The Influence of [110] Compressive Stress on Kinetically Arrested B2–R Transformation in Single-Crystalline Ti–44Ni–6Fe and Ti–42Ni–8Fe Shape-Memory Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
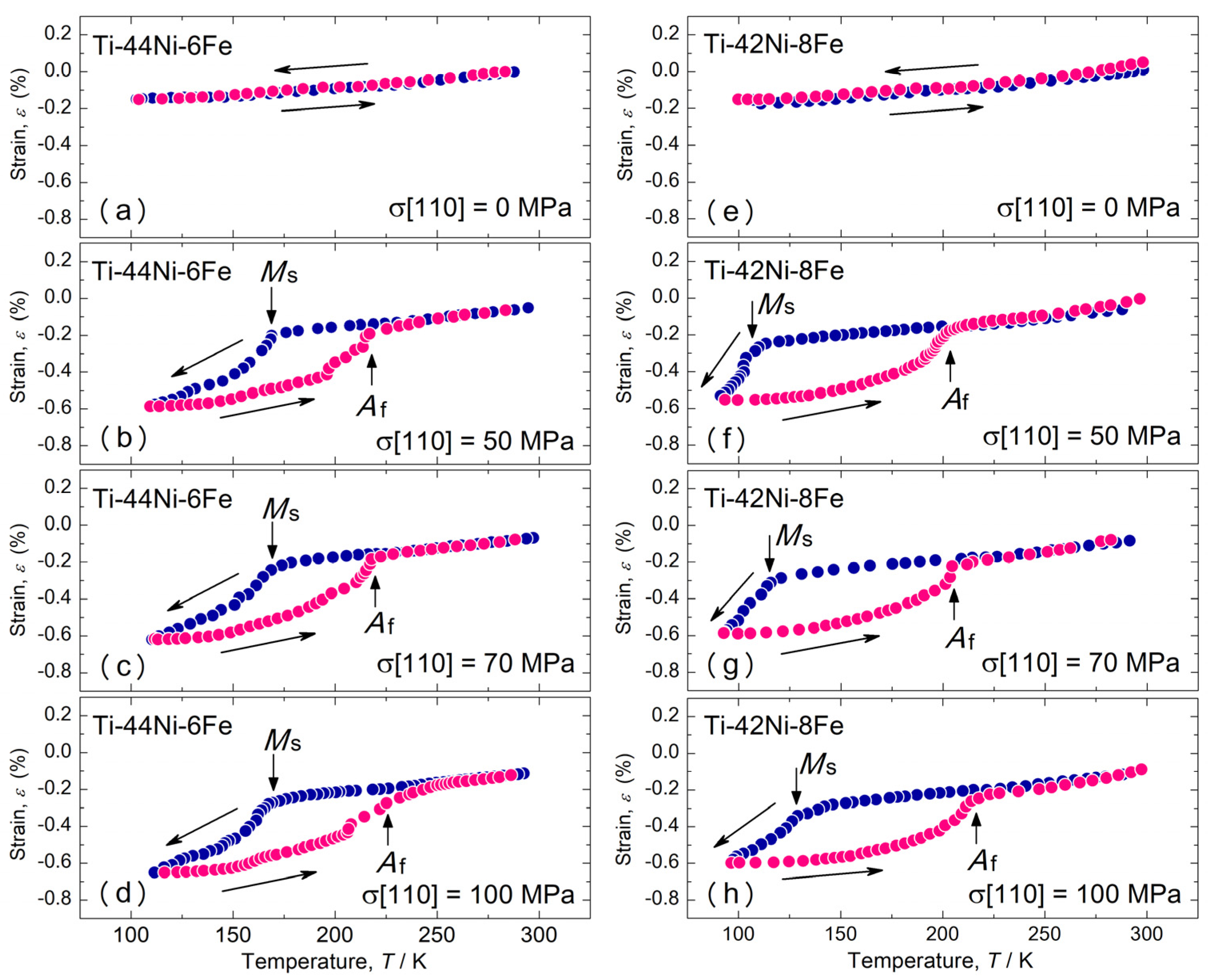
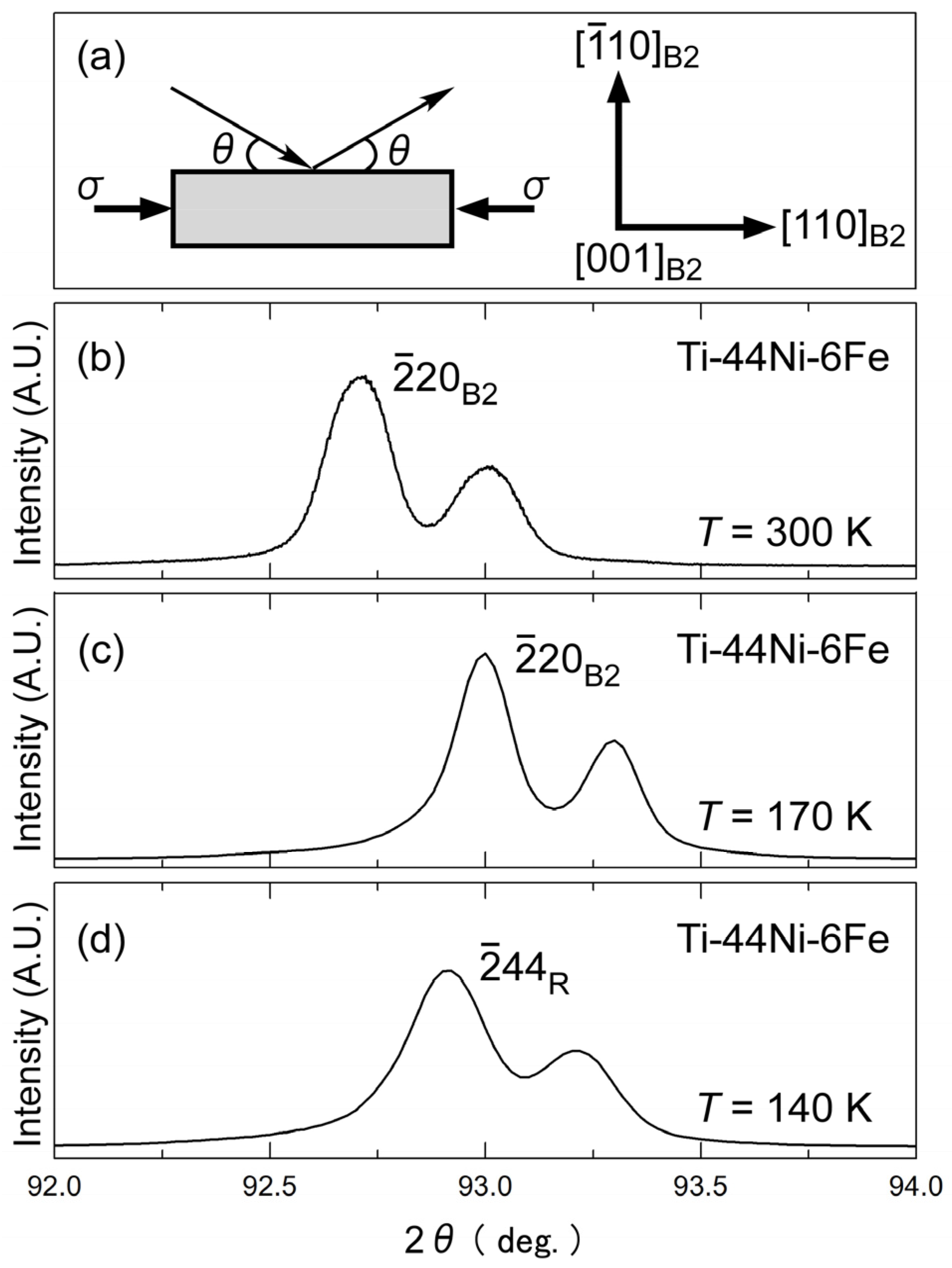
3.1. Martensite Phase Formed under Compressive Stress
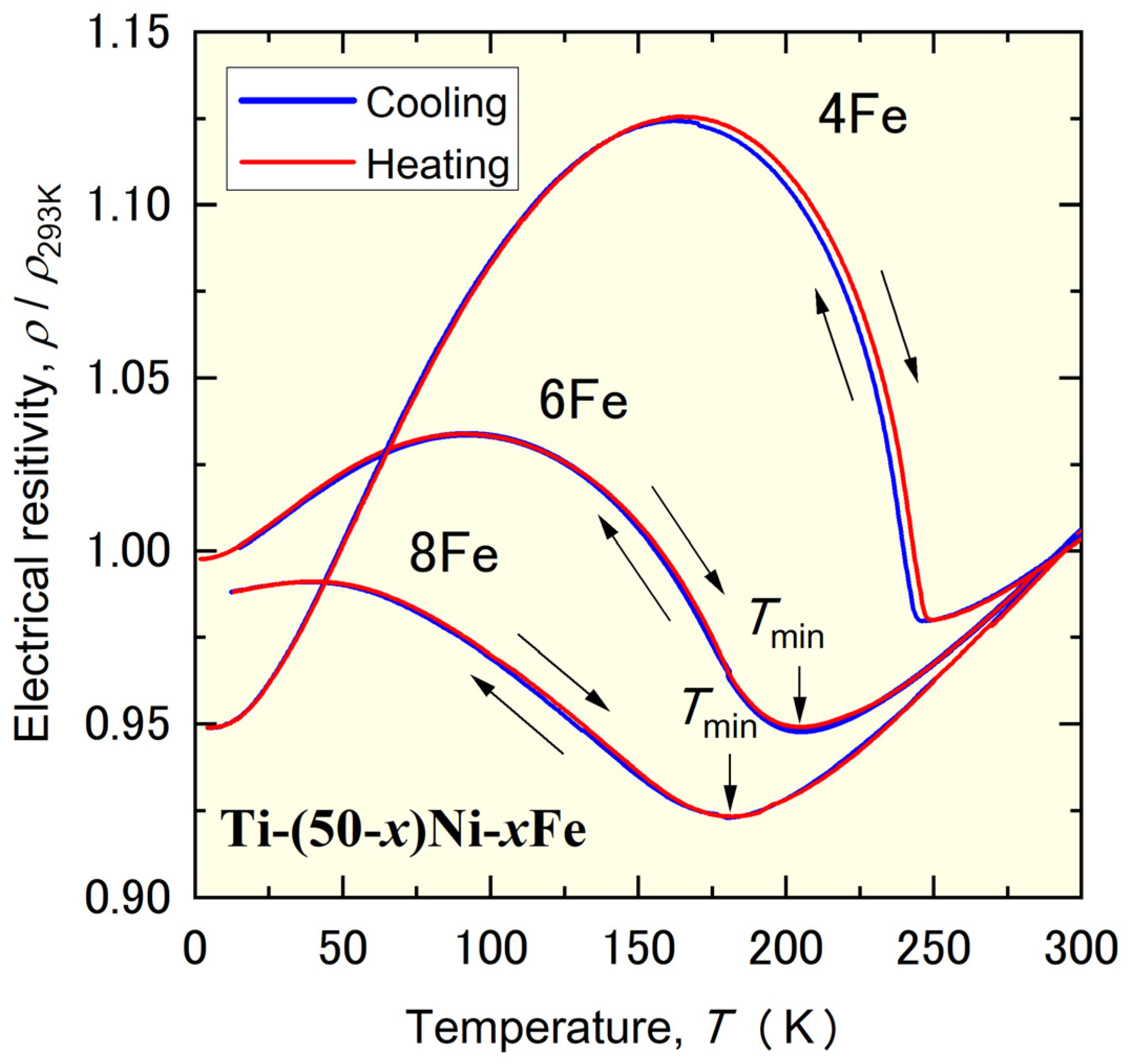
3.2. Reasons for Wide Temperature Hysteresis
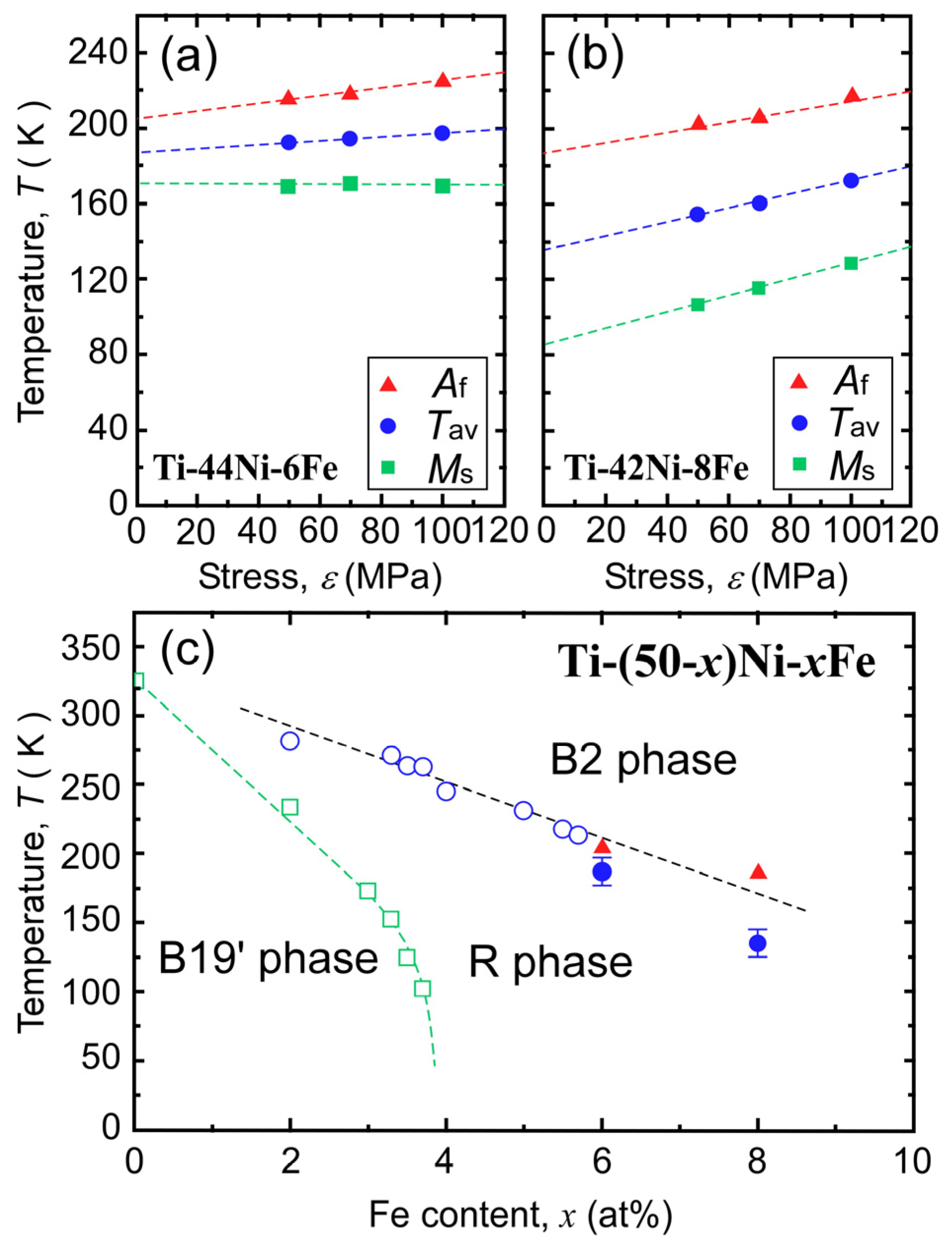
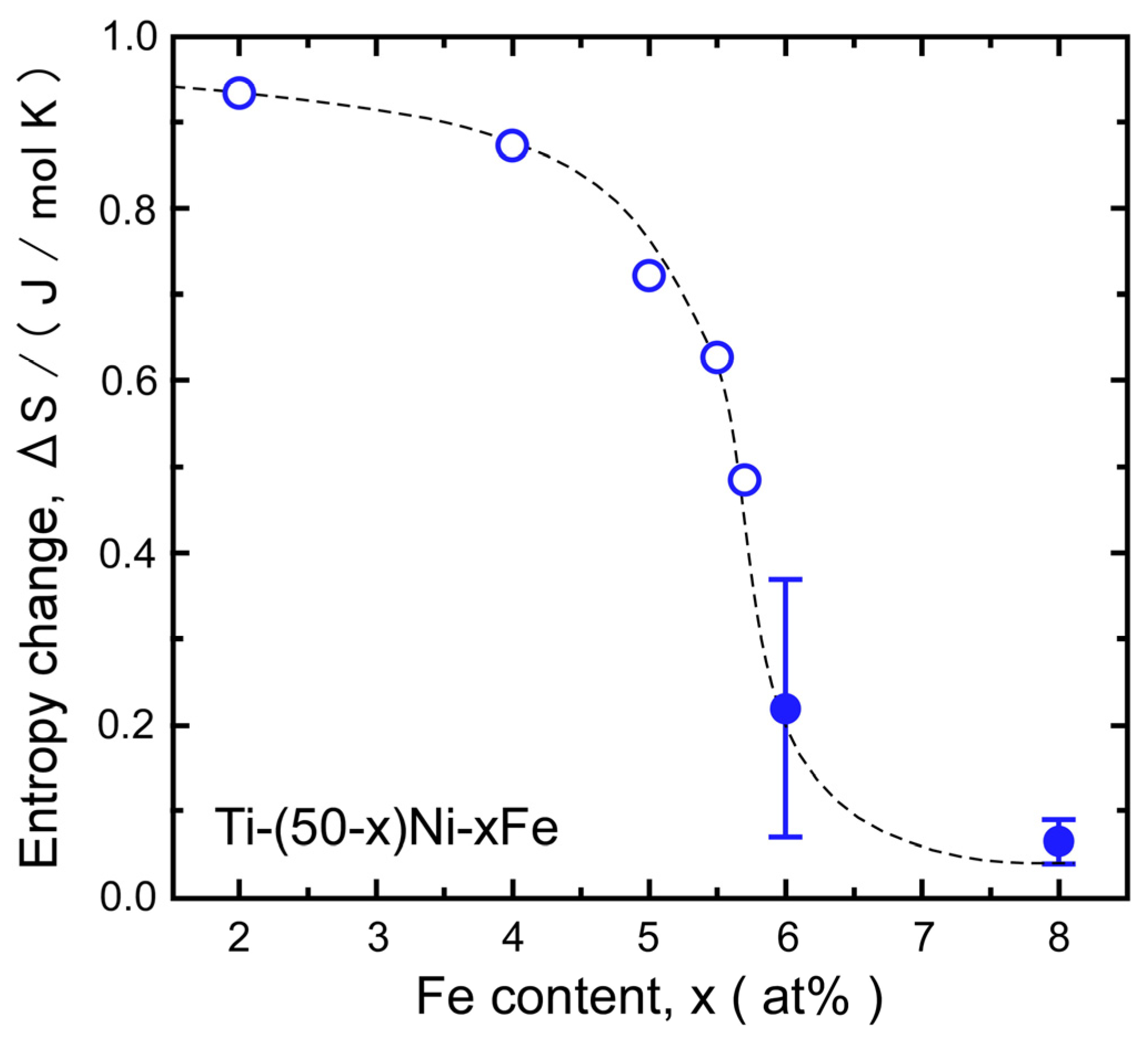
3.3. Kinetics of the B2–R Transformation
3.4. Relation between Softening and R-Phase Martensitic Transformation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishiyama, Z. Martensitic Transformations; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Kakeshita, T.; Saburi, T.; Kindo, K.; Endo, S. Martensitic Transformations in some ferrous and non-ferrous alloys under magnetic field and hydrostatic pressure. Phase Transit. 1998, 70, 65–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Landazébal, J.I.; Recarte, V.; Sánchez-Alarcos, V.; Kustov, S.; Salas, D.; Cesari, E. Effect of magnetic field on the isothermal transformation of a Ni–Mn–In–Co magnetic shape memory alloy. Intermetallics 2012, 28, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurrich, C.; Roth, S.; Potschke, M.; Rellinghaus, B.; Schultz, L. Ithothermal martensitic transformation in polycrystalline Ni50Mn29Ga21. J. Alloys Comp. 2010, 494, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Tong, Y.X.; Zheng, Y.F.; Liu, Y. Time effect of martensitic transformation in Ni43Co7Mn41Sn9. