Influence of High-Speed Ram Transition Position on Porosity and Mechanical Properties of Large One-Piece Die-Casting Al-Si-Mn-Mg Aluminium Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
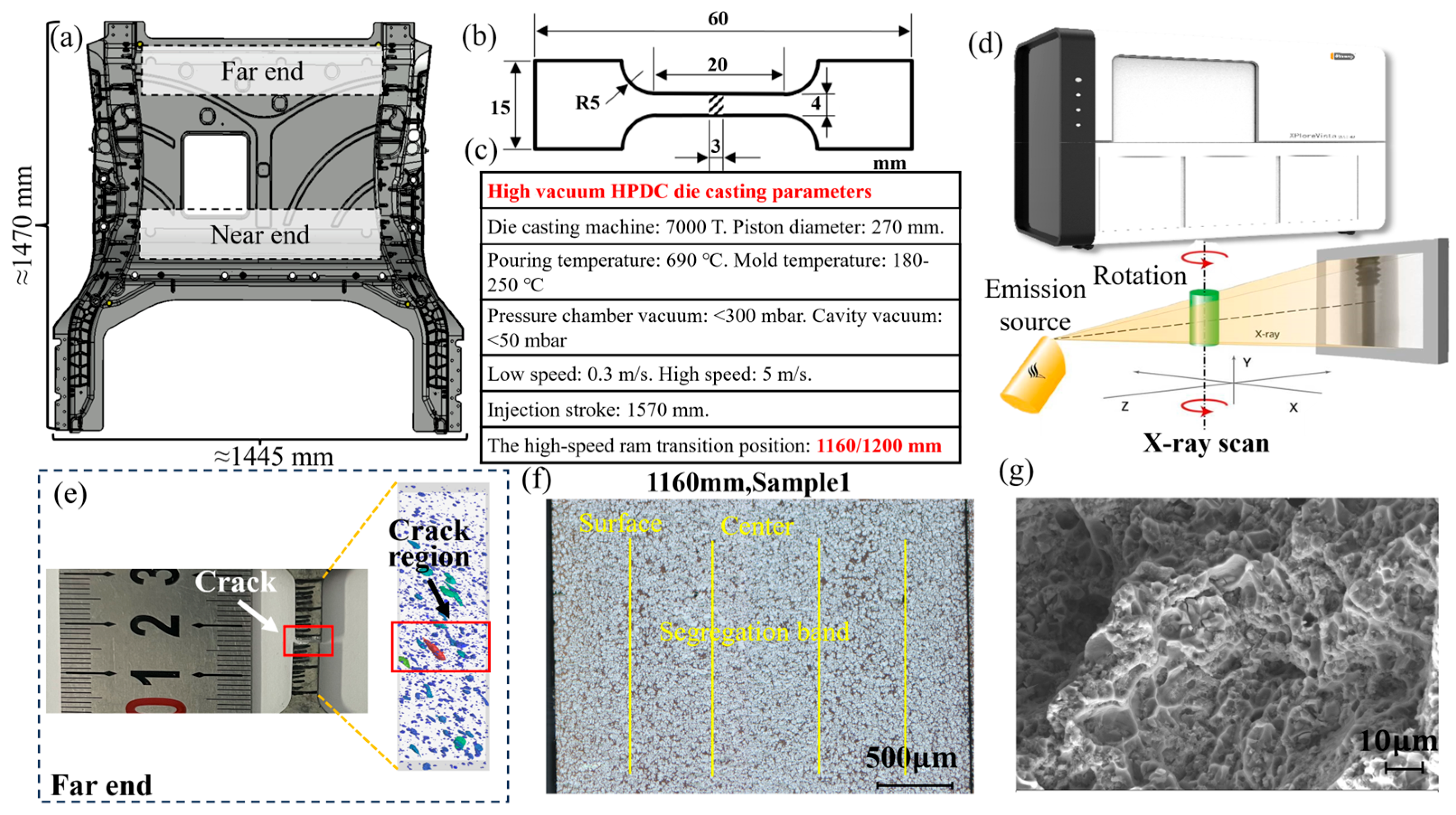
