The Design of a Novel Alkali-Activated Binder for Solidifying Silty Soft Clay and the Study of Its Solidification Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Silty Soft Clay Sample
2.1.2. SGP Ternary Binder
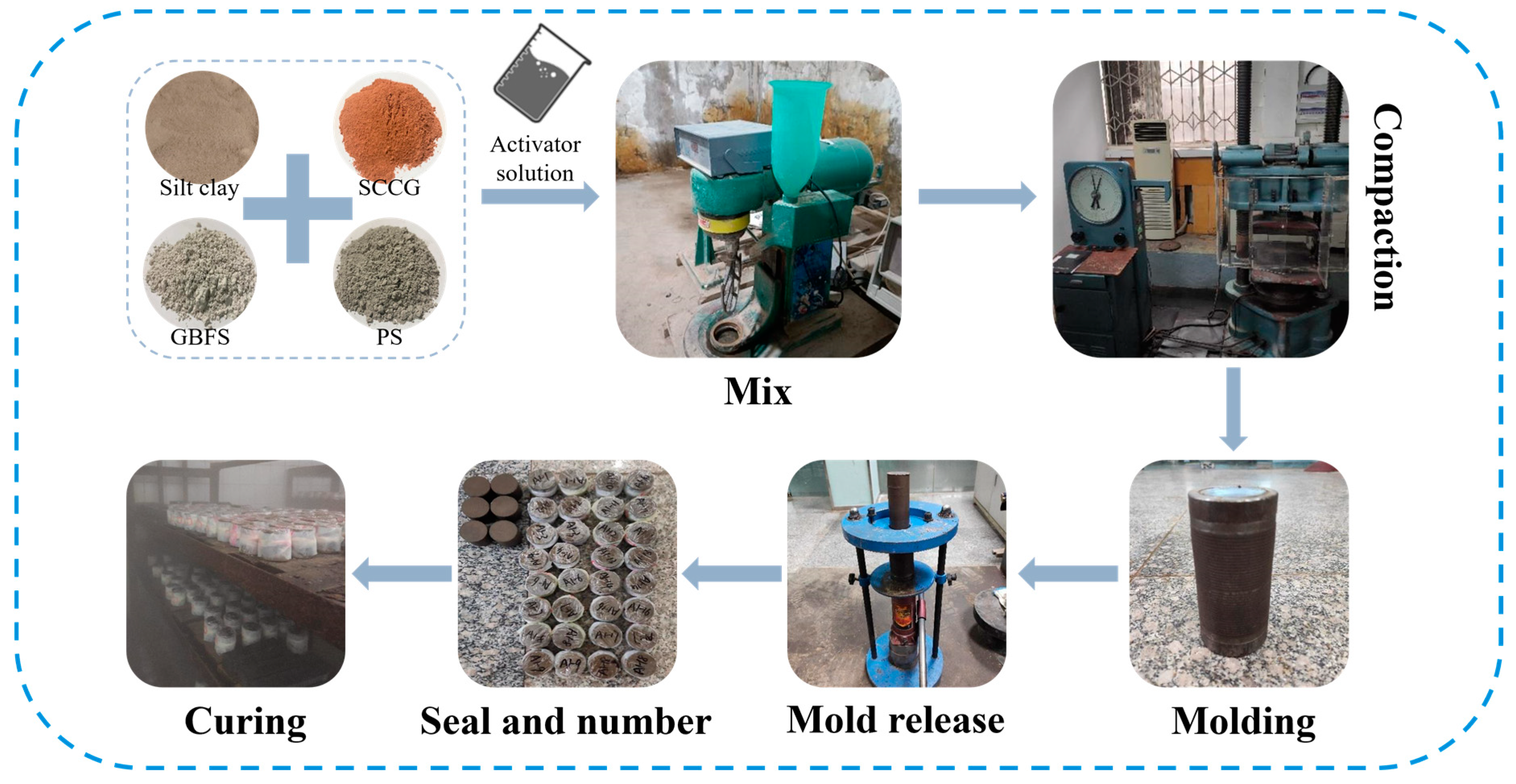
2.2. Mix Proportion Preparation
2.3. Testing and Characterization
2.3.1. Unconfined Compression Strength Test (UCS)
2.3.2. Microstructural Property Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
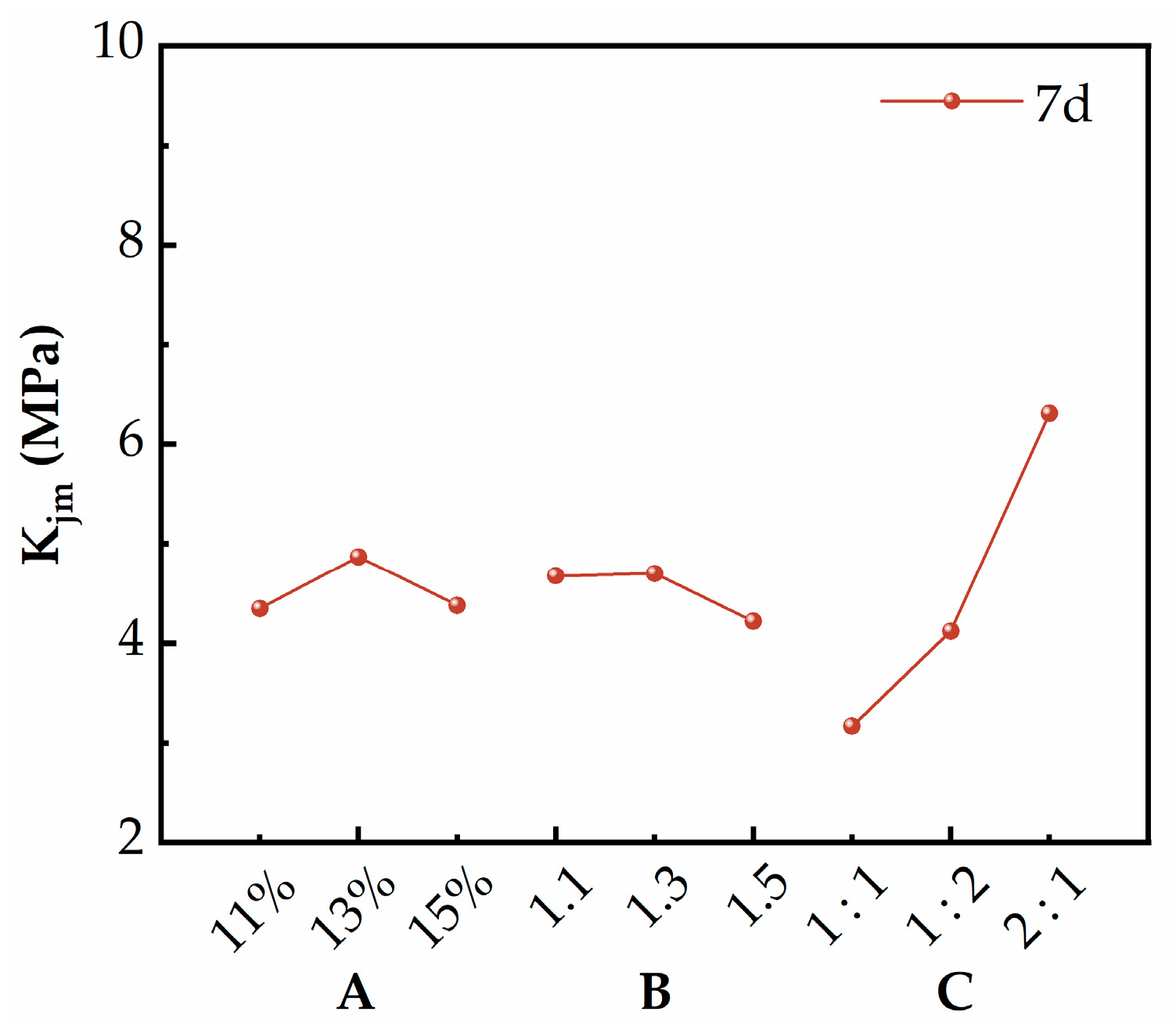
3.1. Orthogonal Experiment Analysis
3.2. The Effect of the SGP Ternary Binder Content on UCS
3.3. The Effect of the Initial Water Content of SC
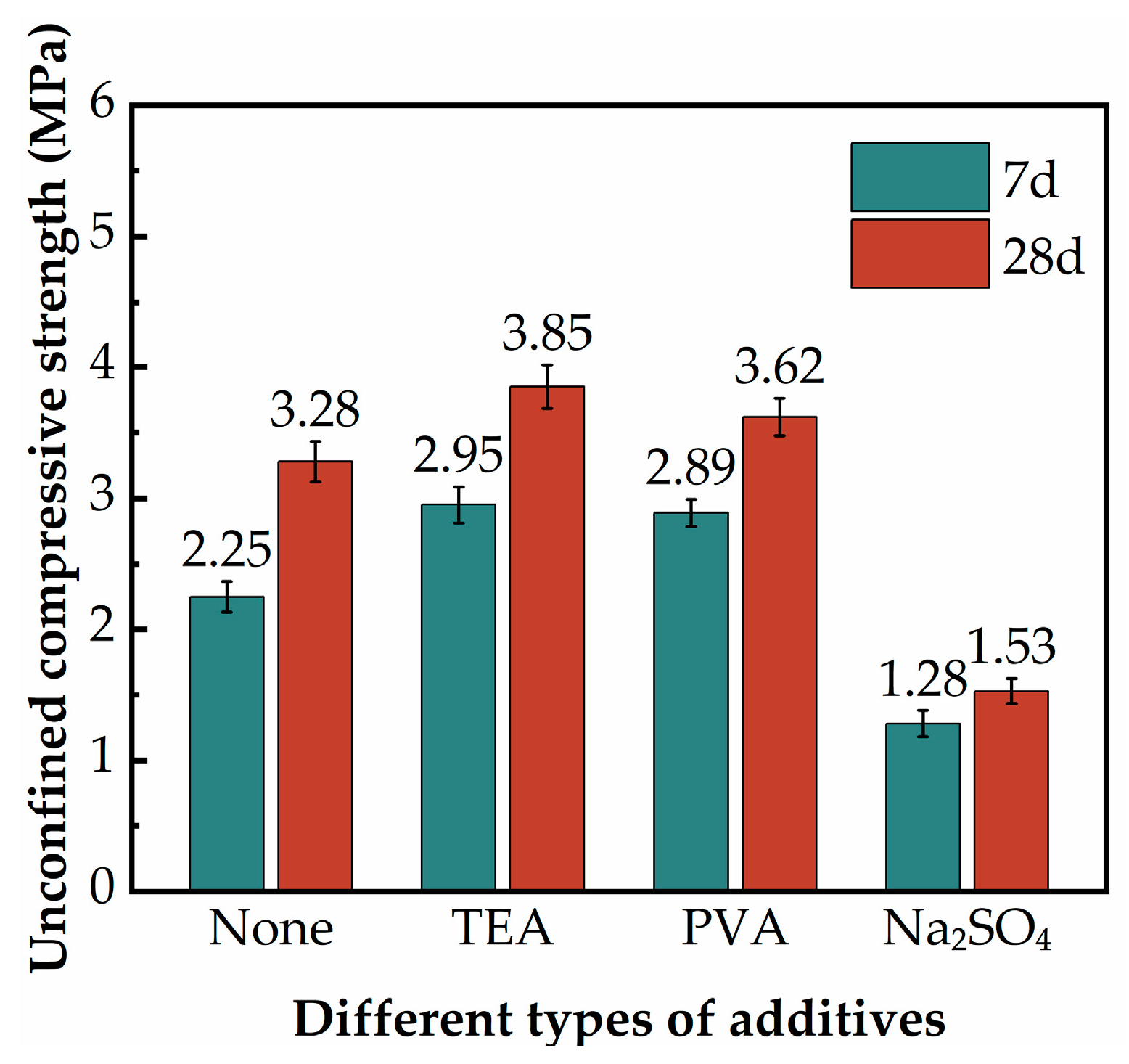
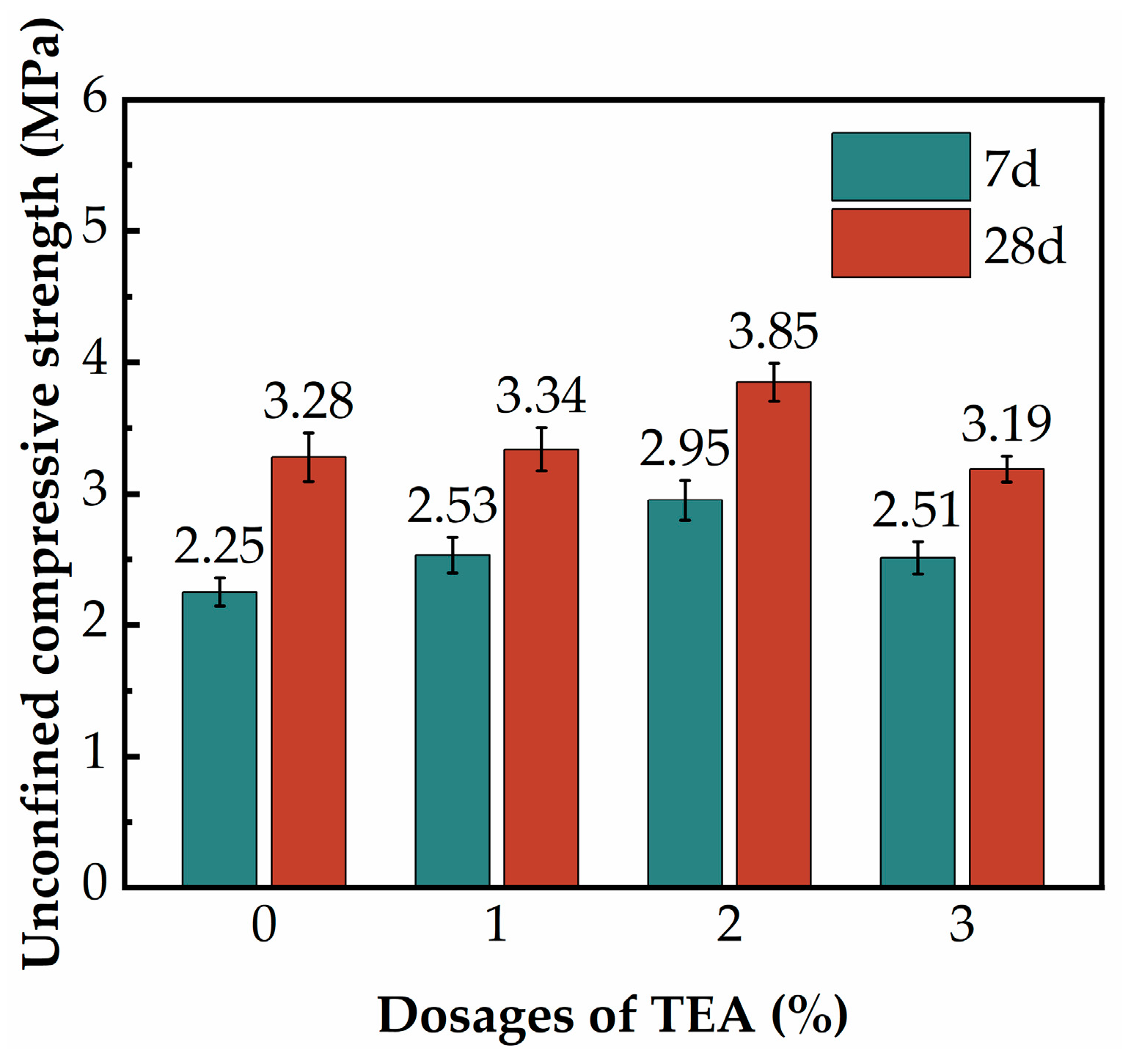
3.4. The Effect of Additives
3.5. Microstructural Property Analysis
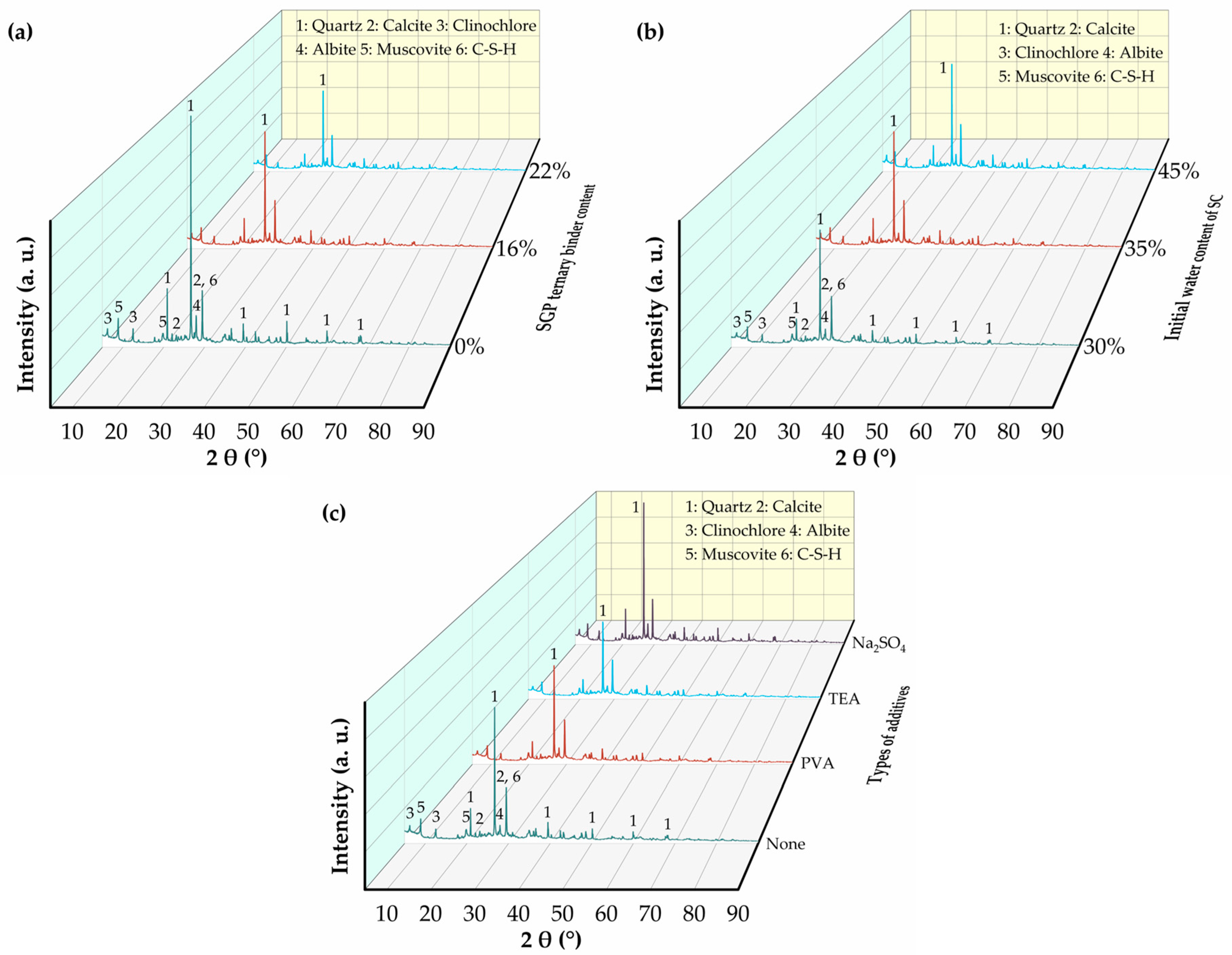
3.5.1. X-ray Diffraction Test Analysis
3.5.2. Micromorphology Analysis
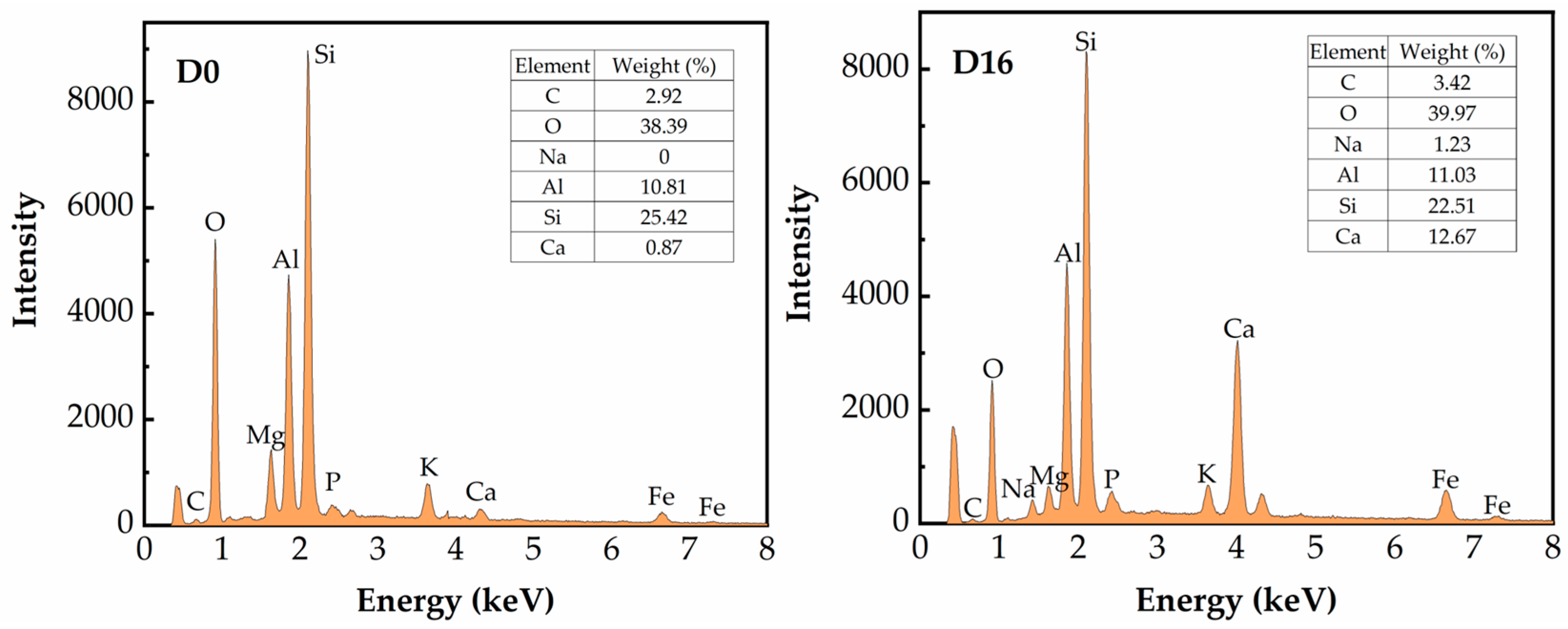
3.5.3. EDS Spectrum Analysis
4. Solidification Mechanism of the SGP-Solidified Soil
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, A.; Dong, W.; Zhan, Q.; Zhou, J. Study on Long Term Property of Soft Soil Solidified with Industrial Waste Residue and Regenerated Fine Aggregate. Materials 2023, 16, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, Y. Experimental Study on the Synergistic Solidification of Soft Soil with Ceramic Powder–Slag–Phosphorus Slag. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Zhan, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Y. Study on the solidification property and mechanism of soft soil based on the industrial waste residue. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2023, 62, 20220303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, E.L.; Najafi, E.K.; Ranjbar, P.Z.; Payan, M.; Chenari, R.J.; Fatahi, B. Recycling industrial alkaline solutions for soil stabilization by low-concentrated fly ash-based alkali cements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 393, 132083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chian, S.C.; Ma, T.; Ding, J. Stabilization of dredged clays with ternary alkali-activated materials: Towards sustainable solid wastes recycling. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Anand, K. Performance appraisal of coal ash stabilized rammed earth. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 18, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, S.M. A critical review of microbially induced carbonate precipitation for soil stabilization: The global experiences and future prospective. