Micro-Addition of Silver to Copper: One Small Step in Composition, a Change for a Giant Leap in Biocidal Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
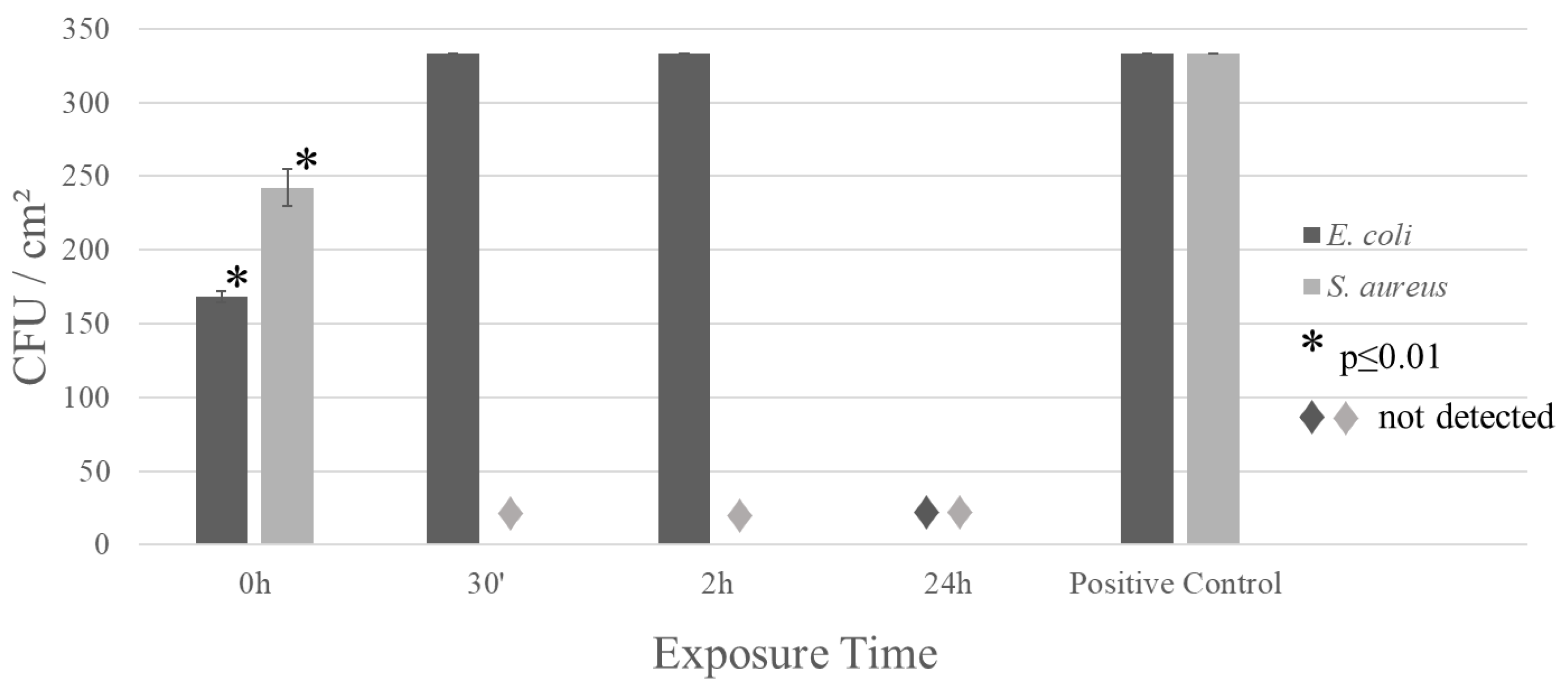
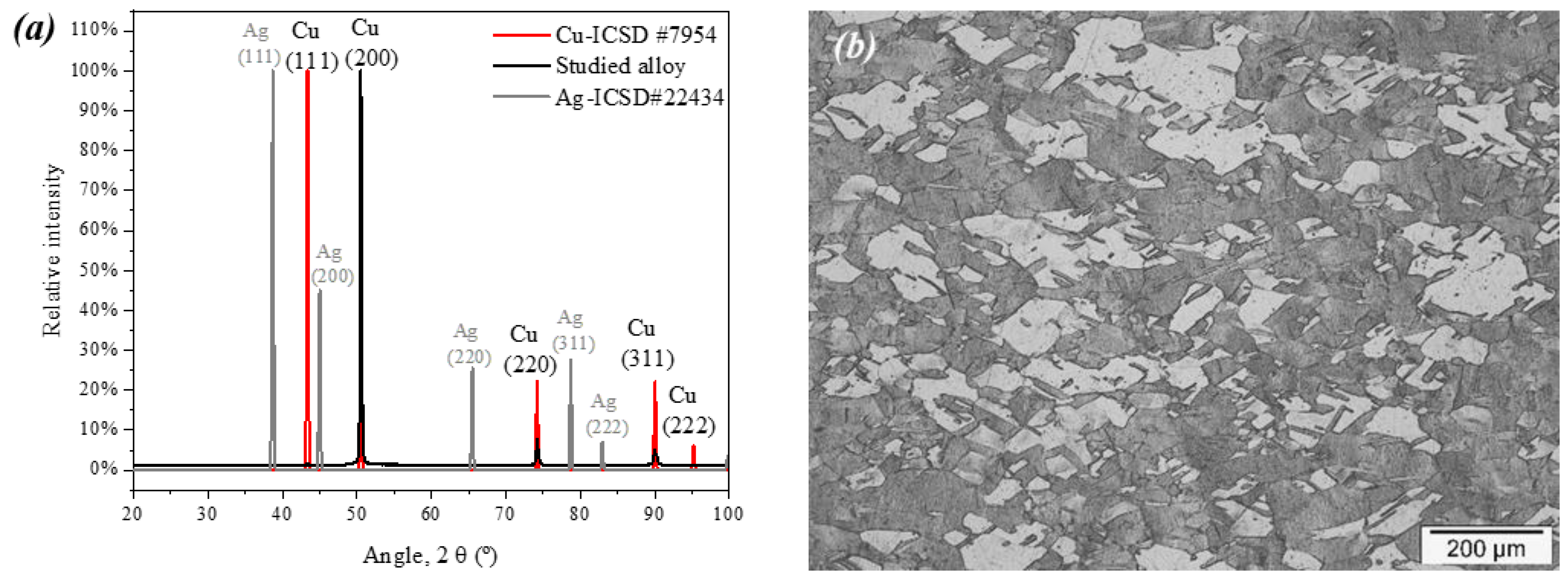
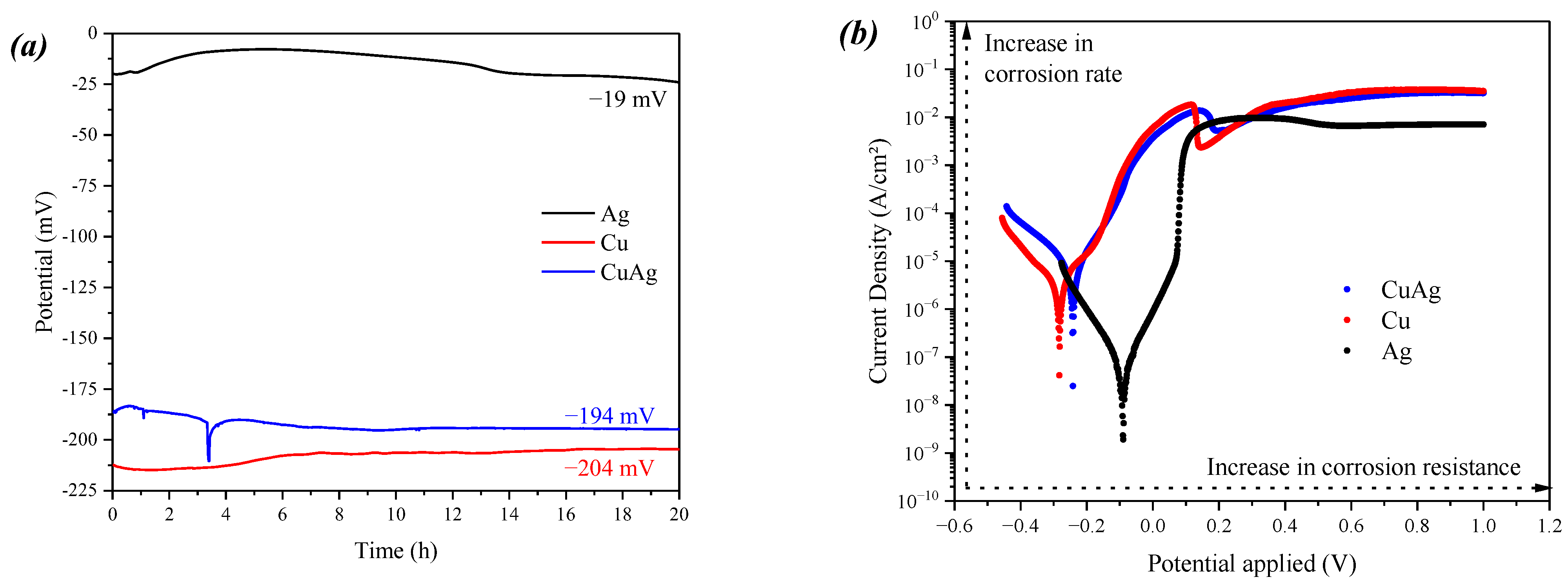