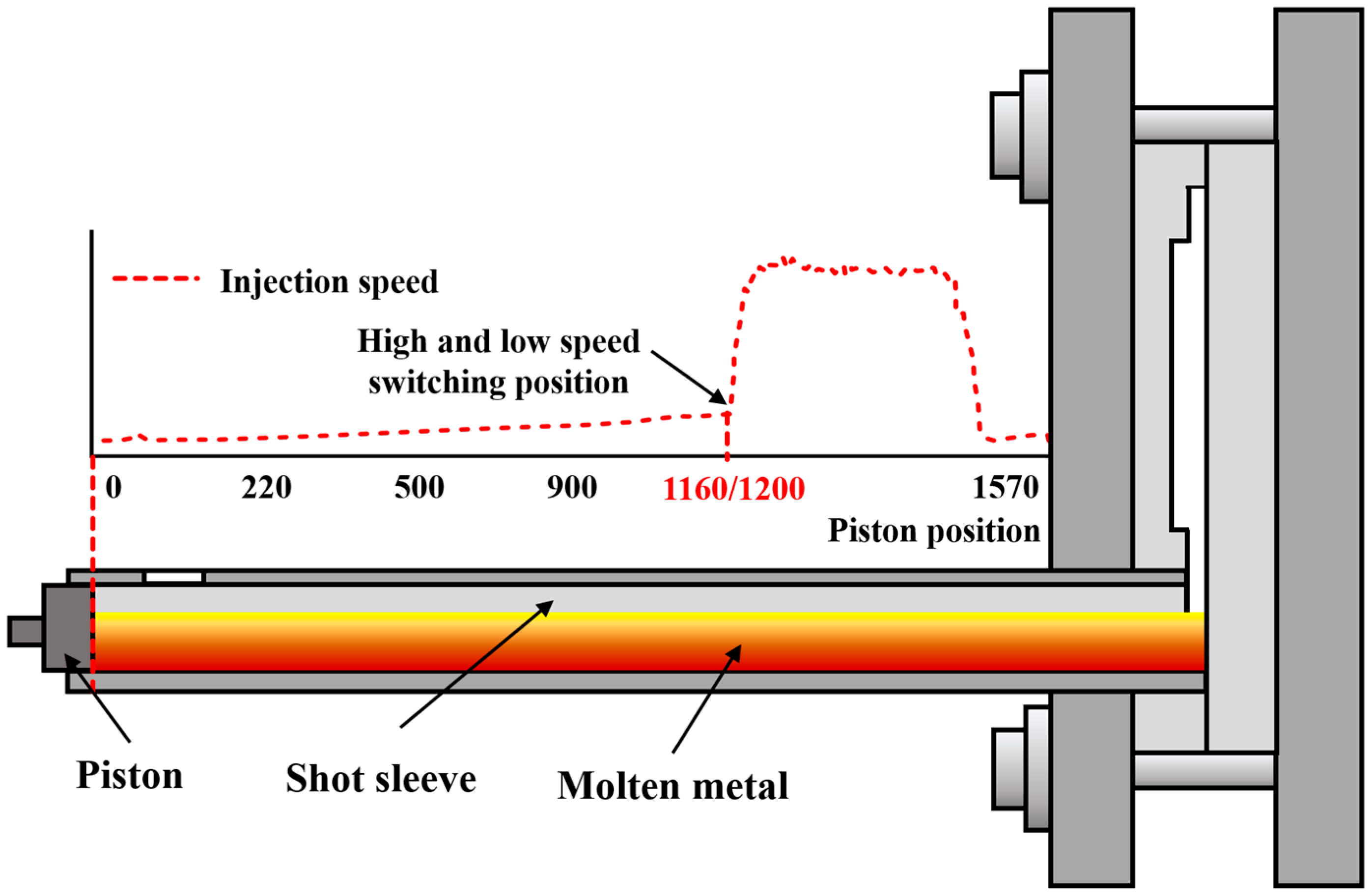
2.1. High Vacuum Die-Casting
2.2. X-Ray CT Scan
2.3. Tensile Test
2.4. Microstructure Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
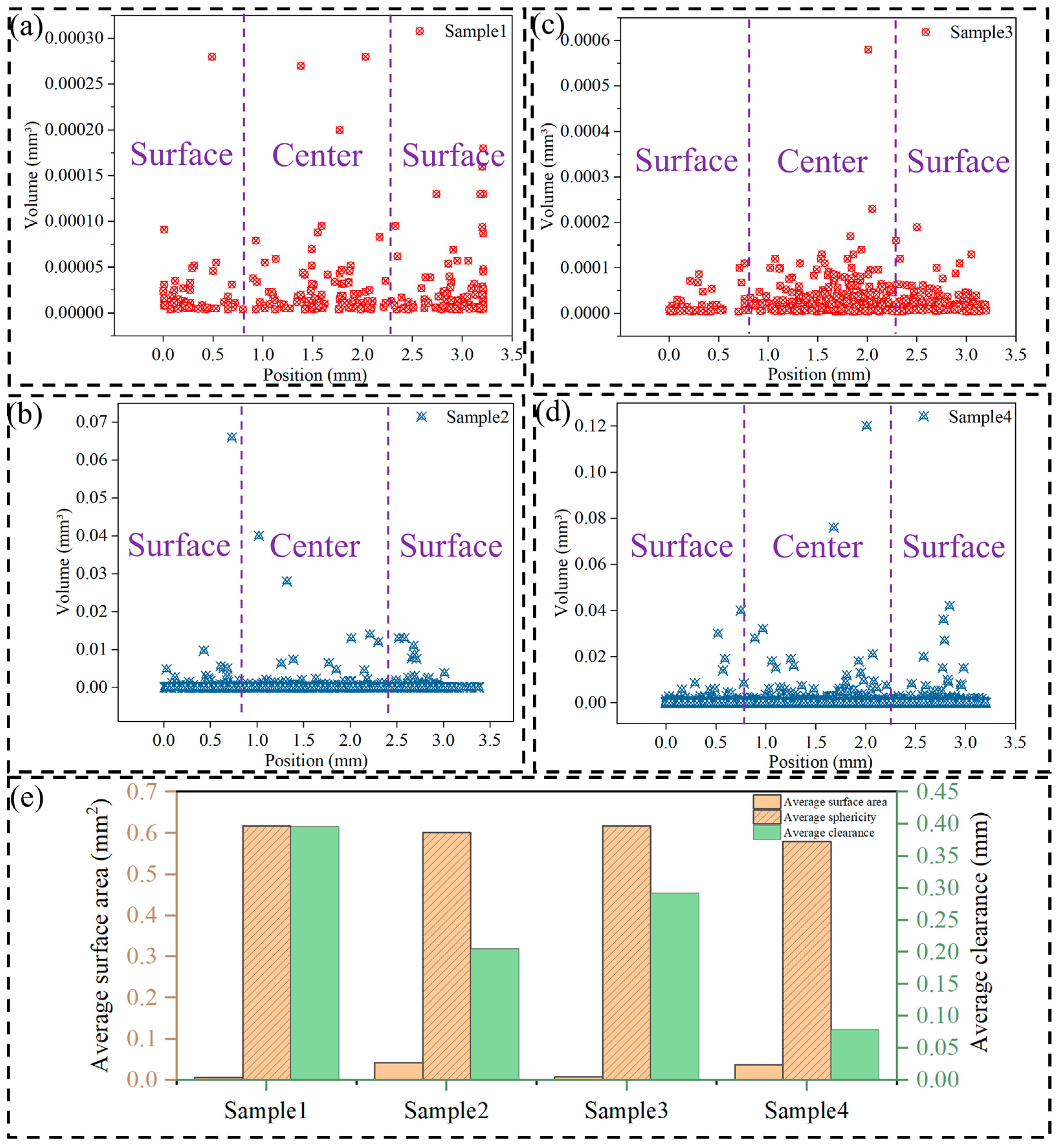
