Abstract
In this study, a phase field method based on the Cahn–Hilliard equation was used to simulate the spinodal decomposition in Zr-Nb-Ti alloys, and the effects of Ti concentration and aging temperature (800–925 K) on the spinodal structure of the alloys for 1000 min were investigated. It was found that the spinodal decomposition occurred in the Zr-40Nb-20Ti, Zr-40Nb-25Ti and Zr-33Nb-29Ti alloys aged at 900 K with the formation of the Ti-rich phases and Ti-poor phases. The spinodal phases in the Zr-40Nb-20Ti, Zr-40Nb-25Ti and Zr-33Nb-29Ti alloys aged at 900 K were in an interconnected non-oriented maze-like shape, a discrete droplet-like shape and a clustering sheet-like shape in the early aging period, respectively. With the increase in Ti concentration of the Zr-Nb-Ti alloys, the wavelength of the concentration modulation increased but amplitude decreased. The aging temperature had an important influence on the spinodal decomposition of the Zr-Nb-Ti alloy system. For the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy, with the increase in the aging temperature, the shape of the rich Zr phase changed from an interconnected non-oriented maze-like shape to a discrete droplet-like shape, and the wavelength of the concentration modulate increased quickly to a stable value, but the amplitude decreased in the alloy. As the aging temperature increased to 925 K, the spinodal decomposition did not occur in the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy.
1. Introduction
Titanium and its alloys have a low density, high specific strength, low elastic modulus and good corrosion resistance, and as such they have been widely used in aerospace, biomedicine and other fields. As biological implanting materials, biocompatibility and biomechanical compatibility are also very important properties. Traditional α titanium alloys with an HCP structure, such as the Ti-6Al-4V alloy, have excellent comprehensive mechanical properties; however, they comprise Al and V elements, which have been proven to be biotoxic after being introduced into the human body, meaning that they result in a range of health problems [1]. In terms of biomechanical compatibility, in comparison to other implantable metal materials, conventional titanium alloys yield a relatively low elastic modulus, and this is much higher than that of the human bones. Thus, after being implanted into the human body as a hard implant, they may cause a “stress-shielding effect”.
Generally, Ti alloys are classified into three types of alloys according to their phase constituents and microstructures, i.e., a-type Ti alloys, (a+β)-type Ti alloys and β-type Ti alloys. It has been well documented that the additions of some biocompatible alloy elements, such as Nb [2], Mo [3], Ta [4], Zr [5], Cu [6], Fe [7] and Sn [8,9], etc., can effectively promote the β phase stability of Ti alloys, and metastable β titanium alloys with a BCC structure can be obtained at room temperature [10]. Compared to the conventional titanium alloys, β titanium alloys not only have good biocompatibility, but also have an extremely low elastic modulus and high strength. Therefore, a variety of β titanium alloys have been developed in recent years, such as Ti-Nb-based alloys [11,12,13,14], Ti-Mo-based alloys [3,15], Ti-Zr-based alloys [16] and Ti-Ta-based [17,18] alloys, etc.
For a β titanium alloy, the strengthening methods mainly include solid solution, precipitation or fine grain strengthening [19,20,21]. However, these methods usually lead to an increase in the elastic modulus of the alloys while increasing the strength of the alloys. A spinodal decomposition refers to a homogeneous phase transition, where a supersaturated solid solution decomposes into two phases which possess the same structure but differ in composition on account of the instability of the solid solution [13,22]. Spinodal decomposition rapidly forms two phases with the same crystal structure by uphill diffusion; this does not require nucleation, which can improve the strength of the alloys dramatically without increasing their elastic modulus [23,24].
Clearly, it can be seen from the phase diagram that there is a large miscibility gap in the solid solution region for the Zr-Nb-Ti alloy system [25], so the spinodal decomposition may occur at a specific temperature for the Zr-Nb-Ti solid solution of a particular composition. Accordingly, a Zr-Nb-Ti alloy strengthened by a spinodal structure with a high strength and low elastic modulus can be obtained.
Previous studies show that spinodal strengthening effects are in close connection with the amplitude, wavelength, volume fraction and shape of the decomposition products [26,27]. Many documents confirm that the amplitude, wavelength, volume fraction and shape of the decomposition products are usually affected by the composition of the alloys and the aging temperature in the alloys. Therefore, it is helpful to study the growth kinetics process of spinodal phases in order to regulate the strengthening effects of spinodal decomposition in the alloy. However, few studies have been conducted on the responses of Zr-Nb-Ti alloys to aging treatments at different temperatures.
It is useful to use phase field simulation to predict the evolution of the microstructure [28]. Moreover, the simulation results can visually show the evolution of the microstructure during the spinodal decomposition process at any time and reveal the effects of the composition of the alloy, aging temperature, aging time and external field on the spinodal structure. However, no study has yet used the phase field method to simulate the spinodal decomposition process of Zr-Nb-Ti alloys. Thus, it is meaningful to study the spinodal microstructure evolution and structural characteristics of Zr-Nb-Ti alloys using the phase field method, which can provide theoretical guidance to design novel implantable β type Zr-Nb-Ti biomedical alloys strengthened by spinodal decomposition.
In view of this, in the current work, the spinodal decomposition in Zr-Nb-Ti alloys was simulated by applying the phase field method based on the Cahn–Hilliard equation, and the nonlinear Cahn–Hilliard partial difference equation was solved by using the finite element method. Accordingly, we applied the phase field method to simulate the morphology, wavelength, amplitude and volume fraction of the spinodal phases. Eventually, the effects of the Ti content and aging temperature on the morphology and volume fraction of the spinodal phases and the wavelength and amplitude of the concentration modulate were discussed. The aim of the study was to figure out the kinetics characteristics of the spinodal decomposition in Zr-Nb-Ti alloys, making it easy to regulate the microstructure of spinodal phases to obtain alloys with improved comprehensive mechanical properties.
2. Phase Field Model
2.1. Cahn–Hilliard Equation
The Cahn–Hilliard diffusion equation can be used to study the spinodal decomposition in Zr-Nb-Ti alloys, which are described as follows:
where and are the mole fractions of Zr and Nb atoms, respectively; and are the migration rates of the Zr and Nb atoms, respectively; Vm is the mole volume; and G is the Gibbs free energy of the alloys.
The migration rate of the Zr and Nb atoms, and , can be written as follows:
where and are the activation energies of the Nb and Zr atoms, respectively, which are expressed as follows:
where , , , , , , , , , and are thermodynamic parameters, which generally appear linear to the temperature.
The total Gibbs energy of the alloys can be described as follows:
where , and refer to the volume free energy, the interface energy and the elastic strain energy, respectively, and , and refer to the densities of the volume free energy, the interface energy and the elastic strain energy, respectively.
For the Zr-Nb-Ti alloy, the density of the volume free energy can be expressed as follows:
where is the excess Gibbs energy of the element, which can be expressed as follows:
where is the mole fraction of the Ti atom; , and refer to the interaction coefficients between Zr and Nb, Ti and Zr, and Ti and Nb, respectively; and , and refer to the interaction coefficients of Zr, Nb and Ti.
