Adsorption Performance for Chromium(VI) of a UiO-66-Ce Metal–Organic Framework Built by DL-Aspartic Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Determinations
2.3. Preparation of MOF Ce-Asp
2.4. Stability Measurements
2.5. Cr(IV) Adsorption Determinations
2.6. Adsorption Kinetics Exploration
2.7. Adsorption Isotherm Exploration
3. Results
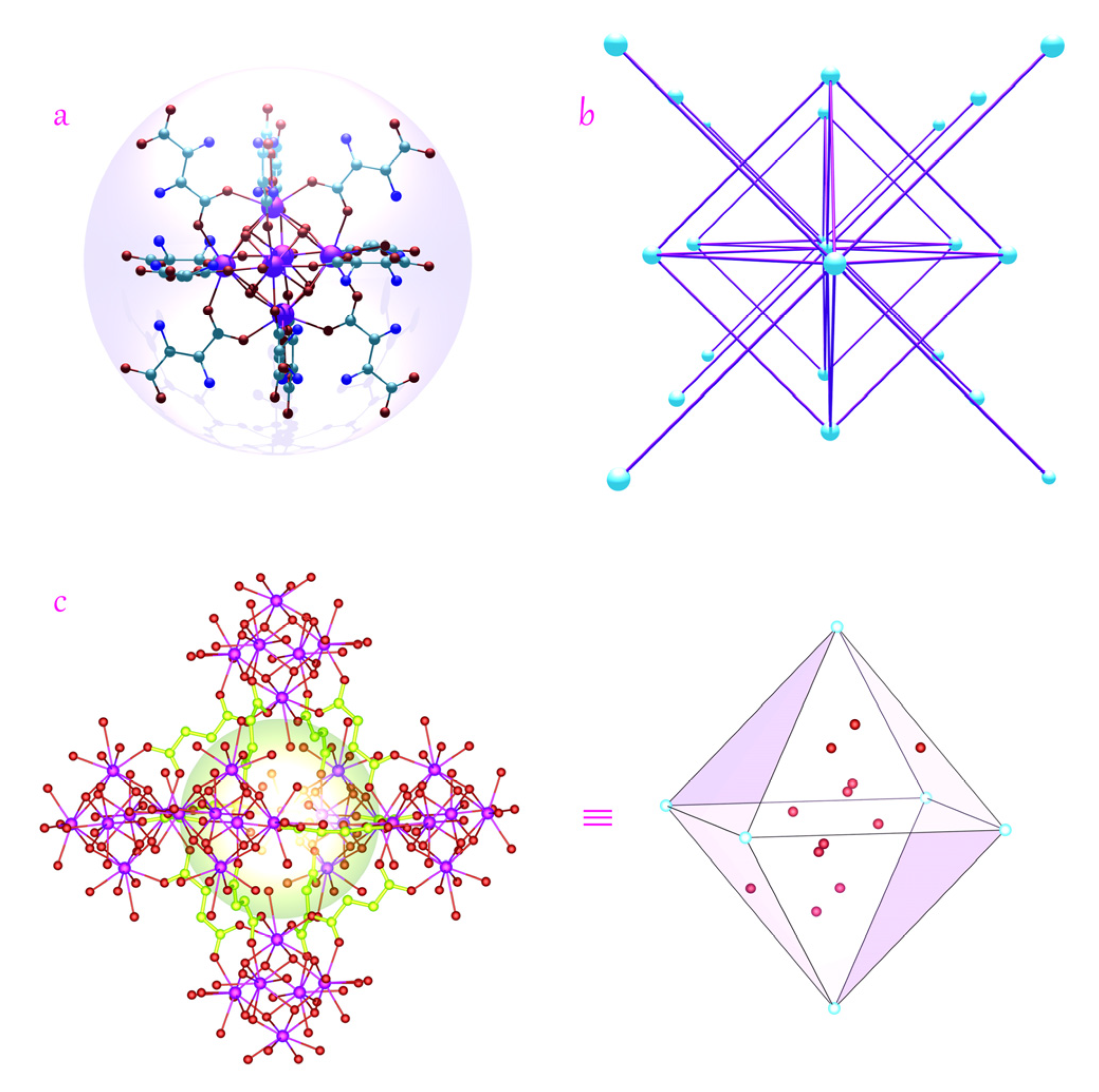
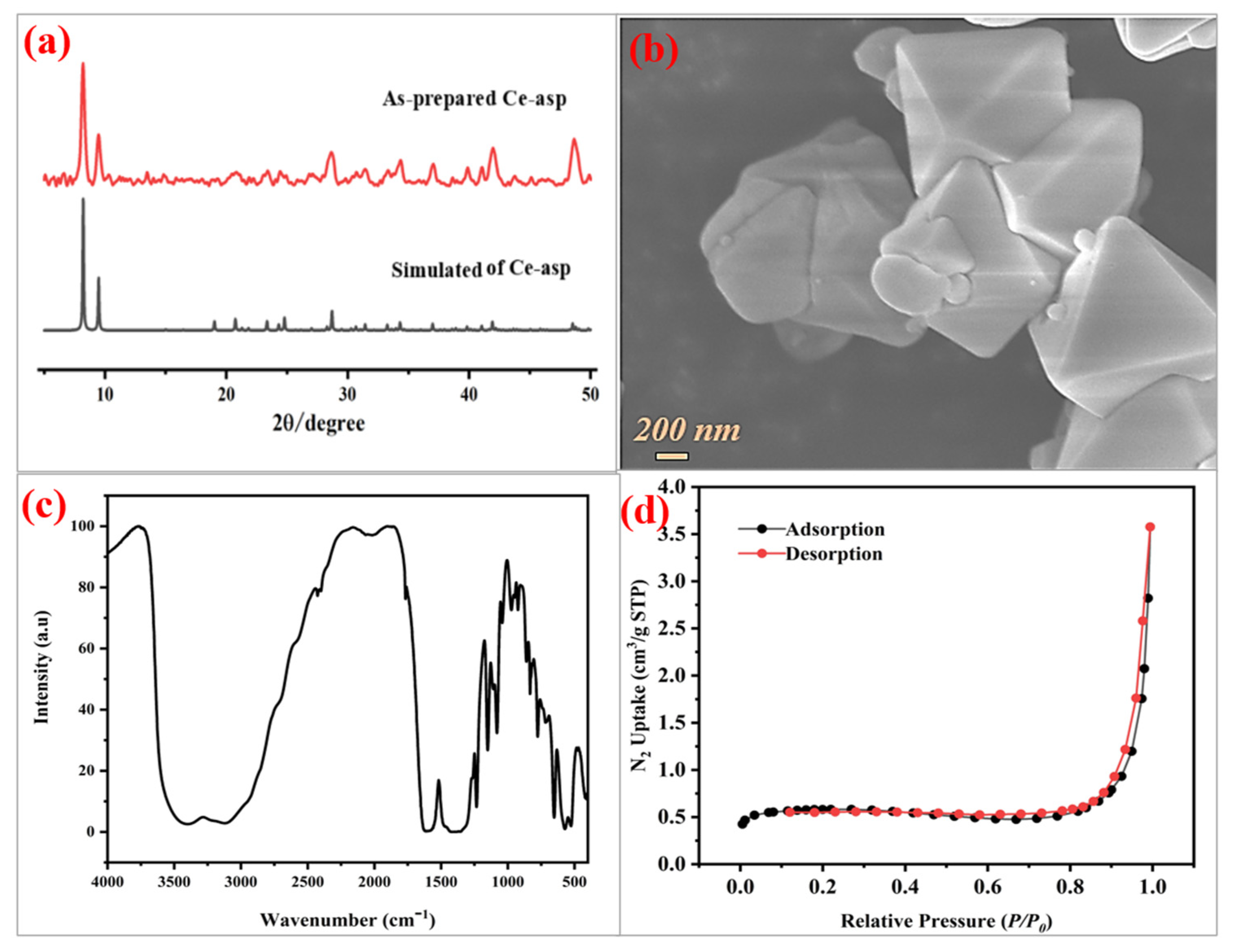
3.1. Characterizations and Structural Features of Ce-Asp
3.2. Structural Stability of Ce-Asp