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, M.; Inamura, T.; Kim, H.Y.; Miyazaki, S.; Hosoda, H. Isothermal martensitic transformation behavior of Ti–Nb–O alloy. Mater. Lett. 2019, 257, 126691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, M.; Kanaya, T.; Kim, H.Y.; Inamura, T.; Hosoda, H.; Miyazaki, S. Heating-induced martensitic transformation and time-dependent shape memory behavior of Ti–Nb–O alloy. Acta Mater. 2014, 80, 314–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeby-Gautier, E.; Settefrati, A.; Bruneseaux, F.; Applolaire, B.; Denand, B.; Dehmas, M. Isothermal α” formation in β metastable titanium alloys. J. Alloys Comp. 2013, 577 (Suppl. S1), S439–S443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustov, S.; Salas, D.; Cesari, E.; Santamarta, R.; Humbeeck, J.V. Isothermal and athermal martensitic transformations in Ni-Ti shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2012, 60, 2578–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustov, S.; Salas, S.; Santamarta, R.; Cesari, E.; Humbeeck, J.V. Isothermal and athermal martensitic transformations in the B2-R-B19′ sequence in Ni–Ti shape memory alloys. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, D.; Cesari, E.; Humbeeck, J.V.; Kostov, S. Isothermal B2-B19′ martensitic transformation in Ti rich Ni-Fe shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater. 2014, 74, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnina, N.; Belyaev, S.; Demidova, E.; Ivanov, A.; Andreev, V. Kinetics of isothermal B2 → B19′ martensitic transformation in Ti49Ni51 shape memory alloy. Mater. Lett. 2018, 228, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnina, N.; Belyaev, S.; Shelyakov, A. Isothermal B2→B19′ martensitic transformation in Ti40.7Hf9.5Ni44.8Cu5 shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater. 2016, 112, 106–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, K.; Meng, X.; Cai, W.; Zhao, L. Isothermal martensitic transformation in Ti–Ni–Cu–Co shape memory alloy: Insight from a thermally activated kinetic model. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 160, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X.; Takeda, T. Experimental test for a possible isothermal martensitic transformation in a Ti–Ni alloy. Scr. Mater. 2001, 45, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Todai, M.; Kakeshita, T. Isothermal martensitic transformation of the R-phase in a Ti–44Ni–6Fe at.% alloy. Scr. Mater. 2013, 69, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.M.; Meichle, M.; Salamon, M.B.; Wayman, C.M. Transformation behavior of Ti50Ni47Fe3 Alloy: I. Incommensurate and commensurate phases. J. Phys. Colloq. 1982, 43, C4-231–C4-236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.M.; Meichle, M.; Salamon, M.B.; Wayman, C.M. Transformation behaviour of a Ti50Ni47Fe3 alloy I. Subsequent premartensitic behaviour and the commensurate phase. Philo. Mag. A 1983, 47, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Ohba, T.; Okunishi, E.; Otsuka, K. Structural Study of R-Phase in Ti–50.23 at.%Ni and Ti–47.75 at.%Ni–1.50 at.%Fe Alloys. Mater. Trans. JIM 1997, 38, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schryvers, D.; Potapov, P.L. R-Phase Structure Refinement Using Electron Diffraction Data. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of Ti-Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Saburi, T.; Doi, K.; Nenmo, S. Nucleation and self-accommodation of the R-phase in Ti–Ni alloys. Mater. Trans. 