Microwave Absorption and Magnetic Properties of M-Type Hexagonal Ferrite Ba0.95Ca0.05Fe12−xCoxO19 (0 ≤ X ≤ 0.4) at 1–18 GHz
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Component
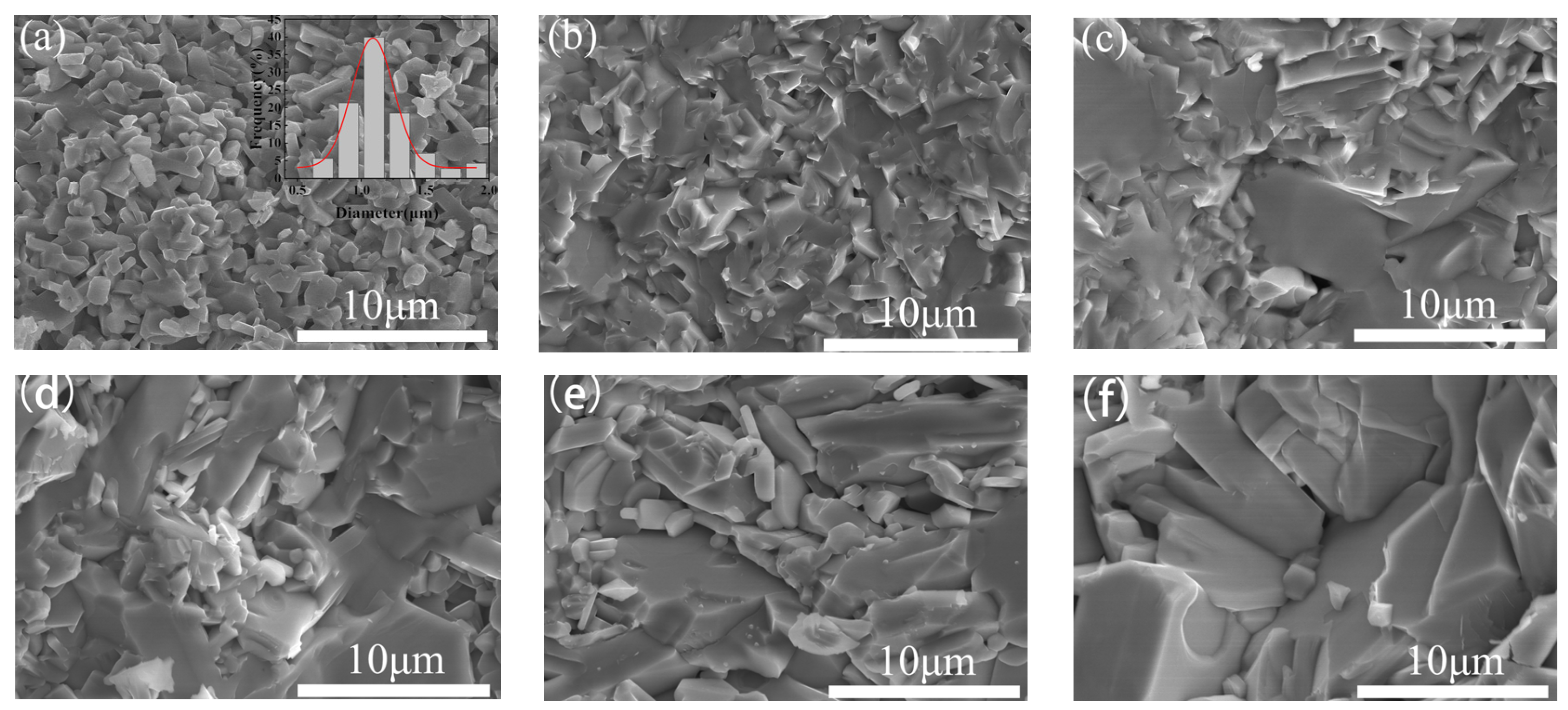
3.2. Micromorphology
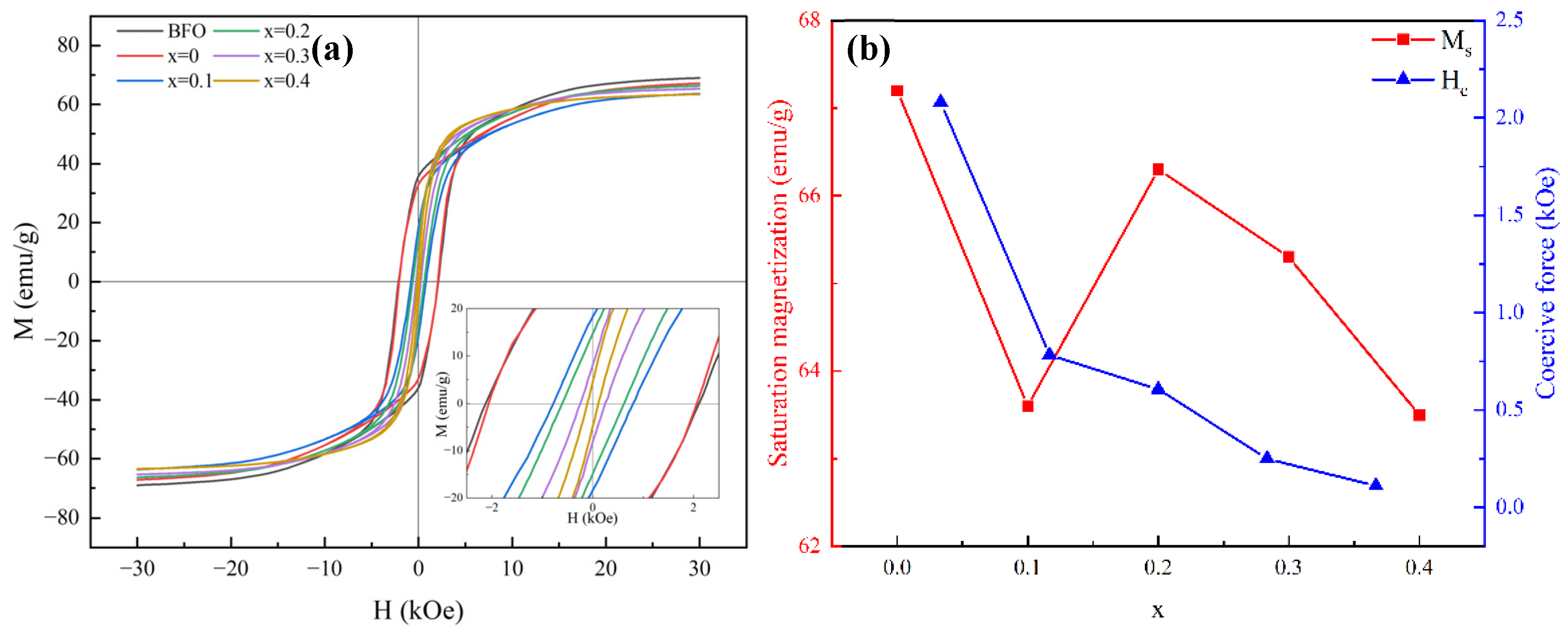
3.3. Static Magnetic Properties
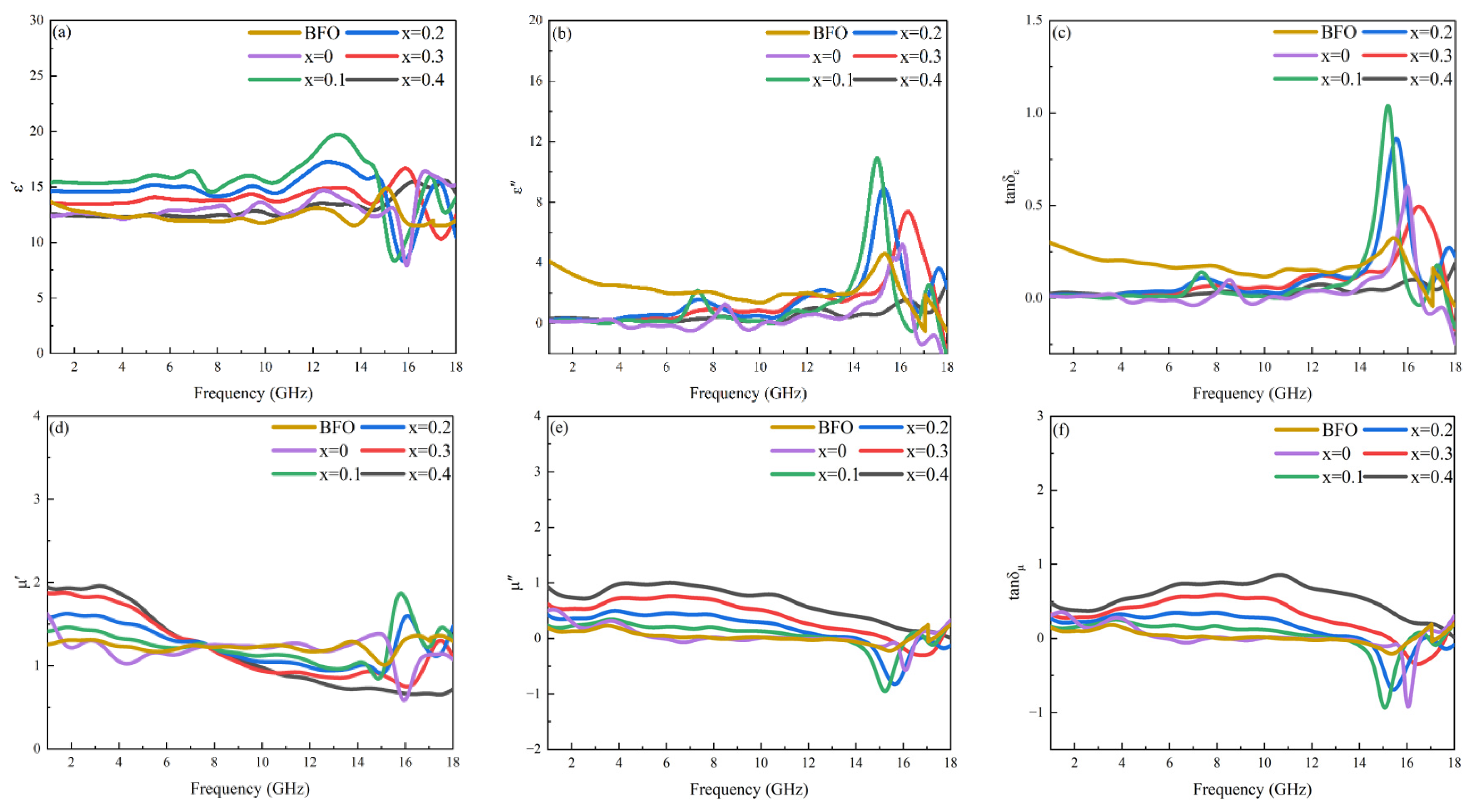
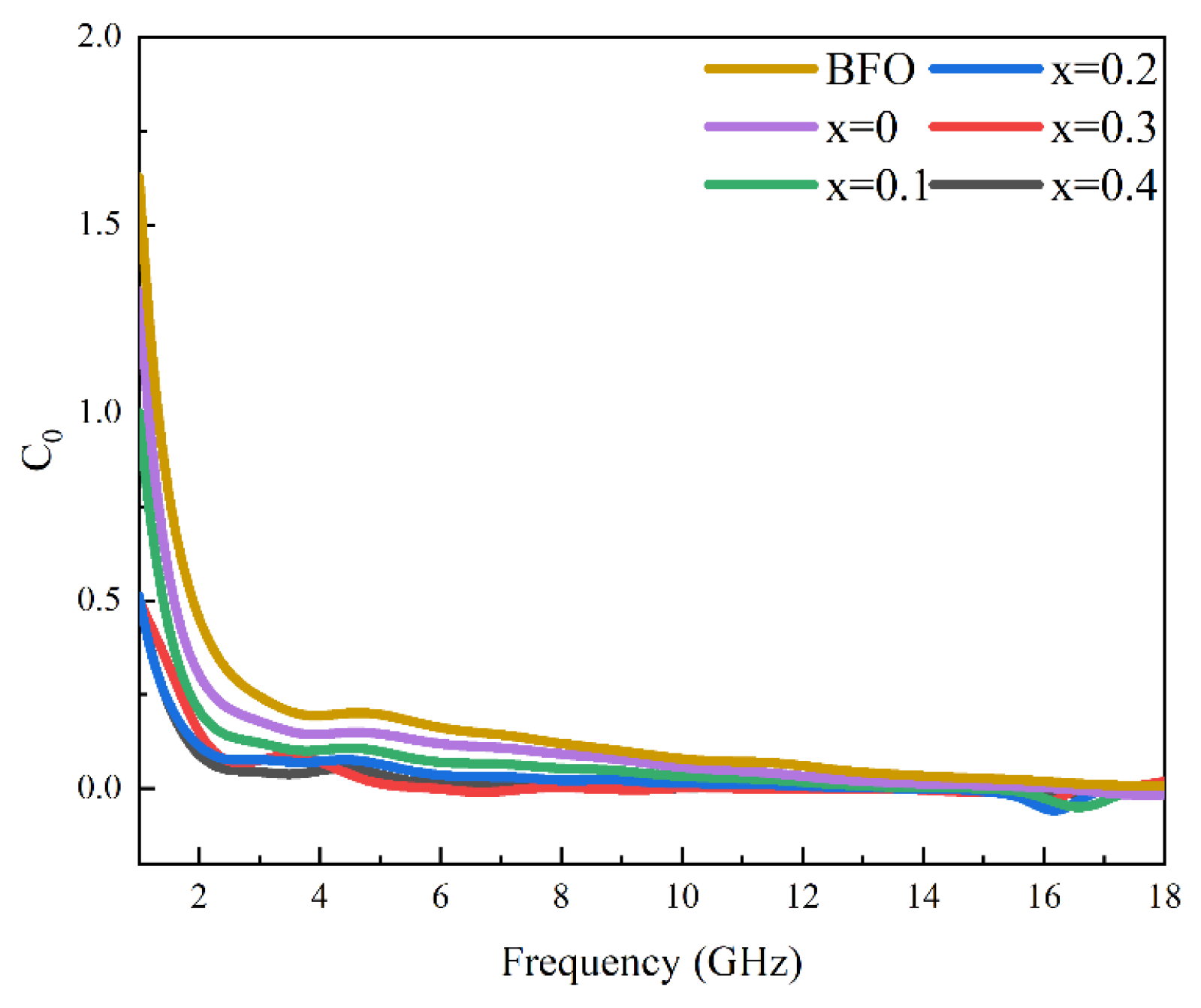
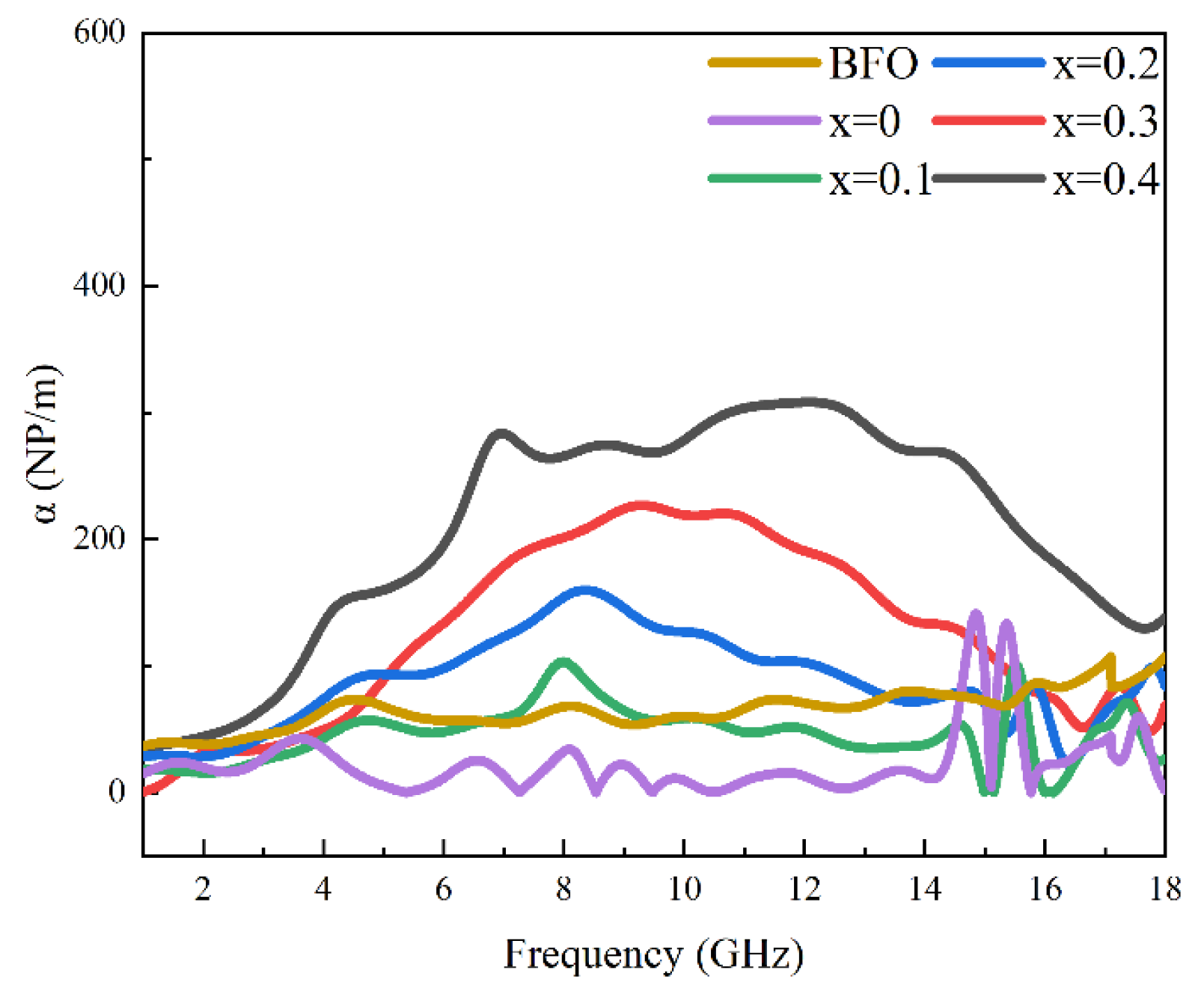
3.4. Microwave Magneto-Dielectric Properties
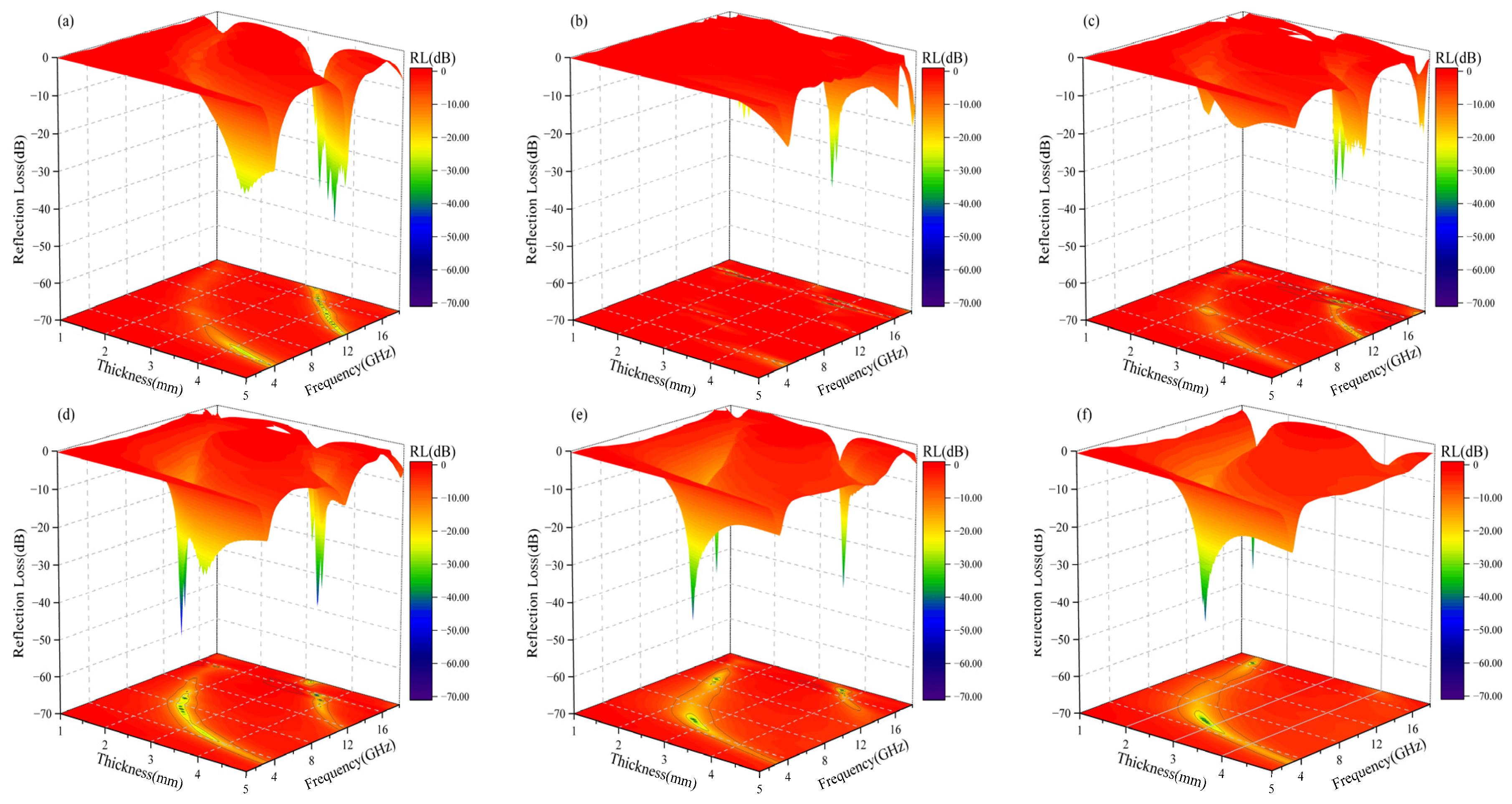
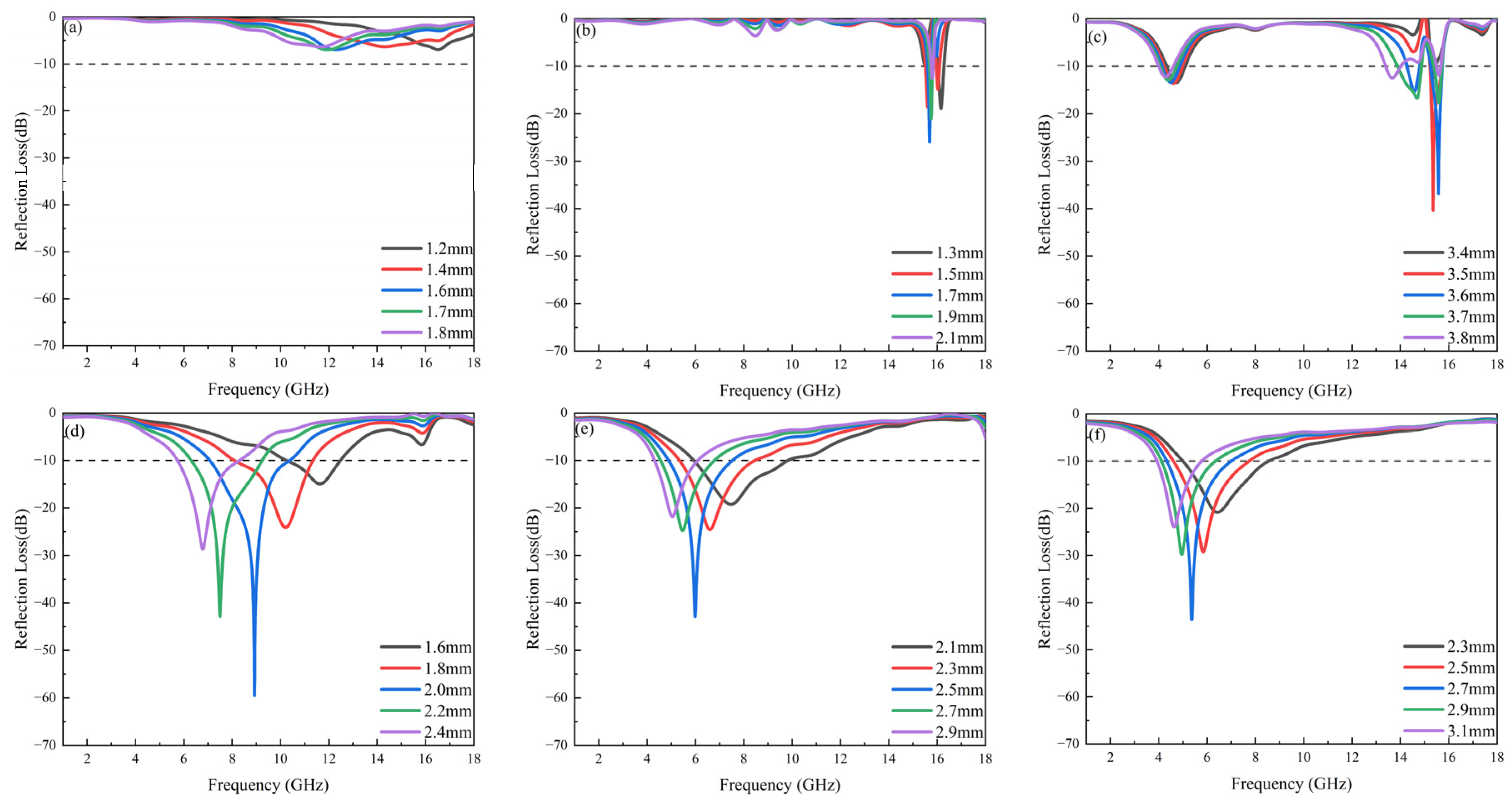
3.5. Microwave-Absorption Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, M.; Qin, R.; Qiu, C.; Zhu, J. Matching design and mismatching analysis towards radar absorbing coatings based on conducting plate. Mater. Des. 2003, 24, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, H.-J.; Yang, W.-G.; Hou, Z.-L.; Jin, J.-B.; Yuan, J.; Cao, M.-S. Structure, ferromagnetism and microwave absorption properties of La substituted BiFeO3 nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2013, 111, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasrotia, R.; Prakash, J.; Himanshi; Thakur, N.; Raj, K.; Kandwal, A.; Sharma, P. Advancements in doping strategies for enhancing applications of M-type hexaferrites: A comprehensive review. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2023, 72, 100427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, M.; Liu, F.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, H.; Jin, H.; Cao, M. Sol–gel synthesis of Nd-doped BiFeO3 multiferroic and its characterization. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 8768–8772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, F.; Huma, F.; Ali, K. Hydrothermal synthesisi and microwave absorption properties of reduced graphene oxide/BaCo0,2 Ti0.2Fe1.6O19 nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 559, 169534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Hong, R. Microstructure and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4/dextran/SnO2 multilayer microspheres. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3241–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q. Simple and reproducible preparation of barium hexagonal ferrite by adsorbent combustion method. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 540, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, T.; Tong, H.; Luo, W.; Yan, M. Electromagnetic wave absorption properties of flaky Fe-Ti-Si-Al nanocrystalline composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2010, 322, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.; Narang, S.B.; Hudiara, I.; Sudheendran, K.; Raju, K.J. Complex permittivity and complex permeability of Sr ions substituted Ba ferrite at X-band. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 1657–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Li, J.; Che, S.; Zheng, J.; Qiao, L.; Ying, Y.; Yu, J.; Li, W. L and S band microwave absorption properties of Z-type hexaferrite Ba3Co2Fe24O41 synthesized at low temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 171926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Dai, J.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, P. Synthesis and enhanced microwave absorption properties of PVB/Co2Z/RGO layered composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 714, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Feng, Y.; Xiong, J.; Yang, Y.; Lu, H. Microwave-absorbing properties of de-aggregated flake-shaped carbonyl-iron particle composites at 2–18 GHz. IEEE Trans. 2006, 42, 1778–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.-Y.; Shen, X.-Q.; Song, F.-Z. Double-layer microwave absorber of nanocrystalline strontium ferrite and iron microfibers. Chin. Phys. B 2012, 21, 028101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praveena, K.; Sadhana, K.; Liu, H.-L.; Bououdina, M. Microwave absorption studies of magnetic sublattices in microwave sintered Cr3+ doped SrFe12O19. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 426, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Bala, M.; Garg, A.; Shivling, V.; Tyagi, S. Lanthanum doped barium hexaferrite nanoparticles for enhanced microwave absorption. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, F.; Poorbafrani, A.; Kameli, P.; Salamati, H. Structural, magnetic and microwave properties of Eu-doped barium hexaferrite powders. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2012, 25, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Li, J.; He, S.; Bai, H.; Hong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Z. A superior microwave absorption material: Ni2+-Zr4+ Co-Doped barium ferrite ceramics with large reflection loss and