In the present work, we use the gradient energy density in the phase field model of the gradient energy contribution to the total free energy in the following form [28,29]:
where and refer to the gradient energy coefficients of Zr and Nb atoms, respectively, whose expressions are as follows:
Regarding the elastic strain energy, because the two phases obtained in spinodal decomposition have exactly the same crystal structure with a coherent interface between them, the elastic strain energy contribution is ignored in the calculation for simplicity. As a result, the final Cahn–Hilliard equation can be obtained as follows:
2.2. Simulation Conditions
We performed two-dimensional (2D) simulations using 64 × 64 computational grids, and the dimension of the model was 60 × 60 nm2. We assumed periodic boundary conditions. The Cahn–Hilliard equations were solved using the conventional finite-difference method with commercial Comsol Multiphysics software.
The boundary conditions of the concentration field are as follows:
The initial conditions for the concentration field are as follows:
The parameters [25,30,31] used in the simulation of the spinodal decomposition in the Zr-Nb-Ti alloys are gathered in Table 1.

Table 1.
The parameters used in simulation of the spinodal decomposition in Zr-Nb-Ti alloys [25,30,31].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of the Concentration of Ti on the Spinodal Decomposition of Zr-Nb-Ti Alloys
To study the effects of Ti concentration on the spinodal decomposition of the Zr-Nb-Ti alloys, we simulated the spinodal decomposition process of the alloys with different Ti concentrations (Zr-33Nb-29Ti, Zr-40Nb-25Ti and Zr-40Nb-20Ti) by using the phase field method at a temperature of 900 K, and the effects of Ti concentration on the morphology, amplitude and wavelength of the spinodal structure are discussed.
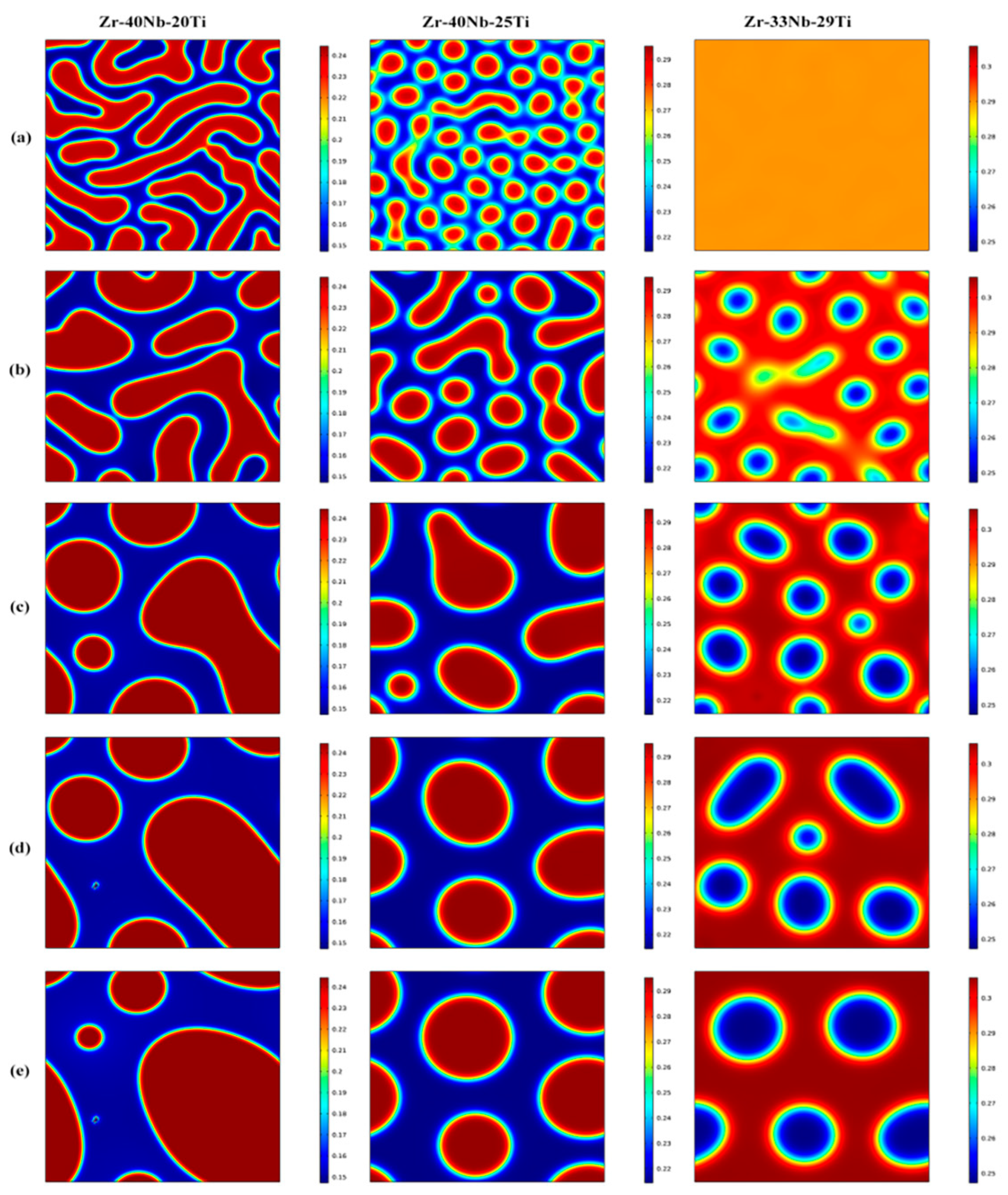
Figure 1 shows the morphology evolution of the Zr-Nb-Ti alloys with different Ti concentrations annealed at 900 K for 20 to 2000 min. It is clear that the spinodal decomposition occurred in the three alloys with the formation of the modulated structure containing Ti-rich phases and Ti-poor phases. Ti concentration had an important influence on the morphology of the microstructure of the alloys. For the Zr-40Nb-20Ti alloy, the Ti-rich phase presented an interconnected non-oriented maze-like shape in the early aging period. With the extension of the aging time, the amount of the Ti-rich phase decreased but its size increased. Moreover, the shape of the Ti-rich phases gradually changed from interconnected maze-like shapes to discrete elliptical or round shapes to reduce the interface energy due to the increase in the size of the phase.
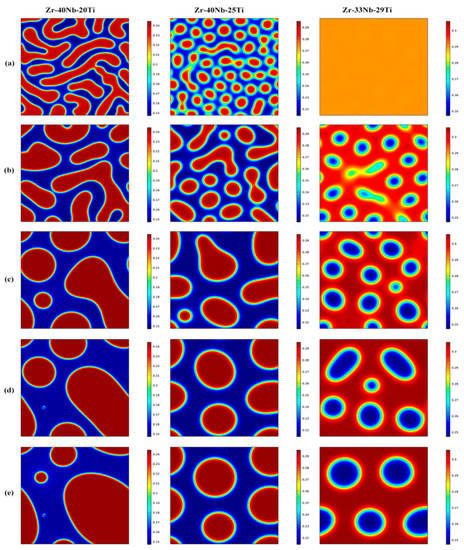
Figure 1.
The microstructure evolution of the Zr-33Nb-29Ti, Zr-40Nb-25Ti and Zr-40Nb-20Ti alloys aged at 900 K for different times (a) 20 min, (b) 100min, (c) 500 min, (d) 1000 min and (e) 2000 min (the blue region refers the Ti-rich phase and the red region refers the Ti-poor phase).
