Ni0.6Zn0.4O Synthesised via a Solid-State Method for Promoting Hydrogen Sorption from MgH2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
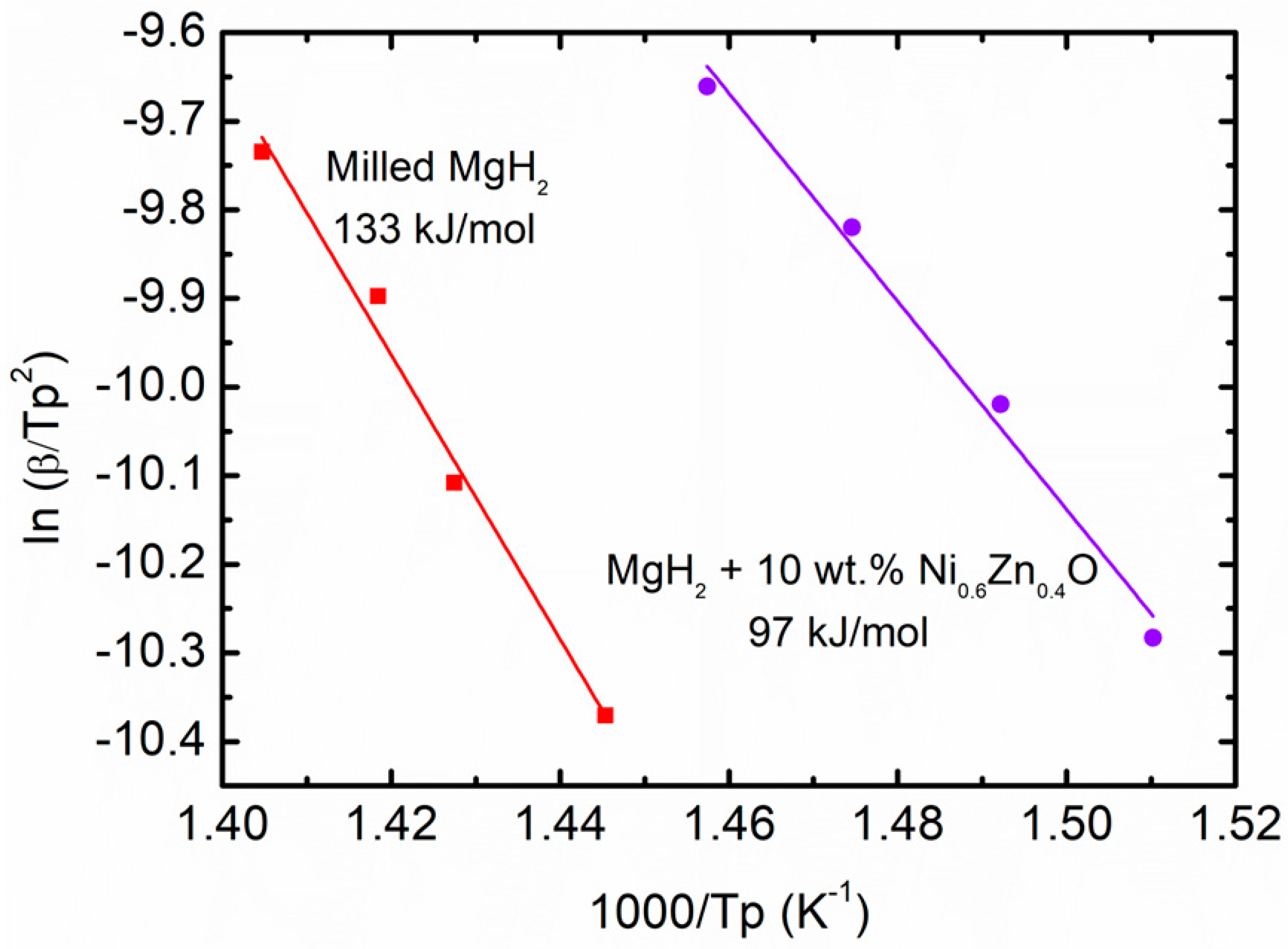
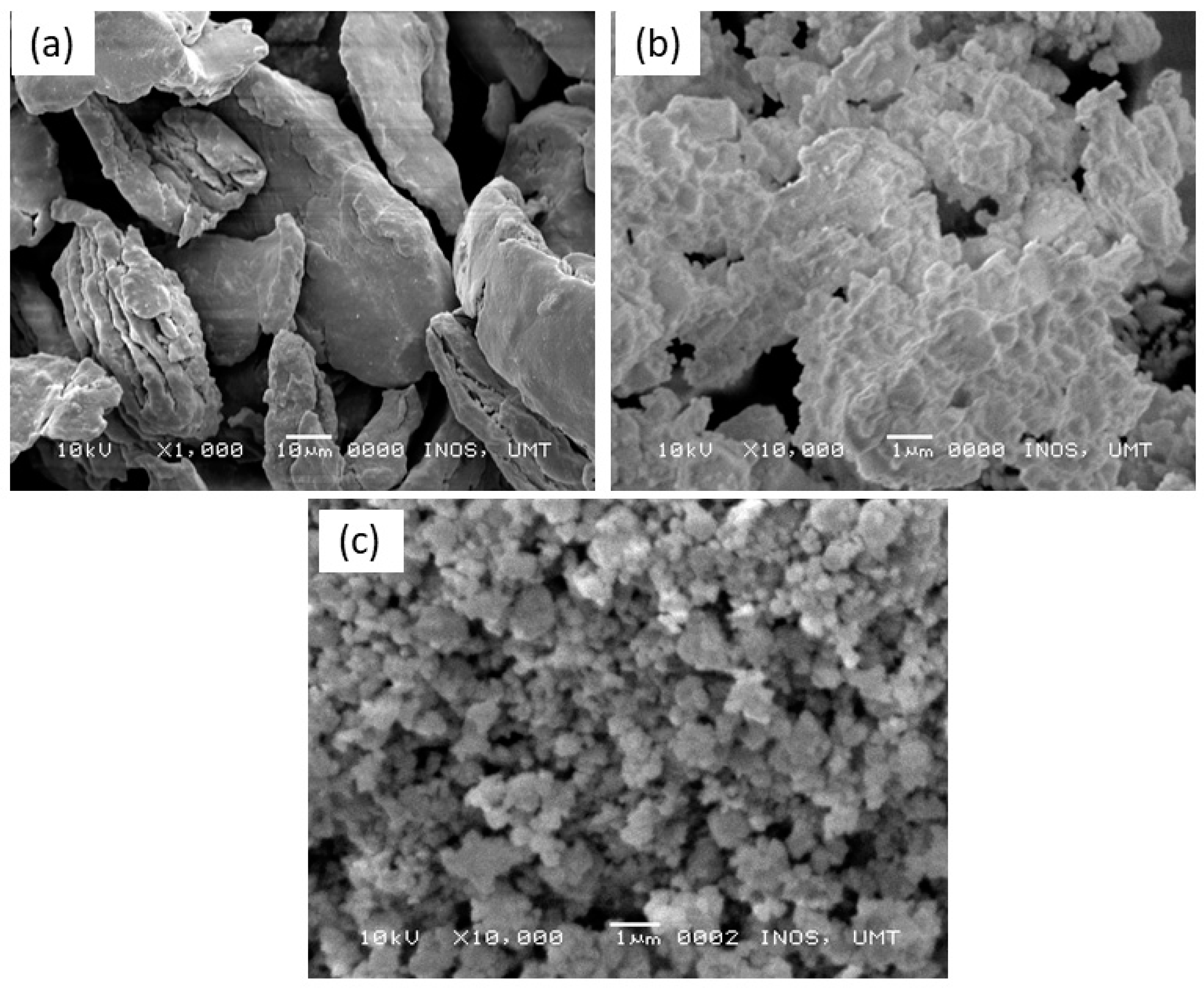
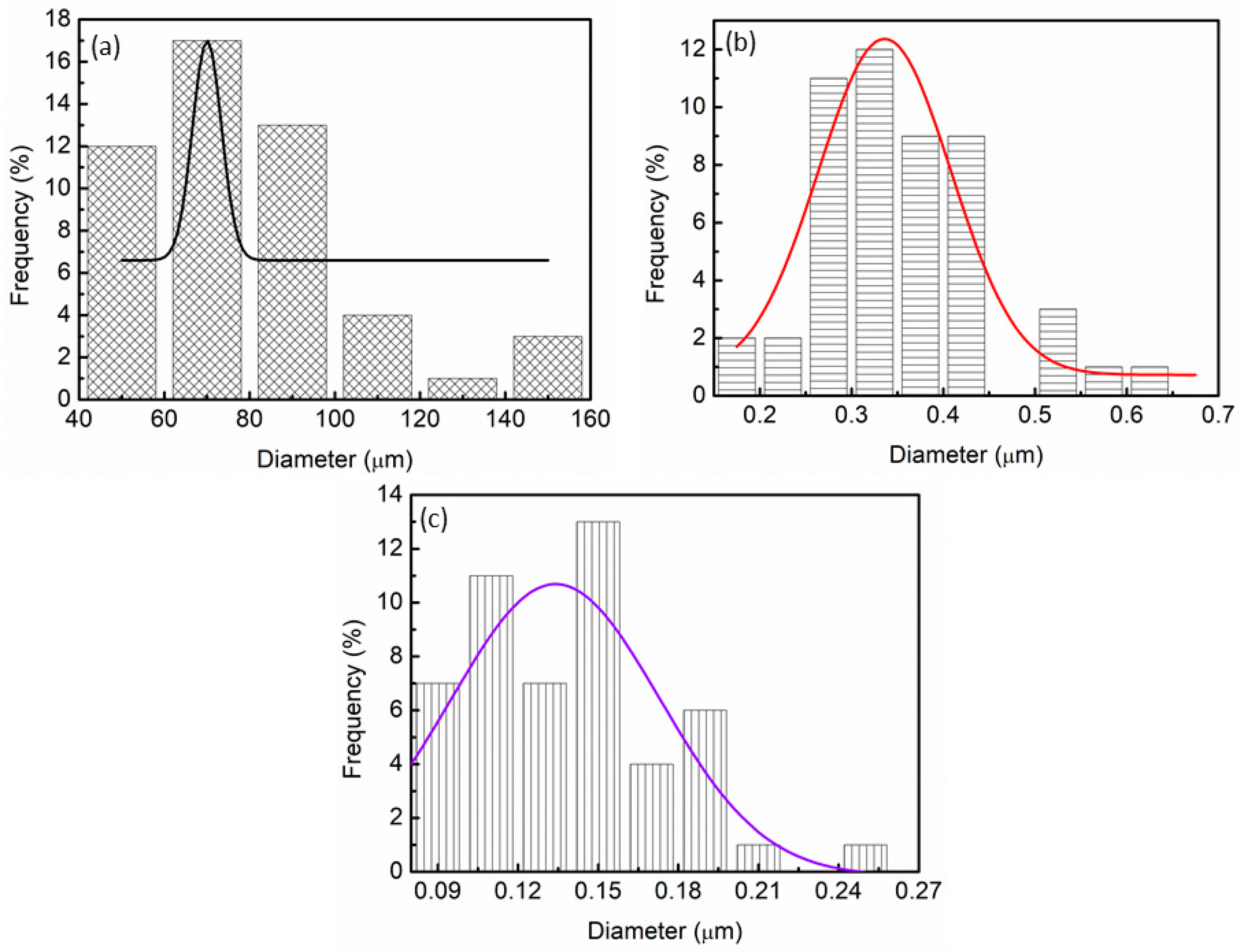
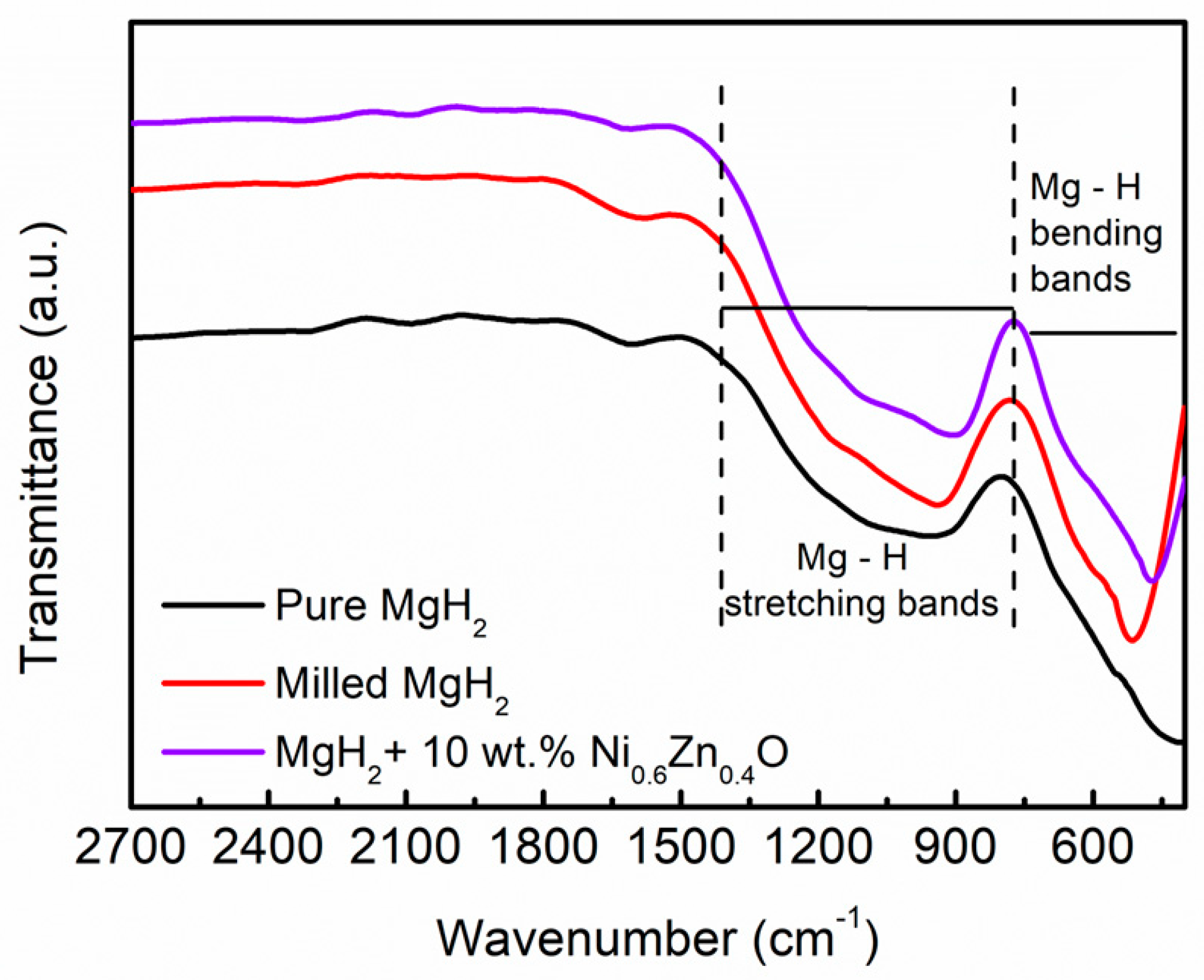
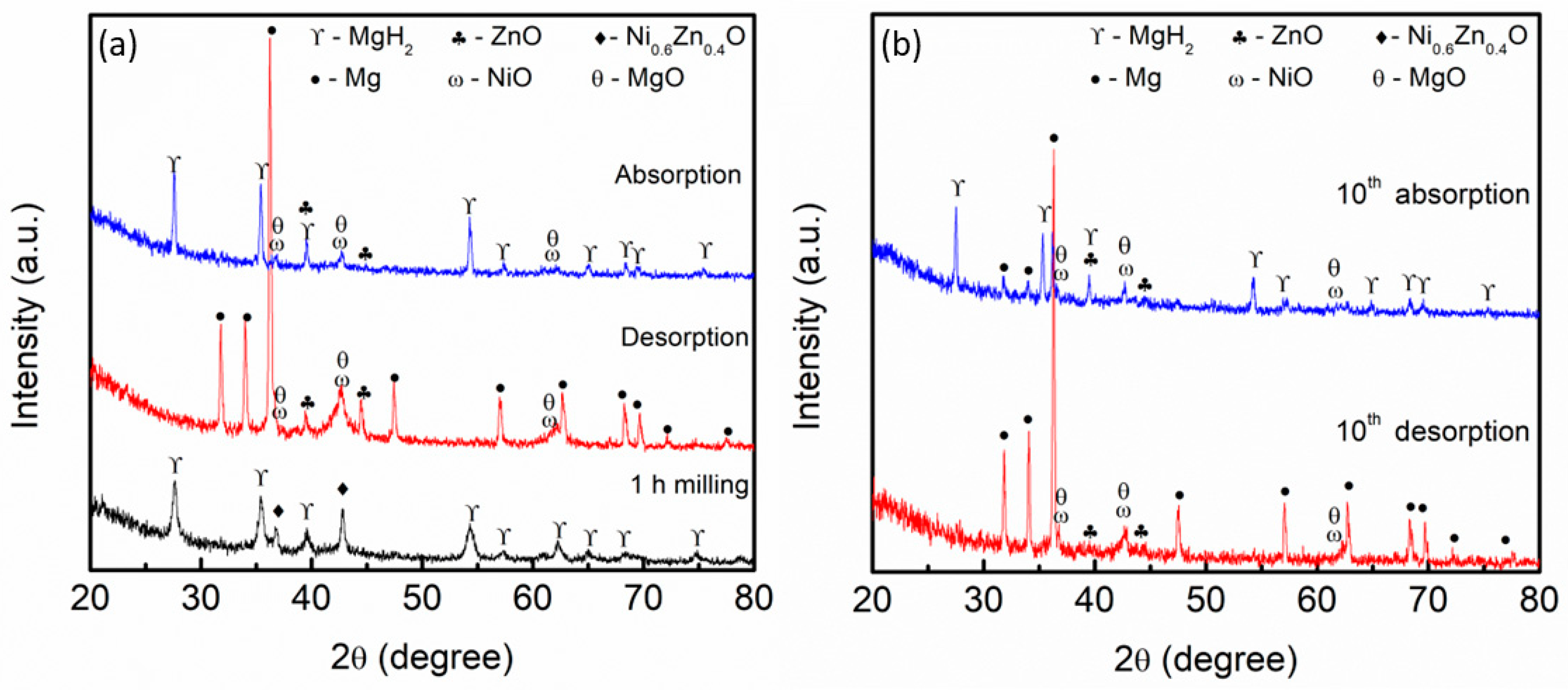
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, D. The future of hydrogen energy: Bio-hydrogen production technology. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 33677–33698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Wei, P.; Li, D.; Ying, Z.; Hao, X.; Xue, Z. Intelligent damping control of renewable energy/hydrogen energy DC interconnection system. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felderhoff, M.; Weidenthaler, C.; von Helmolt, R.; Eberle, U. Hydrogen storage: The remaining scientific and technological challenges. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 2643–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simanullang, M.; Prost, L. Nanomaterials for on-board solid-state hydrogen storage applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 29808–29846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Shao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, C.; Zeng, W.; Tang, J.; Dong, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, H. Interfacial charge transfer induced dual-active-sites of heterostructured Cu0.8Ni0.2WO4 nanoparticles in ammonia borane methanolysis for fast hydrogen production. Appl. Catal. B 2023, 320, 121973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X.; Youxiang, S.; Dong, H.; Liu, Q.; Li, H. Modulation the electronic structure of hollow structured CuO-NiCo2O4 nanosphere for enhanced catalytic activity towards methanolysis of ammonia borane. Fuel 2023, 332, 126045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Sazelee, N.A.; Ismail, M. An overview of reactive hydride composite (RHC) for solid-state hydrogen storage materials. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 31674–31698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Z. Application-oriented hydrolysis reaction system of solid-state hydrogen storage materials for high energy density target: A review. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 74, 218–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazelee, N.; Ali, N.; Yahya, M.; Mustafa, N.; Halim Yap, F.; Mohamed, S.; Ghazali, M.; Suwarno, S.; Ismail, M. Recent advances on Mg–Li–Al systems for solid-state hydrogen storage: A Review. