Influence of Tempering Temperature on Mechanical and Rotational Bending Fatigue Properties of 40CrNi2MoE Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
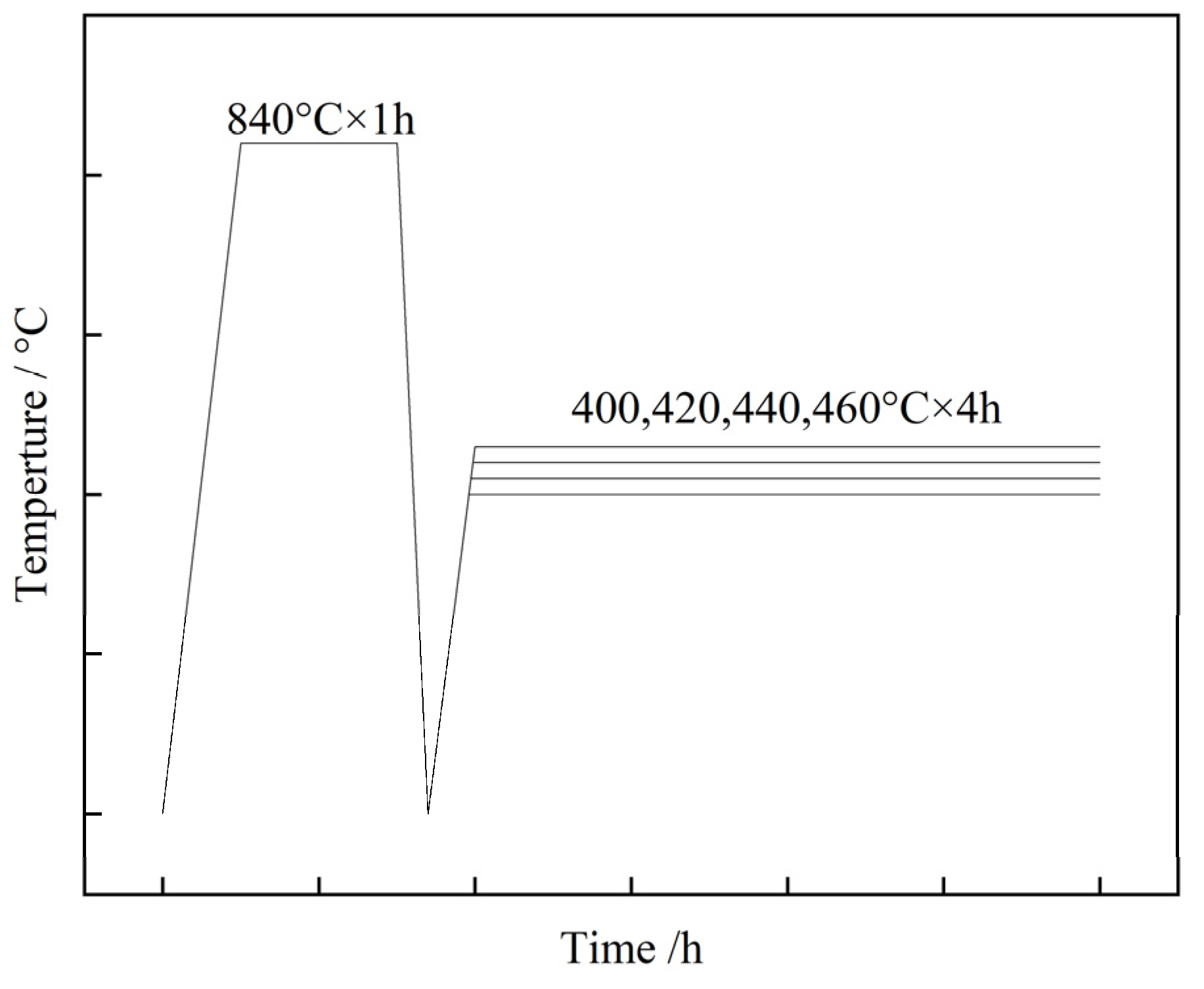
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
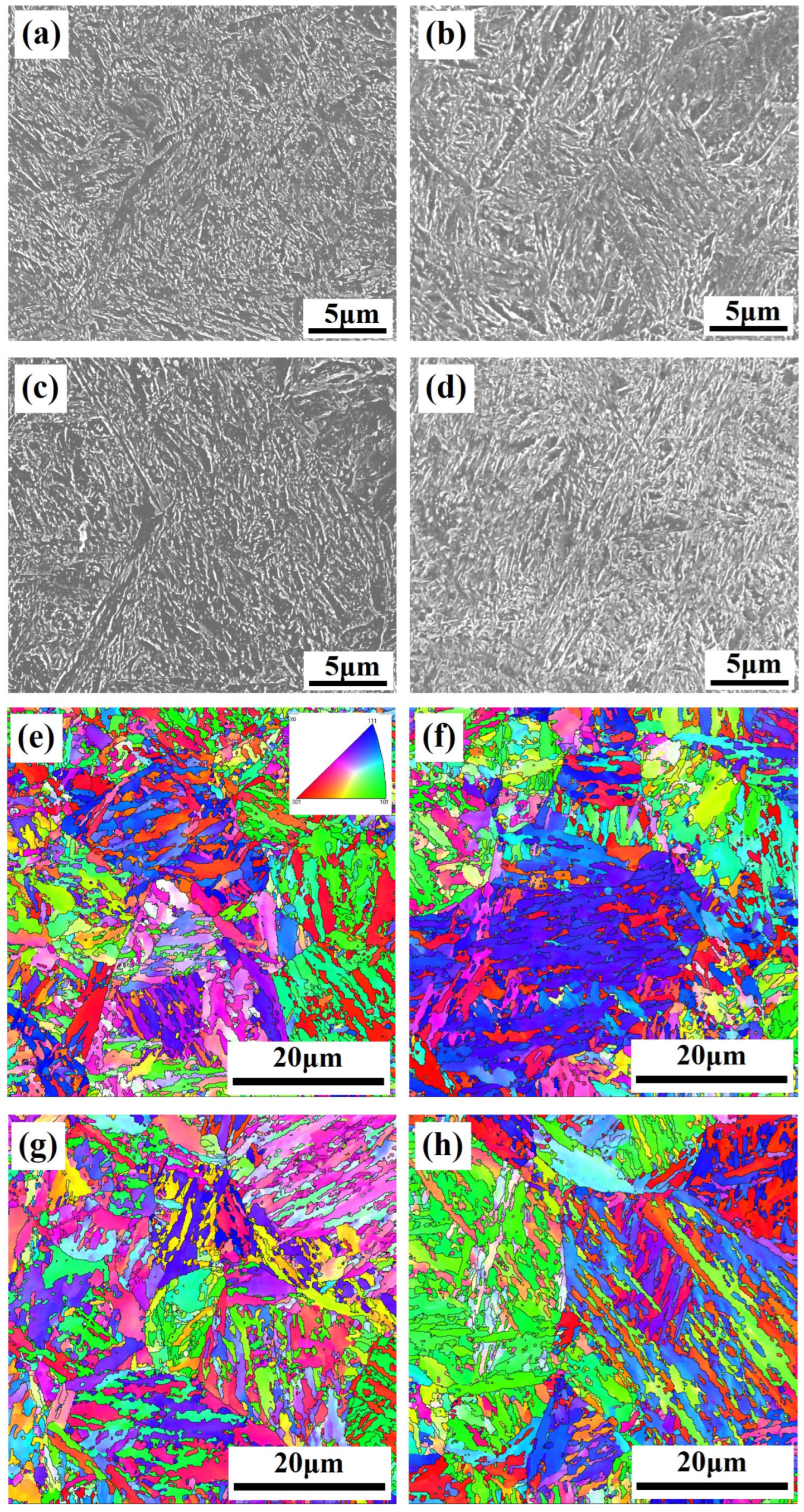
