A Biodegradable Stereo-Complexed Poly (Lactic Acid) Drinking Straw of High Heat Resistance and Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Manufacturing Process
2.2. Material Characterisation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure of SC-PLA Straws
3.2. Crystallisation and Thermal Behaviour of SC-PLA Straws
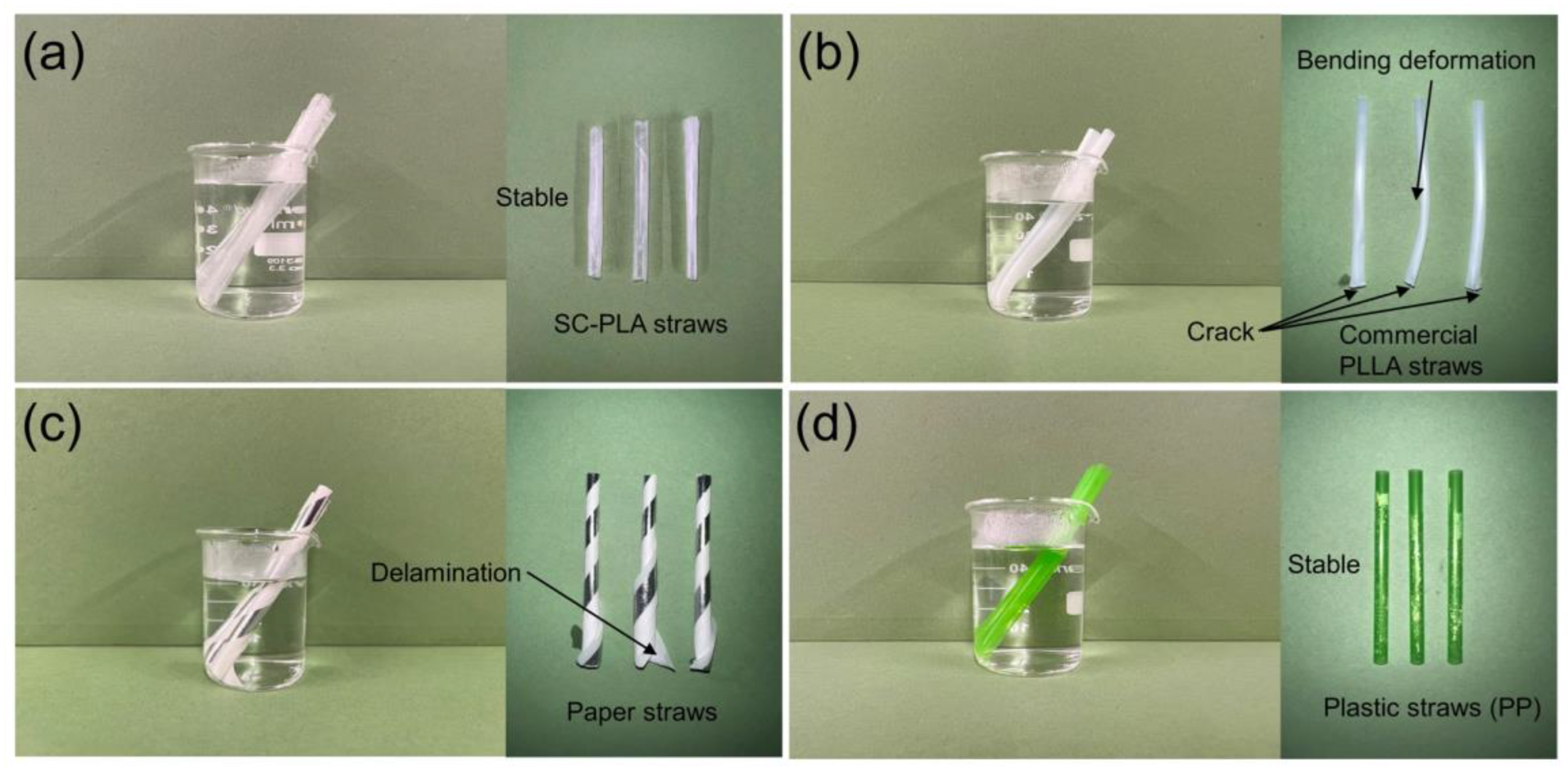
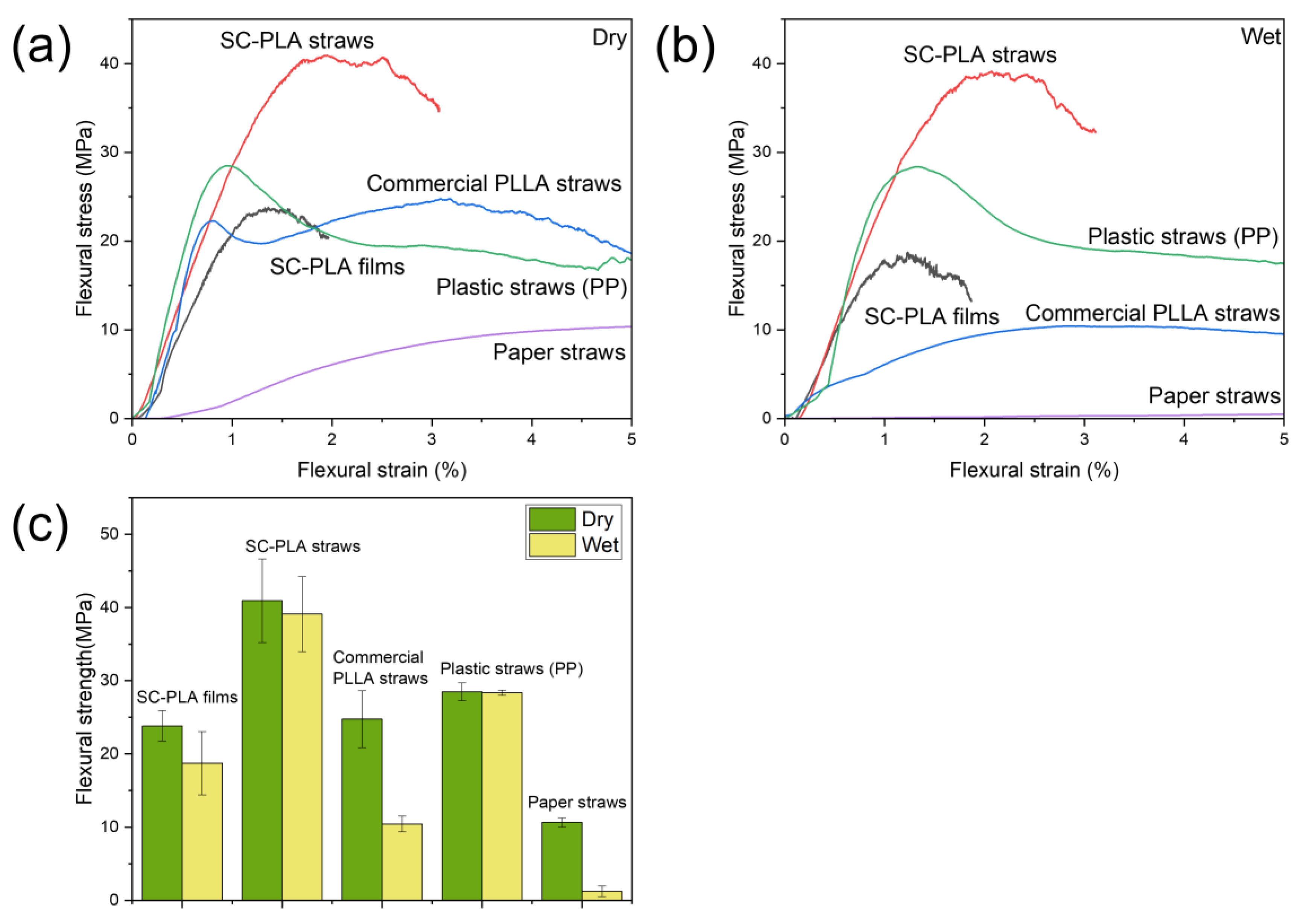
3.3. Mechanical Properties of the SC-PLA Straws
3.4. In Vitro Hydrolysis of SC-PLA Straws
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gu, L.; Ozbakkaloglu, T. Use of recycled plastics in concrete: A critical review. Waste Manag. 2016, 51, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rillig, M.C. Microplastic in Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Soil? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6453–6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, X.; Su, M.; Zou, X.; Duan, L.; Zhang, H. Characteristics of Plastic Pollution in the Environment: A Review. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochman, C.M.; Browne, M.A.; Halpern, B.S.; Hentschel, B.T.; Hoh, E.; Karapanagioti, H.K.; Rios-Mendoza, L.M.; Takada, H.; Teh, S.; Thompson, R.C. Classify plastic waste as hazardous. Nature 2013, 494, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, J.N.; Royals, A.W.; Jameel, H.; Venditti, R.A.; Pal, L. Evaluation of paper straws versus plastic straws: Development of a methodology for testing and understanding challenges for paper straws. BioResources 2019, 14, 8345–8363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-B.; Liu, Z.-X.; Yin, C.-H.; Han, Z.-M.; Guan, Q.-F.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Ling, Z.-C.; Liu, H.-C.; Yang, K.-P.; Sun, W.-B.; et al. Edible, Ultrastrong, and Microplastic-Free Bacterial Cellulose-Based Straws by Biosynthesis. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2111713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunati, E.; Armentano, I.; Iannoni, A.; Kenny, J.M. Development and thermal behaviour of ternary PLA matrix composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2200–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, L.; Qin, Y.; Ji, N.; Xiong, L.; Shi, R.; Sun, Q. A combined extrusion, retrogradation, and cross-linking strategy for preparing starch-based straws with desirable mechanical properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 1089–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pang, Z.; Chen, C.; Xia, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Jing, S.; Wang, R.; Ray, U.; Gan, W.; Li, C.; et al. All-Natural, Degradable, Rolled-Up Straws Based on Cellulose Micro- and Nano-Hybrid Fibers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1910417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xia, Q.; Jing, S.; Li, C.; Chen, Q.; Chen, B.; Pang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Gan, W.; Chen, G. Strong, hydrostable, and