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 875405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Lin, J.; Leng, H.; Sun, C.; Wu, C.; Li, Q.; Pan, F. The hydrogen storage performance and catalytic mechanism of the MgH2-MoS2 composite. J. Magnes. Alloy 2022, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Lv, Y.; Huang, H.; Yuan, J.; Lv, W.; Wu, Y. Remarkable enhancement and electronic mechanism for hydrogen storage kinetics of Mg nano-composite by a multi-valence Co-based catalyst. Mater. Today Nano 2022, 17, 100168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazelee, N.A.; Idris, N.H.; Md Din, M.F.; Yahya, M.S.; Ali, N.A.; Ismail, M. LaFeO3 synthesised by solid-state method for enhanced sorption properties of MgH2. Results Phys. 2020, 16, 102844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Nyahuma, F.M.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, C.; Zheng, J.; Wu, F.; Chen, L. Metal organic framework supported niobium pentoxide nanoparticles with exceptional catalytic effect on hydrogen storage behavior of MgH2. Green Energy Environ. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.K.; Shaz, M.A.; Yadav, T.P. Enhanced hydrogen absorption and desorption properties of MgH2 with graphene and vanadium disulfide. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Yan, M. Hydrogen storage properties of nano-CoB/CNTs catalyzed MgH2. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Qiu, F.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Yan, C.; Jiao, L.; Yuan, H. NiB nanoparticles: A new nickel-based catalyst for hydrogen storage properties of MgH2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 17111–17117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Hou, C.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Yu, R.; Du, W. In situ formation of multiple catalysts for enhancing the hydrogen storage of MgH2 by adding porous Ni3ZnC0.7/Ni loaded carbon nanotubes microspheres. J. Magnes. Alloy 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Cui, K.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhao, W.; Li, P.; Qu, X. Enhanced hydrogen-storage properties of MgH2 by Fe–Ni catalyst modified three-dimensional graphene. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 34369–34380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Chou, K.-C.; Lyu, T.; Li, Q. Catalytic effect of Ni@rGO on the hydrogen storage properties of MgH2. J. Magnes. Alloy 2020, 8, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Yang, X. Improved MgH2 kinetics and cyclic stability by fibrous spherical NiMoO4 and rGO. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 134, 104311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Huang, Y.; Ye, J.; Xia, G.; Wang, G.; Dong, L.; Yang, Z.; Yu, X. Electrospun carbon nanofibers with in-situ encapsulated Ni nanoparticles as catalyst for enhanced hydrogen storage of MgH2. