In Vitro Comparison of Differences in Setting Time of Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate According to Moisture Content of Gypsum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Material
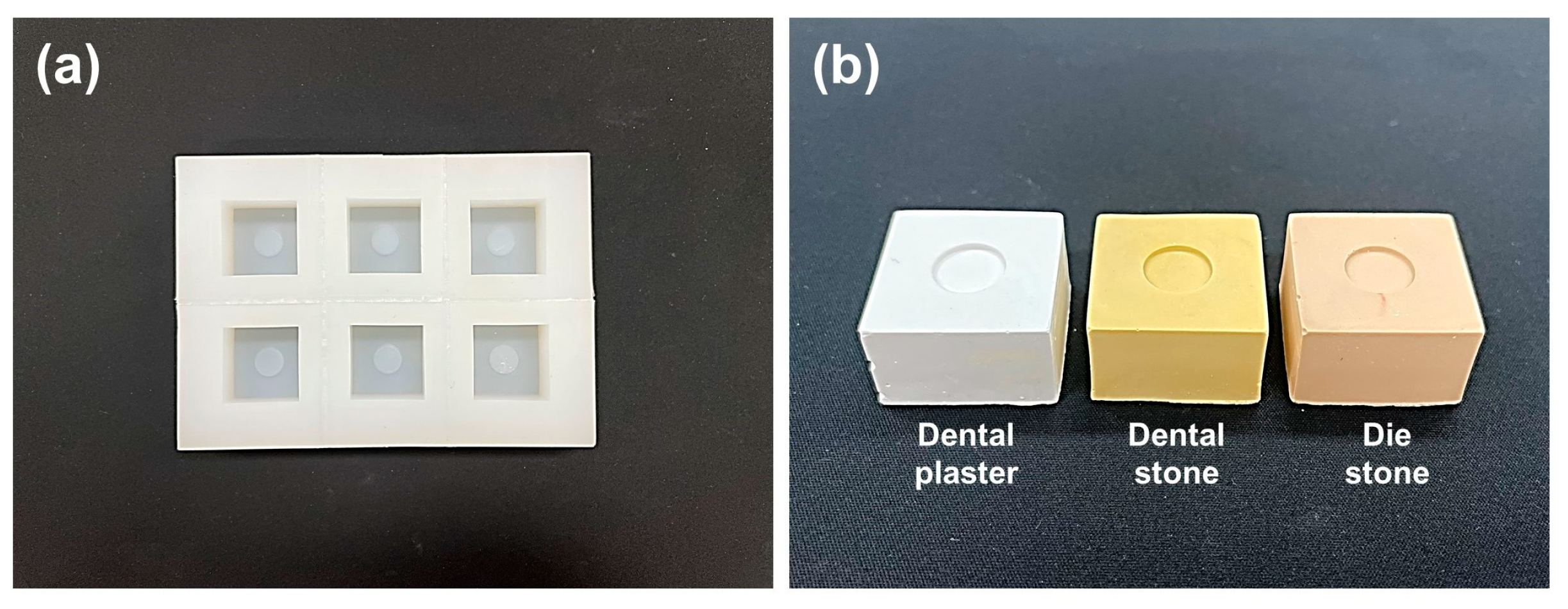
2.2. Fabrication of Gypsum Molds to Reproduce Simulated Root Canal Environment
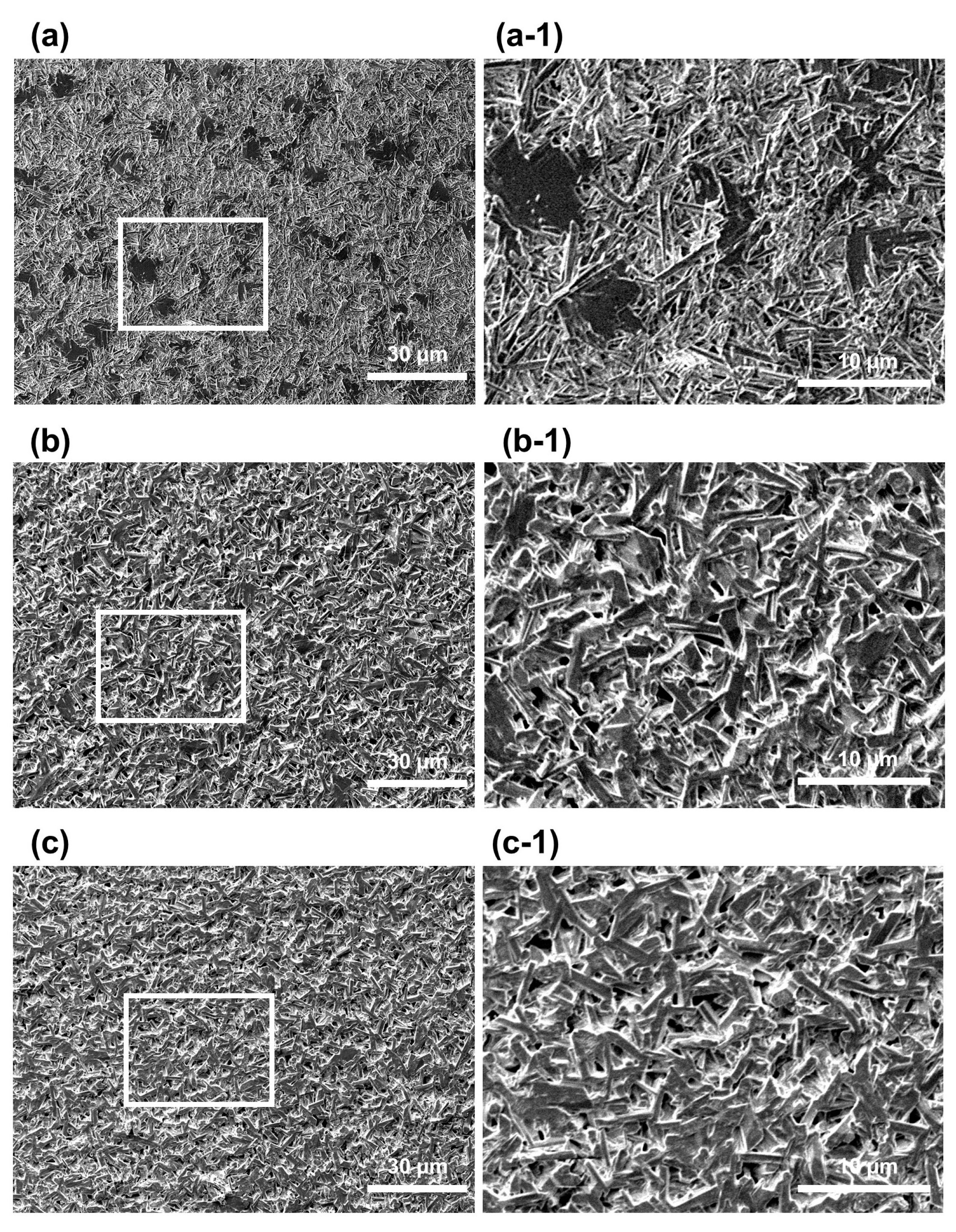
2.3. Gypsum Surface Measurement Using a Scanning Electron Microscope
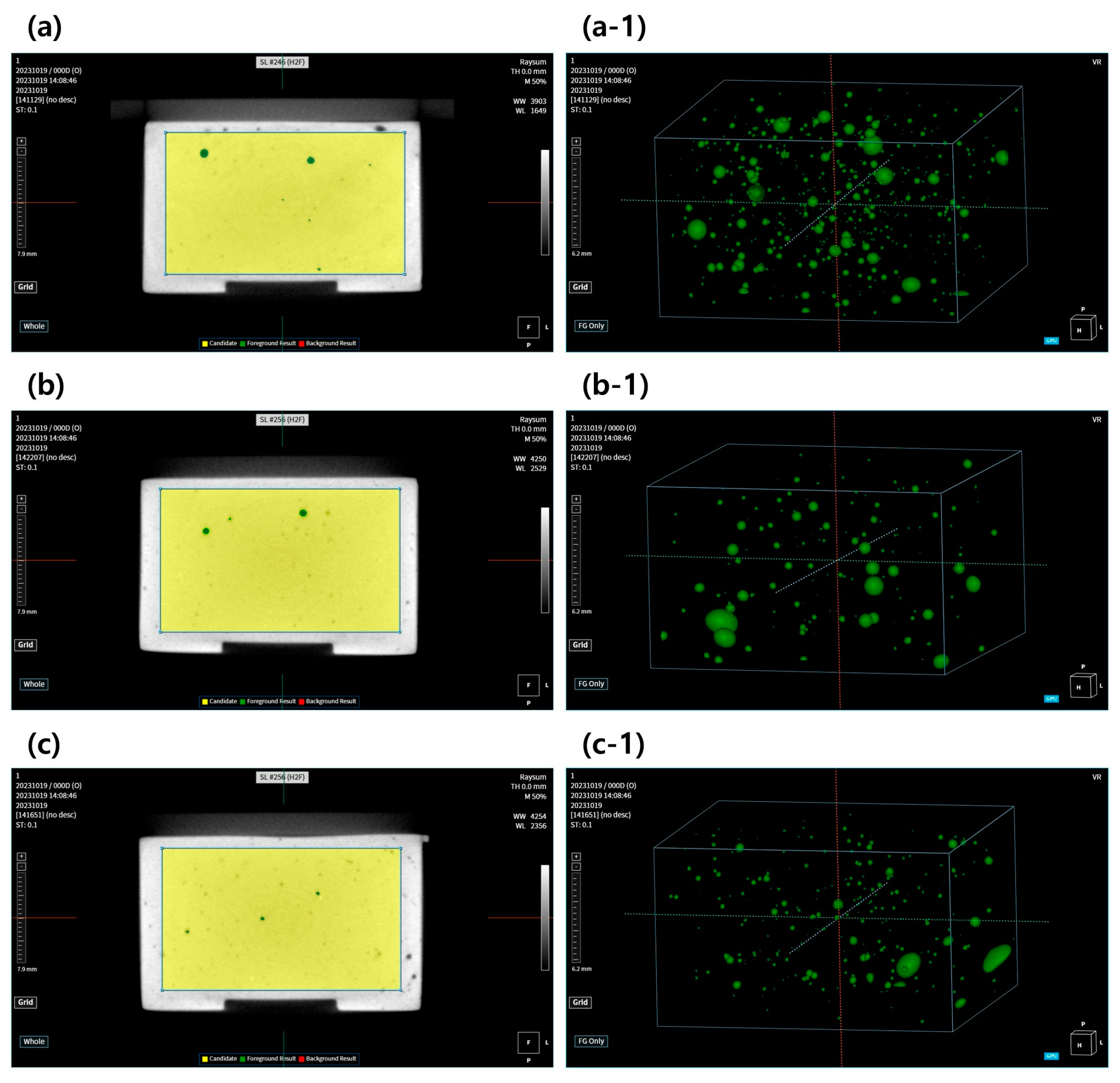
2.4. Measurement of Pore Distribution and Moisture Content of Gypsum Using Micro-CT
2.5. Setting Time Measurement
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Surface Particle Morphology Analysis of Gypsum
3.2. Analysis of Pore Distribution and Moisture Content of Gypsum Using 3D Images of Micro-CT
3.3. Measurement of Setting Time According to the Moisture Content of the Gypsum Mold
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saxena, P.; Gupta, S.K.; Newaskar, V. Biocompatibility of root-end filling materials: Recent update. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2013, 38, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, Y.L.; Mann, V.; Rahbaran, S.; Lewsey, J.; Gulabivala, K. Outcome of primary root canal treatment: Systematic review of the literature-Part 2. Influence of clinical factors. Int. Endod. J. 2008, 41, 6–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, H.W.; Toth, J.M.; Berzins, D.W.; Charlton, D.G. Mineral trioxide aggregate material use in endodontic treatment: A review of the literature. Dent. Mater. 2008, 24, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parirokh, M.; Torabinejad, M. Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A comprehensive literature review—Part III: Clinical applications, drawbacks, and mechanism of action. J. Endod. 