Influential Factors on Diffusion Bonding Strength as Demonstrated by Bonded Multi-Layered Stainless Steel 316L and 430 Stack
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pre-DB Preparation Methods
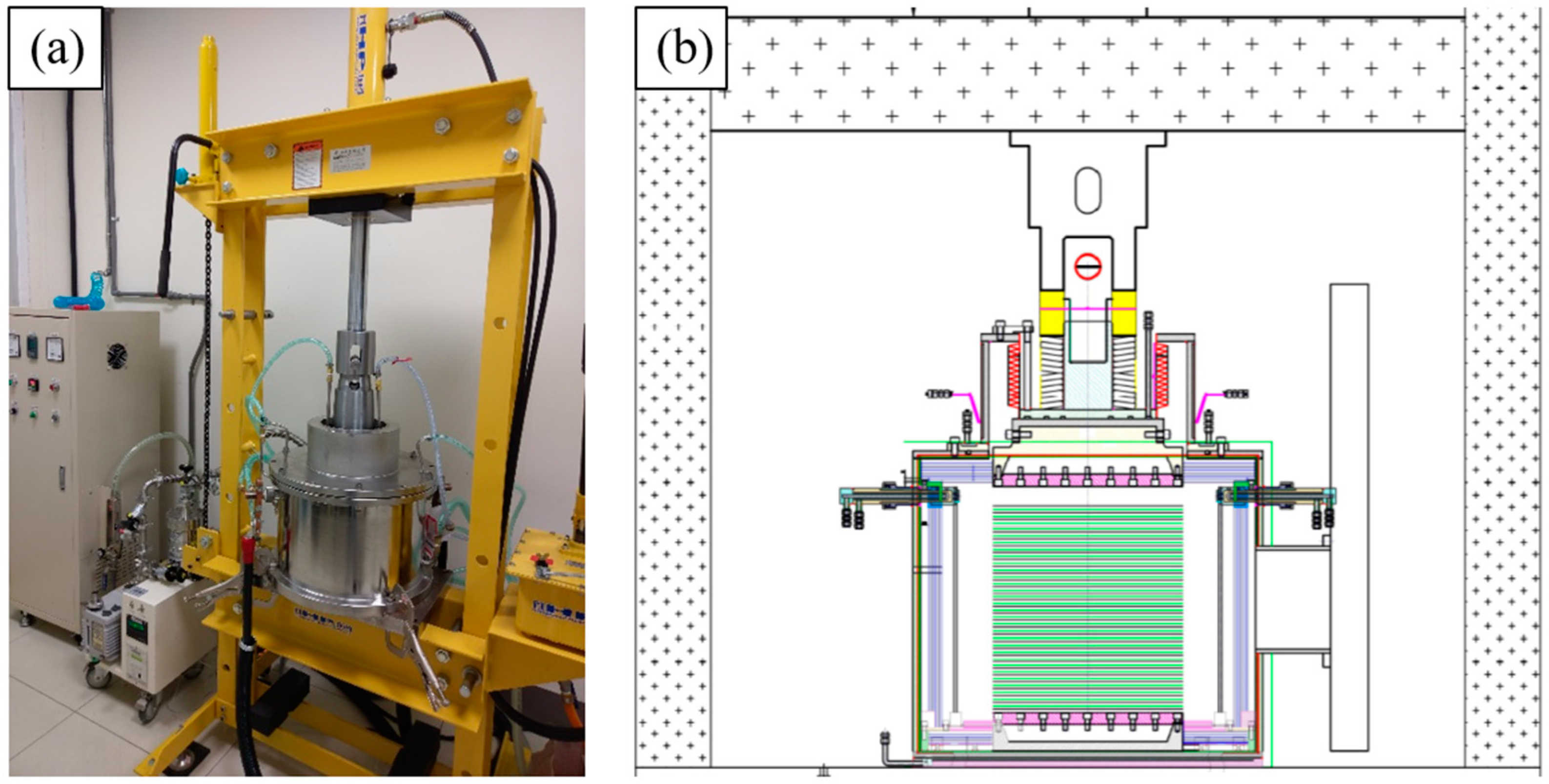
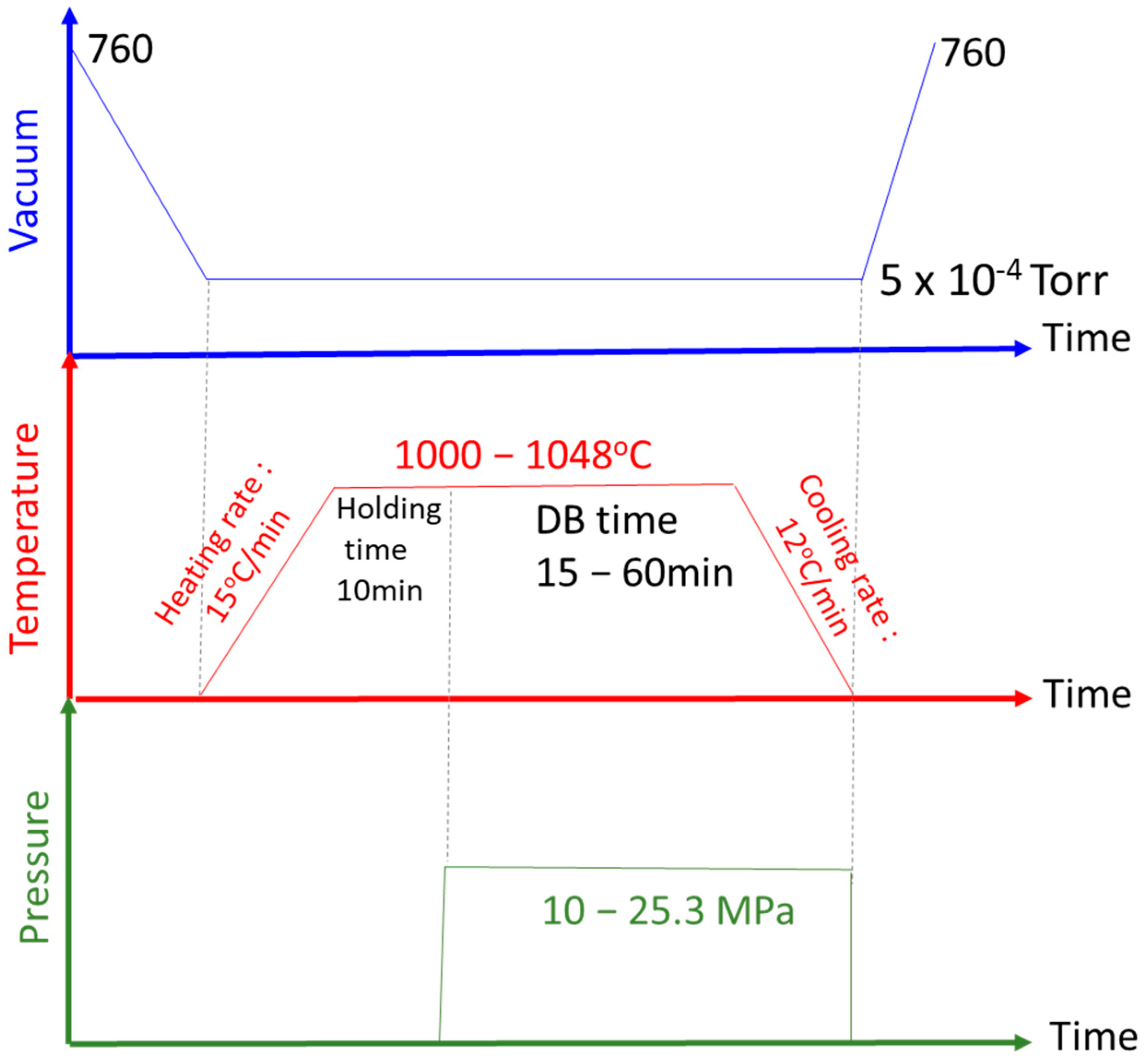