For the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy, the Ti-rich phases were in a discrete droplet-like shape in the early aging stage. With the increase in aging time, the discrete fine droplet-like phases were constantly fused together, resulting in an increasing size and a decreasing number of the Ti-rich phases, but the Ti-rich phases always maintained the discrete droplet-like shape.
In contrast to the first two alloys, the occurrence of spinodal decomposition in the Zr-33Nb-29Ti alloy needed a longer time at 900 K. After being aged at 900 K for 100 min, the spinodal phases can be obviously observed in the Zr-33Nb-29Ti alloy. The Ti-poor phases were in the discrete droplet-like shape, embedding in the substrate of the Ti-rich phase of the Zr-33Nb-29Ti alloy, forming a distinct droplet star spot pattern. With the increase in aging time, the amount of the droplet star-like phases decreased, but their size increased and their shape was still elliptical or round.
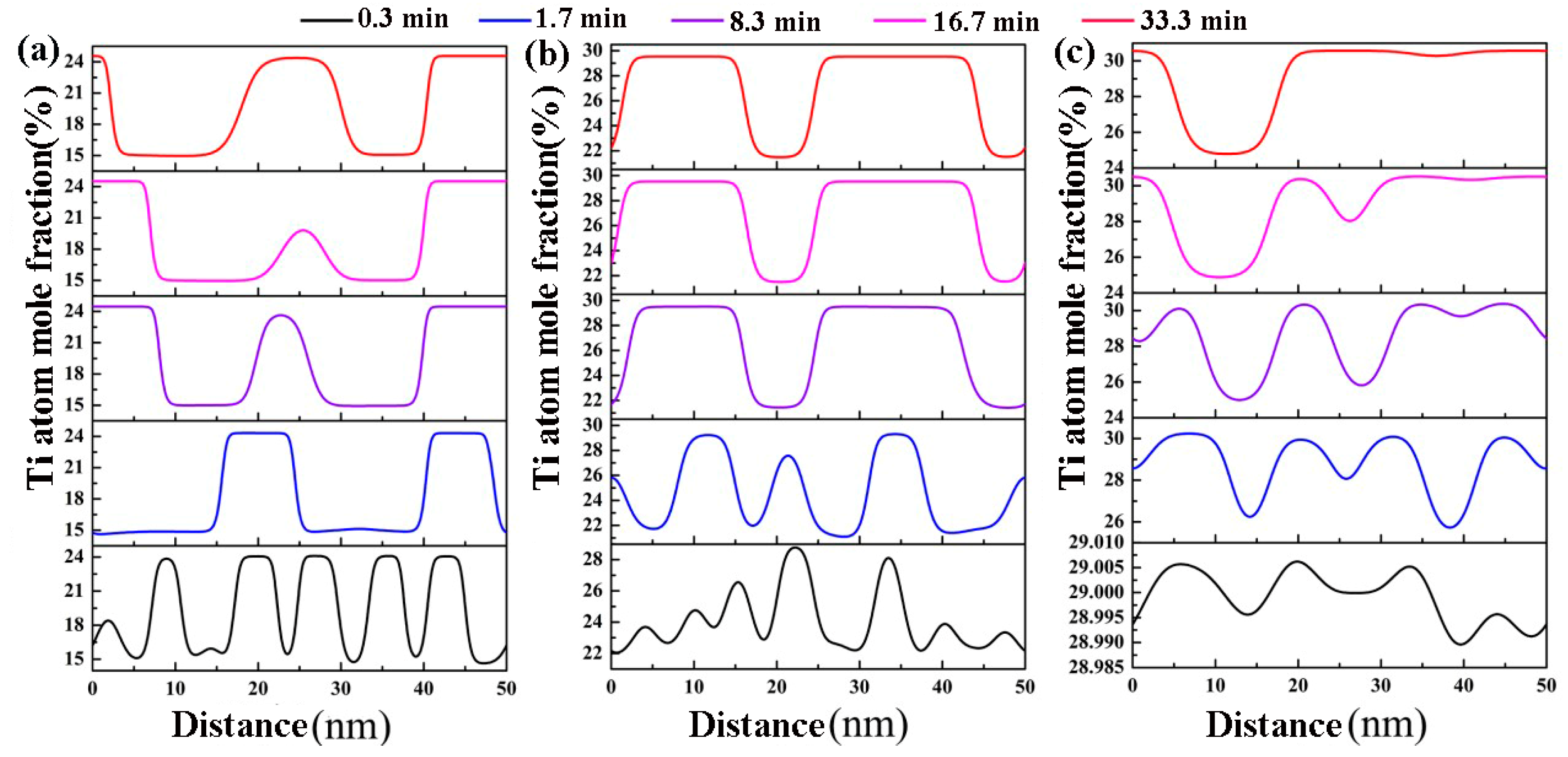
To quantify the effect of Ti content on the amplitude and wavelength of the concentration modulate produced by spinodal decomposition in the Zr-Nb-Ti alloy, we calculated the molar fraction of Ti atoms at different positions along the horizontal direction in the Zr-Nb-Ti alloy aged at different times using the phase field method.
Figure 2 represents the Ti concentration modulate curve along the horizontal direction in the Zr-40Nb-20Ti, Zr-40Nb-25Ti and Zr-33Nb-29Ti alloys aged at 900 K for 0.3, 1.7, 8.3, 16.7 and 33.3 min, respectively. It is obvious that the change in the molar fraction of Ti atoms is divided into three stages as follows:
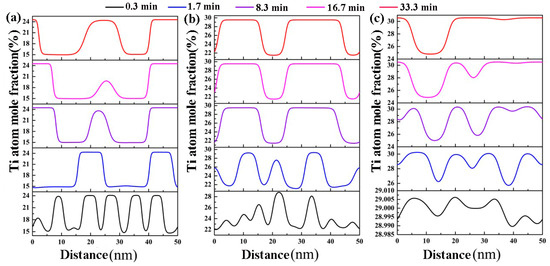
Figure 2.
The Ti concentration fluctuation curve along the horizontal direction of the Zr-Nb-Ti alloys aged at 900 K for different times: (a) Zr-33Nb-29Ti, (b) Zr-40Nb-25Ti and (c) Zr-40Nb-20Ti.
The first stage: the Ti concentration fluctuates in a small length range, corresponding to the stage of the rapid formation of the Ti-rich spinodal phases.
The second stage: The amplitude of the Ti concentration fluctuation reaches the equilibrium value quickly, but its wavelength is basically not widened, corresponding to the stage of the rapid growth of the Ti-rich phases. In this stage, the number of the Ti-rich phases decreases, but the size of the phases quickly increases to an equilibrium value, resulting in the increase in the interface energy of the Zi-Nb-Ti system.
The third stage: The amplitude of the Ti concentration fluctuations basically maintains a stable value, but the wavelength is constantly broadening, corresponding to the coarsening of the Ti-rich phases. In this stage, the shape of the Ti-rich phases tends to be elliptic or circular to reduce the interface energy of the alloy system.
It can also be found that Ti concentration had an important influence on the amplitude and wavelength of the spinodal structures of the alloys. With the increase in Ti concentration, the wavelength increased, but the amplitude decreased in the three alloys. At the aging temperature of 900 K, the equilibrium concentrations of the spinodal phases of the Zr-40Nb-20Ti, Zr-40Nb-25Ti and Zr-33Nb-29Ti alloys were and and , and and , respectively.
