Unloading Model of Elastic–Plastic Half-Space Contacted by an Elastic Spherical Indenter
Abstract
1. Introduction
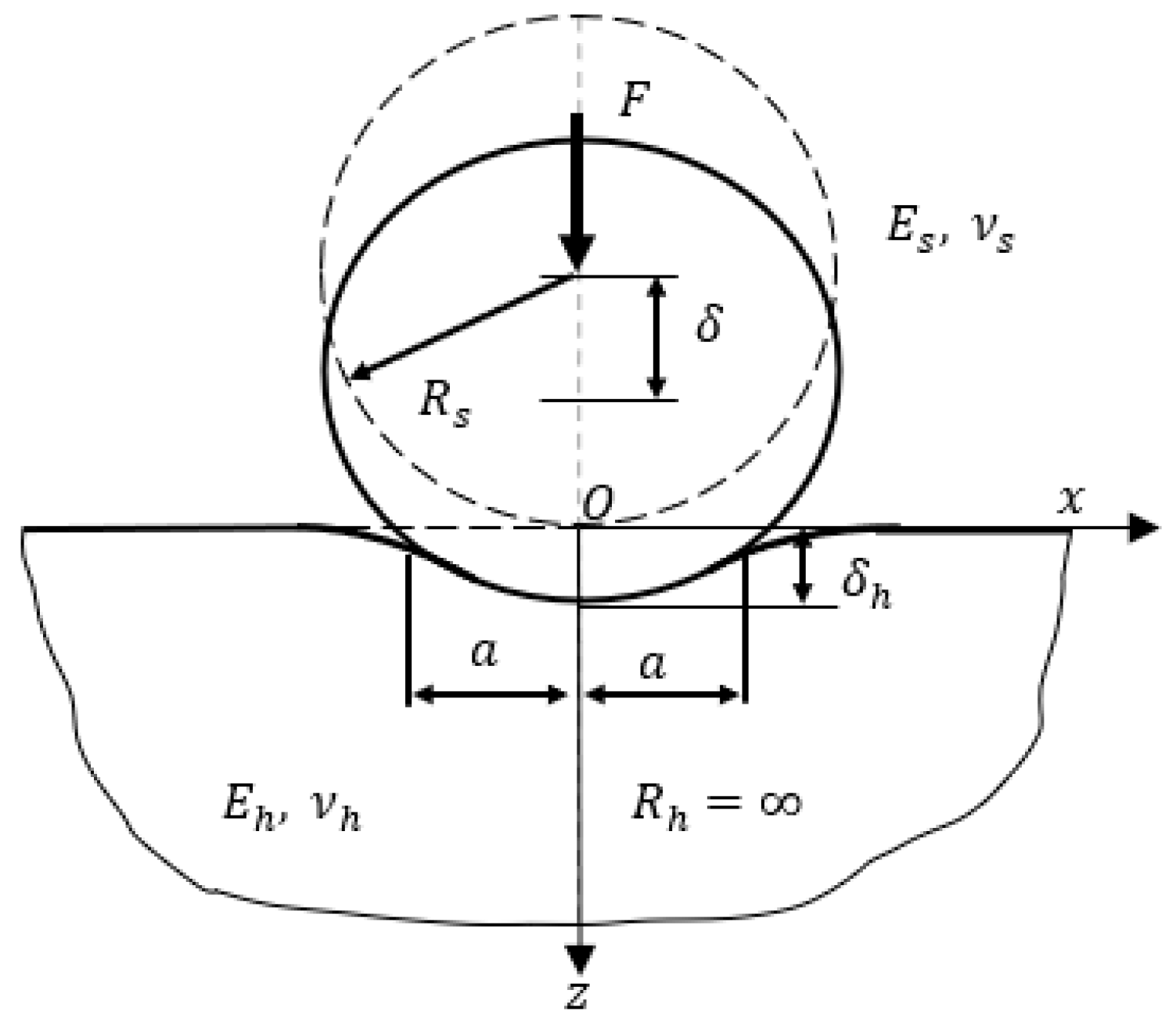
2. Analysis Method
2.1. Hertzian Theory and Critical Indentation
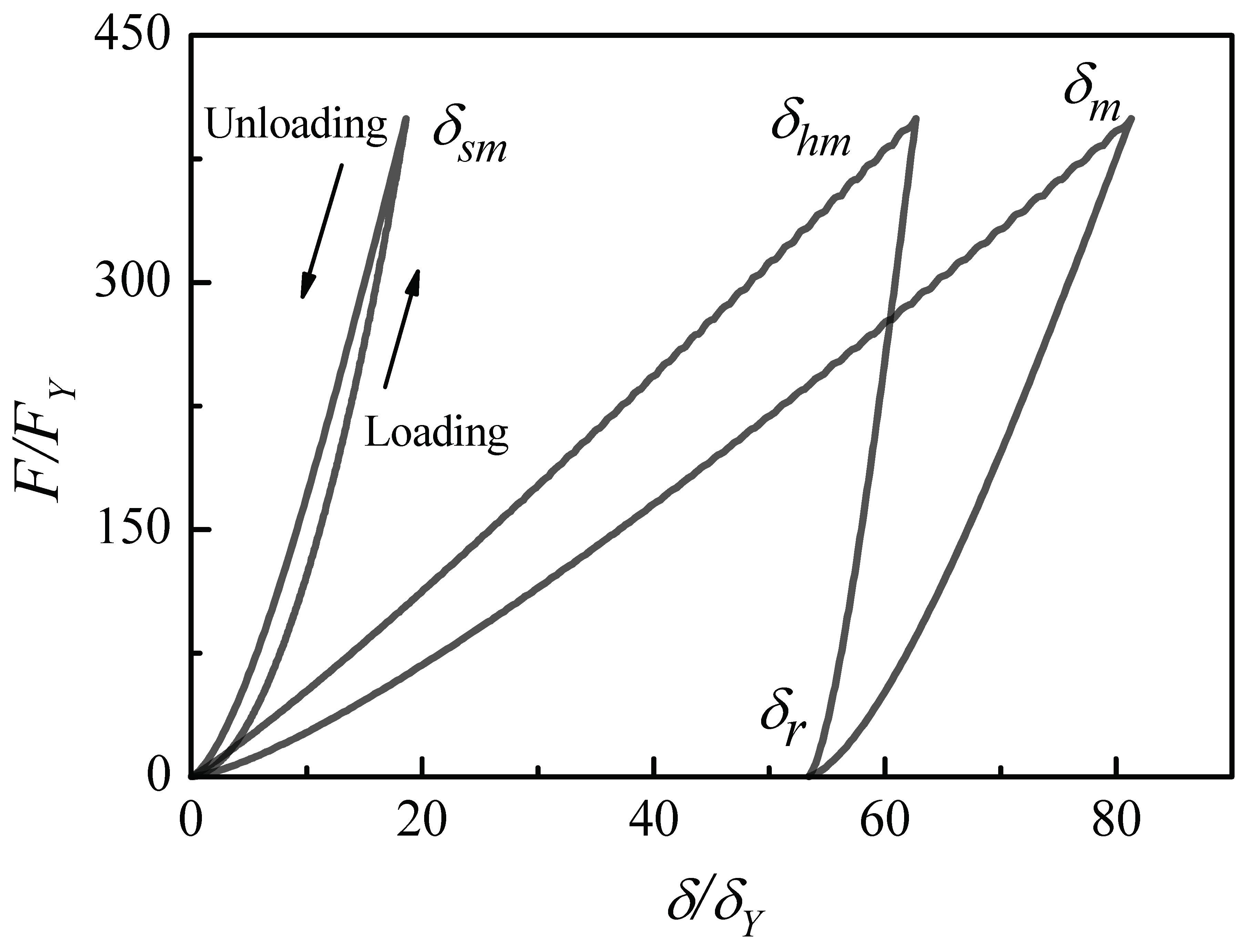