1992, 33, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moine, P.; Allain, J.; Renker, B. Observation of a soft-phonon mode and a pre-martensitic phase in the intermetallic compound Ti50Ni47Fe3 studied by inelastic neutron scattering. J. Phys. F Met. Phys. 1984, 14, 2517–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Shindo, D. Changes in microstructure near the R-phase transformation in Ti50Ni48Fe2 studied by in-situ electron microscopy. Philos. Mag. Lett. 2001, 81, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, Y.; Shindo, D. Lattice modulation preceding to the R-phase transformation in a Ti50Ni48Fe2 alloy studied by TEM with energy-filtering. Mater. Trans. JIM 1999, 40, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, D.; Murakami, Y. Advanced transmission electron microscopy study on premartensitic state of Ti50Ni48Fe2. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2000, 1, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todai, M.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T. Relation between incommensurate satellites and phonon softening in Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Scr. Mater. 2011, 64, 541–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.-S.; Yamamoto, T.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T.; Taguchi, E.; Mori, H. Differences between the R-phase and the commensurate phase in iron-doped Ti–Ni shape memory alloys. Philos. Mag. 2008, 88, 2449–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamon, M.B.; Meichle, M.E.; Wayman, C.M. Premartensitic phases of Ti50Ni47Fe3. Phys. Rev. B 1985, 31, 7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.M.; Noda, Y.; Fujii, Y.; Yamada, Y. X-ray investigation of the premartensitic phase in Ni46.8Ti50Fe3.2. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 30, 4341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Wang, K.; Lv, C.; Hou, H.; Zhao, X. Strain glass transition in Ni47.5+xTi50−xFe2.5 alloys. J. Alloys Comp. 2022, 929, 167287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xue, D.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Otsuka, K.; Sun, J.; Ren, X. Strain glass in doped Ti50(Ni50−xDx) (D = Co, Cr, Mn) alloys: Implication for the generality of strain glass in defect-containing ferroelastic systems. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 5433–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Phase diagram of Ti50−xNi50+x: Crossover from martensite to strain glass. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 81, 224102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X. Strain glass in Fe-doped Ti–Ni. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 6206–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, M.; Liu, C.; Zhao, H. Strain grass in Ti50−xNi35+xCu15 shape memory alloys. Scr. Mater. 2019, 168, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Xu, X.; Han, K.; Niitsu, K.; Omori, T.; Umetsu, Y.R.; Kainuma, R. R-phase transformation in Ti50−xNi47+xFe3 shape memory alloys. Mater. Trans. 2023, 64, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niitsu, K.; Kimura, Y.; Xu, X.; Kainuma, R. Composition dependences of entropy change and transformation temperatures in Ni-rich Ti-Ni system. Shap. Mem. Superelasticity 2015, 1, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Xu, X.; Niitsu, K.; Omori, T.; Kainuma, R. Martensitic transformations and superelastic behavior at low temperatures in Ti50−xNi40+xCu10 shape memory alloys. Mater. Trans. 2016, 57, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todai, M.; Higaki, A.