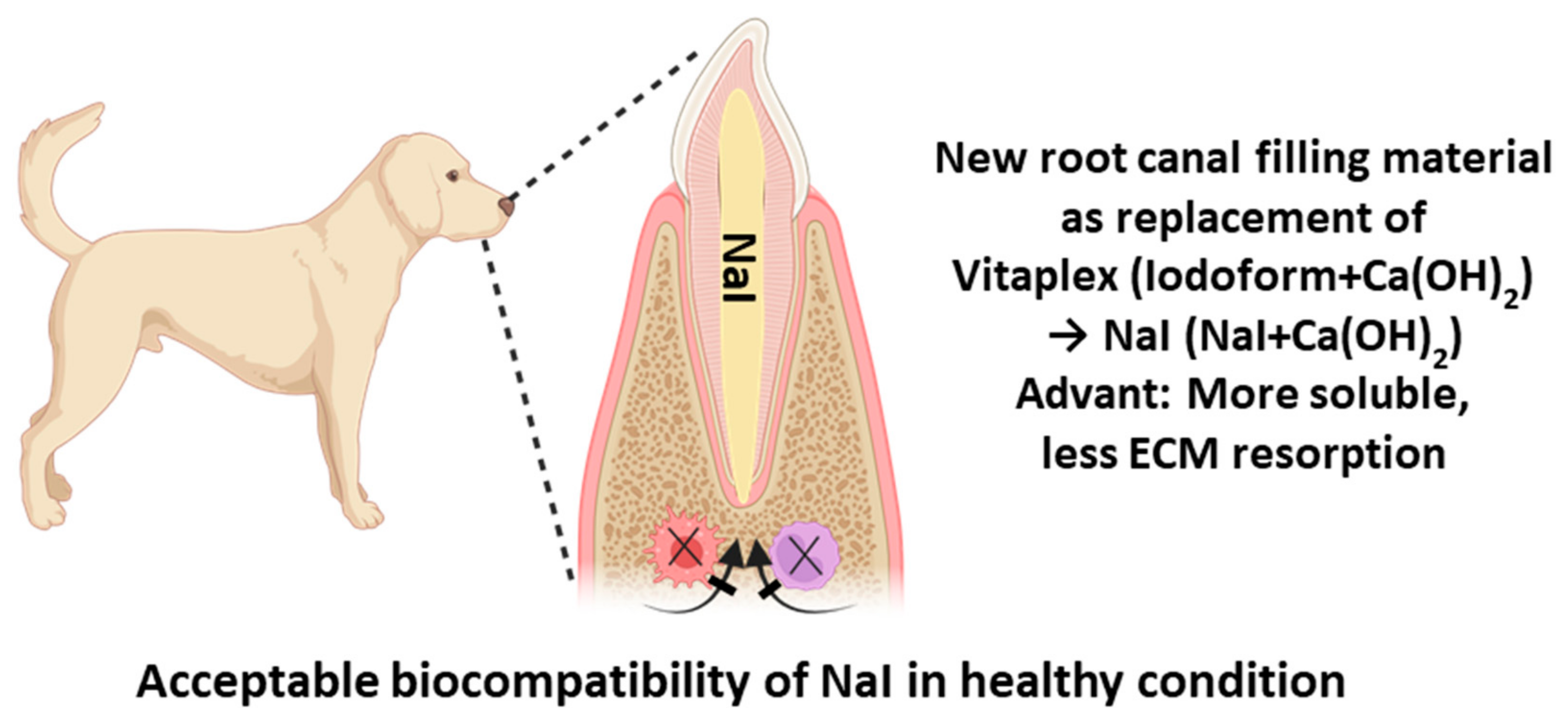
Histological Evaluation of Sodium Iodide-Based Root Canal Filling Materials in Canine Teeth
Highlights
- NaI-based root canal filling shows comparable biocompatibility to commercial products.
- No inflammatory responses observed in periapical tissues after 4-week animal study.
- Gradual loss of radiopacity noted in NaI material, maintaining volumetric stability.