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Luo, B.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X.; Su, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, Q. Experimental Investigation of Unconfined Compression Strength and Microstructure Characteristics of Slag and Fly Ash-Based Geopolymer Stabilized Riverside Soft Soil. Polymers 2022, 14, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.M.; Shahzad, H.M.; Khalid, U.; Farooq, K.; Rehman, Z.U. Experimental Study on Sustainable Utilization of CKD for Improvement of Collapsible Soil. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 5667–5682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.; Farooq, K.; Rehman, Z.U.; Mujtaba, H.; Khalid, U. Utilization of eggshell food waste to mitigate geotechnical vulnerabilities of fat clay: A micro–macro-investigation. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X. Mechanical properties and micro-mechanisms of marine soft soil stabilized by different calcium content precursors based geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 305, 124722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayub, F.; Khan, S.A. An overview of geopolymer composites for stabilization of soft soils. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusty, J.K.; Pradhan, B. Evaluation of durability and microstructure evolution of chloride added fly ash and fly ash-GGBS based geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 401, 132925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, O.; Khalid, U.; Rehman, Z.U.; Kayani, W.I.; Haider, A. Impact of crushing shape and geopolymerization on reclaimed concrete aggregate for recycling in the flexible pavement: An enhanced circular economy solution. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2023, 2023, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerzouri, M.; Hamzaoui, R.; Ziyani, L.; Alehyen, S. Influence of slag based pre-geopolymer powders obtained by mechanosynthesis on structure, microstructure and mechanical performance of geopolymer pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 361, 129637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Bai, C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, T.; Gu, T. Microwave-thermal-assisted curing method on geopolymer preparation from Panzhihua high-titanium slag by alkali activation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, L.; Chen, B.; Chen, B. Strength evolutions of varying water content-dredged sludge stabilized with alkali-activated ground granulated blast-furnace slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 275, 122111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murmu, A.L.; Dhole, N.; Patel, A. Stabilisation of black cotton soil for subgrade application using fly ash geopolymer. