Microstructure Evolution, Hardness, and Tribological Behaviors of Ti-50.8Ni SMA Alloy with Ultrasonic Surface Shot Peening Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microstructure and Hardness Testing
2.3. Dry Sliding Wear Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure Analysis
3.2. Surface Hardness
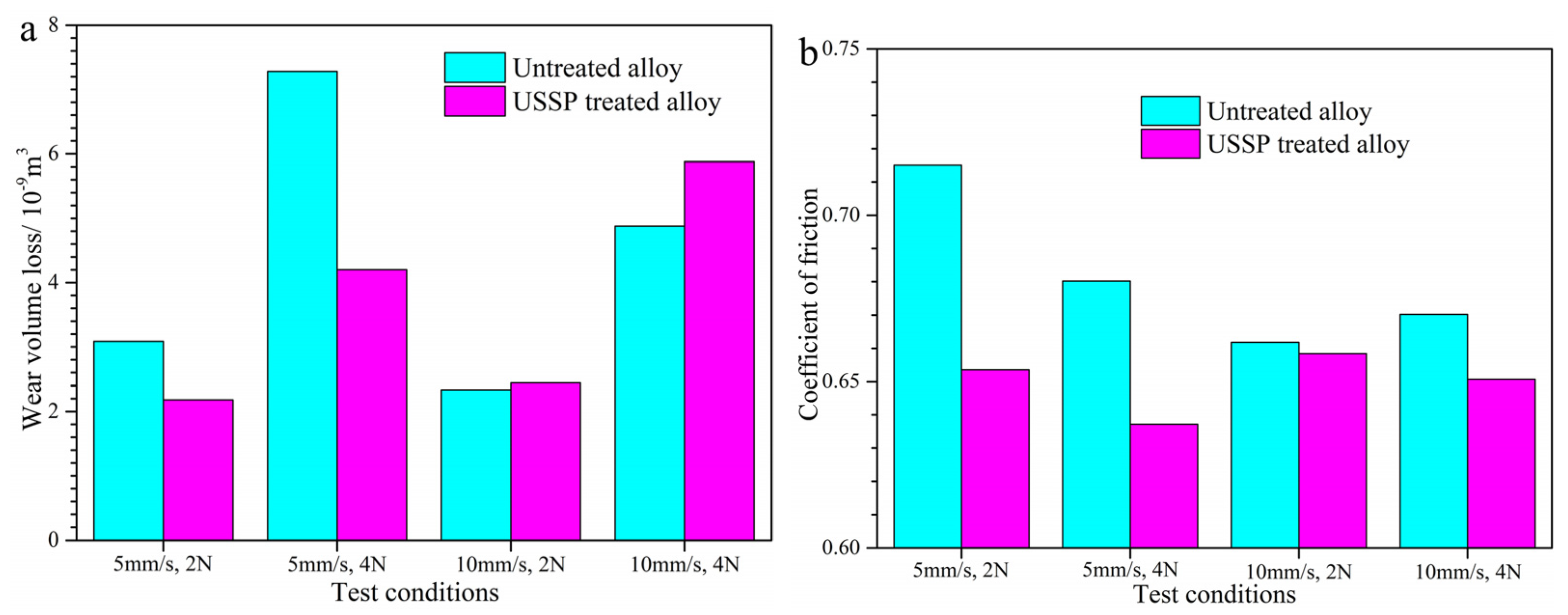
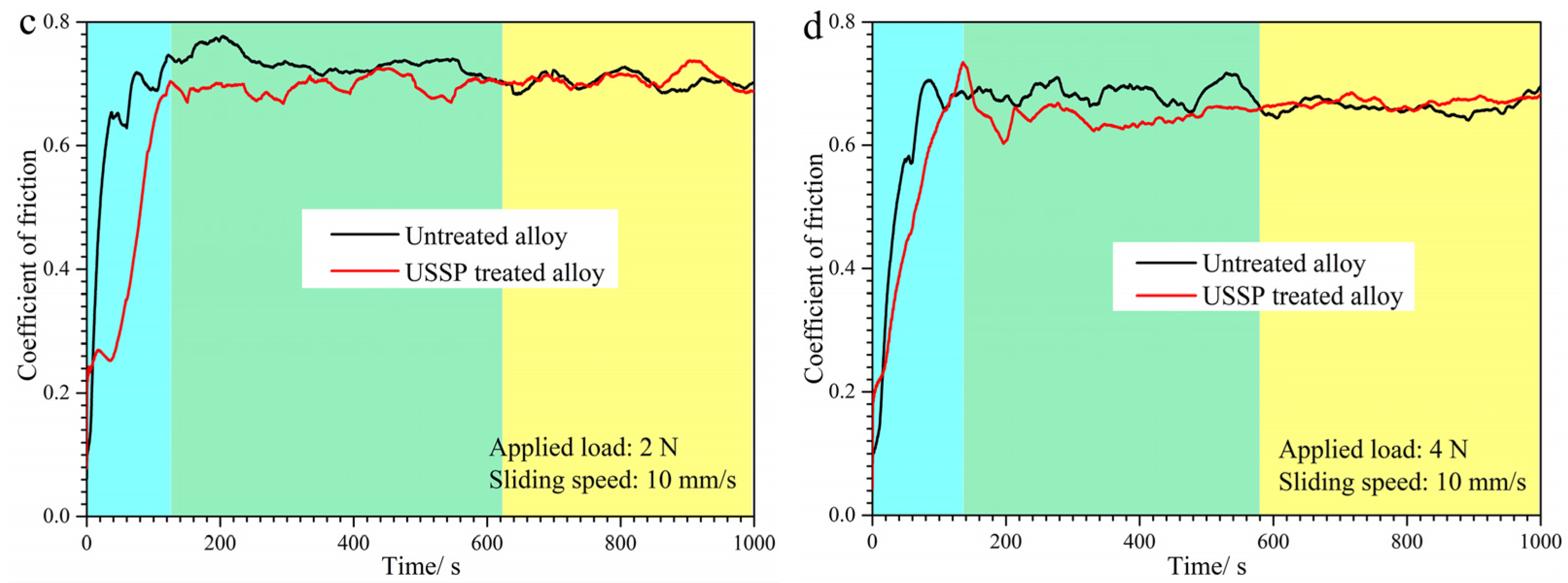
3.3. Dry Sliding Wear Properties
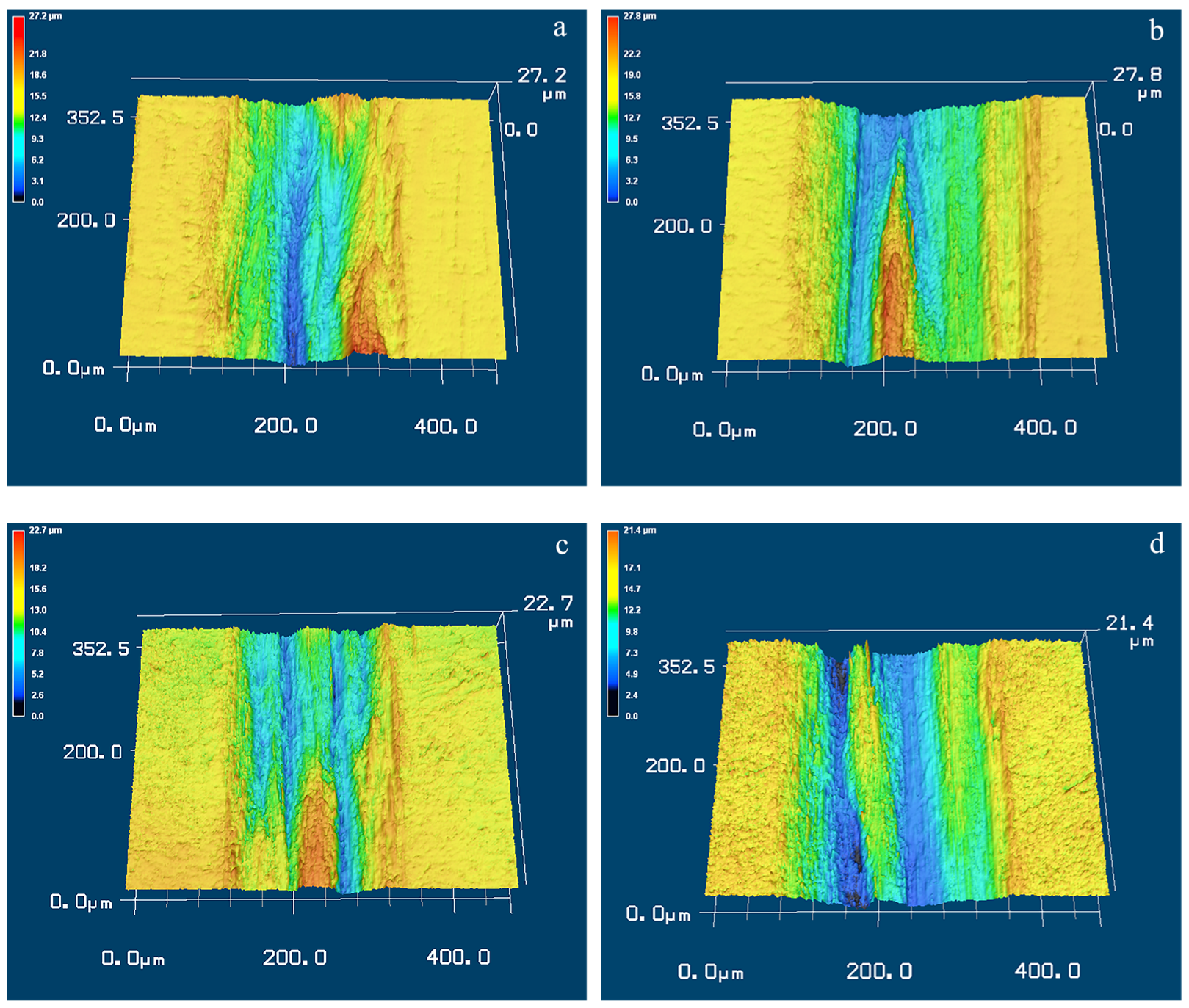
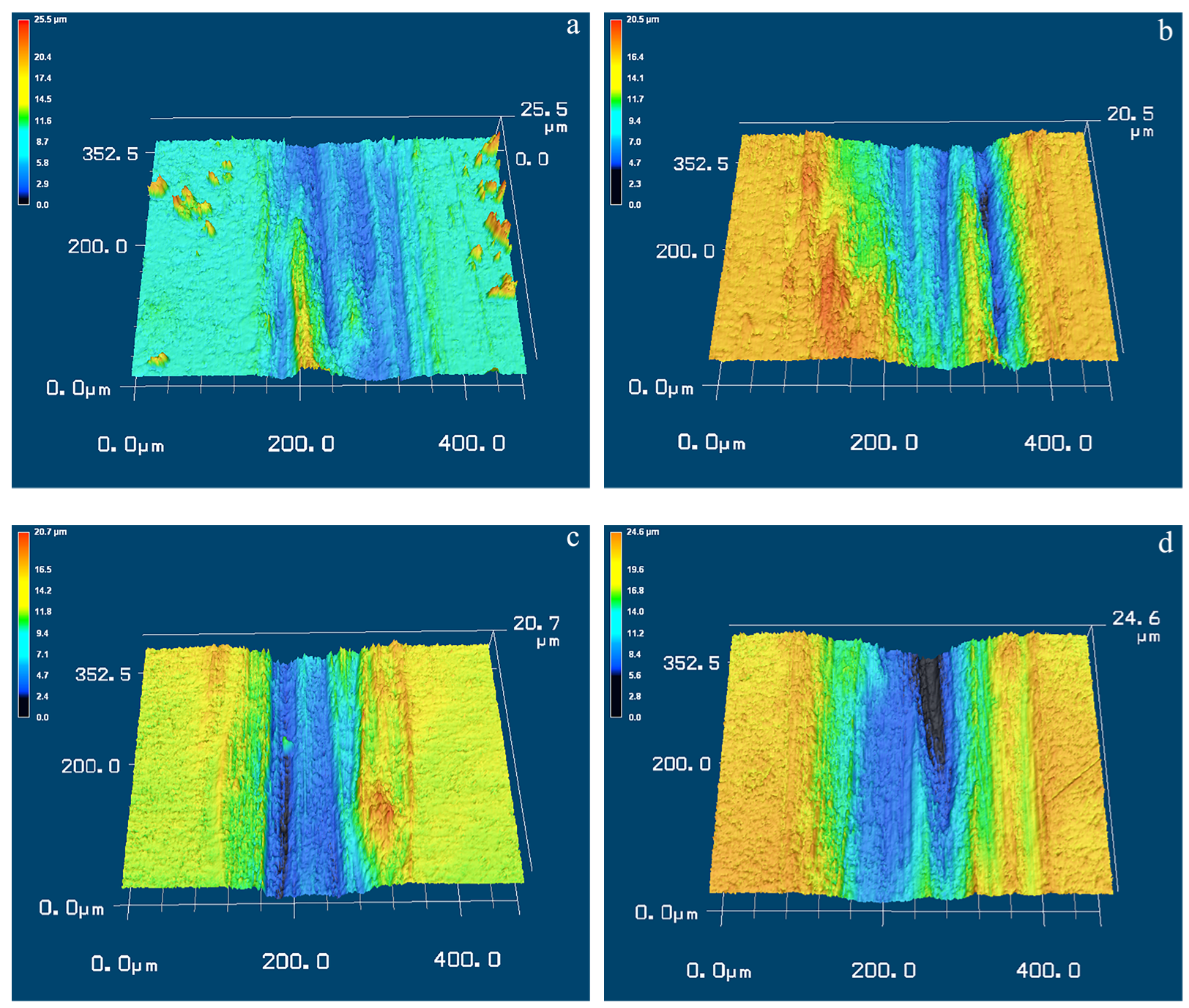
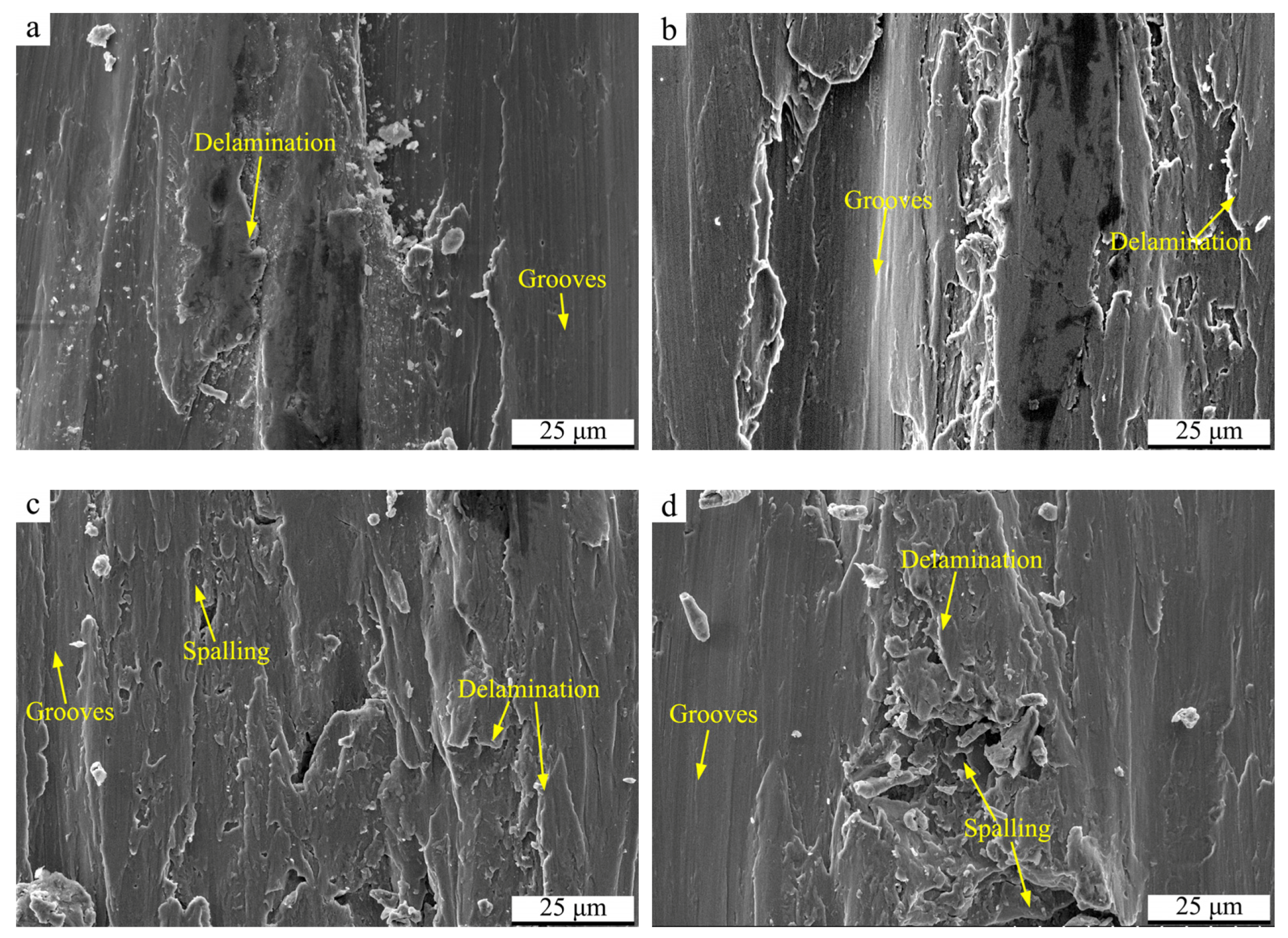
3.4. Wear Surfaces
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- After the USSP treatment, the phase composition has little change, with the B19′ phase slightly increasing; additionally, the main B2 phase grain can be refined to some degree;
- (2)
- The USSP treatment can dramatically improve the surface hardness, with the highest hardness of 541 HV obtained under the test load of 25 g; however, the hardness would decline quickly with the further increase of the test load.
- (3)
- In the case of 5 mm/s, the wear volume loss and COF are much lower for the USSP-treated alloy, implying the improvement of tribological performance; however, when the sliding wear speed increases to 10 mm/s, the wear resistance of the USSP-treated alloy reversely decreases while that of the untreated alloy increases. Stress-induced martensite transformation and degeneration resulting from frictional heating dominate the dry sliding wear mechanism of Ti-50.8Ni alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, X.; Sui, J.H.; Cai, W.; Liu, A.L. Improving wear resistance of TiNi matrix composites reinforced by carbon nanotubes and in situ TiC. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Lin, K.M.; Chen, Y.C. A study on the machining characteristics of TiNi shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2000, 105, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Kong, X.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Selective laser melted high Ni content TiNi alloy with superior superelasticity and hardwearing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 116, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; He, J.L.; Chen, K.C.; Liao, H.M.; Lin, K.M. Wear characteristics of TiNi shape memory alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1997, 28, 1871–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y. Exploration of TiNi shape memory alloy for potential application in a new area: Tribological engineering. Smart Mater. Struct. 2000, 9, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y. A new type of wear-resistant material: Pseudo-elastic TiNi alloy. Wear 1998, 221, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Li, Z.; Xiang, G. Dry sliding wear behavior of TiNi alloy processed by equal channel angular extrusion. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 2218–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.H.; Chan, C.W.; Man, H.C.; Waugh, D.G.; Lawrence, J. NiTi shape memory alloy with enhanced wear performance by laser selective area nitriding for orthopaedic applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 309, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Yin, X.; Lin, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, C. Microstructure and wear behaviors of laser cladding in-situ synthetic (TiBx + TiC)/(Ti2Ni + TiNi) gradient composite coatings. Vacuum 2020, 176, 109305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, R.; Farhat, Z. Wear and dent resistance of superelastic TiNi alloy. Wear 2013, 301, 682–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Ma, W.; Duan, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q. Microstructure responses and deformation mechanisms of solutionized Ti-51.5 at.%Ni alloy during reciprocating sliding. Tribol. Int. 2019, 140, 105816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meddah, S.; Chadli, H.; Bourebia, M.; Montagne, A.; Iost, A.; Labaiz, M.; Taleb, A. Dry sliding wear performance of an annealed TiNi alloy with different nickel contents. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 036508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Han, Q.; Xu, R.; Zhao, K.; Li, J. Localized corrosion behaviour of AA7150 after ultrasonic shot peening: Corrosion depth vs. impact energy. Corros. Sci. 2018, 130, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Mahobia, G.S.; Singh, V. Hot corrosion behaviour of Ti–6Al–4V modified by ultrasonic shot peening. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jian, Y.; Zhao, X.; Meng, D.; Pan, F.; Han, Q. The tribological behavior of a surface-nanocrystallized magnesium alloy AZ31 sheet after ultrasonic shot peening treatment. J. Magnes. Alloys 2021, 9, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillmann, W.; Momeni, S. Tribological performance of near equiatomic and Ti-rich NiTi shape memory alloy thin films. Acta Mater. 