degradable straws based on cellulose-lignin reinforced composites. Small 2021, 17, 2008011. [Google Scholar]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pabjańczyk-Wlazło, E.K.; Puszkarz, A.K.; Bednarowicz, A.; Tarzyńska, N.; Sztajnowski, S. The Influence of Surface Modification with Biopolymers on the Structure of Melt-Blown and Spun-Bonded Poly(lactic acid) Nonwovens. Materials 2022, 15, 7097. [Google Scholar]
- Ghorpade, V.M.; Gennadios, A.; Hanna, M.A. Laboratory composting of extruded poly(lactic acid) sheets. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 76, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nampoothiri, K.M.; Nair, N.R.; John, R.P. An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA) research. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8493–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.T.; Auras, R.; Rubino, M. Processing technologies for poly(lactic acid). Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 820–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Velde, K.; Kiekens, P. Biopolymers: Overview of several properties and consequences on their applications. Polym. Test. 2002, 21, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An overview of polylactides as packaging materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 835–864. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Lu, S.; Zhao, P.; Feng, Z.; Yu, M.; Han, K. Scalable Preparation of Complete Stereo-Complexation Polylactic Acid Fiber and Its Hydrolysis Resistance. Molecules 2022, 27, 7654. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, P.; Yang, J.; Shan, G.; Bao, Y.; Weng, Z.; Cao, A.; Yazawa, K.; Inoue, Y. Temperature-Variable FTIR and Solid-State 13C NMR Investigations on Crystalline Structure and Molecular Dynamics of Polymorphic Poly(l-lactide) and Poly(l-lactide)/Poly(d-lactide) Stereocomplex. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikada, Y.; Jamshidi, K.; Tsuji, H.; Hyon, S.H. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactides). Macromolecules 1987, 20, 904–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Nakano, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Takashima, K.; Katsura, S.; Mizuno, A. Electrospinning of poly (lactic acid) stereocomplex nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3316–3320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.H.; Muiruri, J.K.; Li, Z.; He, C. Recent Progress in Using Stereocomplexation for Enhancement of Thermal and Mechanical Property of Polylactide. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 5370–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ghorai, M.K.; Kar, K.K. 10—Fly ash-reinforced epoxy composites. In Handbook of Fly Ash; Kar, K.K., Ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokiwa, Y.; Calabia, B.P. Biodegradability and biodegradation of poly(lactide). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarasua, J.R.; López-Rodríguez, N.; Zuza, E.; Petisco, S.; Castro, B.; del Olmo, M.; Palomares, T.; Alonso-Varona, A. Crystallinity assessment and in vitro cytotoxicity of polylactide scaffolds for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 2513–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paneva, D.; Spasova, M.; Stoyanova, N.; Manolova, N.; Rashkov, I. Electrospun fibers from polylactide-based stereocomplex: Why? Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2021, 70, 270–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, D.; Ying, T.H.; Mahara, A.; Murakami, S.; Yamaoka, T.; Lee, W.-K.; Iwata, T. In Vivo Tissue Response and Degradation Behavior of PLLA and Stereocomplexed PLA Nanofibers. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundador, N.G.V.; Takemura, A.; Iwata, T. Structural Properties and Enzymatic Degradation Behavior of PLLA and Stereocomplexed PLA Nanofibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2010, 295, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Ikada, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acid)s. XI. Mechanical properties and morphology of solution-cast films. Polymer 1999, 40, 6699–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Ikada, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly (lactic acids). 9. Stereocomplexation from the melt. Macromolecules 1993, 26, 6918–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Sacligil, D.; Carreau, P.J.; Kamal, M.R.; Heuzey, M.-C. Poly (lactic acid) blends: Processing, properties and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 307–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarasua, J.-R.; Rodríguez, N.L.; Arraiza, A.L.; Meaurio, E. Stereoselective Crystallization and Specific Interactions in Polylactides. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 8362–8371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasua, J.; Arraiza, A.L.; Balerdi, P.; Maiza, I. Crystallinity and mechanical properties of optically pure polylactides and their blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarasua, J.-R.; Prud’homme, R.E.; Wisniewski, M.; Le Borgne, A.; Spassky, N. Crystallization and Melting Behavior of Polylactides. Macromolecules 1998, 31, 3895–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.; Kumar, V.; Bhunia, H.; Upadhyay, S.N. Synthesis of Poly(Lactic Acid): A Review. J. Macromol. Sci. Part C 2005, 45, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Daelemans, L.; Fiorio, R.; Gou, M.; D’hooge, D.R.; De Clerck, K.; Cardon, L. Improving Mechanical Properties for Extrusion-Based Additive Manufacturing of Poly(Lactic Acid) by Annealing and Blending with Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate). Polymers 2019, 11, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Chen, Y.; Shao, J.; Hou, H. The Crystallization Behavior of Poly(l-lactic acid)/Poly(d-lactic acid) Electrospun Fibers: Effect of Distance of Isomeric Polymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 8480–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.