Preparation of Alumina Oxo-Cluster/Cellulose Polymers and Dye Adsorption Application
Highlights
- Innovative Adsorbent Synthesis: Developed in situ aluminum oxo-clusters (AlOCs) on cellulose for enhanced dye adsorption, utilizing a solvent thermal method for improved stability and recyclability.
- Superior Anionic Dye Removal: AlOCs/Cellulose exhibits high selectivity and adsorption capacity for anionic dyes, achieving up to 97% removal of methyl orange under optimal conditions.
- Sustainable and Reusable: Demonstrates excellent reusability and regeneration potential, maintaining high adsorption efficiency after multiple cycles, making it a promising solution for wastewater treatment.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Synthesis of AlOCs/Cellulose
2.1. Preparation of Carboxylic Acid Functionalized Woods
2.2. Preparation of AlOCs/Cellulose
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorbent Characterization
3.1.1. SEM and EDX Analysis
3.1.2. BET Analysis
3.1.3. FT-IR Analysis
3.1.4. Thermal Gravimetric Analysis
3.2. Adsorption Performance
3.2.1. Adsorption Selectivity
3.2.2. Effect of pH
3.2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
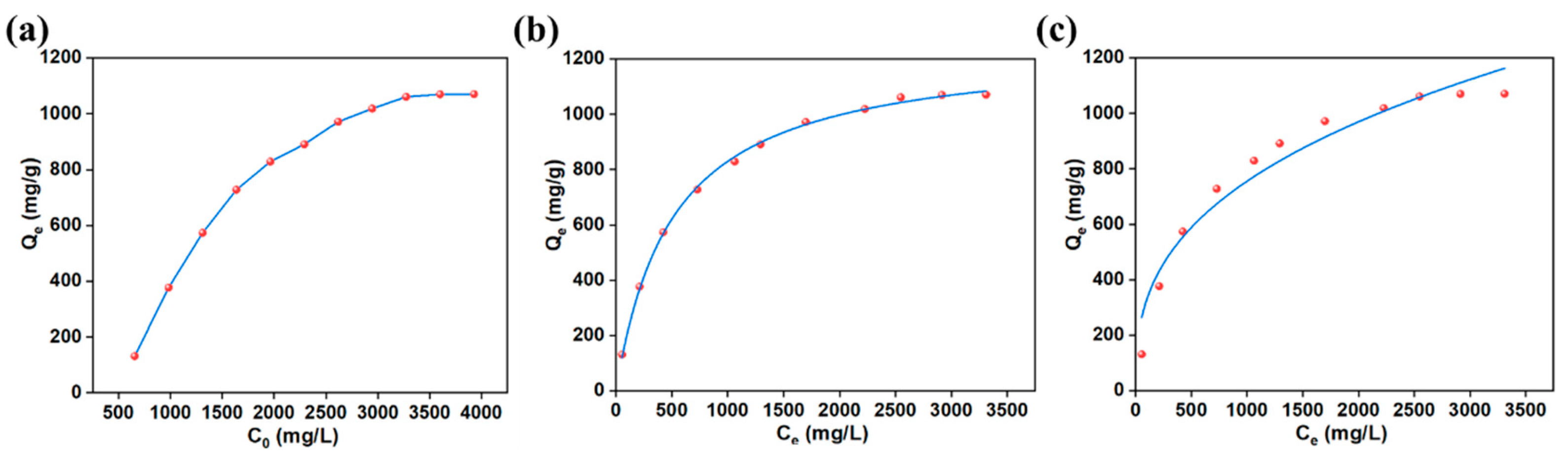
3.2.4. Adsorption Isotherms
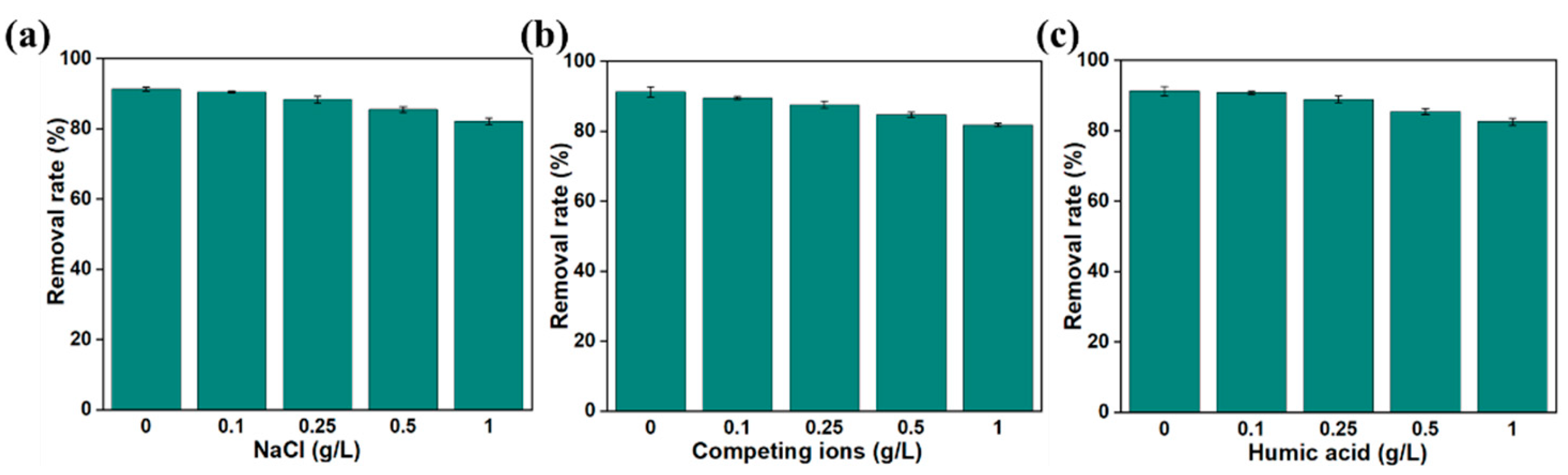
3.2.5. Study on Adsorption Properties in Simulated Real Environment
3.2.6. Comparative Adsorption Performance of Cellulose-Based Adsorbents
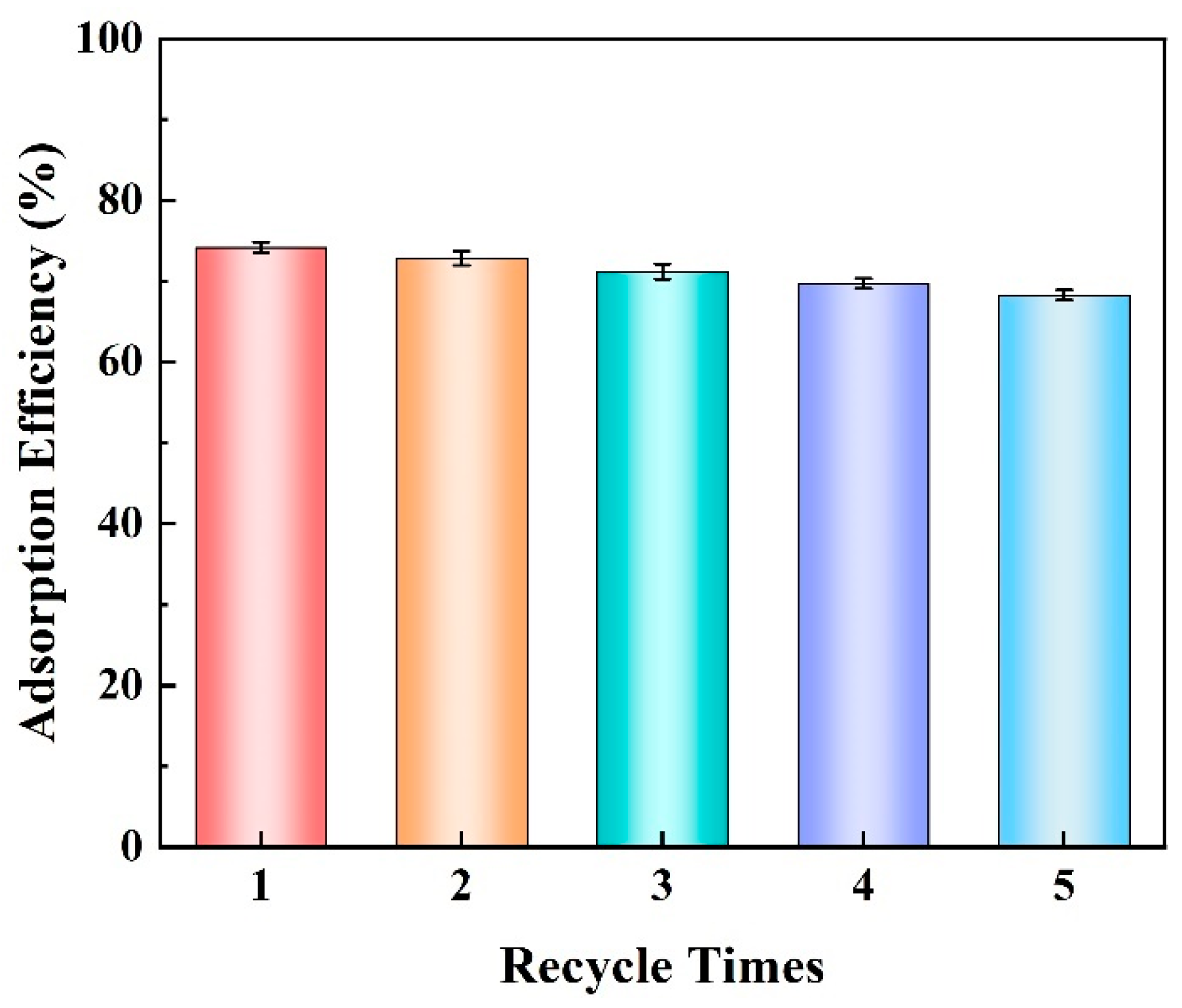
3.2.7. Reusability
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.Y.; Ye, W.Y.; Xie, M.; Seo, D.H.; Luo, J.Q.; Wan, Y.H.; van der Bruggen, B. Environmental Impacts and Remediation of Dye-Containing Wastewater. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 785–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.H.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.X.; Fu, Y.Y.; Sun, J.Z. A Critical Review on the Treatment Of Dye-Containing Wastewater: Ecotoxicological and Health Concerns Of Textile Dyes and Possible Remediation Approaches for Environmental Safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.; Gupta, S. Toxicological Impact of Azo DyesAzo dyes and Their Microbial Degraded Byproducts on Flora and Fauna. In Innovations in Environmental Biotechnology; Arora, S., Kumar, A., Ogita, S., Yau, Y.-Y., Eds.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, G.; Ealias, A.M.; Saravanakumar, M.P. Advancements in Textile Dye Removal: A Critical Review of Layered Double Hydroxides and Clay Minerals as Efficient Adsorbents. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 12748–12779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y. Recent Advances for Dyes Removal Using Novel Adsorbents: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 352–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Rao, L.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; Du, J.; Xu, C. Modification of Microcrystalline Cellulose with Pyridone Derivatives for Removal of Cationic Dyes from Aqueous Solutions. Cellulose 2016, 23, 2917–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, F.; Shaban, M.; Zaki, S.K.; Abd-Elsamie, M.S.; Sayed, R.; Zayed, M.; Khalid, N.; Saad, S.; Omar, S.; Ahmed, A.M.; et al. Activated Carbon Derived from Sugarcane and Modified with Natural Zeolite for Efficient Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye: Experimentally and Theoretically Approaches. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzalat, O.; Wong, D.; Elsayed, M.A. Nano-Porous Composites of Activated Carbon–Metal Organic Frameworks (Fe-BDC@AC) for Rapid Removal of Cr (VI): Synthesis, Adsorption, Mechanism, and Kinetics Studies. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2022, 32, 1924–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, K.; Gupta, V.K.; Moradi, O.; Makhlouf, A.S.H.; Sillanpää, M.; Nadagouda, M.N.; Sadegh, H.; Shahryari-ghoshekandi, R.; Pal, A.; Wang, Z.-j.; et al. A Comparative Study on the Basis of Adsorption Capacity Between Cnts and Activated Carbon as Adsorbents for Removal of Noxious Synthetic Dyes: A Review. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2015, 5, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yao, L.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, L. In Situ Growth Synthesis of the CNTs@AC Hybrid Material for Efficient Nitrate-Nitrogen Adsorption. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 1612–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Xiao, J.; Liu, P.; Yang, G.W. Super Adsorption Capability from Amorphousization of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Dye Removal. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, H.C.S.; Gurunanthanan, V.; Singh, A.; Mantilaka, M.M.M.G.P.G.; Das, G.; Arya, S. Magnesium oxide (MgO) Nanoadsorbents in Wastewater Treatment: A Comprehensive Review. J. Magnes. Alloys 2024, 12, 1709–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Z.; Zhao, F.; Guo, X. Preparation of a Novel Adsorbent with Amino-Rich Carbon Quantum Dots For Efficiently Separating Zn(II) from Fe(II) in Zinc Deplating Waste Liquid. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Peng, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Yuan, G. Facile Construction of ZIF-94/PAN Nanofiber by Electrospinning for the Removal of Co(II) from Wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, Y.