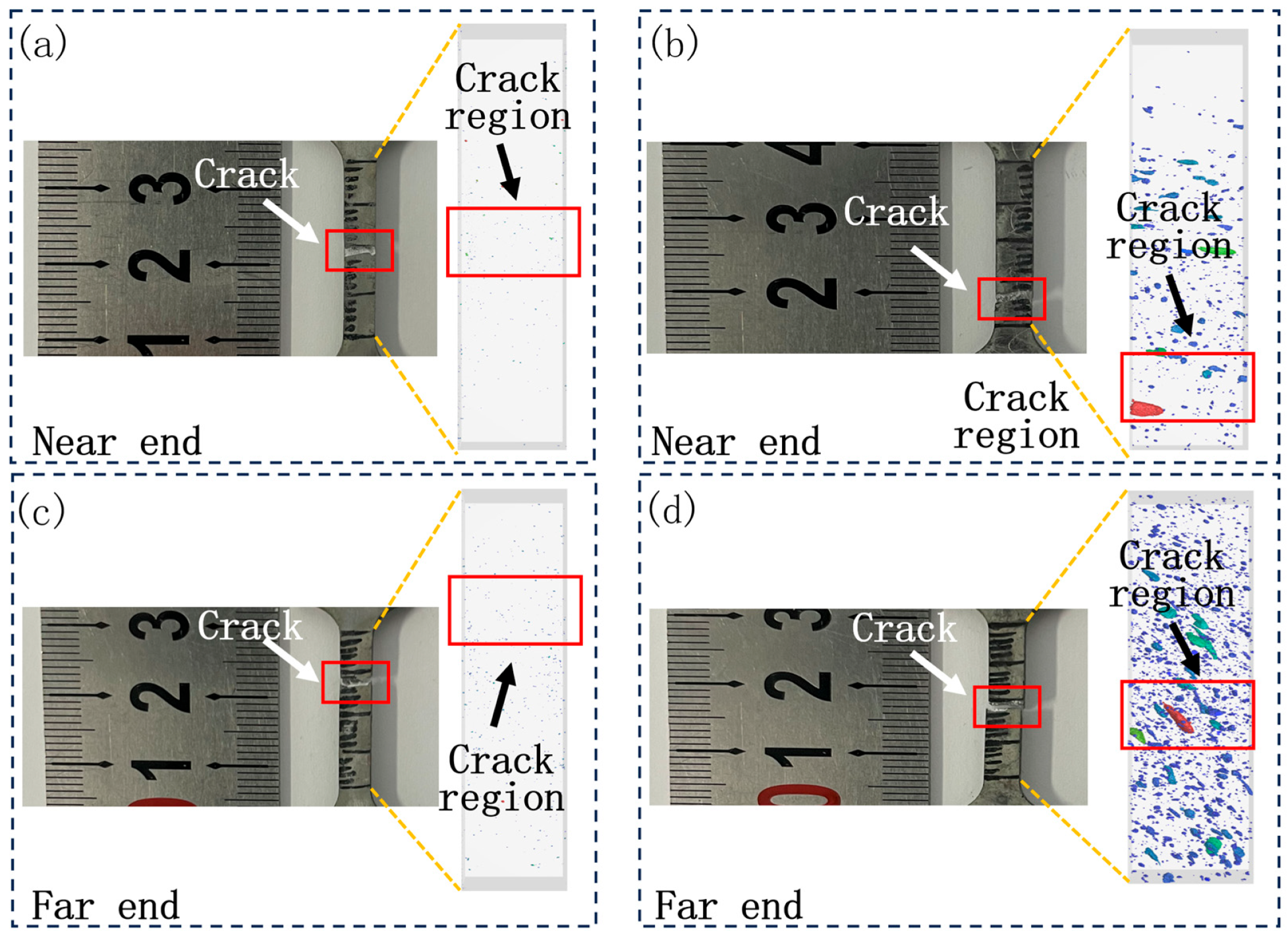
3.1. Pore Results
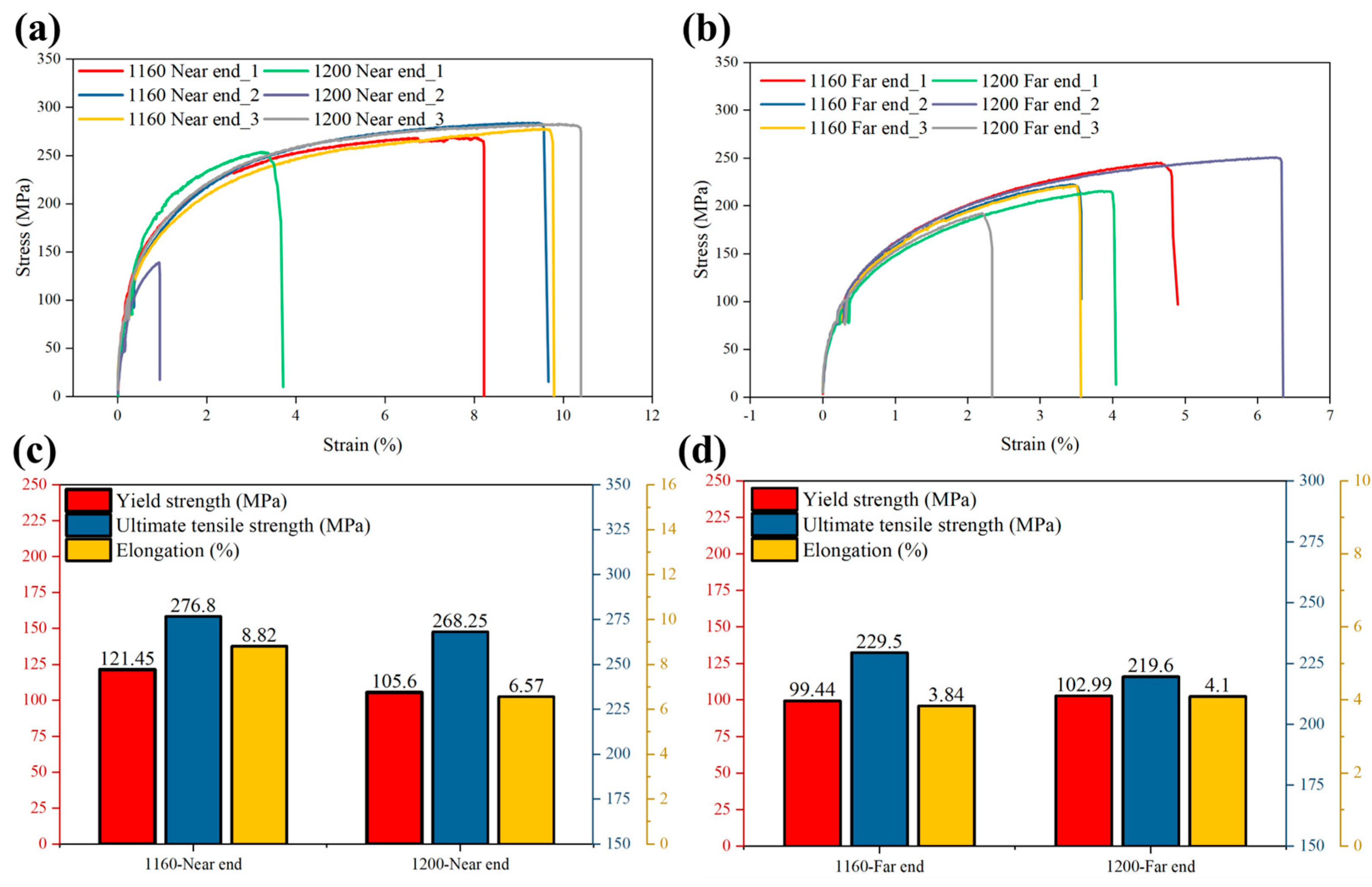
3.2. Mechanical Property Analysis
3.3. Microstructure Analysis
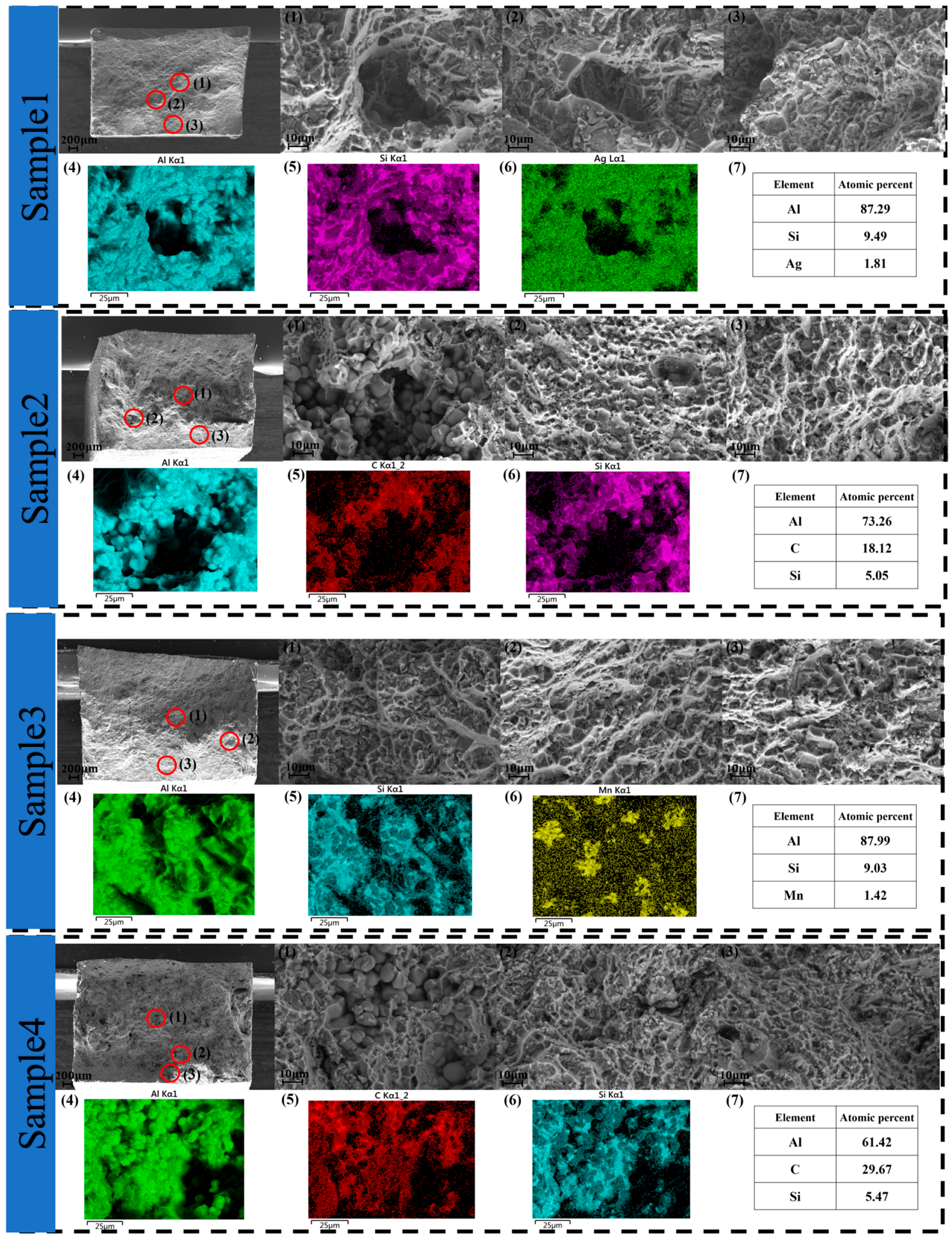
3.4. Fracture Surfaces
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Statistical analysis of the CT results shows that, in the thickness direction, the specimen with a high-speed slide transition position of 1160 mm has a more uniform pore distribution compared to the specimen of 1200 mm.
- (2)
- The results of the tensile test show that, compared to the specimen with a 1200 mm transition position of the high-speed slider, the yield limit of the proximal mechanical properties of the 1160 specimen is increased from 105.6 MPa to 121.45 MPa, which is an increase in 13%, and the elongation is increased from 6.57% to 8.82%, which is an increase in 25%.