2.2. Unloading Analysis
3. Validations
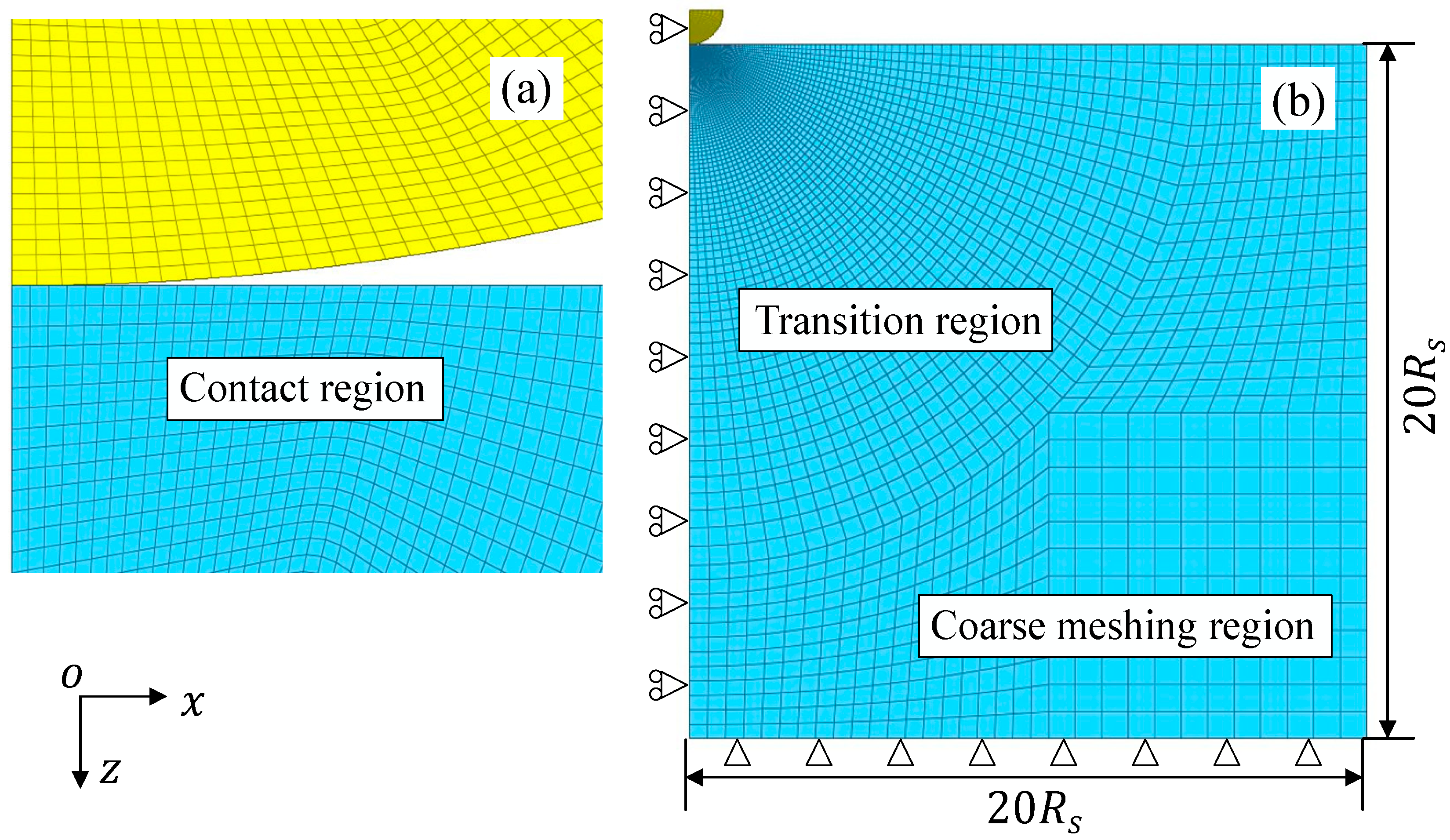
3.1. Finite Element Model
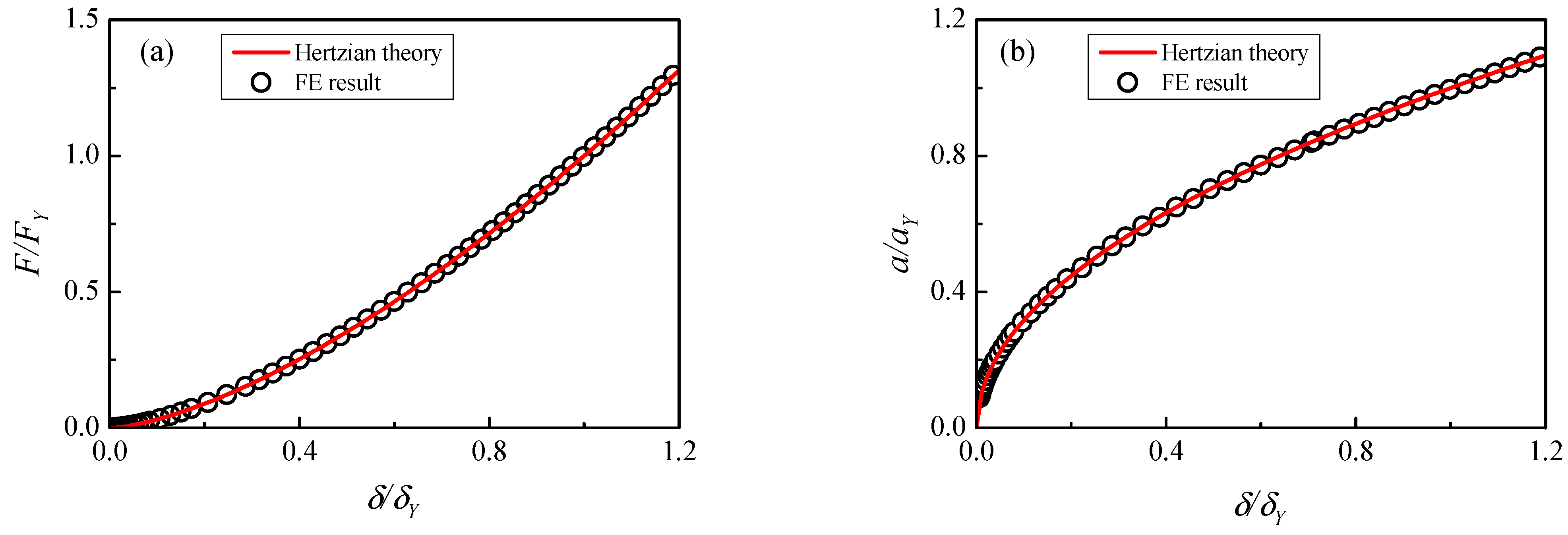
3.2. Hertzian Unloading
3.3. Residual Indentation
3.4. Residual Curvature Radius
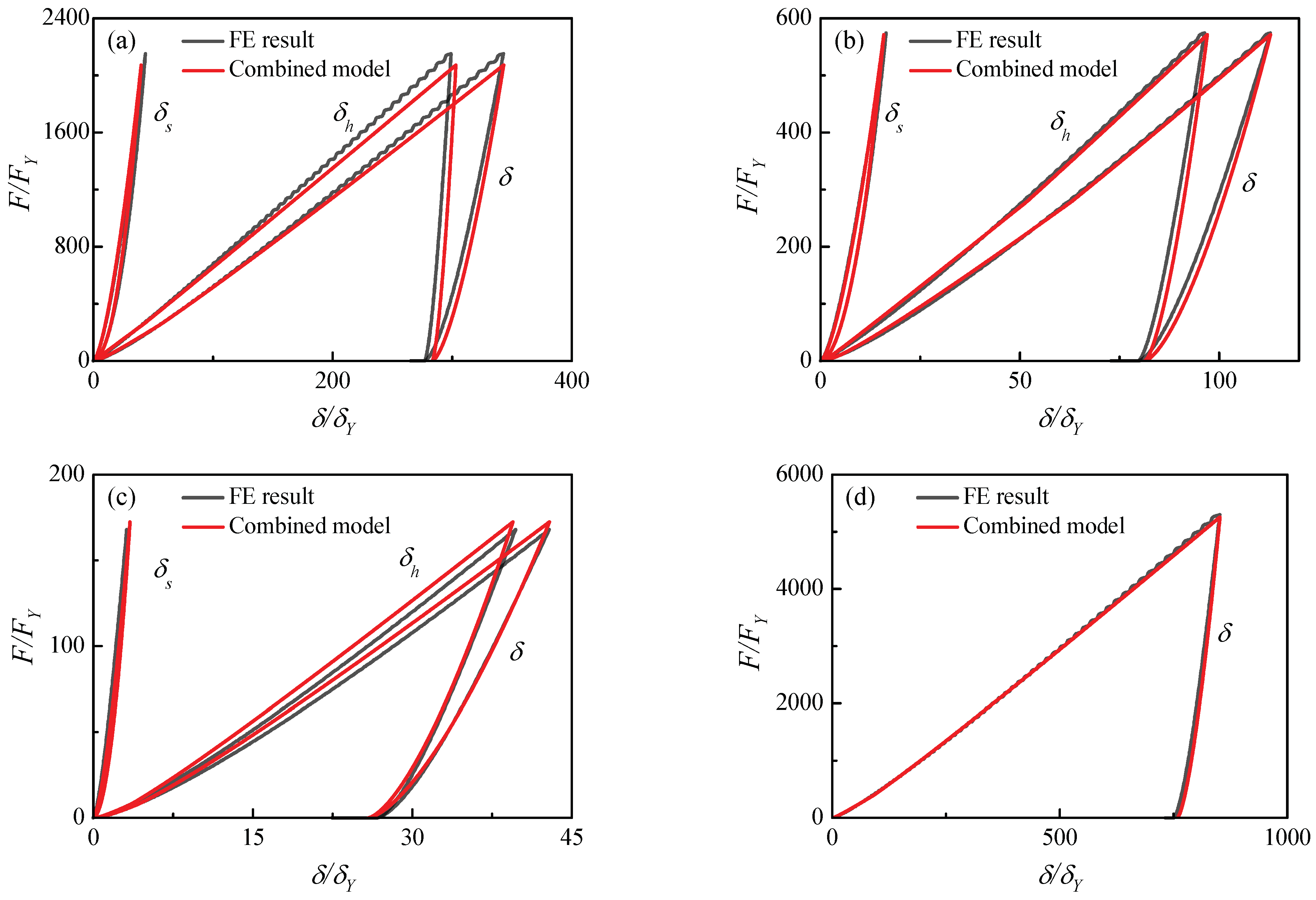
