The Effect of Mechanical Activation of Fly Ash on Cement-Based Materials Hydration and Hardened State Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
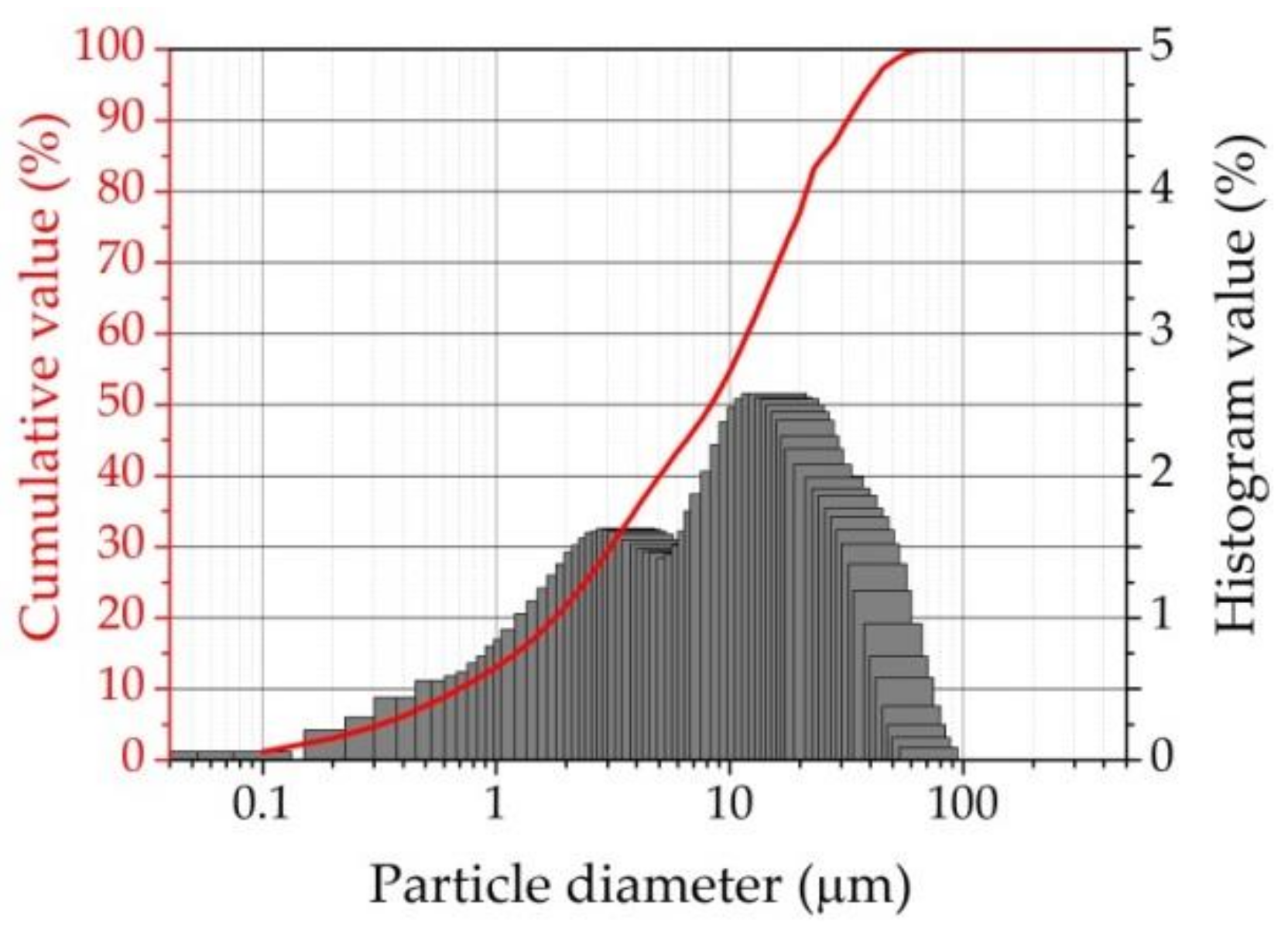
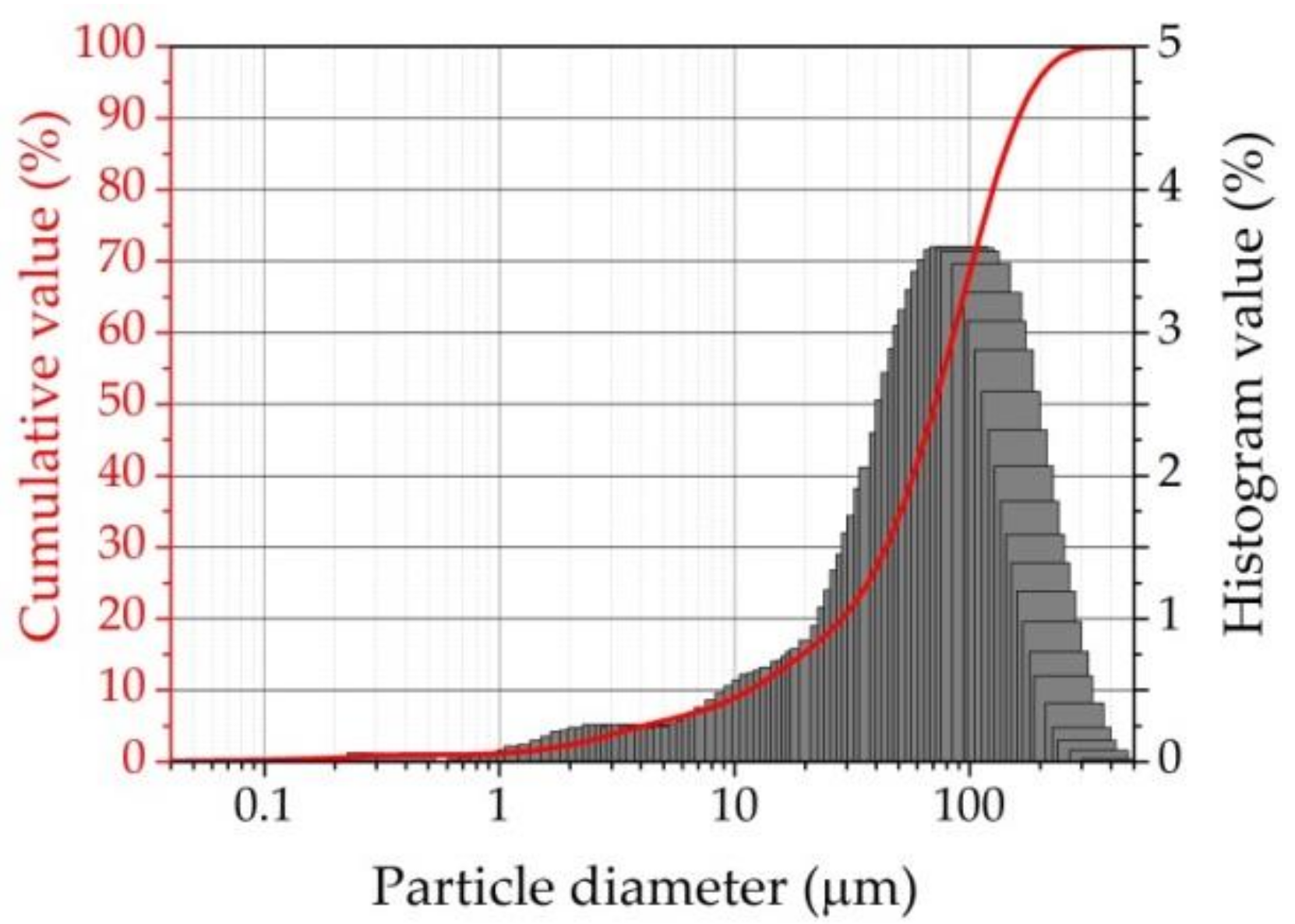
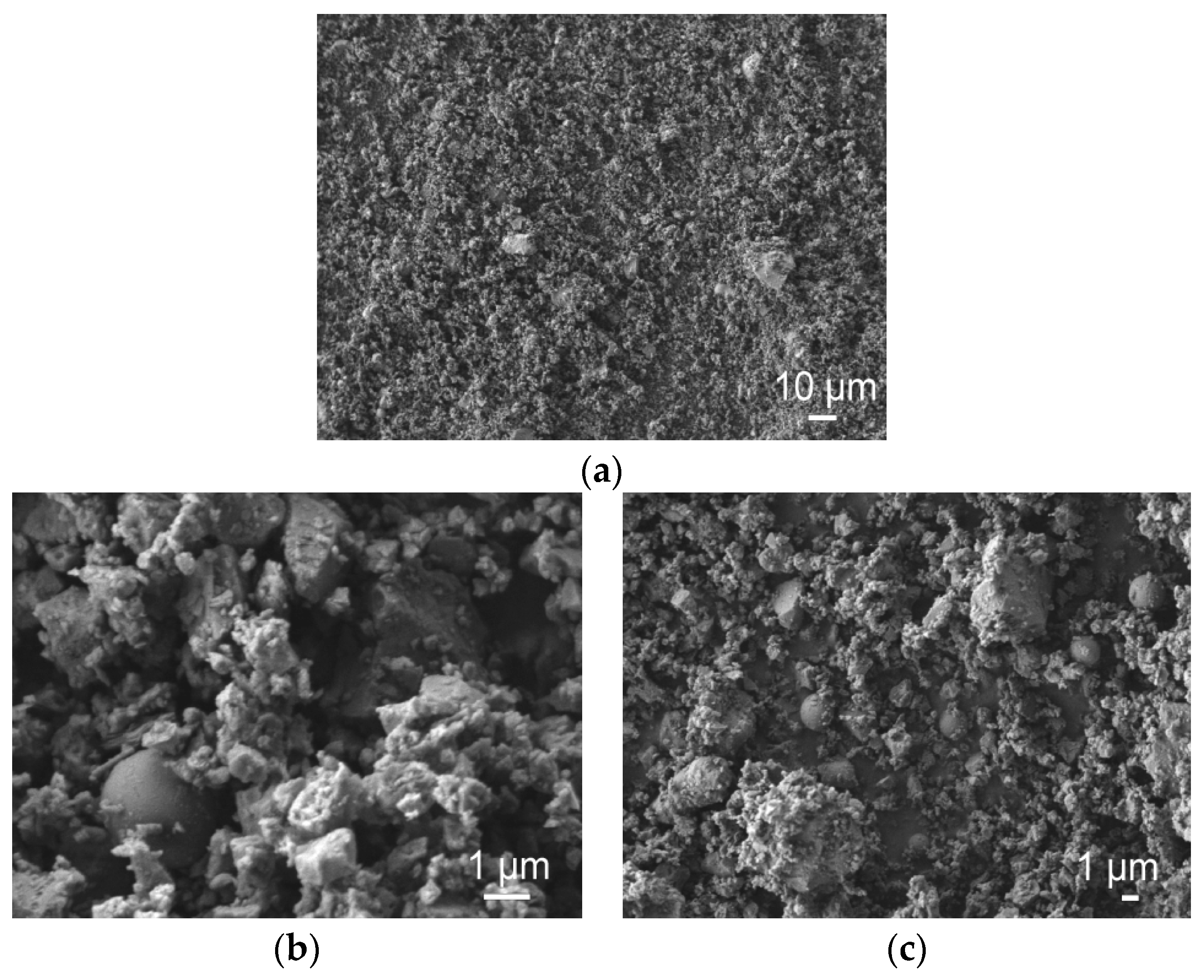
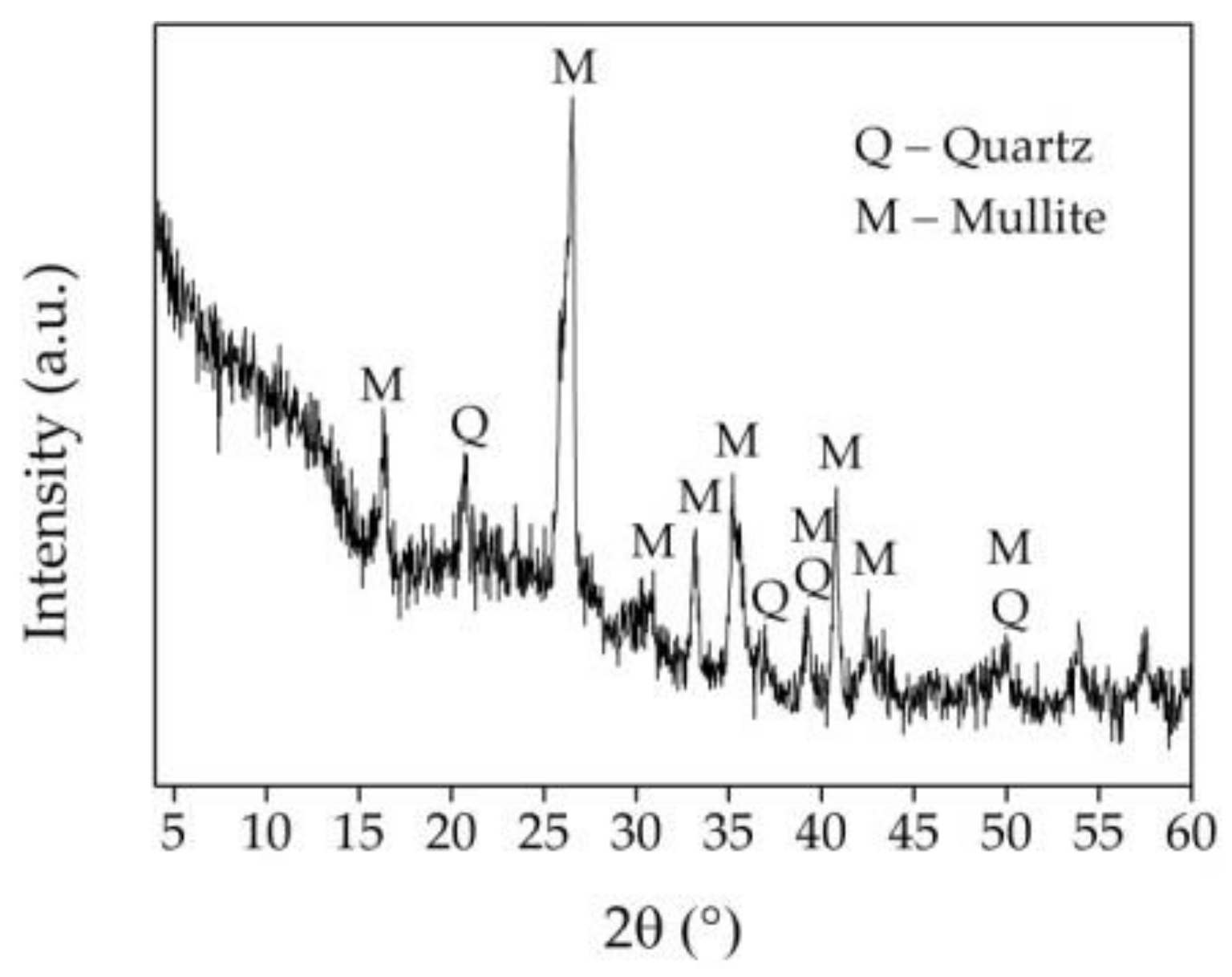