- (3)
- Analysis of the fracture morphology of the die-cast aluminium alloy showed that the 1200 mm specimen exhibited denser tear ridges and more river-like cleavage surfaces in the proximal fracture compared to the specimen with a high-speed slide transition position of 1160 mm, presenting more brittle fracture characteristics, which is consistent with the lower-strength properties at this condition.
- (4)
- EDS image analysis reveals the presence of fine torn grains and a large number of silicon particles in the Al matrix lead to the formation of a eutectic organization that may form river-like cleavage surfaces on the fracture, leading to a failure fracture of the material. Excessive carbon or carbide precipitation leads to grain boundary embrittlement and accelerated crack extension, thus increasing the risk of fracture.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jolly, M.; Katgerman, L. Modelling of defects in aluminium cast products. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 123, 100824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Białobrzeski, A.; Kanikula, Z. Pressure Die Casting, Casting Technology, Construction of Dies; Foundry Institute: Cracow, Poland, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, F.; Wimmer, P. Experimental Determination of the Influence of Casting Conditions on the Solidifaction of Zinc Die Castings. Mater. Sci. Forum 1996, 215, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łągiewka, M.; Konopka, Z.; Nadolski, M.; Zyska, A. The effect of vacuum assistance on the quality of castings produced by high pressure die casting method. Pol. Akad. Nauk. 2014, 14, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiler, J.; Wood, J. Modeling the tensile failure of cast magnesium alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2012, 537, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Hao, M.; Shen, C.; Liang, P. The influence of different vacuum degree on the porosity and mechanical properties of aluminum die casting. Vacuum 2017, 146, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, C.; Shan, Q.; Che, J.; Luo, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, M. Kinetic analysis of pore formation in die-cast metals and influence of absolute pressure on porosity. Vacuum 2019, 168, 108828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlay, C.M.; Dahle, A.K.; Laukli, H.I. Segregation band formation in Al-Si die castings. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 2881–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo´pez, J.; Faura, F.; Herna´ndez, J.; Go´mez, P. On the critical plunger speed and three-dimensional effects in high-pressure die casting injection chambers. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2003, 125, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzepieciński, T.; Najm, S.M. Current trends in metallic materials for body panels and structural members used in the automotive industry. Materials 2024, 17, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalva, P.; Orbulov, I.N. The effect of vacuum on the mechanical properties of die cast aluminum AlSi9Cu3 (Fe) alloy. Int. J. Met. 2019, 13, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhu, X.; Ji, S. Effect of super vacuum assisted high pressure die casting on the repeatability of mechanical properties of Al-Si-Mg-Mn die-cast alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 266, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.Q.; Shao, J.M.; Xiang, G.Q.; Qian, L. Effects of Die Temperature of SSS Die Casting on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of ADC12 Aluminum Alloy. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 97–101, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargusch, M.S.; Dour, G.; Schauer, N.; Dinnis, C.; Savage, G. The influence of pressure during solidification of high pressure die cast aluminium telecommunications components. J. Mech. Work. Technol. 2006, 180, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, T.; Ji, S. Effect of high pressure die casting on the castability, defects and mechanical properties of aluminium alloys in extra-large thin-wall castings. J. Mech. Work. Technol. 2022, 303, 117525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; Kim, Y.C.; Cho, J.I.; Kang, C.S. Influence of die casting process parameters on castability and properties of thin walled aluminium housings. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2008, 21, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, X.Y.; Wang, P.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Jiang, J.J.; Liu, W.N.; Wan, A.X.; Shi, L.J.; Wang, C.G.; Xiong, S.M. Effect of shot speeds on the microstructural framework and abnormal eutectic bands in a high pressure die casting hypoeutectic AlSi10MnMg alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 326, 118312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-N.; Zhang, W.; Wang, P.-Y.; Liu, Y.-X.; Jiao, X.-Y.; Wan, A.-X.; Wang, C.-G.; Tong, G.-D.; Xiong, S.-M. Effect of slow shot speed on externally solidified crystal, porosity and tensile property in a newly developed high-pressure die-cast Al-Si alloy. China Foundry 2024, 21, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, R.; Faura, F.; López, J.; Hernández, J. Experimental verification of numerical predictions for the optimum plunger speed in the slow phase of a high-pressure die casting machine. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2007, 33, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, C. Investigation of Evolution of Microstructure, Mechanical Properties, and Corrosion Resistance of Novel Al-Mg-Si-Ag Alloy. Coatings 2023, 13, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Ding, W.; Peng, L. Improved tensile properties of a new aluminum alloy for high pressure die casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 651, 376–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, B.; Ding, W. Effect of chemical compositions on tensile behaviors of high pressure die-casting alloys Al-10Si-yCu-xMn-zFe. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 661, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zheng, J.; Godlewski, L.; Zindel, J.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Huang, S. Influence of pore characteristics and eutectic particles on the tensile properties of Al–Si–Mn–Mg high pressure die casting alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 783, 139280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E505; Standard Reference Radiographs for Inspection of Aluminium and Magnesium Die Castings. American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM): West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- ASTM E2422; Standard Digital Reference Images for Inspection of Aluminium Castings. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2022.