-F.; Bao, R.-Y.; Cao, Z.-Q.; Yang, W.; Xie, B.-H.; Yang, M.-B. Stereocomplex Crystallite Network in Asymmetric PLLA/PDLA Blends: Formation, Structure, and Confining Effect on the Crystallization Rate of Homocrystallites. Macromolecules 2014, 47, 1439–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yu, H.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X.; Jing, X. Crystallization Behavior of Asymmetric PLLA/PDLA Blends. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 2864–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Zou, J.; Dong, S.; Hao, N.; Xu, H. Influence of different β-nucleation agents on poly(l-lactic acid): Structure, morphology, and dynamic mechanical behavior. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 55364–55370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.; Hegab, H.M.; Nassar, L.; Wadi, V.S.; Naddeo, V.; Yousef, A.F.; Banat, F.; Hasan, S.W. Asymmetrical ultrafiltration membranes based on polylactic acid for the removal of organic substances from wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Hyon, S.H.; Ikada, Y. Stereocomplex formation between enantiomeric poly(lactic acid)s. 3. Calorimetric studies on blend films cast from dilute solution. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 5651–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Tian, R.; Na, B.; Lv, R.; Liu, Q. Intermolecular ordering as the precursor for stereocomplex formation in the electrospun polylactide fibers. Polymer 2015, 60, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Ayyoob, M.; Kim, J.-H.; Nam, S.W.; Kim, Y.J. In situ formation of PLA-grafted alkoxysilanes for toughening a biodegradable PLA stereocomplex thin film. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 21748–21759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Fan, Z. The origin of memory effect in stereocomplex poly (lactic acid) crystallization from melt state. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 89, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H. In vitro hydrolysis of blends from enantiomeric poly(lactide)s Part 1. Well-stereo-complexed blend and non-blended films. Polymer 2000, 41, 3621–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H. In vitro hydrolysis of blends from enantiomeric poly(lactide)s. Part 4: Well-homo-crystallized blend and nonblended films. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaaba, N.F.; Jaafar, M. A review on degradation mechanisms of polylactic acid: Hydrolytic, photodegradative, microbial, and enzymatic degradation. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 2061–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Aguirre, E.; Iñiguez-Franco, F.; Samsudin, H.; Fang, X.; Auras, R. Poly(lactic acid)—Mass production, processing, industrial applications, and end of life. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 333–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Samples | Cold Crystallisation | Homo-Crystallites Melting | Stereocomplex Crystallites Melting | Crystallinity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tc (°C) | ΔHc (J/g) | Tm1 (°C) | ΔHm1 (J/g) | Tm2 (°C) | ΔHm2 (J/g) | Xc (%) | |
