Tuning Biodegradation of Poly (lactic acid) (PLA) at Mild Temperature by Blending with Poly (butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) or Polycaprolactone (PCL)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Biodegradation Test Methods
2.2.1. Home-Composting Biodegradation (ISO 14855 at 28 °C)
2.2.2. Soil Biodegradation Test (ISO 17556)
2.2.3. Marine Biodegradation Test (ASTM D6691)
2.2.4. Freshwater Biodegradation Test (ISO 14851)
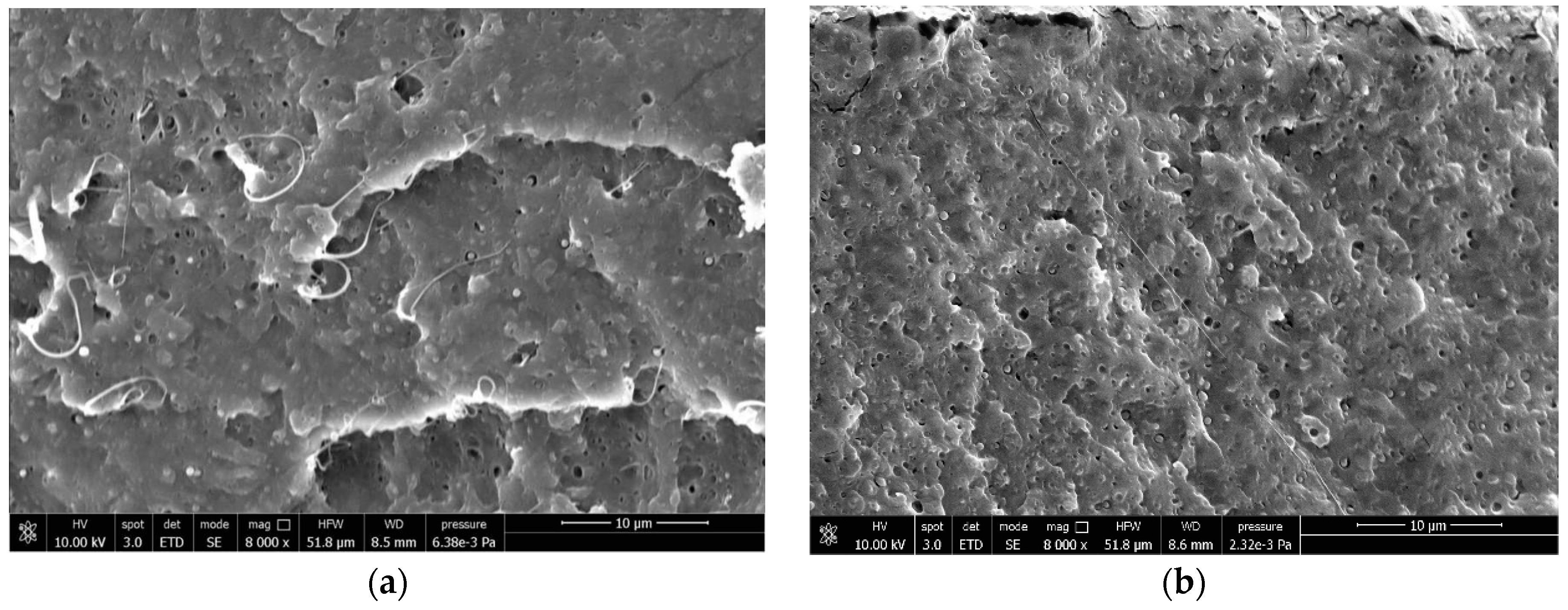
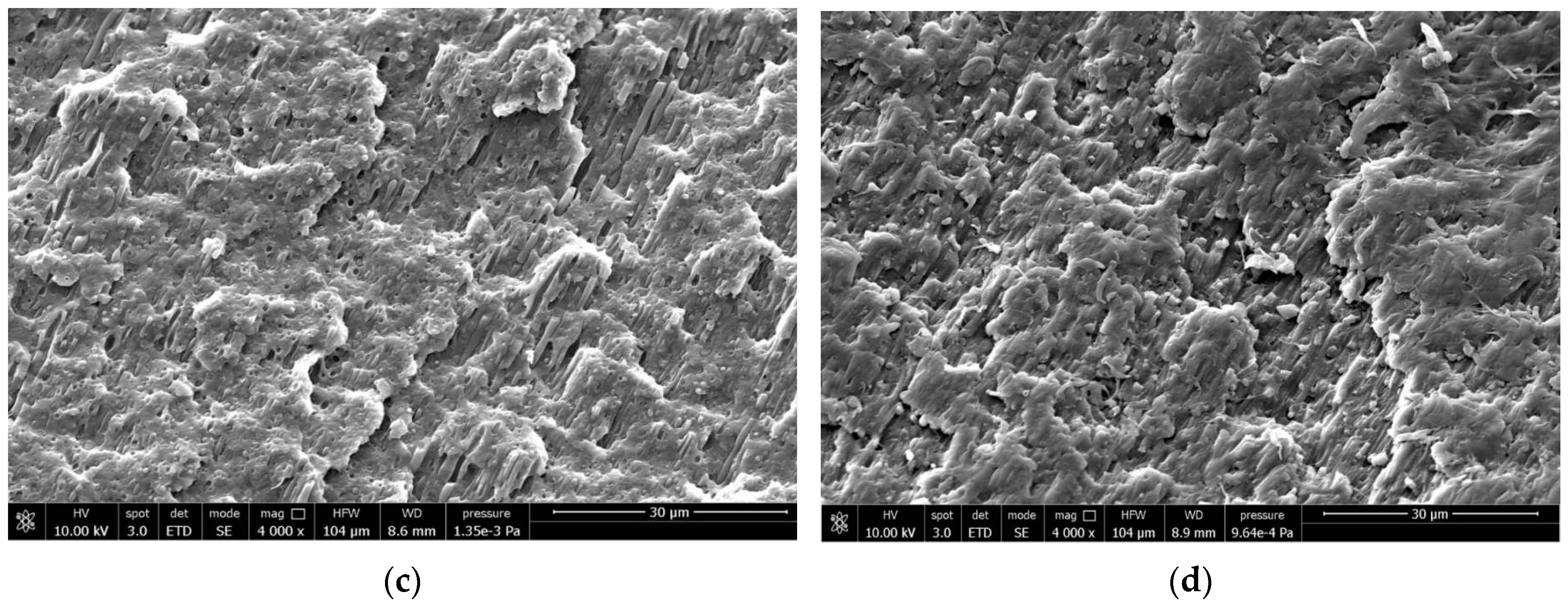
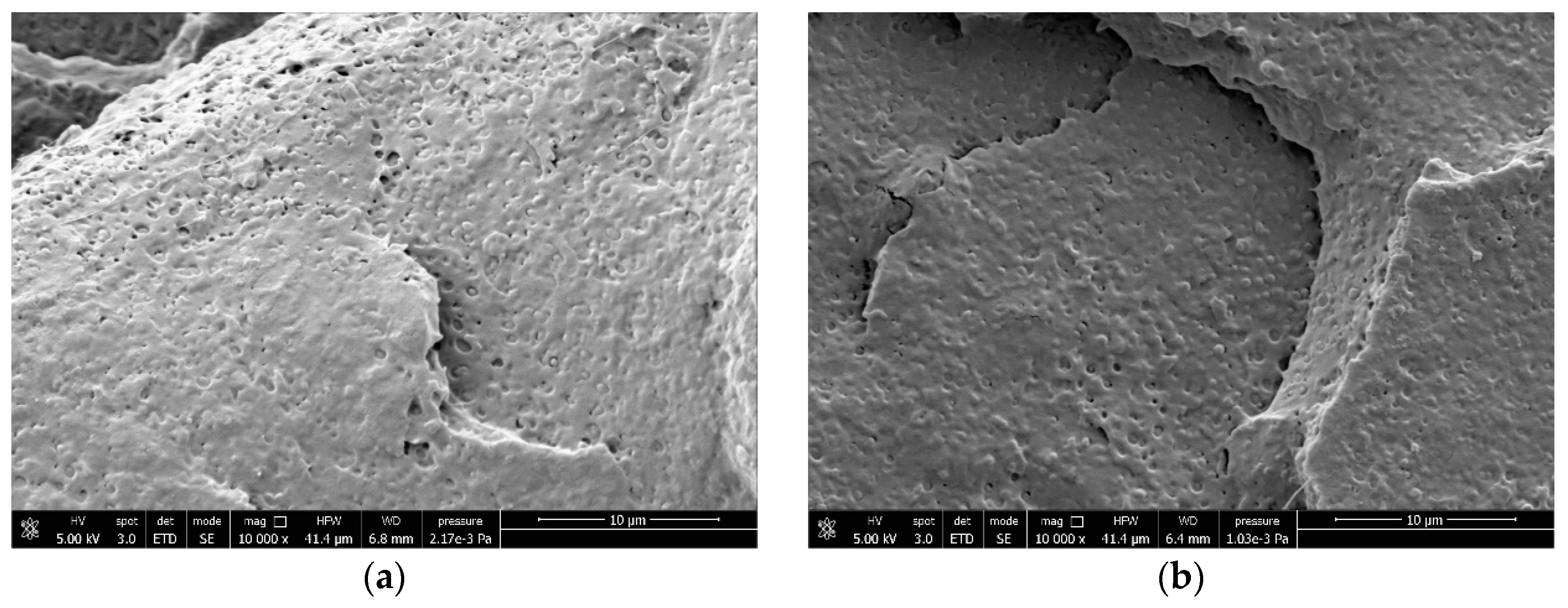
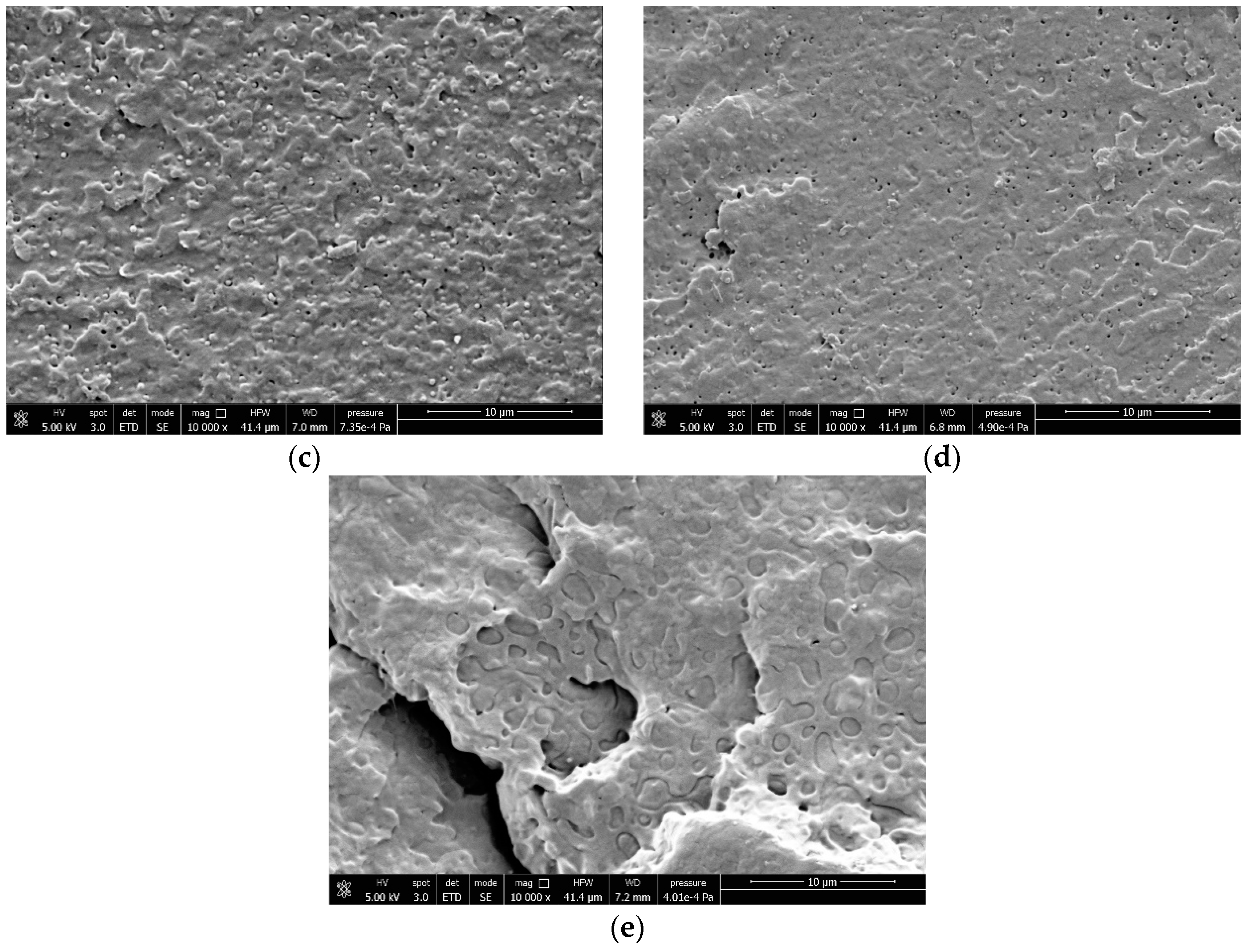
2.3. Field-Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM)
3. Results
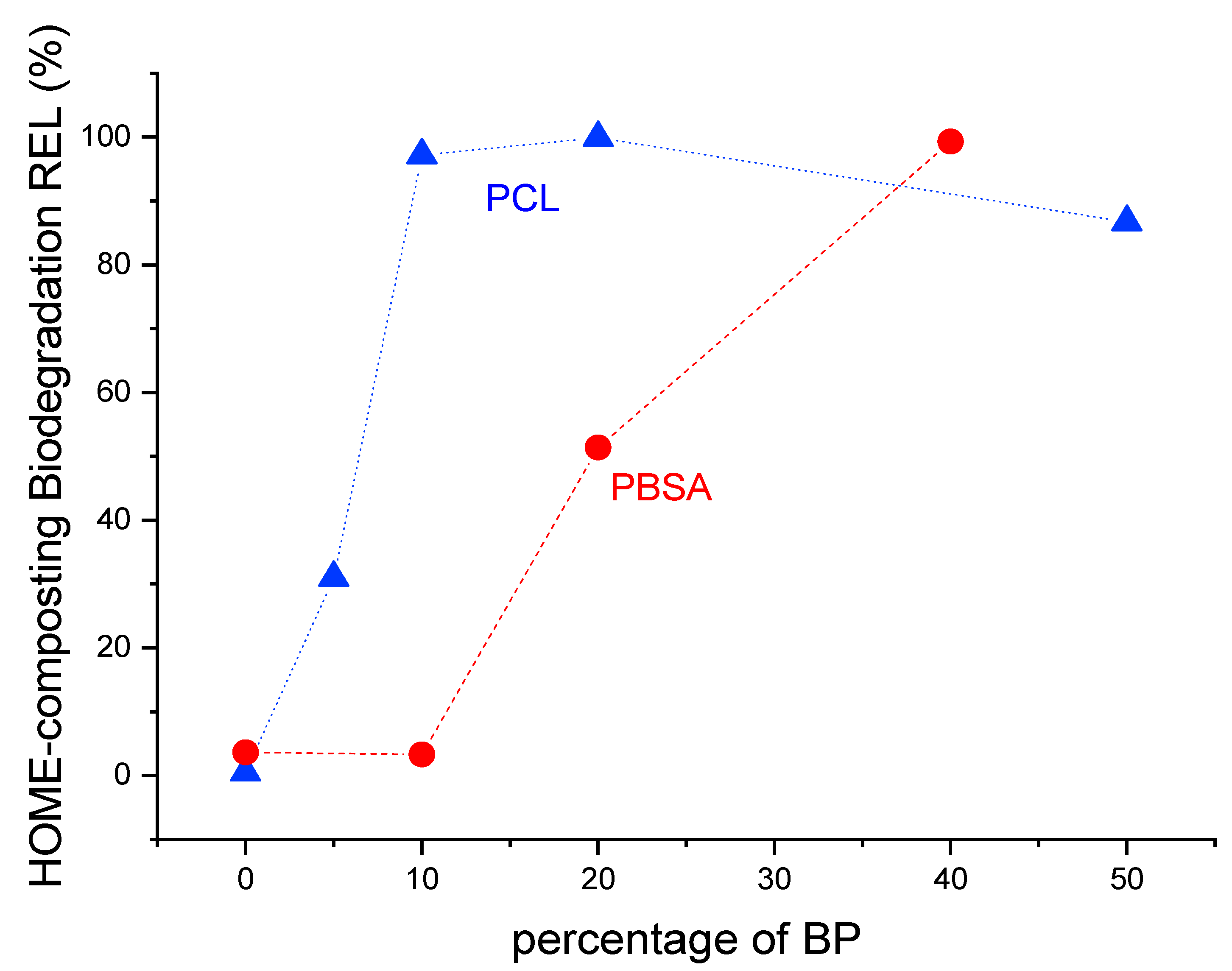
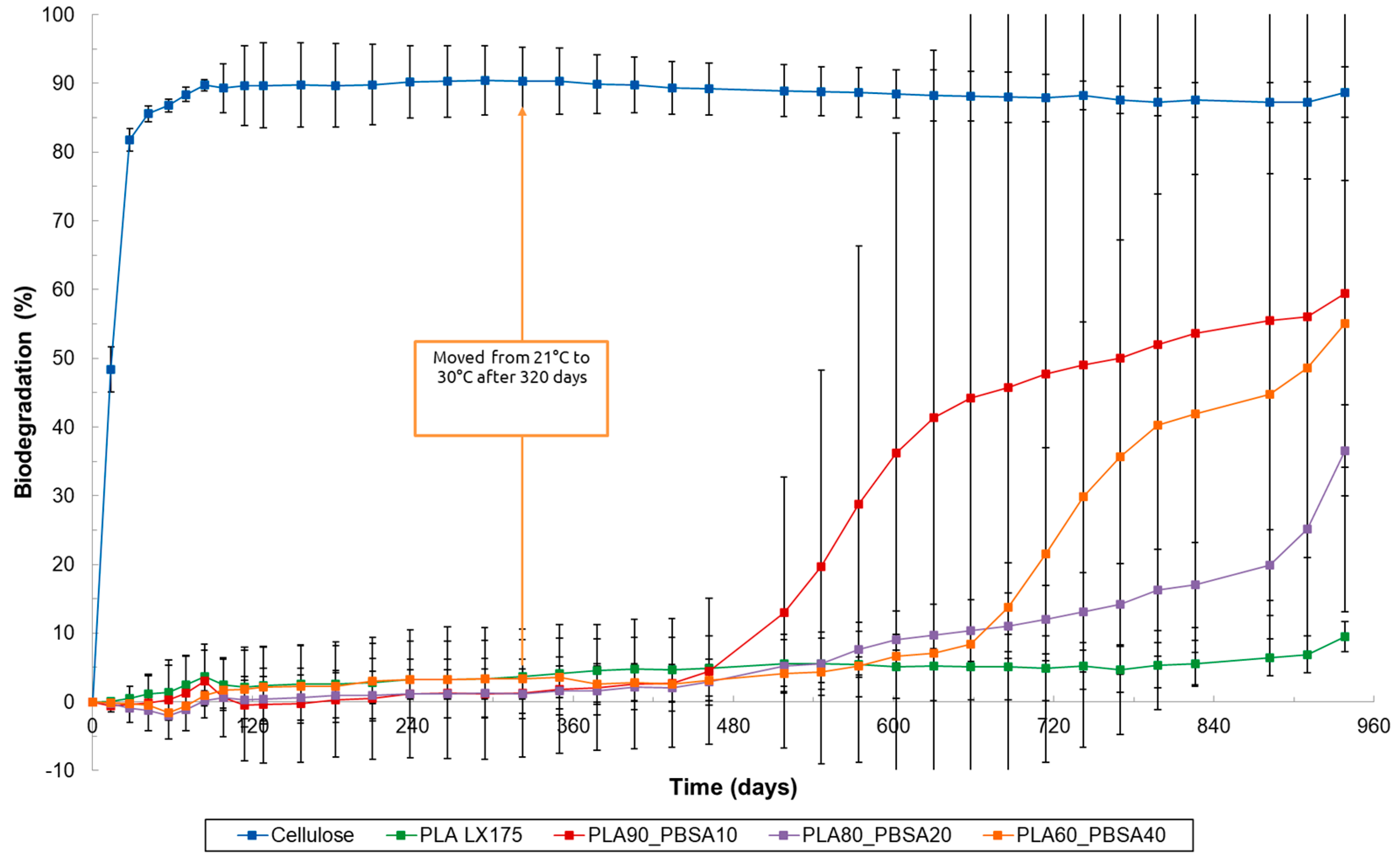
3.1. Results About Home-Composting Biodegradation

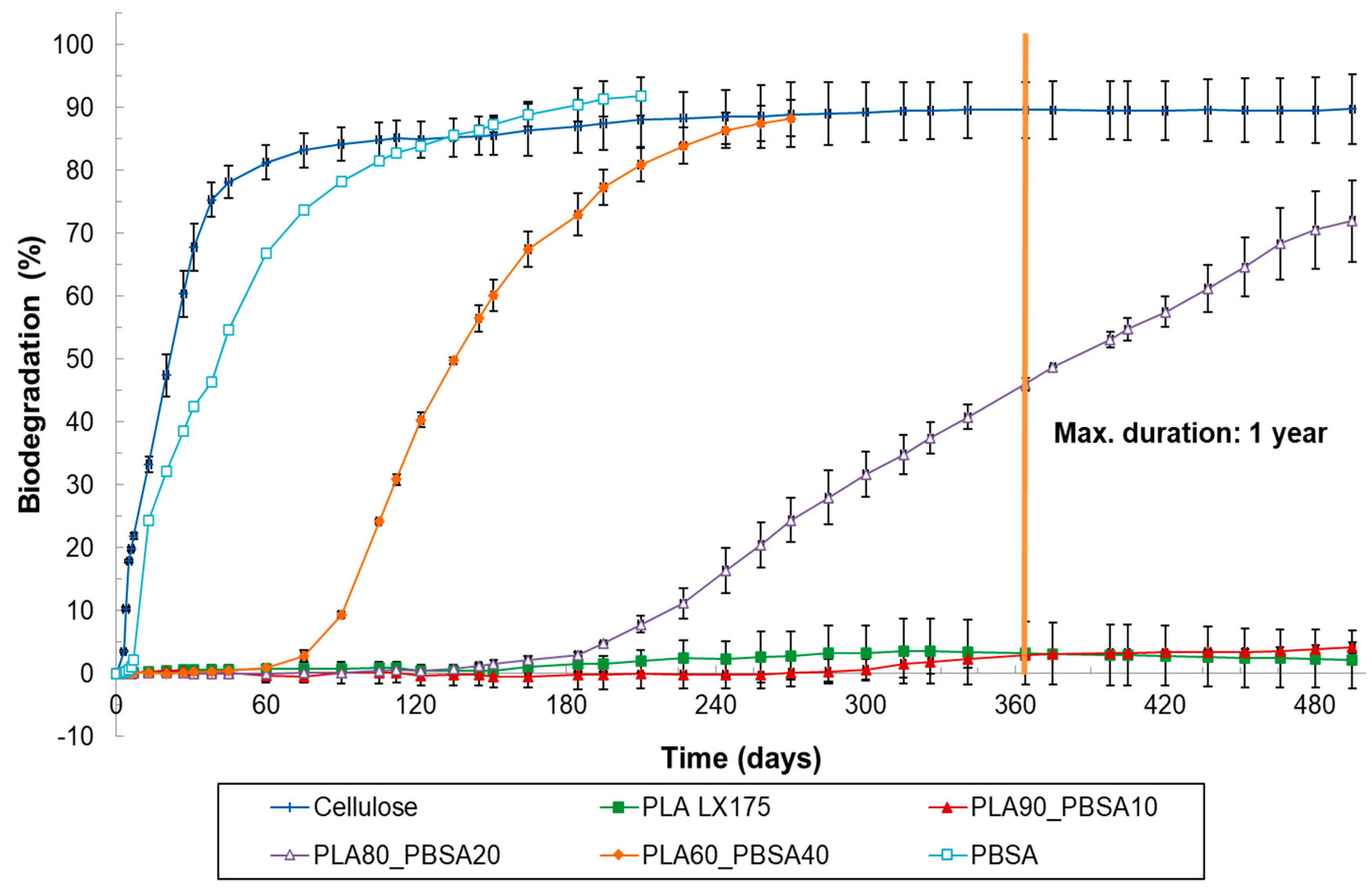
3.2. Results of Soil Biodegradation Test
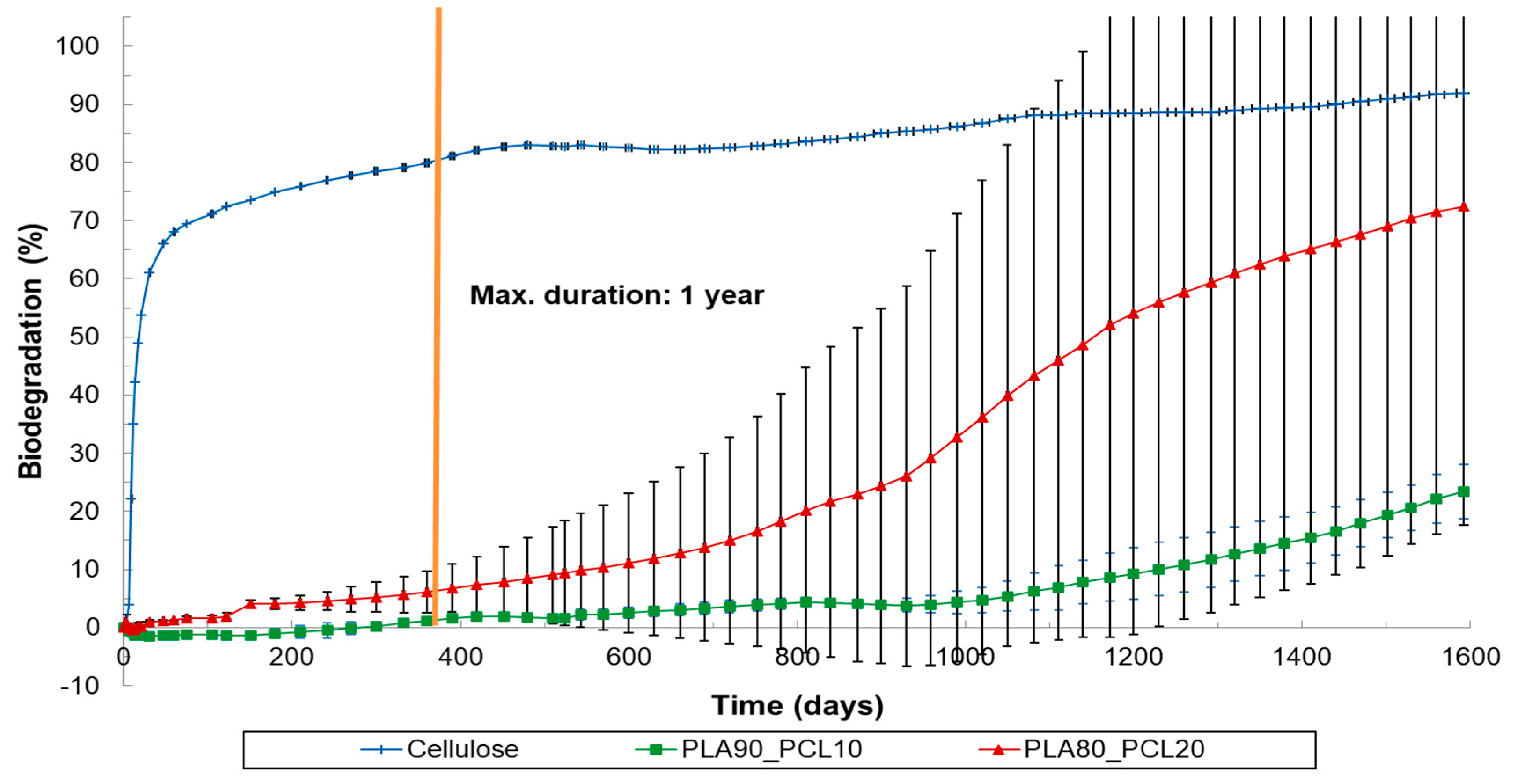


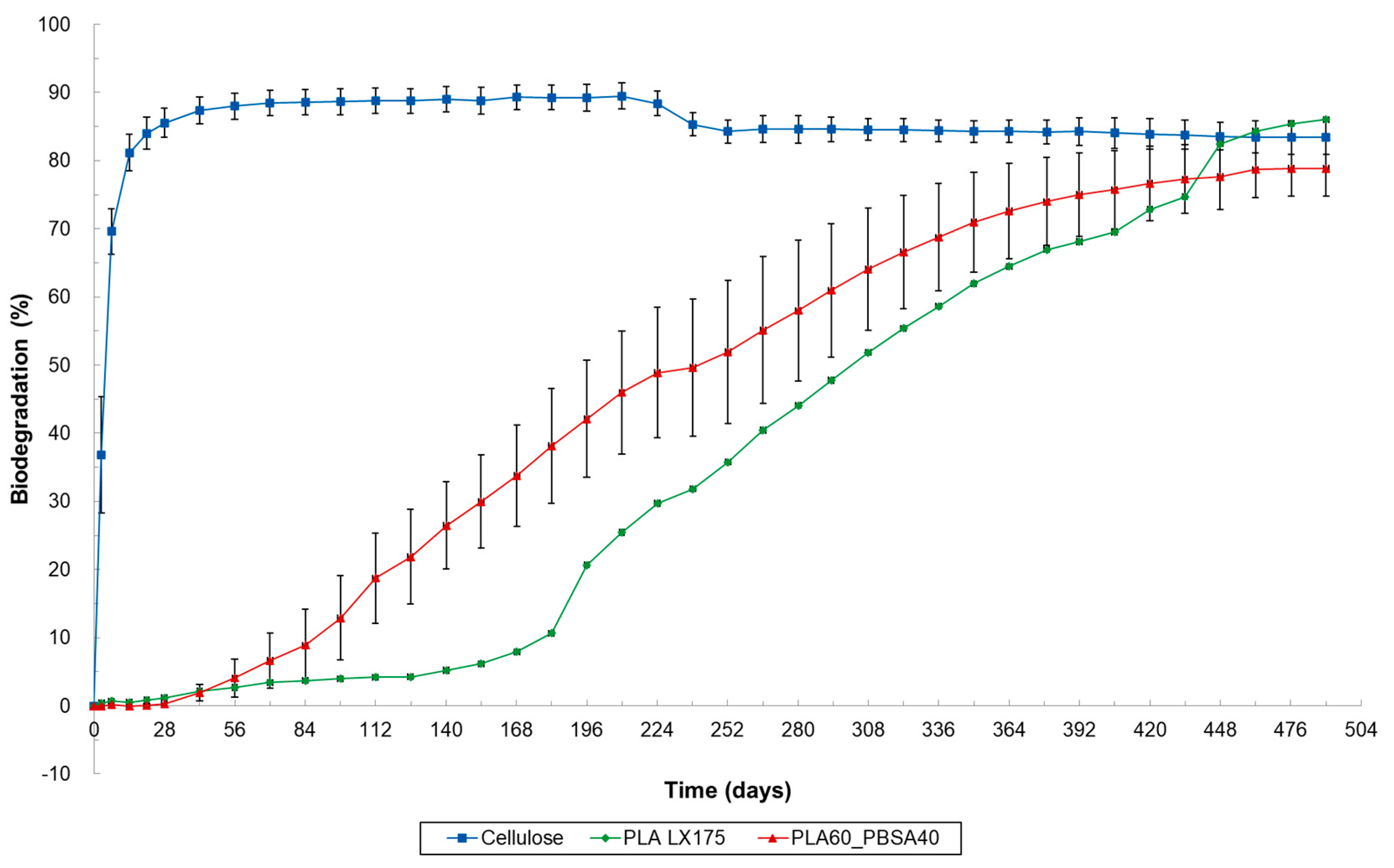
3.3. Results of Marine and Freshwater Biodegradation Tests
3.4. Correlations Between Processing, Phase Morphology and Biodegradation of PLA Blends