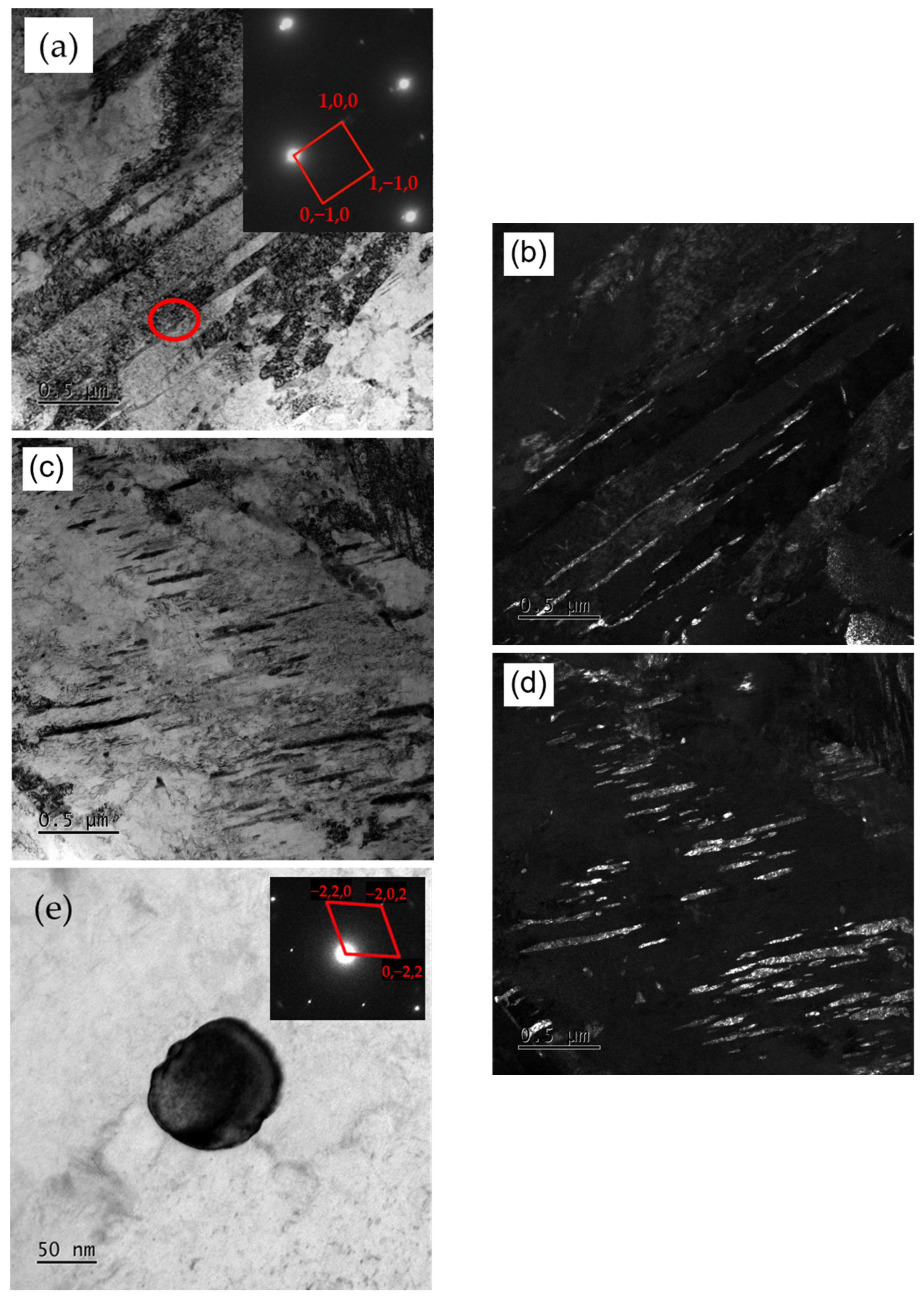
3.1. Microstructure
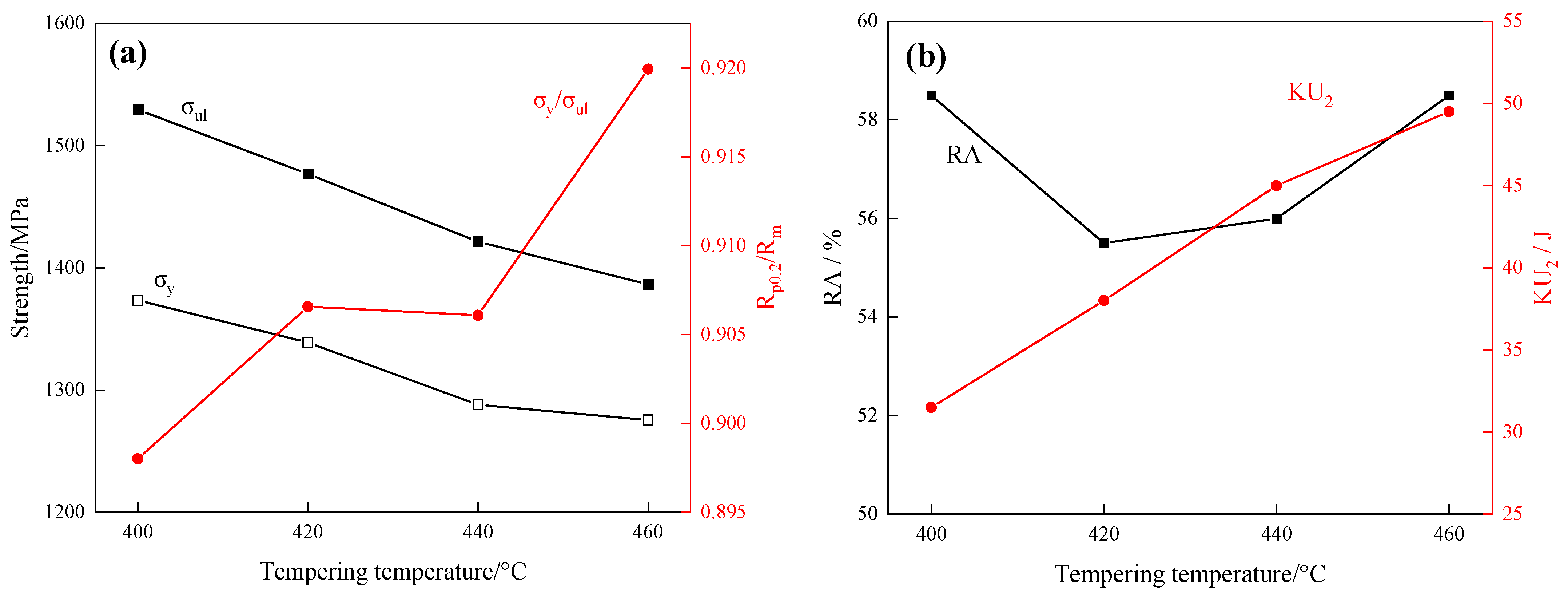
3.2. Mechanical Properties
3.3. Fatigue Life
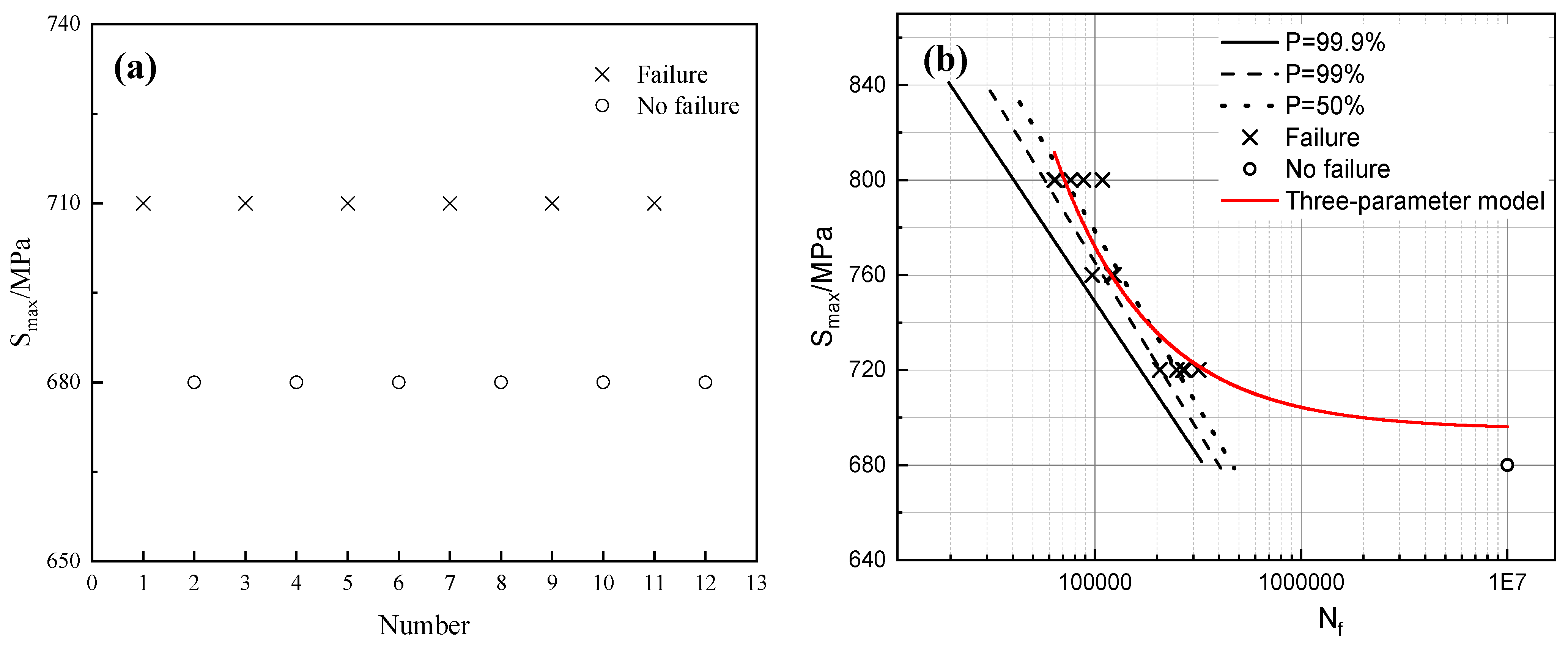
3.4. Fatigue Limit and S-N Curve
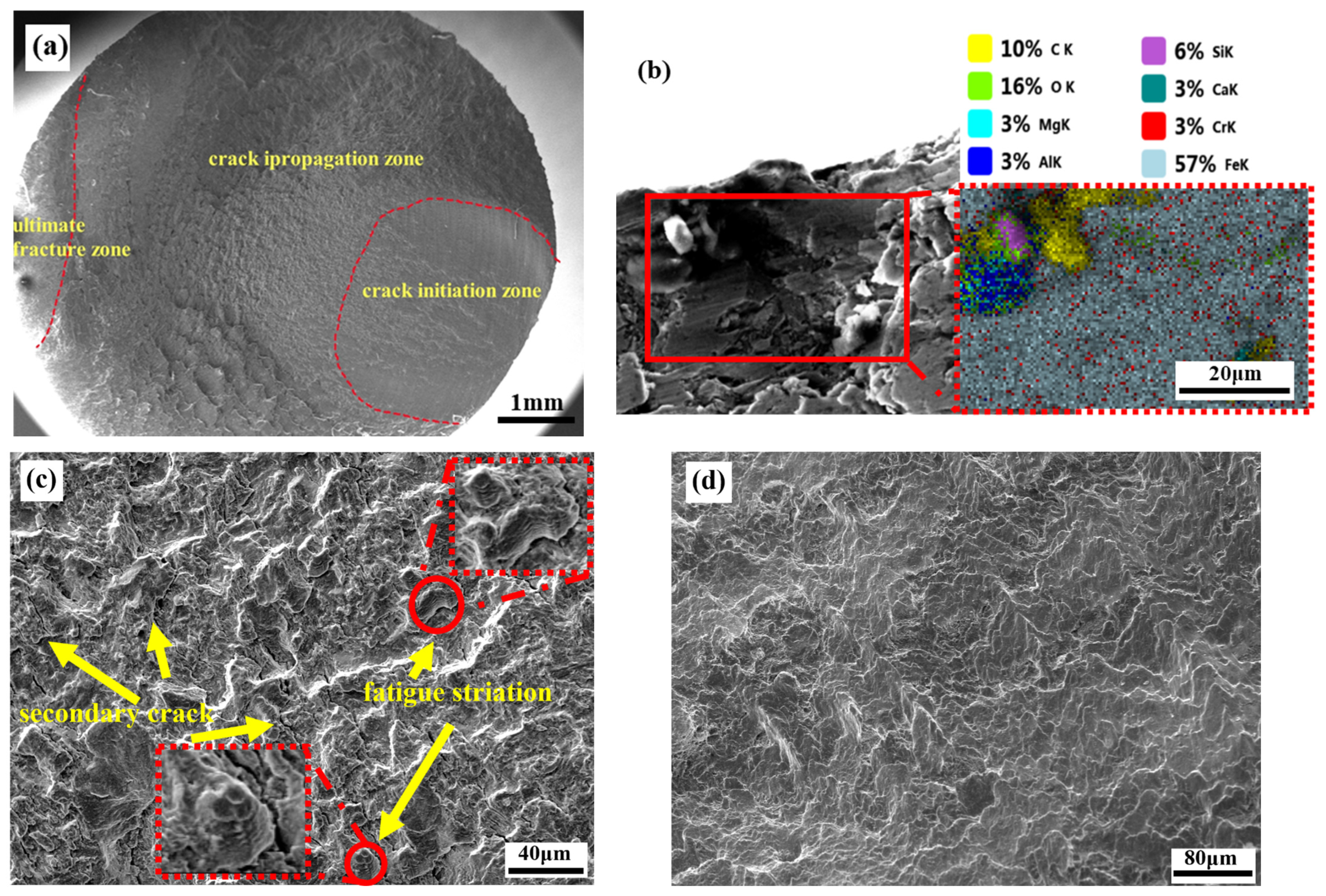
3.5. Fracture Surface
3.6. Dislocation Density
4. Conclusions