3.2.1. Thermal Stability
3.2.2. Water and Acid–Base Stability
3.3. Cr(IV) Adsorption Properties of Ce-Asp
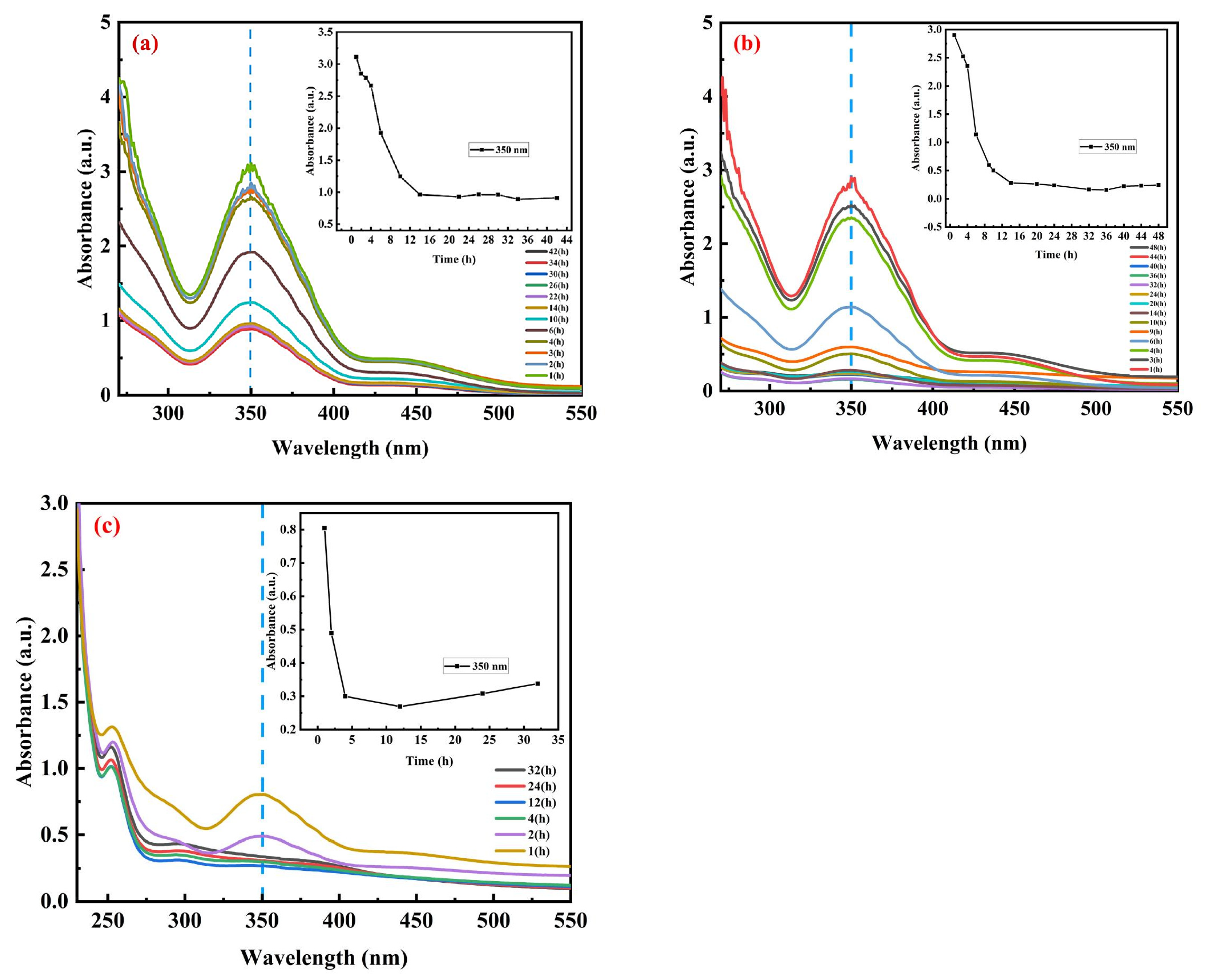
3.3.1. Effect of pH on Adsorption Properties of Ce-Asp
3.3.2. Effect of Time on Adsorption Properties of Ce-Asp