3.5. Unloading Model
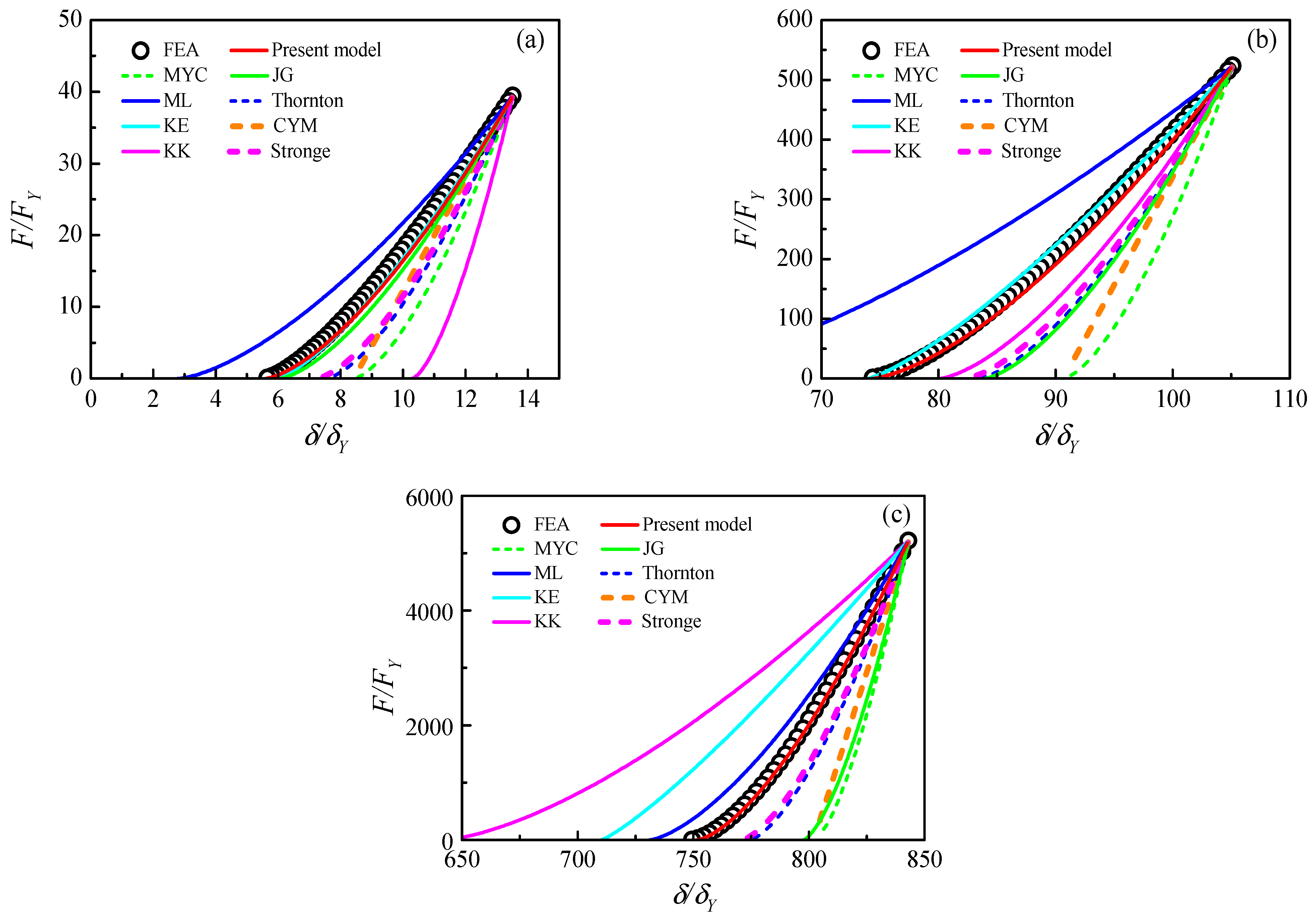
3.6. Comparisons with Existing Unloading Models
4. Applications
4.1. Contact Model
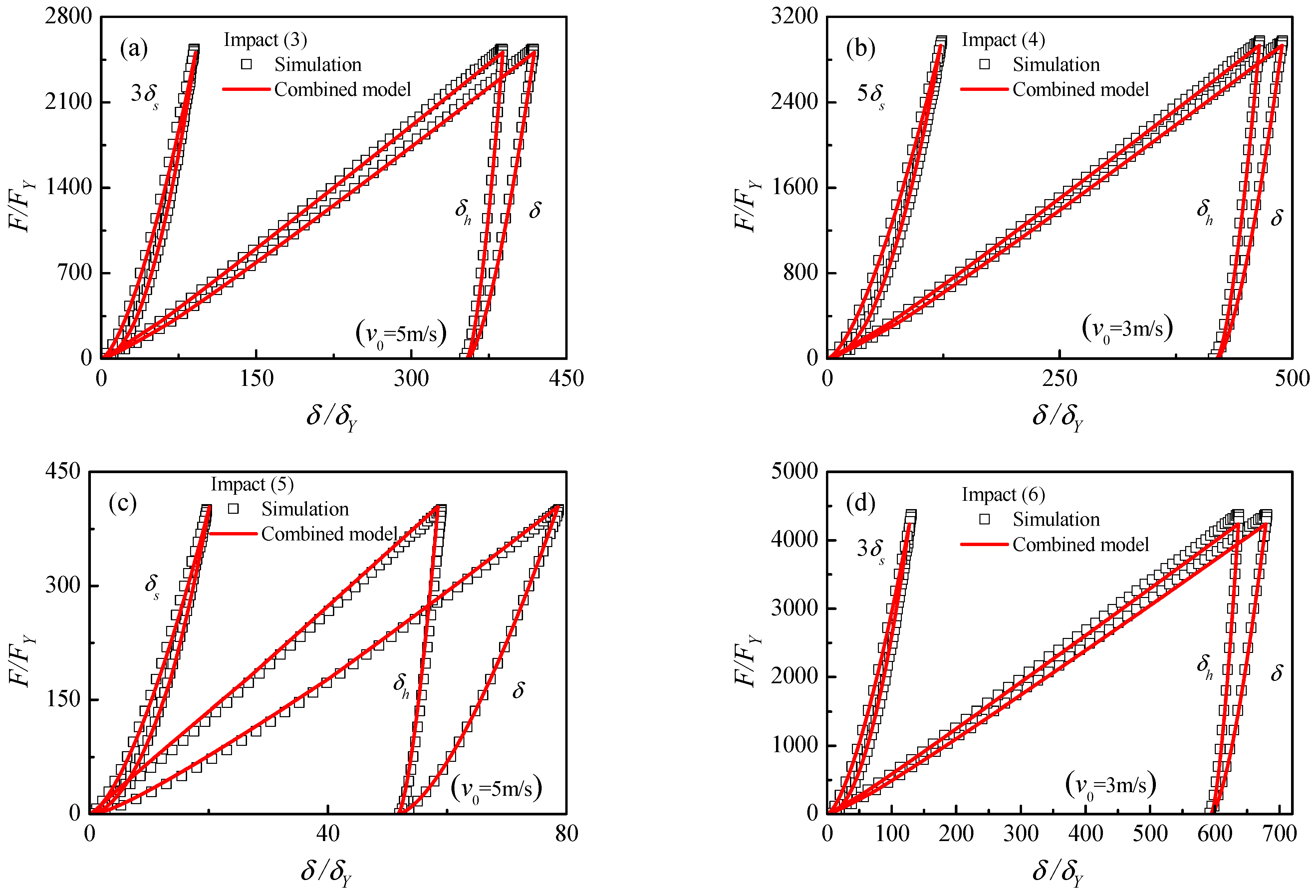
4.2. Impact Simulations
4.3. Nanoindentation Test
5. Conclusions
- A new unloading contact model of an elastic–perfectly plastic half-space indented by an elastic spherical sphere is presented analytically. The model can accurately predict the residual indentation and residual curvature radius after fully unloading.