-T.; Holloman, K. Agricultural Waste as a Low-Cost Adsorbent. In Integrated Natural Resources Research; Wang, L.K., Wang, M.-H.S., Hung, Y.-T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 103–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainth, S.; Sharma, P.; Pandey, O.P. Green Sorbents from Agricultural Wastes: A review of Sustainable Adsorption Materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2024, 19, 100562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Fang, W.H.; Sun, Y.Y.; Yao, S.Y.; Wang, S.T.; Lu, D.F.; Zhang, J. Designable Assembly of Aluminum Molecular Rings for Sequential Confinement of Iodine Molecules. Angew. Chem.-Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 21426–21433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.F.; Liu, Y.J.; Wang, S.T.; Liu, X.Y.; Ma, C.; Fang, W.H.; Zhang, J. Loading Single Lanthanide Ion into Aluminum Molecular rings: Water-Stable Sodalite Cage for Removal of Nuclear-Industry Anions. Sci. China-Chem. 2023, 66, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Wang, F.; Liu, C.H.; Wang, S.T.; Sun, Y.Y.; Fang, W.H.; Zhang, J. Combination of Aluminum Molecular Rings with Chemical Reduction Centers for Iodine Capture and Aggregation. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 4506–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.H.; Fang, W.H.; Zhang, J. Aluminum Molecular Rings Bearing Amino-Polyalcohol For Iodine Capture. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tignol, P.; Pimenta, V.; Dupont, A.L.; Carvalho, S.; Al Mohtar, A.; Severino, M.I.; Nouar, F.; Pinto, M.L.; Serre, C.; Lavédrine, B. A Versatile Shaping Method of Very-High Loading Porous Solids Paper Adsorbent Composites. Small Methods 2024, 8, 2301343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Wang, J. MOF/Graphene Oxide Composite as an Efficient Adsorbent for the Removal of Organic Dyes from Aqueous Solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 5521–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadipouya, S.; Haris, M.H.; Ahmadijokani, F.; Jarahiyan, A.; Molavi, H.; Moghaddam, F.M.; Rezakazemi, M.; Arjmand, M. Magnetic Fe3O4@UiO-66 Nanocomposite for Rapid Adsorption of Organic Dyes from Aqueous Solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 322, 114910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.Z.; Zeng, H.C. Design and Synthesis of Supported Nanoscale Metal-Organic Frameworks: Transformation from Transition Metal Silicates. Acs Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14979–14988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beims, R.F.; Arredondo, R.; Sosa