Relevant Aspects in the Mechanical and Aging Degradation of NiTi Alloy with R-Phase in Endodontic Files
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
- Protaper UltimateTM F2 008v (Denstply Sirona, Ballaigues, Switzerland). Diameter 2.5 mm and length of working 16.0 mm. (Protaper)
- F6 SkyTaper® files 25 mm. (Komet Lemgo, Nordrhein Westfalen, Germany). Diameter 2.5 mm and length of working 16.5 mm. (F6)
- Reciproc®. V040252025025. 25 mm, (VDW, Munchen, Germany). Diameter 2.5 mm and length of working 16.2 mm. (Reciproc)
- M-wire. Vortex Rotary Files. 25 mm (Dentsply Sirona, Johnson City, TN, USA). Diameter 2.5 mm and length of working 16.0 mm. (M-wire)
2.2. Calorimetric Tests
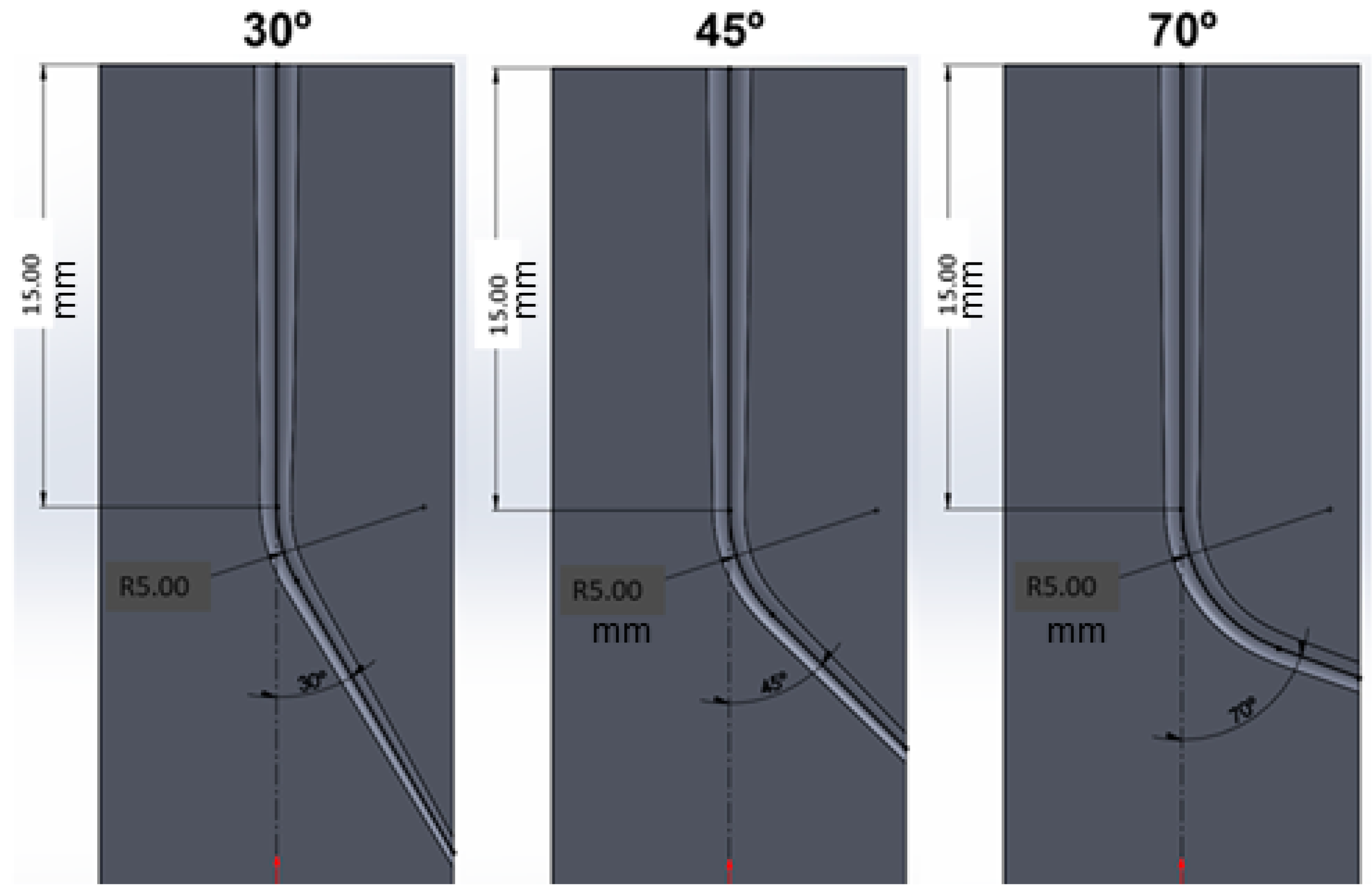
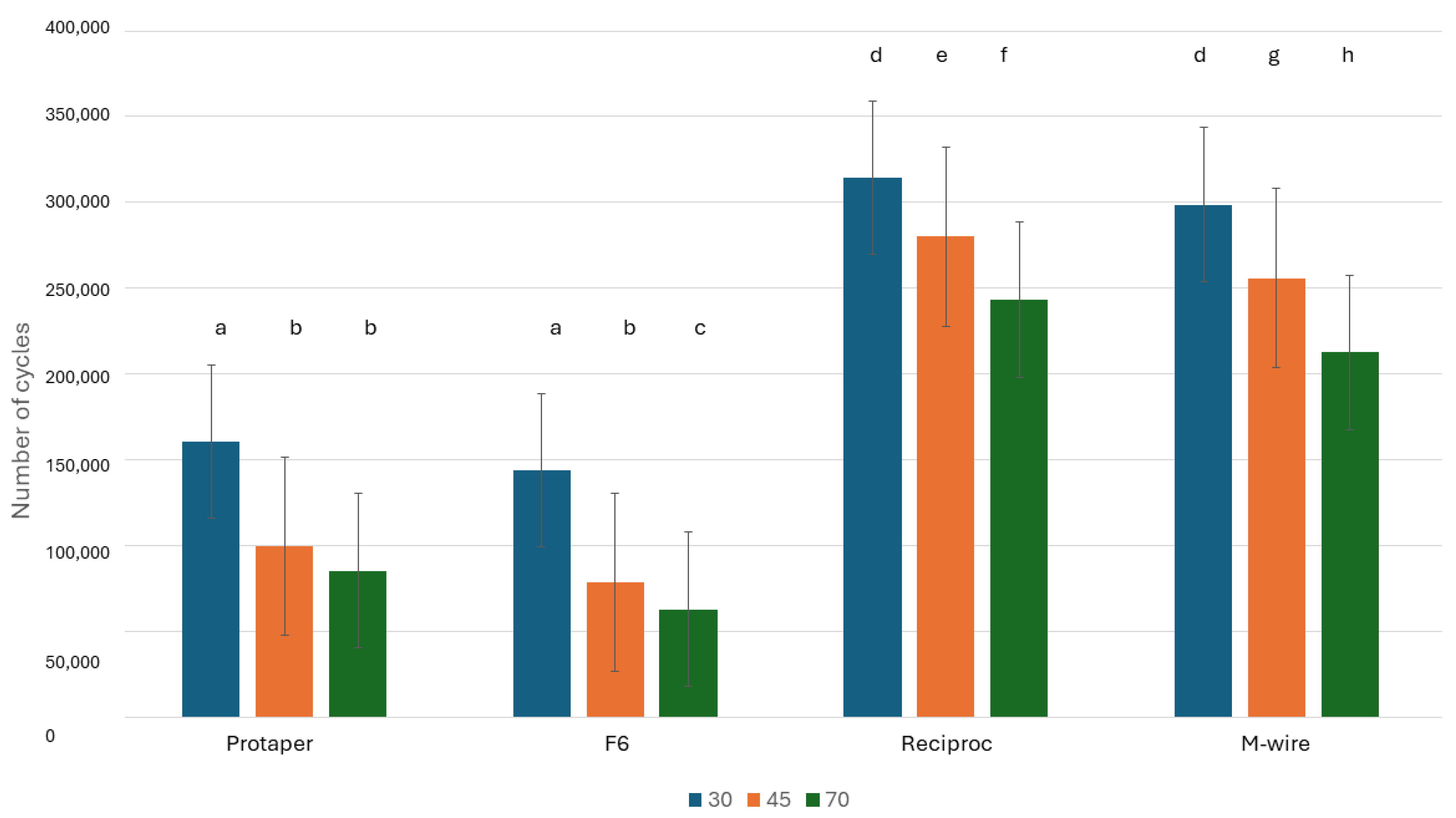
2.3. Mechanical Cycles
2.4. Aging Treatment
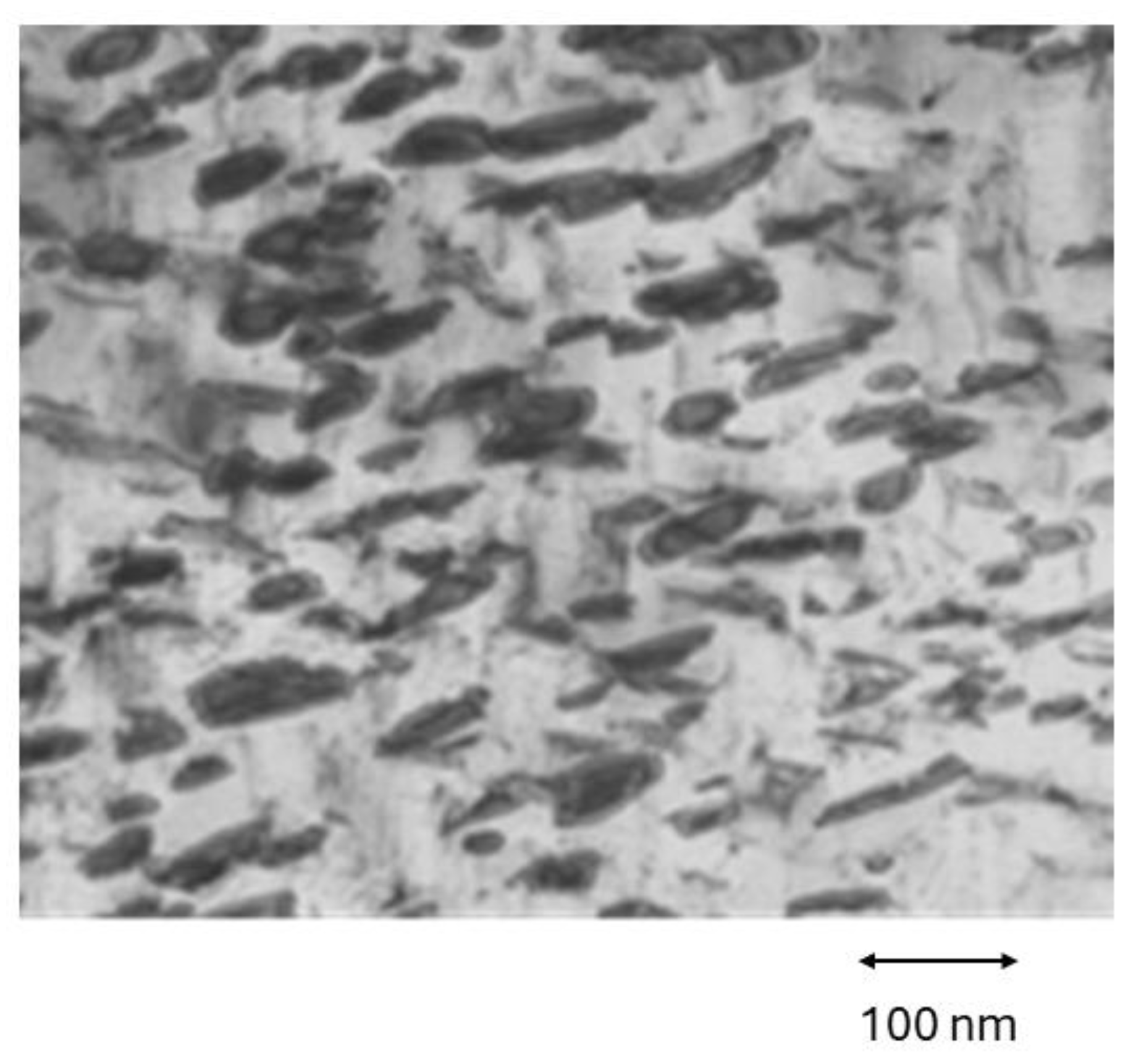
2.5. Preparation of the Samples for the Observation by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, X.; Liu, Y. Effect of annealing on the transformation behavior and superelasticity of NiTi shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, C.; de la Flor, S.; Ferrando, F. R-phase transformation in NiTi alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, A501, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, C.; de la Flor, S.; Ferrando, F. R-phase influence on different two-way shape memory training methods in NiTi shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 490, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Miyazaki, S. Effect of nano-scaled precipitates on shape memory behavior of Ti-50.9 at.% Ni alloy. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 4545–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Humbeeck, J. Shape memory alloys: A material and a technology. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2001, 3, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerig, T.W.; Melton, K.N.; Stöckel, D.W. Engineering Aspects of Shape Memory Alloys; Duering, T.W., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: London, UK, 2013; pp. 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Song, J.; Huang, C.; Xia, B.; Chen, B.; Sun, X.; Xie, C. Microstructures evolution and phase transformation behaviors of Ni-rich TiNi shape memory alloys after equal channel angular extrusion. J. Alloys Comp. 2011, 509, 3006–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Schryvers, D.; Van Humbeeck, J. Grain growth and precipitation in an annealed cold-rolled Ni50.2Ti49.8 alloy. Intermetallics 2007, 15, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiang, F.; Li, L.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y. Effect of ageing treatment on the transformation behaviour of Ti–50.9 at.% Ni alloy. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomozawa, M.; Kim, H.Y.; Miyazaki, S. Microactuators using R-phase transformation of sputter-deposited Ti-47.3 Ni shape memory alloy thin films. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2006, 17, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.L. Evaluation of Nitinol for Use as a Material in the Construction of Orthopaedic Implants; DAMD 17-74-C-4041; US Army Medical Research and Development Command: Frederick, MD, USA, 1997; pp. 306–315. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, F.; Mogi, M.; Ohura, Y.; Hamanaka, H. The super-elastic property of the Japanese NiTi alloy wire for use in orthodontics. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 1986, 90, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.X.; Manero, J.M.; Planell, J.A. Relevant aspects in the clinical applications of NiTi shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1996, 7, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Qian, W.; Abtin, H.; Gao, Y.; Haapasalo, M. Fatigue Testing of Controlled Memory Wire Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, S.E.D.M.; Nagy, M.M.; Schafer, E. Comparative evaluation of the shaping ability of ProTaper Next, iRaCe and Hyflex CM rotary NiTi files in severely curved root canals. Int. Endod. J. 2015, 48, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.X.; Rodríguez, D.; Planell, J.A. Grain growth kinetics of pure titanium. Scr. Met. Mat. 1995, 33, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciniegas, M.; Aparicio, C.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J. Low elastic modulus metals for joint prosthesis: Tantalum and nickel–titanium foams. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 27, 3391–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, F.J.; Fernández, E.; Manero, J.M.; Planell, J.A.; Sabrià, J.; Cortada, M.; Giner, L. A study of load cycling in a NiTi alloy with superelastic behaviour used in dental prosthetic fixators. Biomed. Mat. Eng. 1996, 6, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, P.; Vidi, B.; Mena-Alvarez, J.; Gil, J.; Rico, C.; Aragoneses, J.M. Effect of Stabilized Martensite on the Long-Term Performance of Superelastic NiTi Endodontic Files. Materials 2023, 16, 4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, F.J.; Planell, J.A. Thermal cycling and ageing effects in NiTi shape memory alloys used in biomedical applications. J. Biomech. 