Fiber-Reinforced Equibiaxial Dielectric Elastomer Actuator for Out-of-Plane Displacement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling of Anisotropic Circular DEAs
2.1. Circular DEAs
- The material is incompressible;
- The deformation in the -plane is homogeneous.
2.2. Pre-Stretch and Influence of Passive Regions
2.3. Out-of-Plane Displacement Prediction
- No strain on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) covered by fibers;
- The fibers are rigid and non-stretchable;
- No force hindering the electrodes and active area from out-of-plane movement.
2.4. Numerical Simulations
3. Materials and Methods
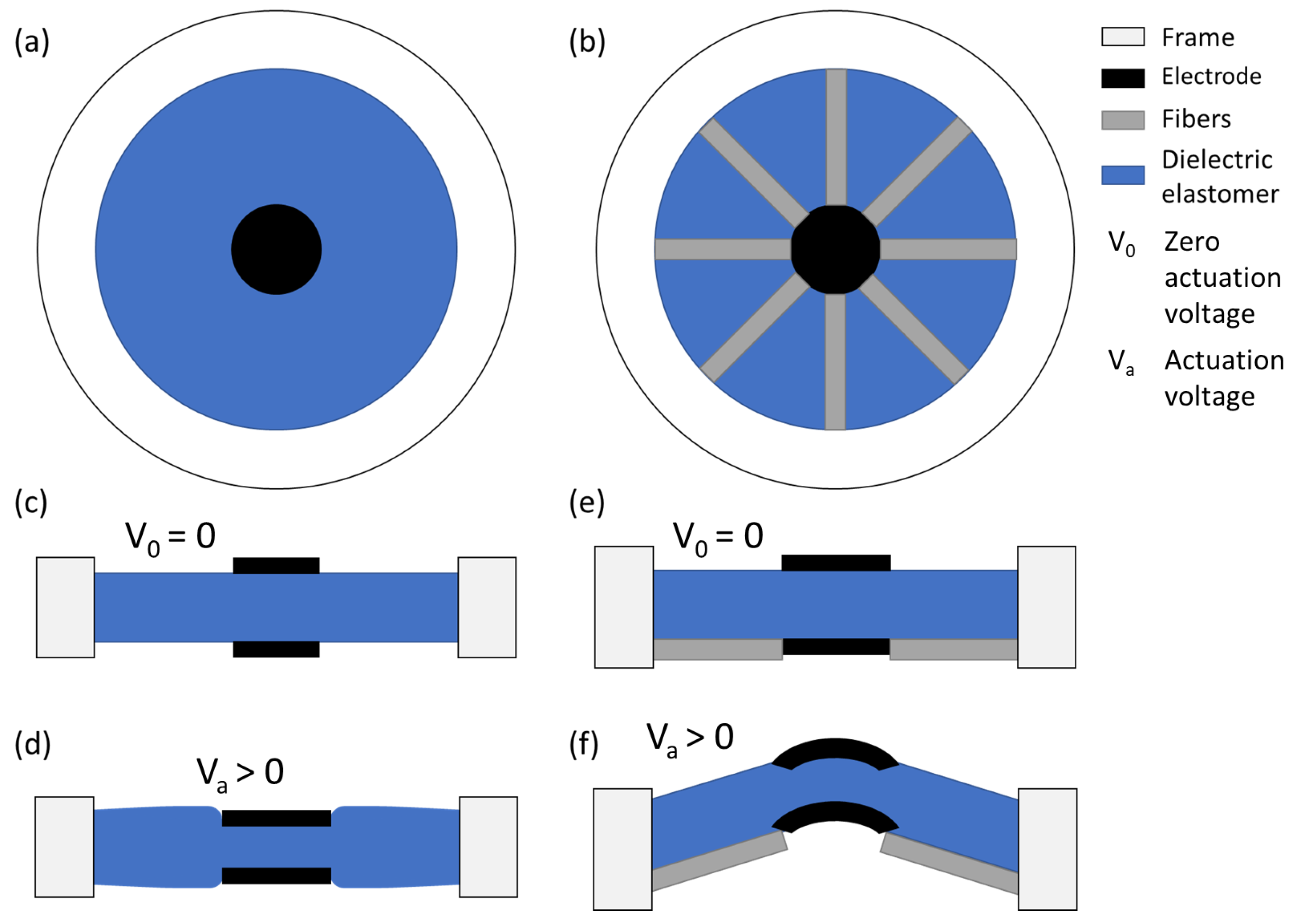
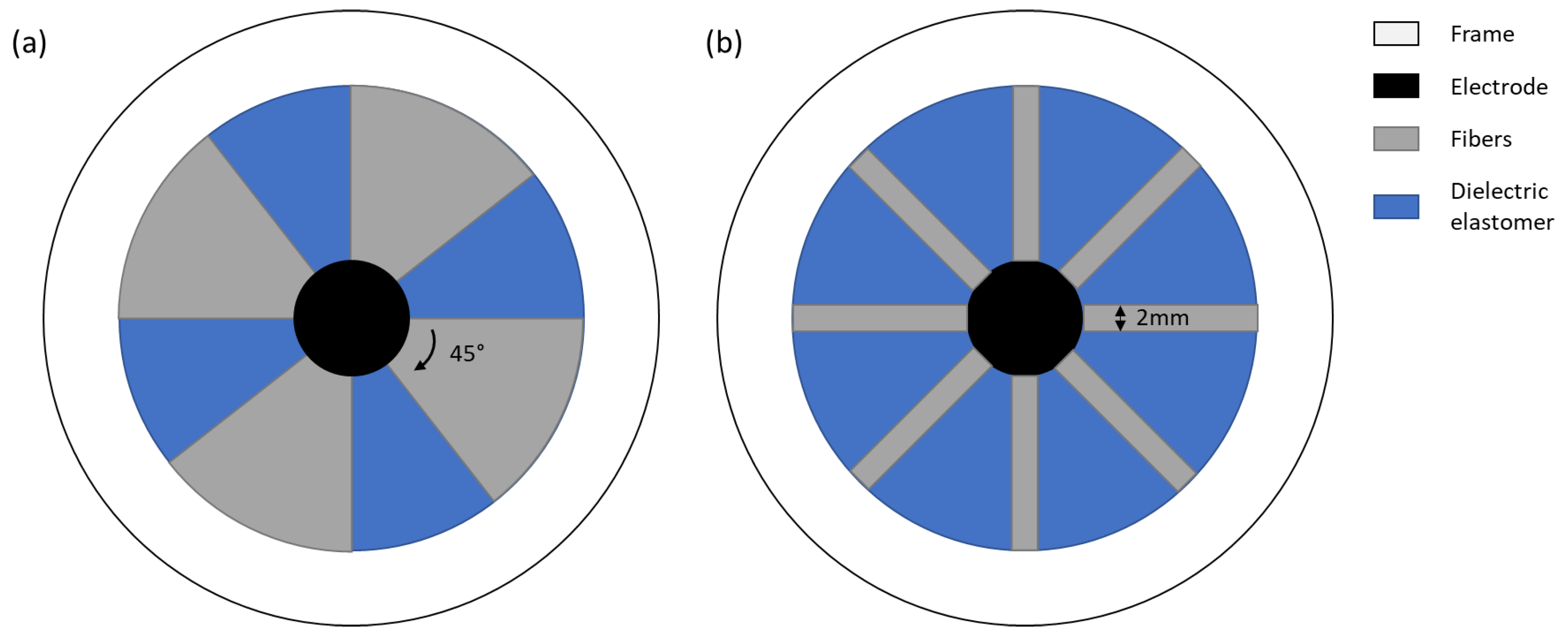
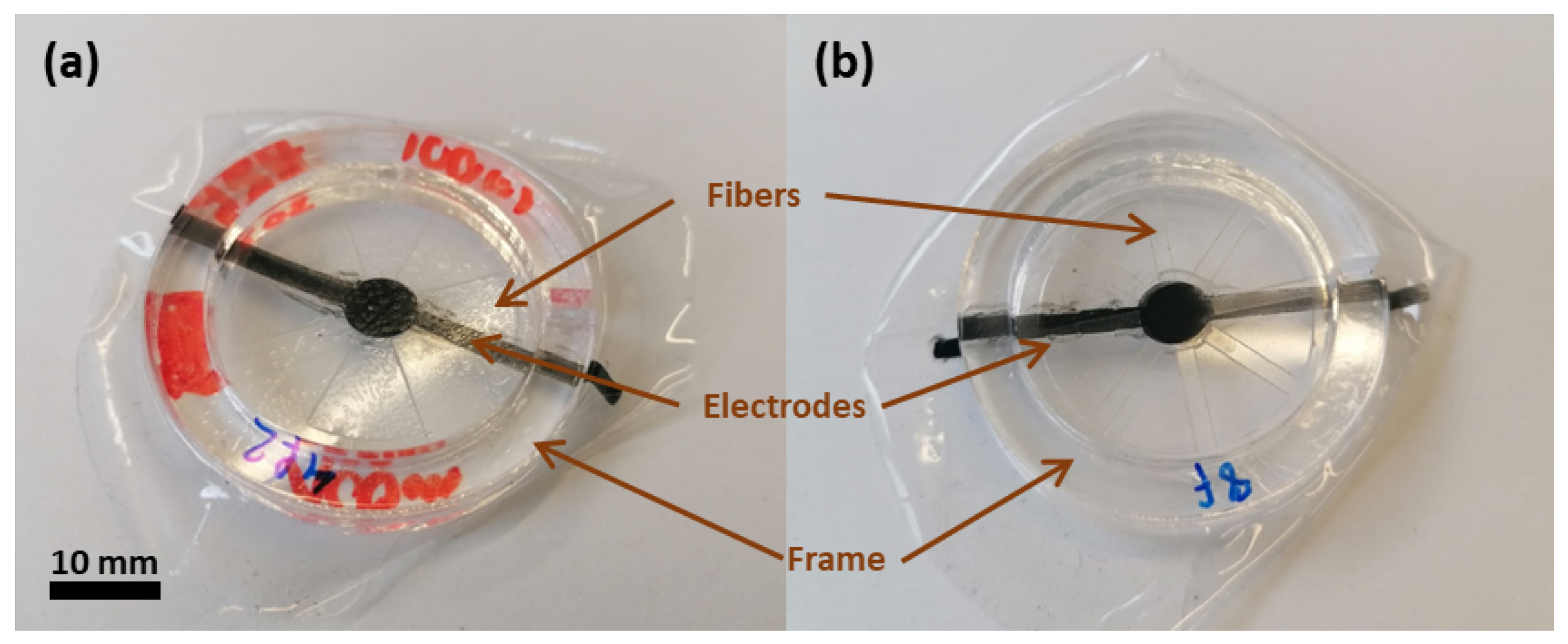
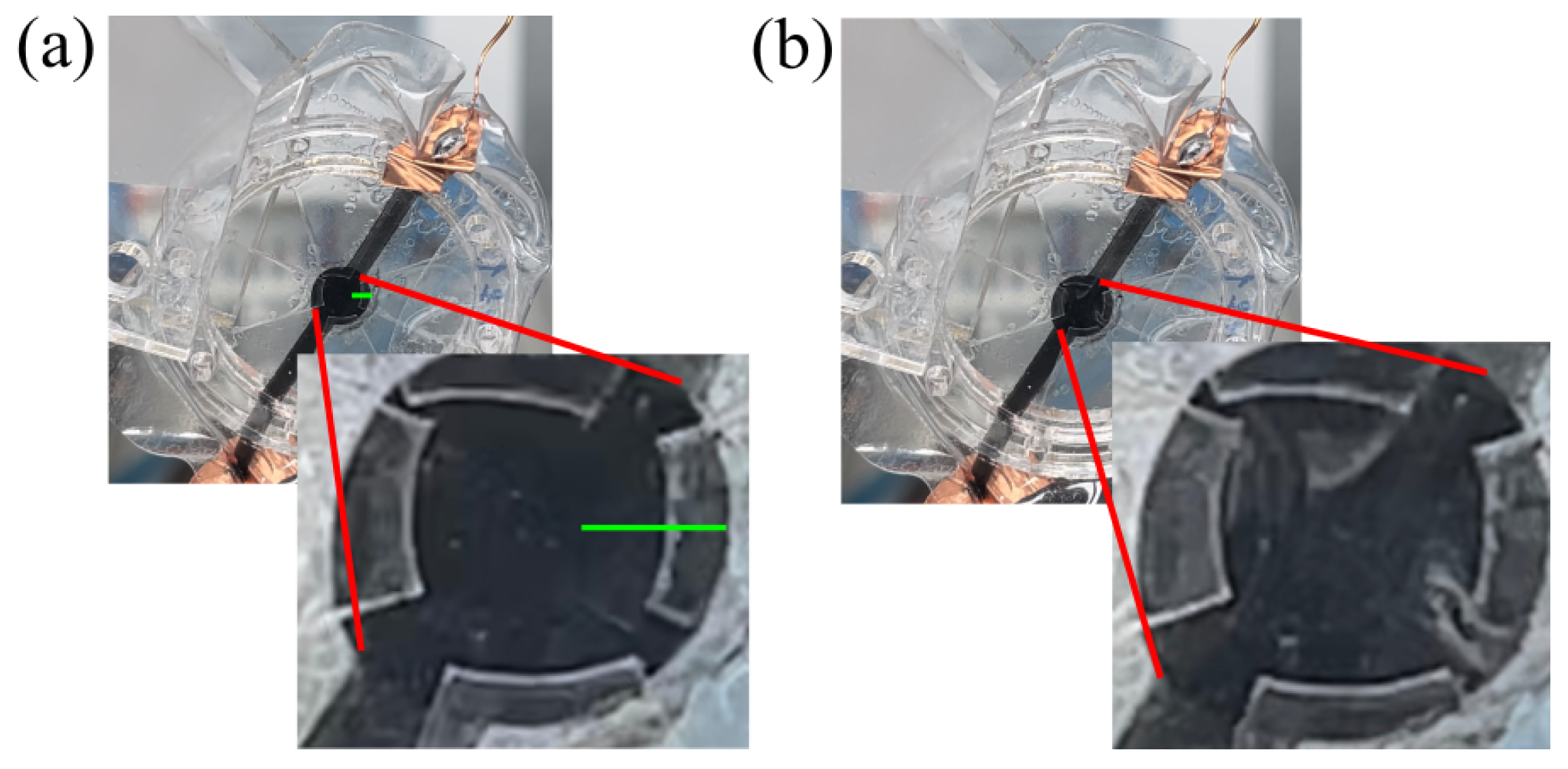
3.1. Design and Fabrication
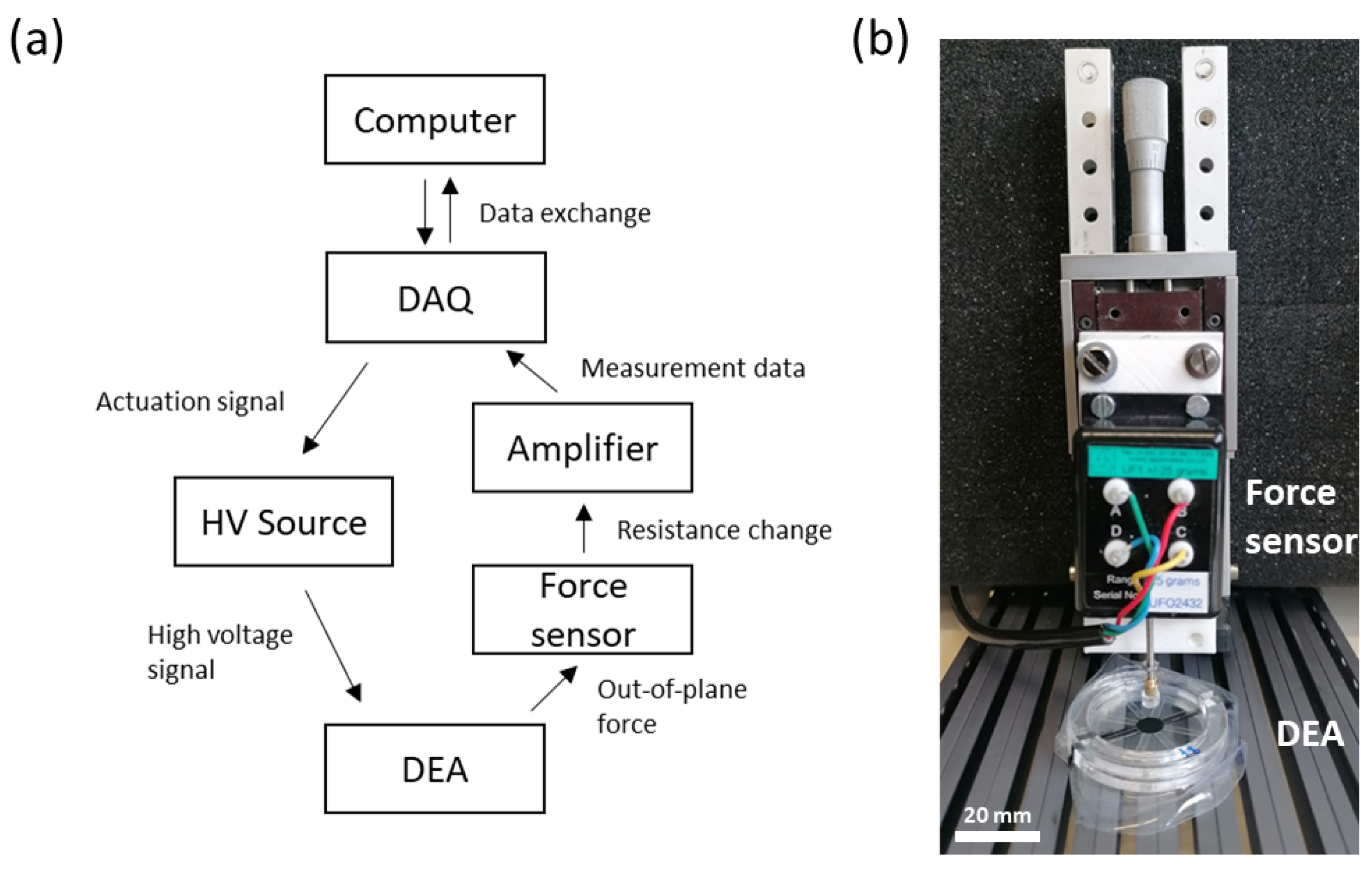
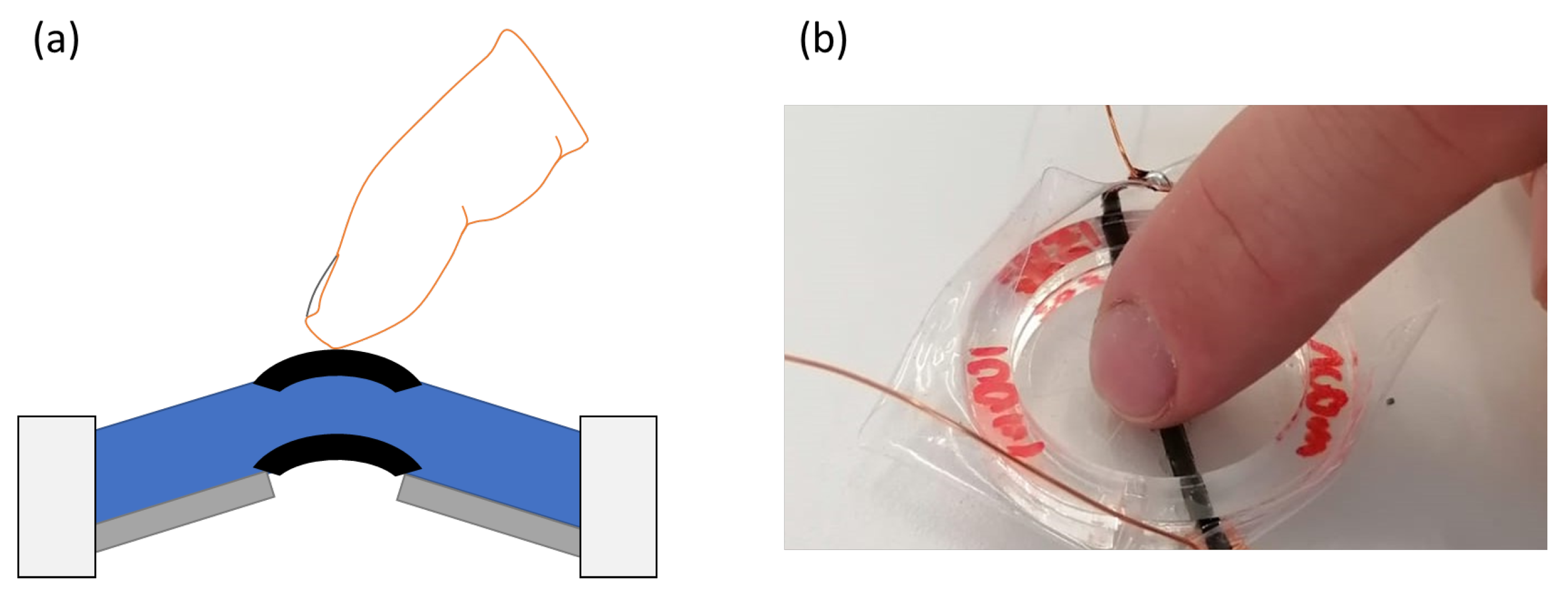
3.2. Setup and Characterization
4. Results
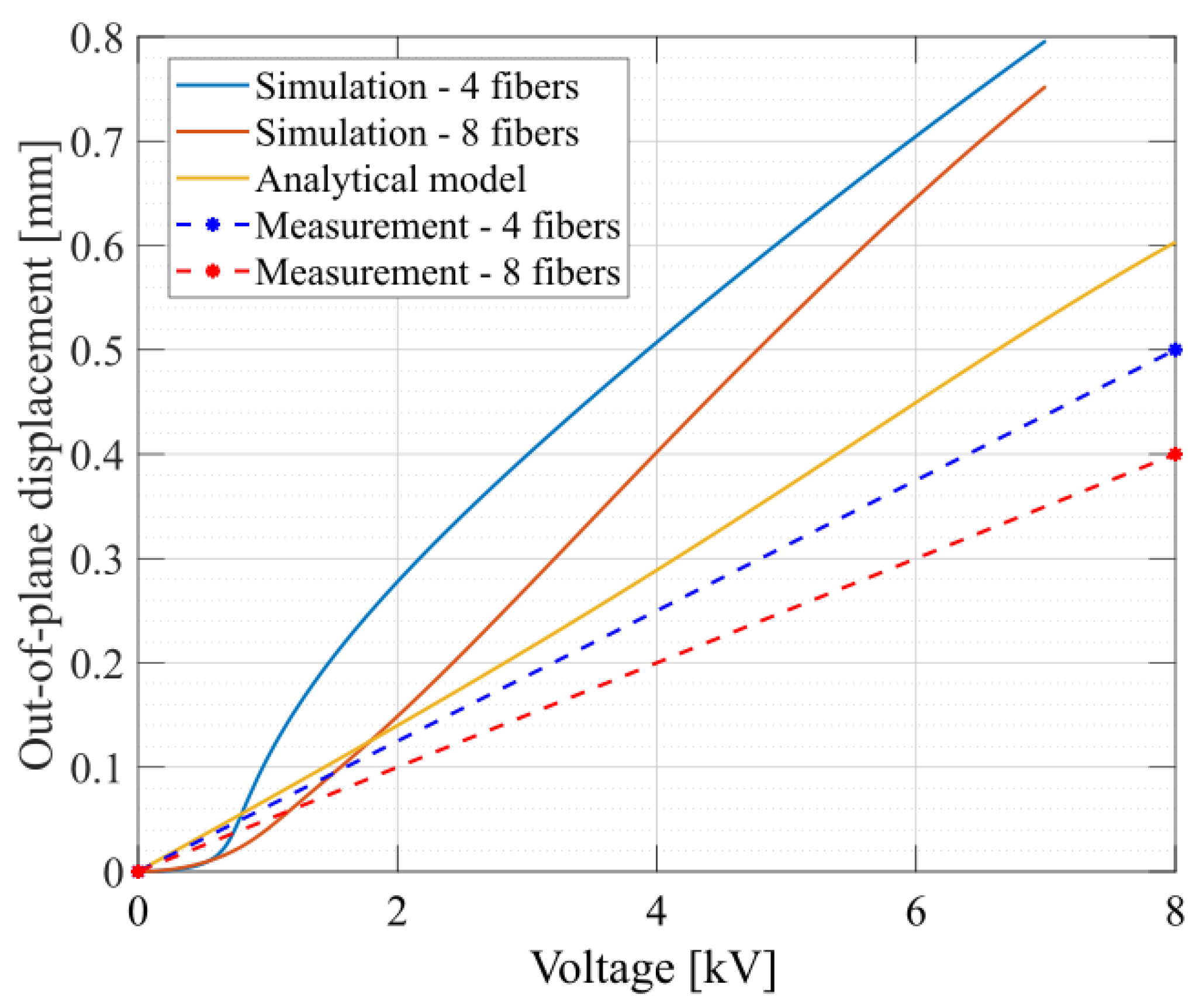
4.1. Simulation Results
4.2. Experiments
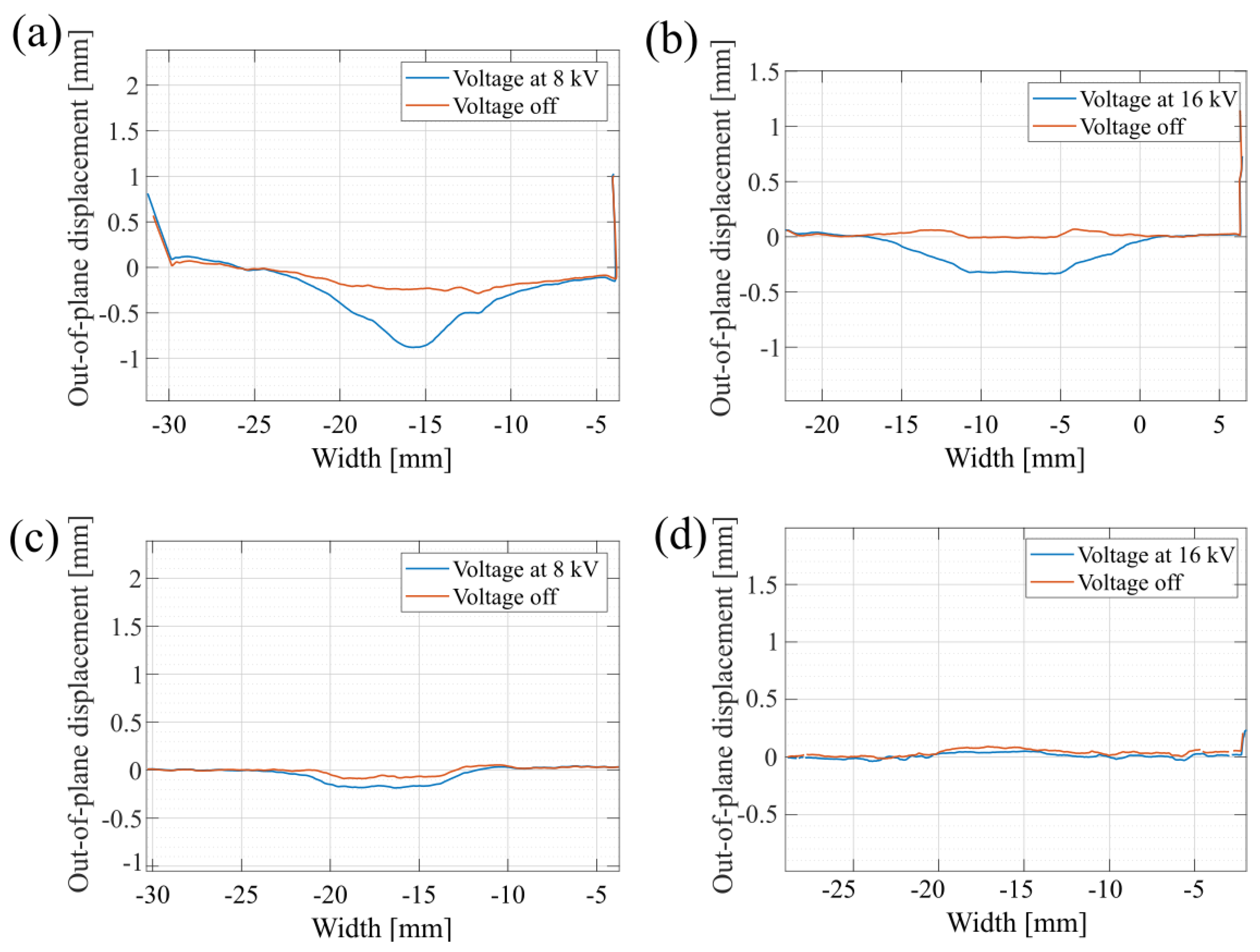
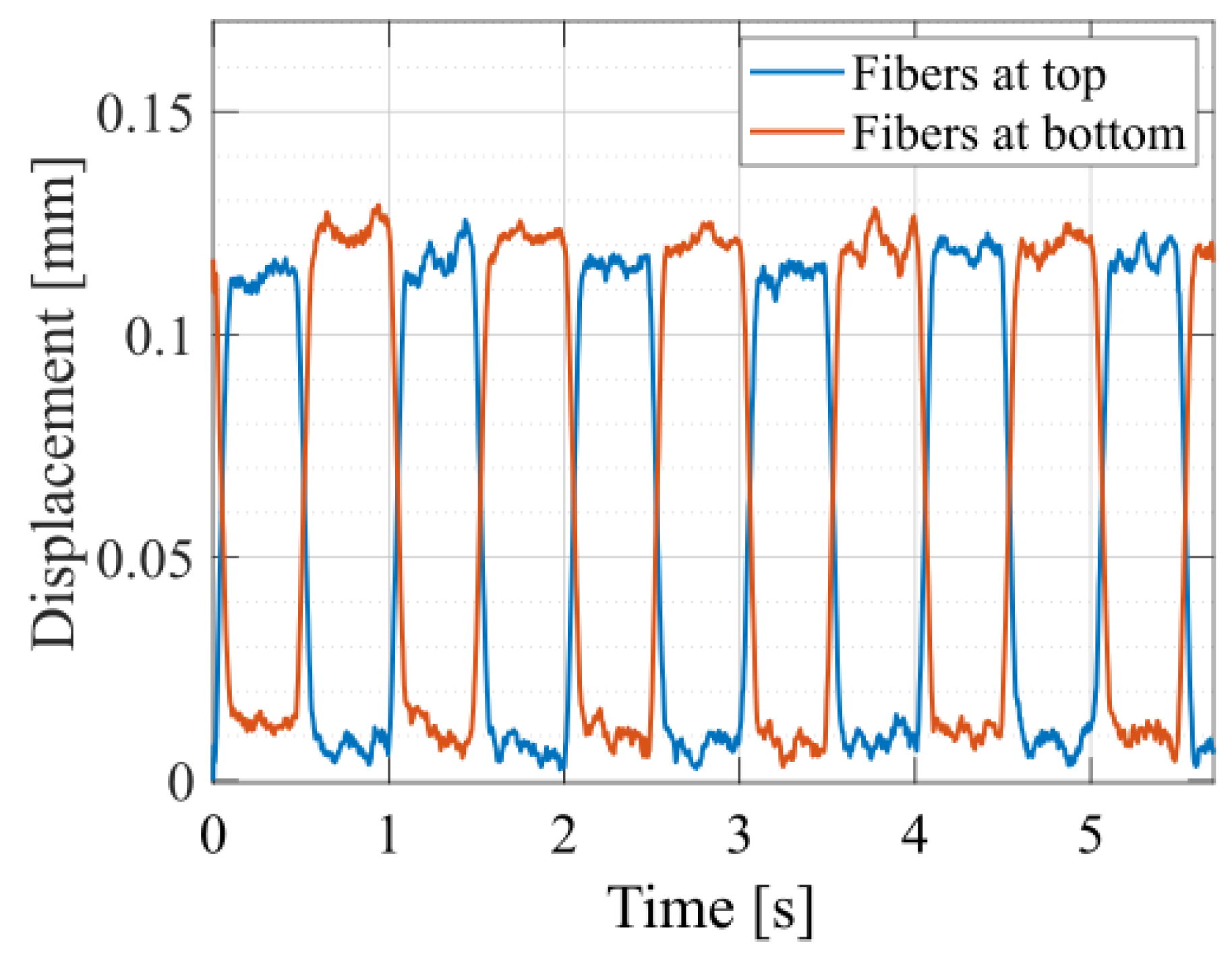
4.2.1. Out-of-Plane Displacement
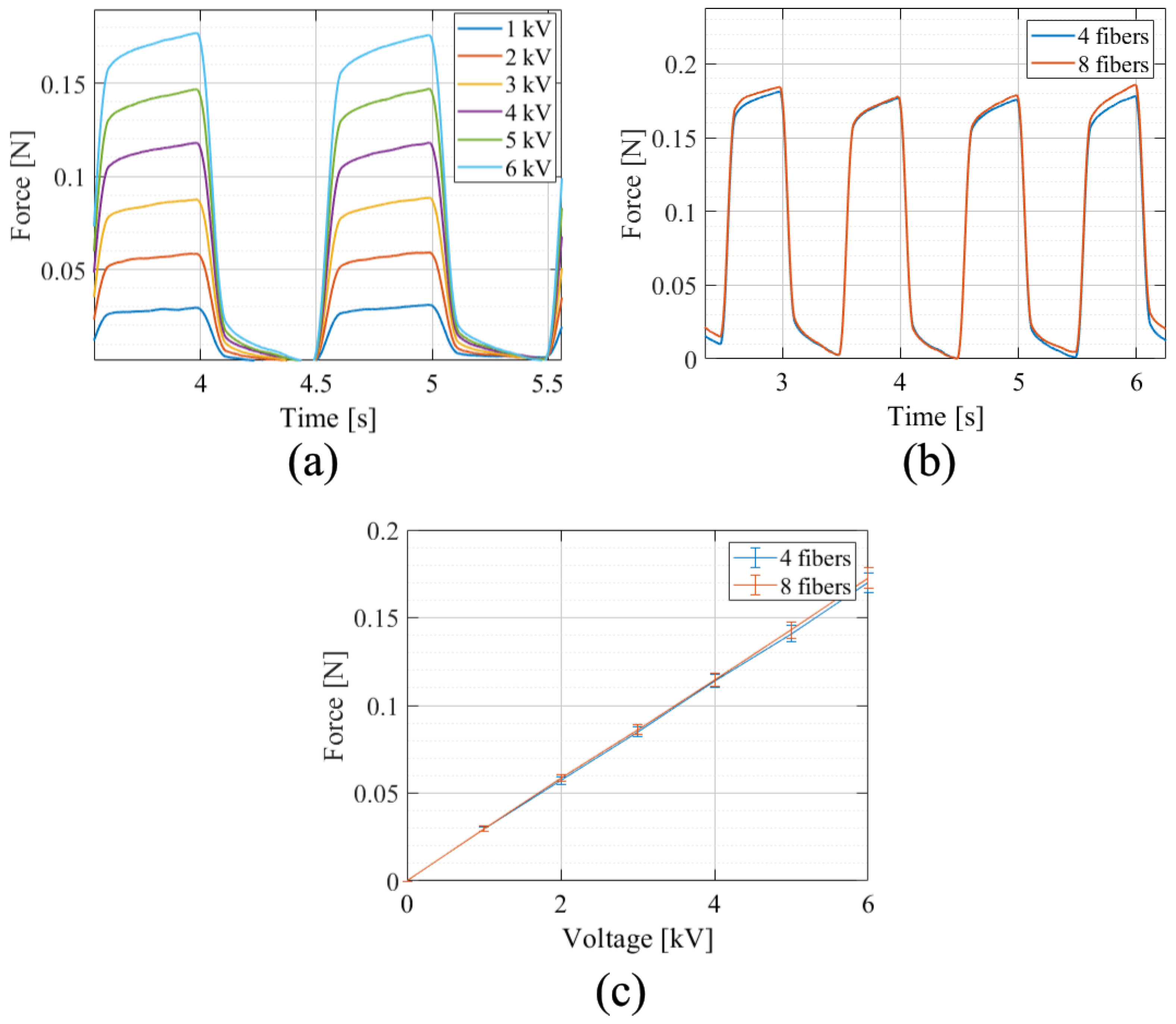
4.2.2. Out-of-Plane Force
5. Discussion
5.1. Analysis of Proposed Device
5.2. Possible Applications of FRDEAs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEA | Dielectric Elastomer Actuator |
| FR | Fiber-reinforced |
References