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 851, 156874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, Z.; Rahwanto, A.; Handoko, E.; Akhyar, H. Hydrogen storage properties of mechanical milled MgH2-nano Ni for solid hydrogen storage material. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 432, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, S.; Li, Y.; Han, S. Remarkable kinetics of novel Ni@CeO2–MgH2 hydrogen storage composite. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 35352–35364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Lu, Z.; Song, M.; He, J.; Wu, F.; Zhang, L. Boosting the hydrogen storage performance of magnesium hydride with metal organic framework-derived Cobalt@Nickel oxide bimetallic catalyst. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 52, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hou, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhang, J. Improvement of the hydrogen storage characteristics of MgH2 with a flake Ni nano-catalyst composite. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, C.D.; You, B.S.; Na, Y.S.; Bae, J.S. Hydriding properties of Mg–xNi alloys with different microstructures. Catal. Today 2007, 120, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Yu, H.; Wang, W.; Ren, K.; Zhang, W.; Han, S. Effect of ternary transition metal sulfide FeNi2S4 on hydrogen storage performance of MgH2. J. Magnes. Alloy 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tome, K.C.; Xi, S.; Fu, Y.; Lu, C.; Lu, N.; Guan, M.; Zhou, S.; Yu, H. Remarkable catalytic effect of Ni and ZrO2 nanoparticles on the hydrogen sorption properties of MgH2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 4716–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Ding, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, L. Effect of rGO supported NiCu derived from layered double hydroxide on hydrogen sorption kinetics of MgH2. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 789, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Guo, Z.; Yu, X.; Liu, H.; Wu, Z.; Ni, J. Enhanced hydrogen sorption properties of Ni and Co-catalyzed MgH2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 4569–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shan, J.; Li, P.; Zhai, F.; Wan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Qu, X. Dehydrogenation mechanism of ball-milled MgH2 doped with ferrites (CoFe2O4, ZnFe2O4, MnFe2O4 and Mn0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4) nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 643, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanski, M.; Bystrzycki, J. Comparative studies of the influence of different nano-sized metal oxides on the hydrogen sorption properties of magnesium hydride. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 486, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eskandarany, M.S. Metallic glassy Zr70Ni20Pd10 powders for improving the hydrogenation/dehydrogenation behavior of MgH2. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Jiang, W.; Yang, X.-S.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L.; Zhu, M. Enhancing (de) hydrogenation kinetics properties of the Mg/MgH2 system by adding ANi5 (A= Ce, Nd, Pr, Sm, and Y) alloys via ball milling. J. Rare Earth 2021, 39, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eskandarany, M.S.; Saeed, M.; Al Nasrallah, E.; Al Ajmi, F.; Banyan, M. Effect of LaNi3 amorphous alloy nanopowders on the performance and hydrogen storage properties of MgH2. Energies 2019, 12, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ding, W.; Sun, C. Enhancement of hydrogen storage properties by in situ formed LaH3 and Mg2NiH4 during milling MgH2 with porous LaNiO3. Catal. Today 2018, 318, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Qian, L.; Jia, D.; Miao, Y. Synthesis of 3D flower-like Ni0.6Zn0.4O microspheres for electrocatalytic oxidation of methanol. Electrocatalysis 2019, 10, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, P.; Saikia, B.J.; Dolui, S.K. Effects of nickel oxide (NiO) nanoparticles on the performance characteristics of the jatropha oil based alkyd and epoxy blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahdar, A.; Aliahmad, M.; Azizi, Y. NiO nanoparticles: Synthesis and characterization. J. Nanostruct. 2015, 5, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, K.; Ramesh, P.S.; Geetha, D. Structural, FTIR and photoluminescence studies of Fe doped ZnO nanopowder by co-precipitation method. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 131, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handore, K.; Bhavsar, S.; Horne, A.; Chhattise, P.; Mohite, K.; Ambekar, J.; Pande, N.; Chabukswar, V. Novel green route of synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by using natural biodegradable polymer and its application as a catalyst for oxidation of aldehydes. J. Macromol. Sci. A 2014, 51, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhunia, A.; Jha, P.; Rout, D.; Saha, S. Morphological properties and raman spectroscopy of ZnO nanorods. J. Phys. Sci. 2016, 21, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Marinho, J.Z.; Romeiro, F.d.C.; Lemos, S.C.S.; Motta, F.V.d.; Riccardi, C.; Li, M.S.; Longo, E.; Lima, R.C. Urea-based synthesis of zinc oxide nanostructures at low temperature. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, P.; Ghosh, S.; Basak, S.; Naskar, M.K. A facile synthesis of mesoporous NiO nanosheets and their application in CO oxidation. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2016, 4, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Johnson, J.K.; Shaz, M.; Srivastava, O. TiH2 as a dynamic additive for improving the de/rehydrogenation properties of MgH2: A combined experimental and theoretical mechanistic investigation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 21248–21261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazelee, N.A.; Idris, N.H.; Md Din, M.F.; Mustafa, N.S.; Ali, N.A.; Yahya, M.S.; Halim Yap, F.A.; Sulaiman, N.N.; Ismail, M. Synthesis of BaFe12O19 by solid state method and its effect on hydrogen storage properties of MgH2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 20853–20860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Idris, N.H.; Md Din, M.F.; Mustafa, N.S.; Sazelee, N.A.; Halim Yap, F.A.; Sulaiman, N.N.; Yahyaa, M.S.; Ismail, M. Nanolayer-like-shaped MgFe2O4 synthesised via a simple hydrothermal method and its catalytic effect on the hydrogen storage properties of MgH2. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 15667–15674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juahir, N.; Mustafa, N.; Sinin, A.; Ismail, M. Improved hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 by addition of Co2NiO nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 60983–60989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yu, L.; Lu, X.; Zhou, D. Catalytic effect and mechanism of NiCu solid solutions on hydrogen storage properties of MgH2. Renew. Energy 2020, 154, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; An, X.-H.; Pan, Y.-B.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Li, Q. The hydriding kinetics of Mg–Ni based hydrogen storage alloys: A comparative study on Chou model and Jander model. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 7842–7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Kong, L.; Li, Y.; Wan, D.; Xue, Y. Hydrogen desorption kinetics of V30Nb10(TixCr1-x)60 high-entropy alloys. Metals 2023, 13, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yong, H.; Yao, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, B.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Y. Influence of the phase evolution and hydrogen storage behaviors of Mg-RE alloy by a multi-valence Mo-based catalyst. J. Energy Storage 2023, 58, 106397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, G.A.; Ranong, C.N.; Bellosta von Colbe, J.M.; Bormann, R.; Fieg, G.; Hapke, J.; Dornheim, M. Empirical kinetic model of sodium alanate reacting system (I). Hydrogen absorption. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 6763–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Li, Q. A review on kinetic models and corresponding analysis methods for hydrogen storage materials. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 18072–18087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, S.; Xia, G.; Zhou, X.; Lu, X.; Yu, L.; Yu, X.; Peng, P. Stabilization of low-valence transition metal towards advanced catalytic effects on the hydrogen storage performance of magnesium hydride. J. Magnes. Alloys 2020, 9, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Yahya, M.S.; Sazelee, N.; Din, M.F.M.; Ismail, M. Influence of nanosized CoTiO3 synthesized via a solid-state method on the hydrogen storage behavior of MgH2. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Xiao, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, J.; Chen, L. Self-templated carbon enhancing catalytic effect of ZrO2 nanoparticles on the excellent dehydrogenation kinetics of MgH2. Carbon 2020, 166, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, Q.; Chang, J.; Zhang, D.; Peng, Y.; Yang, X. Improvement of hydrogen storage performance of MgH2 by MnMoO4 rod composite catalyst. Solid State Sci. 2021, 121, 106750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fan, G.; Fan, Y.; Liu, B. Ultrathin K2Ti8O17 nanobelts for improving the hydrogen storage kinetics of MgH2. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 881, 160571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafatnejad, M.; Raygan, S.; Sefidmooy Azar, M. Investigation of dehydrogenation performance and air stability of MgH2–PMMA nanostructured composite prepared by direct high-energy ball-milling. Mater. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2020, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czujko, T.; Oleszek, E.E.; Szot, M. New aspects of MgH2 morphological and structural changes during high-energy ball milling. Materials 2020, 13, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, R.R.; Raghubanshi, H.; Shaz, M.; Srivastava, O. Studies on the de/re-hydrogenation characteristics of nanocrystalline MgH2 admixed with carbon nanofibres. Appl. Nanosci. 2012, 2, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somo, T.R.; Maponya, T.C.; Davids, M.W.; Hato, M.J.; Lototskyy, M.V.; Modibane, K.D. A comprehensive review on hydrogen absorption behaviour of metal alloys prepared through mechanical alloying. Metals 2020, 10, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyahuma, F.M.; Zhang, L.; Song, M.; Lu, X.; Xiao, B.; Zheng, J.; Wu, F. Significantly improved hydrogen storage behaviors in MgH2 with Nb nanocatalyst. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2022, 29, 1788–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddah, M.; Rajabi, M.; Rabiee, S.M. Hydrogen desorption properties of nanocrystalline MgH2-10 wt.% ZrB2 composite prepared by mechanical alloying. J. Ultrafine Grained Nanostruct. Mater. 