2.3. DB Process and Conditions
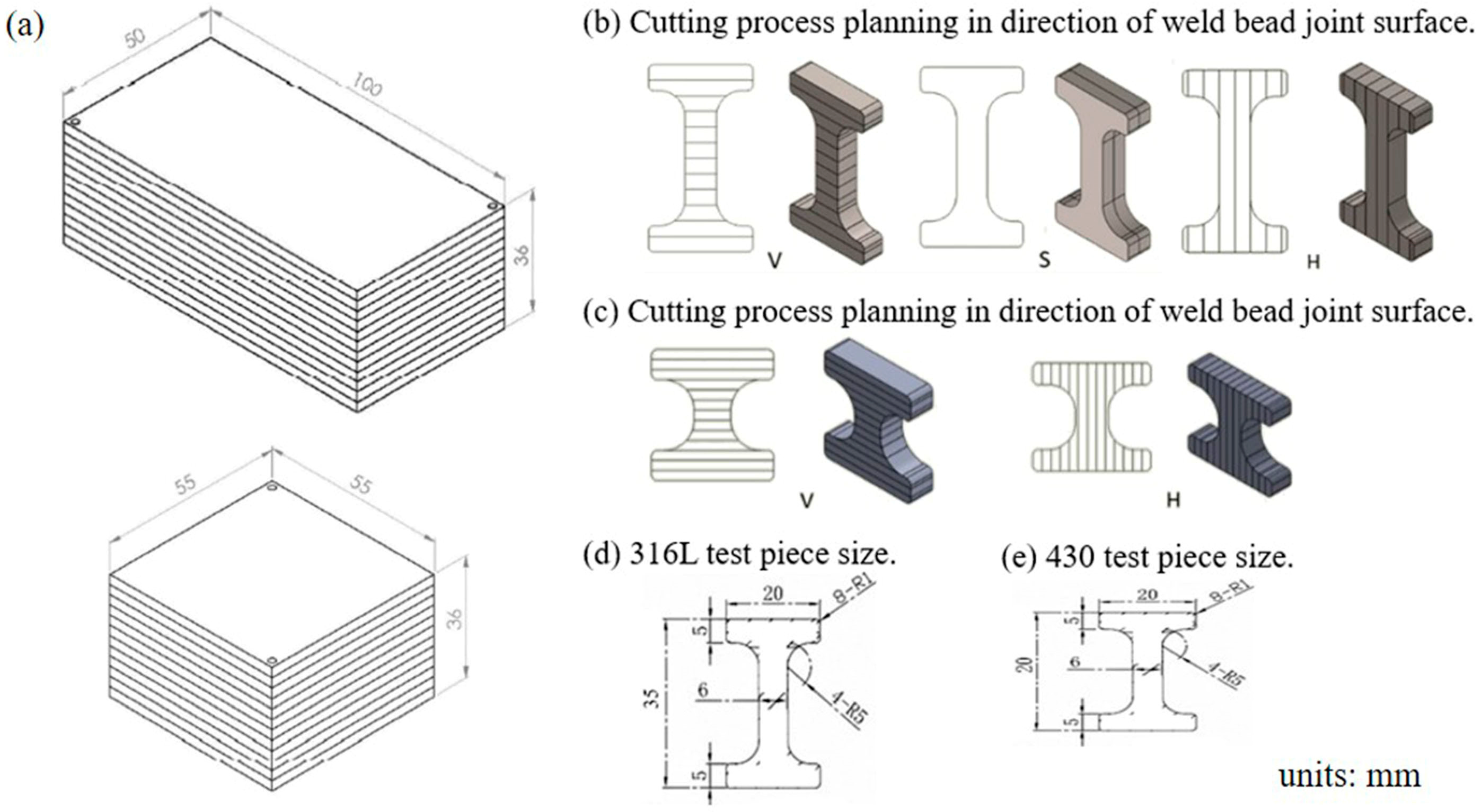
2.4. Test Pieces’ Preparation
3. Results
3.1. Impact Testing
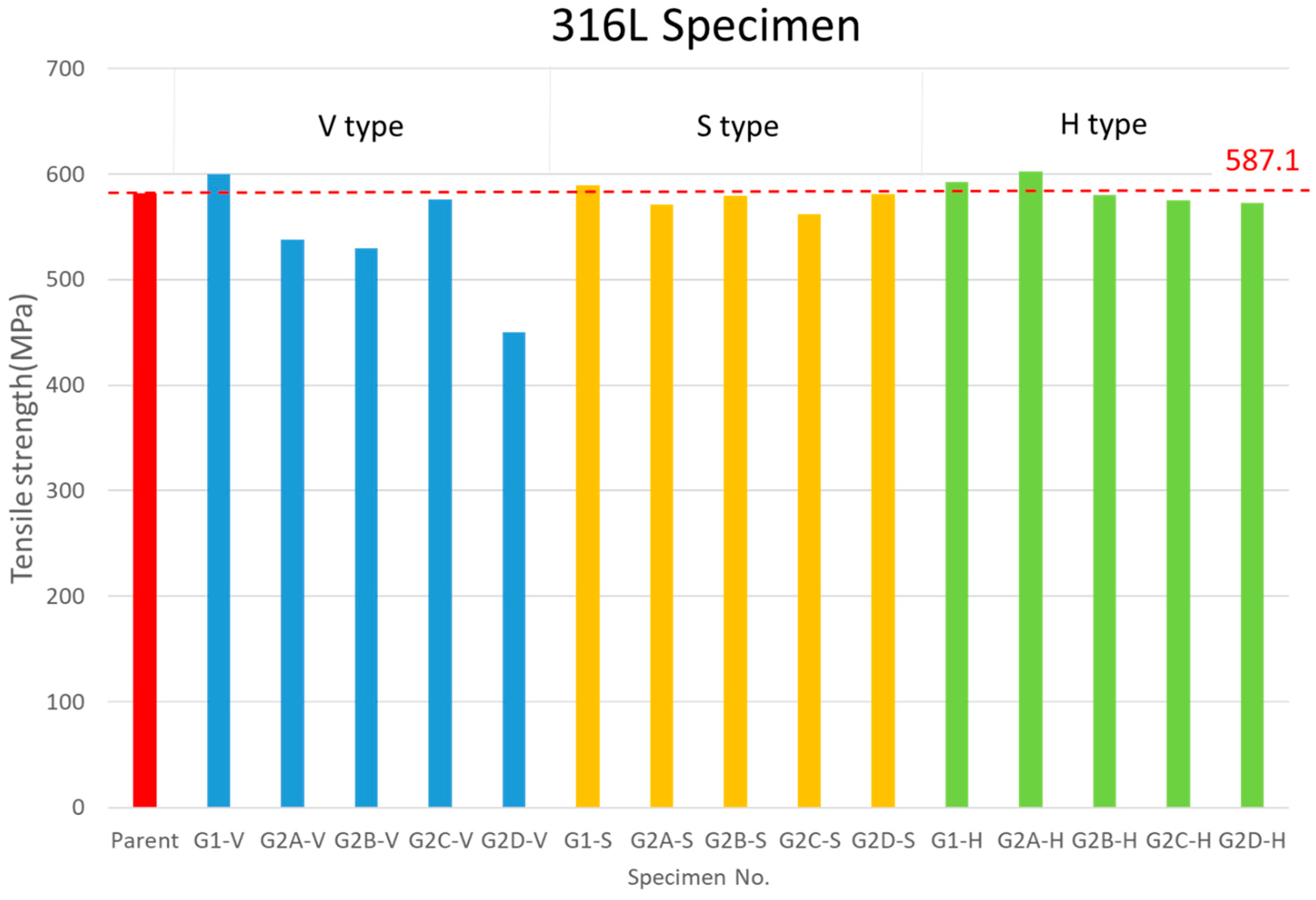
3.2. Tensile Test
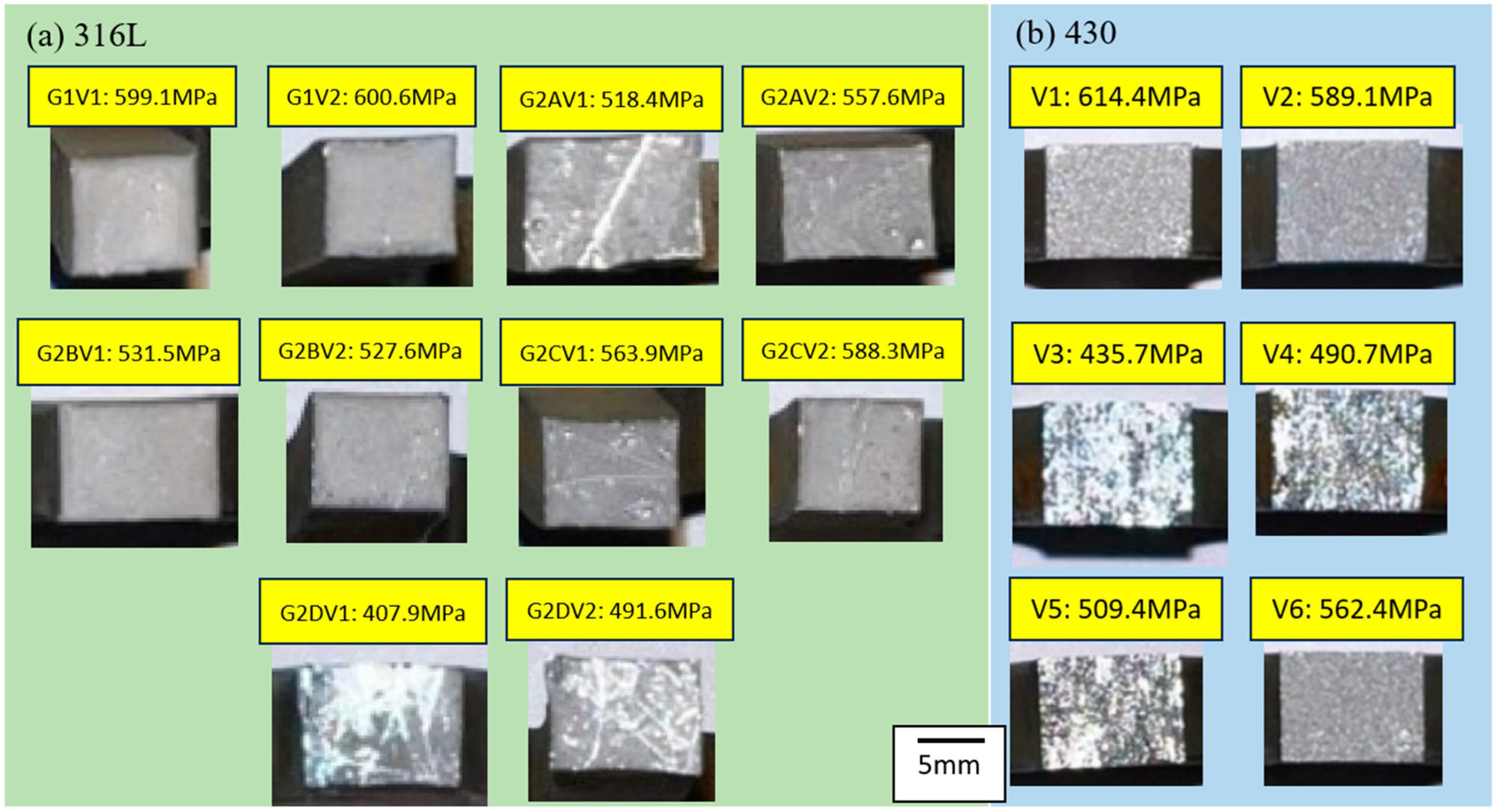