3.2. Effects of Aging Temperature and Time on the Spinodal Decomposition of Zr-Nb-Ti Alloys
Limited to the length of the article, we only chose one alloy with titanium content in the middle value, and the results indicated that temperature also plays an important role in the evolution of the spinodal structure of the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy, and the other two alloys should also have similar results. According to the cross section of the Zr-Nb-Ti phase diagram at 923 K, there is a large miscibility gap in the β solid solution region. Thus, we selected aging temperatures ranging from 800 K to 925 K, and simulated the spinodal structure evolution of the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy aged at 800, 825, 850, 875, 900 and 925 K. The effects of the aging time and temperature on the spinodal decomposition of the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy are discussed.
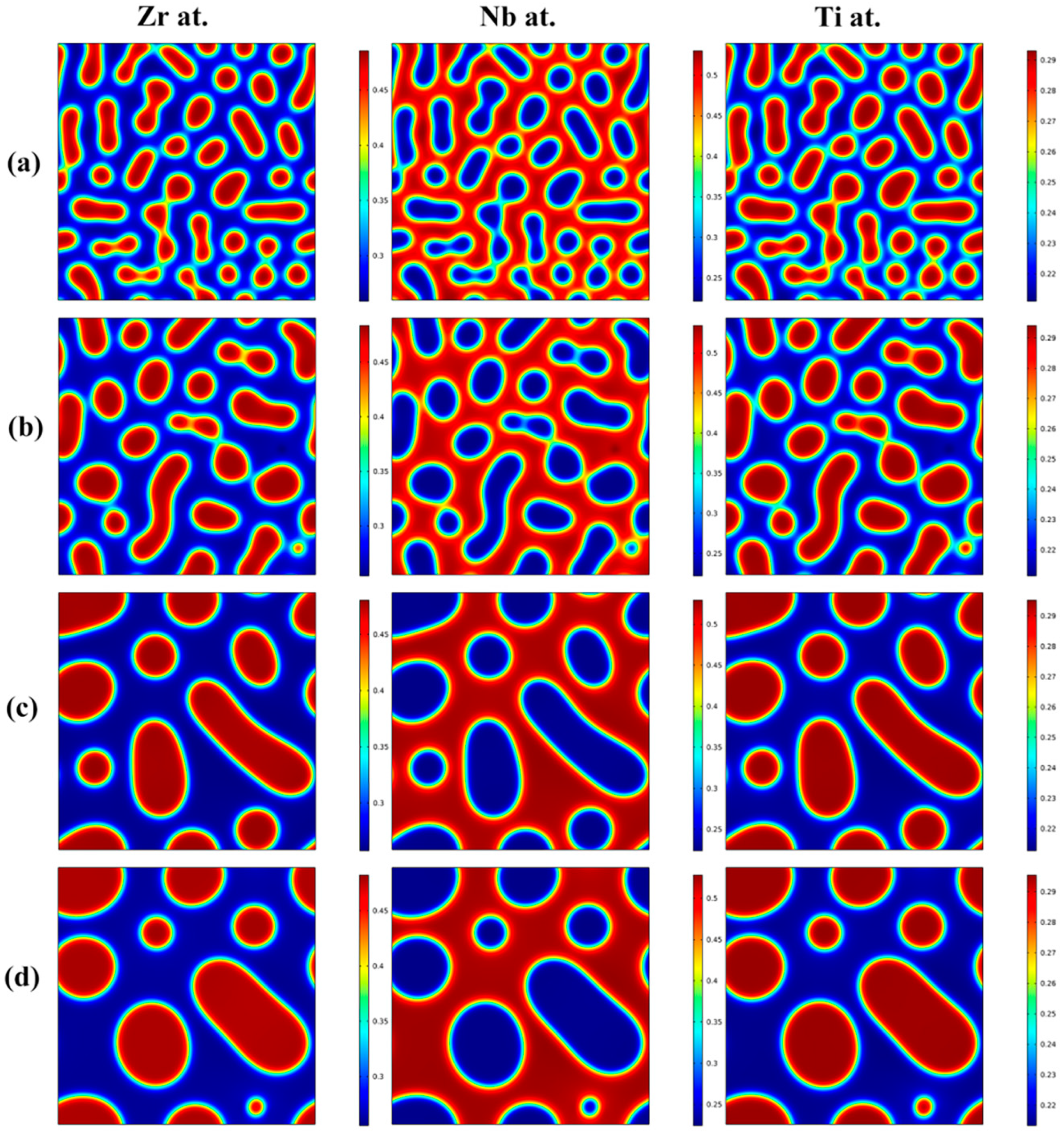
Figure 3 shows the morphology evolution of the Zr-rich, Nb-rich and Ti-rich phases with increasing aging time for the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy aged at 900 K for different times. It is clear that the morphology evolution of the Zr-rich phase was similar to that of the Ti-rich phase with the increase in aging time. The two phases were both in discrete droplet-like shapes, embedding in the Nb-rich substrate. With the increase in aging time, the discrete spinodal phases continued to fuse together, leading to an increase in their size but decrease in their number, and the spinodal phases always maintained elliptical or round shapes.
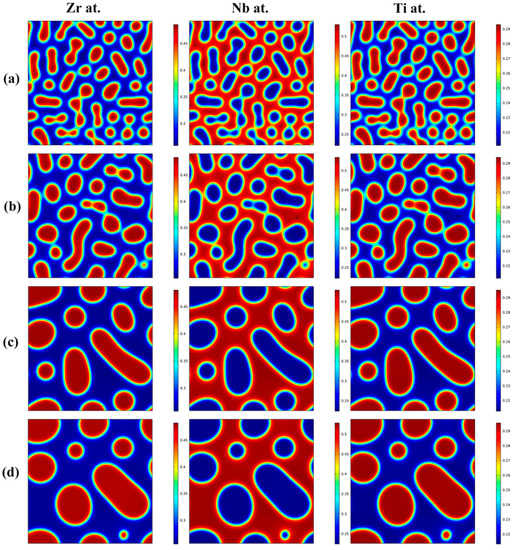
Figure 3.
The morphology evolution of the Zr-rich, Nb-rich and Ti-rich phases with aging time increasing for the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy aged at 900 K for different times: (a) 50 min, (b) 100 min, (c) 500 min and (d) 1000 min.