2014, 47, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, Z.; Saremi-Yarahmadi, S.; Gregory, D.H. Facile preparation of β-/γ-MgH2 nanocomposites under mild conditions and pathways to rapid dehydrogenation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 10492–10498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Xu, L.; Zang, L.; Guo, H.; Jiao, L.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Y. Highly dispersed MgH2 nanoparticle-graphene nanosheet composites for hydrogen storage. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 3828–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X.; Dou, S. Improved hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 doped with chlorides of transition metals Hf and Fe. Energy Educ. Sci. Technol. A Energy Sci. Res. 2012, 30, 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, Q.; Guo, X.; Yang, X. Achieve high-efficiency hydrogen storage of MgH2 catalyzed by nanosheets CoMoO4 and rGO. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 911, 165153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, R.; Adedeji Bolarin, J.; Lei, G.; Gao, W.; Li, Z.; Cao, H.; Chen, P. Microwave-assisted reduction of Ti species in MgH2-TiO2 composite and its effect on hydrogen storage. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.X.; Yuan, J.G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.G.; Zhu, Y.F.; Li, L.Q.; Wu, Y. A noteworthy synergistic catalysis on hydrogen sorption kinetics of MgH2 with bimetallic oxide Sc2O3/TiO2. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 839, 155387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguey-Zinsou, K.F.; Ares Fernandez, J.R.; Klassen, T.; Bormann, R. Using MgO to improve the (de)hydriding properties of magnesium. Mater. Res. Bull. 2006, 41, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Li, P.; Wan, Q.; Zhai, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Volinsky, A.A.; Qu, X. Significantly improved dehydrogenation of ball-milled MgH2 doped with CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Power Sources 2014, 268, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Idris, N.; Din, M.M.; Yahya, M.; Ismail, M. Nanoflakes MgNiO2 synthesised via a simple hydrothermal method and its catalytic roles on the hydrogen sorption performance of MgH2. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 796, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, L.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, X.J.; Jiang, L.K.; Peng, P. Hydrogen storage properties of magnesium hydride catalyzed by Ni-based solid solutions. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patah, A.; Takasaki, A.; Szmyd, J.S. The effect of Cr2O3/ZnO on hydrogen desorption properties of MgH2. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 2009, 1148, 1148-PP03-38. [Google Scholar]

