Functional Technical Textile-Based Polymer Nanocomposites with Adsorbent Properties of Toxins and Dyes also Have Antibacterial Behavior
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Chemical Modification of Cloisite 20A by Ultrasonic Tip
2.3. Nanocomposite Preparation
2.4. Preparation of Non-Woven Fabric Materials
2.5. Characterization
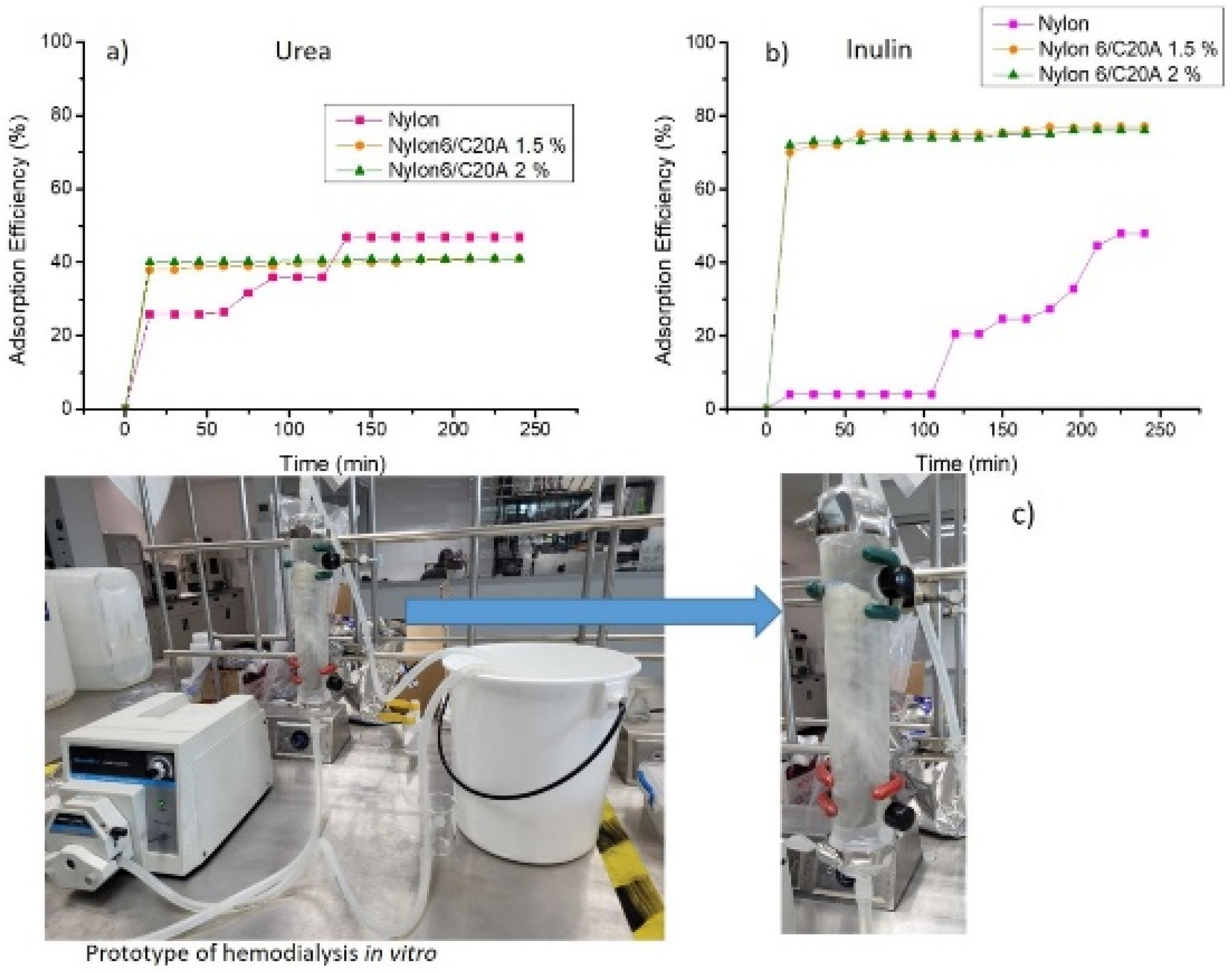
2.5.1. Adsorption of Uremic Toxins
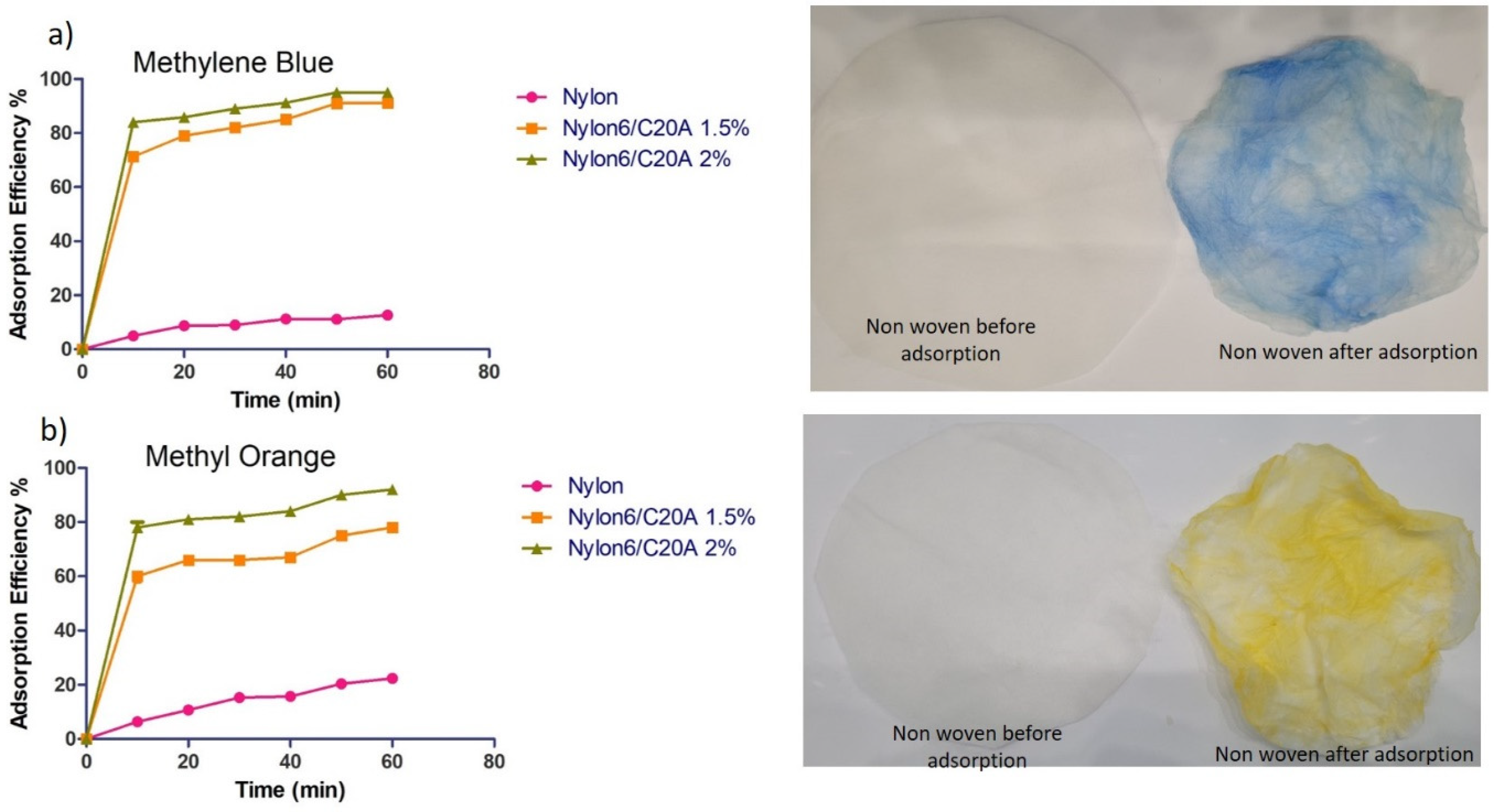
2.5.2. Adsorption of Dyes (Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange)
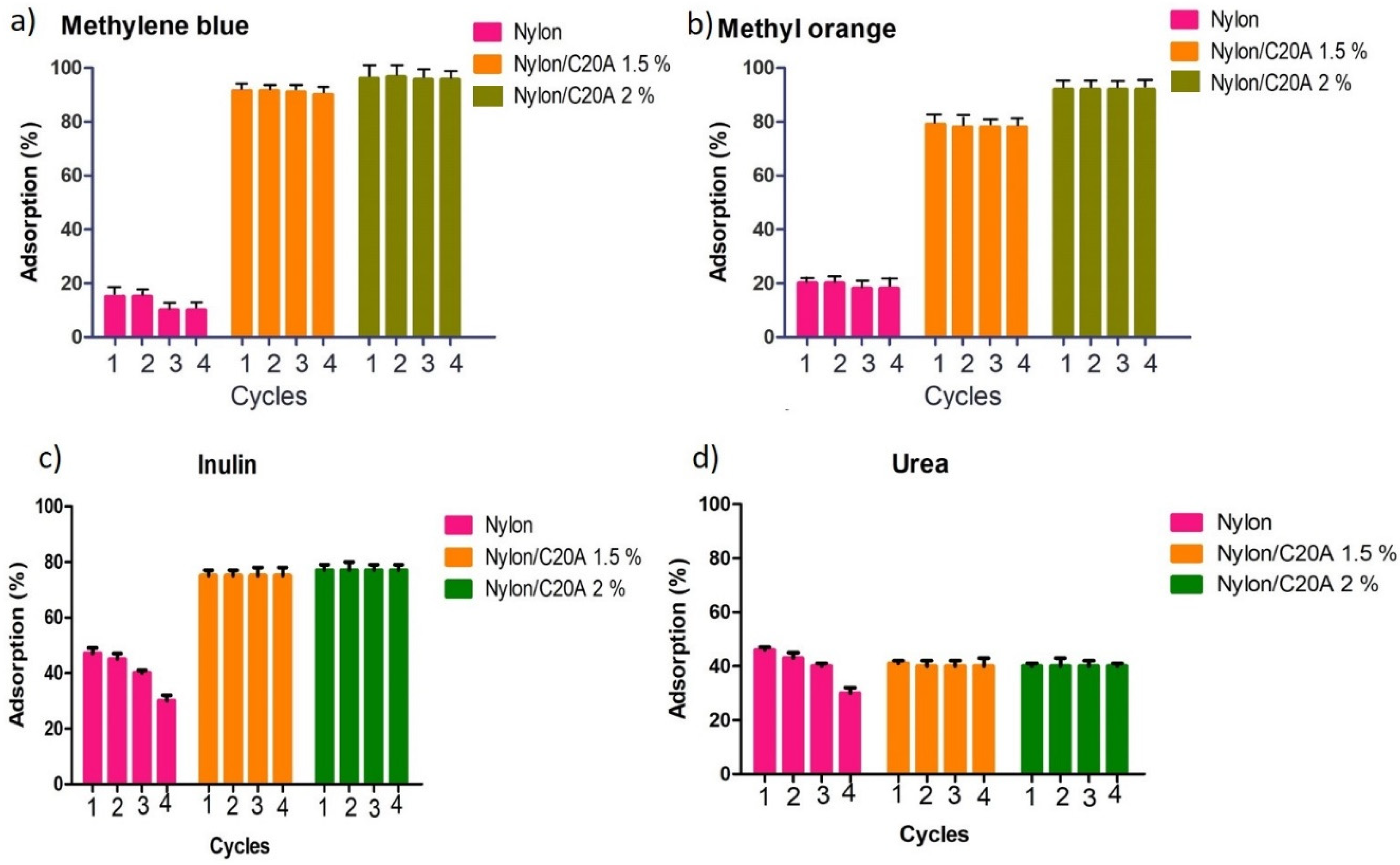
2.5.3. Reusability Study
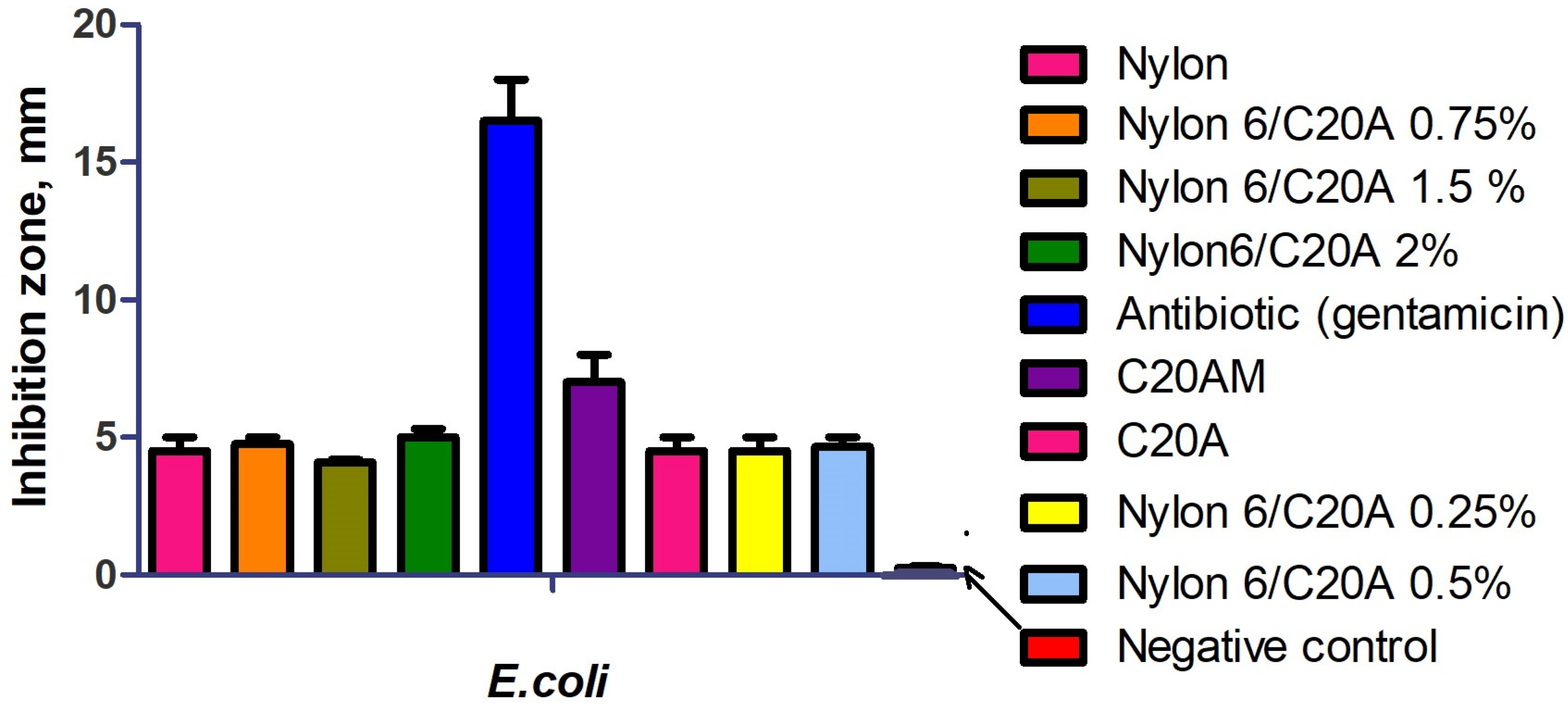
2.5.4. Antibacterial Activity
3. Results and Discussion
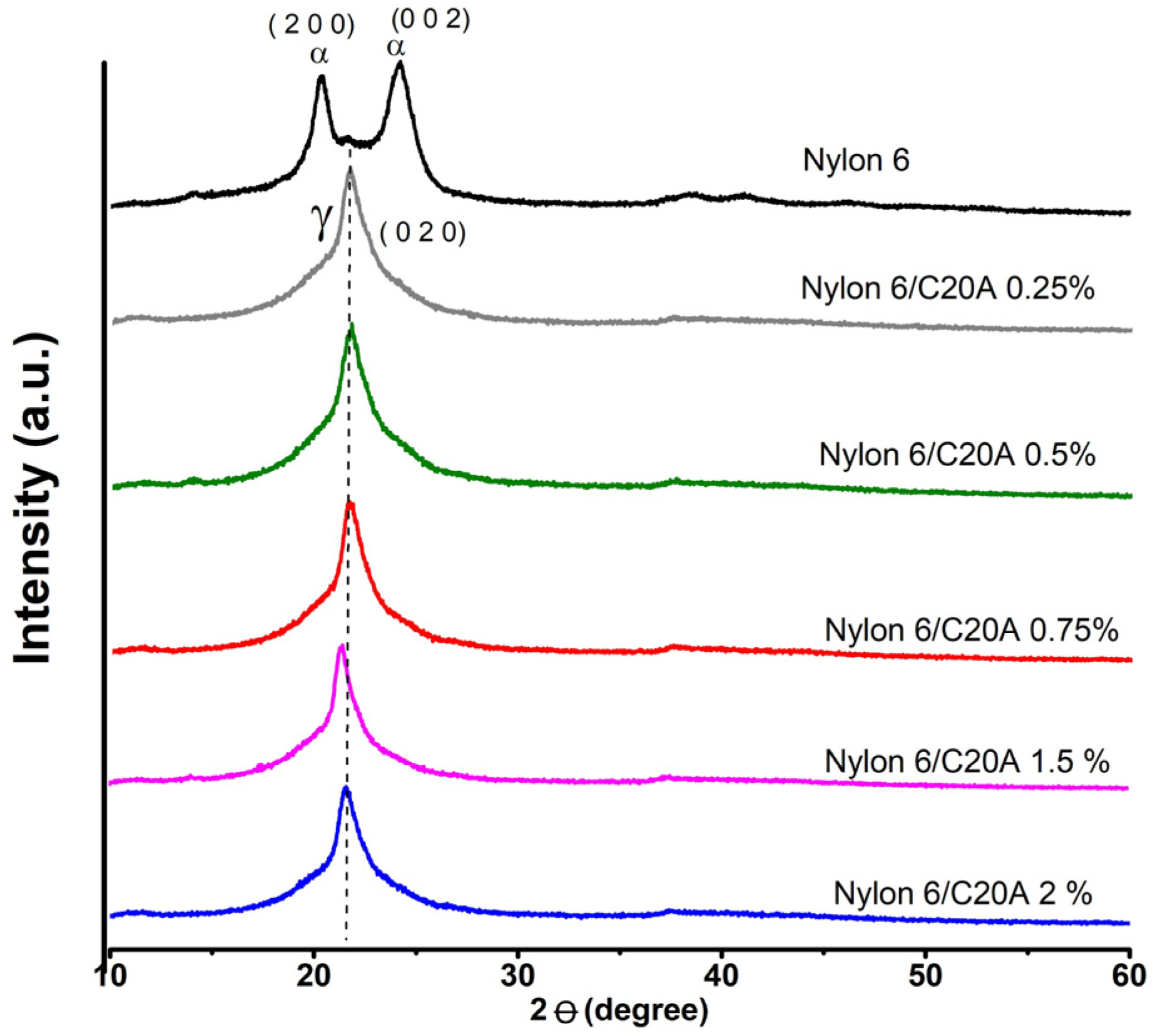
3.1. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
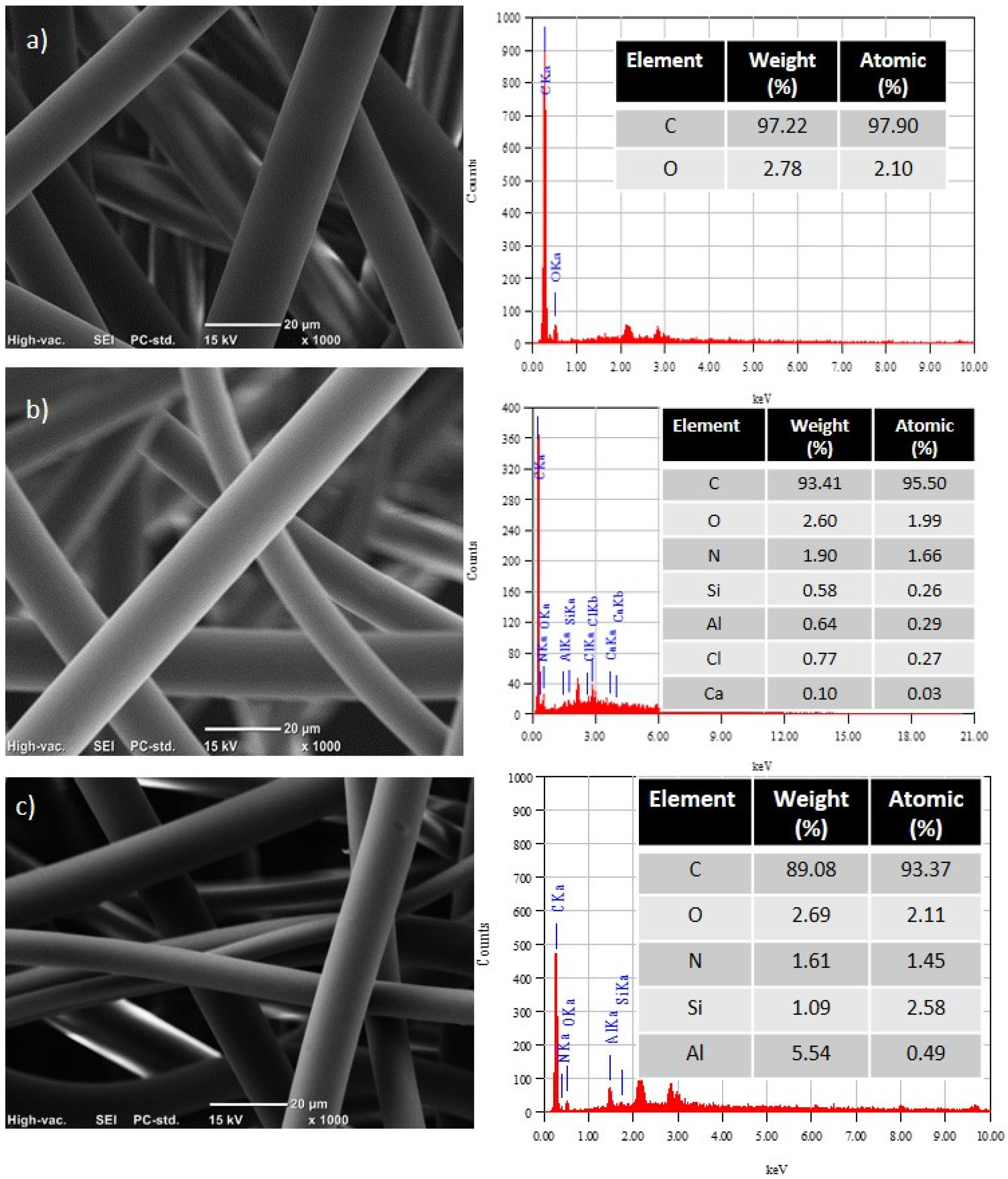
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
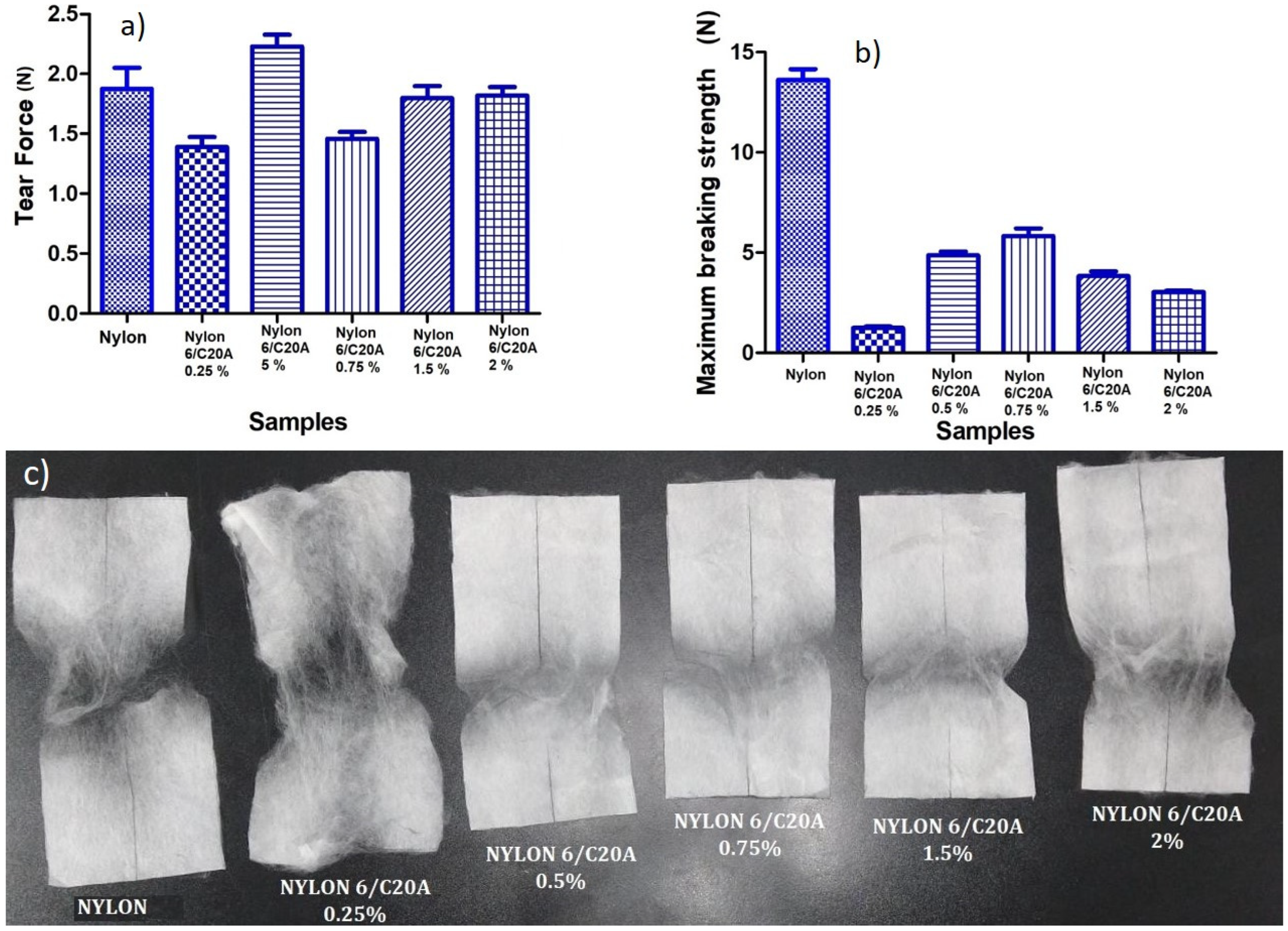
3.3. Mechanical Tests
3.4. Toxin Adsorption of Non-Woven Nylon 6/C20A
3.5. Dye Adsorption
3.6. Reusability of Non-Woven Fabric Nylon 6/C20A for the Adsorption of Dyes and Uremic Toxins
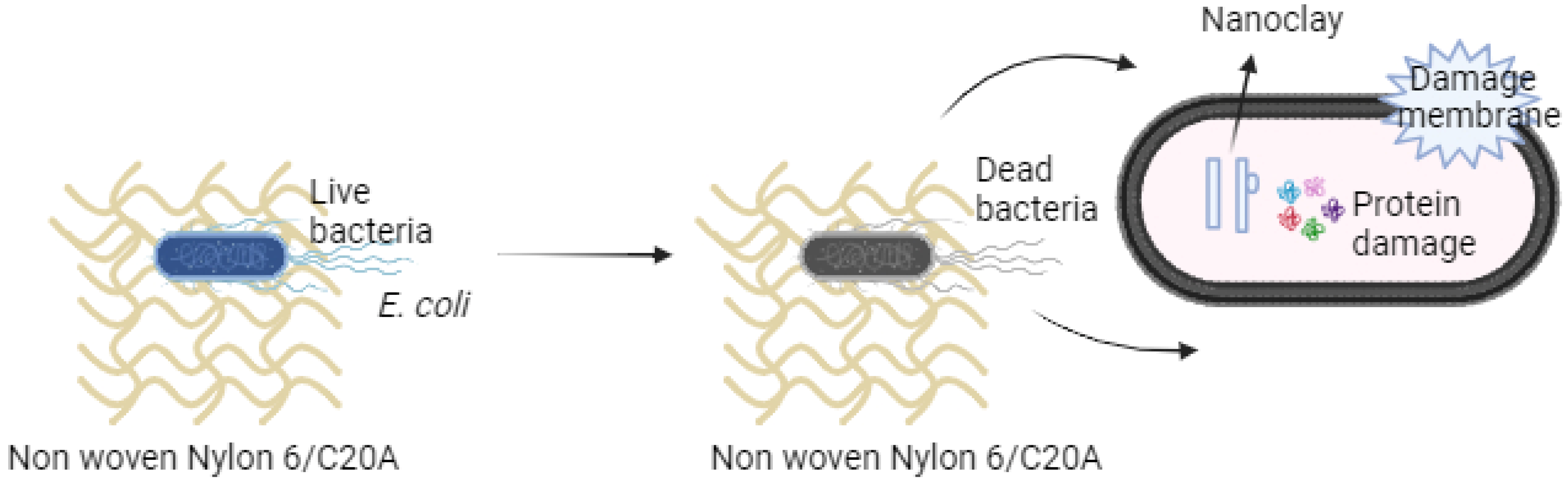
3.7. Antibacterial Activity
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fernandes, M.; Padrão, J.; Ribeiro, A.I.; Fernandes, R.D.; Melro, L.; Nicolau, T.; Mehravani, B.; Alves, C.; Rodrigues, R.; Zille, A. Polysaccharides and metal nanoparticles for functional textiles: A review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Alvarado, C.J.; Andrade-Guel, M.L.; Medellín-Banda, D.I.; Melo-Lopez, L.; Ávila-Orta, C.A. Polymer Composites: Smart Synthetic Fibers Approach in Energy and Environmental Care. In Handbook of Nanomaterials and Nanocomposites for Energy and Environmental Applications; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Gao, X.; Gao, X.; Seliem, M.K.; Dhaoudi, F.; Sellaoui, L.; Deng, S.; Bonilla-Petriciolet, A.; et al. Adsorption of food dyes from aqueous solution on a sweet potato residue-derived carbonaceous adsorbent: Analytical interpretation of adsorption mechanisms via adsorbent characterization and statistical physics modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, A.; Chen, M.; Seliem, M.K.; Mobarak, M.; Diao, Z.; Li, Z. Adsorption of azo dyes and Naproxen by few-layer MXene immobilized with dialdehyde starch nanoparticles: Adsorption properties and statistical physics modeling. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 473, 145385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Pei, L.; Xue, H.; Li, Z. Adsorption of methylene blue and Congo red from aqueous solution on 3D MXene/carbon foam hybrid aerogels: A study by experimental and statistical physics modeling. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massella, D.; Argenziano, M.; Ferri, A.; Guan, J.; Giraud, S.; Cavalli, R.; Antonello, A.B.; Salaün, F. Bio-functional textiles: Combining pharmaceutical nanocarriers with fibrous materials for innovative dermatological therapies. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmus, M.N.; Gibbons, D.F.; Cebon, D. Biocompatibility: Meeting a key functional requirement of next-generation medical devices. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 36, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, E.; Lee, Y.T. Development of an embossed nanofiber hemodialysis membrane for improving capacity and efficiency via 3D printing and electrospinning technology. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, A.; Tetta, C.; Ersoy, F.F.; D’intini, V.; Ratanarat, R.; De Cal, M.; Bordoni, V.; Salvatori, G.; Andrikos, E.; Yakupoglu, G.; et al. Uremic toxins: A new focus on an old subject. Semin. Dial. 2005, 18, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, M.N.Z.; Goh, P.S.; Said, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Othman, M.H.D.; Abdullah, M.S.; Ng, B.C.; Hasbullah, H.; Hamimah, S.; Abdul Kadir, S.; et al. Polysulfone/amino-silanized poly (methyl methacrylate) dual-layer hollow fiber membrane for uremic toxin separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Guel, M.; Reyes-Rodríguez, P.Y.; Cabello-Alvarado, C.J.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Ávila-Orta, C.A. Influence of Modified Carbon Black on Nylon 6 Nonwoven Fabric and Performance as Adsorbent Material. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Alvarado, C.; Andrade-Guel, M.; Medellin-Banda, D.I.; Ávila-Orta, C.A.