The Effect of Silanized Halloysite Nanotubes on the Structure of Polyethylene–Based Composite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
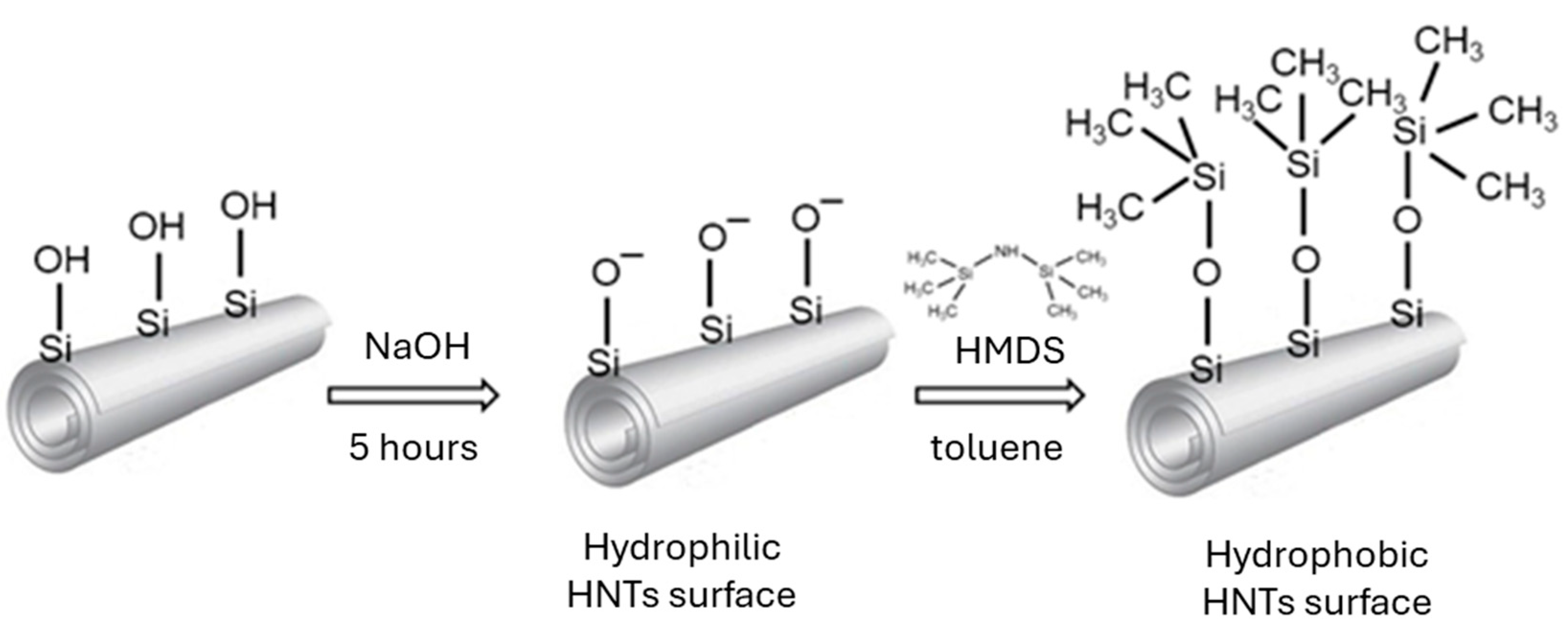
2.2. HNTs Modification
2.2.1. Alkali Treatment
2.2.2. Modification of HNTs by Hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS)
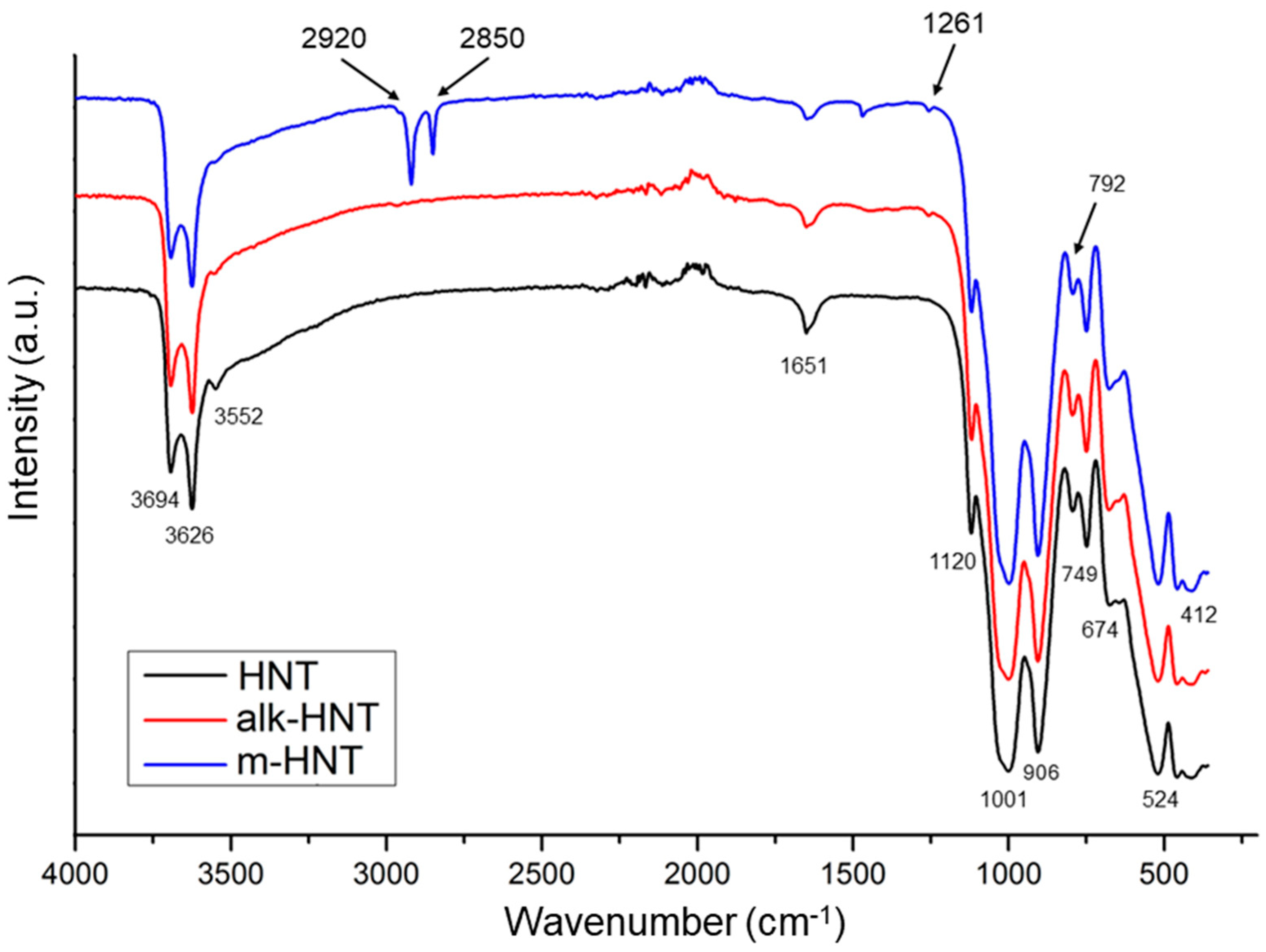
2.3. Characterization Methods of HNTs and Modified HNTs
2.4. Preparation of HDPE/HNT, HDPE/alk–HNT, HDPE/m–HNT Composites
2.5. Testing Methods of HDPE/HNTs Composites
3. Results
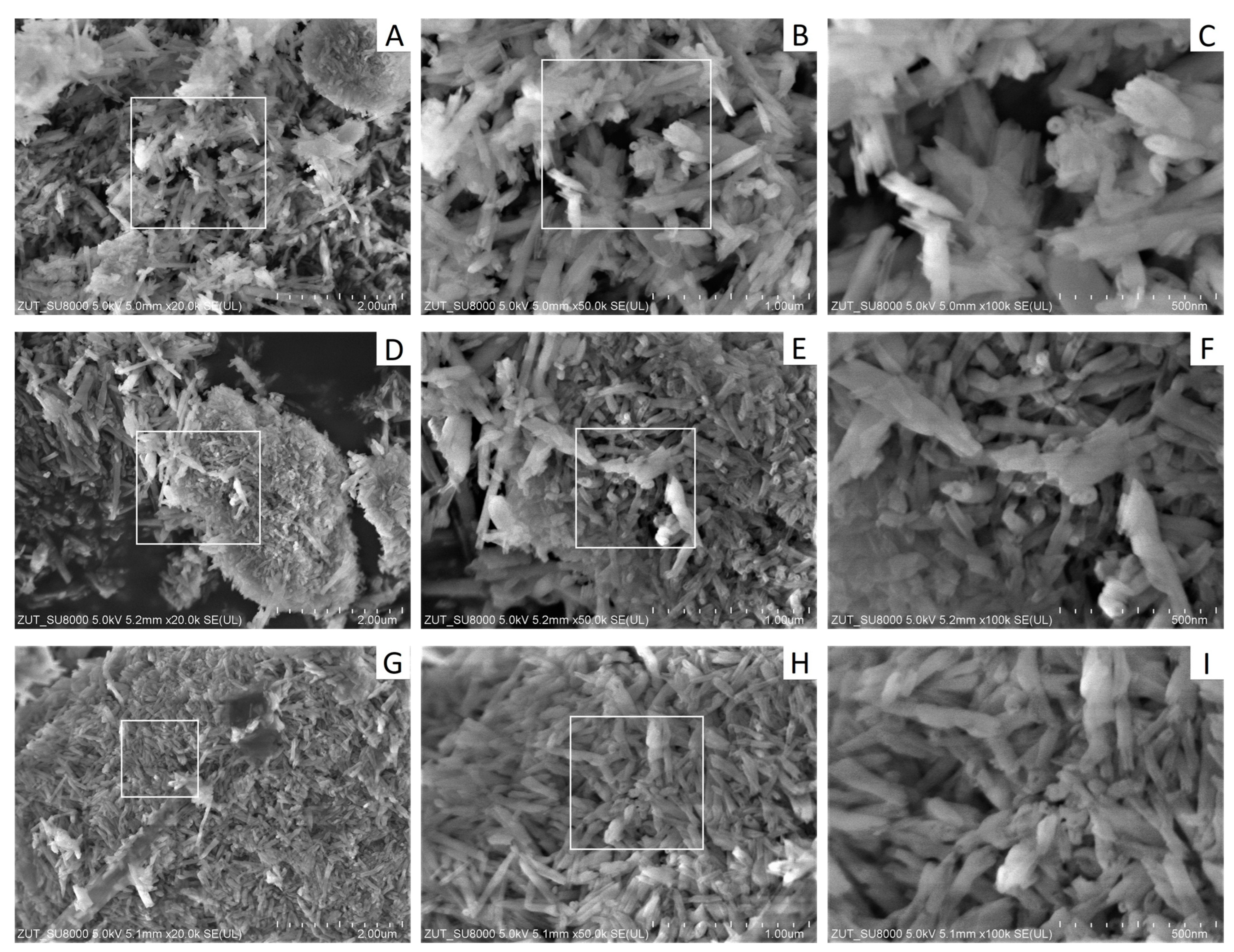
3.1. Effects of Halloysite Modification
3.2. Properties of HDPE/Halloysite Composites
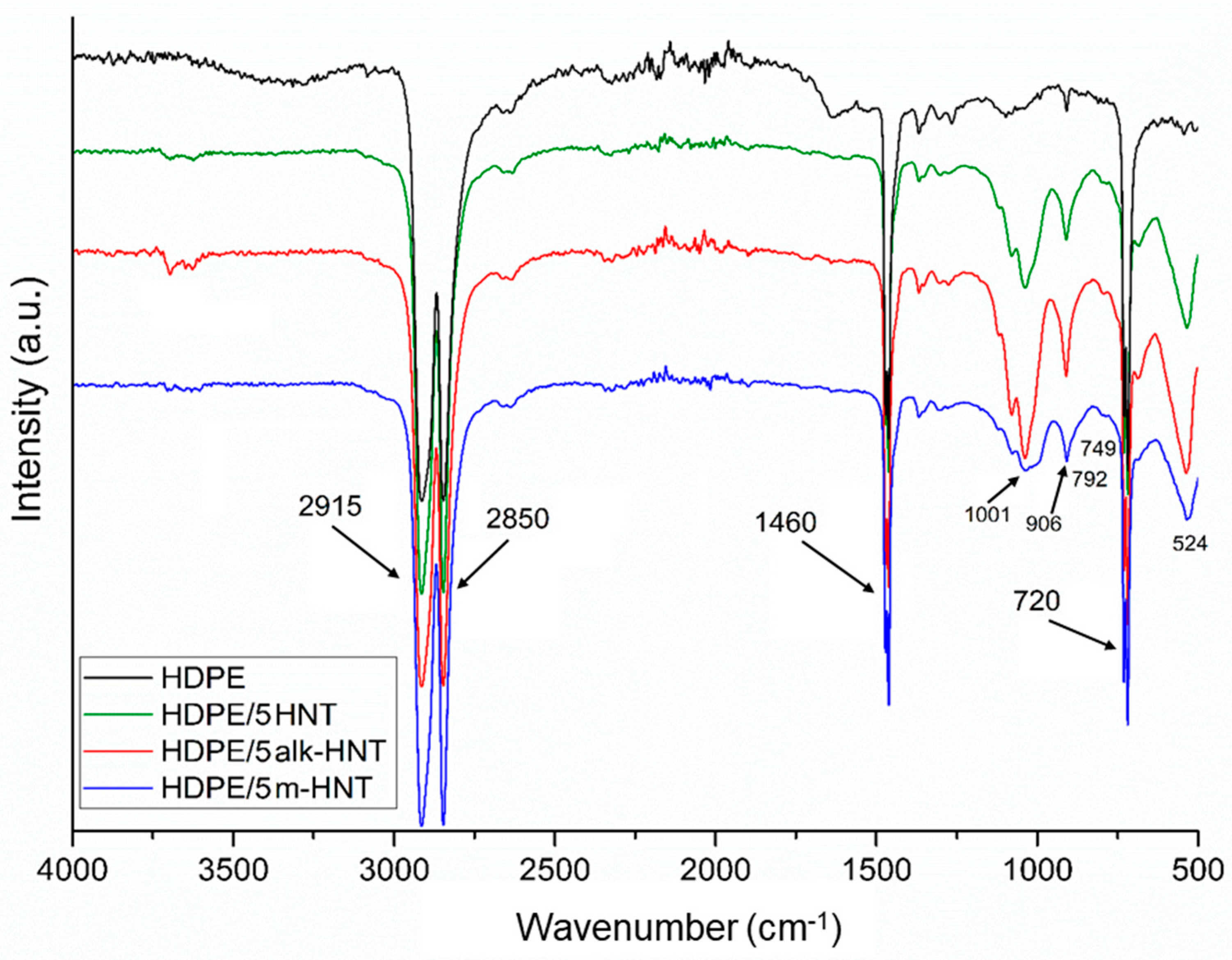
3.2.1. Structure of HDPE/HNTs Composites
3.2.2. Thermal Properties of HDPE/HNTs Composites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plastic Europe. Plastics—The Fast Facts 2023. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/resources/publications/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Zhang, J.; Hirschberg, V.; Goecke, A.; Wilhelm, M.; Yu, W.; Orfgen, M.; Rodrigue, D. Effect of Mechanical Recycling on Molecular Structure and Rheological Properties of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE). Polymer 2024, 297, 126866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.; Ravekar, V.; Rama Rao, P.; Waigokar, S.; Hingankar, S. Recycling of Waste HDPE and PP Plastic in Preparation of Plastic Brick and Its Mechanical Properties. Clean. Mater. 2022, 5, 100113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthpalani, P.G.I.; Premachandra, J.K.; De Silva, D.S.M.; Weerasinghe, V.P.A. Pyrolysis as a Value Added Method for Plastic Waste Management: A Review on Converting LDPE and HDPE Waste into Fuel. Ceylon J. Sci. 2023, 52, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güney, O.; Bilici, İ.; Doğan, D.; Metin, A.Ü. Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Recycled Polyethylene/Surface Treated Hemp Fiber Bio-Composites. Polym. Compos. 2023, 44, 4976–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardalis, N.; Xanthopoulou, E.; Zamboulis, A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Olive Stone as a Filler for Recycled High-Density Polyethylene: A Promising Valorization of Solid Wastes from Olive Oil Industry. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2024, 6, 100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, E.; Chrysafi, I.; Polychronidis, P.; Zamboulis, A.; Bikiaris, D.N. Evaluation of Eco-Friendly Hemp-Fiber-Reinforced Recycled HDPE Composites. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, R.K.; Hakim, L.; Akhila, K.; Ramakanth, D.; Gaikwad, K.K. Nano Clays and Its Composites for Food Packaging Applications. Int. Nano Lett. 2023, 13, 131–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, B.C. Mechanical Properties of Wood-Plastic Composites Produced with Recycled Polyethylene, Used Tetra Pak® Boxes, and Wood Flour. BioResources 2022, 17, 6569–6577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoensri, K.; Shin, Y.J.; Park, H.J. Innovative HDPE Composites Enriched with UV Stabilizer and Diatomaceous Earth/Zinc Oxide for Enhanced Seafood Packaging and