- The assumptions and the unloading model have been demonstrated by numerical simulations. The proposed unloading can cover a wide range of indentations and material properties and is compared with existing unloading models.
- Combining the present unloading law with the existing contact loading model, cyclical behavior including loading and unloading can be predicted. The combined model has been verified by static FE simulations, low-velocity impact simulations and nanoindentation tests.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiao, X.; Terentyev, D.; Yu, L. Model for the Spherical Indentation Stress-Strain Relationships of Ion-Irradiated Materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2019, 132, 103694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.; Sebastiani, M.; Gigliotti, R.; D’Amato, M. An Innovative Procedure for the In-Situ Characterization of Elastomeric Bearings by Using Nanoindentation Test. Int. J. Archit. Herit. 2021, 15, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinowicz, M.; Parry, G.; Volpi, F.; Mercier, D.; Eve, S.; Lüders, U.; Lallemand, F.; Choquet, M.; Braccini, M.; Boujrouf, C.; et al. Failure of a Brittle Layer on a Ductile Substrate: Nanoindentation Experiments and FEM Simulations. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2022, 163, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Berndt, C.; Raman, R.; Singh, H.; Ang, A. Applications and Developments of Thermal Spray Coatings for the Iron and Steel Industry. Materials 2023, 16, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabiscol, R.; Shi, H.; Wünsch, I.; Magnanimo, V.; Finke, J.H.; Luding, S.; Kwade, A. Effect of Particle Size on Powder Compaction and Tablet Strength Using Limestone. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Z.; Wei, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, X. Meshing Contact Impact Properties of Circular Arc Tooth Trace Cylindrical Gear Based on Rotating Knife Dish Milling Process. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 8819818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Han, Y.; Sun, X.; Shao, Y.; Gu, F.; Ball, A.D. Vibration Characteristics and Condition Monitoring of Internal Radial Clearance within a Ball Bearing in a Gear-Shaft-Bearing System. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 165, 108280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, K.; Gunes, R.; Apalak, M.K.; Reddy, J.N. Evaluation of Geometrically Nonlinear and Elastoplastic Behavior of Functionally Graded Plates under Mechanical Loading–Unloading. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2022, 29, 1587–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W. A Review of Unloading-Induced Fault Instability. Undergr. Space 2021, 6, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforou, A.P.; Yigit, A.S. Inelastic Impact and the Coefficient of Restitution. J. Eng. Res. 2017, 4, 194–213. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, D.; Higgs, C.F. A Coefficient of Restitution Model for Sphere–Plate Elastoplastic Impact with Flexural Vibrations. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 88, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, M.; Bartier, O.; Mauvoisin, G.; Hernot, X. A Phenomenological Study of the Influence of the Hardening Type on the Indentation F-h Cyclic Curve. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2021, 197, 106336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharr, G.M. Recent Advances in Small-Scale Mechanical Property Measurement by Nanoindentation. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2015, 19, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider-Maunoury, C.; Albayda, A.; Bartier, O.; Weiss, L.; Mauvoisin, G.; Hernot, X.; Laheurte, P. On the Use of Instrumented Indentation to Characterize the Mechanical Properties of Functionally Graded Binary Alloys Manufactured by Additive Manufacturing. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer-Cripps, A.C. Introduction to Contact Mechanics; Mechanical Engineering Series; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; ISBN 978-0-387-98914-3. [Google Scholar]
- Fauvel, V.; Gaillard, Y.; Guillemet, R.; Garabédian, P.; Richard, F. Simultaneous Extraction of the Elastic-Plastic Properties of a Thin Film and Its Substrate from an Identifiability-Based Design of Depth-Sensing Nanoindentation Testing. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2022, 163, 104860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Peng, G.; Hu, Y.; Dou, G.; Chen, P.; Zhang, T. Spherical Indentation Model for Evaluating the Elastic Properties of the Shell of Microsphere with Core-Shell Structure. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2021, 230–231, 111159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.; Chusoipin, I.; Green, I. A Finite Element Study of the Residual Stress and Deformation in Hemispherical Contacts. J. Tribol. 2005, 127, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Ding, H.; Hu, W.; Xie, W.; Weng, P.; Jiang, L.; Yin, X. Contact Unloading Behaviors of Elastic-Power-Law Strain Hardening Material Considering Indenter Elasticity Effect. J. Tribol. 2022, 144, 121501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.L.; Li, L.Y. Finite Element Analysis of Cyclic Indentation of an Elastic-Perfectly Plastic Half-Space by a Rigid Sphere. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2003, 217, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kral, E.R.; Komvopoulos, K.; Bogy, D.B. Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis of Repeated Indentation of a Half-Space by a Rigid Sphere. J. Appl. Mech. 1993, 60, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Yin, X.; Deng, Q.; Yu, B.; Wang, H.; Weng, P.; Chen, C.; Yuan, H. Local Contact Behavior between Elastic and Elastic–Plastic Bodies. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 150, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, P.; Yin, X.; Hu, W.; Yuan, H.; Chen, C.; Ding, H.; Yu, B.; Xie, W.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H. Piecewise Linear Deformation Characteristics and a Contact Model for Elastic-Plastic Indentation Considering Indenter Elasticity. Tribol. Int. 2021, 162, 107114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etsion, I.; Kligerman, Y.; Kadin, Y. Unloading of an Elastic–Plastic Loaded Spherical Contact. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2005, 42, 3716–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yin, X.; Wang, H.; Jin, T.; Zhang, L.; Xie, W.; Weng, P. Unloading Behavior of Low Velocity Impact between Elastic and Elastic–Plastic Bodies. Tribol. Int. 2020, 151, 106485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L. Contact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985; ISBN 0-521-34796-3. [Google Scholar]