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological degradation of plastics: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246–265, ISSN 0734-9750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, R.B. Polymer science before & after 1899: Notable developments during the lifetime of Maurtis Dekker. J. Macromol. Sci. Chem. 1989, 26, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.T.; Rangel-Buitrago, N. The past, present, and future of plastic pollution. Mar. Pollut. 2022, 176, 113429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD. Plastic Leakage and Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Increasing. Available online: https://web-archive.oecd.org/temp/2022-08-18/622468-increased-plastic-leakage-and-greenhouse-gas-emissions.htm (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Rochman, C.; Hoh, E.; Kurobe, T. Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Li, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Z.; Ouyang, Z.; Guo, X. Review of the toxic effect of microplastics on terrestrial and aquatic plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Economic Forum, Ellen MacArthur Foundation and McKinsey & Company. The New Plastics Economy: Rethinking the Future of Plastics 2016. Available online: https://emf.thirdlight.com/file/24/_A-BkCs_skP18I_Am1g_JWxFrX/The%20New%20Plastics%20Economy%3A%20Rethinking%20the%20future%20of%20plastics.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Narancic, T.; Verstichel, S.; Reddy Chaganti, S.; Morales-Gamez, L.; Kenny, S.T.; De Wilde, B.; Babu Padamati, R.; O’Connor, K.E. Biodegradable plastic blends create new possibilities for end-of-life management of plastics but they are not a panacea for plastic pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10441–10452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koitabashi, M.; Noguchi, M.T.; Sameshima-Yamashita, Y.; Syuntaro, H.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshida, S.; Watanabe, T.; Shinozaki, Y.; Tsushima, S.; Kitamoto, H.K. Degradation of biodegradable plastic mulch films in soil environment by phylloplane fungi isolated from gramineous plants. AMB Express 2012, 1, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BioSinn. Products for Which Biodegradation Makes Sense. 2021. Available online: https://renewable-carbon.eu/publications/product/biosinn-products-for-which-biodegradation-makes-sense-pdf (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Teixeira, S.; Eblagon, K.M.; Miranda, F.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Figueiredo, J.L. Towards controlled cegradation of poly(lactic) acid in technical applications. C 2021, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taib, N.A.A.B.; Rahman, M.R.; Huda, D.; Kuok, K.K.; Hamdan, S.; Bakri, M.K.B.; Julaihi, M.R.M.B.; Khan, A. A