Antimicrobial Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoensri, K.; Shin, Y.J.; Kim, K.C.; Park, H.J. Active Packaging Material Based on Immobilized Diatomaceous Earth/Zinc Oxide/High-Density Polyethylene Composite for Sea Food and Products. Polymers 2022, 14, 5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, N.; Oza, S. Thermal Stability and Thermo-Mechanical Properties of Hemp-High Density Polyethylene Composites: Effect of Two Different Chemical Modifications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 44, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, L.; Brüggemann, O.; Putz, R.F. Polyolefin Composites with Natural Fibers and Wood-Modification of the Fiber/Filler-Matrix Interaction. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaaba, N.F.; Ismail, H. Thermoplastic/Natural Filler Composites: A Short Review. J. Phys. Sci. 2019, 30, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Cai, X.; Jia, Z.; Liu, M.; Jia, D. Morphology and Properties of Halloysite Nanotubes Reinforced Polypropylene Nanocomposites. E-Polymers 2008, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Królikowski, W.; Rosłaniec, Z. Nanokompozyty Polimerowe. Kompozyty 2004, 4, 3–15. [Google Scholar]
- Montanes, N.; Garcia-Sanoguera, D.; Segui, V.J.; Fenollar, O.; Boronat, T. Processing and Characterization of Environmentally Friendly Composites from Biobased Polyethylene and Natural Fillers from Thyme Herbs. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obasi, H.C. Peanut Husk Filled Polyethylene Composites: Effects of Filler Content and Compatibilizer on Properties. J. Polym. 2015, 2015, 189289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.P.; Vimal, K.K.; Kapur, G.S.; Sharma, S.; Choudhary, V. High-Density Polyethylene/Halloysite Nanocomposites: Morphology and Rheological Behaviour under Extensional and Shear Flow. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joussein, E.; Petit, S.; Churchman, J.; Theng, B.; Righi, D.; Delvaux, B. Halloysite Clay Minerals—A Review. Clay Miner. 2005, 40, 383–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpilska, K.; Czaja, K.; Kudła, S. Halloysite Nanotubes as Polyolefin Fillers. Polimery/Polymers 2015, 60, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danyliuk, N.; Tomaszewska, J.; Tatarchuk, T. Halloysite Nanotubes and Halloysite-Based Composites for Environmental and Biomedical Applications. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Tan, D.; Annabi-Bergaya, F. Properties and Applications of Halloysite Nanotubes: Recent Research Advances and Future Prospects. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 112–113, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risyon, N.P.; Othman, S.H.; Basha, R.K.; Talib, R.A. Characterization of Polylactic Acid/Halloysite Nanotubes Bionanocomposite Films for Food Packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 23, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Review on Polymer/Halloysite Nanotube Nanocomposite. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2018, 57, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, C.E.; Ozbulut, E.B.S.; Ceven, O.F.; Tas, B.A.; Unal, S.; Unal, H. Purification and Sorting of Halloysite Nanotubes into Homogeneous, Agglomeration-Free Fractions by Polydopamine Functionalization. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17962–17972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.L.; Chow, W.S. Multifunctional Halloysite Nanotube–Reinforced Polypropylene/Polyamide Binary Nanocomposites. Polym. Polym. Compos. 2020, 28, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, M.; Abouelmagd, A.; Sundararaj, U. Silane Functionalization of Sodium Montmorillonite Nanoclay and Its Effect on Rheological and Mechanical Properties of HDPE/Clay Nanocomposites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 146, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krásný, I.; Lapčík, L.; Lapčíková, B.; Greenwood, R.W.; Šafářová, K.; Rowson, N.A. The Effect of Low Temperature Air Plasma Treatment on Physico-Chemical Properties of Kaolinite/Polyethylene Composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2014, 59, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, H. Selective Modification of Inner Surface of Halloysite Nanotubes: A Review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2017, 6, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.; Yuan, P.; Liu, D.; Du, P. Surface Modifications of Halloysite. In Developments in Clay Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 7, ISBN 9780081002933. [Google Scholar]
- Saif, M.J.; Asif, H.M.; Naveed, M. Properties and Modification Methods of Halloysite Nanotubes: A State-of-The-Art Review. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2018, 63, 4109–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrakhiz, F.Z.; El Achaby, M.; Kakou, A.C.; Vaudreuil, S.; Benmoussa, K.; Bouhfid, R.; Fassi-Fehri, O.; Qaiss, A. Mechanical Properties of High Density Polyethylene Reinforced with Chemically Modified Coir Fibers: Impact of Chemical Treatments. Mater. Des. 2012, 37, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, G.; Lv, D.; Dong, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, D. Effective Activation of Halloysite Nanotubes by Piranha Solution for Amine Modification via Silane Coupling Chemistry. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 52916–52925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Liu, G.; Lv, D.; Dong, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, D. Simultaneous Improvement in Strength, Toughness, and Thermal Stability of Epoxy/Halloysite Nanotubes Composites by Interfacial Modification. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xian, Y.; Smith, L.M.; Wang, G.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, S. Interfacial Properties of Bamboo Fiber-Reinforced High-Density Polyethylene Composites by Different Methods for Adding Nano Calcium Carbonate. Polymers 2017, 9, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Smith, L.M.; Wang, G.; Shi, S.Q.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, S. Characterization of Interfacial Interactions in Bamboo Pulp Fiber/High-Density Polyethylene Composites Treated by Nano CaCO3 Impregnation Modification Using Fractal Theory and Dynamic Mechanical Analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 141, 111712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.C.; Erdmann, E.; Destéfanis, H.A. Barrier Properties and Structural Study of Nanocomposite of HDPE/Montmorillonite Modified with Polyvinylalcohol. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 679567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, M.Y.; Chow, W.S. Kinetics of Crystallization for Polypropylene/Polyethylene/Halloysite Nanotube Nanocomposites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2020, 33, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, P.; Polansky, R. Effect of Different Type of Polyethylene Matrix on the Properties of PE/HNT Composites. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Dielectrics (ICD), Budapest, Hungary, 1–5 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höfler, G.; Lin, R.J.T.; Jayaraman, K. Rotational Moulding and Mechanical Characterisation of Halloysite Reinforced Polyethylenes. J. Polym. Res. 2018, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Deshmukh, R.K.; Hakim, L.; Gaikwad, K.K. Halloysite Nanotube as a Functional Material for Active Food Packaging Application: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, X. Effect of an Alkalized-Modified Halloysite on PLA Crystallization, Morphology, Mechanical, and Thermal Properties of PLA/Halloysite Nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Guo, H.; Yuan, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Deng, L.; Liu, D. Geopolymerization of Halloysite via Alkali-Activation: Dependence of Microstructures on Precalcination. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 185, 105375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.D.; Bavykin, D.V.; Walsh, F.C. The Stability of Halloysite Nanotubes in Acidic and Alkaline Aqueous Suspensions. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 065705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albdiry, M.T.; Yousif, B.F. Role of Silanized Halloysite Nanotubes on Structural, Mechanical Properties and Fracture Toughness of Thermoset Nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2014, 57, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jlassi, K.; Mallick, S.; Mutahir, H.; Ahmad, Z.; Touati, F. Synthesis of In Situ Photoinduced Halloysite-Polypyrrole@silver Nanocomposite for the Potential Application in Humidity Sensors. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, A.; Kalagi, S.; Viana, Í.E.L.; Martins, V.M.; Duarte, S.; Gregory, R.L.; Youngblood, J.P.; Platt, J.A.; Feitosa, S. Resin-Based Dental Materials Containing 3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane Modified Halloysite-Clay Nanotubes for Extended Drug Delivery. Dent. Mater. 2021, 37, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, D.; Garcia-Sanoguera, D.; Fombuena, V.; Lopez-Martinez, J.; Balart, R. Improvement of Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) Blends with Surface-Modified Halloysite Nanotubes (HNT). Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 162, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W.; Xu, T.; Fong, H. Fabrication and Evaluation of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA Dental Resins/Composites Containing Halloysite Nanotubes. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El-Soad, A.M.; Pestov, A.V.; Tambasova, D.P.; Osipova, V.A.; Martemyanov, N.A.; Cavallaro, G.; Kovaleva, E.G.; Lazzara, G. Insights into Grafting of (3-Mercaptopropyl) Trimethoxy Silane on Halloysite Nanotubes Surface. J. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 915, 121224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, V.; Najafi, F.; Vahabi, H.; Jouyandeh, M.; Badawi, M.; Morisset, S.; Ganjali, M.R.; Saeb, M.R. Surface Chemistry of Halloysite Nanotubes Controls the Curability of Low Filled Epoxy Nanocomposites. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 135, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaltin, N.; Sanli, D.; Jonáš, A.; Kiraz, A.; Erkey, C. Preparation and Characterization of Superhydrophobic Surfaces Based on Hexamethyldisilazane-Modified Nanoporous Alumina. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subasri, R.; Hima, H. Investigations on the Use of Nanoclay for Generation of Superhydrophobic Coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 264, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.S.; Kim, J. Surface Modification of Clay and Its Effect on the Intercalation Behavior of the Polymer/Clay Nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2004, 42, 2367–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudy, S.; Gierałtowska, U.; Krzywdzińska-Bartkowiak, M.; Piątek, M. Pomiar Barwy Produktów Mleczarskich. Współczesne Trendy W Kształtowaniu Jakości Żywności 2016, 1, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Hejna, A.; Barczewski, M.; Skórczewska, K.; Szulc, J.; Chmielnicki, B.; Korol, J.; Formela, K. Sustainable Upcycling of Brewers’ Spent Grain by Thermo-Mechanical Treatment in Twin-Screw Extruder. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, L.; Cheng, C.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, H. A Novel Surface Modification Method upon Halloysite Nanotubes: A Desirable Cross-Linking Agent to Construct Hydrogels. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 182, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos-Ramírez, S.; De Oca-Ramírez, G.M.; Ramos-Fernández, E.V.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Pastor-Blas, M.M.; González-Montiel, A. Surface Modification of Natural Halloysite Clay Nanotubes with Aminosilanes. Application as Catalyst Supports in the Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization of Methyl Methacrylate. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 406, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, M.; Demirci, S.; Yildrim, Y.; Çoban, C.Ç.; Turk, M.; Sahiner, N. Modification of Halloysite Clay Nanotubes with Various Alkyl Halides, and Their Characterization, Blood Compatibility, Biocompatibility, and Genotoxicity. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 259, 124013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubeva, O.Y.; Alikina, Y.A.; Kalashnikova, T.A. Influence of Hydrothermal Synthesis Conditions on the Morphology and Sorption Properties of Porous Aluminosilicates with Kaolinite and Halloysite Structures. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 199, 105879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahidah, K.A.; Kakooei, S.; Ismail, M.C.; Bothi Raja, P. Halloysite Nanotubes as Nanocontainer for Smart Coating Application: A Review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 111, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecílio, D.M.; Cerrada, M.L.; Pérez, E.; Fernandes, A.; Lourenço, J.P.; McKenna, T.F.L.; Ribeiro, M.R. A Novel Approach for Preparation of Nanocomposites with an Excellent Rigidity/Deformability Balance Based on Reinforced HDPE with Halloysite. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 184, 111765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelto, J.; Heino, V.; Karttunen, M.; Rytöluoto, I.; Ronkainen, H. Tribological Performance of High Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Composites with Low Nanofiller Loading. Wear 2020, 460–461, 203451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, J.W.; Gajdoš, I.; Puszka, A. Polyethylene-Matrix Composites with Halloysite Nanotubes with Enhanced Physical/Thermal Properties. Polymers 2019, 11, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.B.; Pan, L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, S.T.; Ye, Y.; Xia, M.S.; Chen, X.G. Effects of Acid Treatment on the Physico-Chemical and Pore Characteristics of Halloysite. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2012, 396, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boro, U.; Priyadarsini, A.; Moholkar, V.S. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly(Lactic Acid)/Clove Essential Oil/Alkali-Treated Halloysite Nanotubes Composite Films for Food Packaging Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, P.; Southon, P.D.; Liu, Z.; Green, M.E.R.; Hook, J.M.; Antill, S.J.; Kepert, C.J. Functionalization of Halloysite Clay Nanotubes by Grafting with γ-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15742–15751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Fauzi, M.N.A.; Abu Bakar, A. Morphological, Thermal and Tensile Properties of Halloysite Nanotubes Filled Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, N.Y.; Yin, Q.J.; Luo, F.; Zhang, Q.; Du, R.; Fu, Q. Crystallization Behavior and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene/Halloysite Composites. Polymer 2007, 48, 7374–7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, K.K.; Singh, S.; Lee, Y.S. High Adsorption of Ethylene by Alkali-Treated Halloysite Nanotubes for Food-Packaging Applications. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Alkali Activation of Halloysite for Adsorption and Release of Ofloxacin. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 287, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El-Soad, A.M.; Lazzara, G.; Pestov, A.V.; Tambasova, D.P.; Antonov, D.O.; Cavallaro, G.; Kovaleva, E.G. Grafting of (3-Chloropropyl)-Trimethoxy Silane on Halloysite Nanotubes Surface. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles, J.; Ramkumaar, G.R. Qualitative Analysis of High Density Polyethylene Using FTIR Spectroscopy. Asian J. Chem. 2009, 21, 4477–4484. [Google Scholar]