- Great potential as safer alternative to iodoform-containing materials for primary teeth.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
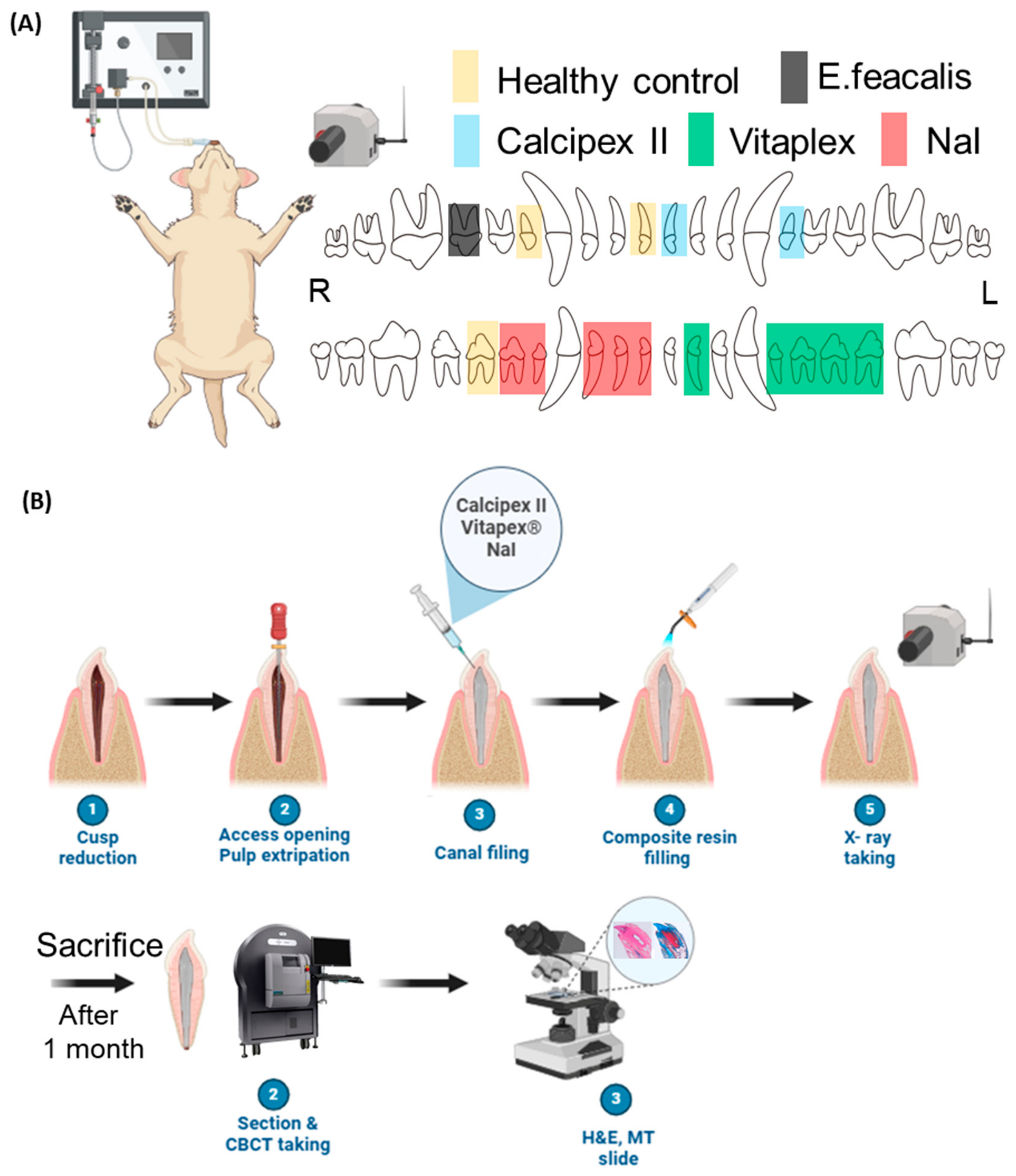
2.1. Preparation for Sample
2.2. Animal Study
2.3. Radiopacity Test in Endodontic-Treated Resin Tooth
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
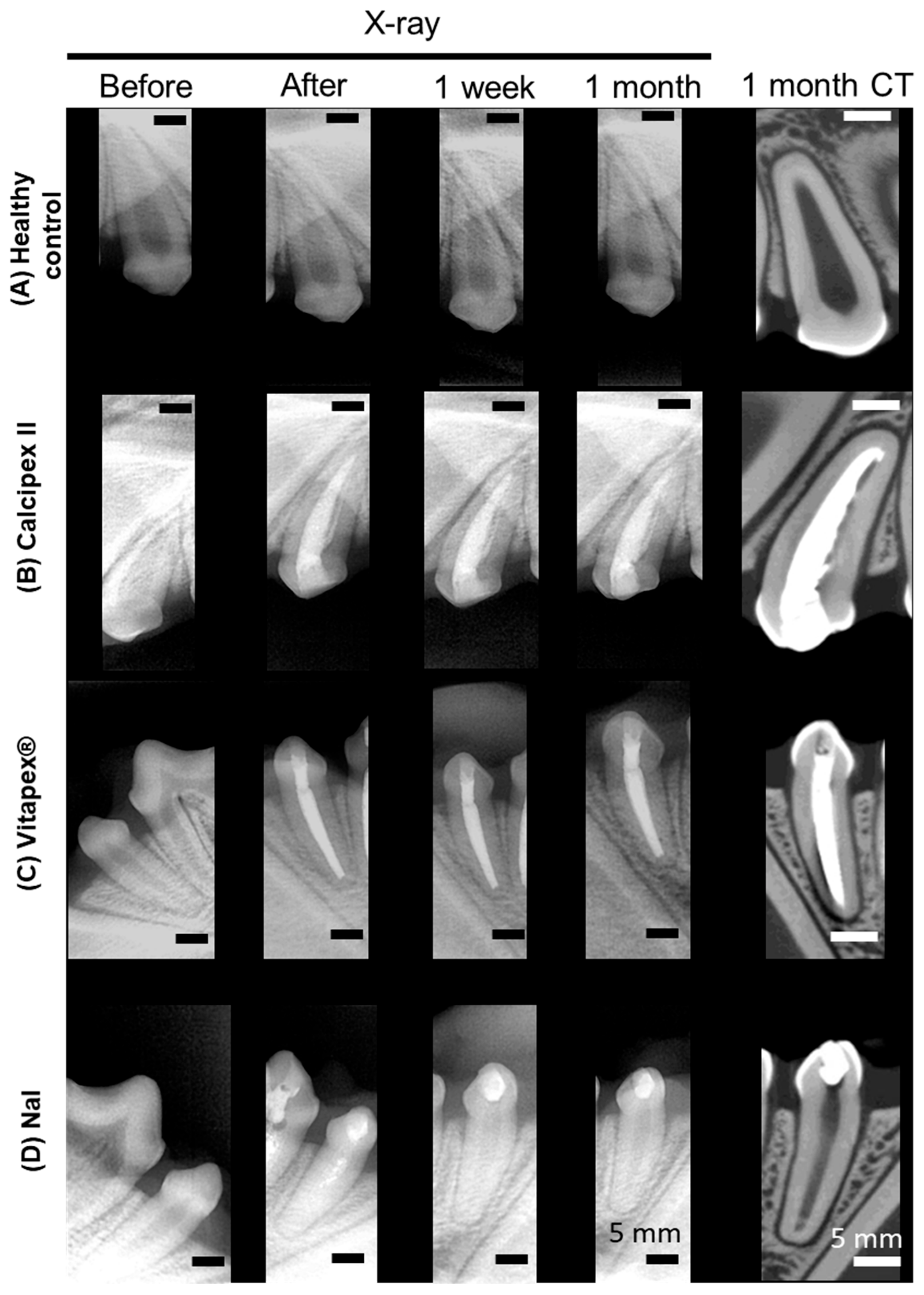
3.1. Radiographic and Micro-Computed Tomographic Evaluation
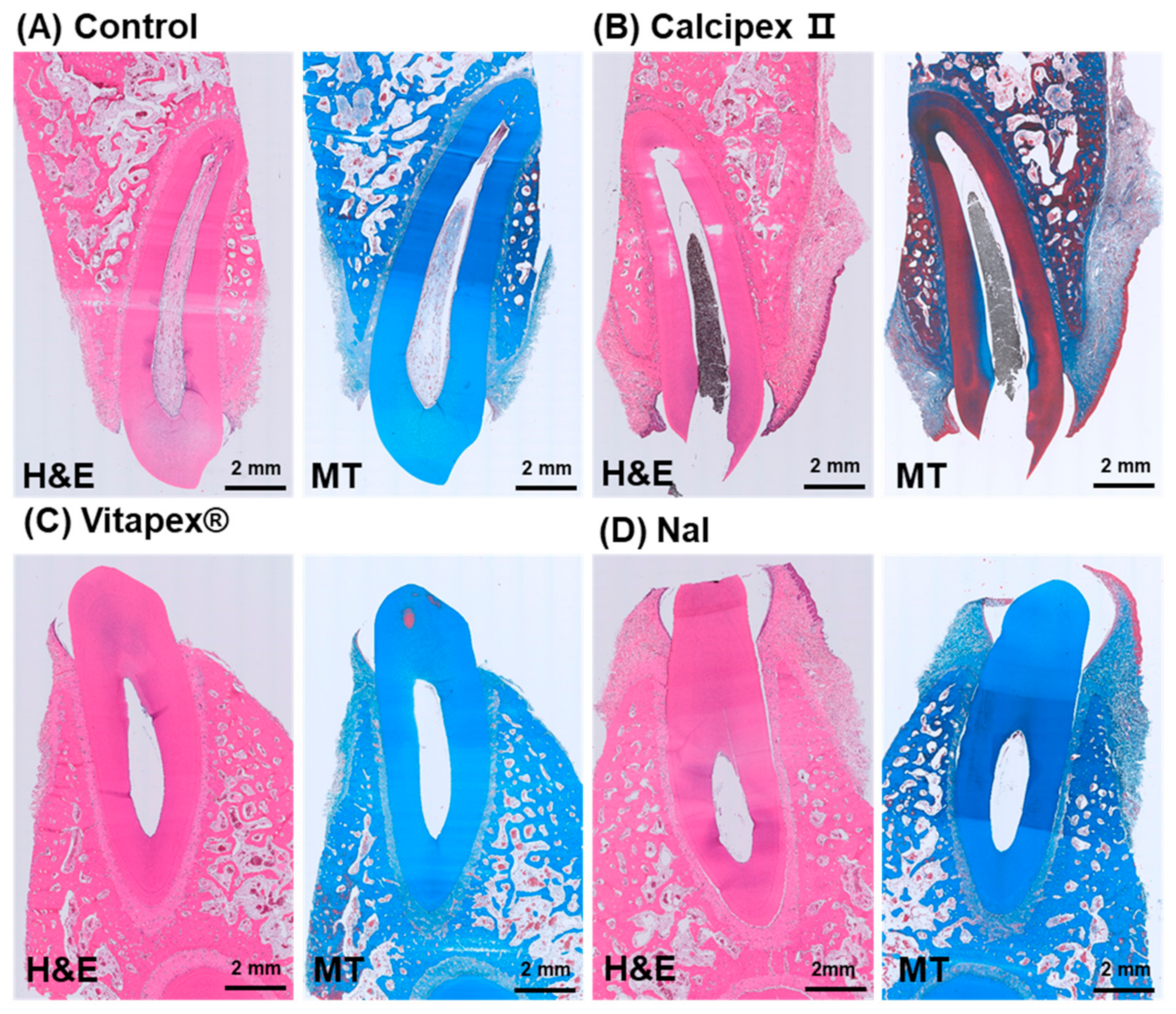
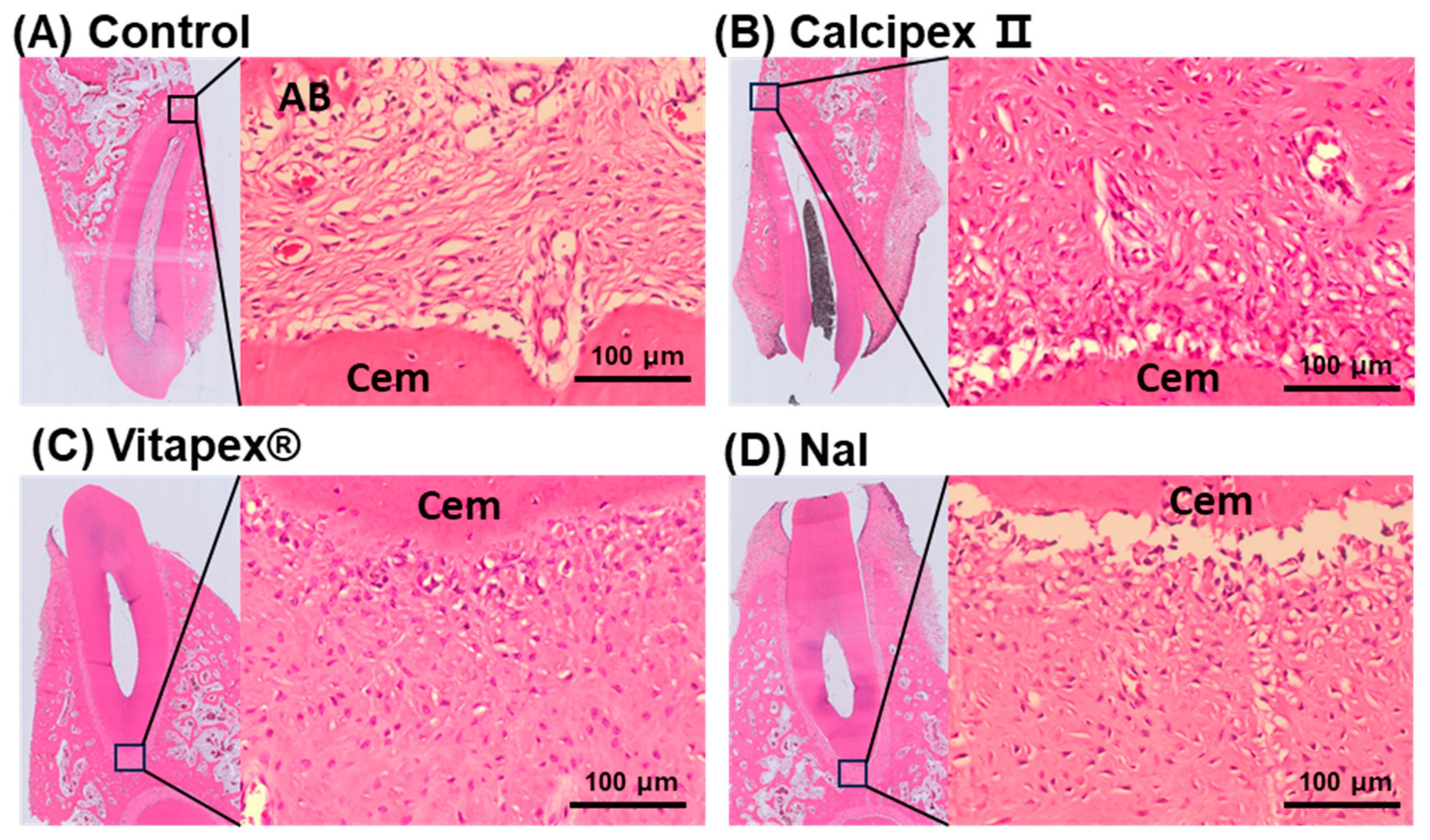
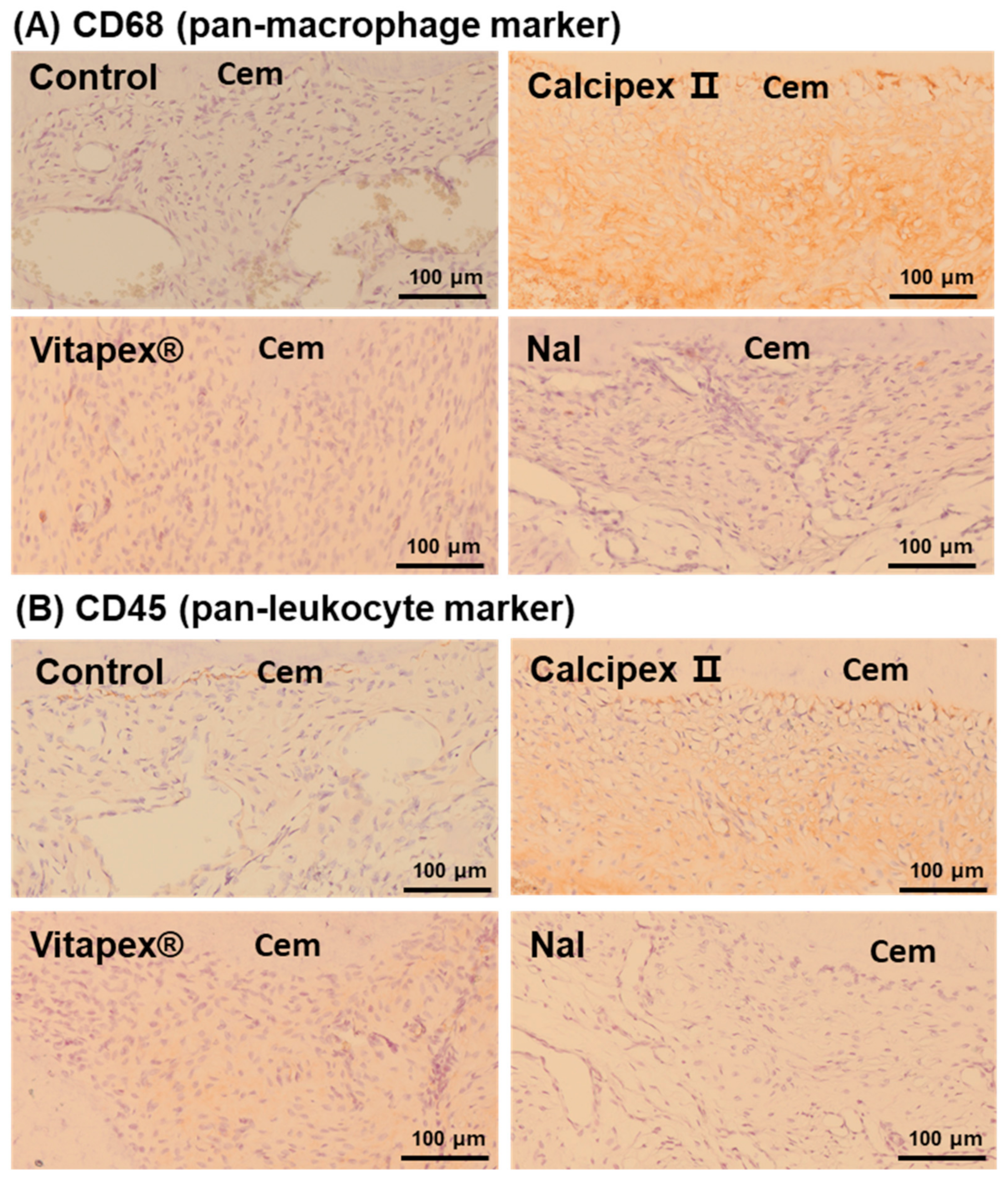
3.2. Histological Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takiguchi, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Sobue, S.; Ooshima, T. Radicular cyst associated with a primary molar following pulp therapy: A case report. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2001, 11, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mass, E.; Kaplan, I.; Hirshberg, A. A clinical and histopathological study of radicular cysts associated with primary molars. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 1995, 24, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savage, N.; Adkins, K.; Weir, A.; Grundy, G. An histological study of cystic lesions following pulp therapy in deciduous molars. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 1986, 15, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.S.; Vidhya, M.; Sargod, S. Radicular cyst associated with endodontically treated deciduous tooth: A case report. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 2003, 21, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rifkin, A. The root canal treatment of abscessed primary teeth—A three to four year follow-up. ASDC J. Dent. Child. 1982, 49, 428–431. [Google Scholar]
