The Influence of High-Energy Milling on the Phase Formation, Structural, and Photoluminescent Properties of CaWO4 Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Direct Mechanochemical Synthesis
2.2. Solid-State Reaction
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Formation and Morphology
3.1.1. X-ray Powder Diffraction Analysis
3.1.2. TEM Analysis
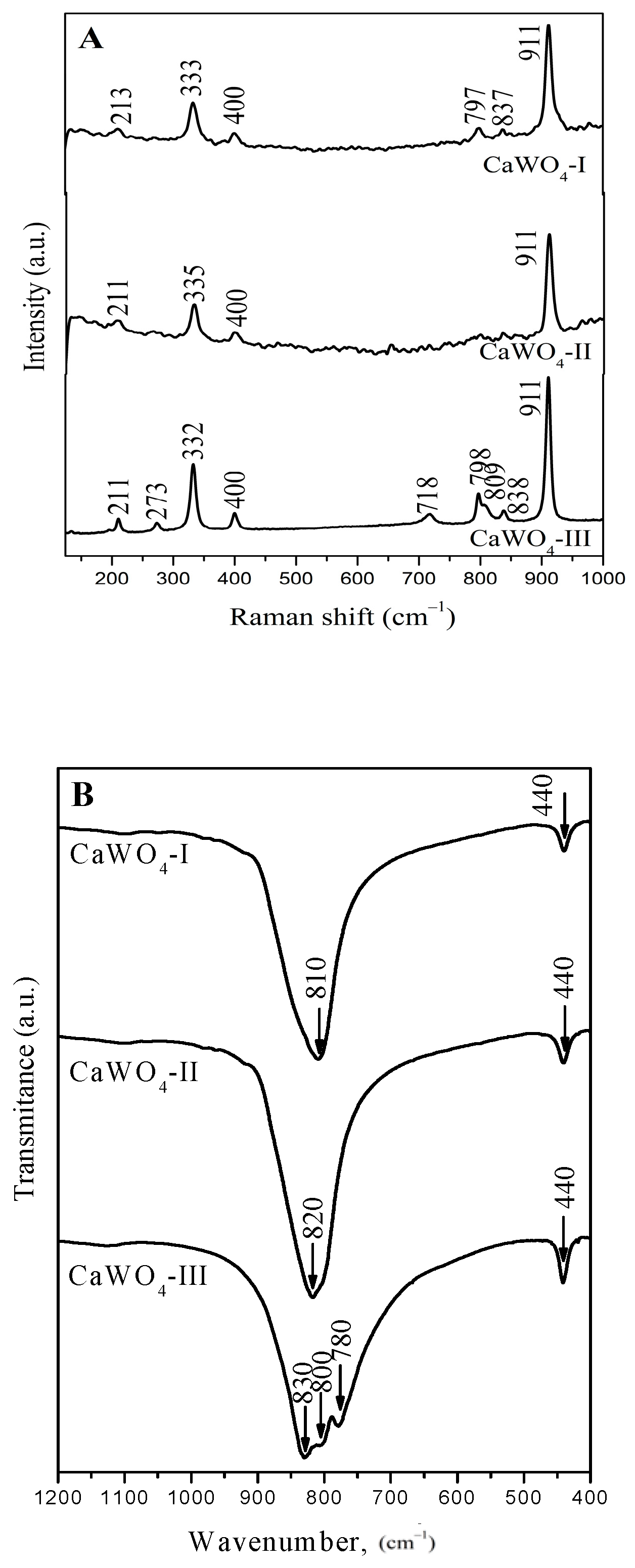
3.2. Raman and Infrared Spectroscopy
3.3. Optical Properties
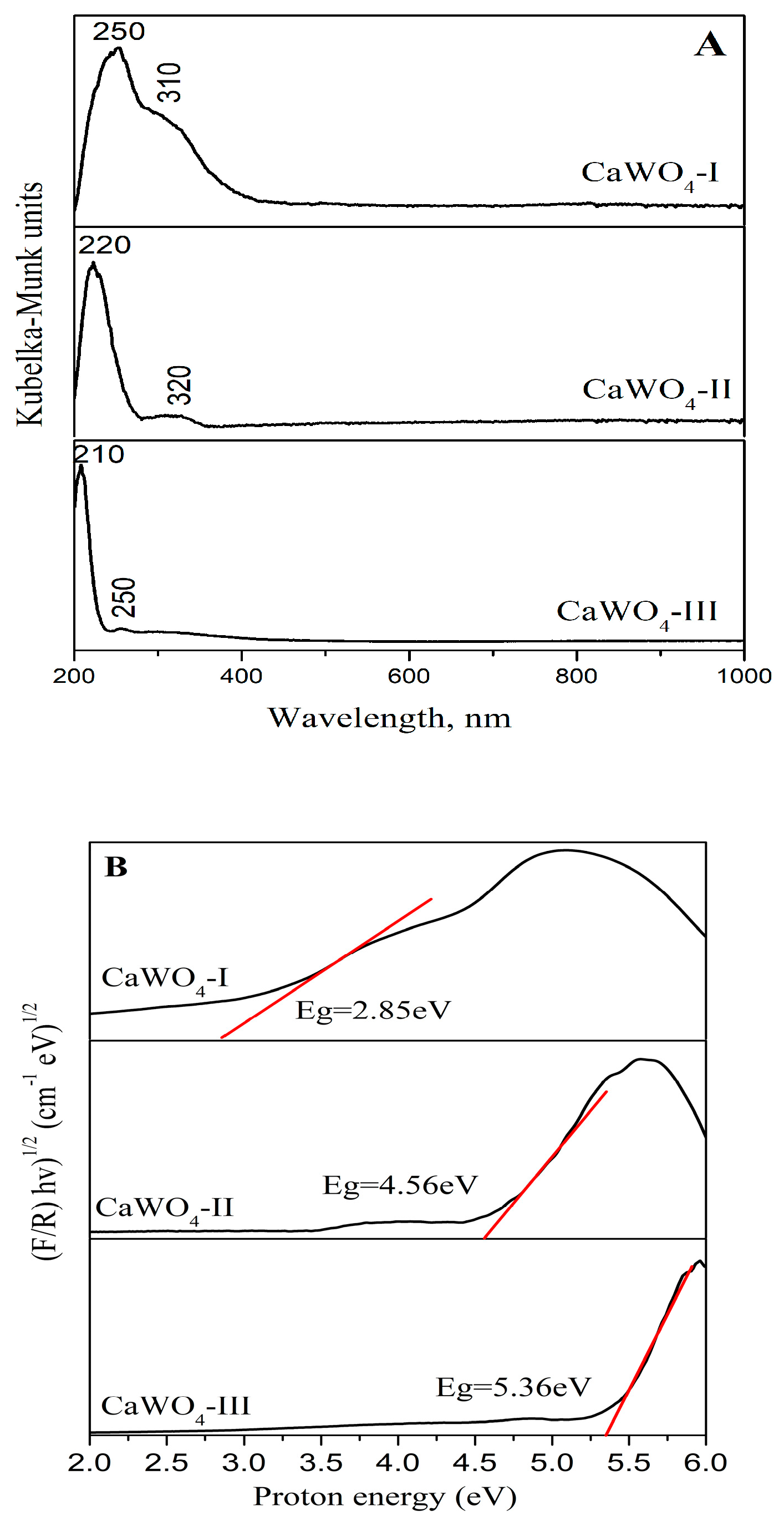
3.3.1. UV–Vis Absorbance Spectroscopy
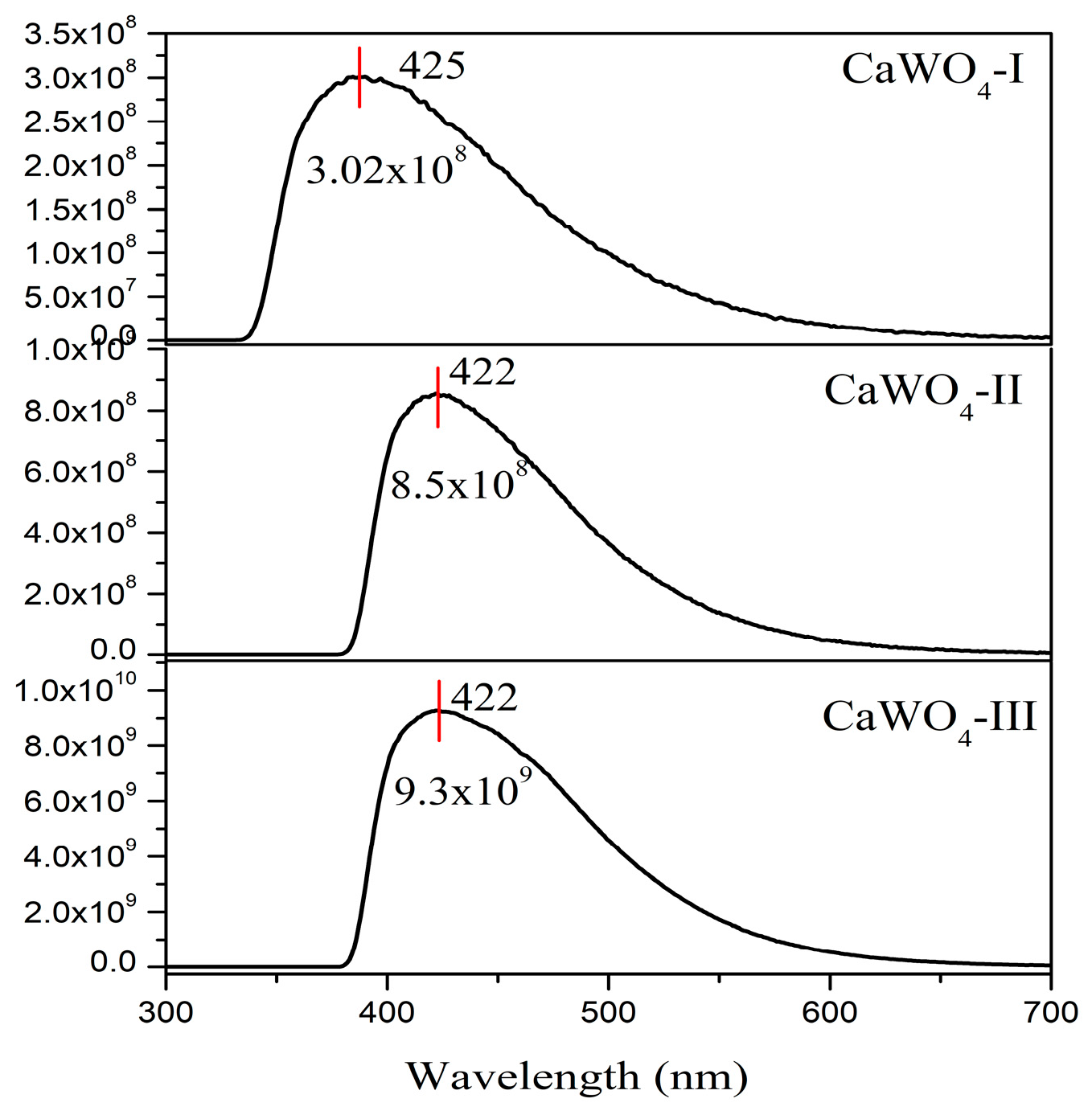
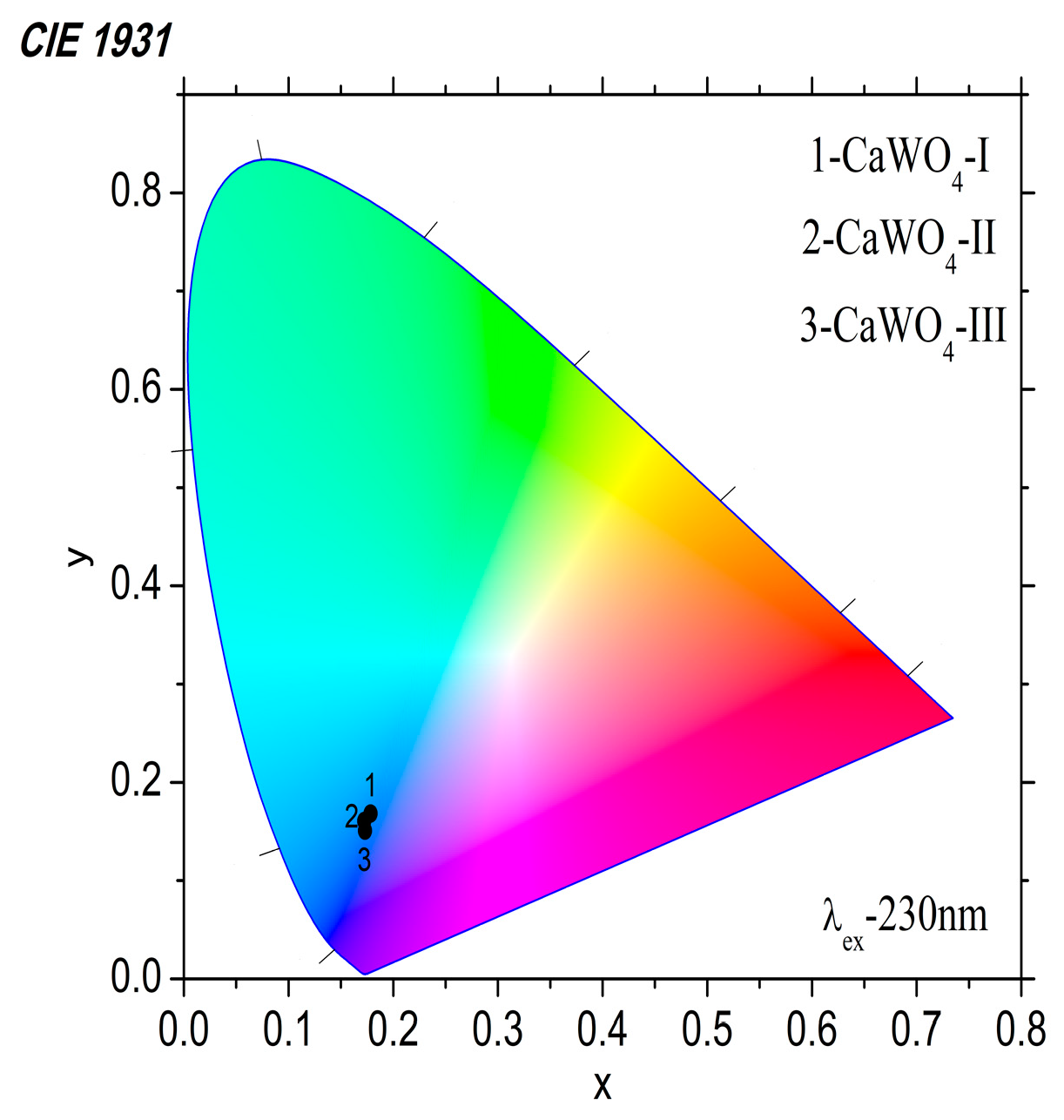
3.3.2. Luminescent Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nitsch, K.; Nikl, M.; Ganschow, S.; Reiche, P.; Uecker, R. Growth of lead tungstate single crystal scintillators. J. Cryst. Growth 1996, 165, 163–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagirnyi, V.; Feldbach, E.; Onsson, L.J.; Kirm, M.; Lushchik, A.; Lushchik, C.; Nagornaya, L.L.; Ryzhikov, V.D.; Savikhiu, F.; Svensson, G.; et al. Excitonic and recombination processes in CaWO4 and CdWO4 scintillators under synchrotron irradiation. Radiat. Meas. 1998, 29, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminskii, A.A.; Eichler, H.J.; Ueda, K.; Klassen, N.V.; Redkin, B.S.; Li, L.E.; Findeisen, J.; Jaque, D.; Garcia-Sole, J.; Fernandez, J.; et al. Properties of Nd3+-doped and undoped tetragonal PbWO4, NaY(WO4)2, CaWO4, and undoped monoclinic ZnWO4 and CdWO4 as laser-active and stimulated Raman scattering-active crystals. Appl. Opt. 1999, 38, 4533–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, B.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Jin, L.; Yan, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. Luminescent hollow CaWO4 microspheres: Template-free synthesis, characterization and application in drug delivery. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 104172–104178. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade Neto, N.F.; Dias, B.P.; Tranquilin, R.L.; Longo, E.; Li, M.; Bomio, M.R.D.; Motta, F.V. Synthesis and characterization of Ag+ and Zn2+ co doped CaWO4 nanoparticles by a fast and facile sonochemical method. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 823, 153617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, P.B.; Gouveia, A.F.; Sczancoski, J.C.; Nogueira, I.C.; Longo, E.; San-Miguel, M.A.; Cavalcante, L.S. Electronic structure, optical and sonophotocatalytic properties of spindle-like CaWO4 microcrystals synthesized by the sonochemical method. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 855, 157377–157386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shana, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ding, H.; Huang, F. Structure-dependent photocatalytic activities of MWO4 (M = Ca, Sr, Ba). J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2009, 302, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Tao, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, L.; Tian, H. Synthesis of CaWO4 nanoparticles by a molten salt method. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Geng, L.; Chen, S. Unexpected formation of scheelite-structured Ca1−xCdxWO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) continuous solid solutions with tunable photoluminescent and electronic properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 23204–23212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Abraha, A.; Zhang, R.; Shahbazyan, T.; Fadavi, M.; Heydari, E.; Dai, Q. Luminescence properties of CaWO4 and CaWO4:Eu3+ nanostructures prepared at low temperature. Opt. Mater. 2018, 84, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, D.; Hu, Z.; Chou, S.; Li, L.; et al. Enhanced photoluminescence of hollow CaWO4 microspheres: The fast fabrication, structural manipulation, and exploration of the growth mechanism. Mater. Chem. Front. 2022, 6, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Cho, I.S.; Shina, S.S.; Lee, S.; Noh, T.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, H.S.; Hong, K.S. Electronic band structures and photovoltaic properties of MWO4 (M = Zn, Mg, Ca, Sr) compounds. J. Solid State Chem. 2011, 184, 2103–2107. [Google Scholar]
- Khobragade, N.; Sinha, E.; Rout, S.K.; Kar, M. Structural, optical and microwave dielectric properties of Sr1−xCaxWO4 ceramics prepared by the solid-state reaction route. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 9527–9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Jia, X.J.; Wu, J.H.; Chen, P. Controlled synthesis and room-temperature ferromagnetism of CaWO4 nanostructures. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 653, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieva, R.; Gancheva, M.; Ivanov, G.; Shipochka, M.; Markov, P.; Nihtianova, D.; Iordanova, R.; Naydenov, A. Synthesis, characterization and activity of Pd/CaWO4 catalyst in the complete oxidation of C1–C6 alkanes and toluene. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2021, 132, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, F.X.; Muniz, R.; Nascimento, E.R.; Amorim, R.S.; Silva, R.S.; Almeida, A.; Agostinho Moreira, J.; Tavares, P.B.; Brito, W.R.; Couceiro, P.R.C.; et al. Hydrothermal temperature dependence of CaWO4 nanoparticles: Structural, optical, morphology and photocatalytic activity. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 9776–9794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.F.S.; Gouveia, A.F.; Assis, M.; Oliveira, R.C.; Pinatti, I.M.; Penha, M.; Gonçalves, R.F.; Gracia, L.; Andrés, J.; Longo, E. ZnWO4 nanocrystals: Synthesis, morphology, and photoluminescence and photocatalytic properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 1923–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbank, R.D. Absolute integrated intensity measurement: Application to CaWO4 and comparison of several refinements. Acta Cryst. 1965, 18, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, P.; Kumar, D.; Verma, N.K.; Singh, A.K. Estimation of Lattice Strain and Optical Properties of Scheelite-Type AWO4 (A = Ca, Sr, Ba) Nanocrystalline Materials Synthesized by Mechanical Activation. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2115, 030199–030204. [Google Scholar]
- Balamurugan, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Ashika, S.A.; Sana Fathima, T.K. Profound impact on different properties of calcium tungstate scheelite, CaWO4 phase stabilized via wider synthesis conditions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 155, 111090–111099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurera, M.A.M.A.; Souza, A.G.; Soledade, L.E.B.; Pontes, F.M.; Longo, E.; Leite, E.R.; Varela, J.A. Microstructural and optical characterization of CaWO4 and SrWO4 thin films prepared by a chemical solution method. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paikaray, R.; Badapanda, T.; Mohapatra, H.; Richhariya, T. Investigation of Structural, Photoluminescence and Thermoluminescence Properties of Scheelite-Type CaWO4 Phosphor. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2023, 24, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcante, L.S.; Longo, V.M.; Sczancoski, J.C.; Almeida, M.A.P.; Batista, A.A.; Varela, J.A.; Orlandi, M.O.; Longo, E.; Siu Li, M. Electronic structure, growth mechanism and photoluminescence of CaWO4 crystals. Cryst. Eng. Commun. 2012, 14, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Khanna, K.; Kumar, R.; Chandra, E. Rare earth doped CaWO4 and CaMoO4 thin film for white light emission. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2021, 39, 012205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, H.; Sun, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H. Structure characterization, optical and photoluminescence properties of scheelite-type CaWO4 nanophosphors: Effects of calcination temperature and carbon skeleton. Opt. Mater. 2020, 99, 109562–109573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compos, A.B.; Simoes, A.Z.; Longo, E.; Varela, J.A.; Lang, V.M. Mechanisms behind blue, green, and red photoluminescence emissions in CaWO4 and CaMoO4 powders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 051923–051927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikl, M. Wide Band Gap Scintillation Materials: Progress in the Technology and Material Understanding. Phys. Status Solidi A 2000, 178, 595–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Li, J.; Chen, X.T.; Hong, J.M.; Xue, Z.; You, X.Z. Solvothermal synthesis and characterization of crystalline CaWO4 nanoparticles. J. Cryst. Growth 2003, 253, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gong, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, Y.P.; Qian, L.W.; Qian, X.F. Controllable synthesis of hierarchical nanostructures of CaWO4 and SrWO4 via a facile low-temperature route. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yao, W.T.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Sheng, L.; Yu, S.H. Nearly Monodisperse Tungstate MWO4 Microspheres (M = Pb, Ca): Surfactant-Assisted Solution Synthesis and Optical Properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2007, 8, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaowphong, S.; Thongtem, T.; Thongtem, S. Solvothermal Preparation of nano-sized CaWO4 particles. Solid State Phenom. 2007, 124–126, 1265–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.K.; Chudasama, B. Crystallization and optical properties of CaWO4 and SrWO4. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2006, 41, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Lian, H.; Yang, P.; Chai, R.; Chenga, Z.; Lin, J. One-dimensional CaWO4 and CaWO4:Tb3+ nanowires and nanotubes: Electrospinning preparation and luminescent properties. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2015, 636, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Liu, P.; Qu, S.X.; Zhang, H.W. Microwave dielectrical properties of AWO4 (A = Ca, Ba, Sr) ceremics synthesized via high energy ball milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 581, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, W.H.; Kim, D.H.; Kang, S.H.; Kwon, H.S. Electrochemical properties of nanosized Li-rich layered oxide as positive electrode materials for Li-Ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8527–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, A.; Chauhan, V.S.; Vaish, R. Planetary ball milling induced piezocatalysis for dye degradation using BaTiO3 ceramics. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2023, 2, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolle, A.; Szuppa, T.; Leonhardt, S.E.S.; Ondruschka, B. Ball milling in organic synthesis: Solutions and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2317–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, S.; Du, X.; Hong, S.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Sang, K. Boosting the electrical double-layer capacitance of graphene by self-doped defects through ball-milling. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901127–1901137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancheva, M.; Iordanova, R.; Dimitriev, Y. Mechanochemical synthesis of nanocrystalline ZnWO4 at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriev, Y.; Gancheva, M.; Iordanova, R. Effects of the mechanical activation of zinc carbonate hydroxide on the formation and properties of zinc oxides. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 519, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancheva, M.; Koseva, I.; Iordanova, R.; Avdeev, G.; Burdina, G.; Ivanov, P. Synthesis and luminescent properties of barium molybdate nanoparticles BaMoO4. Materials 2023, 16, 7025–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şimsek, T.; Ceylan, A.; Askin, G.S.; Özcan, S. Band gap engineering of ZnO nanocrystallites prepared via ball-milling. J. Polytech. 