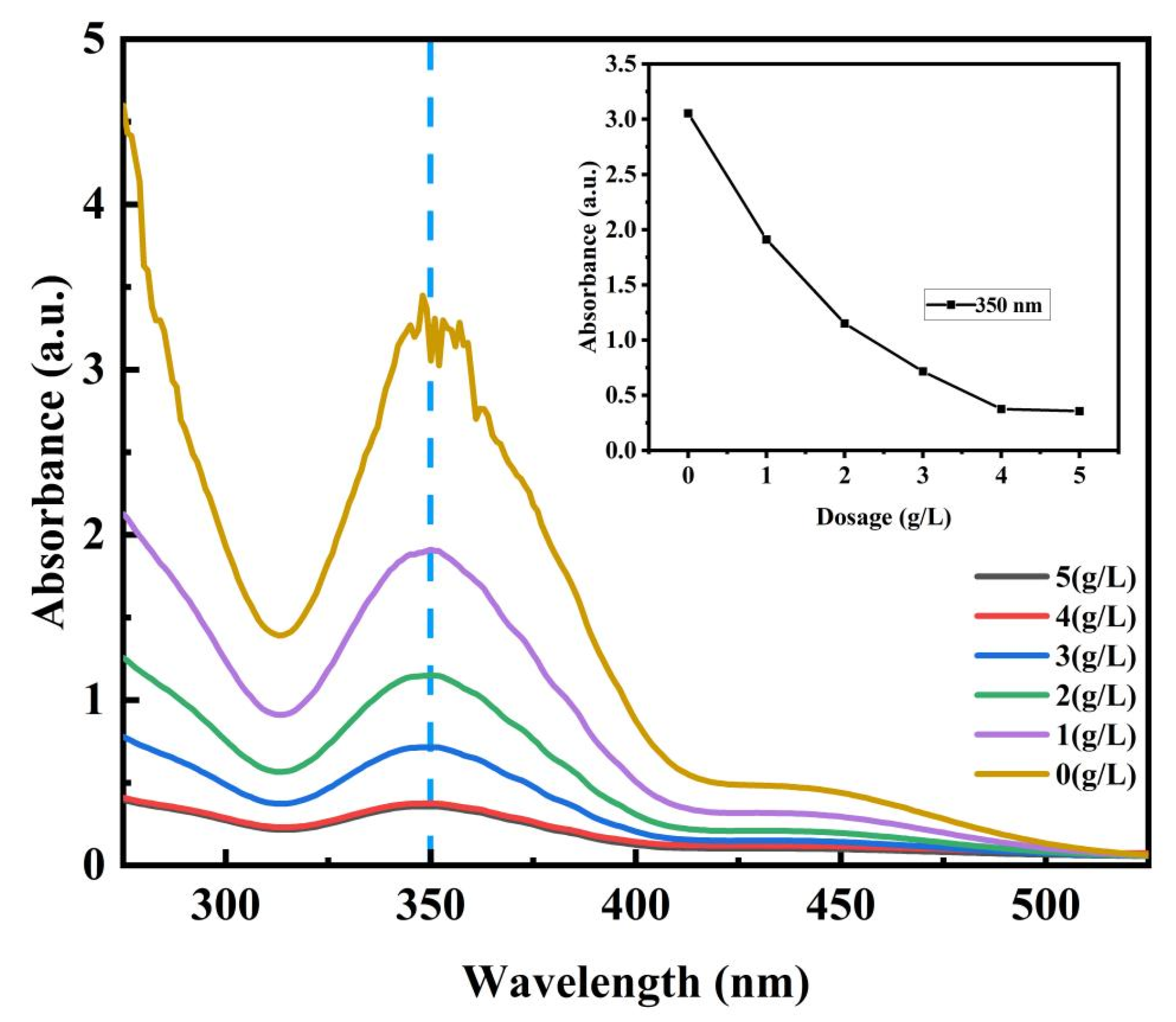
3.3.3. Effect of Initial Dosage of the MOF on Adsorption Properties
3.3.4. Effect of Initial Solution Concentration on Adsorption Properties of the MOF
3.3.5. Study on Adsorption Mechanism of MOF
- Adsorption kinetics exploration
- 2.