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2018, 21, 867–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Guo, H.; El-Korchi, T.; Zhang, G.; Tao, M. Experimental feasibility study of geopolymer as the next-generation soil stabilizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1468–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraki, H.; Shariatmadari, N.; Ghadir, P.; Jahandari, S.; Tao, Z.; Siddique, R. Clayey soil stabilization using alkali-activated volcanic ash and slag. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 14, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Han, X.; Sun, Z.; Jin, P.; Li, K.; Wang, F.; Gong, J. Study on the Reactivity Activation of Coal Gangue for Efficient Utilization. Materials 2023, 16, 6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Guo, X.; Guan, J.; Yao, X.; Hao, Y. Activation Mechanism of Coal Gangue and Its Impact on the Properties of Geopolymers: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Song, L.; Ma, M. Experimental Research on Improving Activity of Calcinated Coal Gangue via Increasing Calcium Content. Materials 2023, 16, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Qiao, Y.; Shao, J.; Bai, C.; Li, H.; Lu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, K.; Colombo, P. Sodium-based alkali-activated foams from self-ignition coal gangue by facile microwave foaming route. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 33914–33925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, X.; Lu, S.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z. Fabrication and characterization of self-ignition coal gangue autoclaved aerated concrete. Mater. Des. 2016, 97, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Deng, X.; Liu, J.; Hui, D. Mechanical properties and microstructures of hypergolic and calcined coal gangue based geopolymer recycled concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 691–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Gao, X. Properties of coal gangue-Portland cement mixture with carbonation. Fuel 2019, 245, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, X.; He, X.; Su, Y.; Zeng, J.; Dai, F.; Guan, S. Effect of Ultrafine Fly Ash and Water Glass Content on the Performance of Phosphorus Slag-Based Geopolymer. Materials 