review on poly lactic acid (PLA) as a biodegradable polymer. Polym. Bull. 2023, 80, 1179–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and 564 their functions in widespread applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, N.R.; Sekhar, V.C.; Nampoothiri, K.M.; Pandey, A. Biodegradation of biopolymers. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Ashok, P., Sangeeta, N., Carlos, R.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 32, pp. 739–755. ISBN 9780444636621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Vannozzi, A.; Canesi, I.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Lazzeri, A. Poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/Poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) compatibilized binary biobased blends: Melt fluidity, morphological, thermo-mechanical and micromechanical analysis. Polymers 2021, 13, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliotta, L.; Gigante, V.; Geerinck, R.; Coltelli, M.; Lazzeri, A. Micromechanical analysis and fracture mechanics of poly (lactic acid) (PLA)/polycaprolactone (PCL) binary blends. Polym. Test. 2023, 121, 107984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, V.; Canesi, I.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.B.; Lazzeri, A. Rubber toughening of polylactic acid (PLA) with poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT): Mechanical properties, fracture mechanics and analysis of ductile-to-brittle behavior while varying temperature and test speed. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 115, 125–137, ISSN 0014-3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.; Franco, L.; Puiggalí, J. Study on the crystallization of poly(butylene azelate-co-butylene succinate) copolymers. Thermochim. Acta 2014, 575, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debuissy, T.; Pollet, E.; Avérous, L. Synthesis and characterization of biobased poly(butylene succinate-ran-butylene adipate). Analysis of the composition-dependent physicochemical properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 87, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E.; Wei, Y.; Jiao, H.; Muhuo, Y. Dynamic mechanical properties and thermal stability of poly(lactic acid) and poly(butylene succinate) blends composites. J. Fiber Bioeng. Inform. 2013, 6, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-itry, R.; Lamnawar, K.; Maazouz, A. Improvement of thermal stability, rheological and mechanical properties of PLA, PBAT and their blends by reactive extrusion with functionalized epoxy. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 1898–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltelli, M.B.; Aliotta, L.; Fasano, G.; Miketa, F.; Brkić, F.; Alonso, R.; Romei, M.; Cinelli, P.; Canesi, I.; Gigante, V.; et al. Recyclability studies on poly(lactic acid)/poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PLA/PBSA) biobased and biodegradable films. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 308, 2300136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomez, M.; George, M.; Fabre, P.; Touchaleaume, F.; Cesar, G.; Lajarrige, A.; Gastaldi, E. A comparative study of degradation mechanisms of PHBV and PBSA under laboratory-scale composting conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 167, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, H.L.; Tsai, Y.T.; Tseng, W.S.; Wu, J.A.; Kuo, S.L.; Chang, S.L.; Huang, S.J.; Liu, C.T. Biodegradation of PBSA films by Elite Aspergillus isolates and farmland soil. Polymers 2022, 14, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strangis, G.; Rossi, D.; Cinelli, P.; Seggiani, M. Seawater biodegradable poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate)-wheat bran biocomposites. Materials 2023, 16, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Matta, A.K.; Rao, R.U.; Suman, K.N.S.; Rambabu, V. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable PLA/PCL polymeric blends. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 6, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hu, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhou, W.; Peng, S. Super tough poly(lactic acid) blends: A comprehensive review. RSC Adv. 2020, 22, 13316–13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.X.; Huang, D.; Ji, J.H.; Völker, C.; Wurm, F.R. Seawater-degradable polymers-fighting the marine plastic pollution. Adv. Sci. 2020, 8, 2001121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Majgaonkar, P.; Hanich, R.; Malz, F.; Brüll, R. Chemical recycling of post-consumer PLA waste for sustainable production of ethyl lactate. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 129952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backes, E.H.; Pires, L.N.; Costa, L.C.; Passador, F.R.; Pessan, L.A. Analysis of the degradation during melt processing of PLA/biosilicate® composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2019, 3, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perstorp, Physical Properties of CapaTM. Thermoplastics Technical Information Leaflet TI 2018, 1658. Available online: https://www.triiso.com/documents/Physical_Properties_of%20Capa_Thermoplastic_Resins.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2024).