- Stronge, W.J. Impact Mechanics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Thornton, C. Coefficient of Restitution for Collinear Collisions of Elastic-Perfectly Plastic Spheres. J. Appl. Mech. 1997, 64, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu-Quoc, L.; Zhang, X.; Lesburg, L. A Normal Force-Displacement Model for Contacting Spheres Accounting for Plastic Deformation: Force-Driven Formulation. J. Appl. Mech. 2000, 67, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brake, M.R. An Analytical Elastic-Perfectly Plastic Contact Model. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2012, 49, 3129–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brake, M.R.W. An Analytical Elastic Plastic Contact Model with Strain Hardening and Frictional Effects for Normal and Oblique Impacts. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2015, 62, 104–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Liu, C. Contact Law and Coefficient of Restitution in Elastoplastic Spheres. J. Appl. Mech. 2015, 82, 121006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathbone, D.; Marigo, M.; Dini, D.; van Wachem, B. An Accurate Force–Displacement Law for the Modelling of Elastic–Plastic Contacts in Discrete Element Simulations. Powder Technol. 2015, 282, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, L.; Komvopoulos, K. Analysis of the Spherical Indentation Cycle for Elastic–Perfectly Plastic Solids. J. Mater. Res. 2004, 19, 3641–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.L.; Green, I.; Marghitu, D.B. Predicting the Coefficient of Restitution of Impacting Elastic-Perfectly Plastic Spheres. Nonlinear Dyn. 2010, 60, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, S. Energy Dissipation in Normal Elastoplastic Impact between Two Spheres. J. Appl. Mech. 2009, 76, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaednia, H.; Marghitu, D.B.; Jackson, R.L. Predicting the Permanent Deformation after the Impact of a Rod with a Flat Surface. J. Tribol. 2015, 137, 011403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zait, Y.; Kligerman, Y.; Etsion, I. Unloading of an Elastic–Plastic Spherical Contact under Stick Contact Condition. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovcharenko, A.; Halperin, G.; Verberne, G.; Etsion, I. In Situ Investigation of the Contact Area in Elastic–Plastic Spherical Contact during Loading–Unloading. Tribol. Lett. 2007, 25, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeed, M.A.; Yigit, A.S.; Christoforou, A.P. Elastoplastic Contact/Impact of Rigidly Supported Composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.F.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, P. Loading and Unloading of a Power-Law Hardening Spherical Contact under Stick Contact Condition. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2015, 94–95, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforou, A.P.; Yigit, A.S.; Majeed, M. Low-Velocity Impact Response of Structures with Local Plastic Deformation: Characterization and Scaling. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 2013, 8, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmans, B.D.; Sinka, I.C. Unloading of Elastoplastic Spheres from Large Deformations. Powder Technol. 2020, 374, 618–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaednia, H.; Brake, M.R.; Berryhill, M.; Jackson, R.L. Strain Hardening from Elastic–Perfectly Plastic to Perfectly Elastic Flattening Single Asperity Contact. J. Tribol. 