2022, 25, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Havasi, V.; Tátrai, D.; Szabó, G.; Varga, E.; Erdőhelyi, A.; Sipos, G.; Kónya, Z.; Kukovecz, A. On the effects of milling and thermal regeneration on the luminescence properties of Eu2+ and Dy3+ doped strontium aluminate phosphors. J. Lumin. 2020, 219, 116917–116939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Rodríguez, R.; Valiente, R.; Pesquera, C.; González, F.; Blanco, S.; Potin, V.; Marco de Lucas, M.C. Optical properties of nanocrystalline-coated Y2O3:Er3+, Yb3+ obtained by mechano-chemical and combustion synthesis. J. Lumin. 2009, 129, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIFFRAC. EVA V.4, User’s Manual; Bruker AXS: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2014.
- TOPAS V4.2: General Profile and Structure Analysis Software for Powder Diffraction Data, User’s Manual; Bruker AXS: Karlsruhe, Germany, 2009.
- Porto, S.P.S.; Scoot, J.K. Raman spectra of CaWO4, SrWO4, CaMoO4 and SrMoO4. Phys. Rev. 1967, 157, 716–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiev, T.T.; Sobol, A.A.; Voronko, Y.K.; Zverev, P.C. Spontaneous Raman spectroscopy of tungstate and molybdate crystals for Raman lasers. Opt. Mater. 2000, 15, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Inarered and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA; Chichester, UK; Brisbane, Australia; Toronto, ON, Canada, 1978; pp. 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- García-Lopez, K.B.; Martínez-Martínez, R.; Meza-Rocha, A.N.; Vargas-García, V.; Lozada-Morales, R.; Agustín-Serrano, R.; Rubio-Rosas, E.; Cedillo del Rosario, G.; Carmona-Tellez, S. Commercial 3D resin blended with TTA functionalized CaWO4:Eu (III), synthesis route and a luminescence study. Opt. Mater. 2023, 142, 114008–114018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.F. Lattice Perturbations in CaWO4 and CaMoO4. J. Chem. Phys. 1968, 48, 874–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iordanova, R.S.; Milanova, M.K.; Kostov, K.L. Glass formation in the MoO3–CuO system. Phys. Chem. Glasses Eur. J. Glass Sci. Technol. B 2006, 47, 631–637. [Google Scholar]