2022, 15, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Xiao, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Structural Characterization of Phosphorous Slag Regarding Occurrence State of Phosphorus in Dicalcium Silicate. Materials 2022, 15, 7450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Wang, Q.; Luo, T. Investigation of the relationship among the hydration, microstructure and compressive strength of alkali-activated phosphorus slag. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Wang, Q.; Luo, T. Understanding the workability of alkali-activated phosphorus slag pastes: Effects of alkali dose and silicate modulus on early-age hydration reactions. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 133, 104649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, D.; Wang, Q. Performance study of alkali-activated phosphate slag-granulated blast furnace slag composites: Effect of the granulated blast furnace slag content. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2023, 23, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhu, Z.; Pu, S.; Wan, Y.; Huo, W.; Song, S.; Zhang, J.; Yao, K.; Hu, L. Efficient use of steel slag in alkali-activated fly ash-steel slag-ground granulated blast furnace slag ternary blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 119814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lu, M.; Sheng, K.; Shao, Z.; Yao, Y.; Hong, B. Development of new material for geopolymer lightweight cellular concrete and its cementing mechanism. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, C.; Hu, X.; Shi, C. Effect of silica fume on rheology of slag-fly ash-silica fume-based geopolymer pastes with different activators. Cem. Concr. Res. 2023, 174, 107336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X. Research on hydration characteristics of OSR-GGBFS-FA alkali-activated materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, K.; Zeng, G.; Shu, B.; Luo, D. Study on the Performance and Solidification Mechanism of Multi-Source Solid-Waste-Based Soft Soil Solidification Materials. Materials 2023, 16, 4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T50123-2019; Standard for Geotechnical Testing Methods. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, K.; Qu, F.; Yan, C.; Wu, Z. Toward understanding the activation and hydration mechanisms of composite activated coal gangue geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 318, 125999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Li, Y.