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T. Martensitic transformation from incommensurate state with nano-scale domain structure in a Ti–42Ni–8Fe (at.%) alloy under a compressive stress. Phil. Mag. Lett. 2011, 91, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, T.; Yamasaki, G.; Yoshinobu, H.; Kakeshita, T. Mechanical Properties of the R-Phase and the Commensurate Phase under [111] Tensile Stress in Iron-Doped Titanium-Nickel Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2016, 57, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trong, D.N.; Long, V.C.; Talu, S. The Study of the Influence of Matrix, Size, Rotation Angle, and Magnetic Field on the Isothermal Entropy, and the Néel Phase Transition Temperature of Fe2O3 Nanocomposite Thin Films by the Monte-Carlo Simulation Method. Coatings 2021, 11, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayman, C.M.; Tong, H.C. On the equilibrium temperature in thermoelasticm martensitic transformations. Scr. Metall. 1977, 11, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzolai, G.; Biscarini, A.; Coluzzi, B.; Mazzolai, F.M.; Ross, A.R.; Lograsso, T.A. Ultrasonic investigation of the B2↔B19 martensitic trasition in Ni40Ti50Cu10 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 370, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Miura, N.; Zhang, J.; Otsuka, K.; Tanaka, K.; Koiwa, M.; Suzuki, T.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Asai, M. A comparative study of elastic constants of Ti–Ni-based alloys prior to martensitic transformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 312, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Miura, N.; Taniwaki, K.; Otsuka, K.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, K.