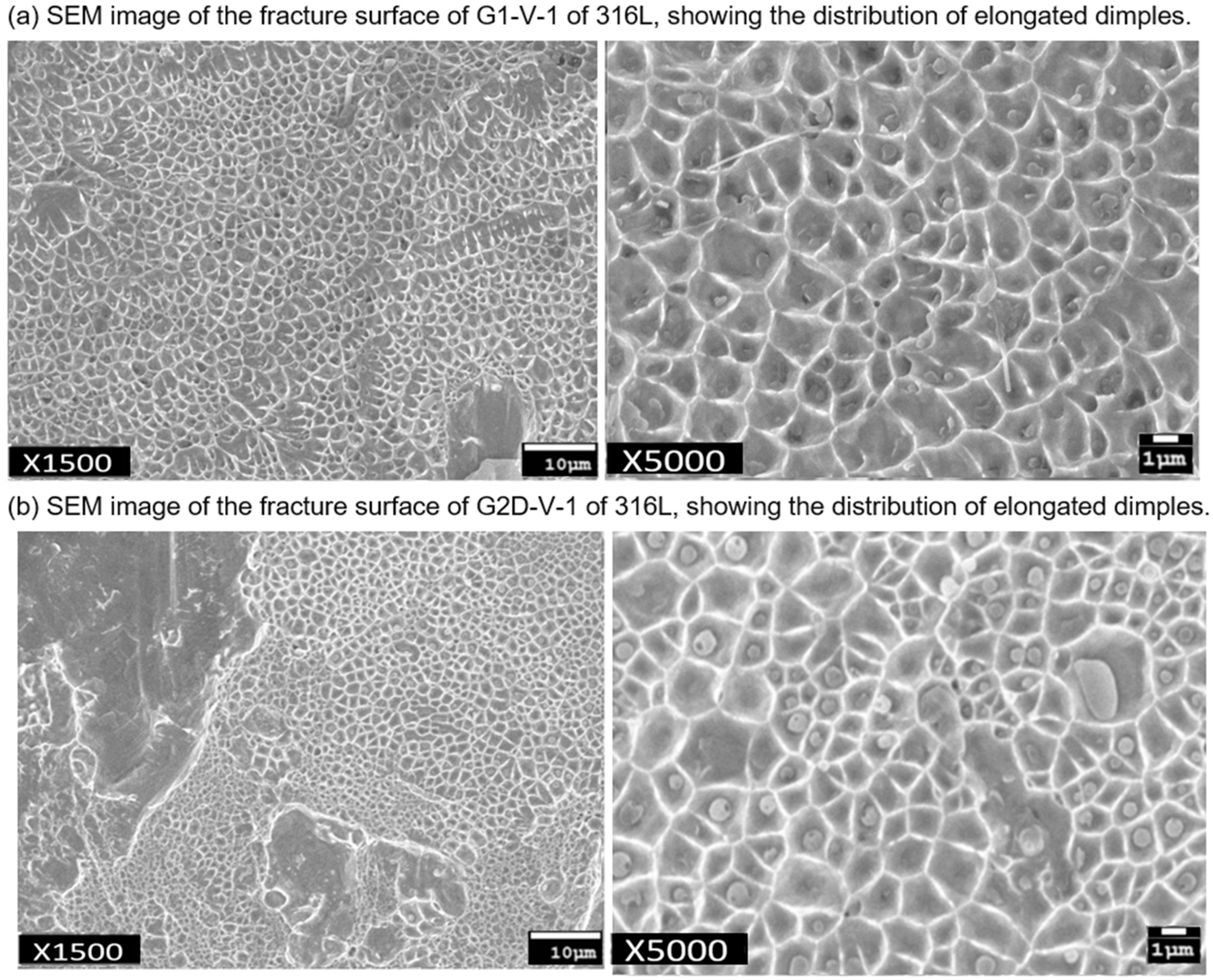
3.3. Fracture Surface
4. Discussion
4.1. Tensile Strength, Deformation, and Microstructure Analysis
4.2. Specific Product Application and Economic Contributions
5. Conclusions
- The compression creep rate of SS430 is much higher than that of SS316L.
- The experimental results of SS316L and SS430’s mechanical properties show that the compressibility of diffusion welding materials does not affect the DB strength.
- Multi-axial (vertical, horizontal, and diagonal) DB joint tensile strength tests were conducted, indicating that after inspecting the weld bead in different axes, the bonding joint strength was confirmed to be good.
- The tensile strengths of the monolithic and DB specimens tested in parallel directions are essentially identical, as logically anticipated.