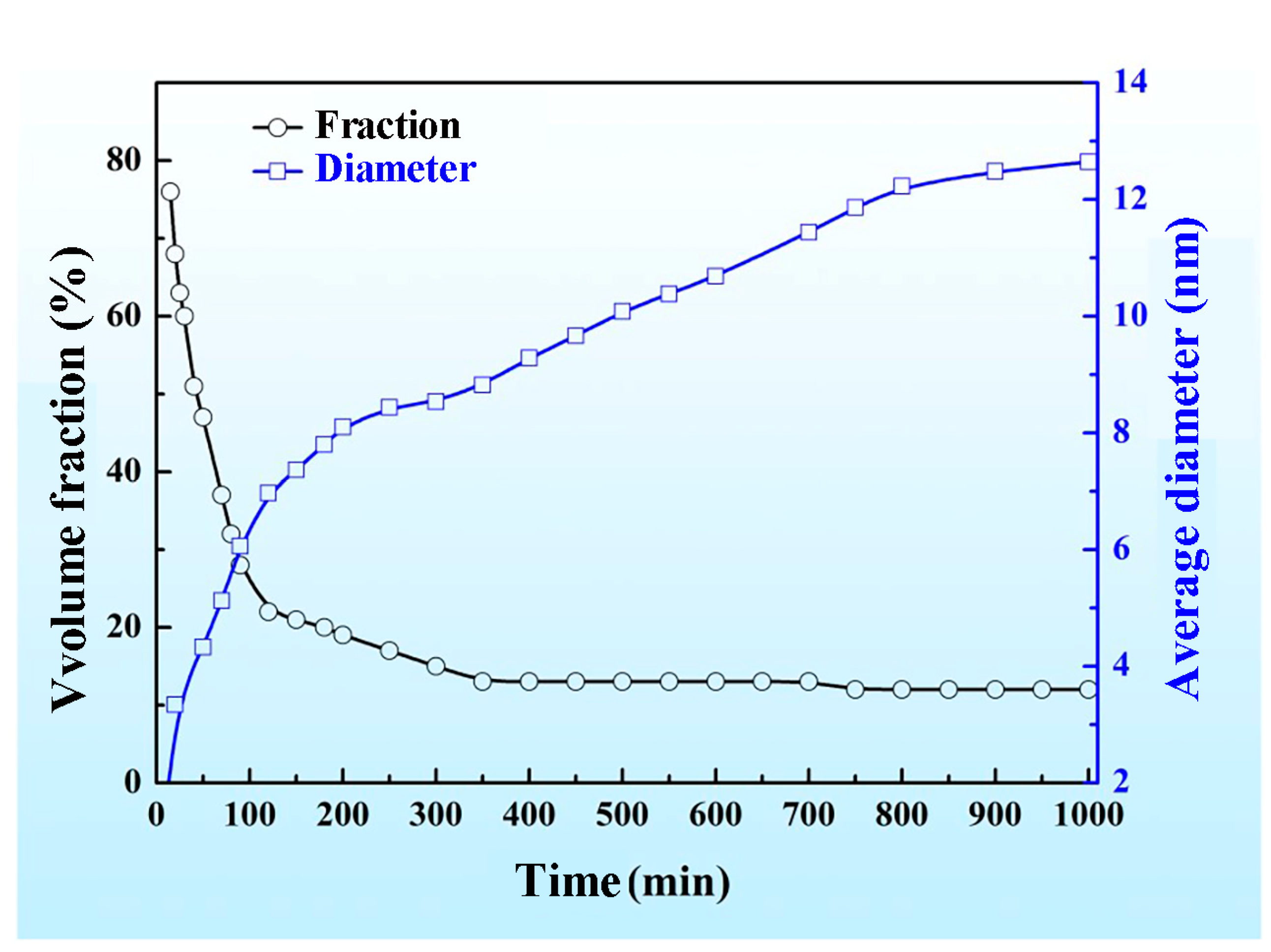
To more intuitively indicate the change in the size and the volume fraction of the spinodal phases with the aging time increasing, we calculated the diameter and volume fraction of the droplet-like Zr-rich and Ti-rich phases, and the change in the mean diameter and the volume fraction of the two phases as a function of the aging time is shown in Figure 4. It is clear that the amount of the droplet-like phases dropped rapidly in the initial aging period; then, the decline rate slowed down and eventually tended to a stable value. In contrast, the size of the droplet-like phases rapidly increased in the initial aging period, and then the increase rate slowed down.
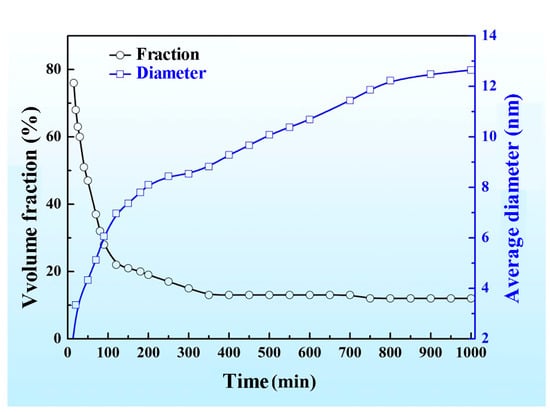
Figure 4.
The change in the number and volume fraction of Zr-rich phases and Ti-rich phases in the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy aged at 900 K as a function of aging time.
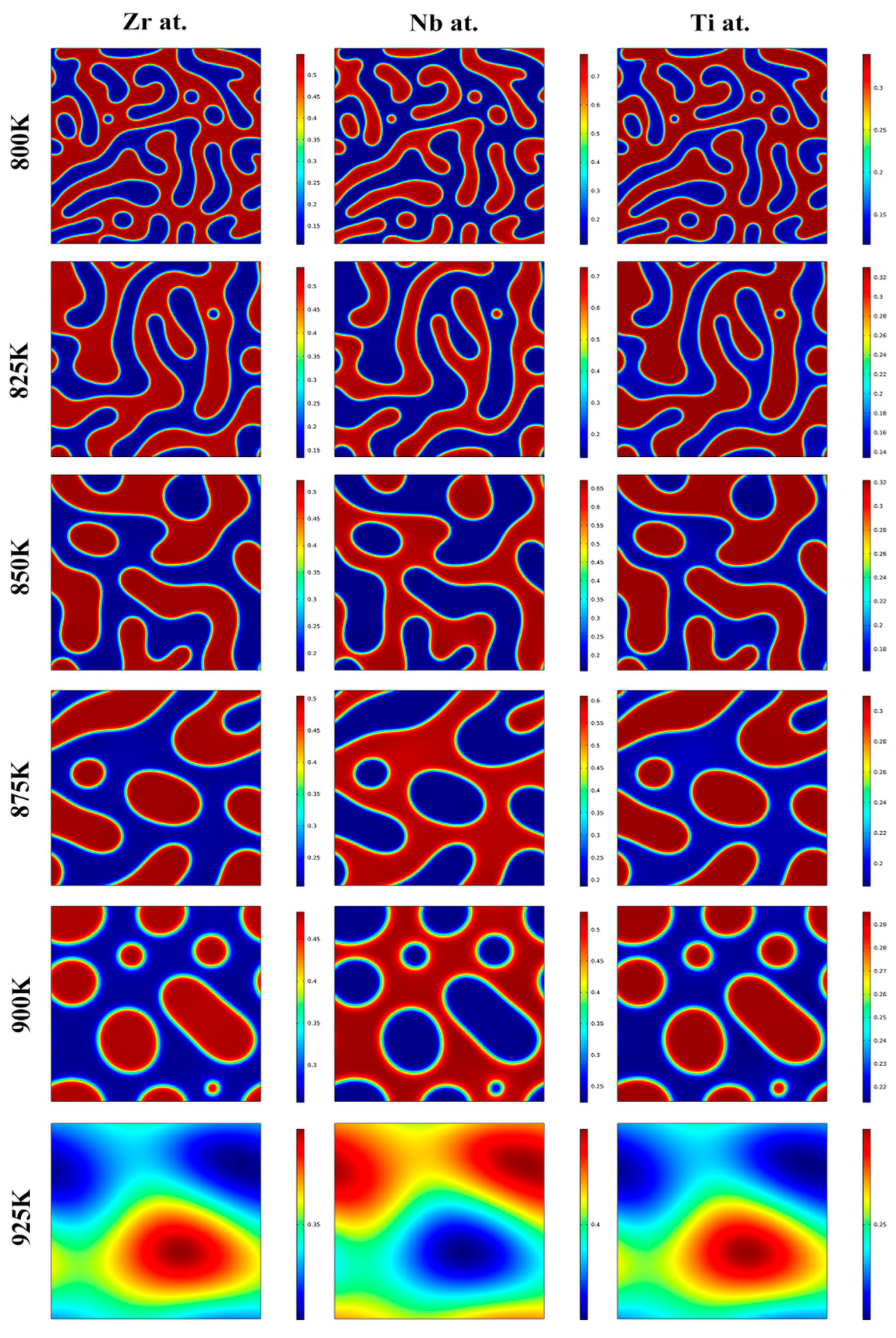
Moreover, the morphology evolution of the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy aged at 800, 825, 850, 875, 900 and 925 K was simulated, and the effects of the aging temperature on it is discussed. Figure 5 shows the morphology evolution of the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy aged at the different temperatures. It is clear that the Ti-rich phases (marked in red) and Ti-poor phases (marked in blue) exhibited a similar morphology in the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy. With the aging temperature increasing from 800 K to 900 K, the rate of the spinodal decomposition of the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy increased. As the aging temperature further increased to 925 K, no spinodal decomposition occurred in the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy. The size of the spinodal phases increased with the aging temperature, reaching a maximum value of about 10 nm at 875 K, and with the aging temperature further increasing, the size of the spinodal phases almost no longer increased. Furthermore, the aging temperature also had an important effect on the morphology of the spinodal phases. With the aging temperature increasing, the shape of the spinodal phases changed from the initial interconnected unoriented maze-like shape to the discrete droplet-like shape, and the amount of the spinodal phases constantly decreased.