2010, 36, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawil, P.Z.; Duggan, D.J.; Galicia, J.C. MTA: A Clinical Review. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2015, 36, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pushpalatha, C.; Dhareshwar, V.; Sowmya, S.v.; Augustine, D.; Vinothkumar, T.S.; Renugalakshmi, A.; Shaiban, A.; Kakti, A.; Bhandi, S.H.; Dubey, A.; et al. Modified Mineral Trioxide Aggregate-A Versatile Dental Material: An Insight on Applications and Newer Advancements. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 941826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, H.; Lotfi, M.; Rahbar, M.; Mozafari, A.; Badri-Nozadi, M.H.; Mokhtari-Zonouzi, H.R. Comparison of setting time of white mineral trioxide aggregate with and without disodium hydrogen phosphate at different liquid-to-powder ratios. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2018, 19, 988–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, W.N.; Nicholson, T.; Kahler, B.; Walsh, L.J. Mineral trioxide aggregate—A review of properties and testing methodologies. Materials 2017, 10, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan, H.; Tosun, G. The setting mechanism of mineral trioxide aggregate. J. Istanb. Univ. Fac. Dent. 2016, 50, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Fridland, M.; Rosado, R. Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) solubility and porosity with different water/powder ratios. J. Endod. 2003, 29, 814–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.K.; Kim, S.I.; Park, J.W.; Kim, E.S.; Shin, S.J. Different setting conditions affect surface characteristics and microhardness of calcium silicate-based sealers. Scanning 2018, 2018, 7136345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.L.