- Krishna, S.; Nagarajan, T.; Ahmad-Majdi, A.R. Review of Current Development of Pneumatic Artificial Muscle. J. Appl. Sci. 2011, 11, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidi, S.; Martinez, T.; Benouhiba, A.; Civet, Y.; Perriard, Y. Soft Actuators for Facial Reanimation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 11109–11114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sheng, J.; O’Neill, C.; Walsh, C.; Wood, R.; Ryu, J.H.; Desai, J.; Yip, M. Robotic Artificial Muscles: Current Progress and Future Perspectives. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2019, 35, 7611–7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Ghilardi, M.; Mamone, V.; Ferrari, V.; Busfield, J.J.C.; Ahluwalia, A.; Carpi, F. Bioreactor with Electrically Deformable Curved Membranes for Mechanical Stimulation of Cell Cultures. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, T.; Jahren, S.E.; Walter, A.; Chavanne, J.; Clavica, F.; Ferrari, L.; Heinisch, P.P.; Casoni, D.; Haeberlin, A.; Luedi, M.M.; et al. A novel soft cardiac assist device based on a dielectric elastomer augmented aorta: An in vivo study. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2022, 8, e10396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidi, S.; Imholz, C.; Martinez, T.; Benouhiba, A.; Walter, A.; Civet, Y.; Lindenblatt, N.; Perriard, Y. Real-time actuation of a dielectric elastomer actuator neuroprosthesis for facial paralysis. Smart Mater. Med. 2023, 5, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Liu, X.; Cacucciolo, V.; Civet, Y.; El