1998, 1001, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Duerig, T.W.; Bhattacharya, K. The influence of the R-phase on the superelastic behavior of NiTi. Shape Mem. Superelasticity 2015, 1, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.N.R.; Silva, E.J.N.L.; Marques, D.; Belladonna, F.; Simões-Carvalho, M.; Vieira, V.T.L.; Antunes, H.S.; Fernandes, F.M.B.; Versiani, M.A. Design, metallurgical features, mechanical performance and canal preparation of six reciprocating instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2021, 54, 1623–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, K.; Schryvers, D.; Verlinden, B.; Van Humbeeck, J. R-phase transition and related mechanical properties controlled by low-temperature aging treatment in a Ti–50.8 at. % Ni thin wire. Scr. Mate. 2014, 72, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbricht, J.; Yawny, A.; Pelegrina, J.L.; Eggeler, G.; Yardley, V.A. Characteristics of the stress-induced formation of R-phase in ultrafine-grained NiTi shape memory wire. J. All.Comp. 2013, 579, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirry, W.; Schryvers, D. Quantitative determination of strain fields around Ni4Ti3 precipitates in NiTi. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciniegas, M.; Casals, J.; Manero, J.M.; Peña, J.; Gil, F.J. Study of hardness and wear behaviour of NiTi shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 460, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Manzanares-Céspedes, M.C.; Sevilla, P.; Nart, J.; Manzanares, N.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Boyd, S.K.; Rodríguez, D. Evaluation of bone loss in antibacterial coated dental implants: An experimental study in dogs. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 69, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.T.; Duarte, M.A.H.; de Almeida, M.M.; de Andrade, F.B.; Bernardineli, N. Efficacy of CM-Wire, M-Wire, and Nickel-Titanium Instruments for Removing Filling Material from Curved Root Canals: A Micro–Computed Tomography Study. J. Endod. 2016, 42, 1651–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, E.S.; Peixoto, I.F.; Viana, A.C. Physical and mechanical properties of a thermomechanically treated NiTi wire used in the manufacture of rotary endodontic instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2012, 45, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prati, C.; Foschi, F.; Nucci, C.; Montebugnoli, L.; Marchionni, S. Appearance of the root canal walls after preparation with NiTi rotary instruments: A comparative SEM investigation. Clin. Oral Investig. 2004, 8, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prati, C.; Tribst, J.P.M.; Dal Piva, A.M.d.O.; Borges, A.L.S.; Ventre, M.; Zamparini, F.; Ausiello, P. 3D Finite Element Analysis of Rotary Instruments in Root Canal Dentine with Different Elastic Moduli. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Lde, A.; Resende, P.D.; Bahia, M.G.; Buono, V.T. Effects of R-Phase on Mechanical Responses of a Nickel-Titanium Endodontic Instrument: Structural Characterization and Finite Element Analysis. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 7617493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Guillem-Marti, J.; Sevilla, P.; Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Rodriguez, D. Anhydride-functional silane immobilized onto titanium surfaces induces osteoblast cell differentiation and reduces bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 59, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manero, J.M.; Gil, F.J.; Padrós, E.; Planell, J.A. Applications of environmental scanning electron microscopy (ESEM) in biomaterials field. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 61, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goo, E.; Sinclair, R. The B2 to R transformation in Ti50Ni47Fe3 and Ti49.5Ni50.5 alloys. Acta Metall. 1985, 33, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbricht, J.; Yawny, A.; Pelegrina, J.L.; Dlouhy, A.; Eggeler, G. On the stress-induced formation of R-phase in ultra-fine-grained Ni-rich NiTi shape memory alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 2556–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Liu, Y.; Miyazaki, S. Ageing-induced two-stage R-phase transformation in Ti–50.9 at. % Ni. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.K.; Lin, H.C.; Yen, Y.C.; Chen, J.C. Wire drawing conducted in the R-phase of TiNi shape memory alloys. Mater. Lett. 2000, 46, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Humbeeck, J.; Kustov, S. Active and passive damping of noise and vibrations through shape memory alloys: Applications and mechanisms. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 14, S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schryvers, D.; Tirry, W.; Yang, Z.Q. Measuring strain fields and concentration gradients around Ni4Ti3 precipitates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiqing, Y.; Schryvers, D. Study of changes in composition and EELS ionization edges upon Ni4Ti3 precipitation in a NiTi alloy. Micron 2006, 37, 503–507. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.B.; Amin Ahmadi, B.; Schryvers, D.; Verlinden, B.; Van Humbeeck, J. Effect of annealing on the transformation behavior and mechanical properties of two nanostructured Ti-50.8 at. % Ni thin wires produced by different methods. Mater. Sci. Forum 2013, 738, 306–310. [Google Scholar]