- The present study was undertaken to scrutinize the impact of tempering temperature upon the mechanical attributes of 40CrNi2MoE steel. Notably, subsequent to tempering at 400 °C, the tensile strength of 40CrNi2MoE steel attains its zenith, registering at Rm = 1530 MPa. With the incremental elevation in the tempering temperature, both the strength and yield ratio manifest a discernible decrement, predominantly ascribed to the diminishment in dislocation density. Moreover, it is noteworthy that toughness evinces a correlation with the tempering temperature.
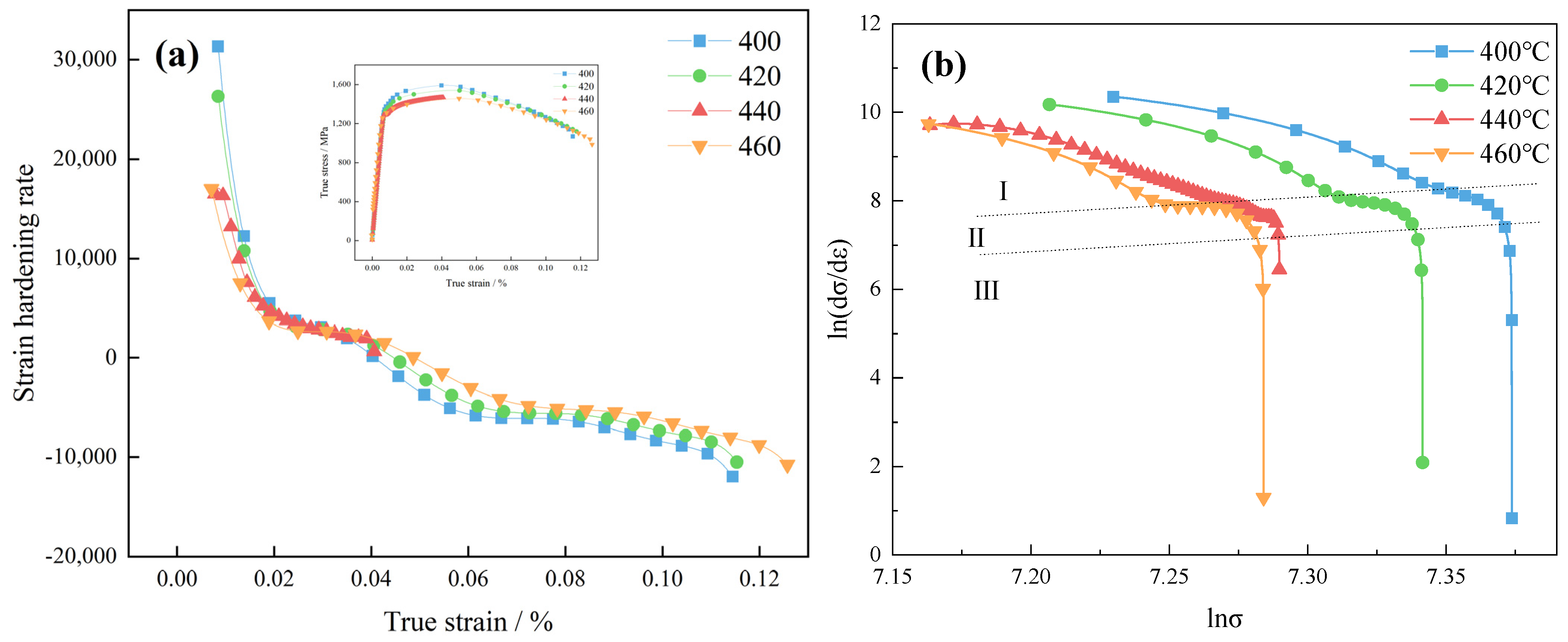
- A modified C–J analysis illuminates that, concomitant with the escalation in tempering temperature, the strain-hardening capacity experiences a gradual attenuation. Dislocations, together with precipitations, along with their interplay, constitute the chief determinants governing the strain-hardening demeanor of the examined steel.