- Adsorption isotherm exploration
3.3.6. Reuse Experiment of MOF
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cong, Y.; Shen, L.; Wang, B.; Cao, J.; Pan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, Q.; Li, X. Efficient removal of Cr(VI) at alkaline phs by sulfite/iodide/UV: Mechanism and modeling. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Fu, F.; Zhang, L.; Tang, B. Insight into efficient co-removal of Se(IV) and Cr(VI) by magnetic mesoporous carbon microspheres: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, S.; Leong, K.; Lim, P. Removal and transformation of hexavalent chromium in sequencing batch reactor. Water SA 2012, 38, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gou, Z.; Lu, J.; Zang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zou, X.; Cui, J. Efficient removal of Cr(VI) from contaminated kaolin and anolyte by electrokinetic remediation with foamed iron anode electrode and acetic acid electrolyte. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathi, S.; Amanullah, M.; Al-Samghan, A.S.; Joseph, J.J.; Pazhanisamy, P.; Addich, M.; Gomathi, T. Sustainable heavy metal (cr(vi) ion) remediation: Ternary blend approach with chitosan, carboxymethyl cellulose, and bioactive glass. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, K.; Zhao, L.; Peng, H.; Gong, Y. Edac-modified chitosan/imidazolium-polysulfone composite beads for removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 278, 134867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tianyu, L.; Feng, Z.; Weiqi, H.; Han, P.; Hongyan, L.; Jiali, C. Investigating simultaneous removal of rhodamine B and Cr(VI) via electrolysis-coordinated cr(vi)-activated sulfites under neutral condition. J. Water Process. Eng. 2024, 66, 105950. [Google Scholar]
- Metwaly, T.S.; Ali, S.I.; Moustafa, M.H.; Shata, H.M.; El-Mosalamy, S.E.; El-Sayed, G.O.; Aboubaraka, A.E.; Abdel-Fatah, A.S.; El-Shorbagy, H.G. Utilization of thermally treated sludge for the removal of hexavalent chromium from drainage wastewater: A laboratory and field study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dang, Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, L. Distinguished adsorption behaviors and micro-mechanisms of Cr(VI) onto mesoporous polydopamine with different pore architectures: Classical theory and electron-scale perspectives. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Sharma, U.; Samanta, S.K. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of heavy metal remediation by modified bentonite. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, C.; Peng, W.; Huang, D.; Liao, W.; Cui, H. Phytic acid inhibits Cr(VI) reduction on Fe(II)-bearing clay minerals: Changing reduction sites and electron transfer pathways. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 360, 127701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hojabri, S.; Rajic, L.; Zhao, Y.; Alshawabkeh, A.N. Simulation of hexavalent chromium removal by electrocoagulation using iron anode in flow-through reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 135195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Zeng, B.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Hu, T.; Zhang, L. A systematic review of metal organic frameworks materials for heavy metal removal: Synthesis, applications and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.; Kumar, S.; Virender; Kumar, A.; Kumar, K.; Modi, K.; Jiao, T.; Chen, Q. Analogize of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) adsorbents functional sites for Hg2+ ions removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 297, 121471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Cui, X.; Du, X.; Lu, X. Uio series of metal-organic frameworks composites as advanced sorbents for the removal of heavy metal ions: Synthesis, applications and adsorption mechanism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamim, M.A.; Zia, H.; Zeeshan, M.; Khan, M.Y.; Shahid, M. Metal organic frameworks MOFs) as a cutting-edge tool for the selective detection and rapid removal of heavy metal ions from water: Recent progress. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adil, H.I.; Thalji, M.R.; Yasin, S.A.; Saeed, I.A.; Assiri, M.A.; Chong, K.F.; Ali, G.A.M. Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) based nanofiber architectures for the removal of heavy metal ions. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 1433–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhong, W.; Xie, L.; Xie, Y.; Li, J. Recent advances in adsorptive removal of Cr(VI) ions by metal-organic frameworks. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 37, 385–400. [Google Scholar]