- Espinar, E.; Llamas, J.M.; Michiardi, A.; Ginebra, M.P.; Gil, F.J. Reduction of Ni release and improvement of the friction behaviour of NiTi orthodontic archwires by oxidation treatments. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briceño, J.; Romeu, A.; Espinar, E.; Llamas, J.M.; Gil, F.J. Influence of the microstructure on electrochemical corrosion and nickel release in NiTi orthodontic archwires. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 4989–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, F.J.; Solano, E.; Peña, J.; Engel, E.; Mendoza, A.; Planell, J.A. Microstructural, mechanical and citotoxicity evaluation of different NiTi and NiTiCu shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2004, 15, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villani, F.A.; Zamparini, F.; Spinelli, A.; Aiuto, R.; Prati, C. Apical debris extrusion and potential risk of endodontic flare-up: Correlation with rotating and reciprocating instruments used in daily clinical practice. Guárnale Ital. Endod. 2024, 38, 301–310. [Google Scholar]
- Nouri, H.; Amini, K.; Jahromi, M.Z. Comparison of full rotation and reciprocating movements in regaining apical patency during endodontic retreatment. Dent. Res. J. 2021, 18, 85. [Google Scholar]
- Berutti, E.; Paolino, D.S.; Chiandussi, G.; Alovisi, M.; Cantatore, G.; Castellucci, A. Root canal anatomy preservation of WaveOne reciprocating files with or without glide path. J. Endod. 2012, 38, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, A.; Prati, C.; Schiavon, R.; Fitzgibbon, R.M.; Pirani, C.; Iacono, F.; Pelliccioni, G.A.; Spinelli, A.; Zamparini, F.; Puddu, P.; et al. In-Depth Metallurgical and Microstructural Analysis of Oneshape and Heat Treated Onecurve Instruments. Eur. Endod. J. 2021, 6, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