Haitami, A.; Cantin, S.; Perriard, Y.; Shea, H. Untethered Feel-Through Haptics Using 18-µm Thick Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Jeong, S.H.; Cohen, A.J.; Vogt, D.M.; Kollosche, M.; Lansberry, G.; Mengüç, Y.; Israr, A.; Clarke, D.R.; Wood, R.J. A Wearable Textile-Embedded Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Haptic Display. Soft Robot. 2022, 9, 1186–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Cohen, Y. Electroactive Polymers as Artificial Muscles: A Review. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2002, 39, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tian, A.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Lau, H.Y.K. On the failure modes and maximum stretch of circular dielectric elastomer actuators. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 105701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbach, S.; Banda, R.M.; Croce, S.; Rizzello, G.; Naso, D.; Seelecke, S. Modeling and Design Optimization of a Rotational Soft Robotic System Driven by Double Cone Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Front. Robot. AI 2020, 6, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Dong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Tang, L.; Chen, X.; Yao, Z.; Cao, K. Self-healing High-performance dielectric elastomer actuator with novel Liquid-solid interpenetrating structure. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 149, 106519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareis, M.; Maas, J. Buckling Dielectric Elastomer Transducers as Loudspeakers. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2022, 70, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berselli, G.; Vertechy, R.; Vassura, G.; Parenti-Castelli, V. Optimal Synthesis of Conically Shaped Dielectric Elastomer Linear Actuators: Design Methodology and Experimental Validation. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2011, 16, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgins, M.; York, A.; Seelecke, S. Experimental comparison of bias elements for out-of-plane DEAP actuator system. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 094016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Conn, A. Performance Optimization of a Conical Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. Actuators 2018, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follador, M.; Cianchetti, M.; Mazzolai, B. Design of a compact bistable mechanism based on dielectric elastomer actuators. Meccanica 2015, 50, 2741–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaiser, I.; Schulz, S.; Breitwieser, H.; Bretthauer, G. Enhanced Flexible Fluidic actuators for biologically inspired lightweight robots with inherent compliance. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, ROBIO 2010, Tianjin, China, 14–18 December 2010; pp. 