broad bandwidth. Cur. Appl. Phys. 2019, 19, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Zhou, W.; Deng, H.; Chen, D.; Qing, Y.; Wang, C.; Luo, F.; Zhou, Y. Co substituted BaFe12O19 ceramics with enhanced magnetic resonance behavior and microwave absorption properties in 2.6–18 GHz. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 13859–13864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Supriya, S.; Pandey, R.; Pradhan, L.; Singh, R.; Kar, M. Effect of lattice strain on structural and magnetic properties of Ca substituted barium hexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 458, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lin, Y.; Yang, H.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, S. A novel plate-like BaFe12O19@MoS2 core-shell structure composite with excellent microwave absorbing properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 817, 153265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahwa, C.; Narang, S.; Sharma, P. Composition dependent magnetic and microwave properties of exchange-coupled hard/soft nanocomposite ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 815, 152391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Song, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Jing, M.; Wang, Y. Hexaferrite/a-iron composite nanowires: Microstructure, exchange-coupling interaction and microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 621, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Yin, Q. Computational and experimental study on cation distribution of cobalt substituted barium hexaferrites BaFe12-xCoxO19 (x = 0, 0.3, 0.6, 0.9) for circulator applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 891, 161917. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, F.; Shao, J.; Huang, D.; Trukhanov, A.; Trukhanov, S. Preparation of Al3+-Co2+ co-substituted M-type SrCaNd hexaferrites and their controlled magnetic properties. AIP Adv. 2018, 8, 075212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.; Choi, Y.; Phan, T.; Yang, D.; Lee, B. Electronic structure and magnetic and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of BaFe12-xCoxO19 M-type hexaferrites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2019, 19, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, N.; Du, P. The tunable magnetic and microwave absorption properties of the Nb5+–Ni2+ co-doped M-type barium ferrite. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 3461–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamishima, K.; Hosaka, N.; Kakizaki, K.; Hiratsuka, N. Crystallographic and magnetic properties of Cu2X, Co2X, and Ni2X hexaferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 013904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotopoulos, I. A simple approach to the First Order Reversal Curves (FORC) of two-phase magnetic systems. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 2148–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarou, N.; Slimani, Y.; Almessiere, M.; Alahmari, F.; Vakhitov, M.; Klygach, D.; Trukhanov, S.; Trukhanov, A.; Baykal, A. Magnetic and microwave properties of SrFe12O19/MCe0.04Fe1.96O4 (M = Cu, Ni, Mn, Co and Zn) hard/soft nanocomposites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 5858–5870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hao, Y.; Zheng, S.; Fang, G.; Li, J.; Tao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Du, P. Abating dopant competition between dual high-valence ions in single-phased barium ferrite towards ultra-broad microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2023, 11, 15500–15511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batoo, K.; Kumar, S.; Lee, C.; Alimuddin. Finite size effect and influence of temperature on electrical properties of nanocrystalline Ni–Cd ferrites. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2009, 9, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, A.; Vest, R.; Vest, G. Dielectric properties of ultra fine grained BaTiO3. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Applications of Ferroelectrics, Bethlehem, PA, USA, 8–11 June 1986; pp. 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Kong, L.; Fang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Jin, H.; Cao, M. Microwave permittivity and permeability experiments in high-loss dielectrics: Caution with implicit Fabry-Pérot resonance for negative imaginary permeability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 162905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J. Core–shell CoNi@graphitic varbon decorated on B,N-codoped hollow carbon polyhedrons toward lightweight and high-efficiency microwave attenuation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25624–25635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L. Research on Microwave Absorbing Properties of Doped Co2Z Type Hexagonal Ferrite and Its Composites. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, C. Hexagonal ferrites: A review of the synthesis, properties and applications of hexaferrite ceramics. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 1191–1334. [Google Scholar]
- Goel, S.; Garg, A.; Baskey, H.; Pandey, M.; Tyagi, S. Studies on dielectric and magnetic properties of barium hexaferrite and bio-waste derived activated carbon composites for X-band microwave absorption. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 875, 160028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xie, Z.; Liu, Z.; Tao, C.; Deng, R. Magnetic and microwave absorbing properties of low-temperature sintered BaZrxFe12−xO19. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 42009–42016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narang, S.B.; Kaur, P.; Bahel, S.; Singh, C. Microwave characterization of Co-Ti substituted barium hexagonal ferrites in X-band. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2016, 405, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

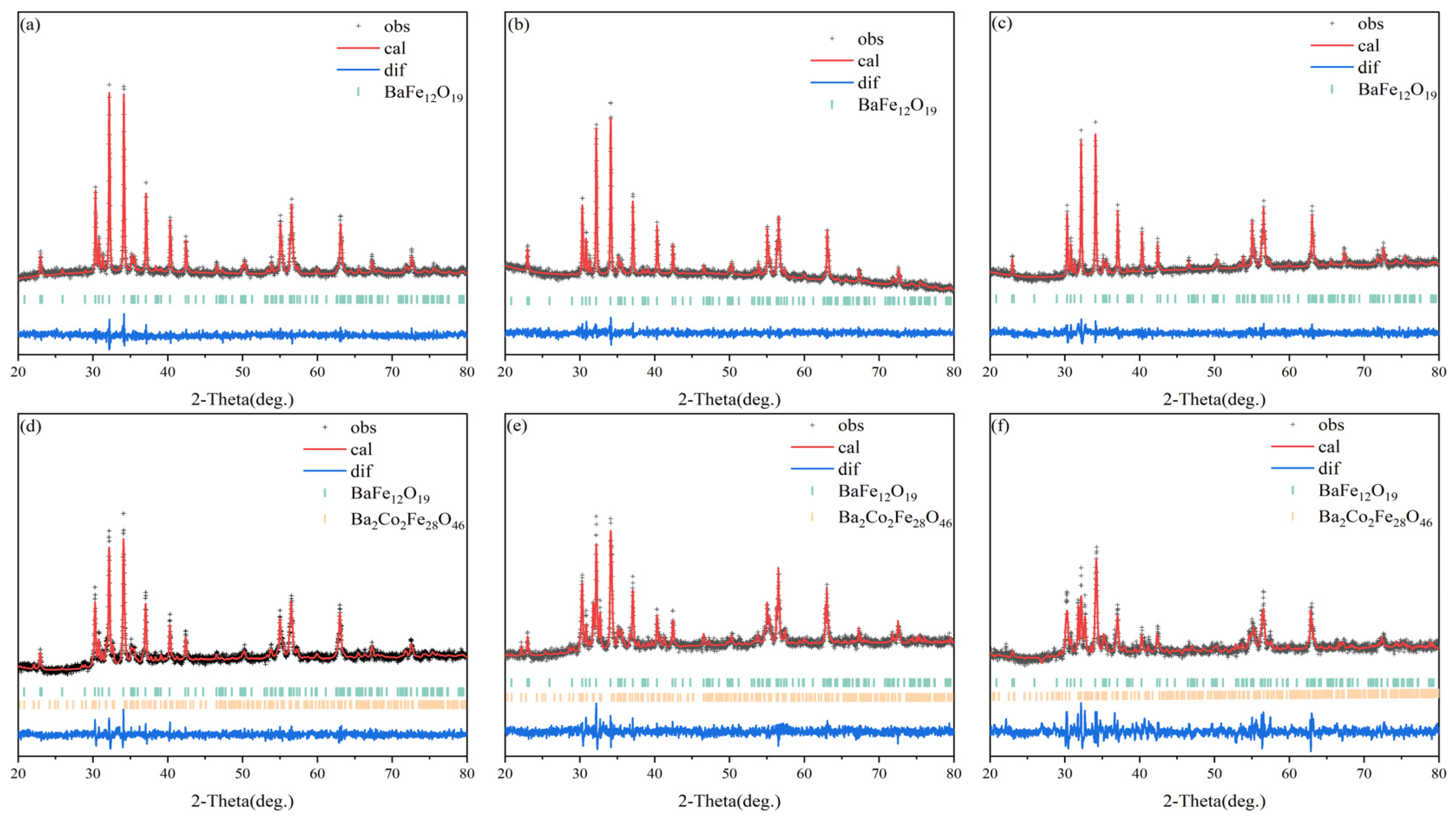
| Samples | BaM-Phase (%) | Co2X-Phase (%) | Rwp (%) | GOF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaFe12O19 | 100 | 0 | 2.48 | 1.16 |
| x = 0 | 100 | 0 | 2.48 | 1.08 |
| x = 0.1 | 100 | 0 | 2.41 | 1.10 |
| x = 0.2 | 93.3 | 6.7 | 2.34 | 1.14 |
| x = 0.3 | 67.2 | 22.8 | 2.44 | 1.19 |
| x = 0.4 | 43.7 | 56.3 | 3.44 | 1.64 |