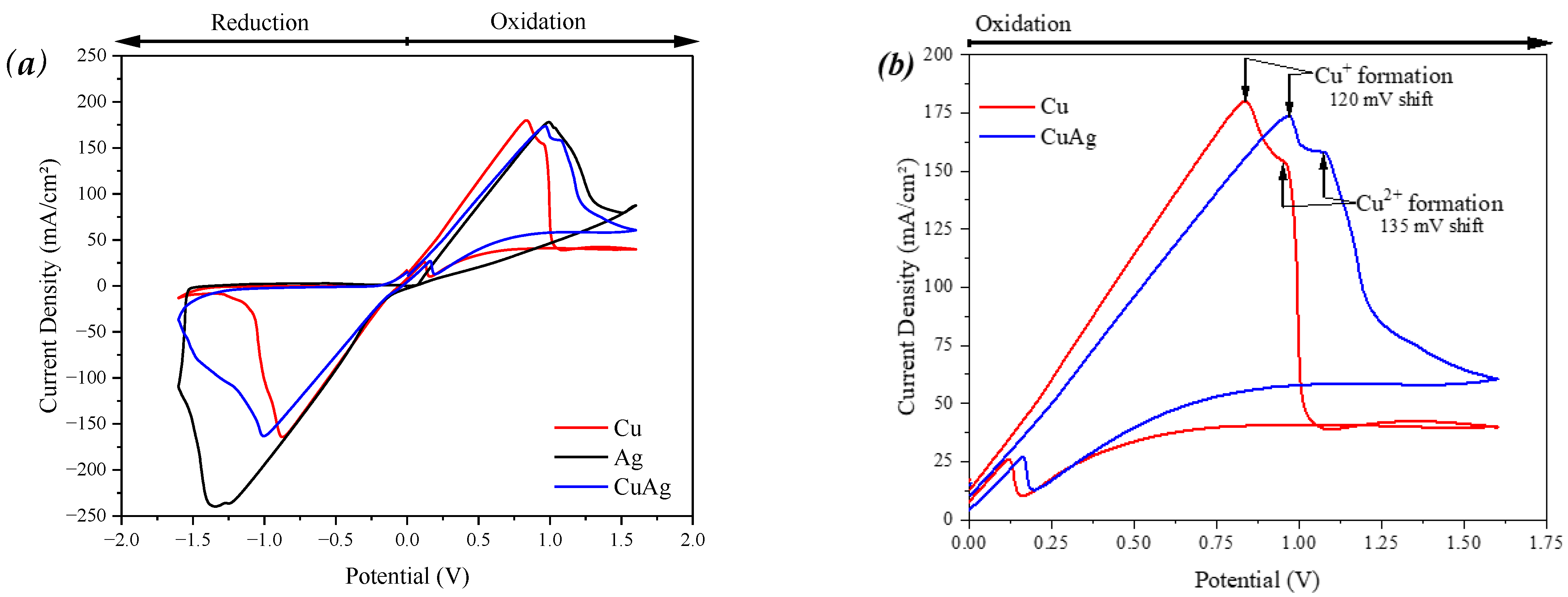
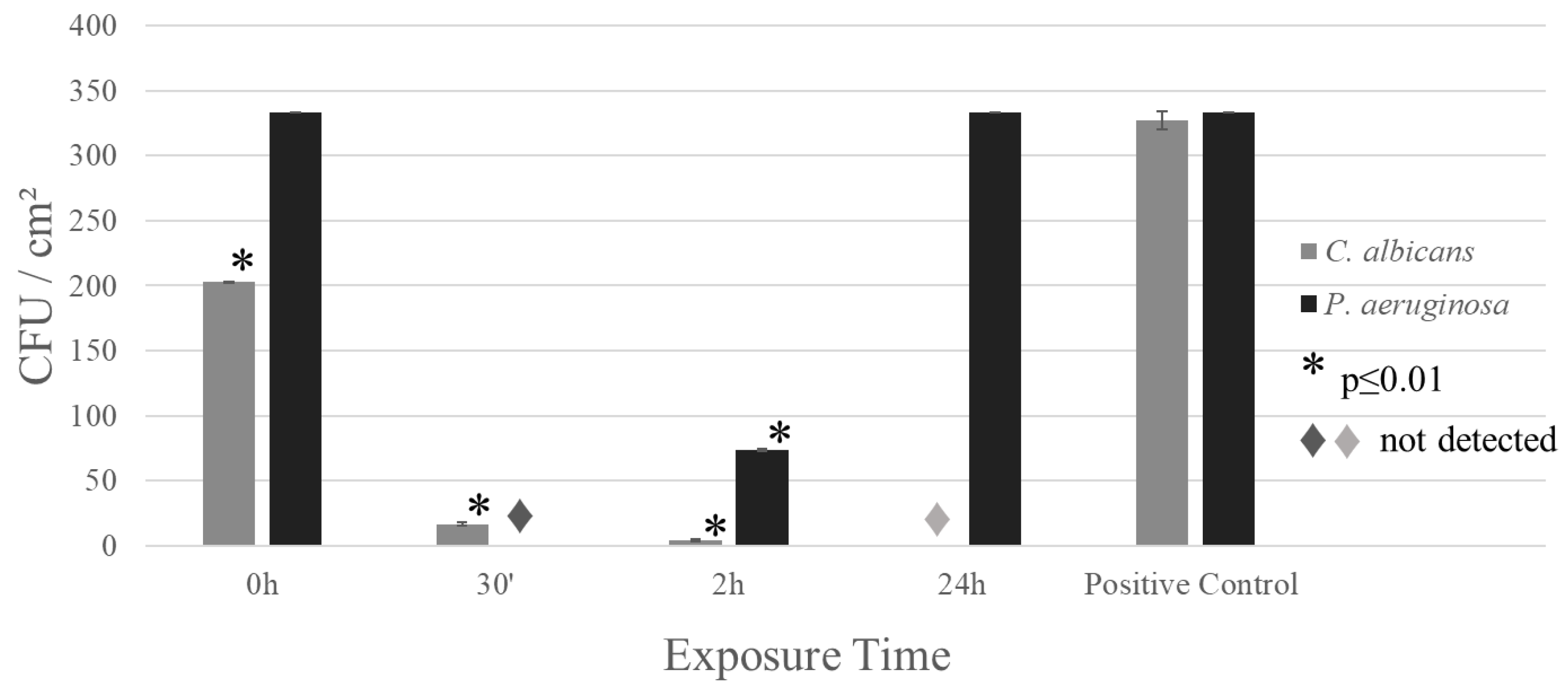
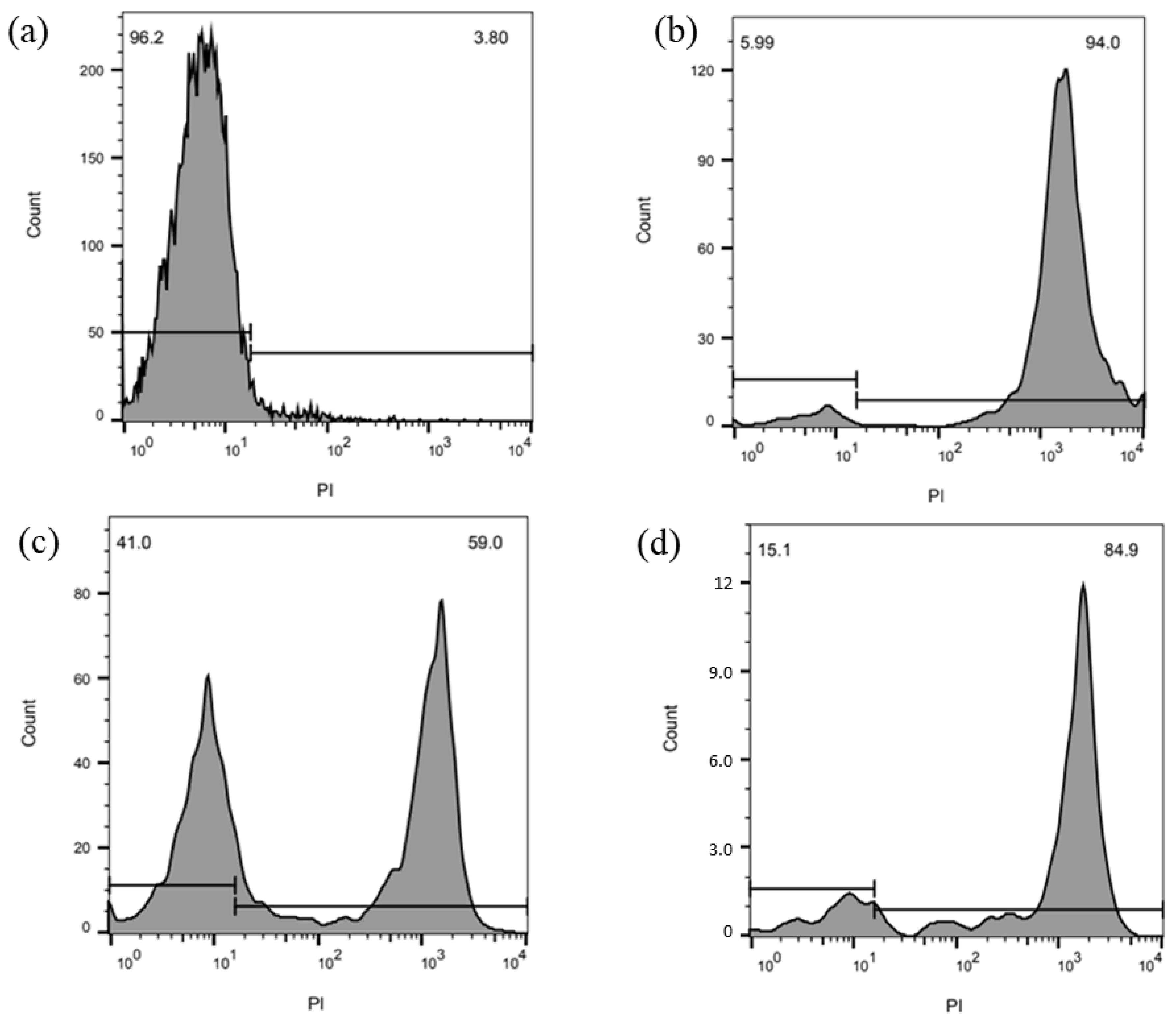
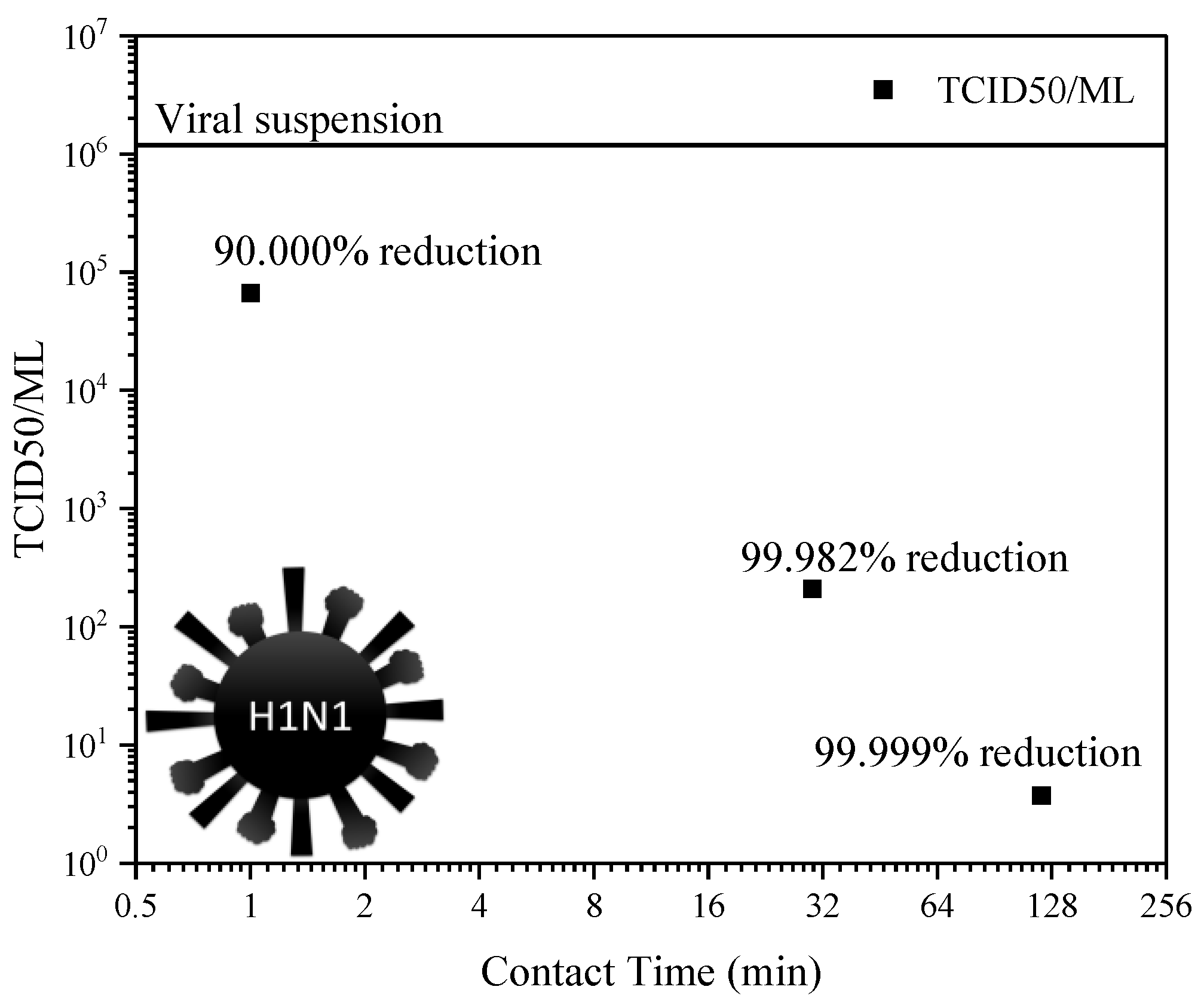
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grass, G.; Rensing, C.; Solioz, M. Metallic Copper as an Antimicrobial Surface. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, M.I.; Skaar, E.P. Nutritional Immunity: Transition Metals at the Pathogen–Host Interface. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, C.D.; Sepkowitz, K.A.; John, J.F.; Cantey, J.R.; Attaway, H.H.; Freeman, K.D.; Sharpe, P.A.; Michels, H.T.; Schmidt, M.G. Copper Surfaces Reduce the Rate of Healthcare-Acquired Infections in the Intensive Care Unit. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2013, 34, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caro-Lara, L.; Vargas, I.T.; Ramos-Moore, E.; Galarce, C.; Diaz-Droguett, D.; Pizarro, G.E. Enhancing the Contact-Killing Effect of Copper by Surface Laser Texturing. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver Nanoparticles as a New Generation of Antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes, C.; Gutierrez-Corona, F. Copper Resistance Mechanisms in Bacteria and Fungi. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 14, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolrd Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 9 April 2023).
