Reduced Slit Rolling Power in Rebar Steel Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
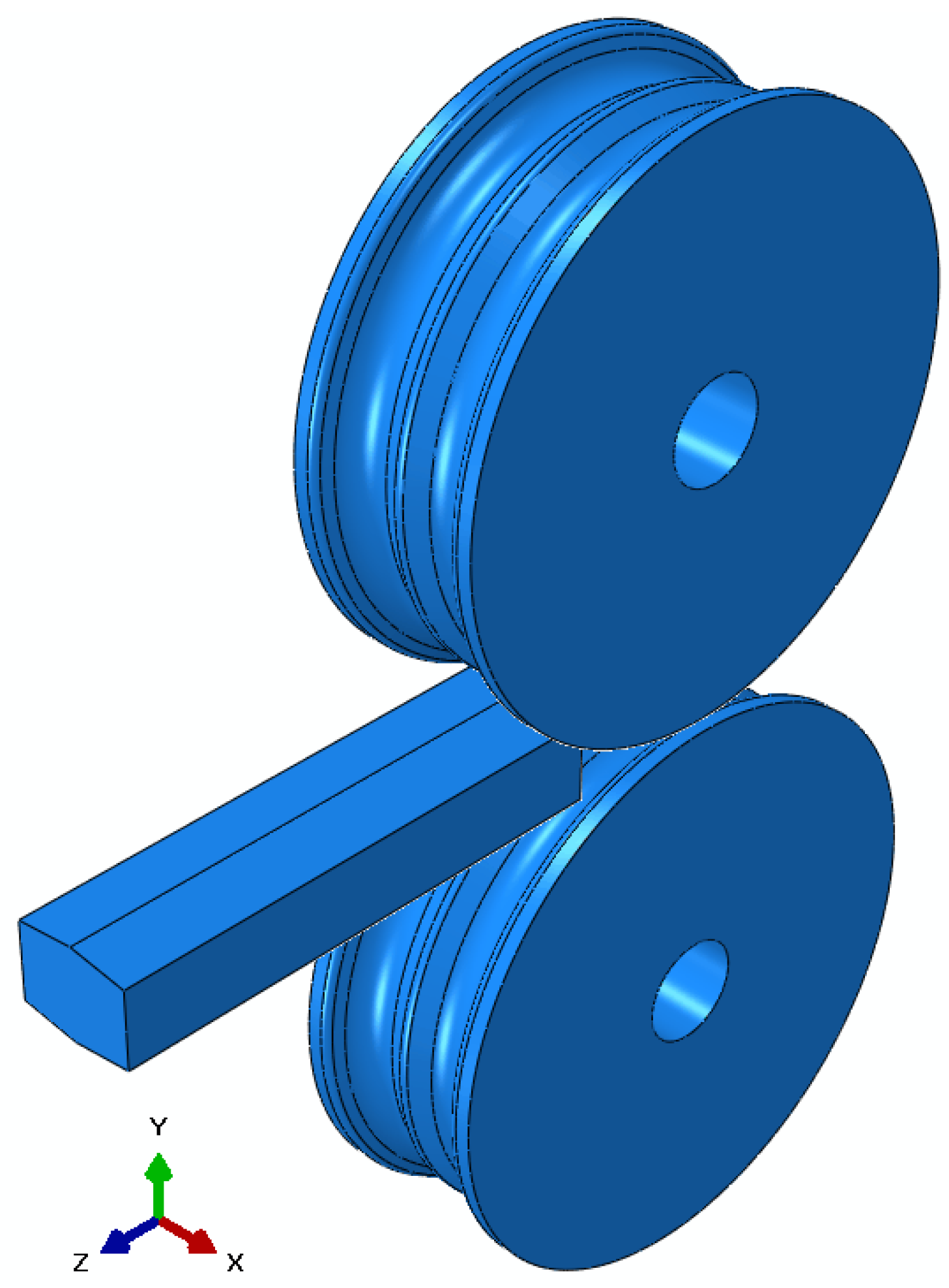
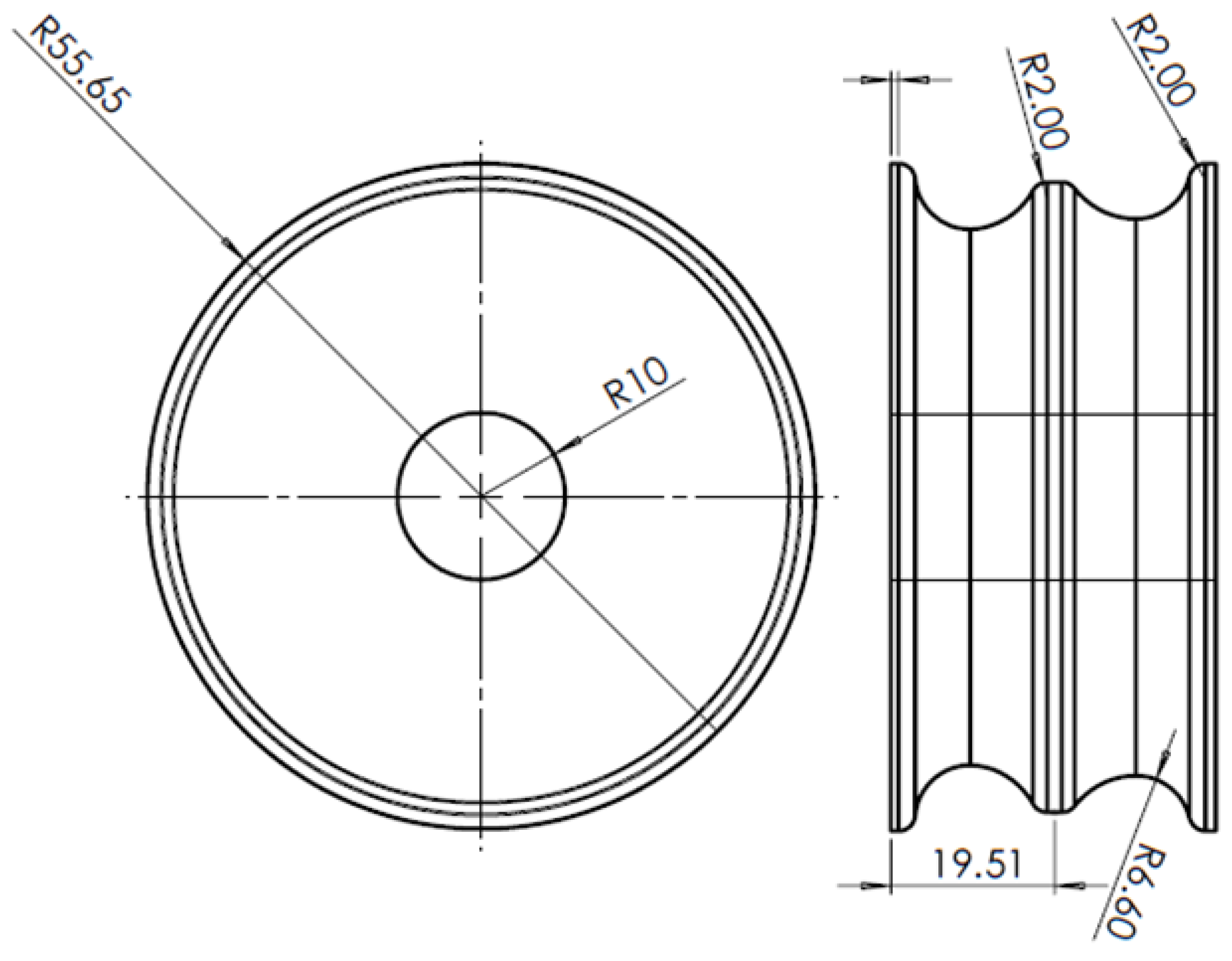
2. Material and Method