- The optimized DB parameters (G2C) identified in our study are particularly suitable for producing SS316L stainless steel cores in compact heat exchangers. These parameters provide the best bonding quality and lower cost.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Z.X.; Ridley, N. Modelling of diffusion bonding of metals. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1987, 3, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findik, F. Recent developments in explosive welding. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmatabadi, D.; Tayyebi, M.; Hashemi, R.; Faraji, G. Evaluation of microstructure and mechanical properties of multilayer Al5052–Cu composite produced by accmulative roll bonding. Powder Metall. Met. 2018, 57, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyebi, M.; Rahmatabadi, D.; Karimi, A.; Adhami, M.; Hashemi, R. Investigation of annealing treatment on the interfacial and mechanical properties of Al5052/Cu multilayered composites subjected to ARB process. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 871, 159513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chokshi, A.H. (Ed.) Superplasticity in Advanced Materials—ICSAM-97; Trans Tech Publications, Ltd.: Bäch, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lavernia, E.J.; Grant, N.J. Aluminium-lithium alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 1997, 22, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunford, D.; Partridge, P.; Gilmore, C. Diffusion Bonding of Al-Li 8090 Alloy. Diffus. Bond. 1991, 2, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureña, A.; Gomez De Salazar, J.M.; Quiñones, J.; Merino, S.; Martin, J. Diffusion bonding of an aluminium-lithium alloy (AA8090) using aluminium-copper alloy interlayers: Part I Microstructure. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlHazaa, A.; Haneklaus, N. Diffusion bonding and transient liquid phase (TLP) bonding of type 304 and 316 austenitic stainless steel—A review of similar and dissimilar material joints. Metals 2020, 10, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Z.L.; Luan, W.L.; Xuan, F.Z.; Tu, S.T. High temperature performance of 316L-SS joint produced by diffusion bonding. Key Eng. Mater. 2005, 297, 2795–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harumoto, T.; Yamashita, Y.; Ohashi, O.; Ishiguro, T. Influence of cold rolling on diffusion bondability of SUS316L stainless steel sheets. Metall. Trans. 2014, 55, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-X.; Xuan, F.-Z.; Tu, S.-T.; Yu, S.-R. Microstructure evolution and interfacial failure mechanism in 316LSS diffusion-bonded joints. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 491, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus, L.; George, G.; Nuernberg, V.; Henriques, M.; Mantelli, B. 316L Stainless Steel Diffusion Bonding Optimized Parameters. In Proceedings of the COBEM 2017, Curitiba, Brazil, 3–8 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kolukisa, S.; Taskin, M.; Ozan, S. The effect of the process temperature on the bondability in diffusion bonding of ferritic (AISI 430) with martensitic (AISI 420) stainless steels. Pract. Metallogr. 2022, 43, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskin, M.; Ozan, S.; Kolukisa, S. The effect of the process temperature on the bondability in diffusion bonding of AISI 430 with nodular cast iron. Pract. Metallogr. 