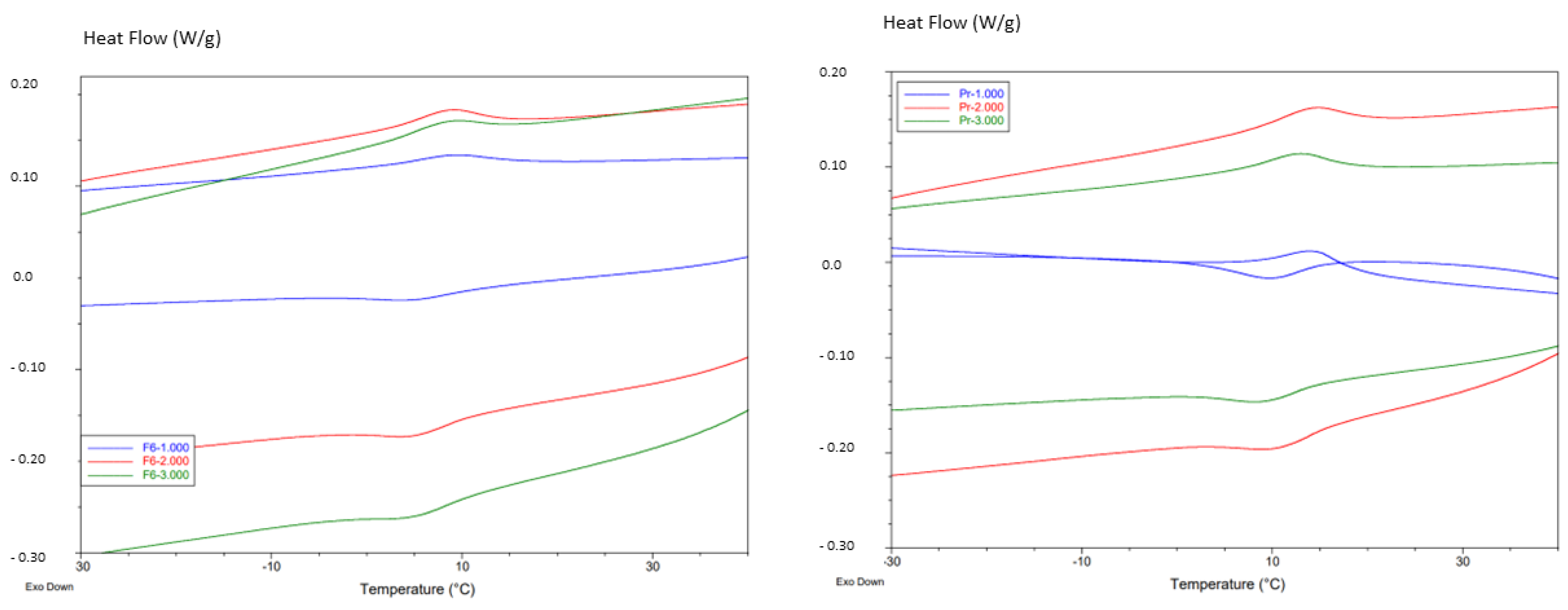
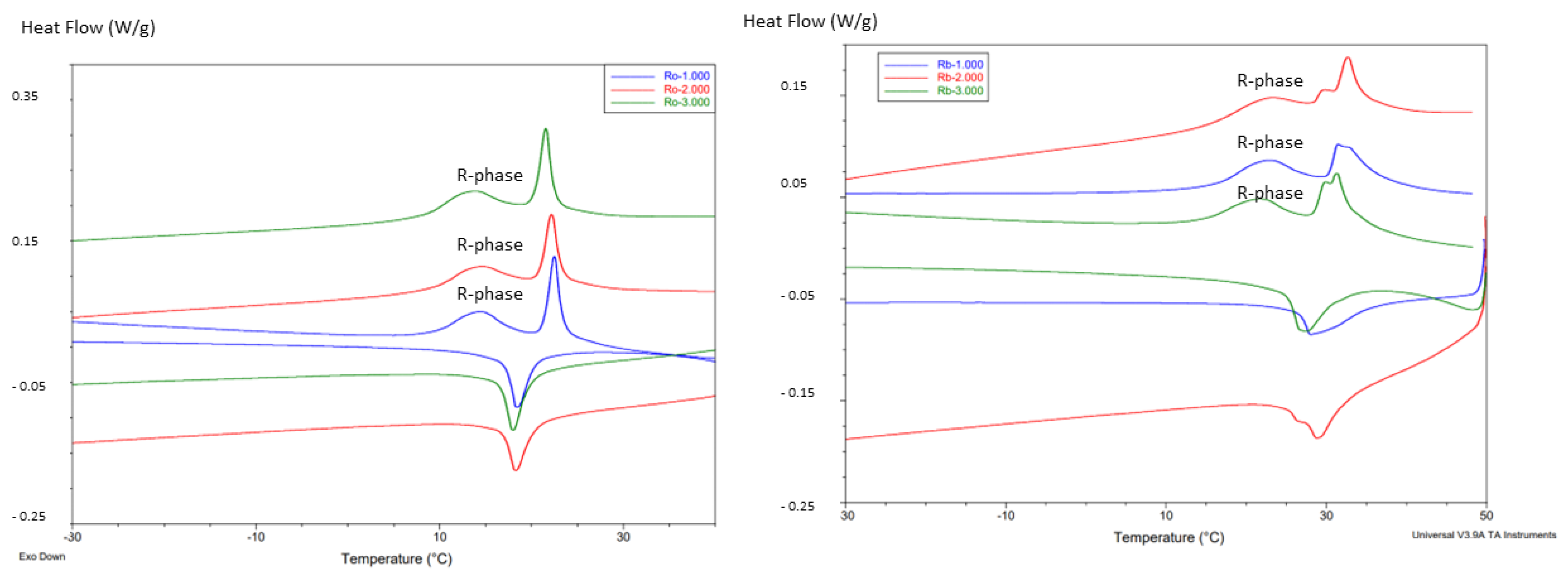
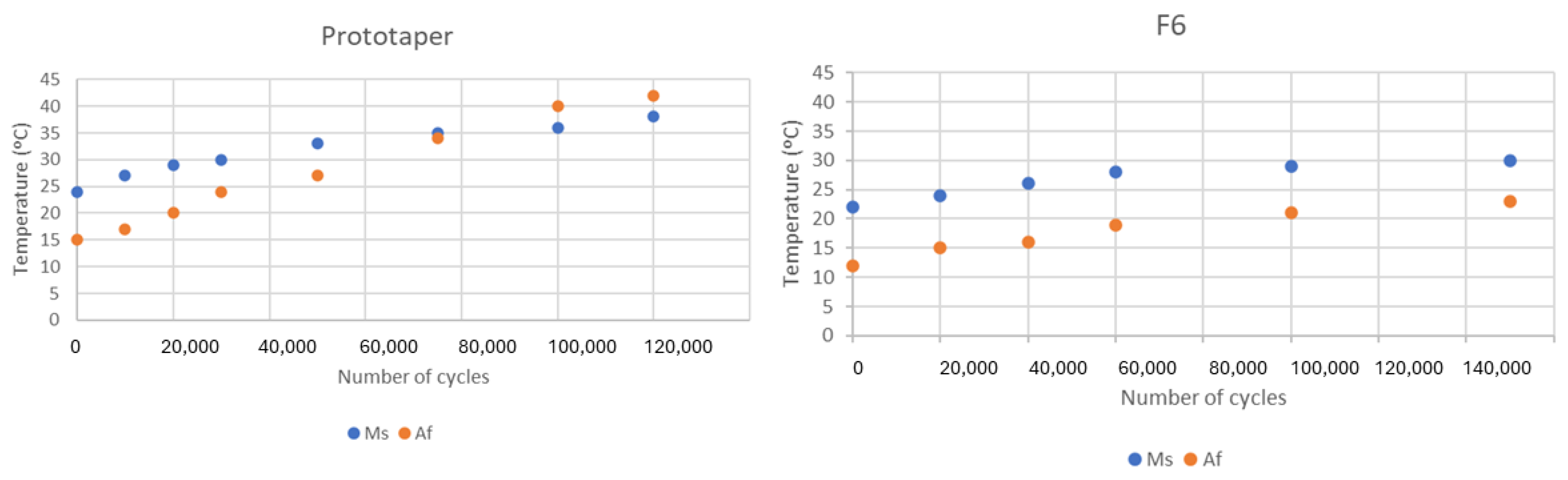




| Endodontic File | Ms | Mf | As | Af | Rs | Rf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protaper | 24 ± 3 | 15 ± 1 | 3 ± 4 | 34 ± 3 | - | - |
| F6 | 22 ± 4 | 12 ± 2 | −4 ± 3 | 30 ± 2 | - | - |
| Reciproc | 36 ± 5 | 35 ± 3 | 25 ± 5 | 40 ± 7 | 20 ± 2 | 29 ± 4 |
| M-wire | 25 ± 4 | 22 ± 2 | 15 ± 4 | 29 ± 6 | 10 ± 3 | 18 ± 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez, P.; Vidi, B.; Rico, C.; Mena-Alvarez, J.; Gil, J.; Aragoneses, J.M. Relevant Aspects in the Mechanical and Aging Degradation of NiTi Alloy with R-Phase in Endodontic Files. Materials 2024, 17, 3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133351
Sánchez P, Vidi B, Rico C, Mena-Alvarez J, Gil J, Aragoneses JM. Relevant Aspects in the Mechanical and Aging Degradation of NiTi Alloy with R-Phase in Endodontic Files. Materials. 2024; 17(13):3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133351
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez, Patricia, Benedetta Vidi, Cristina Rico, Jesús Mena-Alvarez, Javier Gil, and Juan Manuel Aragoneses. 2024. "Relevant Aspects in the Mechanical and Aging Degradation of NiTi Alloy with R-Phase in Endodontic Files" Materials 17, no. 13: 3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133351
APA StyleSánchez, P., Vidi, B., Rico, C., Mena-Alvarez, J., Gil, J., & Aragoneses, J. M. (2024). Relevant Aspects in the Mechanical and Aging Degradation of NiTi Alloy with R-Phase in Endodontic Files. Materials, 17(13), 3351. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133351