-F.; Zhang, C. Modeling of discharge voltage for lithium-ion batteries through orthogonal experiments at subzero environment. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 105058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Li, A.; Ma, J.; Cui, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y. Relative importance of certain factors affecting the thermal environment in subway stations based on field and orthogonal experiments. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 56, 102107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Li, L.; He, P.; Chen, Z.; Lao, C.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y. Effects of kinds of alkali-activated ions on geopolymerization process of geopolymer cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 293, 123536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, B.S.; Haruna, S.; Wahab, M.; Liew, M.; Haruna, A. Mechanical and microstructural properties of high calcium fly ash one-part geopolymer cement made with granular activator. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoo-Ngernkham, T.; Maegawa, A.; Mishima, N.; Hatanaka, S.; Chindaprasirt, P. Effects of sodium hydroxide and sodium silicate solutions on compressive and shear bond strengths of FA–GBFS geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksiripattanapong, C.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Yeanyong, C.; Arulrajah, A. Evaluation of polyvinyl alcohol and high calcium fly ash based geopolymer for the improvement of soft Bangkok clay. Transp. Geotech. 2020, 27, 100476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CJJ/T286-2018; Technical Standard for Application of Soil Stabilizer. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Suksiripattanapong, C.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Boongrasan, S.; Udomchai, A.; Chinkulkijniwat, A.; Arulrajah, A. Unit weight, strength and microstructure of a water treatment sludge–fly ash lightweight cellular geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 94, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phetchuay, C.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Arulrajah, A.; Suksiripattanapong, C.; Udomchai, A. Strength development in soft marine clay stabilized by fly ash and calcium carbide residue based geopolymer. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 127–128, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YBJ 225-91; Technical Regulations for Deep Mixing Reinforcement Method of Soft Soil Foundation. Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1991.