- Kubelka, P. New contributions to the optics of intensely light-scattering materials. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1948, 38, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna, A.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; Ntwaeaborwa, O.M. Structural and photoluminescence features of Pr3+-activated different alkaline sodium-phosphate-phosphors. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 686, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spassky, D.A.; Ivanov, S.N.; Kolobanov, V.N.; Mikhailin, V.V.; Zemskov, V.N.; Zadneprovski, B.I.; Potkin, L.I. Optical and luminescent properties of the lead and barium molybdates. Radiat. Meas. 2004, 38, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alencara, L.D.S.; Lima, N.A.; Mesquita, A.; Fernando, L.; Probst, D.; Batalhad, D.C.; Rosmaninho, M.G.; Fajardod, H.V.; Balzer, R.; Bernardia, M.I.B. Effect of different synthesis methods on the textural properties of calcium tungstate CaWO4 and Its Catalytic Properties in the Toluene Oxidation. Mater. Res. 2018, 21, 20170961–20170975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.S.; Zhen, L.; Xu, C.Y.; Yang, L.; Shao, W.Z.; Chen, Z.L. Aqueous solution synthesis and photoluminescence properties of two-dimensional dendritic PbWO4 nanostructures. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 56, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongtem, T.; Kungwankunakorn, S.; Kuntalue, B.; Phuruangrat, A.; Thongtem, S. Limunescence and absorbance of highly crystalline CaMoO4, SrMoO4, CaWO4 and SrWO4 nanoparticleas synthesized by co-precipitation method at room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 506, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, T.J.; Yang, P.; Hattar, K.; Hernandez-Sanchez, B.A.; Neville, M.L.; Hoppe, S. Synthesis and characterization of solvothermal processed calcium tungstate nanomaterials from alkoxide precursors. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, F.; Chen, H.H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.T. Surfactant-assisted hydrothermal synthesis, physical characterization, and photoluminescence of PbWO4. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 3730–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Sanchez, B.A.; Boyle, T.J.; Pratt, H.D., III; Rodriguez, M.A.; Brewer, L.N.; Dunphy, D.R. Morphological and phase controlled tungsten based nanoparticles: Synthesis and characterization of scheelite, wolframite, and oxide nanomaterials. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 6643–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokul, B.; Matheswaran, P.; Sathyamoorthy, R. Influence of annealing on physical properties of CdO thin films prepared by SILAR method. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