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, C.; Meng, L.; Chen, X.; Li, D.; Chen, H. A biologically inspired artificial muscle based on fiber-reinforced and electropneumatic dielectric elastomers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2017, 26, 085018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Huang, J.; Jordi, C.; Kovacs, G.; Huang, R.; Clarke, D.; Suo, Z. Dielectric elastomer actuators under equal-biaxial forces, uniaxial forces, and uniaxial constraint of stiff fibers. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 6167–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidi, S.; Martinez, T.; Tandon, B.; Civet, Y.; Perriard, Y. Uni-axial reinforced dielectric elastomer actuators with embedded 3D printed fibers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2023, 32, 125011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelrine, R.E.; Kornbluh, R.D.; Joseph, J.P. Electrostriction of polymer dielectrics with compliant electrodes as a means of actuation. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 1998, 64, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Pei, Q.; Joseph, J. High-Speed Electrically Actuated Elastomers with Strain Greater Than 100%. Science 2000, 287, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, Z. Theory of dielectric elastomers. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 2010, 23, 549–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenigsdorff, M.; Liebscher, H.; Osipov, P.; Mersch, J.; Gerlach, G. Influence of Active-to-Passive Ratio on the Deformation in Circular Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Micromachines 2024, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzapfel, G.A. Nonlinear Solid Mechanics—A Continuum Approach for Engineering, 1st ed.; Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; p. 456. [Google Scholar]