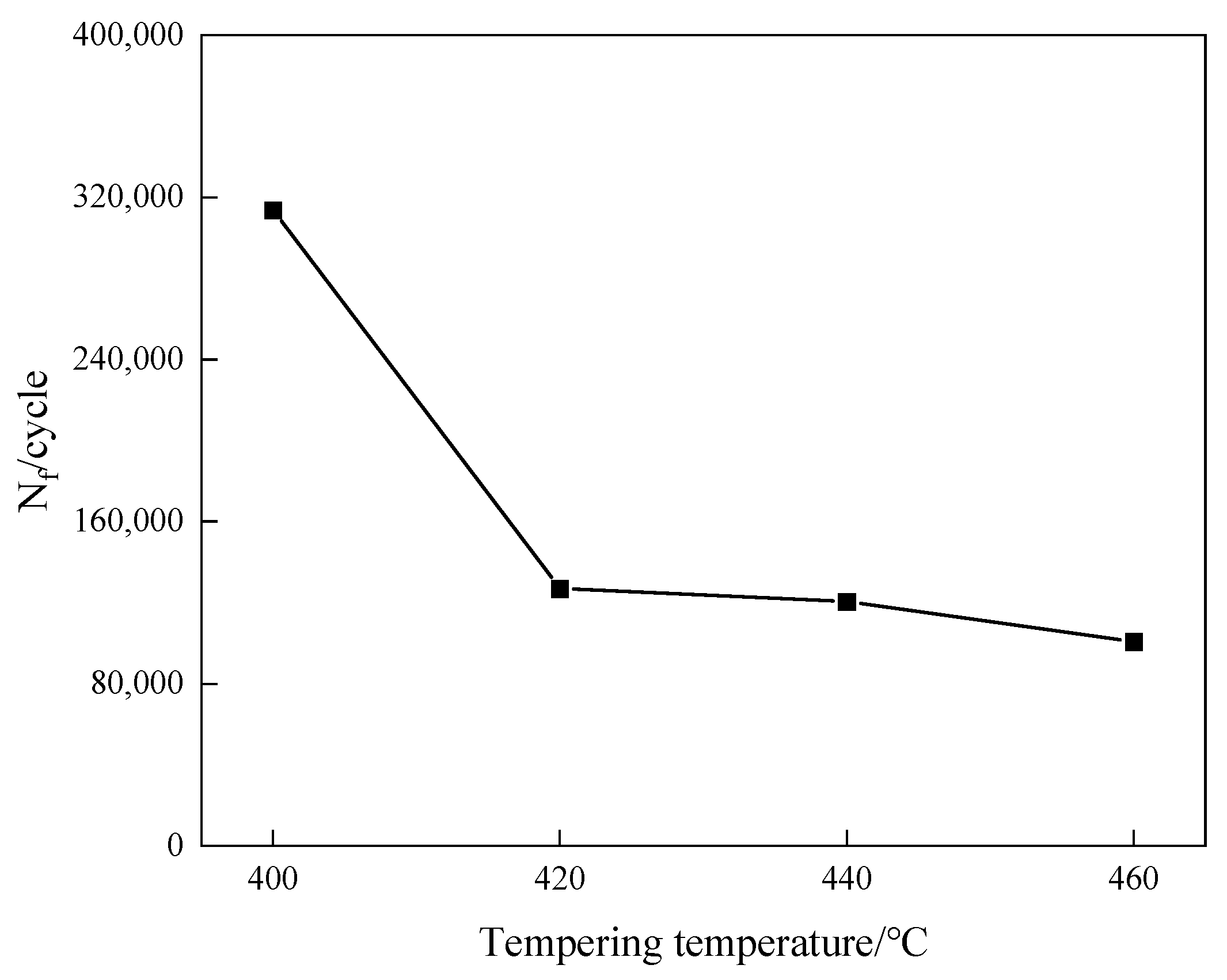
- Under the purview of experimental conditions, the fatigue life of 40CrNi2MoE steel attains its apogee, nearing 320,000 cycles, following tempering at 400 °C. As the tempering temperature ascends, the fatigue life precipitously plummets, in tandem with the trend in the fluctuation of strength. This phenomenon predominantly hinges on the density of dislocations. Additionally, the three-parameter model presents a congruence with the S-N curve.