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Sáenz-Galindo, A.; Radillo-Radillo, R.; Lara-Sánchez, J.F.; Melo-Lopez, L. Non-woven fabrics based on Nylon 6/carbon black-graphene nanoplatelets obtained by melt-blowing for adsorption of urea, uric acid, and creatinine. Mater. Lett. 2022, 320, 132382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaj, P.; Sengupta, A.K. Industrial applications of textiles: Textiles for filtration and coated fabrics. Text. Prog. 1985, 14, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldalbahi, A.; El-Naggar, M.E.; El-Newehy, M.H.; Rahaman, M.; Hatshan, M.R.; Khattab, T.A. Effects of technical textiles and synthetic nanofibers on environmental pollution. Polymers 2021, 13, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Khan, N.A.; Cheng, C.; Shah, S.S.A.; Najam, T.; Arshad, M.; Sharif, A.; Akhtar, S.; Rehman, A. Surface induced growth of ZIF-67 at Co-layered double hydroxide: Removal of methylene blue and methyl orange from water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.H.; Fu, C.C.; Juang, R.S. Degradation of methylene blue and methyl orange by palladium-doped TiO2 photocatalysis for water reuse: Efficiency and degradation pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 413–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, M.U.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Le, V.T.; Hoang, H.Y.; Le, T.T.N.; Pham, T.N.; Nguyen, T.T.; Akhmadullin, R.M.; Le, H.S.; Tran, H.V.; et al. Non-woven polyester fabric-supported cuprous oxide/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 10353–10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.S.; Rahman, N.; Chowdhury, T.A.; Dafader, N.C.; Sultana, S.; Sardar, M.N.; Kayser, M.N. Application of Sulfonated GMA-g-non Woven PE Fabric for the Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Wastewater. Am. J. Polym. Sci. Technol. 2021, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Guel, M.; Ávila-Orta, C.A.; Cabello-Alvarado, C.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Esparza-González, S.C.; Pérez-Alvarez, M.; Quiñones-Jurado, Z.V. Non-woven fabrics Based on Nanocomposite Nylon 6/ZnO Obtained by Ultrasound-Assisted Extrusion for Improved Antimicrobial and Adsorption Methylene Blue Dye Properties. Polymers 2021, 13, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Guel, M.; Cabello-Alvarado, C.; Romero-Huitzil, R.L.; Rodríguez-Fernández, O.S.; Ávila-Orta, C.A.