- Petel, R.; Moskovitz, M.; Tickotsky, N.; Halabi, A.; Goldstein, J.; Houri-Haddad, Y. Cytotoxicity and proliferative effects of Iodoform-containing root canal-filling material on RAW 264.7 macrophage and RKO epithelial cell lines. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Moskovitz, M.; Tickotsky, N.; Ashkar, H.; Holan, G. Degree of root resorption after root canal treatment with iodoform-containing filling material in primary molars. Quintessence Int. 2012, 43, 361. [Google Scholar]
- Nakornchai, S.; Banditsing, P.; Visetratana, N. Clinical evaluation of 3Mix and Vitapex® as treatment options for pulpally involved primary molars. Int. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2010, 20, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.; Fan, W.; Mai, L.; He, H.; Huang, F. Extracellular vesicles delivering nuclear factor I/C for hard tissue engineering: Treatment of apical periodontitis and dentin regeneration. J. Tissue Eng. 2022, 13, 20417314221084095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurko, C.; Garcia-Godoy, F. Evaluation of a calcium hydroxide/iodoform paste (Vitapex) in root canal therapy for primary teeth. J. Clin. Pediatr. Dent. 1999, 23, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Estrela, C.; Estrela, C.R.d.A.; Hollanda, A.C.B.; Decurcio, D.d.A.; Pécora, J.D. Influence of iodoform on antimicrobial potential of calcium hydroxide. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2006, 14, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.E.; Read, M.L.; Turnell, A.S.; Watkins, R.J.; Watkinson, J.C.; Lewy, G.D.; Fong, J.C.; James, S.R.; Eggo, M.C.; Boelaert, K. A novel mechanism of sodium iodide symporter repression in differentiated thyroid cancer. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3393–3402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-M.; Vu, H.T.; Shin, S.-J.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.-J.; Song, S.; Han, M.-R.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Knowles, J.C. Improvement of Biological Effects of Root-Filling Materials for Primary Teeth by Incorporating Sodium Iodide. Molecules 2022, 27, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacenko, O. c-Fos and bone loss: A proto-oncogene regulates osteoclast lineage determination. BioEssays 1995, 17, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisaki, K.; Tanabe, N.; Suzuki, N.; Kawato, T.; Takeichi, O.; Tsuzukibashi, O.; Makimura, M.; Ito, K.; Maeno, M. Receptor activator of NF-κB ligand induces the expression of carbonic anhydrase II, cathepsin K, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in osteoclast precursor RAW264. 7 cells. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.-J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Vu, H.T.; Choi, J.-M.; Park, J.-H.; Shin, S.-J.; Dashnyam, K.; Knowles, J.C.; Lee, H.-H.; Jun, S.-K.; et al. Physicochemical, Pre-Clinical, and Biological Evaluation of Viscosity Optimized Sodium Iodide-Incorporated Paste. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6876:2012; Dentistry—Root Canal Sealing Materials. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Alonso, C.; Collini, I.; Carrer, V.; Barba, C.; Martí, M.; Coderch, L. Permeation kinetics of active drugs through lanolin-based artificial membranes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 192, 111024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Chang, S.-J.; Lee, H.-H.; Han, M.-R.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, J.-B.; Shin, J.-S.; Lee, J.-H. Optimization of Sodium Iodide-Based Root Filling Material for Clinical Applications: Enhancing Physicochemical Properties. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 7405:2018; Dentistry—Evaluation of Biocompatibility of Medical Devices Used in Dentistry. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Kim, D.-S.; Kim, J.H.; Baek, S.-W.; Lee, J.-K.; Park, S.-Y.; Choi, B.; Kim, T.-H.; Min, K.; Han, D.K. Controlled vitamin D delivery with injectable hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel for restoration of tendinopathy. J. Tissue Eng. 2022, 13, 20417314221122089. [Google Scholar]
- Namangkalakul, W.; Nagai, S.; Jin, C.; Nakahama, K.-I.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Ueha, S.; Akiyoshi, K.; Matsushima, K.; Nakashima, T.; Takechi, M.; et al. Augmented effect of fibroblast growth factor 18 in bone morphogenetic protein 2-induced calvarial bone healing by activation of CCL2/CCR2 axis on M2 macrophage polarization. J. Tissue Eng. 2023, 14, 20417314231187960. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, T.; Miao, S.; Shen, J.; Song, W.; Tan, S.; Ma, D. Enhanced effects of antagomiR-3074-3p-conjugated PEI-AuNPs on the odontogenic differentiation by targeting FKBP9. J. Tissue Eng. 2023, 14, 20417314231184512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.; Kim, S.; Sun, T.; Cho, Y.-B.; Song, M. Pulp-dentin regeneration: Current approaches and challenges. J. Tissue Eng. 2019, 10, 2041731418819263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendry, J.A.; Jeansonne, B.G.; Dummett, Jr., C.O.; Burrell, W. Comparison of calcium hydroxide and zinc oxide and eugenol pulpectomies in primary teeth of dogs. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1982, 54, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spedding, R. Incomplete resorption of resorbable zinc oxide root canal fillings in primary teeth: Report of two cases. ASDC J. Dent. Child. 1985, 52, 214–216. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, V. Clinical and radiological evaluation of zinc oxide-eugenol and Maisto’s paste as obturating materials in infected primary teeth—Nine months study. J. Indian Soc. Pedod. Prev. Dent. 1996, 14, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Erausquin, J.; Muruzábal, M. Root canal fillings with zinc oxide-eugenol cement in the rat molar. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1967, 24, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, J.; Sadrian, R. Predicting pulpectomy success and its relationship to exfoliation and succedaneous dentition. Pediatr. Dent. 1996, 18, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Nurko, C.; Ranly, D.; García-Godoy, F.; Lakshmyya, K. Resorption of a calcium hydroxide/iodoform paste (Vitapex) in root canal therapy for primary teeth: A case report. Pediatr. Dent. 2000, 22, 517–520. [Google Scholar]