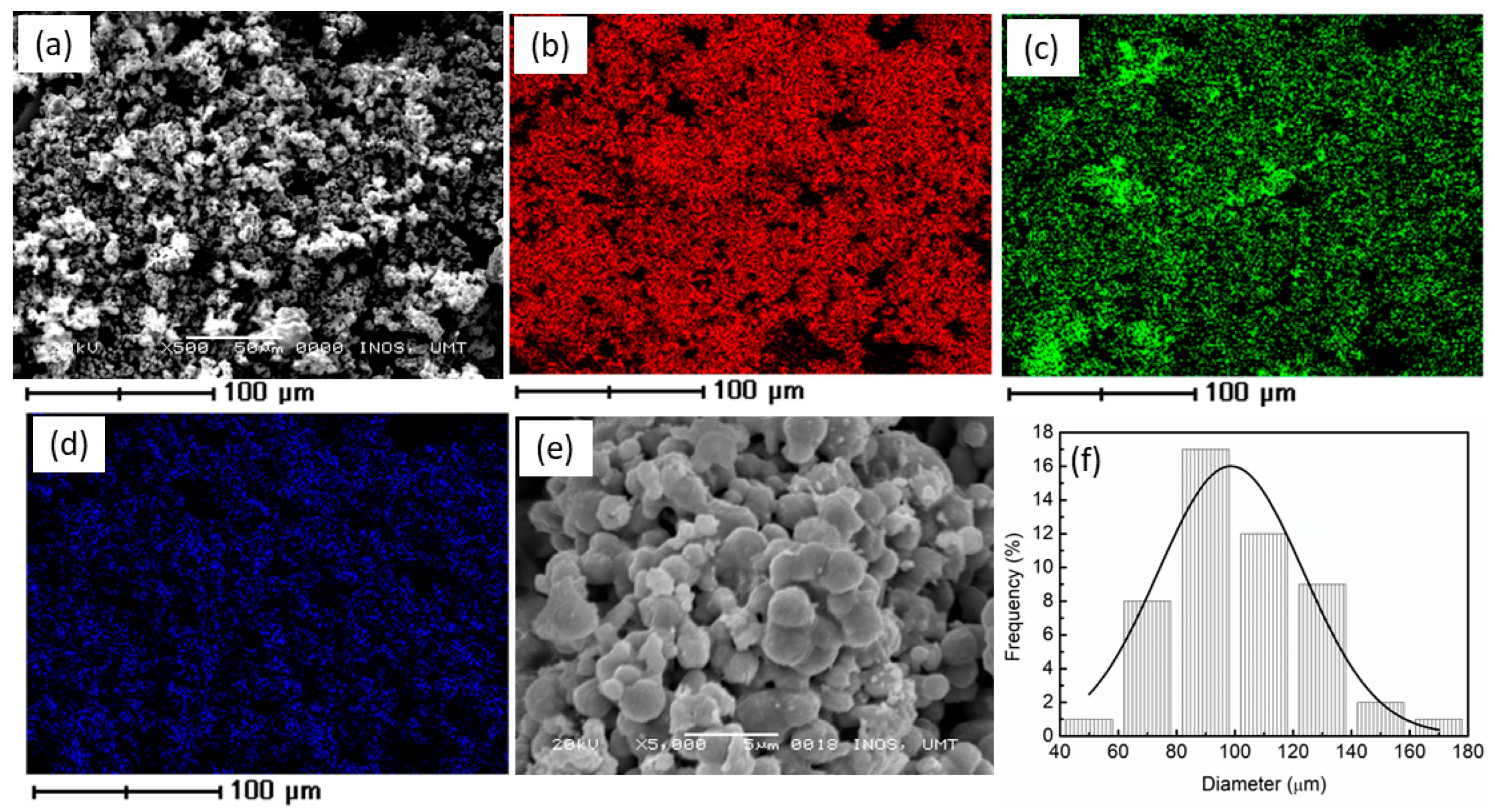
| Element | Mass (%) |
|---|---|
| Ni | 61.88 |
| Zn | 17.08 |
| O | 21.04 |
| Total | 100.00 |
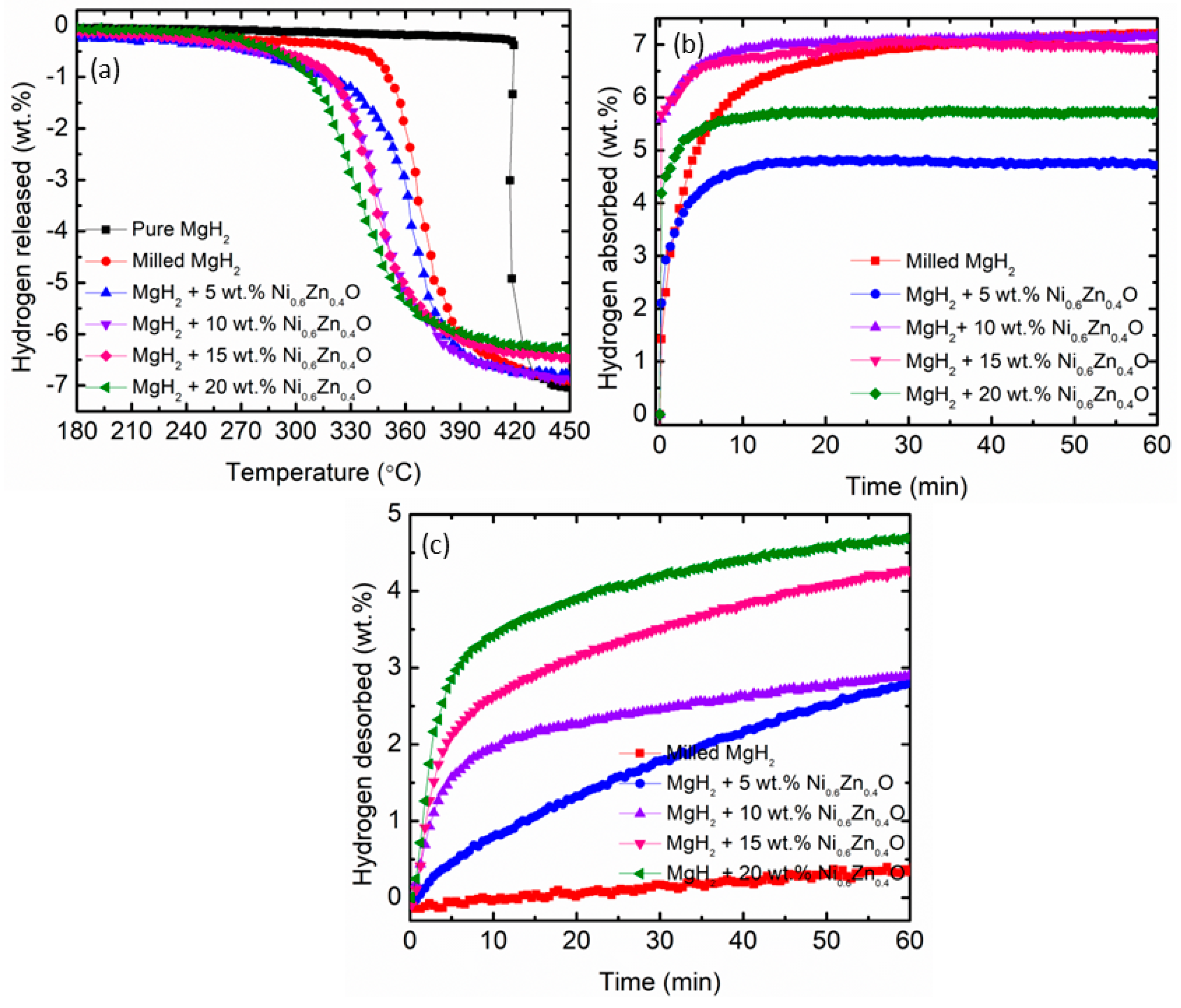
| System | Temperature for Isothermal Absorption Kinetics (°C) | Absorption Capacity (wt.%) | Time (Min) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MgH2 + 10 wt.% BaFe12O19 | 150 | 4.30 | 10 | [46] |
| MgH2 + 10 wt.% MgFe2O4 | 200 | 5.50 | 10 | [47] |
| MgH2 + 10 wt.% Co2NiO | 320 | 2.50 | 1.7 | [48] |
| MgH2 + Ni-50% Cu | 300 | 5.24 | 30 | [49] |
| MgH2–10 wt.% Ni0.6Zn0.4O | 250 | 6.50 | 60 | (this work) |
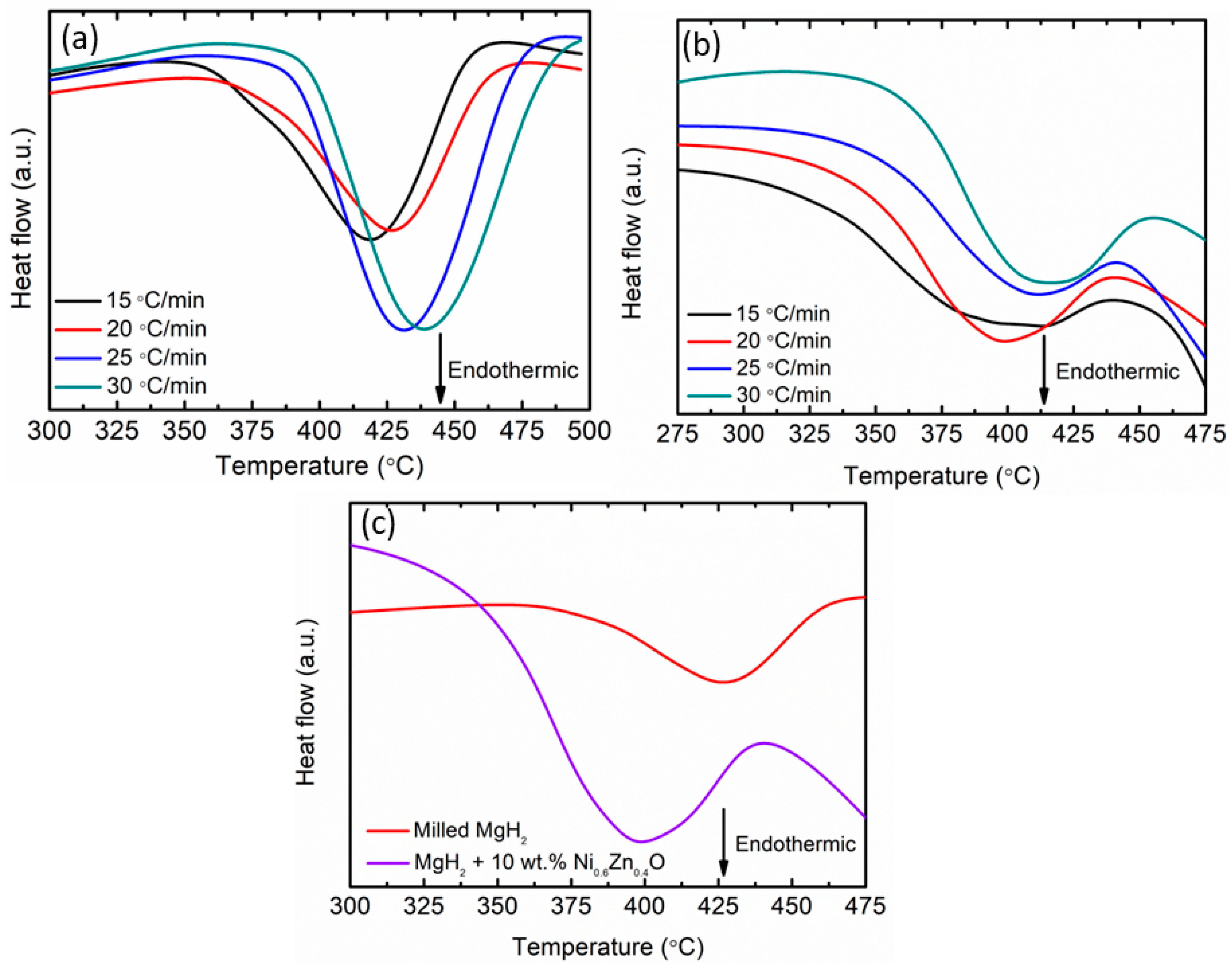
| Onset Desorption Temperature (°C) | Absorption Capacity (wt.%) | Desorption Capacity (wt.%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pure MgH2 | 418 | - | - |
| Milled MgH2 | 341 | 4.8 | 0.3 |
| MgH2–5 wt.% Ni0.6Zn0.4O samples | 280 | 4.1 | 2.7 |
| MgH2–10 wt.% Ni0.6Zn0.4O samples | 285 | 6.5 | 2.9 |
| MgH2–15 wt.% Ni0.6Zn0.4O samples | 305 | 6.5 | 4.3 |
| MgH2–20 wt.% Ni0.6Zn0.4O samples | 293 | 5.4 | 4.7 |
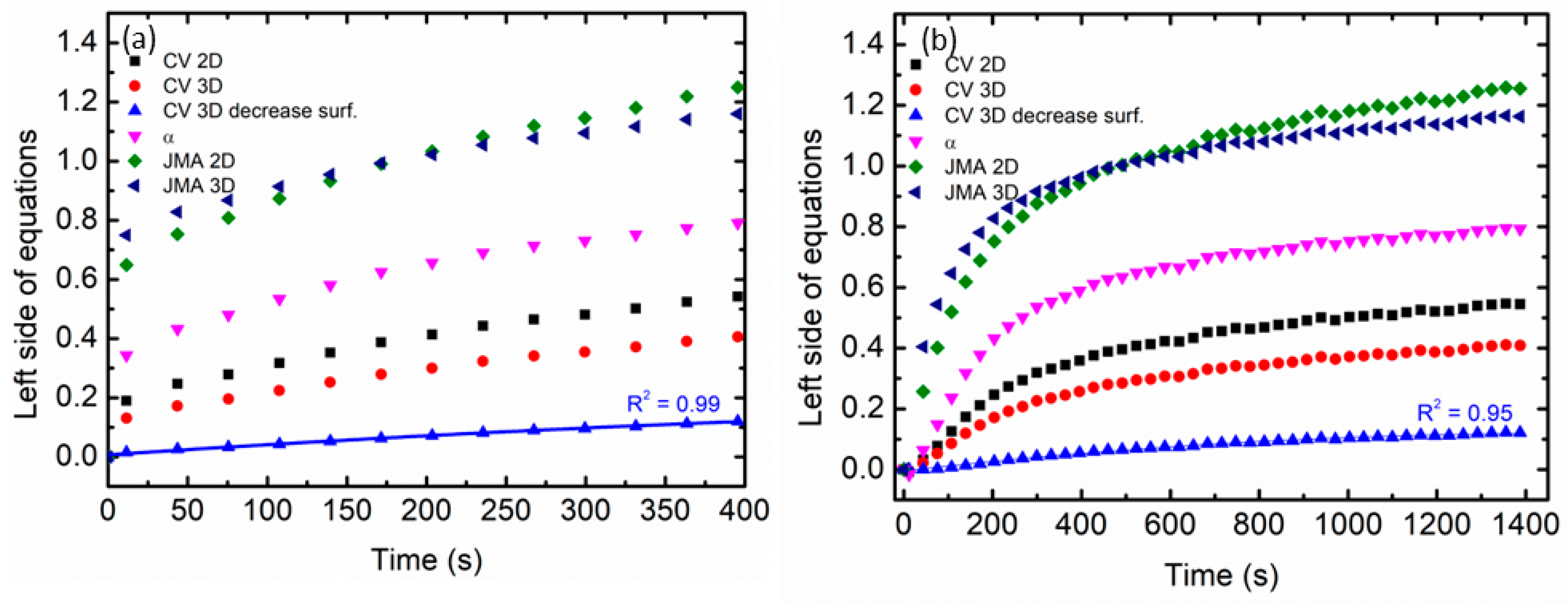
| Integrated Equation | Model |
|---|---|
| A = kt | Surface-controlled (chemisorption) |
| [−ln(1 − α)]1/2 = kt | JMA, n = 2 (e.g., two-dimensional growth of existing nuclei with constant interface velocity) |
| [−ln(1 − α)]1/3 = kt | JMA, n = 3 (e.g., two-dimensional growth of existing nuclei with constant interface velocity) |
| 1 − (1 − α)1/3 = kt | CV 2D: contracting volume, three-dimensional growth with constant interface velocity |
| 1 − (2α/3) − (1 − α)2/3 = kt | CV 3D: contracting volume, three-dimensional growth diffusion controlled with decreasing interface velocity |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sazelee, N.; Md Din, M.F.; Ismail, M. Ni0.6Zn0.4O Synthesised via a Solid-State Method for Promoting Hydrogen Sorption from MgH2. Materials 2023, 16, 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062176
Sazelee N, Md Din MF, Ismail M. Ni0.6Zn0.4O Synthesised via a Solid-State Method for Promoting Hydrogen Sorption from MgH2. Materials. 2023; 16(6):2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062176
Chicago/Turabian StyleSazelee, Noratiqah, Muhamad Faiz Md Din, and Mohammad Ismail. 2023. "Ni0.6Zn0.4O Synthesised via a Solid-State Method for Promoting Hydrogen Sorption from MgH2" Materials 16, no. 6: 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062176
APA StyleSazelee, N., Md Din, M. F., & Ismail, M. (2023). Ni0.6Zn0.4O Synthesised via a Solid-State Method for Promoting Hydrogen Sorption from MgH2. Materials, 16(6), 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062176