2022, 43, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, A.; Kaya, Y.; Kahraman, N. Joint properties and microstructure of diffusion-bonded grade 2 titanium to AISI 430 ferritic stainless steel using pure Ni interlayer. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 86, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livesey, D.; Ridley, N. Diffusion bonding of superplastic aluminium alloys using a transient liquid phase interlayer (zinc). Diffus. Bond. 1991, 2, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, M.S.; Chuang, T.H. Low-pressure diffusion bonding of SAE 316 stainless steel by inserting a superplastic interlayer. Scr. Metall. Mater. 1995, 33, 1277–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.K.; Paul, B.K. Comparison of Nickel Nanoparticle-Assisted Diffusion Brazing of Stainless Steel to Conventional Diffusion Brazing and Bonding Processes. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2010, 132, 030902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8/E8M-22; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024. Available online: www.astm.org/e0008_e0008m-22.html (accessed on 3 March 2024).



| Alloy Type | Iron | Cr | Ni | Mo | Mn | Si | P | N | C | S |
| SS316L | Bal | 17 | 12 | 2.5 | 2 | 0.75 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.03 | 0.03 |
| Alloy Type | Iron | Cr | Mn | Si | Ni | C | P | S | ||
| SS430 | Bal | 17 | 1 | 1 | 0.75 | 0.12 | 0.04 | 0.03 | ||
| Alloy | Interlayer | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Pressure (MPa) | Vacuum | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 316H | SuperDux 65 | 1027 | 30 | 4.2–7 | 10−4 torr | 629~636 | [18] |
| 316L | NiP/NiNP | 1000 | 120 | 10 | 10−5 torr | [19] | |
| 316L | - | 1100 | 180 | 10 | 10−5 torr | 566 | [12] |
| 316L | 945–1100 | 32–179 | 7.5–10 | 10−6 torr | 350–550 | [13] |
| Alloy | SS316L | SS430 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Processing Parameters | G1 | G2A | G2B | G2C | G2D | |
| Stacking Dim. (mm) | 100 × 50 × 3 × 12 pcs | 55 × 55 × 3 × 12 pcs | ||||
| Vacuum (Torr) | 5 × 10−4 | |||||
| Temperature (°C) | 1048 | 1000 | 1048 | 1000 | 1048 | |
| Pressure (MPa) | 25.3 | 20.0 | 25.3 | 10.0 | 25.3 | |
| Time (min) | 25 | 15 | 60 | 30 | ||
| After DB total Thickness (mm) | 35.00 | 35.10 | 34.96 | 34.76 | 35.30 | 20.10 |
| Deformation/pcs (mm) | −0.083 | −0.075 | −0.087 | −0.103 | −0.058 | −1.325 |
| DB compression ratio | 2.8% | 2.5% | 2.9% | 3.4% | 1.9% | 44.2% |
| SS316L | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample No. | Elongation (mm) | Elongation (%) | Cross-Section Area A0 (×10−5 m2) | Max Load (kN) | UTS (MPa) | UTS Avg. (MPa) | DB Ratio (%) |
| Parent-1 | 15.20 | 43.43 | 3 | 17.4 | 578.5 | 581.7 | - |
| Parent-2 | 15.24 | 43.54 | 3 | 17.5 | 582.8 | ||
| Parent-3 | 15.27 | 43.63 | 3 | 17.5 | 583.9 | ||
| G1-V-1 | 12.30 | 35.14 | 3 | 18.0 | 599.1 | 599.7 | 103.1 |
| G1-V-2 | 13.87 | 39.63 | 3 | 18.0 | 600.6 | ||
| G2A-V-1 | 5.71 | 16.27 | 3 | 15.6 | 518.4 | 538.0 | 92.5 |
| G2A-V-2 | 8.46 | 24.10 | 3 | 16.7 | 557.6 | ||
| G2B-V-1 | 11.37 | 32.52 | 3 | 15.9 | 531.5 | 529.6 | 91.0 |
| G2B-V-2 | 11.05 | 31.61 | 3 | 15.8 | 527.6 | ||
| G2C-V-1 | 8.94 | 25.72 | 3 | 16.9 | 563.9 | 576.1 | 99.0 |
| G2C-V-2 | 12.88 | 37.05 | 3 | 17.6 | 588.3 | ||