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Medellín-Banda, D.I.; Gallardo-Vega, C.; Cepeda-Garza, J. Nanocomposite PLA/C20A nanoclay by ultrasound-assisted melt extrusion for adsorption of uremic toxins and methylene blue dye. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Alvarado, C.; Andrade-Guel, M.; Ávila-Orta, C.A.; Gamero-Melo, P.; Reyes-Rodríguez, P.Y.; Quiñones-Jurado, Z.V.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Bartolo-Pérez, P.; Soriano-Corral, F.; Covarrubias-Gordillo, C. Composites based on nylon 6/clinoptilolite by ultrasound-assisted extrusion for enhanced flame retardant and mechanical properties. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 1803–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Rodríguez, P.Y.; Ávila-Orta, C.A.; Andrade-Guel, M.; Cortés-Hernández, D.A.; Herrera-Guerrero, A.; Cabello-Alvarado, C.; Sánchez-Fuentes, J.; Ramos-Martínez, V.H.; Valdez-Garza, J.A.; Hurtado-López, G.F. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles Zn1-xMgxFe2O4 with partial substitution of Mg2+ (x = 0.0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1.0) for adsorption of uremic toxins. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 27913–27921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, G.; Ueda, K.; Rusu, E.; Rusu, M. Polyamides from lactams by centrifugal molding via anionic ring-opening polymerization. Polymer 2001, 42, 5669–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Flores, S.; Martínez-Luévanos, A.; Bartolo-Pérez, P.; García-Cerda, L.A.; Flores-Guia, T.E.; Aguilera-González, E.N. Facile synthesis of novel calcium silicate hydrated-nylon 6/66 nanocomposites by solution mixing method. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 41818–41827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, E.M.; Leite, A.M.D.; da Paz, R.A.; Medeiros, V.D.N.; de Melo, T.J.A.; Lira, H.D.L. Polyamide 6 nanocomposites with inorganic particles modified with three quaternary ammonium salts. Materials 2011, 4, 1956–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.M.; Liao, C.S. Polymorphism in nylon 6/clay nanocomposites. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2000, 201, 2820–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Alvarado, C.J.; Quiñones-Jurado, Z.V.; Cruz-Delgado, V.J.; Avila-Orta, C.A. Pigmentation and degradative activity of TiO2 on polyethylene films using masterbatches fabricated using variable-frequency ultrasound-assisted melt-extrusion. Materials 2020, 13, 3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, K.; Tabuani, D.; Camino, G. Poly (lactic acid)/clay nanocomposites: Effect of nature and content of clay on morphology, thermal and thermo-mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 1790–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, B.B.; Kinloch, A.J.; Mohammed, R.D.; Taylor, A.C.; Sprenger, S. Toughening mechanisms of nanoparticle-modified epoxy polymers. Polymer 2007, 48, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Alvarado, C.; Andrade-Guel, M.; Pérez-Alvarez, M.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Cortés-Hernández, D.A.; Bartolo-Pérez, P.; Ávila-Orta, C.A.; Cruz-Delgado, V.J.; Zepeda-Pedreguera, A. Graphene nanoplatelets modified with amino-groups by ultrasonic radiation of variable frequency for potential adsorption of uremic toxins. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Feng, J.; Yan, W. Influence of metal oxides on the adsorption characteristics of PPy/metal oxides for Methylene Blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 475, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslim, M.; Ali, A.; Neogi, I.; Dege, N.; Shahid, M.; Ahmad, M. Facile synthesis, topological study, and adsorption properties of a novel Co (II)-based coordination polymer for adsorptive removal of methylene blue and methyl orange dyes. Polyhedron 2021, 210, 115519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Esfahani, M.R. Thin-Film Nanocomposite Membranes Functionalized with Fe-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for Enhanced Removal of Urea from Water. ACS EST Water 2024, 4, 2064–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habiba, U.; Siddique, T.A.; Lee, J.J.L.; Joo, T.C.; Ang, B.C.; Afifi, A.M. Adsorption study of methyl orange by chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/zeolite electrospun composite nanofibrous membrane. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 191, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Mansor, E.S.; Taha, G.M. Microfiltration and adsorptive membranes for simultaneous removal of methyl orange and methylene blue using hybrid composites. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 7891–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łatwińska, M.; Sójka-Ledakowicz, J.; Chruściel, J.; Piórkowski, M. PLA and PP composite nonwoven with antimicrobial activity for filtration applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 2016, 2510372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigmatullin, R.; Gao, F.; Konovalova, V. Polymer-layered silicate nanocomposites in the design of antimicrobial materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 5728–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andra, S.; Balu, S.K.; Jeevanandam, J.; Muthalagu, M. Emerging nanomaterials for antibacterial textile fabrication. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 1355–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

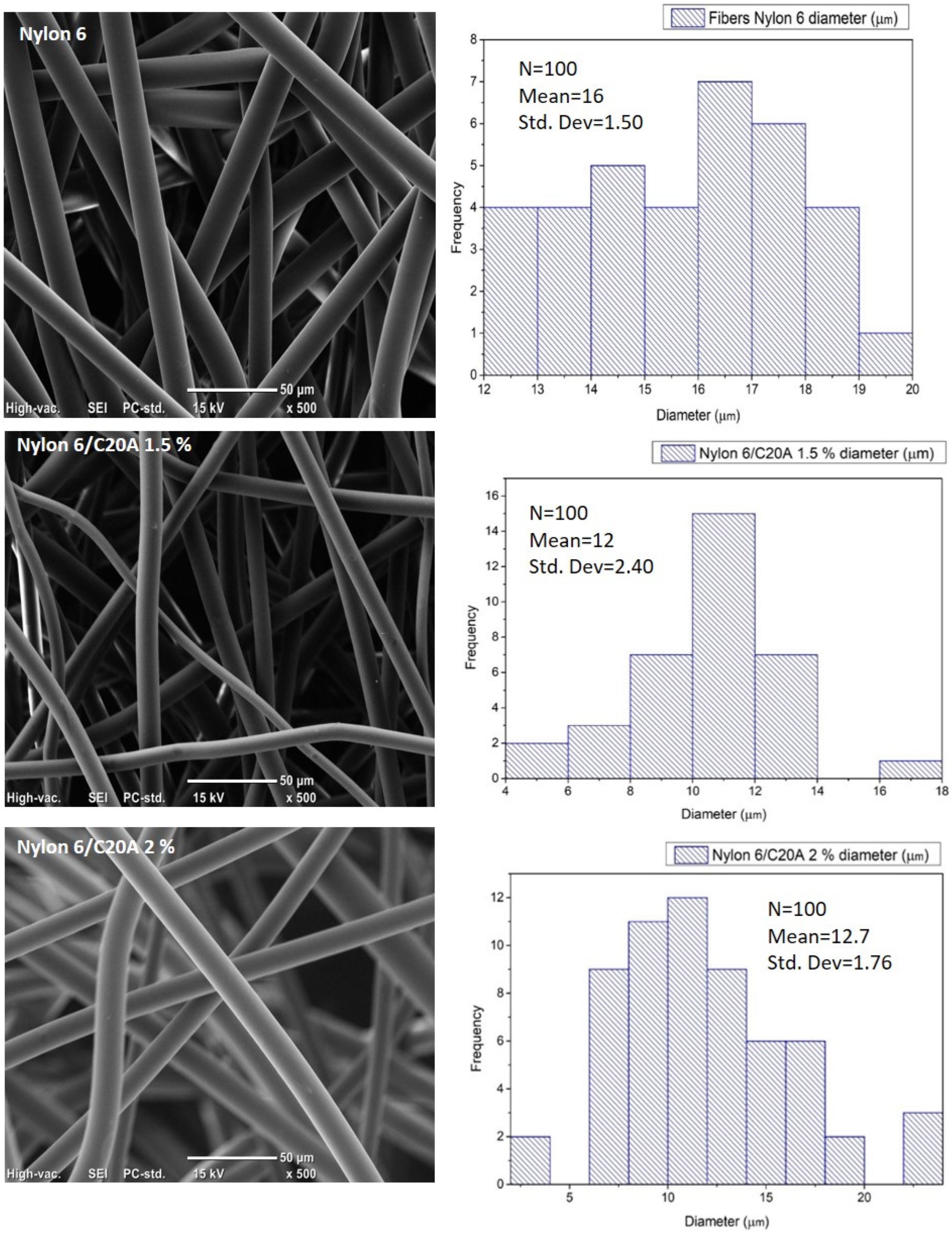
| Sample | Fiber Diameter (µm) |
|---|---|
| Nylon 6 | 16 and 17 ± 1.5 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.25% | 16 ± 0.7 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.5% | 15 ±1.8 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.75% | 13 ± 2.1 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 1.5% | 12 ± 2.4 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 2.0% | 12.7 ± 1.76 |
| Sample | Tear Force (N) | Maximum Breaking Strength (N) |
|---|---|---|
| Nylon 6 | 1.734 | 13.24 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.25% | 1.334 | 1.19 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.5% | 2.334 | 4.73 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.75% | 1.4243 | 5.56 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 1.5% | 1.7348 | 3.66 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 2.0% | 1.7792 | 3.08 |
| Sample | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | qmax | R2 | n | KF | R2 | |