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation of Water Suspensions, Pastes, and Samples
2.3. Test Methods
3. Results and Discussions
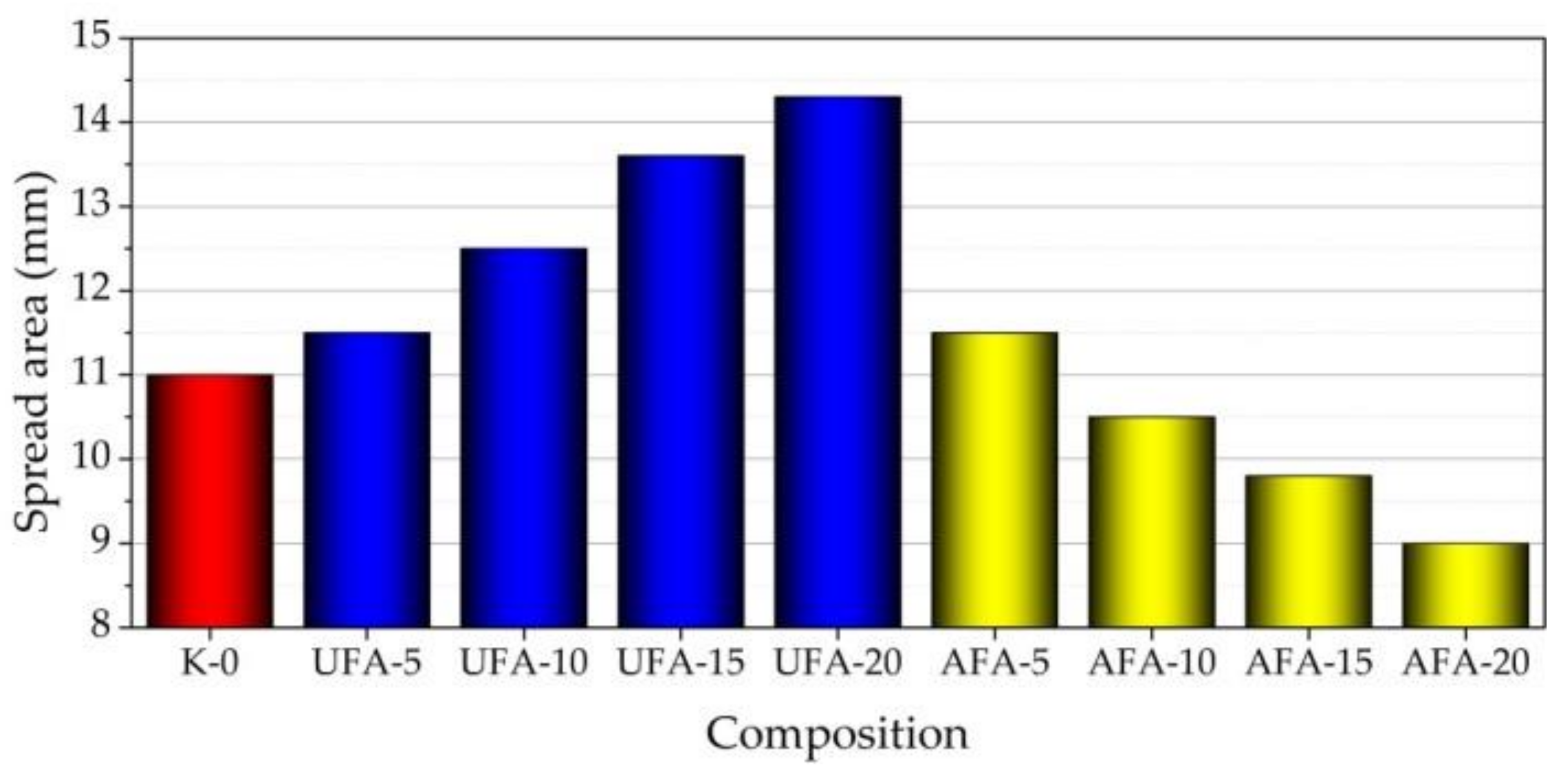
3.1. Pozzolanic Activity
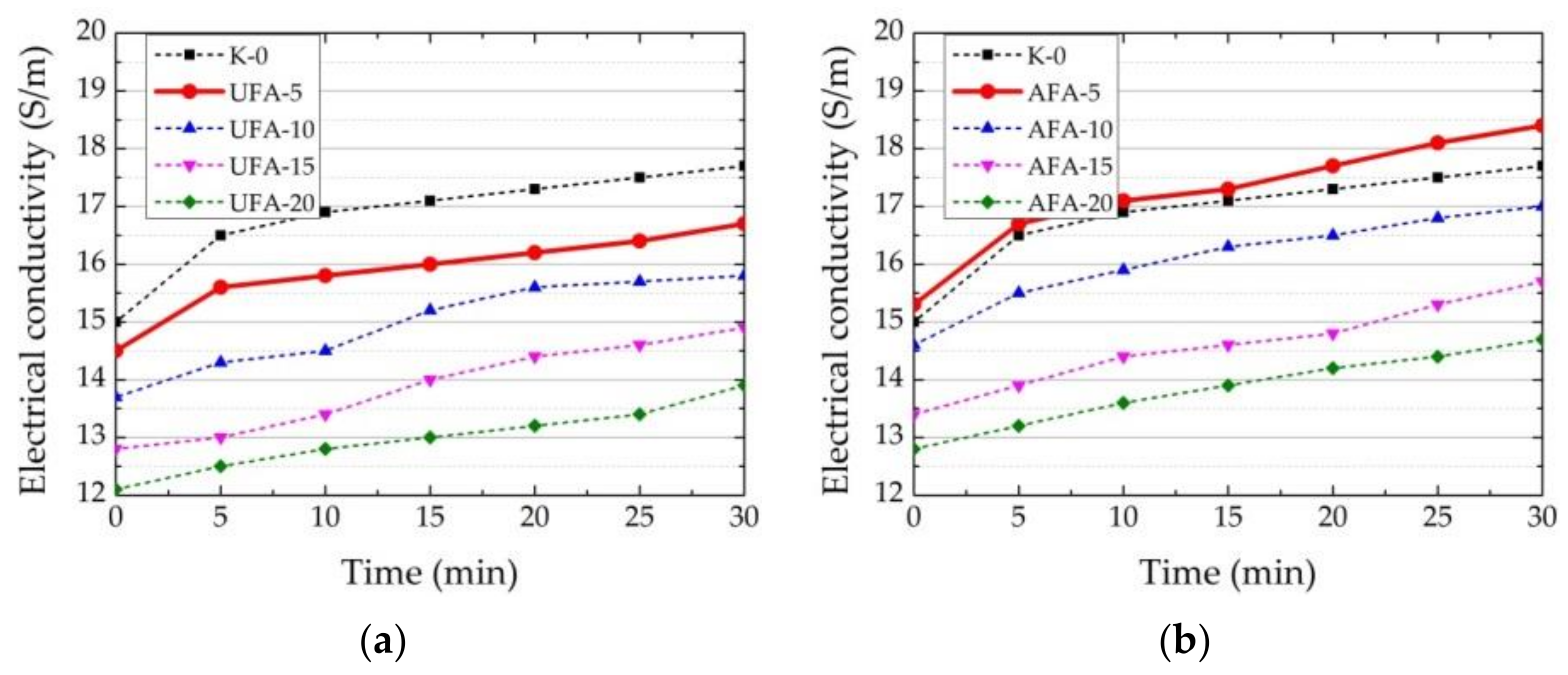
3.2. EC and pH Tests of Suspensions and Pastes
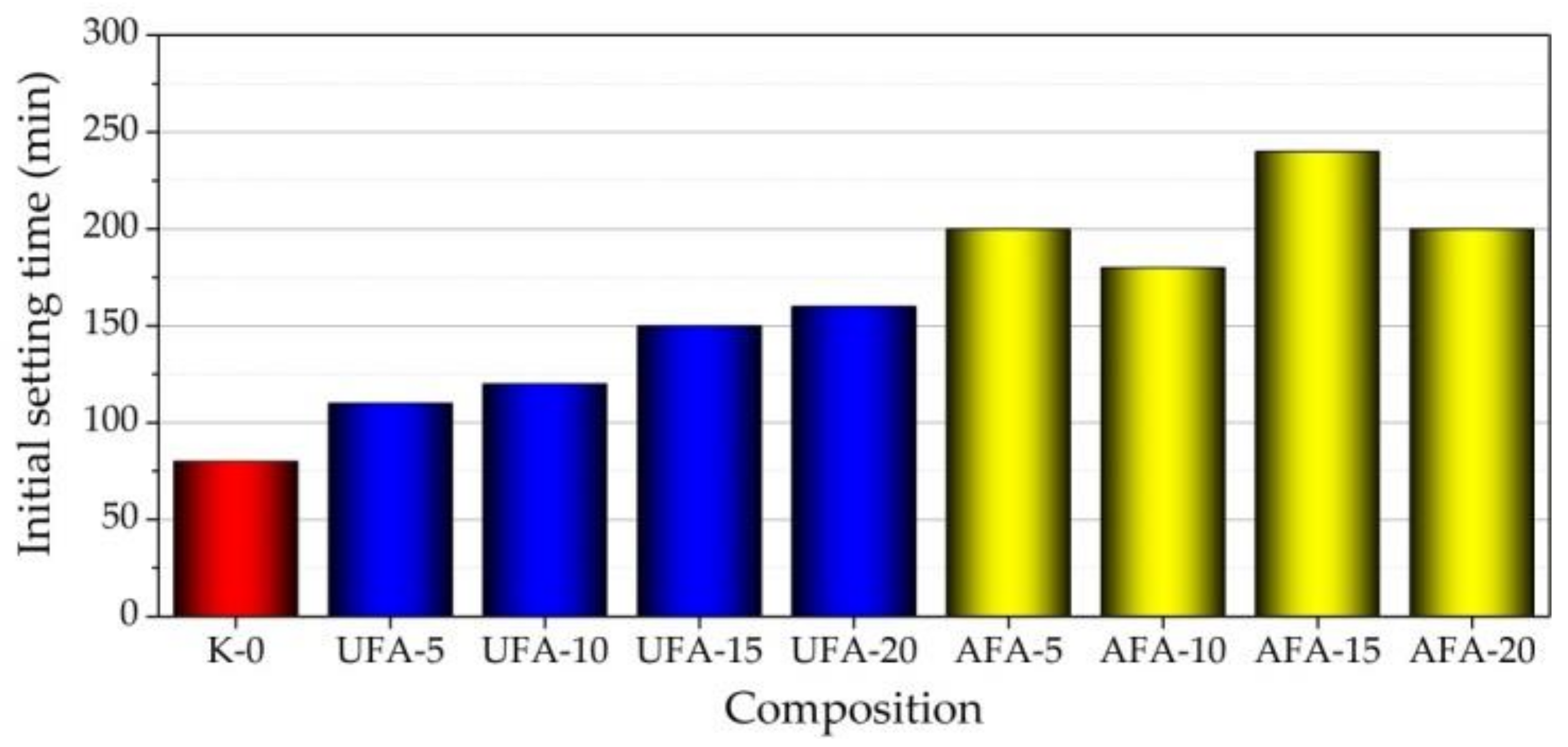
3.3. Setting Time
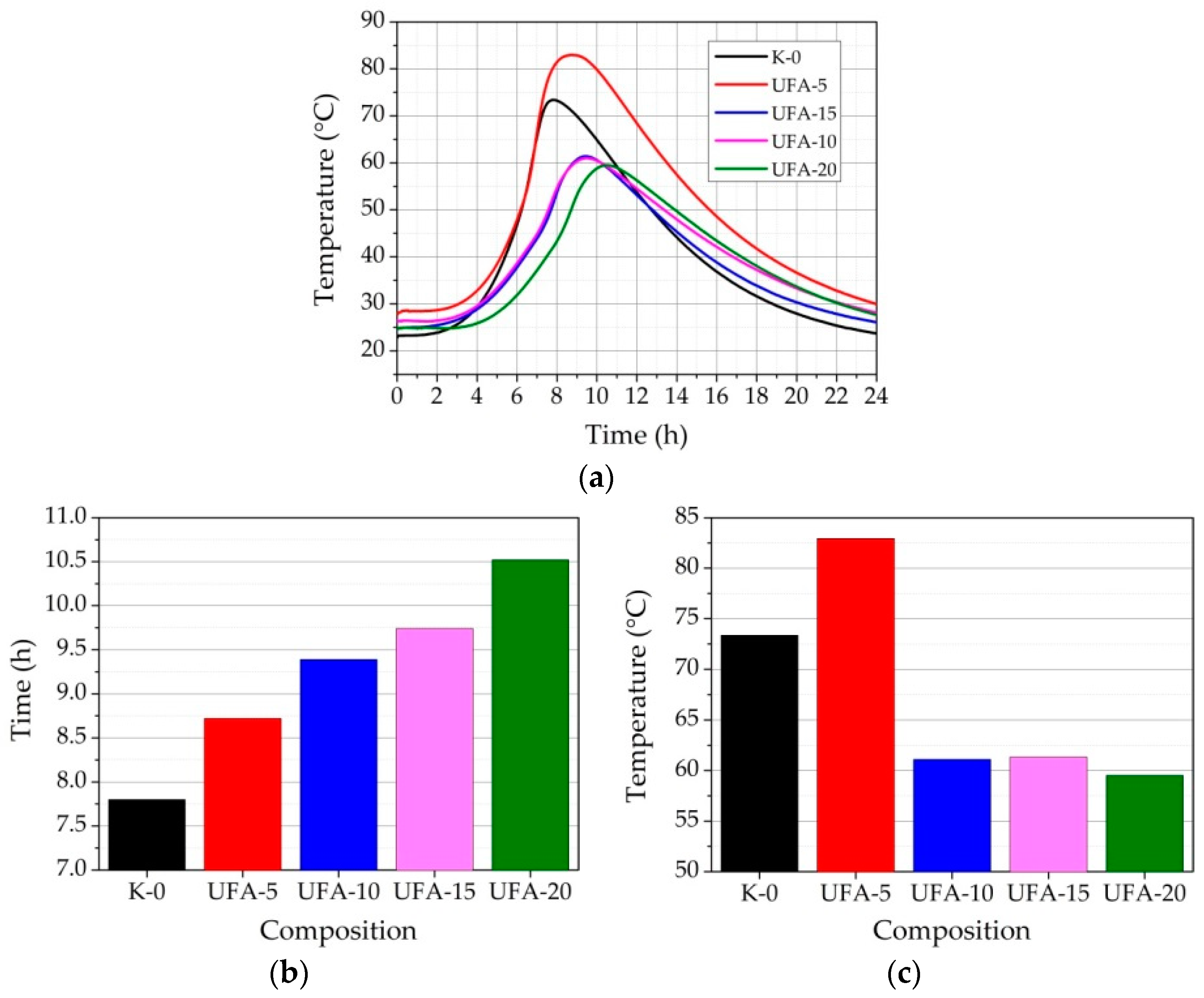
3.4. EXO Profile
3.5. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, G.; Shi, X. Characteristics and Applications of Fly Ash as a Sustainable Construction Material: A State-of-the-Art Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 136, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, T.; Ramaswamy, A. A Review on Fly Ash Characteristics e Towards Promoting High Volume Utilisation in Developing Sustainable Concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provis, J.L.; Palomo, A.; Shi, C. Advances in Understanding Alkali-Activated Materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 78, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrivener, K.L.; John, V.M.; Gartner, E.M. Eco-Efficient Cements: Potential Economically Viable Solutions for a Low-CO2 Cement-Based Materials Industry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 114, 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM–C618-8a; Standard Specification for Coal Fly Ash and Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use in Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2009.