| G2D-V-1 | 2.72 | 7.71 | 3 | 12.2 | 407.9 | 449.8 | 77.3 |
| G2D-V-2 | 5.84 | 16.54 | 3 | 14.7 | 491.6 | ||
| G1-S-1 | 15.38 | 43.94 | 3.6 | 21.1 | 587.3 | 589.2 | 101.3 |
| G1-S-2 | 15.63 | 44.66 | 3.6 | 21.3 | 591.2 | ||
| G2A-S-1 | 15.18 | 43.37 | 3.6 | 20.2 | 560.4 | 571.0 | 98.2 |
| G2A-S-2 | 15.75 | 45.00 | 3.6 | 20.9 | 581.7 | ||
| G2B-S-1 | 16.25 | 46.43 | 3.6 | 20.5 | 570.7 | 579.0 | 99.5 |
| G2B-S-2 | 16.12 | 46.06 | 3.6 | 21.1 | 587.2 | ||
| G2C-S-1 | 16.25 | 46.43 | 3.6 | 19.6 | 543.4 | 562.0 | 96.6 |
| G2C-S-2 | 16.55 | 47.29 | 3.6 | 20.9 | 580.5 | ||
| G2D-S-1 | 16.08 | 45.94 | 3.6 | 20.7 | 574.1 | 580.9 | 99.9 |
| G2D-S-2 | 15.96 | 45.60 | 3.6 | 21.2 | 587.8 | ||
| G1-H-1 | 16.02 | 45.77 | 3 | 17.6 | 586.5 | 592.7 | 101.9 |
| G1-H-2 | 15.46 | 44.17 | 3 | 18.0 | 598.9 | ||
| G2A-H-1 | 15.33 | 43.80 | 3 | 18.1 | 604.3 | 602.3 | 103.5 |
| G2A-H-2 | 15.99 | 45.69 | 3 | 18.0 | 600.2 | ||
| G2B-H-1 | 16.44 | 46.97 | 3 | 17.8 | 591.9 | 580.2 | 99.7 |
| G2B-H-2 | 16.19 | 46.26 | 3 | 17.1 | 568.4 | ||
| G2C-H-1 | 15.09 | 43.11 | 3 | 17.1 | 570.7 | 575.0 | 98.8 |
| G2C-H-2 | 16.13 | 46.09 | 3 | 17.4 | 579.3 | ||
| G2D-H-1 | 16.16 | 46.17 | 3 | 17.2 | 572.9 | 572.3 | 98.4 |
| G2D-H-2 | 15.93 | 45.51 | 3 | 17.2 | 571.8 | ||
| 430 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample No. | Elongation (mm) | Elongation (%) | Cross-Section Area A0 (×10−5 m2) | Max Load (kN) | UTS (MPa) | UTS Avg. (MPa) | DB Ratio (%) |
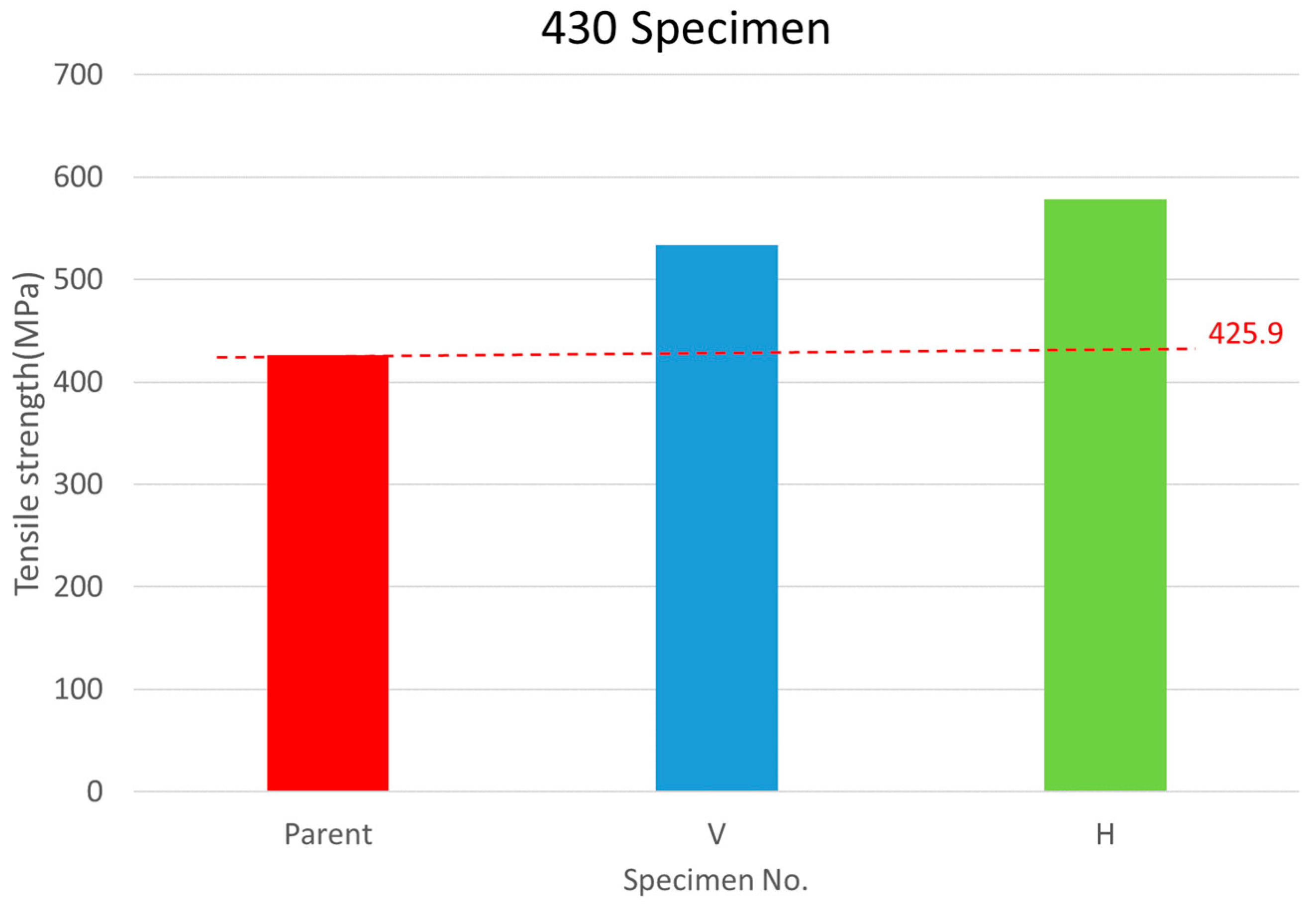
| Parent-1 | 6.09 | 17.40 | 3 | 12.8 | 426.1 | 425.9 | - |
| Parent-2 | 6.12 | 17.49 | 3 | 12.9 | 431.1 | ||
| Parent-3 | 5.64 | 16.11 | 3 | 12.6 | 420.7 | ||
| V-1 | 0.84 | 4.20 | 3 | 18.4 | 614.4 | 533.6 | 125.3% |
| V-2 | 0.86 | 4.30 | 3 | 17.7 | 589.1 | ||
| V-3 | 0.81 | 4.05 | 3 | 13.1 | 435.7 | ||
| V-4 | 0.87 | 4.35 | 3 | 14.7 | 490.7 | ||
| V-5 | 1.04 | 5.20 | 3 | 15.3 | 509.4 | ||
| V-6 | 0.95 | 4.75 | 3 | 16.9 | 562.4 | ||
| H-1 | 2.77 | 13.85 | 3 | 16.9 | 562.9 | 578.6 | 135.8 |
| H-2 | 2.50 | 12.50 | 3 | 17.0 | 565.5 | ||
| H-3 | 2.22 | 11.10 | 3 | 17.4 | 579.8 | ||
| H-4 | 2.73 | 13.65 | 3 | 17.4 | 581.2 | ||
| H-5 | 2.32 | 11.60 | 3 | 17.3 | 576.0 | ||
| H-6 | 2.67 | 13.35 | 3 | 18.2 | 605.9 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.-W.; Lin, C.-N.; Lin, W.-S.; Lee, S.; Gwo, J. Influential Factors on Diffusion Bonding Strength as Demonstrated by Bonded Multi-Layered Stainless Steel 316L and 430 Stack. Materials 2024, 17, 3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153713
Liu D-W, Lin C-N, Lin W-S, Lee S, Gwo J. Influential Factors on Diffusion Bonding Strength as Demonstrated by Bonded Multi-Layered Stainless Steel 316L and 430 Stack. Materials. 2024; 17(15):3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153713
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Da-Wei, Chun-Nan Lin, Wei-Shuai Lin, Shyong Lee, and Jyh Gwo. 2024. "Influential Factors on Diffusion Bonding Strength as Demonstrated by Bonded Multi-Layered Stainless Steel 316L and 430 Stack" Materials 17, no. 15: 3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153713
APA StyleLiu, D.-W., Lin, C.-N., Lin, W.-S., Lee, S., & Gwo, J. (2024). Influential Factors on Diffusion Bonding Strength as Demonstrated by Bonded Multi-Layered Stainless Steel 316L and 430 Stack. Materials, 17(15), 3713. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153713