Carrero, D.J.; Yuan, Z.; Li, H.; Shui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Leitch, M.; Xu, C.C. Functionalized Wood as Bio-Based Advanced Materials: Properties, Applications, and Challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velinov, N.; Radović Vučić, M.; Petrović, M.; Najdanović, S.; Kostić, M.; Mitrović, J.; Bojić, A. The Influence of Various Solvents’ Polarity in the Synthesis of Wood Biowaste Sorbent: Evaluation of Dye Sorption. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 8139–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kuang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Burgert, I.; Keplinger, T.; Gong, A.; Li, T.; Berglund, L.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Hu, L. Structure–Property–Function Relationships of Natural and Engineered Wood. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 642–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Yao, S.M.; Qin, C.R.; Long, Z. Adsorption Properties of UiO-66/Wood Hybrid Adsorbent for Organic Dye Removal. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.Y.; Fang, W.H.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wang, S.T.; Zhang, J. Mesoporous Assembly of Aluminum Molecular Rings for Iodine Capture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najdanovic, S.M.; Petrovic, M.M.; Kostic, M.M.; Mitrovic, J.Z.; Bojic, D.V.; Antonijevic, M.D.; Bojic, A.L.J. Electrochemical Synthesis and Characterization of Basic Bismuth Nitrate Bi6O5OH3 (NO3)5•2H2O: A Potential Highly Efficient Sorbent for Textile Reactive Dye Removal. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2020, 46, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Cheng, Z.Y.; Wang, X.Q. Highly Compressible Wood Sponges with a Spring-like Lamellar Structure as Effective and Reusable Oil Absorbents. Acs Nano 2018, 12, 10365–10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, J.Y.; Xu, H.W.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, X.Z.; Huang, W.C. Characterization and Comparison of Carboxymethylation and TEMPO-Mediated Oxidation for Polysaccharides Modification. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.W.; Choi, B.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Ahn, K.H.; Lee, Y.J. Green Synthesis of Aluminum-Based Metal Organic Framework for the Removal of Azo Dye Acid Black 1 from Aqueous Media. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 67, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; You, X.; Yang, C.; Cheng, J.H. Adsorption Behavior of Methyl Orange onto an Aluminum-Based Metal Organic Framework, MIL-68(Al). Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 2800–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ediati, R.; Aulia, W.; Nikmatin, B.A.; Hidayat, A.R.P.; Fitriana, U.M.; Muarifah, C.; Sulistiono, D.O.; Martak, F.; Prasetyoko, D. Chitosan/UiO-66 Composites as High-Performance Adsorbents for the Removal of Methyl Orange In Aqueous Solution. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 21, 100533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, Y.H.; Yu, Z.S.; Huang, Z.G.; Li, M.R.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Ma, X.Q. Investigation on the Co-Pyrolysis of Municipal Solid Waste and Sawdust: Pyrolysis Behaviors, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Analysis. Energy Sources Part A-Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2022, 44, 8001–8011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogalakshmi, K.N.; Devi, T.P.; Sivashanmugam, P.; Kavitha, S.; Kannah, R.Y.; Varjani, S.; AdishKumar, S.; Kumar, G.; Banu, J.R. Lignocellulosic Biomass-Based Pyrolysis: A Comprehensive Review. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.M.; Fu, S.H.; Tang, H.L.; Sun, C. Selective Organic Dye Adsorption Properties of Aluminum Oxide Cluster. Chem. Pap. 2024, 78, 2885–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, K.; Petrović, M.; Najdanović, S.; Velinov, N.; Hurt, A.; Bojić, A.; Kostić, M. Highly Efficient Nano Sorbent as a Superior Material for the Purification of Wastewater Contaminated with Anthraquinone Dye Rb19. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 67, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najdanovic, S.M.; Petrovic, M.M.; Kostic, M.M.; Velinov, N.D.; Vucic, M.D.R.; Matovic, B.Z.; Bojic, A.L. New Way of Synthesis of Basic Bismuth Nitrate by Electrodeposition from Ethanol Solution: Characterization and Application for Removal of RB19 from Water. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 9939–9950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, J.; Peng, X.; Hu, T.; Zhang, L.; Rong, X.; Xue, C.; Xu, L. Coal-Fly-Ash Magnetic Sphere Based Magnetic Adsorbent for Multiple-Dye Adsorption. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 015504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.E.d.F.; Gama, B.M.V.d.; Gonçalves, A.H.d.S.; Medeiros, J.A.; Abud, A.K.d.S. Basic-Dye Adsorption in Albedo Residue: Effect of pH, Contact Time, Temperature, Dye Concentration, Biomass Dosage, Rotation and Ionic Strength. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2020, 32, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajumon, R.; Anand, J.C.; Ealias, A.M.; Desai, D.S.; George, G.; Saravanakumar, M.P. Adsorption of Textile Dyes with Ultrasonic Assistance Using Green Reduced Graphene Oxide: An In-Depth Investigation on Sonochemical Factors. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Li, A.M.; Zhou, M.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q. Nonporous Amorphous Superadsorbents for Highly Effective and Selective Adsorption of Iodine In Water. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiess, A.; Wiebe, J.; Iwaschko, E.; Woschko, D.; Janiak, C. Wood Modification for the Synthesis of MOF@Wood Composite Materials with Increased Metal-Organic Framework (MOF) Loading. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2022, 7, 1682–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; El-Sharkawy, R.M.; Ibrahim, G.A.A. A Novel Bionanocomposite from Doped Lipase Enzyme into Magnetic Graphene Oxide-Immobilized-Cellulose for Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue and Malachite Green Dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 368, 120676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Ansari, K. Novel In-Situ Fabrication of L-Methionine Functionalized Bionanocomposite for Adsorption of Amido Black 10B dye. Process Biochem. 2022, 119, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrik, B.; El Amri, A.; Bensalah, J.; Jebli, A.; Lebkiri, A.; Hsissou, R.; Hbaiz, E.; Rifi, E.; Lebkiri, A. Adsorption of Crystal Violet Using a Composite Based on Graphene Oxide-ED@Cellulose: Adsorption Modeling, Optimization and Recycling. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 162, 112179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, A.; Negarestani, M.; Mollahosseini, A.; Shayesteh, H.; Farimaniraad, H. Low-Cost Treated Lignocellulosic Biomass Waste Supported with FeCl3Zn(NO3)2 for Water Decolorization. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagapati, V.S.; Wen, J.C.; Pan, C.L.; Gutha, Y.; Wen, J.H. Enhanced Adsorption Performance of Reactive Red 120 Azo Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Quaternary Amine Modified Orange Peel Powder. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 285, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.L.; Xiao, W.; Shang, Y.; Zhu, H.M.; Han, R.P. Adsorption of Light Green Anionic Dye Using Cationic Surfactant-Modified Peanut Husk in Batch Mode. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S3595–S3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.H.; Hu, D.Y. Molecular Mechanism of Anionic Dyes Adsorption on Cationized Rice Husk Cellulose from Agricultural Wastes. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 276, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

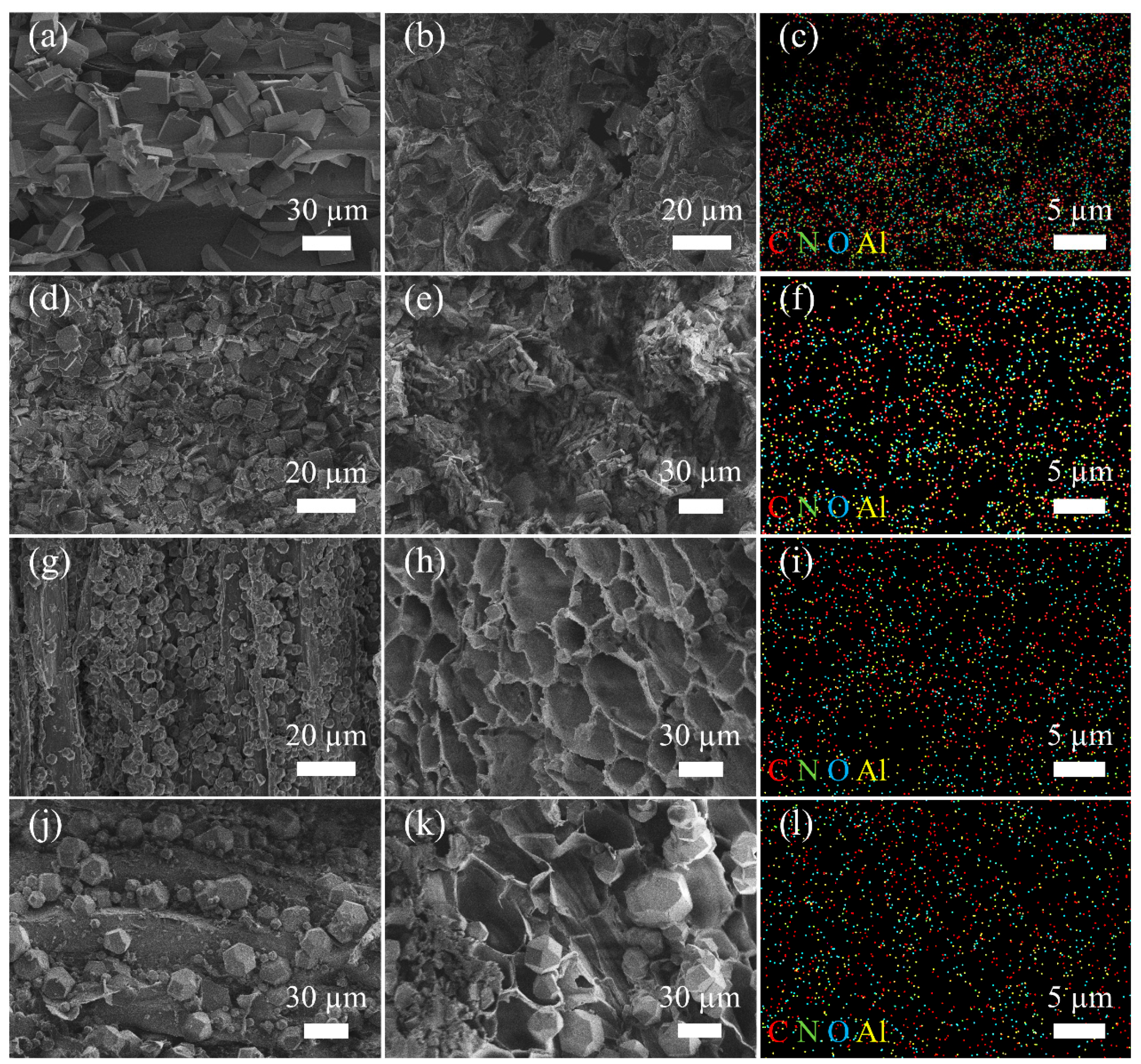