- Clifton, J.R.; Diamond, S.; Daimon, M.; Dutron, M.; Feldman, R.F.; Gjorv, O.E.; Gutt, W.; Almeborg, J.; Joshi, C.; Kruger, J. Final Report Siliceous Byproducts for Use in Concrete. Mater. Struct. 1988, 21, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klima, K.M.; Schollbach, K.; Brouwers, H.J.H.; Yu, Q. Thermal and Fire Resistance of Class F Fly Ash Based Geopolymers—A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 323, 126529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, F.U.A. 23–Fibre-Reinforced Geopolymer Composites (FRGCs) for Structural Applications. In Advances in Ceramic Matrix Composites, 2nd ed.; Low, I.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Composites Science and Engineering; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2014; pp. 569–593. ISBN 978-0-08-102166-8. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Jiménez, A.; Palomo, A. Characterisation of Fly Ashes. Potential Reactivity as Alkaline Cements. Fuel 2003, 82, 2259–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, M.H.; Thomas, M.D.A. The Effect of Fly Ash Composition on the Expansion of Concrete Due to Alkali–Silica Reaction. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Park, D.J.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, H.S.; Yan, S.R.; Lee, H.S. Analysis of the Isothermal Hydration Heat of Cement Paste Containing Mechanically Activated Fly Ash. Thermochim. Acta 2022, 715, 179273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giergiczny, Z. Fly Ash and Slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 124, 105826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideris, K.; Justnes, H.; Soutsos, M.; Sui, T. Fly Ash. In Properties of Fresh and Hardened Concrete Containing Supplementary Cementitious Materials: State-of-the-Art Report of the RILEM Technical Committee 238-SCM, Working Group 4; De Belie, N., Soutsos, M., Gruyaert, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 55–98. ISBN 978-3-319-70606-1. [Google Scholar]
- El Fami, N.; Ez-zaki, H.; Sassi, O.; Boukhari, A.; Diouri, A. Rheology, Calorimetry and Electrical Conductivity Related-Properties for Monitoring the Dissolution and Precipitation Process of Cement-Fly Ash Mixtures. Powder Technol. 2022, 411, 117937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Li, K. Reaction and Microstructure of Cement–Fly-Ash System. Mater. Struct. Constr. 2015, 48, 1703–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Liao, S.; Lin, H. Ultrafine Grinding of Fly Ash with Grinding Aids: Impact on Particle Characteristics of Ultrafine Fly Ash and Properties of Blended Cement Containing Ultrafine Fly Ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 78, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.; Chi, M.; Huang, R. Effect of Fineness and Replacement Ratio of Ground Fly Ash on Properties of Blended Cement Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lee, H.S. Effect of Fly Ash with or without Mechanical Activation on Early-Age Cement Hydration: A Comparative Case Study by Boundary Nucleation and Growth Model. Thermochim. Acta 2022, 716, 179306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, T.R.; Singh, S.S.; Hossain, M.M. Permeability of Concrete Containing Large Amounts of Fly Ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 1994, 24, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanghui, H.; Qiang, W.; Jingjing, F. The Differences among the Roles of Ground Fly Ash in the Paste, Mortar and Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somna, R.; Jaturapitakkul, C.; Chalee, W.; Rattanachu, P. Effect of the Water to Binder Ratio and Ground Fly Ash on Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 24, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glinicki, M.A.; Jóźwiak-Niedzwiedzka, D.; Dabrowski, M. The Influence of Fluidized Bed Combustion Fly Ash on the Phase Composition and Microstructure of Cement Paste. Materials 2019, 12, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollakota, A.R.K.; Volli, V.; Shu, C.-M. Progressive utilisation prospects of coal fly ash: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 951–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezanianpour, A.A. Fly Ash. In Cement Replacement Materials: Properties, Durability, Sustainability; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 47–156. ISBN 978-3-642-36721-2. [Google Scholar]
- Marinkovič, S.; Dragaš, J.; Ignjatovic, I.; Tošič, N. Environmental Assessment of Green Concretes for Structural Use. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 154, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozic, D.; Zelic, J. The Effect of Fly Ash on Cement Hydration in Aqueous Suspensions. Ceram. Silik. 2006, 50, 98–105. [Google Scholar]
- Pundienė, I.; Korjakins, A.; Pranckevičienė, J.; Kligys, M. Effect of Silicon Carbide Aggregate, Prepared by Different Methods, on the Properties of Refractory Concrete with Cenospheres. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 15944–15953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumanis, G.; Bajare, D.; Goljandin, D. Performance Evaluation of Cement Mortar and Concrete with Incorporated Micro Fillers Obtained by Collision Milling in Disintegrator. Ceram. Silik. 2017, 61, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Tang, M.; Ding, J.; Buekens, A.; Yang, J.; Qiu, Q.; Yan, J. Mechanical Activation of Fly Ash from MSWI for Utilization in Cementitious Materials. Waste Manag. 2019, 88, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Mao, Q.; Buekens, A.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J. Energy Transfer and Kinetics in Mechanochemistry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 24562–24571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wu, X. Influence of Fly Ash and Its Mean Particle Size on Certain Engineering Properties of Cement Composite Mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supit, S.W.M.; Shaikh, F.U.A.; Sarker, P.K. Effect of Ultrafine Fly Ash on Mechanical Properties of High Volume Fly Ash Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 51, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Zanganeh, H.; Alizadeh, H.; Shakerinia, M.; Marian, M.A.S. Comparing the Performance of Fine Fly Ash and Silica Fume in Enhancing the Properties of Concretes Containing Fly Ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volland, S. Influence of the Mechanical Activation of Raw Mixes on the Properties of Foam Glass from Sand Sludge. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldyrev, V. V Mechanochemistry and Mechanical Activation of Solids. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2006, 75, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejdoub, R.; Hammi, H.; Khitouni, M.; Suñol, J.J.; M’nif, A. The Effect of Prolonged Mechanical Activation Duration on the Reactivity of Portland Cement: Effect of Particle Size and Crystallinity Changes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Toit, G.; Kruger, R.A.; Kearsley, E.P.; Van Der Merwe, E.M.; Mc Donald, J.M. Chemical and Mechanical Activation of Hybrid Fly Ash Cement. Adv. Cem. Res. 2018, 30, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, S.; Mehrotra, S.P. Towards Sustainable Solutions for Fly Ash through Mechanical Activation. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 52, 157–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 197-1:2011; Cement—Part 1: Composition, Specifications and Conformity Criteria for Common Cements. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2011.