| SC-PLA films | 81.96 ± 1.14 | 6.92 ± 1.10 | 165.19 ± 0.63 | 16.90 ± 1.42 | 217.43 ± 0.37 | 62.37 ± 4.77 | 53.86 ± 1.93 |
| SC-PLA straws | - | - | - | - | 221.25 ± 2.53 | 101.30 ± 7.77 | 71.34 ± 5.47 |
| PLLA films | 116.24 ± 0.30 | 42.56 ± 5.31 | 162.75 ± 0.53 | 49.64 ± 5.09 | - | - | 6.68 ± 0.96 |
| PLLA straws | - | - | 164.34 ± 0.42 | 40.89 ± 4.15 | - | - | 38.58 ± 3.92 |
| Commercial PLLA straws | 96.72 ± 0.73 | 4.51 ± 1.07 | 156.46 ± 0.46 | 19.74 ± 1.84 | - | - | 14.37 ± 1.34 |
| Samples | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Wet Tensile Strength (MPa) | Loss of Tensile Strength (%) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SC-PLA films | 65.55 | 55.05 | 16.02 |
| SC-PLA straws | 85.09 | 81.10 | 4.69 |
| Commercial PLLA straws | 34.96 | 23.97 | 31.44 |
| Plastic straws (PP) | 38.89 | 37.77 | 2.88 |
| Paper straws | 13.36 | 1.34 | 89.97 |
| Samples | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Wet Flexural Strength (MPa) | Loss of Flexural Strength (%) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SC-PLA films | 23.81 | 18.73 | 21.34 |
| SC-PLA straws | 40.92 | 39.11 | 4.42 |
| Commercial PLLA straws | 24.76 | 10.43 | 57.88 |
| Plastic straws (PP) | 28.49 | 28.37 | 0.42 |
| Paper straws | 10.64 | 1.22 | 88.53 |
| Raw Materials and Processing Cost | Approximate Usage Mass (mg/per Straw) | Approximate Cost (cents/per Straw) |
|---|---|---|
| PLLA | 200.00 | 0.09 |
| PDLA | 200.00 | 0.17 |
| Chloroform | 7600.00 | 0.65 |
| Other costs 1 [7] | 1.15 | |
| Total | 2.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; Feng, Y.; Gong, R.H.; Soutis, C. A Biodegradable Stereo-Complexed Poly (Lactic Acid) Drinking Straw of High Heat Resistance and Performance. Materials 2023, 16, 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062438
Li R, Feng Y, Gong RH, Soutis C. A Biodegradable Stereo-Complexed Poly (Lactic Acid) Drinking Straw of High Heat Resistance and Performance. Materials. 2023; 16(6):2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062438
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Renzhi, Yangyang Feng, R. Hugh Gong, and Constantinos Soutis. 2023. "A Biodegradable Stereo-Complexed Poly (Lactic Acid) Drinking Straw of High Heat Resistance and Performance" Materials 16, no. 6: 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062438
APA StyleLi, R., Feng, Y., Gong, R. H., & Soutis, C. (2023). A Biodegradable Stereo-Complexed Poly (Lactic Acid) Drinking Straw of High Heat Resistance and Performance. Materials, 16(6), 2438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062438