| Adsorbent | Specific Surface Area (m2/g) | Pore Volume (cm3/g) | Average Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood | 1.06 | 0.004 | 15.90 |
| AlOC-15/Cellulose | 3.05 | 0.014 | 7.34 |
| AlOC-20/Cellulose | 10.18 | 0.016 | 6.19 |
| AlOC-22/Cellulose | 18.33 | 0.023 | 3.64 |
| AlOC-26-NC/Cellulose | 20.66 | 0.021 | 4.06 |
| Adsorbent | PFO | PSO | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlOC-26-NC/Cellulose | Qe (mg/g) | K1 | R2 | Qe (mg/g) | K2 | R2 |
| 1102.59 | 0.00186 | 0.9879 | 1846.25 | 5.724 × 10−7 | 0.9971 | |
| Adsorbent | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlOC-26-NC/Cellulose | Qm (mg/g) | KL | R2 | n | KF | R2 |
| 1249.10 | 0.0020 | 0.9986 | 63.01 | −0.3596 | 0.9497 | |
| Composites | Dyes | Qmax (mg/g) | Experimental Conditions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOF@wood (MIL-53(Al)@Pine-MA) | Methylene blue | 54.00 | pH 6.0, 48 h, 298 K | [46] |
| MGO@Cellulose@Lipase | Methylene blue, Malachite green | 66.79, 51.87 | pH 6.0, 30 min and 40 min, 298 K | [47] |
| Meth-Kal@Cellulose | Amido black 10B | 172.14 | 180 min, 303 K | [48] |
| Graphene Oxide-ED@Cellulose | Crystal violet | 260.00 | pH 6.0, 80 min, 298 K | [49] |
| Lignocellulosic sawdust-Fe/Zn | Reactive orange 16 | 60.97 | pH 4.0, 110 min, 298 K | [50] |
| Quaternary amine-modified orange peel powder | Reactive red 120 azo | 344.80 | pH 2.0, 110 min, 338 K | [51] |
| CPB-modified peanut husk | LG anionic dye | 146.20 | pH 2–4, 200 min, 303 k | [52] |
| Cationized rice husk cellulose | Congo red | 580.09 | pH 8, 303 K | [53] |
| AlOC-26-NC/Cellulose | Methyl orange | 1070.37 | pH 5.0, 1320 min, 298 K | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, H.; Yao, S.; Long, Z.; Yang, X.; Si, P.; Sun, C.; Zhang, D. Preparation of Alumina Oxo-Cluster/Cellulose Polymers and Dye Adsorption Application. Materials 2024, 17, 6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17236023
Tang H, Yao S, Long Z, Yang X, Si P, Sun C, Zhang D. Preparation of Alumina Oxo-Cluster/Cellulose Polymers and Dye Adsorption Application. Materials. 2024; 17(23):6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17236023
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Henglong, Simeng Yao, Zhu Long, Xuefei Yang, Pengxiang Si, Chang Sun, and Dan Zhang. 2024. "Preparation of Alumina Oxo-Cluster/Cellulose Polymers and Dye Adsorption Application" Materials 17, no. 23: 6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17236023
APA StyleTang, H., Yao, S., Long, Z., Yang, X., Si, P., Sun, C., & Zhang, D. (2024). Preparation of Alumina Oxo-Cluster/Cellulose Polymers and Dye Adsorption Application. Materials, 17(23), 6023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17236023