- Fava, L.; Saunders, W. Calcium hydroxide pastes: Classification and clinical indications. Int. Endod. J. 1999, 32, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Junior, J.R.; Correr-Sobrinho, L.; Correr, A.B.; Sinhoreti, M.A.; Consani, S.; Sousa-Neto, M.D. Solubility and dimensional change after setting of root canal sealers: A proposal for smaller dimensions of test samples. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuga, M.C.; Faria, G.; So, M.V.; Keine, K.C.; Santos, A.D.d.; Duarte, M.A.H.; Kopper, P.M.P. The impact of the addition of iodoform on the physicochemical properties of an epoxy-based endodontic sealer. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2014, 22, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, G.K.; Enwemeka, C.S. A simplified method for the analysis of hydroxyproline in biological tissues. Clin. Biochem. 1996, 29, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangione, F.; Salmon, B.; EzEldeen, M.; Jacobs, R.; Chaussain, C.; Vital, S. Characteristics of Large Animal Models for Current Cell-Based Oral Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2022, 28, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
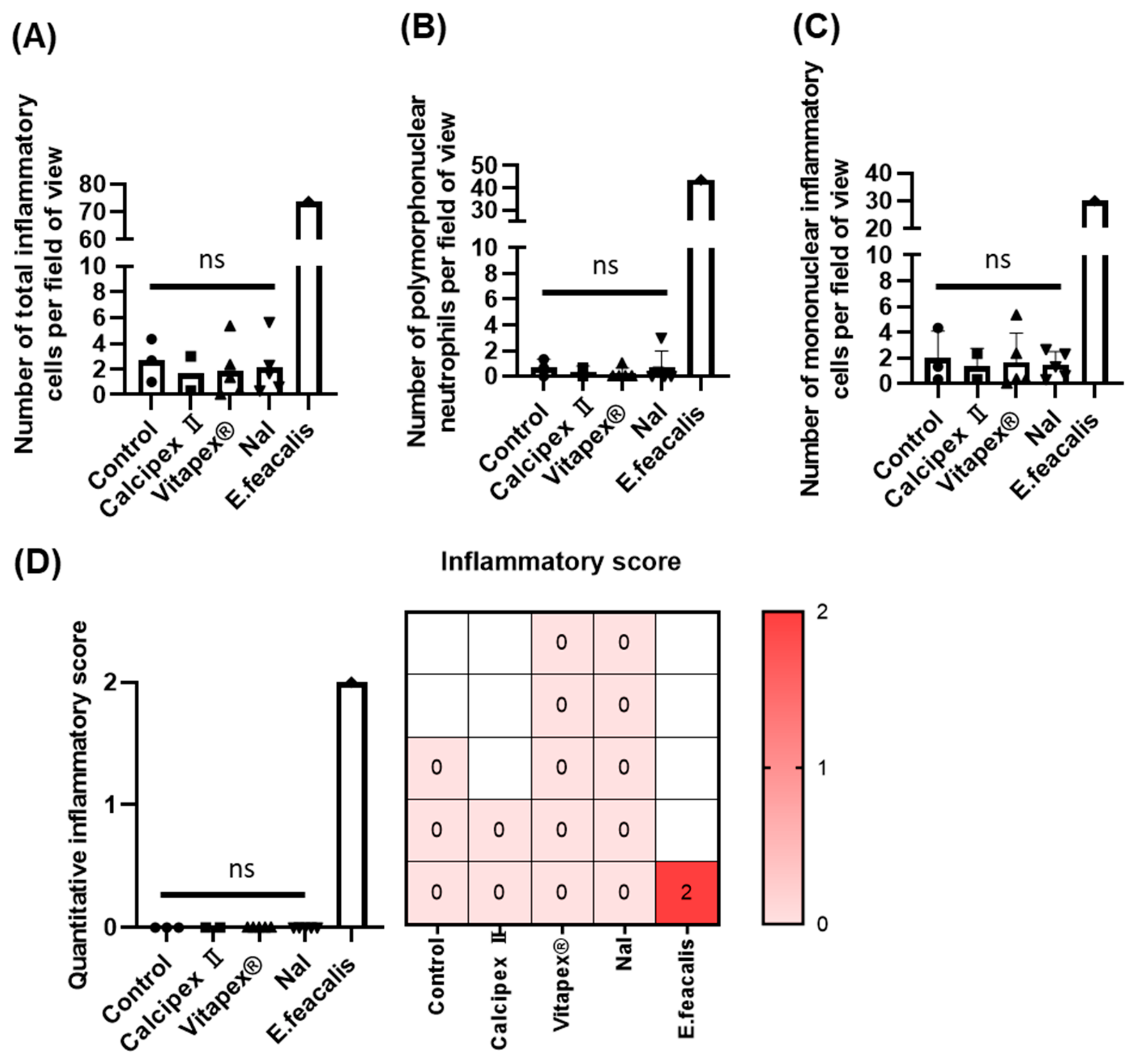
| Score | Histological Findings | Number of Inflammatory Cells |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Fibrovascular tissue with mild acute and chronic inflammation | An average of fewer than 10 inflammatory cells observed at 400× magnification |