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, S.M.; Choi, N.K.; Moon, H.J.; Hwang, M.J.; Song, H.J.; Park, Y.J. Comparison of setting time, compressive strength, solubility, and pH of four kinds of MTA. Kor. J. Dent. Mater. 2016, 43, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6876:2012, 3rd ed.; Dental Root Canal Sealing Materials. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Jo, S.B.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, H.N.; Kim, Y.J.; Patel, K.D.; Knowles, J.C.; Lee, J.H.; Song, M.J. Physical Properties and Biofunctionalities of Bioactive Root Canal Sealers In Vitro. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 6873:2013, 3rd ed.; Gypsum Products. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Darvell, B.W.; Wu, R.C.T. “MTA”—An Hydraulic Silicate Cement: Review update and setting reaction. Dent. Mater. 2011, 27, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, R.S.; Mauger, M.; Clement, D.J.; Walker, W.A. Mineral trioxide aggregate: A new material for endodontics. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1999, 130, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oraie, E.; Ghassemi, A.R.; Eliasifar, G.; Sadeghi, M.; Shahravan, A. Apical sealing ability of MTA in different liquid to powder ratios and packing methods. Iran. Endod. J. 2012, 7, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torres, F.F.E.; Perinoto, P.; Bosso-Martelo, R.; Chávez-Andrade, G.M.; Guerreiro-Tanomaru, J.M.; Tanomaru-Filho, M. Influence of powder-to-gel ratio on physicochemical properties of a calcium silicate sealer. Odovtos Int. J. Dent. Sc. 2020, 22, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavenago, B.C.; Pereira, T.C.; Duarte, M.A.; Ordinola-Zapata, R.; Marciano, M.A.; Bramante, C.M.; Bernardineli, N. Influence of powder-to-water ratio on radiopacity, setting time, pH, calcium ion release and a micro-CT volumetric solubility of white mineral trioxide aggregate. Int. Endod. J. 2014, 47, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.D.; Seok, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lim, B.S. Comparison of physical properties between paste type mineral trioxide aggregates (MTA) and powder-liquid mix type MTA. Korean J. Dent. Mater. 2017, 44, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, N.; Agarwal, A.; Mala, K. Mineral trioxide aggregate: A review of physical properties. Compend. Contin. Educ. Dent. 2013, 34, e25-32. [Google Scholar]
- Storm, B.; Eichmiller, F.C.; Tordik, P.A.; Goodell, G.G. Setting expansion of gray and white mineral trioxide aggregate and Portland cement. J. Endod. 2008, 34, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, H.; Jafarizadeh, S.; Zonouzi, H.R.M.; Lotfi, M.; Reyhani, M.F.; Sohrabi, A. Bond Strength of White Mineral Trioxide Aggregate with and without Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate with Different Liquid-to-Powder Ratios. Iran. Endod. J. 2017, 12, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Zeid, S.T.; Edrees, H.Y. Hydration Characterization of Two Generations of MTA-Based Root Canal Sealers. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haddad, A.; Che Ab Aziz, Z.A. Bioceramic-Based Root Canal Sealers: A Review. Int. J. Biomater. 2016, 2016, 9753210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9917-1:2007; Dentistry—Water-Based Cements—Part 1: Powder/Liquid Acid-Base Cements. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007.