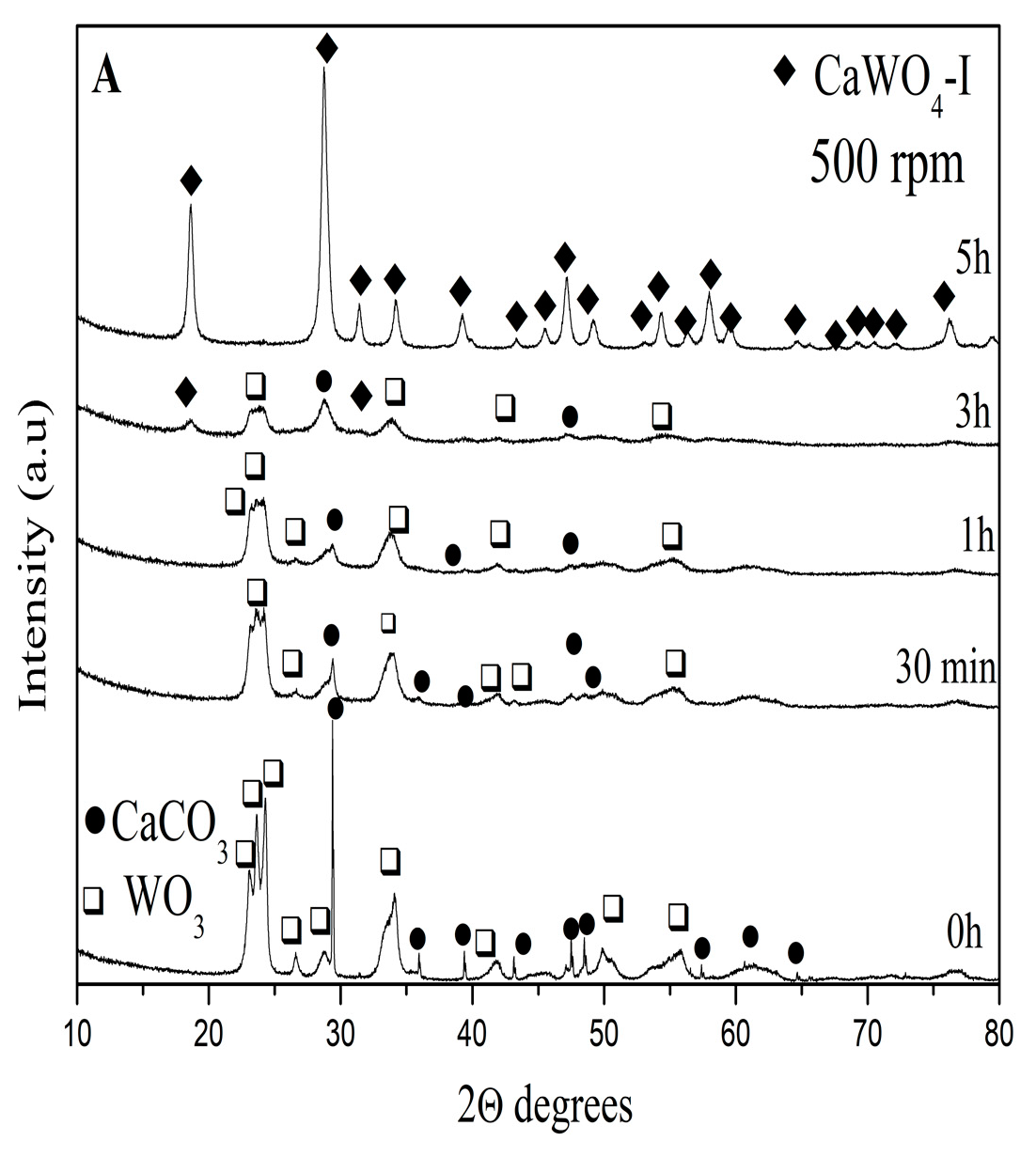
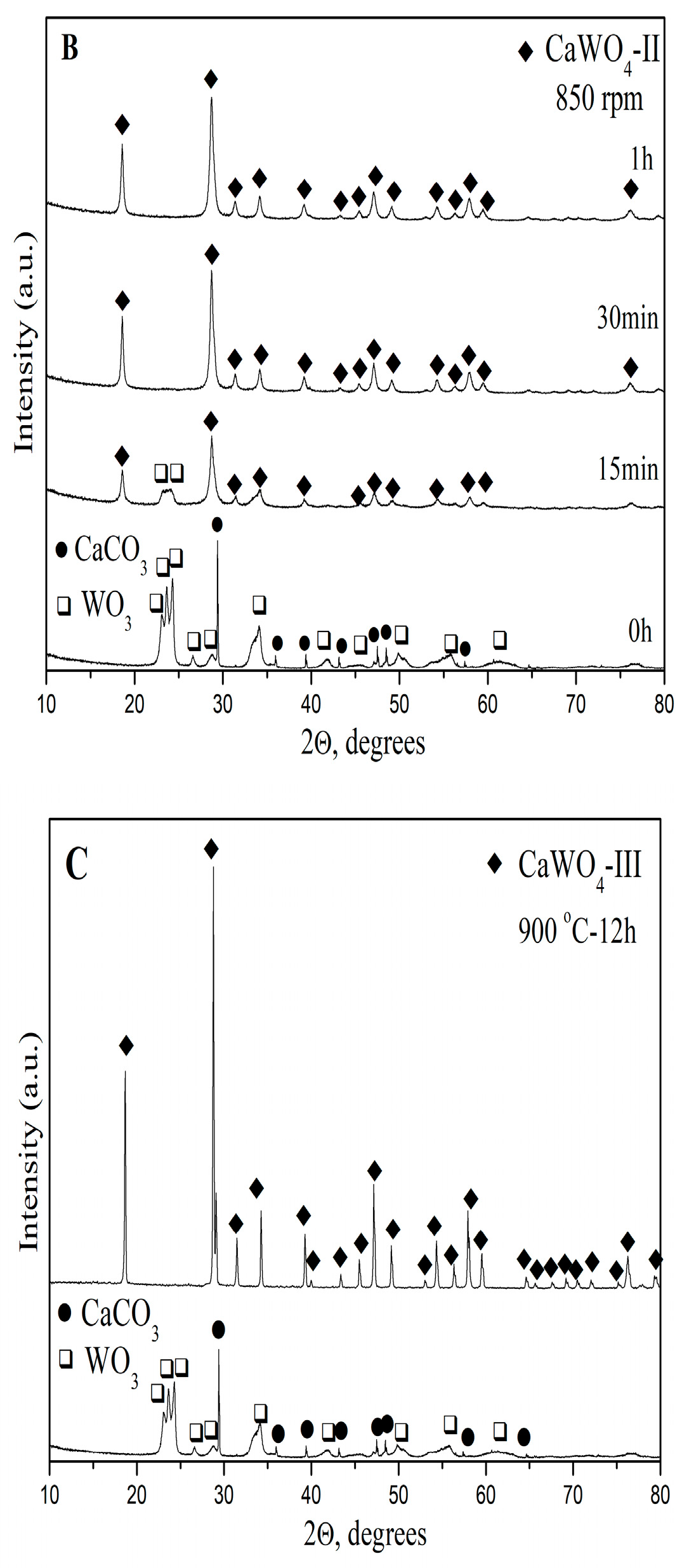
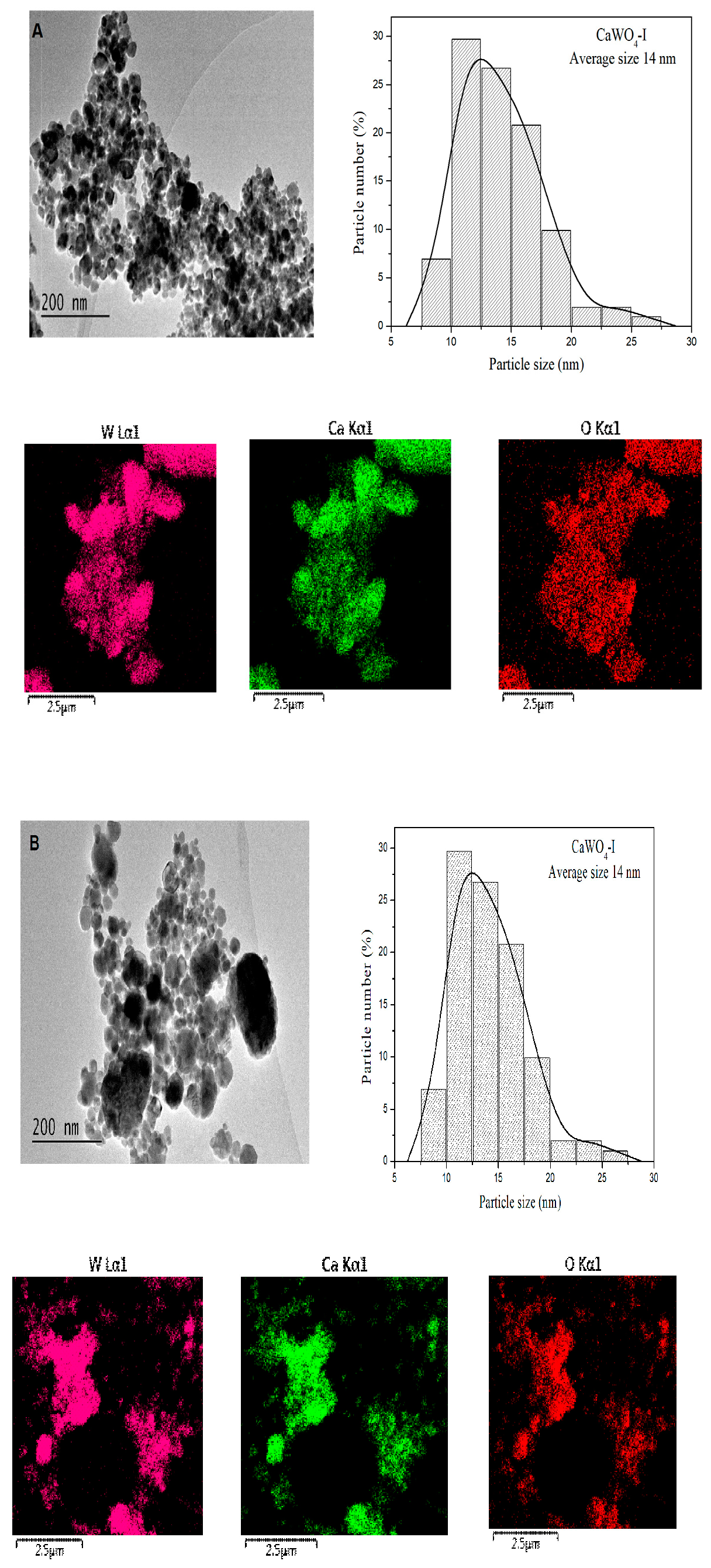
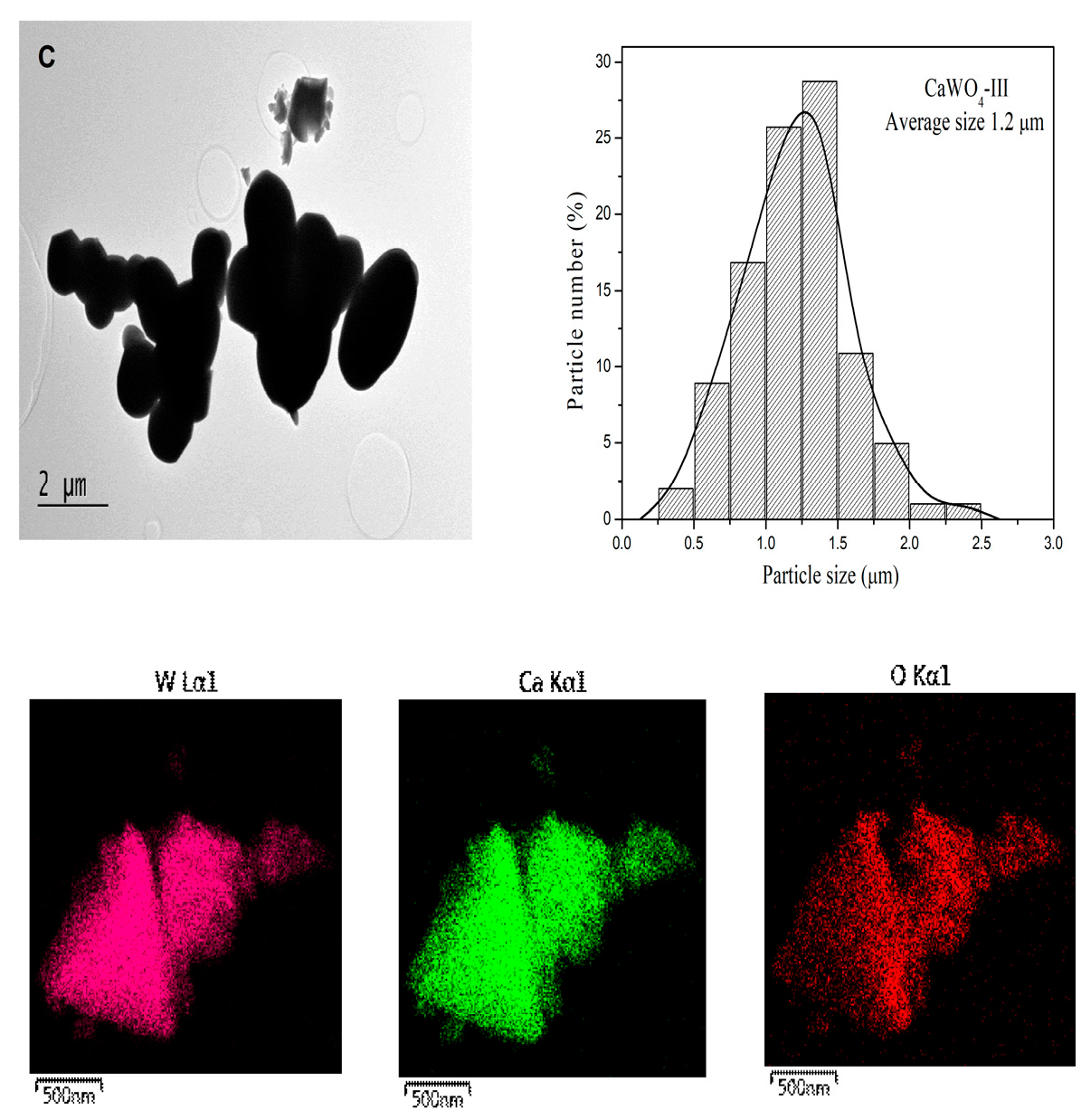
| CaWO4-I 5 h, 500 rpm | CaWO4-II 1 h, 850 rpm | CaWO4-III 900 °C-12 h | CaWO4 (PDF#00-041-1431) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit cell parameters a/c (Å) | 5.244(1) 11.388(2) | 5.242(1) 11.375(2) | 5.238(1) 11.377(2) | 5.243 11.373 |
| Unit cell volume (Å3) | 313.19(1) | 312.598(3) | 312.22(1) | 312.63 |
| Crystallites size (nm) | 31.5(1) | 24.4(7) | 369(5) | n.a. |
| Lattice strain ε0 × 10−4 | 6.92(10) | 12.55(8) | 2.067(15) | n.a. |
| Samples | Emission Peak, nm | FWHM, nm | x | y |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaWO4-I, 5 h at 500 rpm | 425 | 98 | 0.178 | 0.168 |
| CaWO4-II 1 h at 850 rpm | 422 | 92 | 0.173 | 0.150 |
| CaWO4-III 900 °C for 12 h | 422 | 100 | 0.172 | 0.161 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iordanova, R.; Gancheva, M.; Koseva, I.; Tzvetkov, P.; Ivanov, P. The Influence of High-Energy Milling on the Phase Formation, Structural, and Photoluminescent Properties of CaWO4 Nanoparticles. Materials 2024, 17, 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153724
Iordanova R, Gancheva M, Koseva I, Tzvetkov P, Ivanov P. The Influence of High-Energy Milling on the Phase Formation, Structural, and Photoluminescent Properties of CaWO4 Nanoparticles. Materials. 2024; 17(15):3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153724
Chicago/Turabian StyleIordanova, Reni, Maria Gancheva, Iovka Koseva, Peter Tzvetkov, and Petar Ivanov. 2024. "The Influence of High-Energy Milling on the Phase Formation, Structural, and Photoluminescent Properties of CaWO4 Nanoparticles" Materials 17, no. 15: 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153724
APA StyleIordanova, R., Gancheva, M., Koseva, I., Tzvetkov, P., & Ivanov, P. (2024). The Influence of High-Energy Milling on the Phase Formation, Structural, and Photoluminescent Properties of CaWO4 Nanoparticles. Materials, 17(15), 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153724