- Gulmine, J.V.; Janissek, P.R.; Heise, H.M.; Akcelrud, L. Polyethylene Characterization by FTIR. Polym. Test. 2002, 21, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, S.; Sajwan, M.; Singh, R. Crystallinity of Hdpe Pipes by Dsc, Xrd and Ftir Spectroscopy-a Forensic Comparison. Indian J. Criminol. Crim. 2008, 29, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lefrant, S.; Baibarac, M.; Baltog, I. Raman and FTIR Spectroscopy as Valuable Tools for the Characterization of Polymer and Carbon Nanotube Based Composites. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 5690–5704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajith, S. Investigation on Effect of Chemical Composition of Bio-Fillers on Filler/Matrix Interaction and Properties of Particle Reinforced Composites Using FTIR. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 166, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Yousefi, A.A.; Ehsani, M. Characterizing Films of Polyethylene Blends: An Application of Colorimetric Parameters Measurements. Prog. Color. Color. Coat. 2015, 8, 219–235. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhry, A.U.; Lonkar, S.P.; Chudhary, R.G.; Mabrouk, A.; Abdala, A.A. Thermal, Electrical, and Mechanical Properties of Highly Filled HDPE/Graphite Nanoplatelets Composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 29, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Liu, M.; Jia, D. Preparation and Characterization of Polypropylene Grafted Halloysite and Their Compatibility Effect to Polypropylene/Halloysite Composite. Polym. J. 2006, 38, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaiah, P.; Ratnam, C.T.; Manickam, S. Development of Silane Grafted Halloysite Nanotube Reinforced Polylactide Nanocomposites for the Enhancement of Mechanical, Thermal and Dynamic-Mechanical Properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 135, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogan, A.R.; Kaygusuz, I.; Kaynak, C. Influences of Aminosilanization of Halloysite Nanotubes on the Mechanical Properties of Polyamide-6 Nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 1350–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewda, K.; Maiti, S.N. Crystallization and Melting Behavior of HDPE in HDPE/Teak Wood Flour Composites and Their Correlation with Mechanical Properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 118, 2264–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.M.; Mckinley, B.M. Crystallinity as a Selection Criterion for Engineering Properties of High Density Polyethylene. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1985, 25, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Guo, B.; Wan, J.; Zou, Q.; Jia, D. Effects of Halloysite Nanotubes on Kinetics and Activation Energy of Non-Isothermal Crystallization of Polypropylene. J. Polym. Res. 2010, 17, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaaz, T.S.; Sulong, A.B.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Al-Amiery, A.A.; Nassir, M.H.; Jaaz, A.H. The Impact of Halloysite on the Thermo-Mechanical Properties of Polymer Composites. Molecules 2017, 22, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajwan, M.; Aggarwal, S.; Singh, R.B. Forensic Characterization of HDPE Pipes by DSC. Forensic Sci. Int. 2008, 175, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

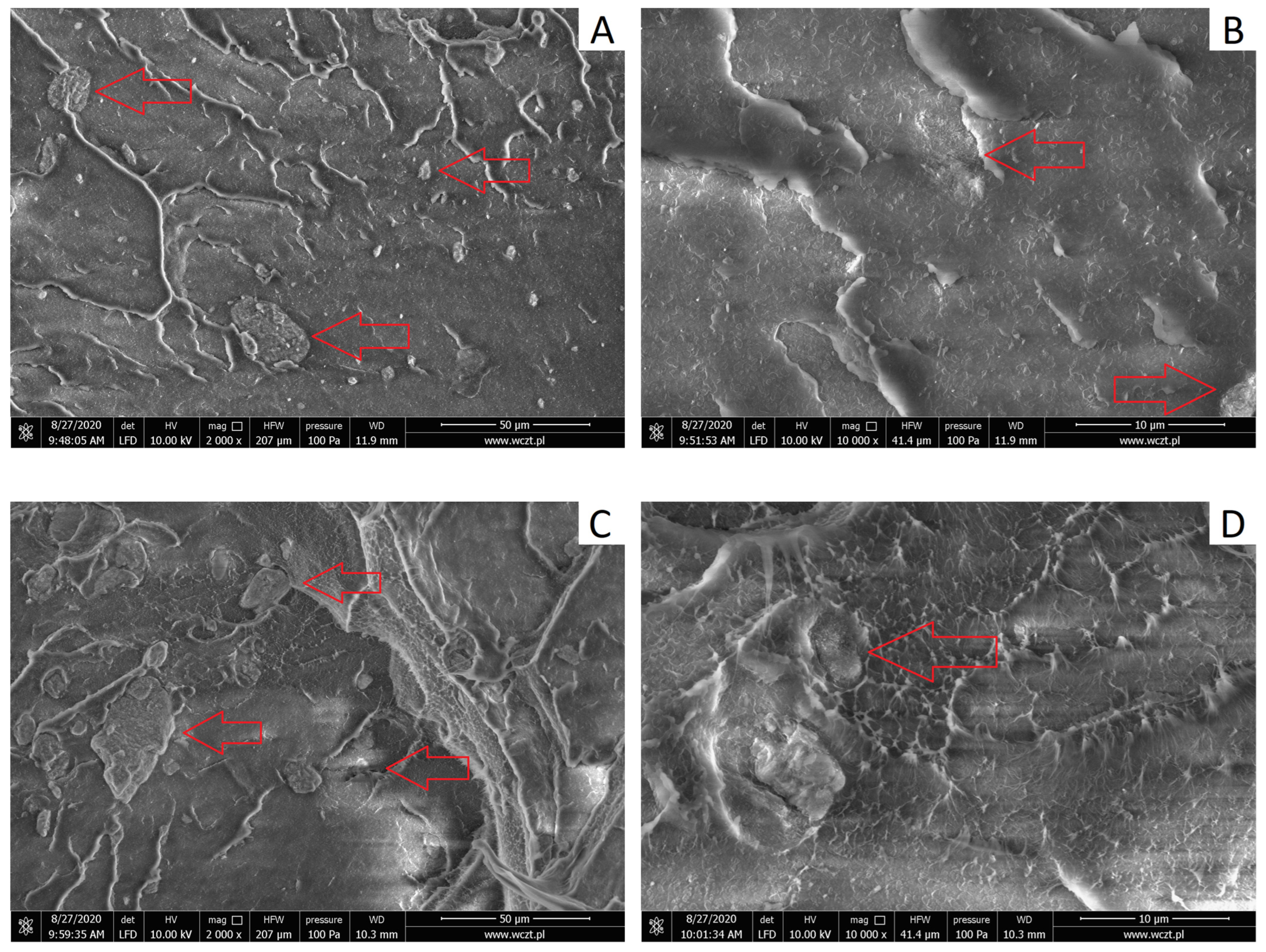
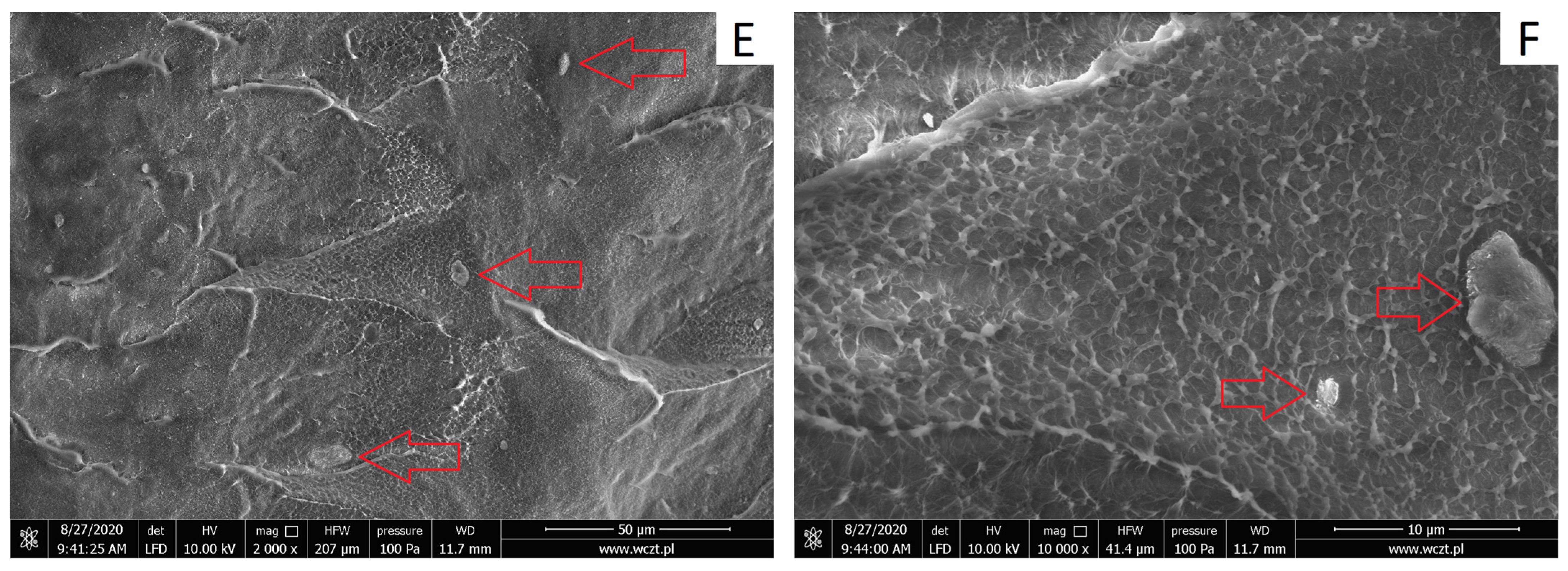
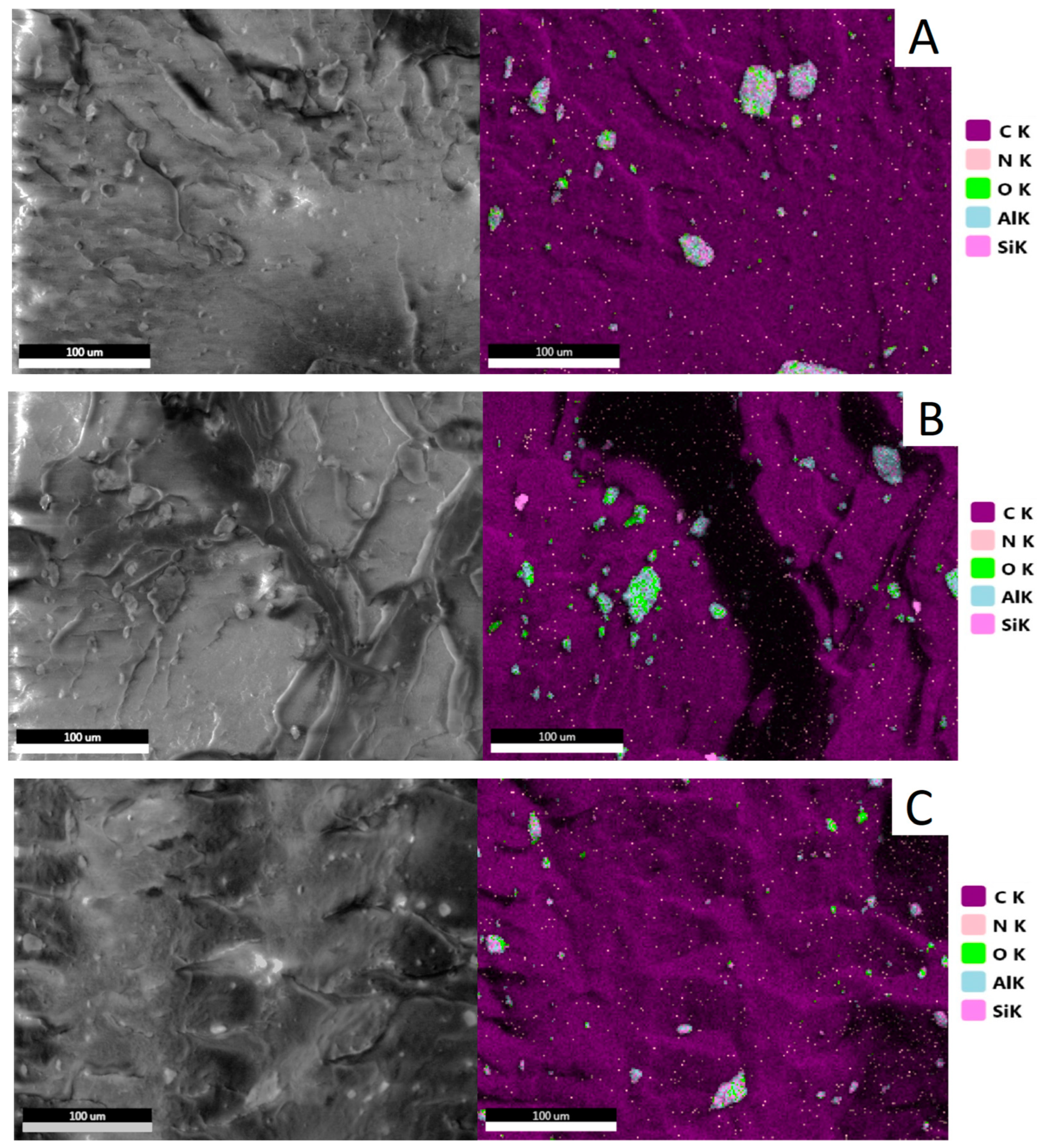
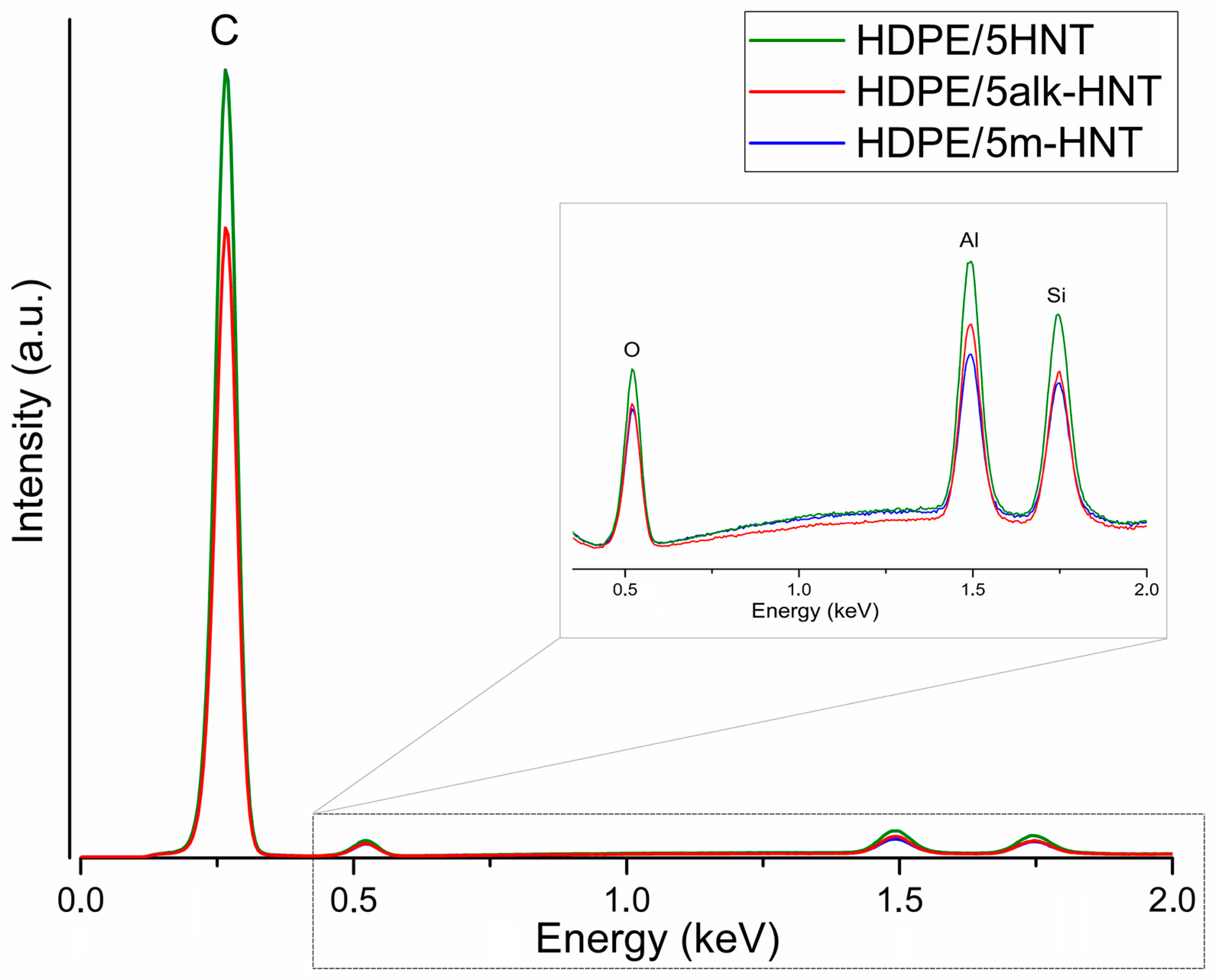

| Sample | Filler Type | Filler Content, wt% |
|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 0 | |