- The predominant origins of fatigue initiation in the context of rotational bending were inclusions, such as Al2O3, CaO, and MgO. Remarkably, the tempering temperature exerts no significant sway upon either the fount of initiation or the fracture morphology.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wagri, N.K.; Jain, N.K.; Petare, A.; Das, S.R.; Tharwan, M.Y.; Alansari, A.; Alqahtani, B.; Fattouh, M.; Elsheikh, A. Investigation on the Performance of Coated Carbide Tool during Dry Turning of AISI 4340 Alloy Steel. Materials 2023, 16, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, S.; Asadi Asadabad, M.; Bakhshi, S. Influence of the heat treatment on the quantitative features of the fracture surfaces and the mechanical properties of AISI 4340 steel sheets. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2023, 50, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manokaran, M.; Kashinath, A.S.; Jha, J.S.; Toppo, S.P.; Singh, R.P. Influence of Tempering in Different Melting Routes on Toughness Behavior of AISI 4340 Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perf. 2015, 29, 6748–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.Y.; Wood, W.E.; Clark, R.A.; Zackay, V.F.; Parker, E.R. The effect of austenitizing temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of as-quenched 4340 steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1974, 5, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, S.; Mirak, A. Textural development, martensite lath formation and mechanical properties variation of a super strength AISI4340 steel due to austenitization and tempering temperature changes. Mater. Charact. 2022, 188, 111923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.Z.; Lee, Y.; Liu, X.H.; Wang, G.D. On the martensite transformation kinetics of AISI 4340 steel. J. Northeast Univ. Nat. Sci. 2006, 27, 650–653. [Google Scholar]
- Zhirafar, S.; Rezaeian, A.; Pugh, M. Effect of cryogenic treatment on the mechanical properties of 4340 steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 186, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, M.F.; Serrão, L.F.; Pardal, J.M.; Tavares, S.S.M.; Fonseca, M.C. Tempering influence on residual stresses and mechanical properties of AISI 4340 steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Wang, Y.P.; Niu, Z.Q.; Hu, G.J.; Zhou, W.L.; Chen, G.Q.; Fu, X.S. Effect of tempering temperature on mechanical properties and dry friction properties of 40CrNi2Mo steel. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2020, 41, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, A.J.; Miller, M.K.; Field, R.D.; Coughlin, D.R.; Gibbs, P.J.; Clarke, K.D.; Alexander, D.J.; Powers, K.A.; Papin, P.A.; Krauss, G. Atomic and nanoscale chemical and structural changes in quenched and tempered 4340 steel. Acta Mater. 2014, 77, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.J.; Klemm-Toole, J.; Clarke, K.D.; Coughlin, D.R.; Pierce, D.T.; Euser, V.K.; Poplawsky, J.D.; Clausen, B.; Brown, D.; Almer, J.; et al. Perspectives on Quenching and Tempering 4340 Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 4984–5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Wang, S.G.; Zhang, P.; Qu, R.T.; Zhang, Z.F. Crack propagation mechanisms of AISI 4340 steels with different strength and toughness. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 729, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.M.; Yaqoob, K.; Zahid, M.H.; Haq, E.U.; Tanveer, W.H.; Wadood, A.; Ahmed, B. Effect of austempering conditions on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AISI 4340 and AISI 4140 steels. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5194–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, X.J.; Yang, M.S.; Tang, H.Y.; Li, J.X.; Pang, X.D.; Sun, Y. Inclusion control and fatigue performance in high performance GCr15 bearing steel. Steel 2018, 53, 76–85+101. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhshi, S.; Mirak, A. The effect of low temperature transformation time on microstructural & textural evolution, mechanical properties and fracture behavior of a low alloy, medium carbon, super strength AISI 4340 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 831, 142247. [Google Scholar]
- Euser, V.K.; Williamson, D.L.; Clarke, K.D.; Findley, K.O.; Speer, J.G.; Clarke, A.J. Effects of short-time tempering on impact toughness, strength, and phase evolution of 4340 steel within the tempered martensite embrittlement regime. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 3654–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.T.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.W.; Shiozawa, K.; Zhang, W.H. Analysis of rotary bending gigacycle fatigue properties of bearing steel GCr15. Acta Metall. Sin. 2009, 45, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Yang, M.S.; Lu, D.H.; Li, X.Y. Rotational bending fatigue life and fatigue crack initiation mechanism of Cr4Mo4V bearing steel. J. Mater. Eng. 2019, 47, 134–143. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, F.; Mao, K.; Cao, C.; Hu, A.; Tu, J.; Lin, Y. Rotating Bending Fatigue Behaviors of C17200 Beryllium Copper Alloy at High Temperatures. Materials 2023, 16, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 228.1; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. State Administration for Market Regulation, and Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB/T 229; Metallic Materials—Charpy Pendulum Impact Test Method. State Administration for Market Regulation, and Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2020.