2015, 92, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhu, M.; Jian, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lu, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, C. In-situ synchrotron diffraction study of the localized phase transformation and deformation behavior in NiTi SMA. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 805, 140560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Liu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Chen, G.; Lan, B.; Lu, X.; Li, C. Evaluation of the microstructure and property of TiNi SMA prepared using VIM in BaZrO3 crucible. Vacuum 2019, 168, 108843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahmir, H.; Nili-Ahmadabadi, M.; Huang, Y.; Jung, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Langdon, T.G. Shape memory characteristics of a nanocrystalline TiNi alloy processed by HPT followed by post-deformation annealing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 734, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.E.; Pickart, S.J.; Alperin, H.A. Mechanism of the TiNi Martensitic Transformation and the Crystal Structures of TiNi-II and TiNi-III Phases. J. Appl. Phys. 1972, 43, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroozmehr, A.; Kermanpur, A.; Ashrafizadeh, F.; Kabiri, Y. Investigating microstructural evolution during homogenization of the equiatomic NiTi shape memory alloy produced by vacuum arc remelting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 7952–7955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zeng, P.; Lei, L.; Zhang, Y. In situ observation on temperature dependence of martensitic transformation and plastic deformation in superelastic NiTi shape memory alloy. Mater. Des. 2017, 134, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Chen, W.; Yang, S.; Zhu, J.; Ren, X.; Otsuka, K. Origin of abnormal multi-stage martensitic transformation behavior in aged Ni-rich Ti–Ni shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4351–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-C.; Shen, J.-J.; Chang, Y.-T.; Wu, C.-T.; Chen, C.-H. Evolutions of superelasticity and elastocaloric effect of Ti50Ni48Fe2 and aged-hardened Ni-rich Ti49.2Ni49.3Fe1.5 shape memory alloys under cyclic compressive deformation. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 893, 162352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Chen, N.; Wang, C.; Wei, L.; Chen, J. Method for Determining Crystal Grain Size by X-ray Diffraction. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2018, 53, 1700157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xing, J.; Li, J. Effects of chromium additions on the three-body abrasive wear behavior of Fe-3.0 wt% B alloy. Wear 2017, 378–379, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jian, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qi, H.; Huang, Z.; Huang, G.; Xing, J. Microstructure, hardness and slurry erosion-wear behaviors of high-speed laser cladding Stellite 6 coatings prepared by the inside-beam powder feeding method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 2596–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang Shri, D.N.; Tsuchiya, K.; Yamamoto, A. Surface characterization of TiNi deformed by high-pressure torsion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 289, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciniegas, M.; Casals, J.; Manero, J.M.; Peña, J.; Gil, F.J. Study of hardness and wear behaviour of NiTi shape memory alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 460, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Qi, H.; Zhang, J.; Kong, H.; Huang, Z.; Xing, J. Effects of trace Si addition on the microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of MoAlB ceramic. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 941, 168873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qi, H.; He, P.; Huang, G.; Huang, Z. Effects of scanning speed on the microstructure, hardness and corrosion properties of high-speed laser cladding Fe-based stainless coatings. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 3380–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Cui, X.; Liu, E.; Feng, X.; Dong, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, G. Influence of microstructure on phase transformation behavior and mechanical properties of plasma arc deposited shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, H.; Nouri, M. Effects of Yttrium Addition on Microstructure, Hardness and Resistance to Wear and Corrosive Wear of TiNi Alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2011, 27, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.; Huang, Z.; Xing, J.; Zheng, B.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y. Effect of improving Fe2B toughness by chromium addition on the two-body abrasive wear behavior of Fe–3.0wt% B cast alloy. Tribol. Int. 2016, 101, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benamor, A.; Kota, S.; Chiker, N.; Haddad, A.; Hadji, Y.; Natu, V.; Abdi, S.; Yahi, M.; Benamar, M.E.A.; Sahraoui, T.; et al. Friction and wear properties of MoAlB against Al2O3 and 100Cr6 steel counterparts. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartkowski, D.; Bartkowska, A. Wear resistance in the soil of Stellite-6/WC coatings produced using laser cladding method. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2017, 64, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Cui, X.; Jin, G.; Dong, M.; Fang, Y.; Wen, X.; Ma, W. Effect of La2O3 addition on mechanical properties and wear behaviour of NiTi alloy fabricated by direct metal deposition. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 129, 106290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Lukitsch, M.; Weiner, A.M.; Lev, L.C.; Grummon, D.S. Novel layered tribological coatings using a superelastic NiTi interlayer. Wear 2005, 259, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, R.; Hu, S.; Tu, F.; Jin, W. Research combining experiment and FEM analysis on sliding wear behaviors and mechanisms of TiNi alloy. Wear 2017, 386–387, 218–222. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, G.; Ho, J.K.L.; Dong, G.; Hua, M. Fabrication self-recovery bulge textures on TiNi shape memory alloy and its tribological properties in lubricated sliding. Tribol. Int. 2016, 96, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Farhat, Z.N. Sliding wear of superelastic TiNi alloy. Wear 2009, 267, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
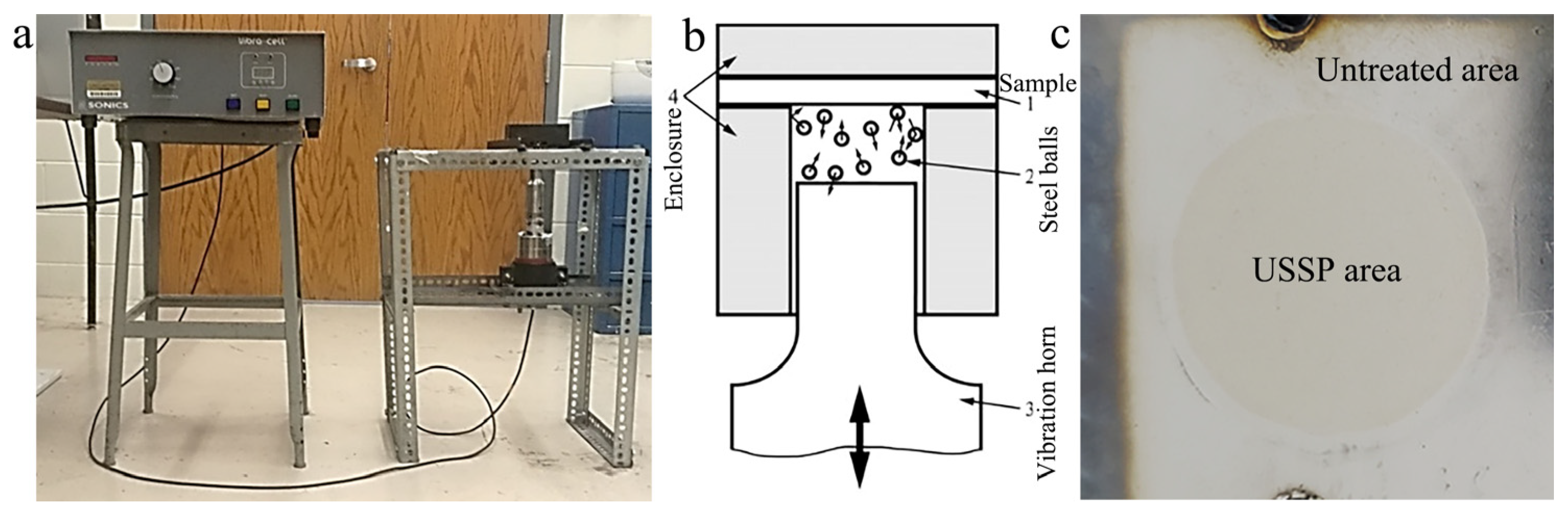
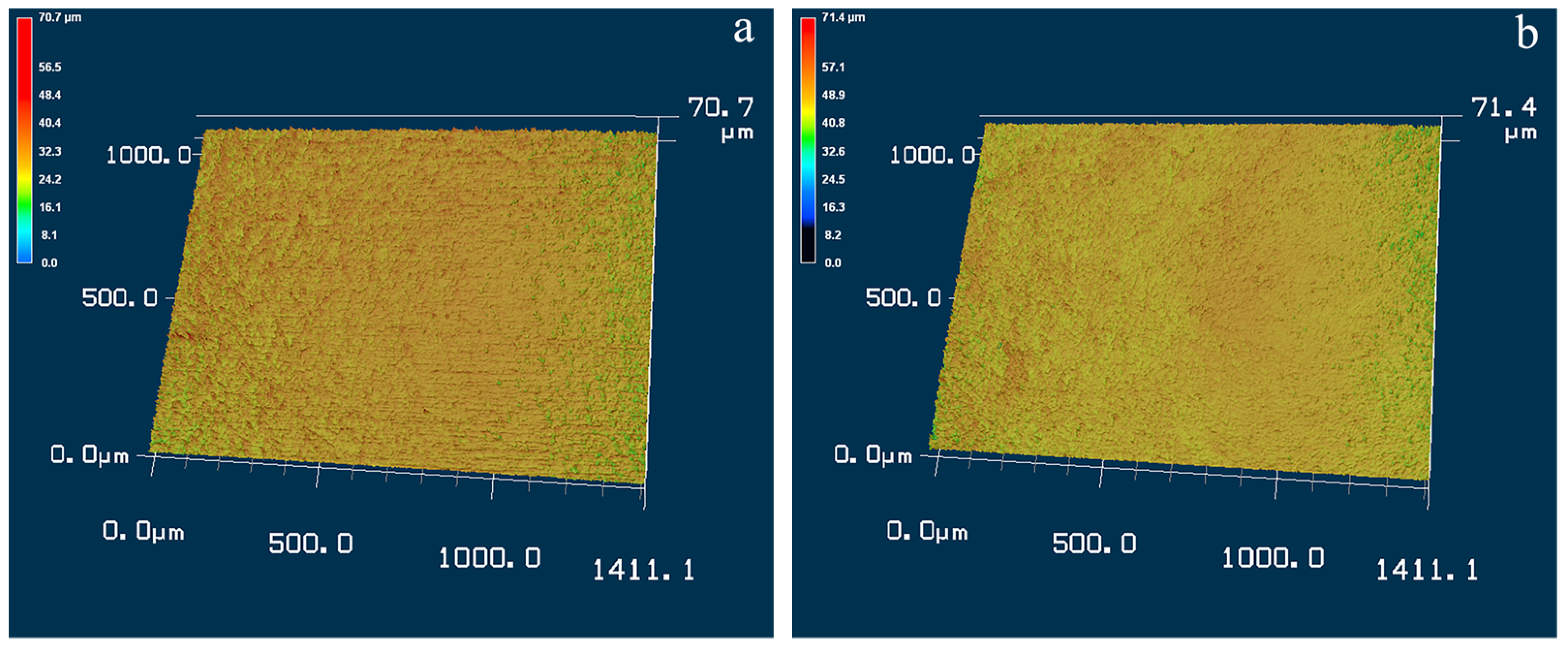
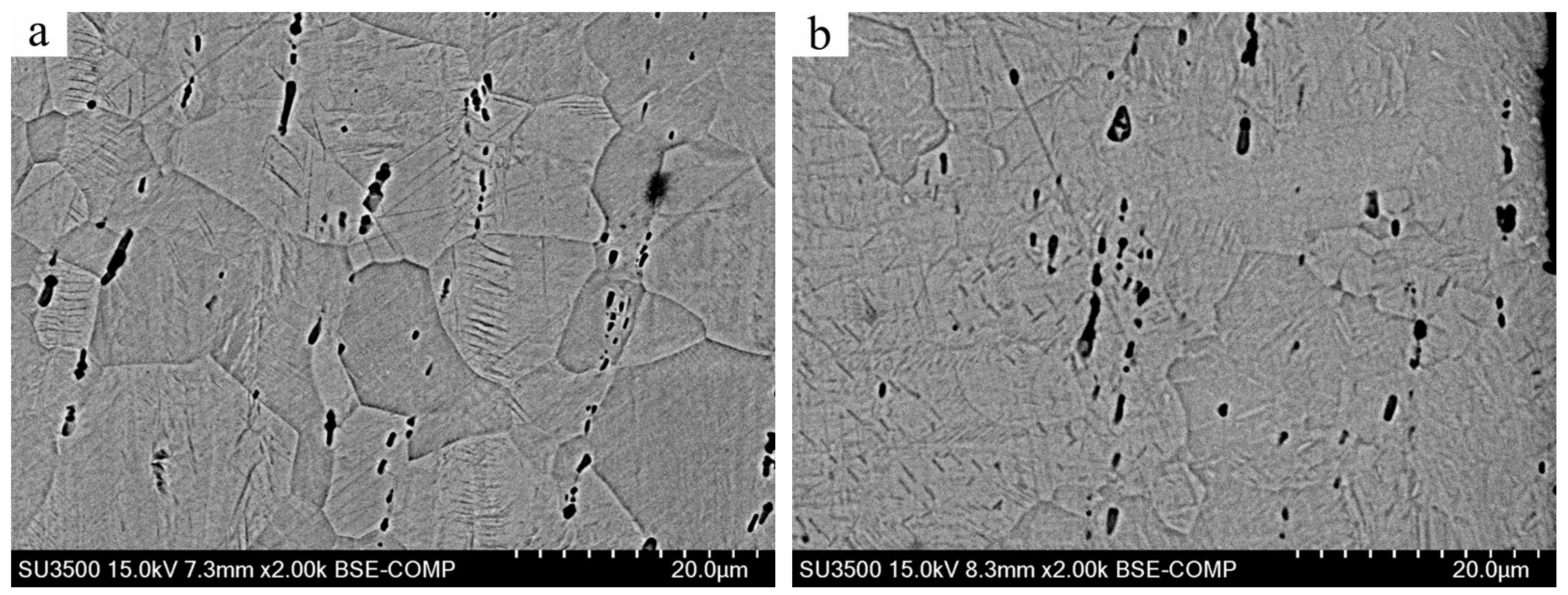