- Yeoh, O.H. Characterization of Elastic Properties of Carbon-Black-Filled Rubber Vulcanizates. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1990, 63, 792–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, S.; Walter, A.; Konstantinidi, S.; Martinez, T.; Civet, Y.; Perriard, Y. Carbon based printed electrodes for DEAs: Study of pad, inkjet, and stencil printing. In Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD) XXVI; Madden, J.D.W., Seelecke, S.S., Skov, A.L., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2024; Volume 12945, p. 129450U. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Mejia, C.; Favier, M.; Ren, X.; Germano, P.; Perriard, Y. Reinforcement Learning and Hardware in the Loop for Localized Vibrotactile Feedback in Haptic Surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Utrecht, The Netherlands, 15–18 September 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz-Kelly, S.; Holz, B.; Krüger, T.; Seelecke, S.; Rizzello, G.; Motzki, P.; Moretti, G. An Integrated Audio-Tactile Interface Based on Dielectric Elastomer Actuators for User Interaction. In Proceedings of the ASME 2023 Conference on Smart Materials, Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, Austin, TX, USA, 11–13 September 2023; p. V001T04A019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gescheider, S.B.A.; Hardick, K. The frequency selectivity of information-processing channels in the tactile sensory system. Somatosens. Mot. Res. 2001, 18, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzfeld, C.; Werthschützky, R. Mechanical Impedance as Coupling Parameter of Force and Deflection Perception: Experimental Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference, EuroHaptics 2012, Tampere, Finland, 13–15 June 2012; Isokoski, P., Springare, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, I.M.; Jung, K.; Koo, J.C.; Nam, J.D.; Lee, Y.K.; Choi, H.R. Development of Soft-Actuator-Based Wearable Tactile Display. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2008, 24, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.; Smith, L. A Simple Transversely Isotropic Hyperelastic Constitutive Model Suitable for Finite Element Analysis of Fiber Reinforced Elastomers. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2011, 133, 021021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Category | Subcategory | Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | PDMS | Relative permittivity | 2.8 | - |
| Density | 970 | kg/m3 | ||
| Yeoh coefficient C1 [25] Yeoh coefficient C2 [25] Yeoh coefficient C3 [25] | 178.4 −6.0 4.2 | kPa kPa kPa | ||
| PET | Relative permittivity | 2.9 | - | |
| Density | 1375 | kg/m3 | ||
| Young’s modulus | 2950 | MPa | ||
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.34 | - | ||