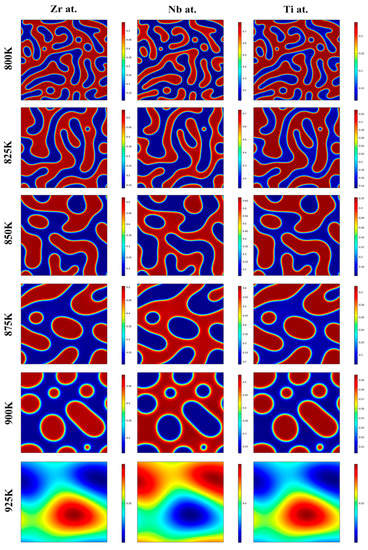
Figure 5.
The morphology evolution of the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy aged at temperatures in the range of 800 K to 925 K for 1000 min.
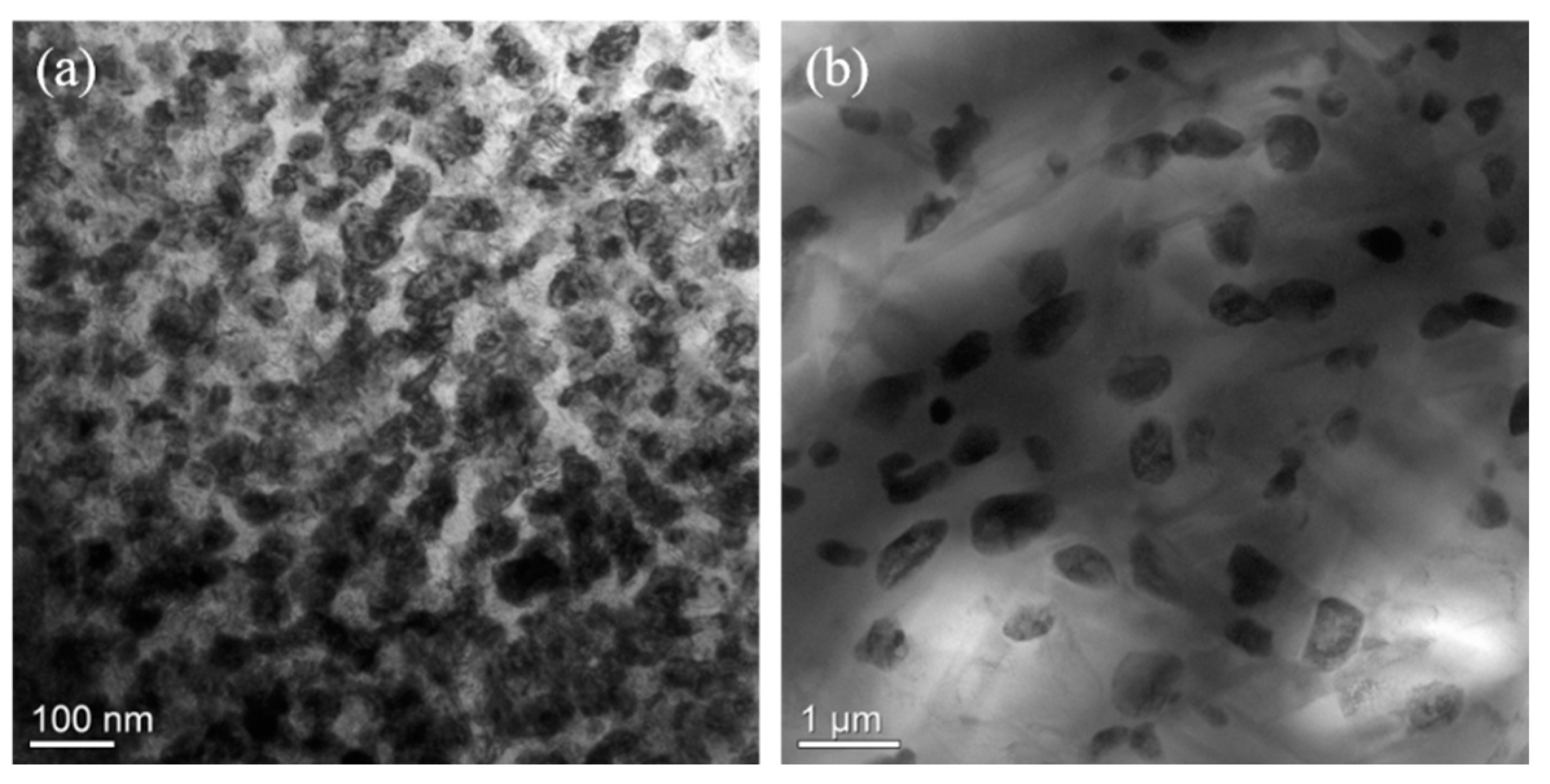
To verify the simulations, we prepared a Ti alloy with the nominal composition of Zr-40Nb-25Ti by melting pure Zr (99.9%), pure Nb (99.9%) and pure Ti (99.9%) in a vacuum arc melting furnace. The alloy samples were first homogenized at 1373K for 0.5h, and then annealed at 850K and 900K, respectively. The microstructures of the samples annealed at the two temperatures were characterized by using transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-2100, JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Figure 6 illustrates the TEM bright images of the alloy samples annealed at 850 K and 900 K. It is clear that alternating dark and bright regions existing in the annealed samples, indicating the occurrence of the spinodal decomposition in the two samples. The morphology of the spinodal phases in the sample annealed exhibited an interconnected maze-like shape, while the morphology of the spinodal phases changed to the discrete droplet-like shape as the annealing increased to 900 K. The result is in good agreement with the simulation.