- Camilleri, J.; Wang, C.; Kandhari, S.; Heran, J.; Shelton, R.M. Methods for testing solubility of hydraulic calcium silicate cements for root-end filling. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, J.N.; Kwak, S.W.; Kim, H.C. Differences in setting time of calcium silicate-based sealers under different test conditions. J. Dent. Sci. 2023, 18, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenneth, J.; Anusavice, D.M.D. Phillips’ Science of Dental Materials, 11th ed.; Park, Y.J., Lee, Y.K., Lim, H.N., Song, H.J., Eds.; CharmYun Publishing: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2015; pp. 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, J.M.; Sakaguchi, R.L. Craig’s Restorative Dental Materials, 12th ed.; Kim, K.H., Kim, Y.K., Park, E.K., Bae, J.M., Lee, K.B., Lim, B.S., Hwang, S.W., Eds.; JeeSeung Publishing: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2008; pp. 341–342, 347–348. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, F.; Renner, B.; Coppens, F.; Dewanckele, J.; Schwotzer, M. Reactivity of Gypsum-Based Materials Subjected to Thermal Load: Investigation of Reaction Mechanisms. Materials 2020, 13, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásárhelyi, L.; Kónya, Z.; Kukovecz, Á.; Vajtai, R. Microcomputed tomography–based characterization of advanced materials: A review. Mater. Today Adv. 2020, 8, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami-Lahiji, M.; Davalloo, R.T.; Tajziehchi, G.; Shams, P. Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2021, 51, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.B.; Lopes, L.I.G.; Bergstrom, T.G.; Silva, A.S.S.; Lopes, R.T.; Neves, A.A. Porosity and pore size distribution in high-viscosity and conventional glass ionomer cements: A micro-computed tomography study. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2021, 46, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, F.; Berástegui, E.; Aspiazu, K. Porosity analysis of mineral trioxide aggregate Fillapex and BioRoot cements for use in endodontics using microcomputed tomography. J. Conserv. Dent. 2018, 21, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rattanasak, U.; Kendall, K. Pore structure of cement/pozzolan composites by X-ray microtomography. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 637–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atmeh, A.R.; Alharbi, R.; Aljamaan, I.; Alahmari, A.; Shetty, A.C.; Jamleh, A.; Farooq, I. The effect of sealer application methods on voids volume after aging of three calcium silicate-based sealers: A micro-computed tomography study. Tomography 2022, 8, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, K.D.; Kono, A. Relationship between the porosity and compressive strength of dental stone. Acta Odontol. Scand. 1971, 29, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, H.J.; Qasim, S.B.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Vallittu, P.; Nogueira, L.P. Nano-CT as tool for characterization of dental resin composites. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Materials | Composition | Manufacture |
|---|---|---|
| Endoseal MTA | Calcium silicates (dicalcium silicate), tricalcium aluminates, calcium aluminoferrite, calcium sulfates, bismuth oxide, zirconium oxide, thickening agents | Maruchi, Wonju, Republic of Korea |
| Well-Root ST | Calcium silicate compound, calcium sulfate dehydrate, calcium sodium phosphosilicate, zirconium oxide, titanium oxide, thickening agents | Vericom, Chuncheon, Republic of Korea |
| Materials | Type | Water/Powder Ratio | Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental plaster | 2 | 45 mL/100 g | Study and mounting use |
| Hard | |||
| Dental stone | 3 | 23 mL/100 g | Various purposes |
| Very hard | |||
| Die stone | 4 | 20 mL/100 g | High strength and low expansion, detailed work |
| Ultra hard |
| Gypsum Product | Whole Volume (mm3) | Pore Volume (mm3) | Pore Surface Area (mm2) | Moisture Content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dental plaster | 1862.6 ± 6.04 | 19.1 ± 1.47 a | 162.54 ± 4.69 a | 1.02 ± 0.07 a |
| Dental stone | 1865.7 ± 4.91 | 12.2 ± 0.91 b | 91.1 ± 3.27 b | 0.65 ± 0.04 b |
| Die stone | 1863.5 ± 6.53 | 7.8 ± 0.70 c | 73.64 ± 3.97 c | 0.41 ± 0.03 c |
| Type of Molds | Setting Time (min) | |
|---|---|---|
| Endoseal MTA | Well-Root ST | |
| Dental plaster | 5.8 ± 0.30 a | 10.4 ± 0.41 a |
| Dental stone | 7.5 ± 0.37 b | 17.5 ± 0.38 b |
| Die stone | 15.6 ± 0.51 c | 23.9 ± 0.78 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.-S.; Gwak, D.-H.; Ko, Y.-S.; Lim, C.-I.; Lee, S.-Y. In Vitro Comparison of Differences in Setting Time of Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate According to Moisture Content of Gypsum. Materials 2024, 17, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010035
Kim H-J, Lee J-S, Gwak D-H, Ko Y-S, Lim C-I, Lee S-Y. In Vitro Comparison of Differences in Setting Time of Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate According to Moisture Content of Gypsum. Materials. 2024; 17(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyun-Jin, Jun-Seok Lee, Dong-Hoon Gwak, Yong-Seok Ko, Chun-Il Lim, and Seung-Youl Lee. 2024. "In Vitro Comparison of Differences in Setting Time of Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate According to Moisture Content of Gypsum" Materials 17, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010035
APA StyleKim, H.-J., Lee, J.-S., Gwak, D.-H., Ko, Y.-S., Lim, C.-I., & Lee, S.-Y. (2024). In Vitro Comparison of Differences in Setting Time of Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate According to Moisture Content of Gypsum. Materials, 17(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17010035





