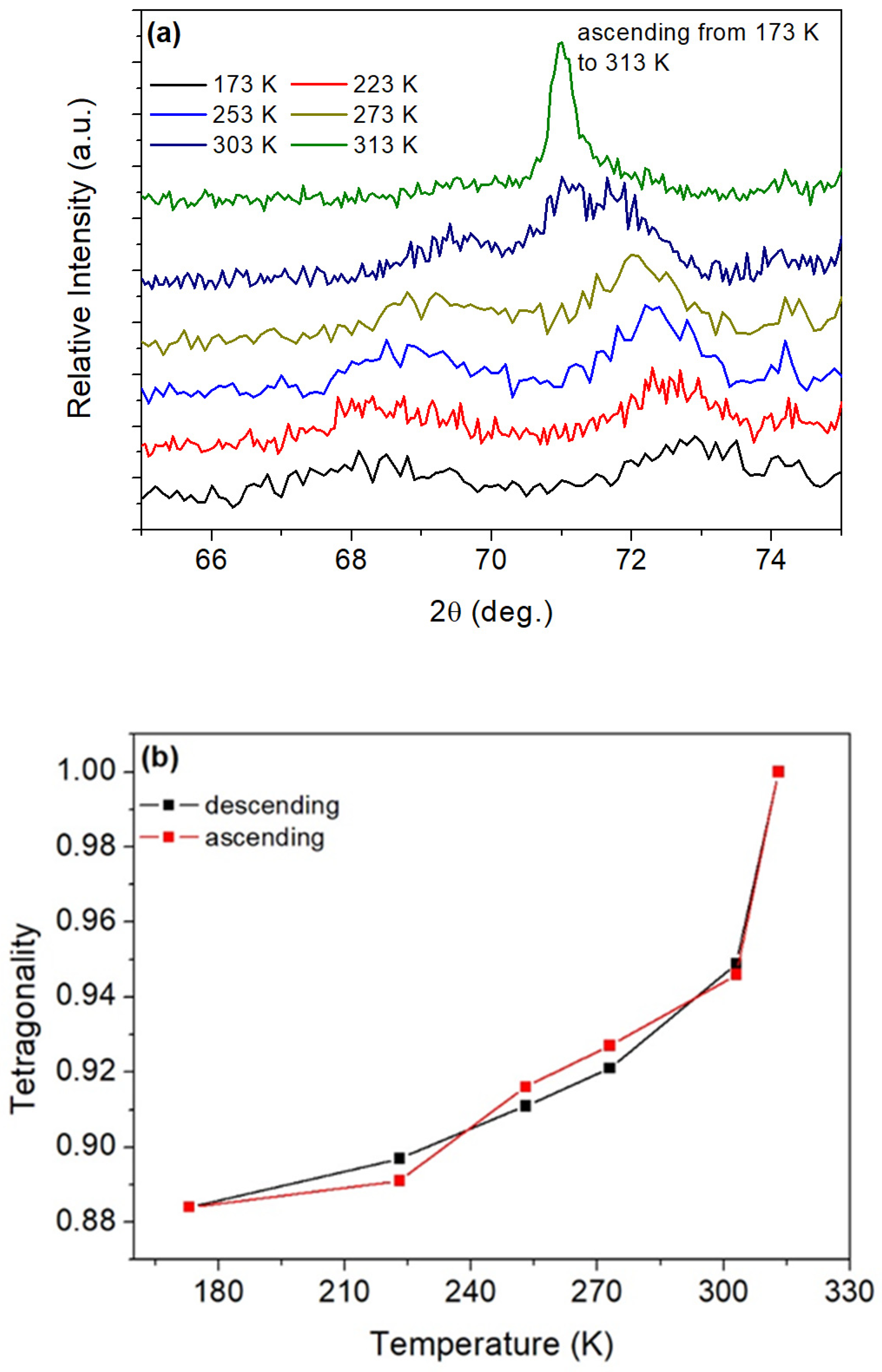

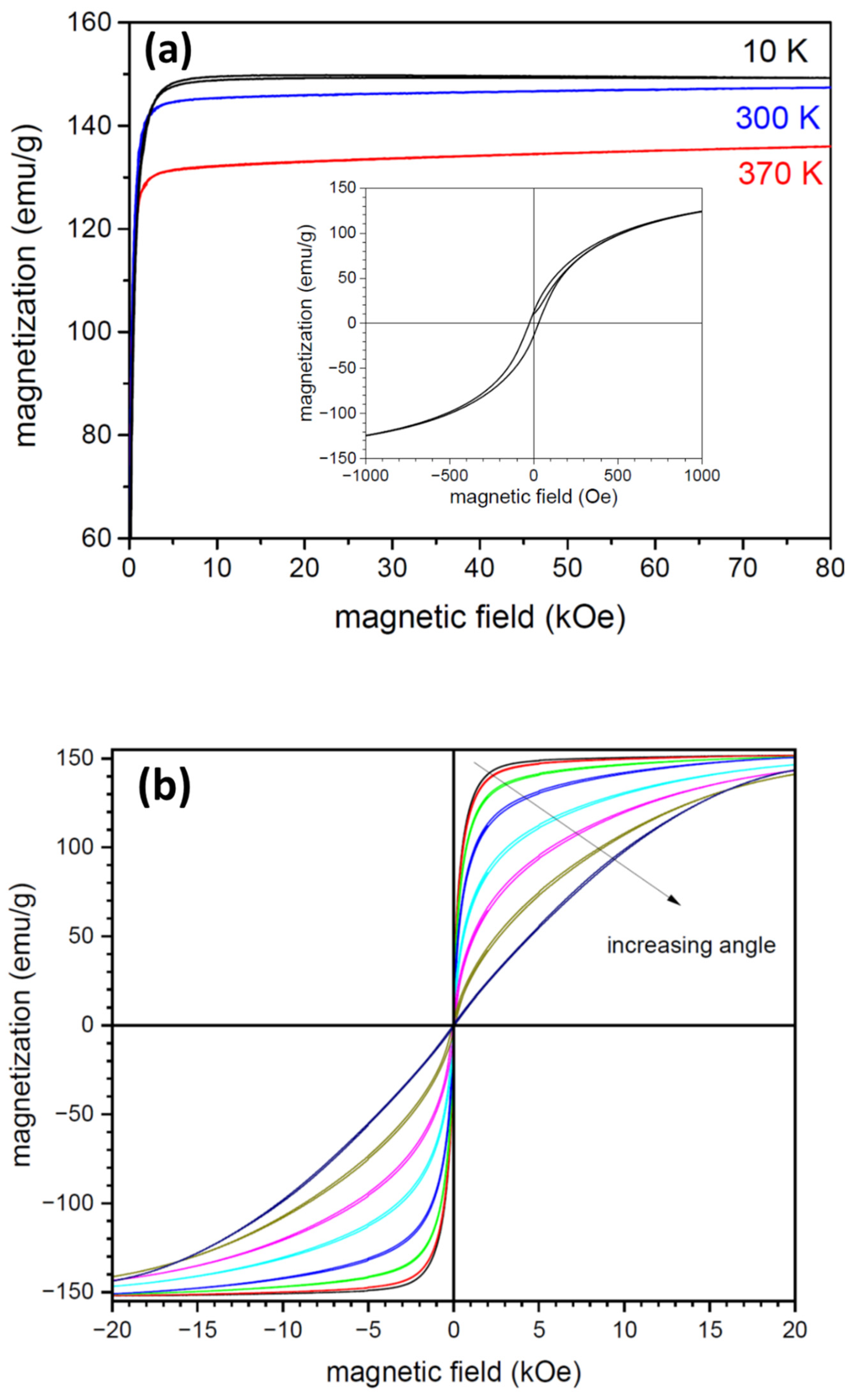
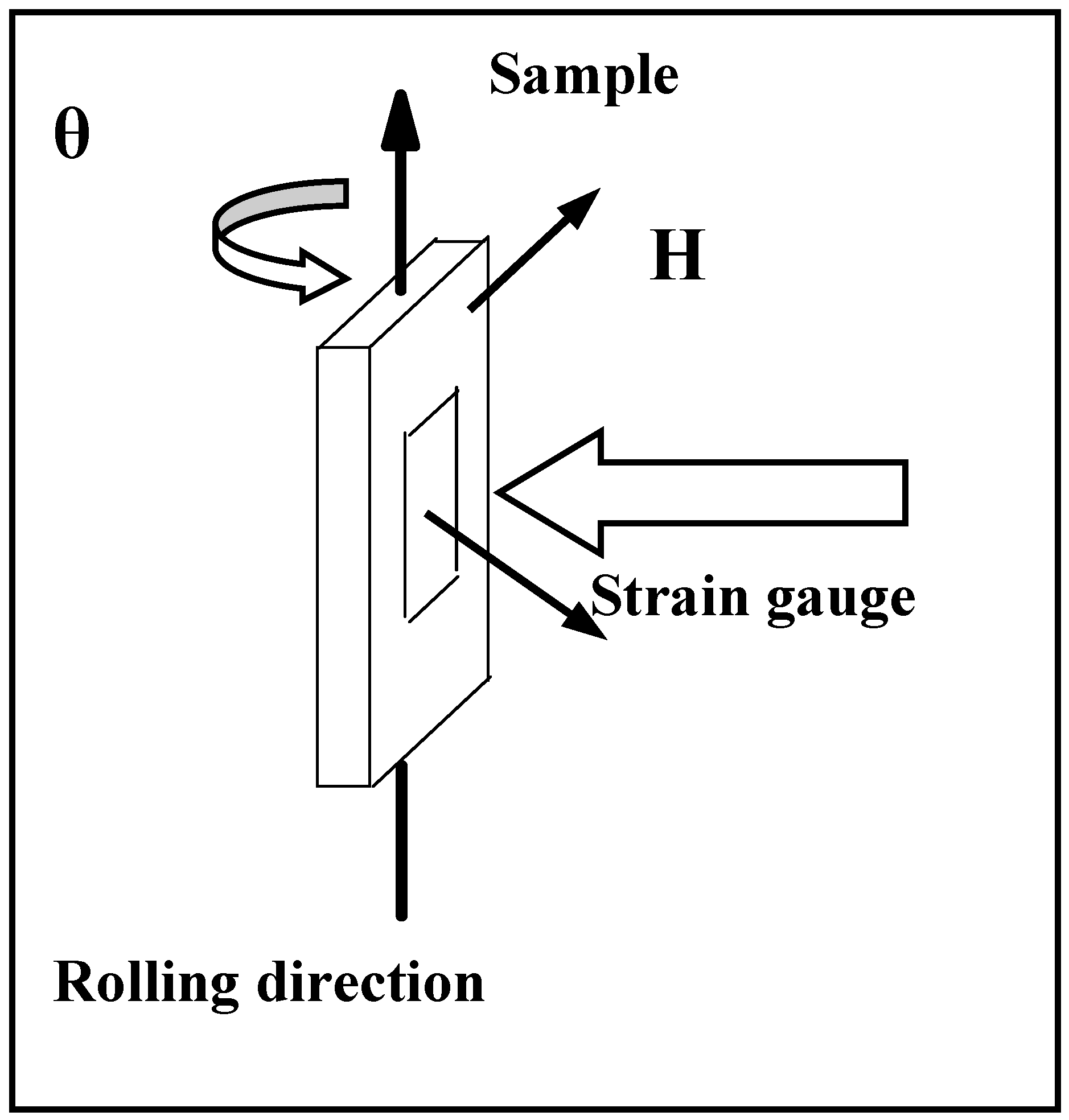

| Chemical Element | Area in the Sample | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Within the White Clusters | Outside of the Clusters | |||||
| Pd (at.%) | 37.60 | 34.00 | 34.80 | 39.39 | 30.90 | 32.17 |
| In (at.%) | 6.97 | 2.65 | 5.01 | 10.59 | 0.90 | 1.12 |
| Fe (at.%) | 55.43 | 63.35 | 59.38 | 50.02 | 68.20 | 66.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vokoun, D.; Lo, Y.-H.; Heczko, O.; Samal, S.; Hu, C.-T. Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Fe67.6-Pd32-In0.4 (at.%) Shape Memory Melt-Spun Ribbons. Materials 2024, 17, 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071674
Vokoun D, Lo Y-H, Heczko O, Samal S, Hu C-T. Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Fe67.6-Pd32-In0.4 (at.%) Shape Memory Melt-Spun Ribbons. Materials. 2024; 17(7):1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071674
Chicago/Turabian StyleVokoun, David, Yuan-Hung Lo, Oleg Heczko, Sneha Samal, and Chen-Ti Hu. 2024. "Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Fe67.6-Pd32-In0.4 (at.%) Shape Memory Melt-Spun Ribbons" Materials 17, no. 7: 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071674
APA StyleVokoun, D., Lo, Y.-H., Heczko, O., Samal, S., & Hu, C.-T. (2024). Microstructure and Magnetic Properties of Fe67.6-Pd32-In0.4 (at.%) Shape Memory Melt-Spun Ribbons. Materials, 17(7), 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17071674