| Samples | Thickness (mm) | RLmin (dB) | Bandwidth (GHz) | Absorption Range (GHz) | Frequency (GHz) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaZr1.2Fe10.8O19 | 5 | −30.2 | 2.46 | - | 16.75 | [38] |
| BaFe10.6Co0.7Ti0.7O19 | 3.3 | −25.15 | 0.94 | - | 9.54 | [39] |
| BaFe11.94La0.06O19 | 2.75 | −14.93 | - | - | - | [15] |
| x = 0.2 | 2.0 | −59.5 | 3.31 | 7.07–10.38 | 8.9 | This work |
| x = 0.3 | 2.5 | −42.9 | 2.63 | 4.9–7.53 | 5.98 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Yao, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H. Microwave Absorption and Magnetic Properties of M-Type Hexagonal Ferrite Ba0.95Ca0.05Fe12−xCoxO19 (0 ≤ X ≤ 0.4) at 1–18 GHz. Materials 2024, 17, 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215327
Li J, Yao H, Huang Y, Wang H. Microwave Absorption and Magnetic Properties of M-Type Hexagonal Ferrite Ba0.95Ca0.05Fe12−xCoxO19 (0 ≤ X ≤ 0.4) at 1–18 GHz. Materials. 2024; 17(21):5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215327
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Juan, Hao Yao, Yuting Huang, and Hongxia Wang. 2024. "Microwave Absorption and Magnetic Properties of M-Type Hexagonal Ferrite Ba0.95Ca0.05Fe12−xCoxO19 (0 ≤ X ≤ 0.4) at 1–18 GHz" Materials 17, no. 21: 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215327
APA StyleLi, J., Yao, H., Huang, Y., & Wang, H. (2024). Microwave Absorption and Magnetic Properties of M-Type Hexagonal Ferrite Ba0.95Ca0.05Fe12−xCoxO19 (0 ≤ X ≤ 0.4) at 1–18 GHz. Materials, 17(21), 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215327