- Hallstein, J.; Gomoll, A.; Lieske, A.; Büsse, T.; Balko, J.; Brüll, R.; Malz, F.; Metzsch-Zilligen, E.; Pfaendner, R.; Zehm, D. Unraveling the cause for the unusual processing behavior of commercial partially bio-based poly(butylene succinates) and their stabilization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, e50669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AS 5810; Biodegradable Plastics—Biodegradable Plastics Suitable for Home Composting. Standards Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2010.
- NF T 51-800; Plastics—Specifications for Plastics Suitable for Home Composting. AFNOR: Saint-Denis, France, 2015.
- Lata Verma, S.; Marschner, P. Compost effects on microbial biomass and soil P pools as affected by particle size and soil properties. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 13, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliem, S.; Kreutzbruck, M.; Bonten, C. Review on the biological degradation of polymers in various environments. Materials 2020, 13, 4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabane, A.B.; Robbe, E.; Schernewski, G.; Schubert, H. Decomposition behavior of biodegradable and single-use tableware items in the warnow estuary (Baltic Sea). Sustainability 2022, 14, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordhamo, G.M.; Manson, J.A.; Sperling, L.H. Phase continuity and inversion in polymer blends and simultaneous interpenetrating networks. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1986, 26, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Polymer | Origin | Trade Name | Supplier | Molecular Weight Mn (Da) | D Content (wt.%) | MFR a (2.16 kg) | MFR (190°, 2.16 kg) | MVR (190°, 2.16 kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | Biobased | Luminy LX175 | Total Corbion, Gorinchem, The Netherlands | 84,410 [29] | 4 | 6 at 210 °C 3 at 190 °C | 2.7 ± 0.2 | 2.2 ± 0.2 |
| PLA | Biobased | Ingeo 4043D | NatureWorks, Plymouth, MN, USA | 106,000 [30] | 4, 5-5 | 6 at 210 °C | 1.9 ± 0.9 | 1.6 ± 0.9 |
| PCL | Petro-chemical | Capa 6500 | Ingevity, North Charleston, SC, USA | 49,000 [31] | - | 7 at 160 °C, | 28.0 ± 5.0 | 26.0 ± 4.0 |
| PBSA | Biobased | FD92 PM | PTT MCC Biochem Company, Bangkok, Thailand | 48,000 [32] | - | 4 at 190 °C | 7.1 ± 0.7 | 7.0 ± 0.7 |
| Blend Name | PLA (wt.%) | PCL (wt.%) | PBSA (wt.%) | Biodegradation Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | 100 | 0 | 0 | ISO 14855, ISO 17556, ASTM D6691, ISO 14851 |
| PCL | 0 | 100 | 0 | NA |
| PBSA | 0 | 0 | 100 | NA |
| PLA95_PCL5 | 95 | 5 | 0 | ISO 14855 |
| PLA90_PCL10 | 90 | 10 | 0 | ISO 14855, ISO 17556 |
| PLA80_PCL20 | 80 | 20 | 0 | ISO 14855, ISO 17556 |
| PLA50_PCL50 | 50 | 50 | 0 | ISO 14855 |
| PLA90_PBSA10 | 90 | 0 | 10 | ISO 14855, ISO 14851 |
| PLA80_PBSA20 | 80 | 0 | 20 | ISO 14855, ISO 14851 |
| PLA60_PBSA40 | 60 | 0 | 40 | ISO 14855, ISO 17556, ASTM D6691, ISO 14851 |
| Blend Name | Absolute Biodegradation (%) | Relative Biodegradation (%) | Day > 90% Relative Biodegradation |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLA 4043D | 1.2 | 1.3 | NA |
| PCL * | 90.1 | 104.3 | 117 |
| PLA95_PCL5 | 78.8 | 80.7 | 407 |
| PLA90_PCL10 ** | 97.7 | 100.7 | 180 |
| PLA80_PCL20 ** | 101.5 | 104.5 | 165 |
| PLA50_PCL50 | 90.2 | 92.3 | 300 |
| PLA LX175 | 3.3 | 3.6 | NA |
| PBSA *** | 91.8 | 103.5 | 105 |
| PLA90_PBSA10 | 2.9 | 3.3 | NA |
| PLA80_PBSA20 | 46.0 | 51.4 | 720 |
| PLA60_PBSA40 | 88.3 | 99.3 | 210 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van de Perre, D.; Serbruyns, L.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Gigante, V.; Aliotta, L.; Lazzeri, A.; Geerinck, R.; Verstichel, S. Tuning Biodegradation of Poly (lactic acid) (PLA) at Mild Temperature by Blending with Poly (butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) or Polycaprolactone (PCL). Materials 2024, 17, 5436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17225436
Van de Perre D, Serbruyns L, Coltelli M-B, Gigante V, Aliotta L, Lazzeri A, Geerinck R, Verstichel S. Tuning Biodegradation of Poly (lactic acid) (PLA) at Mild Temperature by Blending with Poly (butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) or Polycaprolactone (PCL). Materials. 2024; 17(22):5436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17225436
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan de Perre, Dimitri, Lynn Serbruyns, Maria-Beatrice Coltelli, Vito Gigante, Laura Aliotta, Andrea Lazzeri, Ruben Geerinck, and Steven Verstichel. 2024. "Tuning Biodegradation of Poly (lactic acid) (PLA) at Mild Temperature by Blending with Poly (butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) or Polycaprolactone (PCL)" Materials 17, no. 22: 5436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17225436
APA StyleVan de Perre, D., Serbruyns, L., Coltelli, M.-B., Gigante, V., Aliotta, L., Lazzeri, A., Geerinck, R., & Verstichel, S. (2024). Tuning Biodegradation of Poly (lactic acid) (PLA) at Mild Temperature by Blending with Poly (butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PBSA) or Polycaprolactone (PCL). Materials, 17(22), 5436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17225436