- Xie, N.; Shi, X.; Dang, Y.; Pace, A. Upcycling of Waste Materials: Green Binder Prepared with Pure Coal Fly Ash. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 28, 04015138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Gupta, R.; Chaudhary, S. Sustainable Development of Self-Compacting Concrete by Using Granite Waste and Fly Ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikmen, S.; Dikmen, Z.; Yılmaz, G.; Fırat, S. Mechanical Activation Of Fly Ash: Physical, Mineralogical And Morphological Characterization Of Ground Fly Ashes. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 20, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hela, R.; Orsakova, D. The Mechanical Activation of Fly Ash. Procedia Eng. 2013, 65, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erokhin, S.; Roshka, O. Application of Fractal Properties in Studies of Financial Markets. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 170, 01074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ez-zaki, H.; Diouri, A.; Maher, M.; Aidi, A.; Guedira, T. Effect of Mechanical Activation of Fly Ash Added to Moroccan Portland Cement. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 149, 01074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Mao, Q.; Buekens, A.; Chang, W.; Wang, X.; Yan, J.; Eriksson, O. Suppressing Heavy Metal Leaching through Ball Milling of Fly Ash. Energies 2016, 9, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, R. Mechanical Activation of Fly Ash: Effect on Reaction, Structure and Properties of Resulting Geopolymer. Ceram. Int. 2011, 37, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baláž, P. Mechanochemistry in Minerals Engineering. In Mechanochemistry in Nanoscience and Minerals Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 257–296. ISBN 978-3-540-74855-7. [Google Scholar]
- NF P18-513; Addition for concrete—Metakaolin—Specifications and conformity criteria. AFNOR: Ile-de-France, France, 2012.
- Quarcioni, V.A.; Chotoli, F.F.; Br, F.; Coelho, A.C.V.; Br, A.; Cincotto, M.A. Indirect and Direct Chapelle’s Methods for the Determination of Lime Consumption in Pozzolanic Materials. IBRACON Struct. Mater. J. 2015, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berra, M.; Mangialardi, T.; Paolini, A.E. Reuse of Woody Biomass Fly Ash in Cement-Based Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 196-3:2016; Methods of Testing Cement—Part 3: Determination of Setting Times and Soundness. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2016.
- Almatis. Alcoa Calcium Aluminate Cement; Test Methods; Almatis: Frankfurt, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Okino, E.Y.A.; De Souza, M.R.; Santana, M.A.E.; Alves, M.V.D.S.; De Sousa, M.E.; Teixeira, D.E. Cement-Bonded Wood Particleboard with a Mixture of Eucalypt and Rubberwood. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2004, 26, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN 196-1:2016; Methods of Testing Cement—Part 1: Determination of Strength. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2009.
- Sherwood, P.T. Alternative Materials in Road Construction, 2nd ed.; Thomas Telford Ltd.: London, UK, 2001; ISBN 9780727730312. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, C.; Manjunath, M.; Hosamane, S.; Bandekar, S.; Athani, R. Pozzolonic Activity and Strength Activity Index of Bagasse Ash and Fly Ash Blended Cement Mortar. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristelo, N.; Tavares, P.; Lucas, E.; Miranda, T.; Oliveira, D. Quantitative and Qualitative Assessment of the Amorphous Phase of a Class F Fly Ash Dissolved during Alkali Activation Reactions—Effect of Mechanical Activation, Solution Concentration and Temperature. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 103, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.E.; Jun, Y.; Jeong, Y. Characterization of Geopolymers from Compositionally and Physically Different Class F Fly Ashes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 50, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauzi, A.; Nuruddin, M.F.; Malkawi, A.B.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B. Study of Fly Ash Characterization as a Cementitious Material. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glosser, D.; Choudhary, A.; Isgor, O.B.; Weiss, W.J. Investigation of Reactivity of Fly Ash and Its Effect on Mixture Properties. Mater. J. 2019, 116, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myadraboina, H.; Setunge, S.; Patnaikuni, I. Pozzolanic Index and Lime Requirement of Low Calcium Fly Ashes in High Volume Fly Ash Mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 131, 690–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, J.; Su, Y.; He, X.; Tan, H.; Yang, W.; Strnadel, B. Eco-Friendly Treatment of Low-Calcium Coal Fly Ash for High Pozzolanic Reactivity: A Step towards Waste Utilization in Sustainable Building Material. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 238, 117962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Liu, H.; Sun, B. Influence of Flue Gas Torrefaction on the Fuel Properties and Pyrolysis Characteristics of Real Components of Corn Stalk. Thermochim. Acta 2022, 715, 179301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaiskiene, J.; Costa, C.; Baneviciene, V.; Antonovic, V.; Vaiciene, M. The Effect of Nano SiO2 and Spent Fluid Catalytic Cracking Catalyst on Cement Hydration and Physical Mechanical Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 124281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaudin, G.; Russias, J.; Leroux, F.; Cau-dit-Coumes, C.; Frizon, F. Structural Characterization of C–S–H and C–A–S–H Samples—Part II: Local Environment Investigated by Spectroscopic Analyses. J. Solid State Chem. 2009, 182, 3320–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payá, J.; Borrachero, M.V.; Monzó, J.; Peris-Mora, E.; Amahjour, F. Enhanced Conductivity Measurement Techniques for Evaluation of Fly Ash Pozzolanic Activity. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voglis, N.; Kakali, G.; Chaniotakis, E.; Tsivilis, S. Portland-Limestone Cements. Their Properties and Hydration Compared to Those of Other Composite Cements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzal, B.; Turanli, L.; Yücel, H.; Göncüoǧlu, M.C.; Çulfaz, A. Pozzolanic Activity of Clinoptilolite: A Comparative Study with Silica Fume, Fly Ash and a Non-Zeolitic Natural Pozzolan. Cem. Concr. Res. 2010, 40, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Yan, Z.; Chen, X.; Wang, L. Effect of Fly-Ash as Fine Aggregate on the Workability and Mechanical Properties of Cemented Paste Backfill. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e01039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Poon, C.S. Comparative Studies on the Effects of Sewage Sludge Ash and Fly Ash on Cement Hydration and Properties of Cement Mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lee, H. Research on Properties Evolution of Ultrafine Fly Ash and Cement Composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 119935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustabaş, İ.; Kaya, A. Comparing the Pozzolanic Activity Properties of Obsidian to Those of Fly Ash and Blast Furnace Slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaraj, L.; Ravichandran, P.T. Investigation on Grinding Impact of Fly Ash Particles and Its Characterization Analysis in Cement Mortar Composites. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2019, 10, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittrich, S.; Neubauer, J.; Goetz-Neunhoeffer, F. The Influence of Fly Ash on the Hydration of OPC within the First 44 h—A Quantitative in Situ XRD and Heat Flow Calorimetry Study. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 56, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, H.; Júlio, E.; Loureno, J. New Approach for Shrinkage Prediction of High-Strength Lightweight Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 35, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Fami, N.; Ez-zaki, H.; Boukhari, A.; Khachani, N.; Diouri, A. Influence of Mechanical Activation of Fly Ash on the Properties of Portland Cement Mortars. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 58, 1419–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zeng, L.; He, X.; Su, Y.; Li, Y.; Tan, H.; Jiang, B.; Zhu, H.; Oh, S.K. Improving Durability of Heat-Cured High Volume Fly Ash Cement Mortar by Wet-Grinding Activation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 289, 123157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Karatay, Ç.; Baradan, B. The Effect of Grinding Process on Mechanical Properties and Alkali–Silica Reaction Resistance of Fly Ash Incorporated Cement Mortars. Powder Technol. 2010, 197, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y. Effects of Modified Nano-SiO2 Particles on Properties of High-Performance Cement-Based Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Marques, J.C. Feasibility of Eco-Friendly Binary and Ternary Blended Binders Made of Fly-Ash and Oil-Refinery Spent Catalyst in Ready-Mixed Concrete Production. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | TiO2 | MnO | SO3 | Loss on Ignition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 57.03 | 31.71 | 1.66 | 1.12 | 0.45 | 0.33 | 1.10 | 0.10 | 1.16 | 0.02 | 0.12 | 5.20 |
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | TiO2 | MnO | SO3 | Loss on Ignition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 58.71 | 32.57 | 1.66 | 1.39 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.98 | 0.05 | 1.10 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 4.20 |
| Composition | PC, % | UFA, % | AFA, % | S/W for Conductometry Test | W/PC for Another Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K-0 | 100 | 0 | – | 1:5 | 0.27 |
| UFA-5 | 95 | 5 | – | 1:5 | 0.27 |
| UFA-10 | 90 | 10 | – | 1:5 | 0.27 |
| UFA-15 | 85 | 15 | – | 1:5 | 0.27 |
| UFA-20 | 80 | 20 | – | 1:5 | 0.27 |
| AFA-5 | 95 | – | 5 | 1:5 | 0.27 |
| AFA-10 | 90 | – | 10 | 1:5 | 0.27 |
| AFA-15 | 85 | – | 15 | 1:5 | 0.27 |
| AFA-20 | 80 | – | 20 | 1:5 | 0.27 |
| Composition | Activity Index Values (in%) After | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Days | 7 Days | 28 Days | |
| UFA-5 | 1.07 | 1.06 | 1.09 |
| UFA-10 | 0.90 | 0.90 | 0.92 |
| UFA-15 | 0.80 | 0.80 | 0.85 |
| UFA-20 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.74 |
| AFA-5 | 1.20 | 1.24 | 1.22 |
| AFA-10 | 1.27 | 1.32 | 1.33 |
| AFA-15 | 1.14 | 1.12 | 1.15 |
| AFA-20 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 1.04 |
| pH | EC, S/m | |
|---|---|---|
| UFA | 5.2 | 69.20 |
| AFA | 5.0 | 234.6 |
| Composition | Change in ET,% | Change in H,% | Change in C,% |
|---|---|---|---|
| K-0 | – | – | – |
| UFA-5 | +12.3 | +18.1 | +8.20 |
| UFA-10 | −16.4 | +18.1 | −30.1 |
| UFA-15 | −16.6 | +20.2 | −31.5 |
| UFA-20 | −17.8 | +24.5 | −32.2 |
| AFA-5 | +15.1 | +7.30 | +9.60 |
| AFA-10 | −6.80 | +18.1 | −23.3 |
| AFA-15 | −7.00 | +18.1 | −24.7 |
| AFA-20 | −9.60 | +18.1 | −27.4 |
| Composition | CaO/Al2O3 | SiO2/Al2O3 | CaO/SiO2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| K-0 | 12.7 | 3.91 | 3.27 |
| UFA-5 | 9.51 | 3.36 | 2.83 |
| UFA-10 | 7.42 | 3.02 | 2.46 |
| UFA-15 | 5.96 | 2.78 | 2.15 |
| UFA-20 | 4.88 | 2.60 | 1.88 |
| AFA-5 | 9.44 | 3.35 | 2.82 |
| AFA-10 | 7.34 | 3.00 | 2.44 |
| AFA-15 | 5.88 | 2.76 | 2.13 |
| AFA-20 | 4.81 | 2.59 | 1.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akmalaiuly, K.; Berdikul, N.; Pundienė, I.; Pranckevičienė, J. The Effect of Mechanical Activation of Fly Ash on Cement-Based Materials Hydration and Hardened State Properties. Materials 2023, 16, 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16082959
Akmalaiuly K, Berdikul N, Pundienė I, Pranckevičienė J. The Effect of Mechanical Activation of Fly Ash on Cement-Based Materials Hydration and Hardened State Properties. Materials. 2023; 16(8):2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16082959
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkmalaiuly, Kenzhebek, Nazerke Berdikul, Ina Pundienė, and Jolanta Pranckevičienė. 2023. "The Effect of Mechanical Activation of Fly Ash on Cement-Based Materials Hydration and Hardened State Properties" Materials 16, no. 8: 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16082959
APA StyleAkmalaiuly, K., Berdikul, N., Pundienė, I., & Pranckevičienė, J. (2023). The Effect of Mechanical Activation of Fly Ash on Cement-Based Materials Hydration and Hardened State Properties. Materials, 16(8), 2959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16082959