| 1 | Fibrovascular tissue with moderate acute and chronic inflammation | An average of 10 to fewer than 50 inflammatory cells observed at 400× magnification |
| 2 | Fibrovascular tissue with severe acute and chronic inflammation | An average of 50 or more inflammatory cells observed at 400× magnification |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.; Park, H.-s.; Kim, Y.-J.; Lee, H.-H.; Han, M.-R.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, J.-B.; Shin, J.-S.; Kim, J.-S.; et al. Histological Evaluation of Sodium Iodide-Based Root Canal Filling Materials in Canine Teeth. Materials 2024, 17, 6082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246082
Lee JH, Lee S, Park H-s, Kim Y-J, Lee H-H, Han M-R, Lee J-H, Kim J-B, Shin J-S, Kim J-S, et al. Histological Evaluation of Sodium Iodide-Based Root Canal Filling Materials in Canine Teeth. Materials. 2024; 17(24):6082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246082
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jae Hee, Sak Lee, Hye-shin Park, Yu-Jin Kim, Hae-Hyoung Lee, Mi-Ran Han, Jun-Haeng Lee, Jong-Bin Kim, Ji-Sun Shin, Jong-Soo Kim, and et al. 2024. "Histological Evaluation of Sodium Iodide-Based Root Canal Filling Materials in Canine Teeth" Materials 17, no. 24: 6082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246082
APA StyleLee, J. H., Lee, S., Park, H.-s., Kim, Y.-J., Lee, H.-H., Han, M.-R., Lee, J.-H., Kim, J.-B., Shin, J.-S., Kim, J.-S., & Lee, J.-H. (2024). Histological Evaluation of Sodium Iodide-Based Root Canal Filling Materials in Canine Teeth. Materials, 17(24), 6082. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17246082