2019, 141, 031402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaednia, H.; Mifflin, G.; Lunia, P.; O’Neill, E.O.; Brake, M.R.W. Strain Hardening from Elastic-Perfectly Plastic to Perfectly Eastic Indentation Single Asperity Contact. Front. Mech. Eng. 2020, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Big-Alabo, A.; Harrison, P.; Cartmell, M.P. Contact Model for Elastoplastic Analysis of Half-Space Indentation by a Spherical Impactor. Comput. Struct. 2015, 151, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaednia, H.; Pope, S.A.; Jackson, R.L.; Dan, B.M. A Comprehensive Study of the Elasto-Plastic Contact of a Sphere and a Flat. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, S.A.; Alcalá, J.; Souza, R.M. Effects of Elastic Indenter Deformation on Spherical Instrumented Indentation Tests: The Reduced Elastic Modulus. Philos. Mag. 2011, 91, 1370–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertz, H. Über Die Berührung Fester Elastischer Körper. J. Reine Angew. Math. 1882, 1882, 156–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, I. Poisson Ratio Effects and Critical Values in Spherical and Cylindrical Hertzian Contacts. Appl. Mech. Eng. 2005, 10, 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.L.; Green, I. A Finite Element Study of Elasto-Plastic Hemispherical Contact against a Rigid Flat. J. Tribol. 2005, 127, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Li, L.Y.; Thornton, C. Energy Dissipation during Normal Impact of Elastic and Elastic–Plastic Spheres. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2005, 32, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesarovic, S.D.; Fleck, N.A. Frictionless Indentation of Dissimilar Elastic–Plastic Spheres. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2000, 37, 7071–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
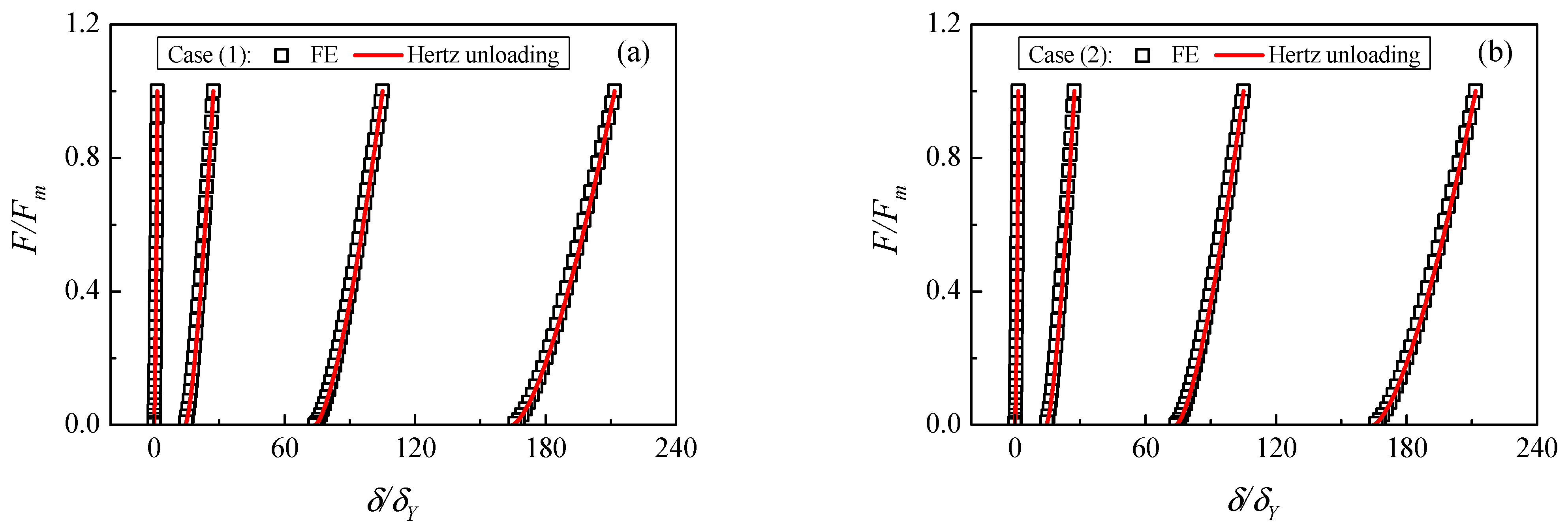
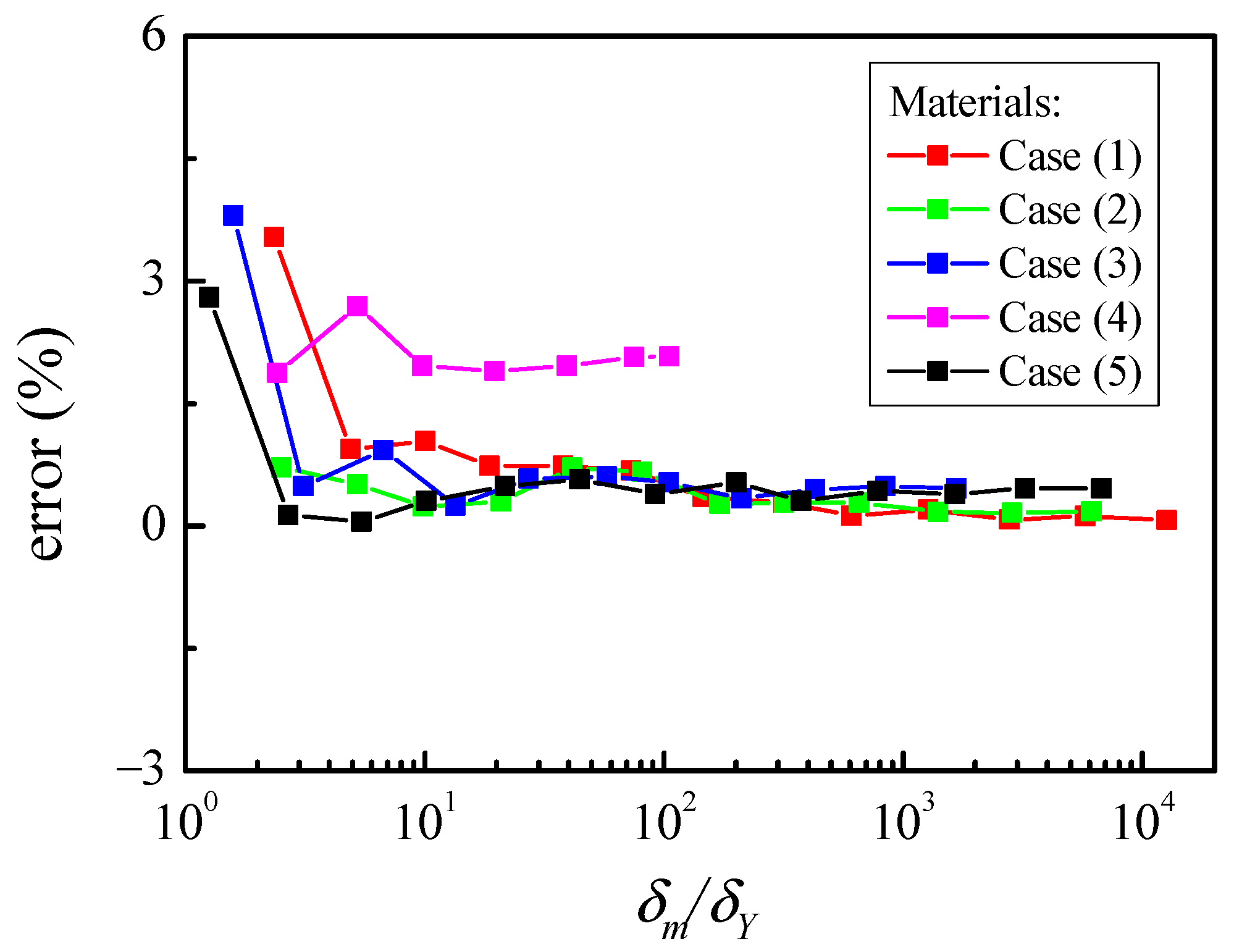

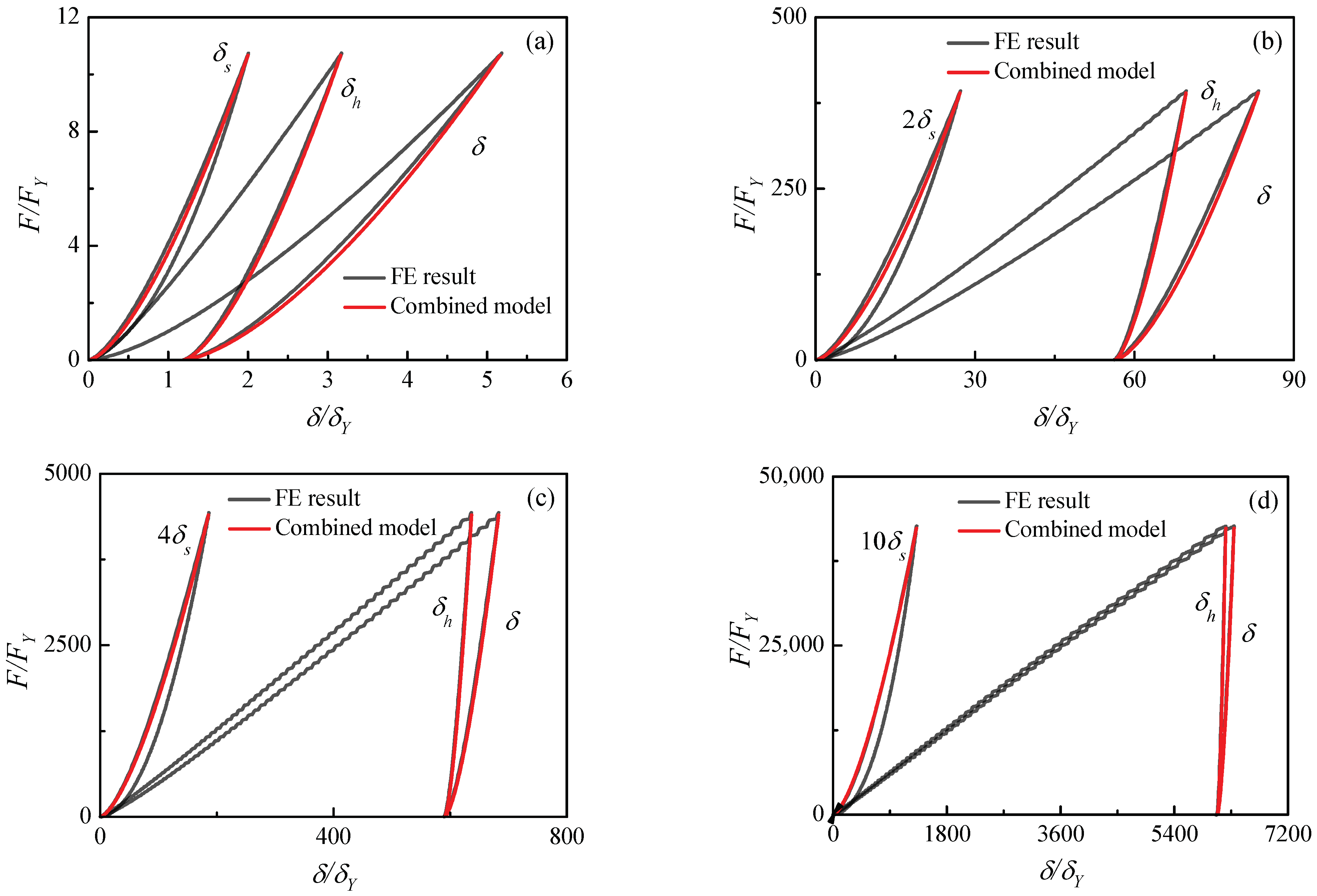
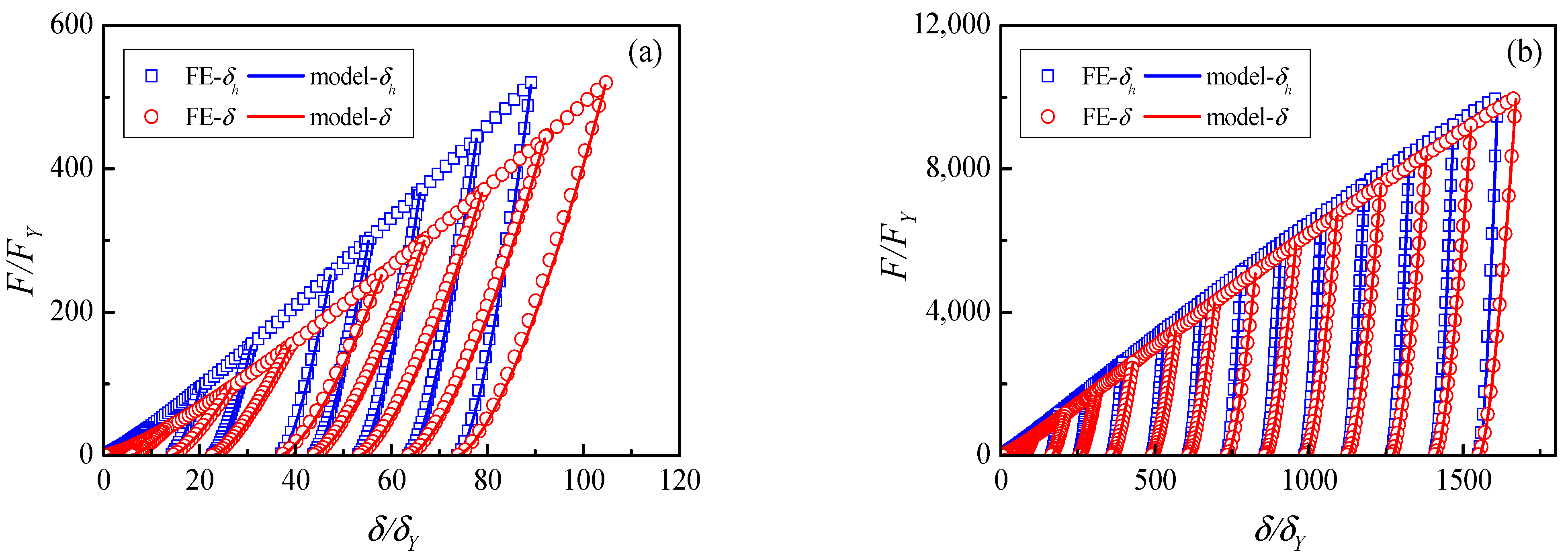

| Case | (GPa) | (GPa) | (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 210 | 52 | 50 | 4 |
| 2 | 210 | 104 | 120 | 2 |
| 3 | 210 | 208 | 345 | 1 |
| 4 | 52.5 | 208 | 550 | 0.25 |
| 5 | 210 | 210,000 | 345 | 0.001 |
| Case | -Fitting | -Equation (25) | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 36.68 | 36.57 | −0.30 |
| 2 | 37.53 | 37.26 | −0.72 |
| 3 | 39.28 | 39.20 | −0.20 |
| 4 | 41.12 | 40.55 | −1.39 |
| 5 | 36.37 | 36.28 | −0.25 |
| Materials | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 ± 12 | 510 ± 23 |
| 2 | 77 ± 10 | 630 ± 22 |
| 3 | 58 ± 8 | 513 ± 19 |
| 4 | 70 ± 7 | 480 ± 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, W.; Guo, Y.; Ding, H.; Yin, X.; Weng, P. Unloading Model of Elastic–Plastic Half-Space Contacted by an Elastic Spherical Indenter. Materials 2024, 17, 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17123018
Xie W, Guo Y, Ding H, Yin X, Weng P. Unloading Model of Elastic–Plastic Half-Space Contacted by an Elastic Spherical Indenter. Materials. 2024; 17(12):3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17123018
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Wenhao, Yuanyuan Guo, Huaiping Ding, Xiaochun Yin, and Panpan Weng. 2024. "Unloading Model of Elastic–Plastic Half-Space Contacted by an Elastic Spherical Indenter" Materials 17, no. 12: 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17123018
APA StyleXie, W., Guo, Y., Ding, H., Yin, X., & Weng, P. (2024). Unloading Model of Elastic–Plastic Half-Space Contacted by an Elastic Spherical Indenter. Materials, 17(12), 3018. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17123018