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Asai, M. Understanding the martensitic transformations in TiNi-based alloys by elastic constants measurement. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 237–235, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.K.; Otsuka, K. The role of Softening in elastic constant c44 in martensitic transformation. Scr. Mater. 1998, 38, 1669–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zener, C. Contributions to the theory of beta-phase alloys. Phys. Rev. 1947, 7, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Todai, M.; Fukuda, T.; Kakeshita, T. The Influence of [110] Compressive Stress on Kinetically Arrested B2–R Transformation in Single-Crystalline Ti–44Ni–6Fe and Ti–42Ni–8Fe Shape-Memory Alloys. Materials 2024, 17, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010051
Todai M, Fukuda T, Kakeshita T. The Influence of [110] Compressive Stress on Kinetically Arrested B2–R Transformation in Single-Crystalline Ti–44Ni–6Fe and Ti–42Ni–8Fe Shape-Memory Alloys. Materials. 2024; 17(1):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010051
Chicago/Turabian StyleTodai, Mitsuharu, Takashi Fukuda, and Tomoyuki Kakeshita. 2024. "The Influence of [110] Compressive Stress on Kinetically Arrested B2–R Transformation in Single-Crystalline Ti–44Ni–6Fe and Ti–42Ni–8Fe Shape-Memory Alloys" Materials 17, no. 1: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010051
APA StyleTodai, M., Fukuda, T., & Kakeshita, T. (2024). The Influence of [110] Compressive Stress on Kinetically Arrested B2–R Transformation in Single-Crystalline Ti–44Ni–6Fe and Ti–42Ni–8Fe Shape-Memory Alloys. Materials, 17(1), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010051