- Alharthi, F.A.; Abutaleb, A.A.; Aljohani, M.M.; Alshareef, M. Recent progress in metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for the detection and removal of heavy metal ions from water: A comprehensive review. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Qin, L.; Lai, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Xiao, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M. Recent advances in the application of water-stable metal-organic frameworks: Adsorption and photocatalytic reduction of heavy metal in water. Chemosphere 2021, 285, 131432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kumar, S.; Yusuf, M.; Lee, J.; Malik, A.K.; Ahmadi, Y.; Kim, K. Schiff base-functionalized metal-organic frameworks as an efficient adsorbent for the decontamination of heavy metal ions in water. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Xu, H.; Hu, W.; Huang, B.; Wang, R.; Shao, J.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Q. MOF-525 and Fe-loaded MOF-525 for the selective adsorption removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI). J. Solid State Chem. 2024, 339, 127927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, Z.; Li, D.; Liu, T.; Yin, H.; Cai, X.; Zhu, W.; Fan, Z.; Li, R. A Tb3+-anchored Zr(IV)-bipyridine MOF to promote photo-induced electron transfer and simultaneously enhance photoluminescence ability and photocatalytic reduction efficiency towards Cr2O72−. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 2957–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Qiang, T. Stable and recyclable polyporous polyurethane foam highly loaded with UiO-66-NH2 nanoparticles for removal of Cr(VI) in wastewater. Polymer 2022, 255, 125117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Huang, P.; Xu, X. Metal-organic framework based photocatalytic membrane for organic wastewater treatment: Preparation, optimization, and applications. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 355, 129540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B. Tuned porous MOFs & COFs for arsenic removal- advanced water remediation approach. Desalination 2024, 592, 118075. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, H.; Sharma, V.K. Water-stable metal-organic frameworks for aqueous removal of heavy metals and radionuclides: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, P.D. Sustainable development in the removal and photocatalytic reduction of heavy metals in wastewaters using environmentally friendly and health benign porphyrin-based metal-organic frameworks. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 322, 124214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Chen, X.; Leng, L.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Li, H. Facile synthesis of amino-functionalized titanium metal-organic frameworks and their superior visible-light photocatalytic activity for Cr(VI) reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 286, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadijokani, F.; Molavi, H.; Rezakazemi, M.; Tajahmadi, S.; Bahi, A.; Ko, F.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Li, J.; Arjmand, M. UiO-66 metal-organic frameworks in water treatment: A critical review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2022, 125, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L. Adenosine-functionalized UiO-66-NH2 to efficiently remove Pb(II) and Cr(VI) from aqueous solution: Thermodynamics, kinetics and isothermal adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 425, 127771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashem, T.; Ibrahim, A.H.; Woell, C.; Alkordi, M.H. Grafting zirconium-based metal-organic framework UiO-66-NH2 nanoparticles on cellulose fibers for the removal of Cr(VI) ions and methyl orange from water. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 5804–5808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.; Lin, S.; Yun, Y. Highly efficient and acid-resistant metal-organic frameworks of mil-101(Cr)-NH2 for Pd(II) and Pt(IV) recovery from acidic solutions: Adsorption experiments, spectroscopic analyses, and theoretical computations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, X. Sorption-catalytic reduction/extraction of hexavalent cr(vi) and u(vi) by porous frameworks materials. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 314, 123615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Jiang, M.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, J.; Wei, G. Metal-organic frameworks functionalized with nucleic acids and amino acids for structure- and function-specific applications: A tutorial review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniyam, V.; Ravi, P.V.; Pichumani, M. Structure co-ordination of solitary amino acids as ligands in metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): A comprehensive review. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1251, 131931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzaib, A.; Shaily, L.A.; Kamran, L.A.; Nishat, N. The biomolecule-mof nexus: Recent advancements in biometal-organic frameworks (bio-mofs) and their multifaceted applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 34, 101781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, J.; Achenbach, B.; Reinsch, H.; Smolders, S.; Lange, F.; Friedrichs, G.; De Vos, D.; Stock, N. The first water-based synthesis of Ce(IV)-MOFs with saturated chiral and achiral c4-dicarboxylate linkers. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 8433–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsen, J.; Ienco, A.; D’Amato, R.; Costantino, F.; Stock, N. The chemistry of Ce-based metal-organic frameworks. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 16551–16586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Ren, H.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Li, G. Icing on the cake: Imidazole-anchored strategy to enhance the proton conductivity of two isostructural Ce(IV)/Hf(IV) metal-organic frameworks. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 21309–21321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Montero-Lanzuela, E.; Tissot, A.; Baldovi, H.G.G.; Garcia, H.; Navalon, S.; Serre, C. Room temperature design of Ce(IV)-mofs: From photocatalytic HER and OER to overall water splitting under simulated sunlight irradiation. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 3451–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosch, J.; Venturi, D.M.; Grape, E.S.; Atzori, C.; Dona, L.; Steinke, F.; Otto, T.; Tjardts, T.; Civalleri, B.; Lomachenko, K.A.; et al. Synthesis, crystal structure, and photocatalytic properties of two isoreticular Ce(IV)-mofs with an infinite rod-shaped inorganic building unit. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 5176–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Liu, B.; Zuo, B.; Li, Z.; Li, G. The effect of free carboxylic acid groups on the proton conductivity of a series of UiO-66-ce(iv) metal-organic frameworks. Microporous Mesoporous Mat. 2023, 351, 112481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Lv, F.; Jiang, B. A dft study on adsorption of sf6 decomposition products on Zr-MOF-808. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, X.; Yu, J.; Lv, X.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Li, J. Zr(IV)-based metal-organic framework with t-shaped ligand: Unique structure, high stability, selective detection, and rapid adsorption of Cr2O72− in water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16650–16659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 7467-87:1987; Water Quality—Determination of Hexavalent Chromium—Diphenylcarbamide Dihydrazine Spectrophotometric Method. China National Standardization Administration Committee: Beijing, China, 1987.