- Wu, Y.; Qian, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jia, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.-Q.; Cui, P. Target-specific modification of diethylenetriamine with hydroxyalkyls: Efficient absorbents for CO2 capture. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 335, 126075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.M.; Wang, D.; Han, J.; Heo, J.; Su, C. Evaluation of the colloidal stability and adsorption performance of reduced graphene oxide–elemental silver/magnetite nanohybrids for selected toxic heavy metals in aqueous solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 471, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Sun, T.; Saleem, A.; Wang, C. Enhanced removal of Cr(III)-EDTA chelates from high-salinity water by ternary complex formation on DETA functionalized magnetic carbon-based adsorbents. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 209, 111858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. Early activation of high volume fly ash by ternary activator and its activation mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 267, 110638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, A.; Maleki, A.; Mahinroosta, M. Chemical activation of slag-blended Portland cement. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 18, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, D.; Chen, R.; Cheng, J.; Tang, Y.; Xiao, C.; Li, Z. Desert sand-high calcium fly ash-based alkali-activated mortar: Flowability, mechanical properties, and microscopic analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 398, 131729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Ren, L.; Gu, X.; Zheng, J.; Cui, L. Synergistic effect of activator nature and curing temperature on time-dependent rheological behavior of cemented paste backfill containing alkali-activated slag. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 12857–12871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Hao, X.; Wei, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z. Activation of low-activity calcium silicate in converter steelmaking slag based on synergy of multiple solid wastes in cementitious material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 351, 128925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wan, Y.; Xu, X.; Pu, S.; Song, S.; Wei, Y. Effect of steel slag on fresh, hardened and microstructural properties of high-calcium fly ash based geopolymers at standard curing condition. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Luna, K.; Perez-Cortes, P.; Garcia, J.E. Influence of quicklime and Portland cement, as alkaline activators, on the reaction products of supersulfated cements based on pumice. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 146, 105379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X.; Gui, Z.; Liu, F. Synthesis and characterization of one-part alkali-activated grouting materials based on granulated blast furnace slag, uncalcined coal gangue and microscopic fly ash sinking beads. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujtaba, H.; Khalid, U.; Farooq, K.; Elahi, M.; Rehman, Z.; Shahzad, H.M. Sustainable Utilization of Powdered Glass to Improve the Mechanical Behavior of Fat Clay. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 3628–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, U.; Rehman, Z.U.; Ullah, I.; Khan, K.; Kayani, W.I. Efficacy of geopolymerization for integrated bagasse ash and quarry dust in comparison to fly ash as an admixture: A comparative study. J. Eng. Res. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Khalid, U.; Rehman, Z.U.; Shah, M.M.; Khan, I.; Ijaz, N. Integrated recycling of geopolymerized quarry dust and bagasse ash with facemasks for the balanced amelioration of the fat clay: A multi-waste solution. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
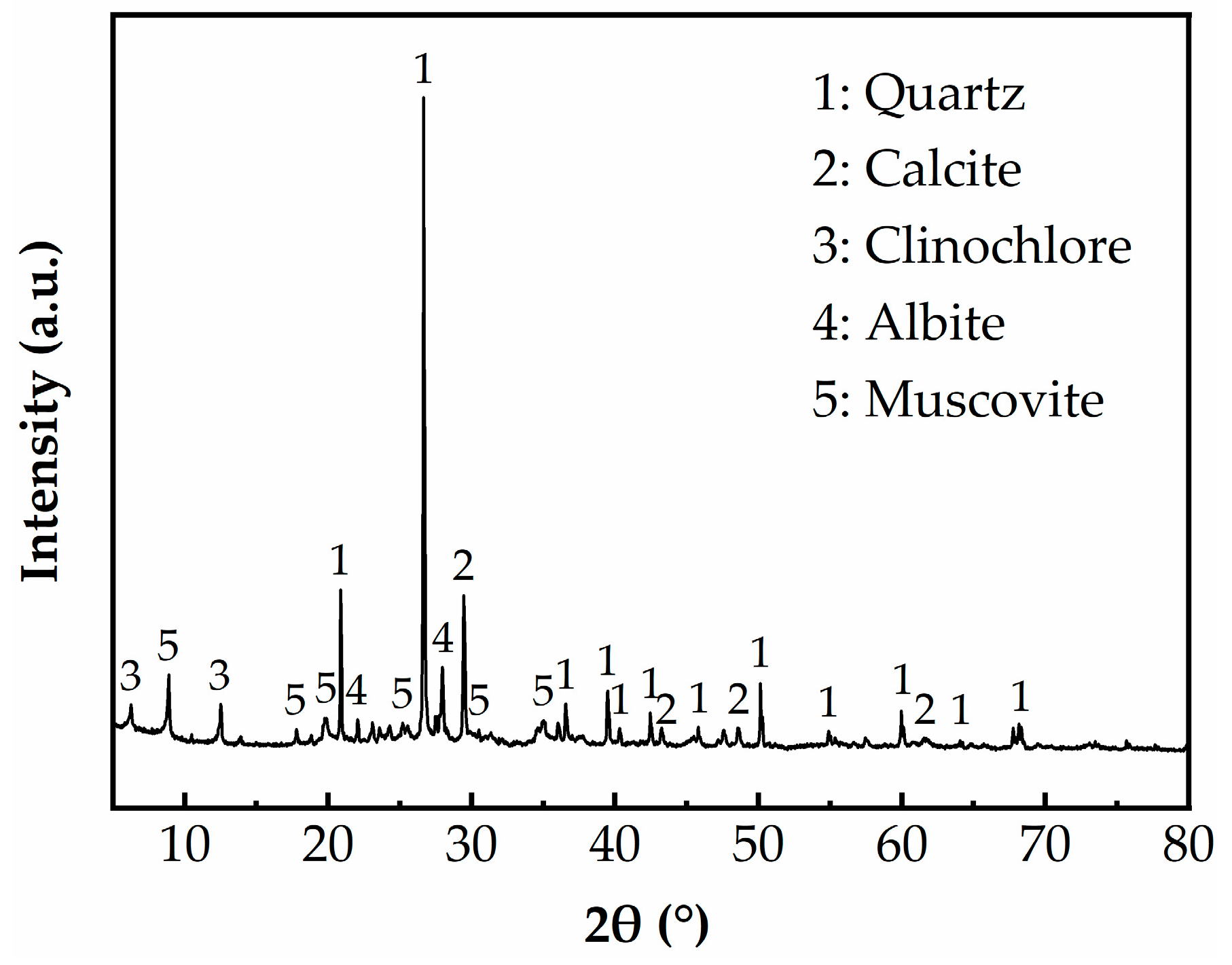
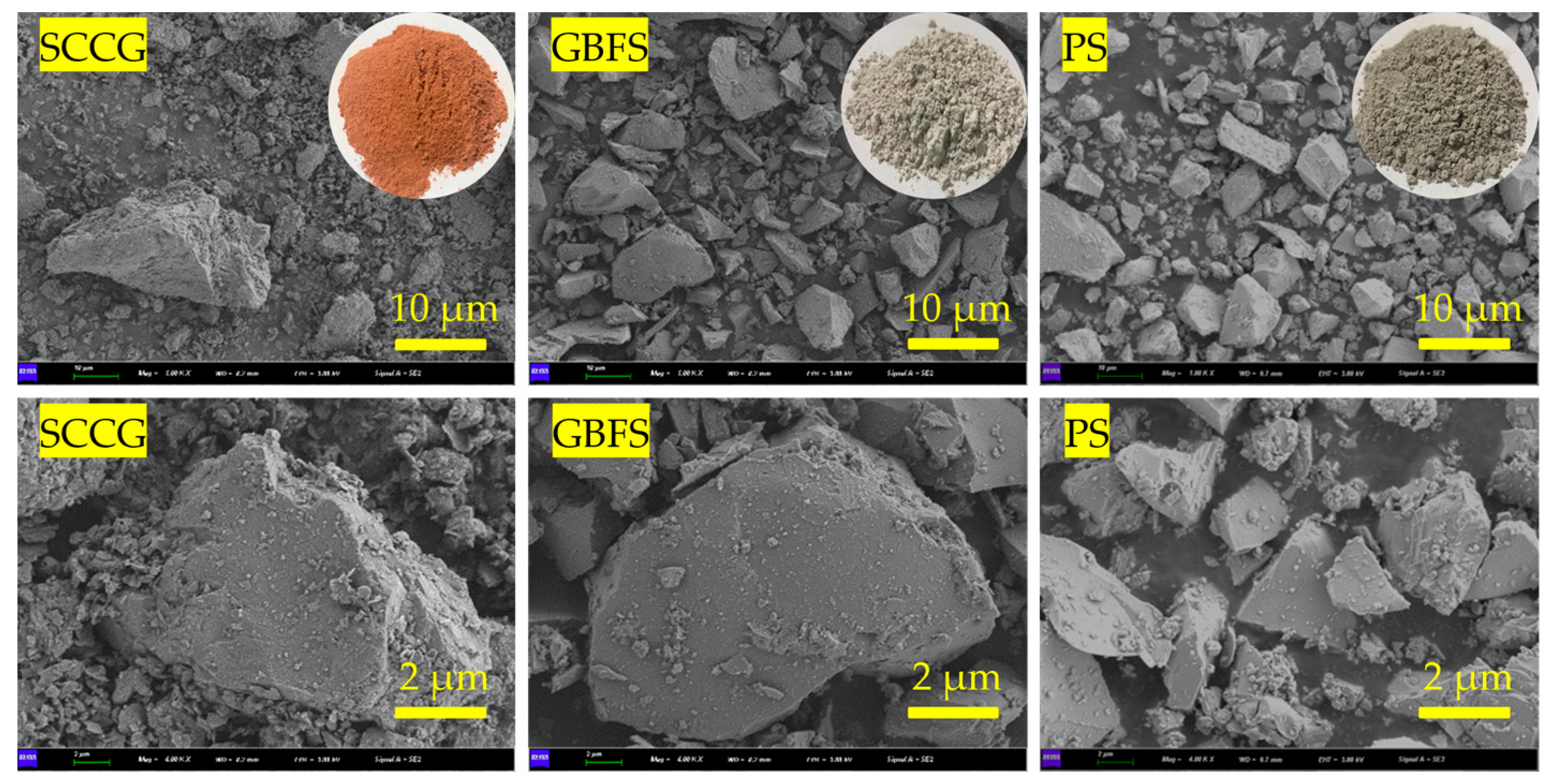
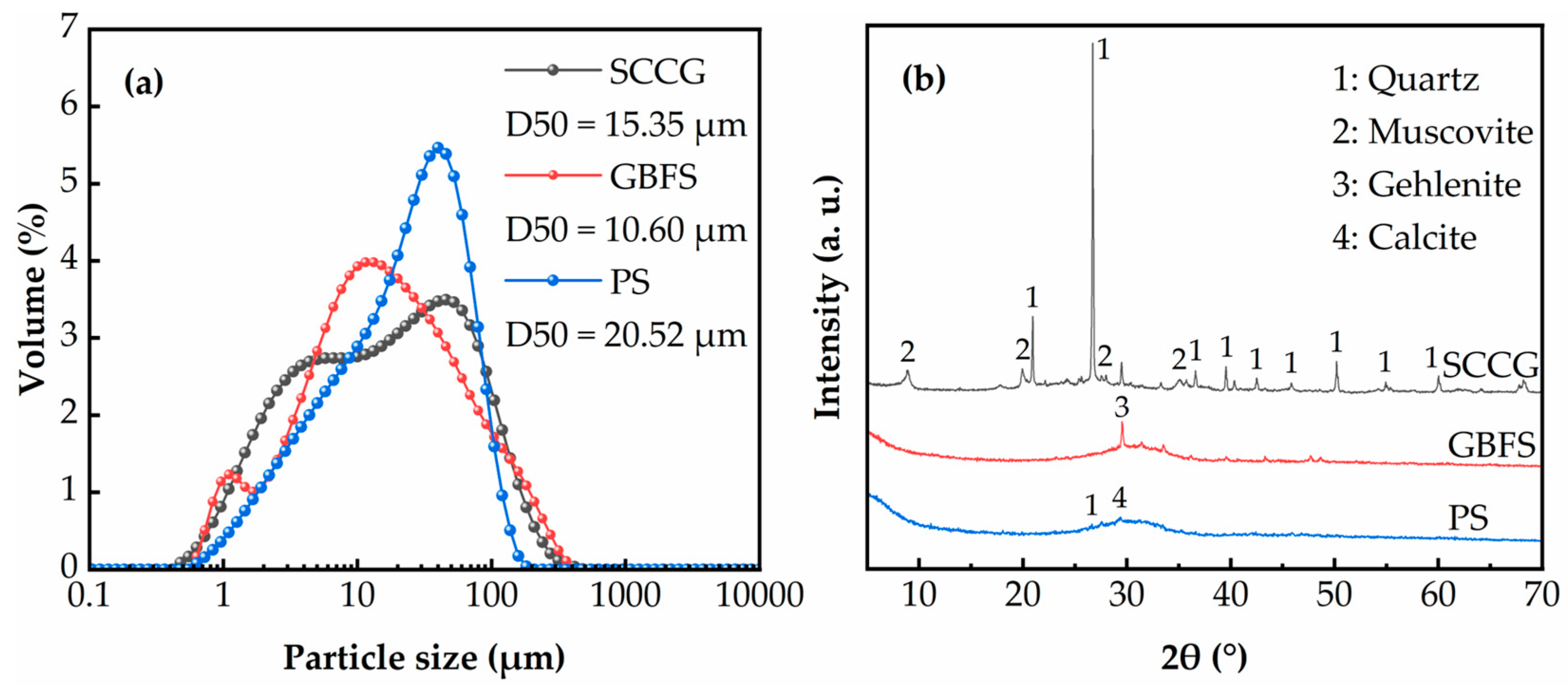



| Sample | Moisture Content | Liquid Limit | Plastic Limit | Plasticity Index | Specific Gravity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated SC | 47% | 41.9% | 22.3% | 19.6 | 2.62 g/cm3 |
| Chemical Composition | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | SO3 | Fe2O3 | P2O5 | K2O | MgO | Na2O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC, % | 60.50 | 20.80 | 1.80 | 0.69 | 8.60 | 1.12 | 3.15 | 0.95 | 0.28 |
| SCCG, % | 64.20 | 21.69 | 3.27 | 0.27 | 4.66 | 0.81 | 0.11 | 2.83 | 0.45 |
| GBFS, % | 25.62 | 12.10 | 50.22 | 2.41 | 0.31 | 5.17 | 0.01 | - | 0.41 |
| PS, % | 39.05 | 3.99 | 47.16 | 0.72 | 2.07 | 2.94 | 1.99 | - | - |
| Factors | Alkali Activator Content (A) | Modulus of Alkali Activator (B) | GBFS:PS (C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 11% | 1.1 | 1:2 |
| Level 2 | 13% | 1.3 | 1:1 |
| Level 3 | 15% | 1.5 | 2:1 |
| Series | Sample | SGP Ternary Binder Content | Initial Water Content of SC | Additives |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | D0 | 0 | 35% | None |
| D13 | 13% | 35% | None | |