- T/CSAE 301-2023; Determination Method of Porosity for Die Castings of Automobile (Porosity Determination Method for Die Castings of Automobile). China Society of Automotive Engineering: Beijing, China, 2023.
- Dahle, A.K.; StJohn, D.H. Rheological behaviour of the mushy zone and its effect on the formation of casting defects during solidification. Acta Mater. 1998, 47, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, D.; Zhou, W.; Hu, B.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Qin, M.; Xu, J.; Zeng, X. Characterization on the formation of porosity and tensile properties prediction in die casting Mg alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2022, 10, 1857–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okayasu, M.; Go, S. Precise analysis of effects of aging on mechanical properties of cast ADC12 aluminum alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 638, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timelli, G.; Fabrizi, A. The effects of microstructure heterogeneities and casting defects on the mechanical properties of high-pressure die-cast AlSi9Cu3 (Fe) alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 5486–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wessén, M. Characteristics of microstructure and banded defects in die cast AM50 magnesium components. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2005, 18, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourlay, C.; Laukli, H.; Dahle, A. Defect band characteristics in Mg-Al and Al-Si high-pressure die castings. Met. Mater. Trans. 2007, 38, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-S.; Xiong, S.-M. Effects of shot speed and biscuit thickness on externaly solidified crystals of high-pressure diet cast AM60B magnesium alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2011, 21, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Du, Z.; Cheng, A.; He, Z.; Tan, H.; Yu, W. Influence of process parameters and heat treatment on self-piercing riveting of high-strength steel and die-casting aluminium. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 8857–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, B.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Hong, J. Data extension-based analysis and application selection of process-composition-properties of die casting aluminum alloy. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, B.; Huang, H. Research on composition-process-property prediction of die casting Al alloys via combining feature creation and attention mechanisms. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Al | Si | Mn | Mg | Ti | Fe | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bal. | 6.83 | 0.56 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.097 | <0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Ren, P.; Wang, K.; Liu, B.; Meng, X. Influence of High-Speed Ram Transition Position on Porosity and Mechanical Properties of Large One-Piece Die-Casting Al-Si-Mn-Mg Aluminium Alloy. Materials 2024, 17, 6169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246169
Zhang S, Ren P, Wang K, Liu B, Meng X. Influence of High-Speed Ram Transition Position on Porosity and Mechanical Properties of Large One-Piece Die-Casting Al-Si-Mn-Mg Aluminium Alloy. Materials. 2024; 17(24):6169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246169
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Sai, Pengfei Ren, Kangle Wang, Bo Liu, and Xianming Meng. 2024. "Influence of High-Speed Ram Transition Position on Porosity and Mechanical Properties of Large One-Piece Die-Casting Al-Si-Mn-Mg Aluminium Alloy" Materials 17, no. 24: 6169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246169
APA StyleZhang, S., Ren, P., Wang, K., Liu, B., & Meng, X. (2024). Influence of High-Speed Ram Transition Position on Porosity and Mechanical Properties of Large One-Piece Die-Casting Al-Si-Mn-Mg Aluminium Alloy. Materials, 17(24), 6169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246169