| HDPE/1HNT | raw halloysite (HNT) | 1 |
| HDPE/3HNT | 3 | |
| HDPE/5HNT | 5 | |
| HDPE/1alk–HNT | alkalized halloysite | 1 |
| HDPE/3alk–HNT | 3 | |
| HDPE/5alk–HNT | 5 | |
| HDPE/1m–HNT | Bis(trimethylsilyl)amine (HMDS)–modified halloysite | 1 |
| HDPE/3m–HNT | 3 | |
| HDPE/5m–HNT | 5 |
| Sample | L* | a* | b* | R (Red) | G (Green) | B (Blue) | ΔE | Color |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 85.96 (±0.23) | 1.30 (±0.13) | 2.41 (±0.31) | 219 | 214 | 210 | 0.0 (±0.63) | |
| HDPE/1HNT | 81.62 (±0.28) | 2.05 (±0.11) | 6.43 (±0.24) | 211 | 201 | 191 | 5.9 (±0.47) | |
| HDPE/3HNT | 63.44 (±0.41) | 3.28 (±0.21) | 10.85 (±0.33) | 165 | 151 | 134 | 24.0 (±0.55) | |
| HDPE/5HNT | 63.94 (±0.34) | 4.66 (±0.19) | 13.91 (±0.37) | 170 | 152 | 130 | 25.0 (±0.62) | |
| HDPE/1alk–HNT | 83.85 (±0.32) | 1.73 (±0.18) | 7.62 (±0.19) | 217 | 208 | 195 | 5.6 (±0.42) | |
| HDPE/3alk–HNT | 76.81 (±0.27) | 4.63 (±0.11) | 12.56 (±0.21) | 205 | 186 | 167 | 14.0 (±0.29) | |
| HDPE/5alk–HNT | 67.24 (±0.37) | 7.89 (±0.14) | 14.64 (±0.23) | 185 | 158 | 138 | 23.2 (±0.41) | |
| HDPE/1m–HNT | 85.87 (±0.21) | 1.41 (±0.16) | 4.82 (±0.28) | 220 | 214 | 206 | 2.4 (±0.46) | |
| HDPE/3m–HNT | 79.79 (±0.56) | 3.19 (±0.18) | 11.05 (±0.31) | 210 | 195 | 177 | 10.7 (±0.52) | |
| HDPE/5m–HNT | 73.67 (±0.42) | 5.67 (±0.20) | 14.38 (±0.36) | 199 | 177 | 155 | 17.6 (±0.68) |
| Sample | Tm, °C | ΔHm, Jg−1 | Tc, °C | Xc, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 133.4 ± 0.2 | 227.4 ± 0.6 | 116.9 ± 0.3 | 77.6 ± 0.3 |
| HDPE/1HNT | 132.8 ± 0.3 | 226.2 ± 0.2 | 117.7 ± 0.6 | 78.0 ± 0.2 |
| HDPE/3HNT | 134.3 ± 0.6 | 217.8 ± 0.5 | 115.7 ± 0.5 | 76.6 ± 0.3 |
| HDPE/5HNT | 134.0 ± 0.5 | 209.9 ± 0.5 | 114.8 ± 0.3 | 76.4 ± 0.2 |
| HDPE/1alk–HNT | 134.7 ± 0.2 | 224.3 ± 0.3 | 113.0 ± 0.5 | 77.3 ± 0.6 |
| HDPE/3alk–HNT | 134.0 ± 0.3 | 218.4 ± 0.2 | 116.6 ± 0.4 | 76.8 ± 0.5 |
| HDPE/5alk–HNT | 135.0 ± 0.4 | 212.5 ± 0.5 | 114.8 ± 0.2 | 76.3 ± 0.4 |
| HDPE/1m–HNT | 135.9 ± 0.4 | 227.5 ± 0.6 | 114.6 ± 0.5 | 78.4 ± 0.2 |
| HDPE/3m–HNT | 134.0 ± 0.3 | 221.5 ± 0.4 | 115.5 ± 0.3 | 77.9 ± 0.5 |
| HDPE/5m–HNT | 136.9 ± 0.6 | 213.5 ± 0.6 | 113.0 ± 0.2 | 76.7 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wieczorek, M.; Tatarchuk, T.; Skórczewska, K.; Szulc, J.; Tomaszewska, J. The Effect of Silanized Halloysite Nanotubes on the Structure of Polyethylene–Based Composite. Materials 2024, 17, 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133260
Wieczorek M, Tatarchuk T, Skórczewska K, Szulc J, Tomaszewska J. The Effect of Silanized Halloysite Nanotubes on the Structure of Polyethylene–Based Composite. Materials. 2024; 17(13):3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133260
Chicago/Turabian StyleWieczorek, Martina, Tetiana Tatarchuk, Katarzyna Skórczewska, Joanna Szulc, and Jolanta Tomaszewska. 2024. "The Effect of Silanized Halloysite Nanotubes on the Structure of Polyethylene–Based Composite" Materials 17, no. 13: 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133260
APA StyleWieczorek, M., Tatarchuk, T., Skórczewska, K., Szulc, J., & Tomaszewska, J. (2024). The Effect of Silanized Halloysite Nanotubes on the Structure of Polyethylene–Based Composite. Materials, 17(13), 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17133260