- Donghai, Z.; Shuangxi, Z.; Ziming, Z.; Rui, L.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shenjie, L.; Yunhai, Z.; Shiyu, M.; Wei, W. Highly efficient and selective removal of cr(vi) by covalent organic frameworks: Structure, performance and mechanism. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 600, 124910–124919. [Google Scholar]
- Xitong, S.; Liangrong, Y.; Huifang, X.; Junmei, Z.; Xiaopei, L.; Yinbin, H.; Huizhou, L. High capacity adsorption of cr(vi) from aqueous solution using polyethylenimine-functionalized poly(glycidyl methacrylate) microspheres. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 457, 160–168. [Google Scholar]
- Fu-Zhi, C.; Rong-Ran, L.; Qiao-Yan, Q.; Guo-Fang, J.; Xin, Z. Efficient removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions by a dual-pore covalent organic framework. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2019, 3, 1800150–1800156. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, X.; Hao, J.; Zheng, X.; Fu, D.; Mo, P.; Jin, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, H.; Liu, G.; Lv, W. High-performance adsorption of chromate by hydrazone-linked guanidinium-based ionic covalent organic frameworks: Selective ion exchange. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 274, 118993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, F.; Yao, B.; Ding, L.; Kan, J.; Liu, F.; Zhao, G.; Wang, S.; Dong, Y. Synthesis of covalent organic frameworks via kabachnik-fields reaction for water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahpour, A.; Moradi, S.E. Hexavalent chromium removal from water by ionic liquid modified metal-organic frameworks adsorbent. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 243, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.R.; Xu, Z.X.; Zhang, J. Water-stable metal–organic frameworks for fast and high dichromate trapping via single-crystal-to-single-crystal ion exchange. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Qin, J.; Zou, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, H. Thermodynamically guided synthesis of mixed-linker zr-mofs with enhanced tunability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 6636–6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.F.; Zhao, B.; Xiong, G.; Hou, Y.L.; Cheng, P. Fast capture and separation of, and luminescent probe for, pollutant chromate using a multi-functional cationic heterometal-organic framework. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 8231–8233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babapour, M.; Hadi Dehghani, M.; Alimohammadi, M.; Moghadam Arjmand, M.; Salari, M.; Rasuli, L.; Mubarak, N.M.; Ahmad Khan, N. Adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution using mesoporous metal-organic framework-5 functionalized with the amino acids: Characterization, optimization, linear and nonlinear kinetic models. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 345, 117835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, H.; Bresler, M.R.; Oliver, S.R.J. A new paradigm for anion trapping in high capacity and selectivity: Crystal-to-crystal transformation of cationic materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11110–11113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; Wang, X.; Fan, W.D.; Wang, Y.T.; Wang, X.K.; Zhang, K.; Sun, D.F. A multifunctional Zr-MOF for the rapid removal of Cr2O72−, efficient gas adsorption/separation, and catalytic performance. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 1150–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, J.; Cai, J.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, B.; Qian, G. A porous Zrcluster-based cationic metal–organic framework for highly efficient Cr2O72− removal from water. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 14732–14734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.J.; Zheng, H.Q.; Zheng, H.Y.; Lin, L.P.; Xin, Q.; Cao, R. Efficient capture and effective sensing of Cr2O72− from water using a zirconium metal–organic framework. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 14178–14188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Hayati, B.; Naghizadeh, M.; Joo, S.W. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium by metal organic frameworks from aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 28, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, X.; Jiang, S.Y.; Li, G. Adsorption Performance for Chromium(VI) of a UiO-66-Ce Metal–Organic Framework Built by DL-Aspartic Acid. Materials 2024, 17, 5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215293
Lin X, Jiang SY, Li G. Adsorption Performance for Chromium(VI) of a UiO-66-Ce Metal–Organic Framework Built by DL-Aspartic Acid. Materials. 2024; 17(21):5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215293
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Xiaoyi, Sabrina Yanan Jiang, and Gang Li. 2024. "Adsorption Performance for Chromium(VI) of a UiO-66-Ce Metal–Organic Framework Built by DL-Aspartic Acid" Materials 17, no. 21: 5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215293
APA StyleLin, X., Jiang, S. Y., & Li, G. (2024). Adsorption Performance for Chromium(VI) of a UiO-66-Ce Metal–Organic Framework Built by DL-Aspartic Acid. Materials, 17(21), 5293. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17215293