| D16 | 16% | 35% | None | |
| D19 | 19% | 35% | None | |
| D22 | 22% | 35% | None | |
| W | W30 | 16% | 30% | None |
| W35 | 16% | 35% | None | |
| W40 | 16% | 40% | None | |
| W45 | 16% | 45% | None | |
| F | F1 | 16% | 35% | None |
| F2 | 16% | 35% | 2% Triethanolamine (TEA) | |
| F3 | 16% | 35% | 2% Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) | |
| F4 | 16% | 35% | 2% Na2SO4 | |
| F5 | 16% | 35% | 1% TEA | |
| F6 | 16% | 35% | 3% TEA |
| Sample | Dosages of Activator (A) | Modules (B) | GBFS:PS (C) | 7 d UCS | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | 1 (11%) | 1 (1.1) | 1 (1:2) | 1.021 | 0.115 |
| O2 | 1 (11%) | 2 (1.3) | 2 (1:1) | 1.331 | 0.136 |
| O3 | 1 (11%) | 3 (1.5) | 3 (2:1) | 1.996 | 0.144 |
| O4 | 2 (13%) | 1 (1.1) | 2 (1:1) | 1.594 | 0.128 |
| O5 | 2 (13%) | 2 (1.3) | 3 (2:1) | 2.249 | 0.136 |
| O6 | 2 (13%) | 3 (1.5) | 1 (1:2) | 1.026 | 0.087 |
| O7 | 3 (15%) | 1 (1.1) | 3 (2:1) | 2.062 | 0.176 |
| O8 | 3 (15%) | 2 (1.3) | 1 (1:2) | 1.121 | 0.153 |
| O9 | 3 (15%) | 3 (1.5) | 2 (1:1) | 1.197 | 0.161 |
| Curing Age | Factor | Kj1 | Kj2 | Kj3 | Rj | Number of Levels | Number of Repetitions per Level | Importance Order |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7d | A | 4.438 | 4.869 | 4.38 | 0.174 | 3 | 3 | C > A > B |
| B | 4.677 | 4.701 | 4.219 | 0.161 | 3 | 3 | ||
| C | 3.168 | 4.122 | 6.307 | 1.046 | 3 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jing, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q. The Design of a Novel Alkali-Activated Binder for Solidifying Silty Soft Clay and the Study of Its Solidification Mechanism. Materials 2024, 17, 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102177
Jing Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Wang Q. The Design of a Novel Alkali-Activated Binder for Solidifying Silty Soft Clay and the Study of Its Solidification Mechanism. Materials. 2024; 17(10):2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102177
Chicago/Turabian StyleJing, Yaohui, Yannian Zhang, Lin Zhang, and Qingjie Wang. 2024. "The Design of a Novel Alkali-Activated Binder for Solidifying Silty Soft Clay and the Study of Its Solidification Mechanism" Materials 17, no. 10: 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102177
APA StyleJing, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., & Wang, Q. (2024). The Design of a Novel Alkali-Activated Binder for Solidifying Silty Soft Clay and the Study of Its Solidification Mechanism. Materials, 17(10), 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102177