- Lara, H.H.; Ayala-Nuñez, N.V.; Ixtepan-Turrent, L.; Rodriguez-Padilla, C. Mode of Antiviral Action of Silver Nanoparticles against HIV-1. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2010, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Durán, M.; de Jesus, M.B.; Seabra, A.B.; Fávaro, W.J.; Nakazato, G. Silver Nanoparticles: A New View on Mechanistic Aspects on Antimicrobial Activity. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones-Ramirez, J.R.; Winkler, J.A.; Spina, C.S.; Collins, J.J. Silver Enhances Antibiotic Activity Against Gram-Negative Bacteria. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 190ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Kang, E.-T.; Neoh, K.G. Antimicrobial Copper-Based Materials and Coatings: Potential Multifaceted Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21159–21182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, A.L.; Adams, D.; Karpanen, T.J.; Lambert, P.A.; Cookson, B.D.; Nightingale, P.; Miruszenko, L.; Shillam, R.; Christian, P.; Elliott, T.S.J. Role of Copper in Reducing Hospital Environment Contamination. J. Hosp. Infect. 2010, 74, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michels, H.T.; Noyce, J.O.; Keevil, C.W. Effects of Temperature and Humidity on the Efficacy of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Challenged Antimicrobial Materials Containing Silver and Copper. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unified Numbering System (UNS) for Copper and Copper Alloys Wrought Copper Alloys: Coppers (C10100-C15999). Available online: https://www.unscopperalloys.org/wrought/coppers.php (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Termomecanica Rolled Products. Available online: https://www.termomecanica.com.br/EN/download/conteudo_tecnico/Rolled_Products.pdf (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- ISO 22196:2011; Measurement of Antibacterial Activity on Plastics and Other Non-Porous Surfaces. ISO (International Organization for Standardization): Geneva, Switzerland, 2011.
- JIS Z 2801:2010; Assessment of Antimicrobial Activity of Hard Non-Porous Surfaces. Japanese Standards Association: Tokyo, Japan, 2010.
- ASTM E1052-11; Standard Test Method to Assess the Activity of Microbicides against Viruses in Suspension. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Hierholzer, J.C.; Killington, R.A. Virus Isolation and Quantitation. In Virology Methods Manual; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 25–46. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, S.; Miller, L.S. Host–Pathogen Interactions between the Skin and Staphylococcus Aureus. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2012, 15, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondusko, D.S.; Nolt, D. Staphylococcus Aureus. Pediatr. Rev. 2018, 39, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odonkor, S.T.; Ampofo, J.K. Escherichia Coli as an Indicator of Bacteriological Quality of Water: An Overview. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 4, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovsek, Z.; Elersic, K.; Gubina, M.; Zgur-Bertok, D.; Erjavec, M.S. Virulence Potential of Escherichia Coli Isolates from Skin and Soft Tissue Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 3462–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamim, S. Biosorption of Heavy Metals. In Biosorption; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarczuk, K.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Molecular Basis of Active Copper Resistance Mechanisms in Gram-Negative Bacteria. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2013, 29, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, R.; Halder, U.; Kabiraj, A.; Mondal, A.; Bandopadhyay, R. Overview on the Role of Heavy Metals Tolerance on Developing Antibiotic Resistance in Both Gram-Negative and Gram-Positive Bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2761–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanella, P.; Cabral, L.; Costa, A.P.; de Oliveira Camargo, F.A.; Gianello, C.; Bento, F.M. Metal Resistance Mechanisms in Gram-Negative Bacteria and Their Potential to Remove Hg in the Presence of Other Metals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 140, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trajanovska, S.; Britz, M.L.; Bhave, M. Detection of Heavy Metal Ion Resistance Genes in Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria Isolated from a Lead-Contaminated Site. Biodegradation 1997, 8, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, C.C.; Skaar, E.P. Nutritional Immunity: The Battle for Nutrient Metals at the Host–Pathogen Interface. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulsen, I.T.; Park, J.H.; Choi, P.S.; Saier, M.H. A Family of Gram-Negative Bacterial Outer Membrane Factors That Function in the Export of Proteins, Carbohydrates, Drugs and Heavy Metals from Gram-Negative Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 156, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhevnenko, S.N.; Vaganov, D.V.; Podgornyi, D.A. Direct Method for Determining the Segregation in Silver-Copper Solid Solutions Not Prone to Brittle Breakage of Grain Boundaries. J. Surf. Investig. X-ray Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 2011, 5, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, P.R.; Perepezko, J.H. The Ag-Cu (Silver-Copper) System. J. Phase Equilibria 1993, 14, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Chang, Y.A.; Zhu, J.; Chen, S.; Oates, W.A. Thermodynamic Modeling of the Cu–Ag–Au System Using the Cluster/Site Approximation. Intermetallics 2007, 15, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Gayathri, N.; Bhattacharya, M.; Mukherjee, P. In Situ XRD Studies of the Process Dynamics During Annealing in Cold-Rolled Copper. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 6281–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidelbach, F.; Wenk, H.-R.; Chen, S.R.; Pospiech, J.; Wright, S.I. Orientation and Misorientation Characteristics of Annealed, Rolled and Recrystallized Copper. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 215, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, N.; Mauzeroll, J. Spatially Resolved Electrochemical Measurements. In Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rajčić-Vujasinović, M.; Nestorović, S.; Grekulović, V.; Marković, I.; Stević, Z. Electrochemical Behavior of Cast CuAg4at% Alloy. Corrosion 2010, 66, 105004–105004-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, C.; Sandwell, A.; Park, S.S. Hybrid Copper–Silver Conductive Tracks for Enhanced Oxidation Resistance under Flash Light Sintering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22369–22373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciacotich, N.; Din, R.U.; Sloth, J.J.; Møller, P.; Gram, L. An Electroplated Copper–Silver Alloy as Antibacterial Coating on Stainless Steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 345, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Gabbay, J. Copper as a Biocidal Tool. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnes, S.L.; Green, S.M.; Michels, H.T.; Keevil, C.W. Biocidal Efficacy of Copper Alloys against Pathogenic Enterococci Involves Degradation of Genomic and Plasmid DNAs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5390–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Gabbay, J. Putting Copper into Action: Copper-impregnated Products with Potent Biocidal Activities. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1728–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, S.; Phung, L.T.; Silver, G. Silver as Biocides in Burn and Wound Dressings and Bacterial Resistance to Silver Compounds. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, M.P.; Tam, J.S.; Assossou, O.M.; Kieny, M.P. The 2009 A (H1N1) Influenza Virus Pandemic: A Review. Vaccine 2010, 28, 4895–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, V.G.; Saivish, M.V.; Santos, D.E.R.; de Lima Silva, R.F.; Moreli, M.L. Comparative Epidemiology between the 2009 H1N1 Influenza and COVID-19 Pandemics. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1797–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples | Ag | Cu | CuAg |
|---|---|---|---|
| Icorr (A) | 3.46 × 10−8 | 9.57 × 10−6 | 4.42 × 10−6 |
| Ecorr (V) | −0.09 | −0.28 | −0.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vital, V.G.; Silva, M.R.; Santos, V.T.; Lobo, F.G.; Xander, P.; Zauli, R.C.; Moraes, C.B.; Freitas-Junior, L.H.; Barbosa, C.G.; Pellosi, D.S.; et al. Micro-Addition of Silver to Copper: One Small Step in Composition, a Change for a Giant Leap in Biocidal Activity. Materials 2024, 17, 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040917
Vital VG, Silva MR, Santos VT, Lobo FG, Xander P, Zauli RC, Moraes CB, Freitas-Junior LH, Barbosa CG, Pellosi DS, et al. Micro-Addition of Silver to Copper: One Small Step in Composition, a Change for a Giant Leap in Biocidal Activity. Materials. 2024; 17(4):917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040917
Chicago/Turabian StyleVital, Vitor G., Márcio R. Silva, Vinicius T. Santos, Flávia G. Lobo, Patrícia Xander, Rogéria C. Zauli, Carolina B. Moraes, Lucio H. Freitas-Junior, Cecíla G. Barbosa, Diogo S. Pellosi, and et al. 2024. "Micro-Addition of Silver to Copper: One Small Step in Composition, a Change for a Giant Leap in Biocidal Activity" Materials 17, no. 4: 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040917
APA StyleVital, V. G., Silva, M. R., Santos, V. T., Lobo, F. G., Xander, P., Zauli, R. C., Moraes, C. B., Freitas-Junior, L. H., Barbosa, C. G., Pellosi, D. S., Silva, R. A. G., Paganotti, A., & Vasconcellos, S. P. (2024). Micro-Addition of Silver to Copper: One Small Step in Composition, a Change for a Giant Leap in Biocidal Activity. Materials, 17(4), 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17040917