- GB/T 4337; Metallic Materials—Fatigue Testing—Rotating Bar Bending Method. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China, and Standardization Administration of the P.R.C.: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Zhou, P.; Wang, L.; Cui, C.; Hu, Y.; Xu, K. Effect of Intercritical Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 10CrMnMoSi Dual-phase Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perf. 2023, 32, 8949–8960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Hu, F.; Yan, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Z.C.; Wu, K.M. Microstructural transformation and plasticity mechanism of 2GPa medium-carbon medium-manganese nano-bainitic steel. Iron Steel 2022, 57, 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.Z.; Xiong, Z.P.; Zhang, C.; Feng, G.Z.; Cheng, Z.F.; Cheng, X.W. Evolution of microstructures and mechanical prop-erties with tempering temperature of a pearlitic quenched and tempered steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2021, 29, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Huang, X.M.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.B.; Chu, L.S.; Dai, G.Z. Characterization and simulation of strain-hardening behavior of a cold-rolled dual phase steel of 780 MPa grade by means of modified C-J method and RVE model. Chin. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 31, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, G.C.; Gonzalez, B.M.; Santos, L.A. Strain hardening behavior and microstructural evolution during plastic deformation of dual phase, non-grain oriented electrical and AISI 304 steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 684, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Cai, Q.; Yu, W.; Cao, J.M.; Yang, Y.F. Effect of tempering temperature on resistance to deformation behavior for low carbon bainitic YP960 steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 618, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.W.; Lu, L.T.; Shen, X.L.; Yi, H.F.; Zhang, W.H. Evaluation method of fatigue damage under variable amplitude stress based on plastic strain. Acta Metall. Sin. 2009, 45, 1464–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Xie, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.H. Determination of the fatigue PSN curves—A critical review and improved backward statistical inference method. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 139, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Li, W.; Xu, J. Study on the P-S-N Curve of Sucker Rod Based on Three-Parameter Weibull Distribution. Materials 2022, 15, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Gao, Q.; Wang, J.N. Unified approach for estimating the probabilistic design S-N curves of three commonly used fatigue stress-life models. Nucl. Power Eng. 2001, 22, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, J.C.; Li, S.X.; Wang, Z.G.; Zhang, Z.F. General relation between tensile strength and fatigue strength of metallic materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 564, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.X.; Liu, X.M.; Li, J.X. Behavior of rotating-bending fatigue failure of AF1410 steel. Iron Steel 2013, 48, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Suresh, S.B.; Maitra, D.; Kumar, P.; Wells, D.; Ma, L. Relationship of residual stress to dislocation density in cold-worked martensitic alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 416, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.F. Study on the Properties and Microstructure of High CoNi Alloy Steel. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China, 2001. [Google Scholar]

| C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.41 | 0.25 | 0.78 | 0.85 | 1.86 | 0.26 | Bal. |
| Tempering Temperature/°C | n | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| I | II | III | |
| 400 | 21.07 | 39.86 | 2132 |
| 420 | 24.17 | 36.93 | 1445 |
| 440 | 23.47 | 30.51 | 580 |
| 460 | 24.03 | 41.00 | 1872 |
| Tempering Temperature/°C | /% | |
|---|---|---|
| I→II | II→III | |
| 400 | 0.064 | 0.130 |
| 420 | 0.070 | 0.100 |
| 440 | 0.220 | 0.245 |
| 460 | 0.073 | 0.011 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, C.-D.; Li, Y.; Zang, Z.-W.; Li, X.-Y.; Han, S. Influence of Tempering Temperature on Mechanical and Rotational Bending Fatigue Properties of 40CrNi2MoE Steel. Materials 2024, 17, 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17061377
Yao C-D, Li Y, Zang Z-W, Li X-Y, Han S. Influence of Tempering Temperature on Mechanical and Rotational Bending Fatigue Properties of 40CrNi2MoE Steel. Materials. 2024; 17(6):1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17061377
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Chang-Da, Yong Li, Zhi-Wei Zang, Xin-Yang Li, and Shun Han. 2024. "Influence of Tempering Temperature on Mechanical and Rotational Bending Fatigue Properties of 40CrNi2MoE Steel" Materials 17, no. 6: 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17061377
APA StyleYao, C.-D., Li, Y., Zang, Z.-W., Li, X.-Y., & Han, S. (2024). Influence of Tempering Temperature on Mechanical and Rotational Bending Fatigue Properties of 40CrNi2MoE Steel. Materials, 17(6), 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17061377