| Nylon | 0.02 | 3.67 | 0.9948 | 0.35 | 12.46 | 0.9994 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.25% | 0.04 | 8.11 | 0.9986 | 0.30 | 7.09 | 0.9989 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.5% | 0.4 | 8.10 | 0.9906 | 0.31 | 7.00 | 0.9989 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.75% | 0.11 | 1.44 | 0.9996 | 0.69 | 9.10 | 0.9997 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 1.5% | 0.01 | 1.60 | 0.9903 | 0.65 | 8.96 | 0.9995 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 2% | 0.01 | 1.47 | 0.9980 | 0.68 | 9.12 | 0.999 |
| Sample | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | qmax | R2 | n | KF | R2 | |
| Nylon | 0.16 | 25.8 | 0.999 | 1.12 | 11.4 | 0.9996 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.25% | 0.06 | 0.94 | 0.9996 | 2.71 | 18.52 | 0.9994 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.5% | 0.006 | 0.7 | 0.9999 | 3.08 | 20.52 | 0.9992 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.75% | 0.04 | 1.13 | 0.9998 | 3.07 | 20.46 | 0.9994 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 1.5% | 0.059 | 66 | 0.9999 | 3.23 | 21.30 | 0.9994 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 2% | 0.042 | 1.24 | 0.9999 | 3.05 | 20.35 | 0.9995 |
| Sample | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | qmax | R2 | n | KF | R2 | |
| Nylon | 9.3 | 312 | 0.9976 | 4.8 | 30.4 | 0.8799 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.25% | 8.3 | 113 | 0.9003 | 0.18 | 50.5 | 0.934 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.5% | 1.5 | 132 | 0.9317 | 4.9 | 52 | 0.9574 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.75% | 2.2 | 210 | 0.9886 | 4.0 | 51 | 0.9297 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 1.5% | 0.29 | 432 | 0.9994 | 2.6 | 8.11 | 0.9977 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 2% | 2 | 67.6 | 0.9998 | 6.5 | 14.77 | 0.9945 |
| Sample | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k | qmax | R2 | n | KF | R2 | |
| Nylon | 1.20 | 196.92 | 0.9387 | 9.61 | 52.17 | 0.9817 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.25% | 0.03 | 199 | 0.9990 | 0.52 | 2.77 | 0.9905 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.5% | 1.5 | 186 | 0.9953 | 1.25 | 9.47 | 0.9545 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 0.75% | 1.66 | 193 | 0.9973 | 1.4 | 6.09 | 0.9038 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 1.5% | 0.23 | 151.4 | 0.9933 | 4.6 | 11.32 | 0.9448 |