| Physics | Solid mechanics | Hyperelastic material | Yeoh model | |
| Prescribed displacement | 1.5 | |||
| Electrostatics | Ground | 0 | kV | |
| Electric potential | 0–6 | kV | ||
| Mesh | Size | Element size | coarser | |
| Generator | Free tetrahedral | |||
| Study | Step 1: Stationary | Add voltage swipe | 0–6 | kV |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Holzer, S.; Konstantinidi, S.; Koenigsdorff, M.; Martinez, T.; Civet, Y.; Gerlach, G.; Perriard, Y. Fiber-Reinforced Equibiaxial Dielectric Elastomer Actuator for Out-of-Plane Displacement. Materials 2024, 17, 3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153672
Holzer S, Konstantinidi S, Koenigsdorff M, Martinez T, Civet Y, Gerlach G, Perriard Y. Fiber-Reinforced Equibiaxial Dielectric Elastomer Actuator for Out-of-Plane Displacement. Materials. 2024; 17(15):3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153672
Chicago/Turabian StyleHolzer, Simon, Stefania Konstantinidi, Markus Koenigsdorff, Thomas Martinez, Yoan Civet, Gerald Gerlach, and Yves Perriard. 2024. "Fiber-Reinforced Equibiaxial Dielectric Elastomer Actuator for Out-of-Plane Displacement" Materials 17, no. 15: 3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153672
APA StyleHolzer, S., Konstantinidi, S., Koenigsdorff, M., Martinez, T., Civet, Y., Gerlach, G., & Perriard, Y. (2024). Fiber-Reinforced Equibiaxial Dielectric Elastomer Actuator for Out-of-Plane Displacement. Materials, 17(15), 3672. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17153672