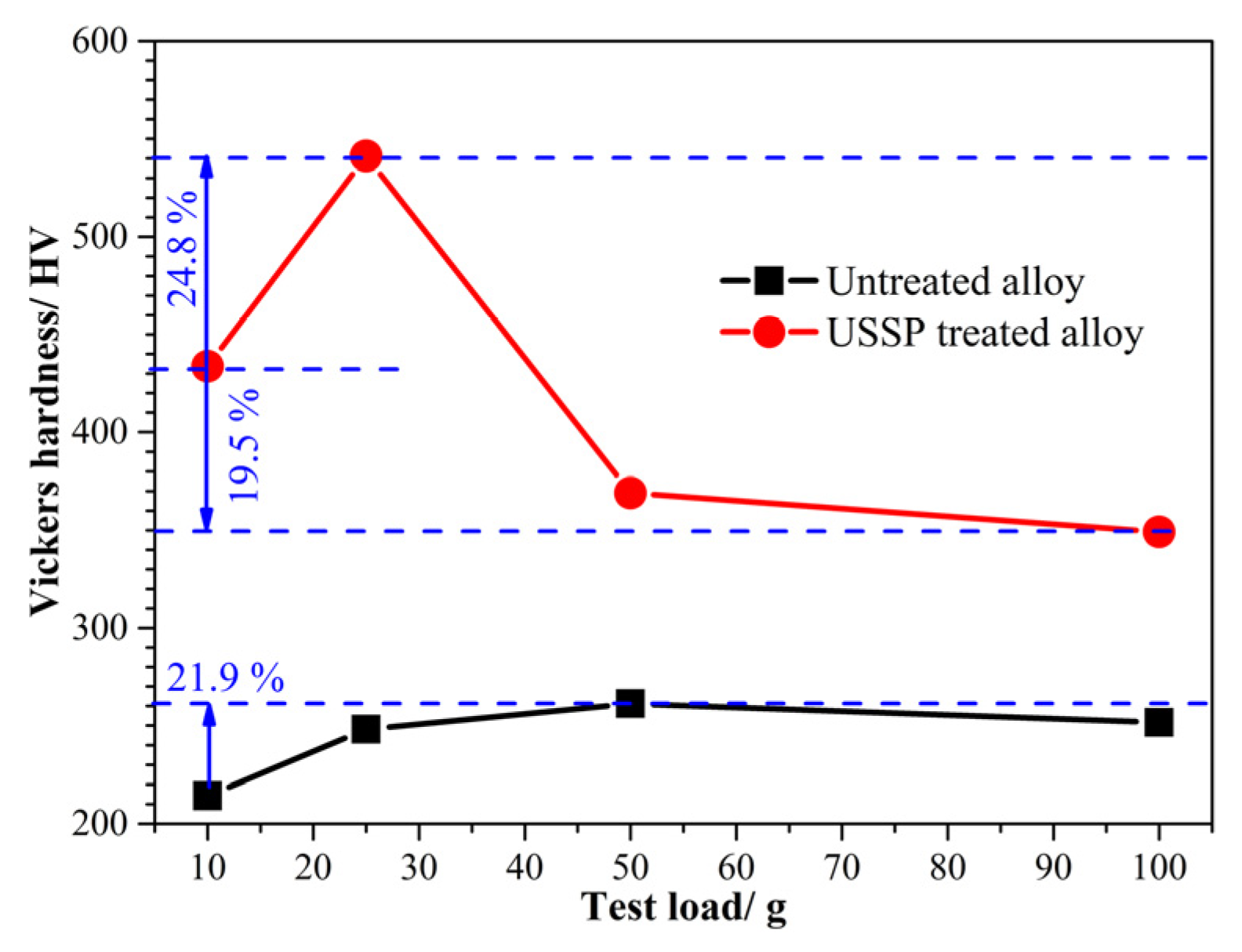


| Parameters | Sliding Speed/mm/s | Applied Load/N |
|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | 5 | 2 |
| Group 2 | 5 | 4 |
| Group 3 | 10 | 2 |
| Group 4 | 10 | 4 |
| Phase | Untreated Alloy | USSP-Treated Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| TiNi (B2) | 79.63 | 71.25 |
| TiNi (B19′) | 0.69 | 3.75 |
| Ni4Ti3 | 3.14 | 2.82 |
| Ni3Ti | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| NiTi2 | 0.24 | 0.22 |
| Unresolved areas | 16.27 | 21.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jian, Y. Microstructure Evolution, Hardness, and Tribological Behaviors of Ti-50.8Ni SMA Alloy with Ultrasonic Surface Shot Peening Treatment. Materials 2024, 17, 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112644
Chen Z, Li X, Li Y, Wang Y, Jian Y. Microstructure Evolution, Hardness, and Tribological Behaviors of Ti-50.8Ni SMA Alloy with Ultrasonic Surface Shot Peening Treatment. Materials. 2024; 17(11):2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112644
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Zihan, Xuanpeng Li, Yong Li, Yu Wang, and Yongxin Jian. 2024. "Microstructure Evolution, Hardness, and Tribological Behaviors of Ti-50.8Ni SMA Alloy with Ultrasonic Surface Shot Peening Treatment" Materials 17, no. 11: 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112644
APA StyleChen, Z., Li, X., Li, Y., Wang, Y., & Jian, Y. (2024). Microstructure Evolution, Hardness, and Tribological Behaviors of Ti-50.8Ni SMA Alloy with Ultrasonic Surface Shot Peening Treatment. Materials, 17(11), 2644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17112644