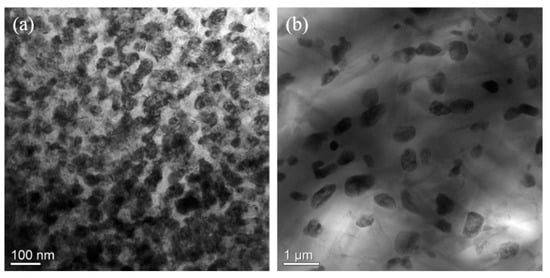
Figure 6.
TEM bright images of the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy samples (a) annealed at 850 K and (b) annealed at 900 K.
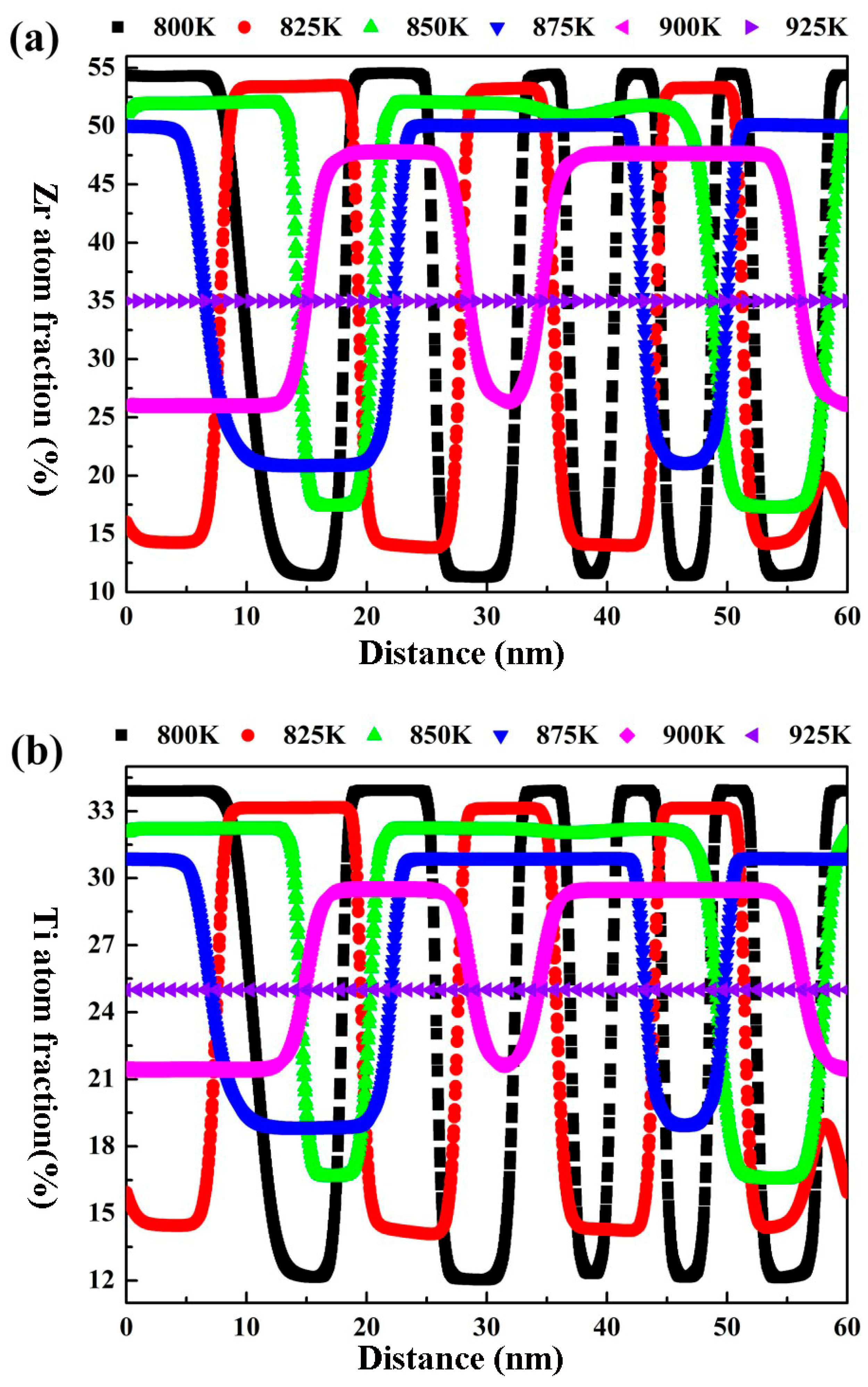
In order to clearly indicate the effect of the aging temperature on the amplitude and wavelength of the spinodal structure of the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy, the molar fraction of Zr and Ti atoms at different positions along the horizontal direction in the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy aged at different temperatures for 1000 min were calculated, and the results are shown in Figure 7. It can be seen that the changes in the amplitude and wavelength on the concentration fluctuation curves for Zr and Ti atoms exhibited similar trends with the aging temperature increasing. The amplitude on the Ti concentration fluctuation curve decreased with the aging temperature increasing. As the aging temperature increased to 925 K, the amplitude was equal to 0, implying that no spinodal decomposition occurred in the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy aged at that temperature. Meanwhile, the wavelength of the Ti concentration fluctuation curve increased with the aging temperature increasing, reaching its maximum value in the alloy aged at 875K, and then tended to a stable value as the aging temperature further increased. As a result, the temperature interval for the spinodal decomposition in the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy was in the range of 800 K to 900 K, and the morphology, amplitude and wavelength of the spinodal structure can be adjusted by changing the aging temperature.
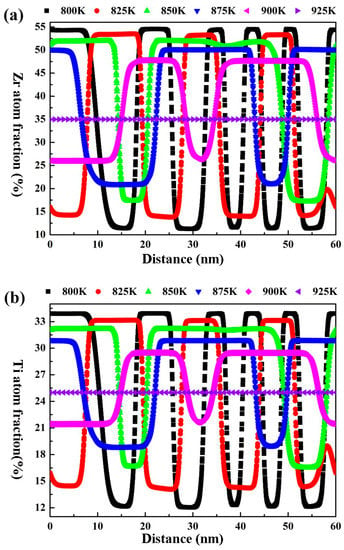
Figure 7.
The Ti and Zr concentration fluctuation curves along the horizontal direction of the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy aged at different temperatures for 1000 min. (a) Zr concentration and (b) Ti concentration.
4. Conclusions
In the present work, the spinodal decomposition of the β phase in the Zr-Nb-Ti alloy system aged at 800–925 K was simulated using the phase field method, and the effects of Ti concentration and aging temperature on the spinodal structure of the alloys were investigated. The main conclusions are drawn as follows:
- (1)
- The spinodal decomposition occurred in the Zr-40Nb-20Ti, Zr-40Nb-25Ti and Zr-33Nb-29Ti alloys aged at 900 K with the formation of the Ti-rich phases and Ti-poor phases.