| Nylon 6/C20A 2% | 0.19 | 343 | 0.9985 | 9.7 | 20.11 | 0.9565 |
| Material | Uremic Toxins (Adsorption %) | Dyes (Adsorption %) | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urea | Inulin | Methylene Blue | Methyl Orange | ||
| Nylon 6/CB | 80–90 | 80–85 | ---- | ---- | [11] |
| PLA/C20A nanoclay | 65 | ---- | 97 | ---- | [20] |
| Nylon 6/ZnO | ---- | ---- | 93 | ---- | [19] |
| Polyamide functionalized with Fe-based metal–organic | 85 | ---- | ---- | ---- | [33] |
| Non-woven polyester fabric-supported cuprous oxide/reduced graphene oxide | ---- | ---- | 96 | ---- | [17] |
| Chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/zeolite electrospun composite | ---- | ---- | ---- | 95 | [34] |
| Polyethylene oxide/bentonite/polyaniline | ---- | ---- | 96 | 94 | [35] |
| Nylon 6/C20A 1.5% | 40 | 75 | 90 | 78 | This study |
| Nylon 6/C20A 2% | 40 | 74 | 90 | 92 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Andrade-Guel, M.; Cabello-Alvarado, C.J.; Ávila Orta, C.A.; Cadenas-Pliego, G.; Cruz-Ortiz, B. Functional Technical Textile-Based Polymer Nanocomposites with Adsorbent Properties of Toxins and Dyes also Have Antibacterial Behavior. Materials 2024, 17, 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17123007
Andrade-Guel M, Cabello-Alvarado CJ, Ávila Orta CA, Cadenas-Pliego G, Cruz-Ortiz B. Functional Technical Textile-Based Polymer Nanocomposites with Adsorbent Properties of Toxins and Dyes also Have Antibacterial Behavior. Materials. 2024; 17(12):3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17123007
Chicago/Turabian StyleAndrade-Guel, Marlene, Christian J. Cabello-Alvarado, Carlos Alberto Ávila Orta, Gregorio Cadenas-Pliego, and Brenda Cruz-Ortiz. 2024. "Functional Technical Textile-Based Polymer Nanocomposites with Adsorbent Properties of Toxins and Dyes also Have Antibacterial Behavior" Materials 17, no. 12: 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17123007
APA StyleAndrade-Guel, M., Cabello-Alvarado, C. J., Ávila Orta, C. A., Cadenas-Pliego, G., & Cruz-Ortiz, B. (2024). Functional Technical Textile-Based Polymer Nanocomposites with Adsorbent Properties of Toxins and Dyes also Have Antibacterial Behavior. Materials, 17(12), 3007. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17123007