- (2)
- The Ti concentration has important effects on the morphology of the spinodal phases and the wavelength and the amplitude of the concentration modulation. The spinodal phases in the Zr-40Nb-20Ti, Zr-40Nb-25Ti and Zr-33Nb-29Ti alloys aged at 900 K were an interconnected non-oriented maze-like shape, a discrete droplet-like shape and a clustering sheet-like shape in the early aging period, respectively. Increasing the Ti concentration of the alloy increased the wavelength of the concentration modulation; decreasing the Ti concentration decreased the amplitude.
- (3)
- The aging temperature also has important effects on the morphology of the spinodal phases and on the wavelength and amplitude of the concentration modulation. For the Zr-40Nb-25Ti alloy, with the increase in the aging temperature, the shape of the Zr-rich phase changed from an interconnected non-oriented maze-like shape to a discrete droplet-like shape, and the wavelength of the concentration modulate increased quickly to a stable value, but the amplitude decreased in the alloy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. and D.Z.; methodology, J.T.; validation, Z.W.; formal analysis, Y.D.; investigation, D.Z.; resources, J.L.; data curation, D.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, K.Y.; writing—review and editing, Y.D.; visualization, J.L.; supervision, Y.D.; project administration, D.Z.; and funding acquisition, J.L., Y.D. and D.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51971190,11872053), the science and technology innovation Program of Hunan Province (2020RC2080) and Undergraduate Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (S202210530052).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Madikizela, C.; Cornish, L.A.; Chown, L.H.; Möller, H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of selective laser melted Ti-3Al-8V-6Cr-4Zr-4Mo compared to Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 747, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, Q.; Song, L.; Yang, G.; Zhang, J. New β-type Ti-Zr-V-Nb alloys used for laser-based direct energy deposition: Design, microstructure, and properties. Mater. Charact. 2022, 189, 111917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Yang, S.; Sun, Y.; Gu, Y.; Mercelis, B.; Zhong, S.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Politis, C. In-situ formation of Ti-Mo biomaterials by selective laser melting of Ti/Mo and Ti/Mo2C powder mixtures: A comparative study on microstructure, mechanical and wear performance, and thermal mechanisms. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 115, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Du, P.; Cai, Z.; Li, K.; Bao, W.; Yang, X.; Xie, G. Phase-tunable equiatomic and non-equiatomic Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta high-entropy alloys with ultrahigh strength for metallic biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 117, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Tian, Y.; Xu, G.; Yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Masset, P.J.; Zhang, L. Diffusivities and atomic mobilities in bcc Ti-Zr-Nb alloys. Calphad 2019, 64, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Maimaitijuma, T.; Yu, B.; Li, X.; Xi, G.; Liu, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, T. Ti-Zr-Nb based BCC solid solution alloy containing trace Cu and Ag with low modulus and excellent antibacterial properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, K.; Wang, Q.; Dai, P.; Fang, H.; Wu, F.; Guo, Q.; Liaw, P.K.; Hua, N. Novel Ti-Zr-Hf-Nb-Fe refractory high-entropy alloys for potential biomedical applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 906, 164383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lim, J.-H.; Rehman, I.U.; Lee, W.-T.; Kim, J.G.; Oh, J.S.; Lee, T.; Nam, T.-H. Tuning the texture characteristics and superelastic behaviors of Ti–Zr–Nb–Sn shape memory alloys by varying Nb content. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 845, 143243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-C.; Wong, K.-K.; Wu, S.-C.; Chen, Y.-X.; Ho, W.-F. Metastable dual-phase Ti–Nb–Sn–Zr and Ti–Nb–Sn–Fe alloys with high strength-to-modulus ratio. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 30, 103168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Song, K.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, F. Structural characterization and nanoscale strain field analysis of alpha/beta interface layer of a near alpha titanium alloy. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, J.W. On Spinodal Decomposition. Acta Metall. 1961, 9, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.A.; Easterling, K.E. Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys (Revised Reprint); CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Findik, F. Improvements in spinodal alloys from past to present. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahn, J.W. Hardening by spinodal decomposition. Acta Metall. 1963, 11, 1275–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Song, K.; Shao, H.; Lu, H.; Xu, J. Effect of Nb content on Ti-Mo-Nb alloy materials for neutron high pressure diffraction. Mater. Lett. 2022, 314, 131821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, N.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Ye, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Q.; Brechtl, J.; Liaw, P.K. Mechanical, corrosion, and wear properties of biomedical Ti-Zr-Nb-Ta-Mo high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 861, 157997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yi, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, K.; Liu, J.; Meng, X.; Gao, Z. Effect of thermo-mechanical treatment on Ti-Ta-Hf high temperature shape memory alloy. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2021, 31, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Sun, K.; Liu, J.; Zheng, X.; Meng, X.; Gao, Z.; Cai, W. Tailoring the microstructure, martensitic transformation and strain recovery characteristics of Ti-Ta shape memory alloys by changing Hf content. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussiba, A.; Artzy, A.B.; Shtechman, A.; Ifergan, S.; Kupiec, M. Grain refinement of AZ31 and ZK60 Mg alloys—Towards superplasticity studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 302, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, T. Precipitation hardening in metals. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1999, 15, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, N.F.; Nabarro, F.R.N. An attempt to estimate the degree of precipitation hardening, with a simple model. Proc. Phys. Soc. 2002, 52, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahn, J.W.; Hilliard, J.E. Spinodal decomposition: A reprise. Acta Metall. 1971, 19, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesiekierski, A.; Ping, D.; Li, Y.; Lin, J.; Munir, K.S.; Yamabe-Mitarai, Y.; Wen, C. Extraordinary high strength Ti-Zr-Ta alloys through nanoscaled, dual-cubic spinodal reinforcement. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozan, S.; Lin, J.; Li, Y.; Ipek, R.; Wen, C. Development of Ti-Nb-Zr alloys with high elastic admissible strain for temporary orthopedic devices. Acta Biomater. 2015, 20, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. Interdiffusion and atomic mobility in bcc Ti-rich Ti-Nb-Zr system. Calphad 2018, 60, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano-Vargas, O.; Avila-Davila, E.O.; Lopez-Hirata, V.M.; Cayetano-Castro, N.; Gonzalez-Velazquez, J.L. Effect of spinodal decomposition on the mechanical behavior of Fe–Cr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 2910–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orthacker, A.; Haberfehlner, G.; Taendl, J.; Poletti, M.C.; Sonderegger, B.; Kothleitner, G. Diffusion-defining atomic-scale spinodal decomposition within nanoprecipitates. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, K.; Koyama, T.; Tsukada, Y. Phase-Field Simulation of Spinodal Decomposition on Metastable Hexagonal Close-Packed Phase in Magnesium-Yttrium-Zinc Alloy. Mater. Trans. 2013, 54, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwa, Y.; Saito, Y.; Ochi, K.; Aoki, T.; Goto, K.; Abe, K. Kinetics of Phase Separation in Fe-Cr-Mo Ternary Alloys. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Tao, X.; Liu, L. Study of low-modulus biomedical beta Ti-Nb-Zr alloys based on single-crystal elastic constants modeling. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 62, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hari Kumar, K.C.; Wollants, P.; Delacy, L. Thermodynamic assessment of the Ti-Zr system and calculation of the Nb-Ti-Zr phase diagram. J. Alloys Compd. 1994, 206, 126–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).