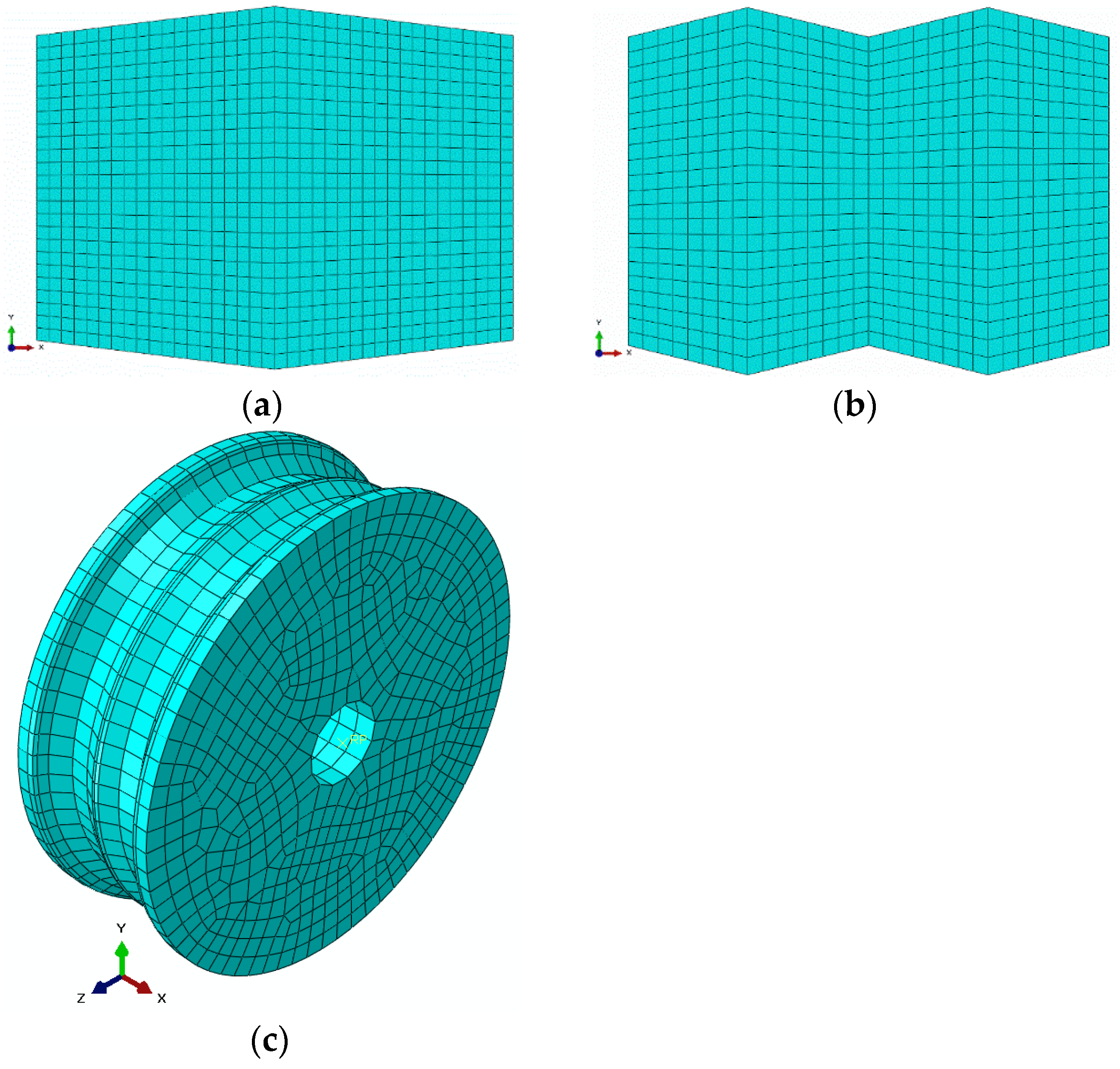
3. Finite Element Modeling
4. Results and Discussion
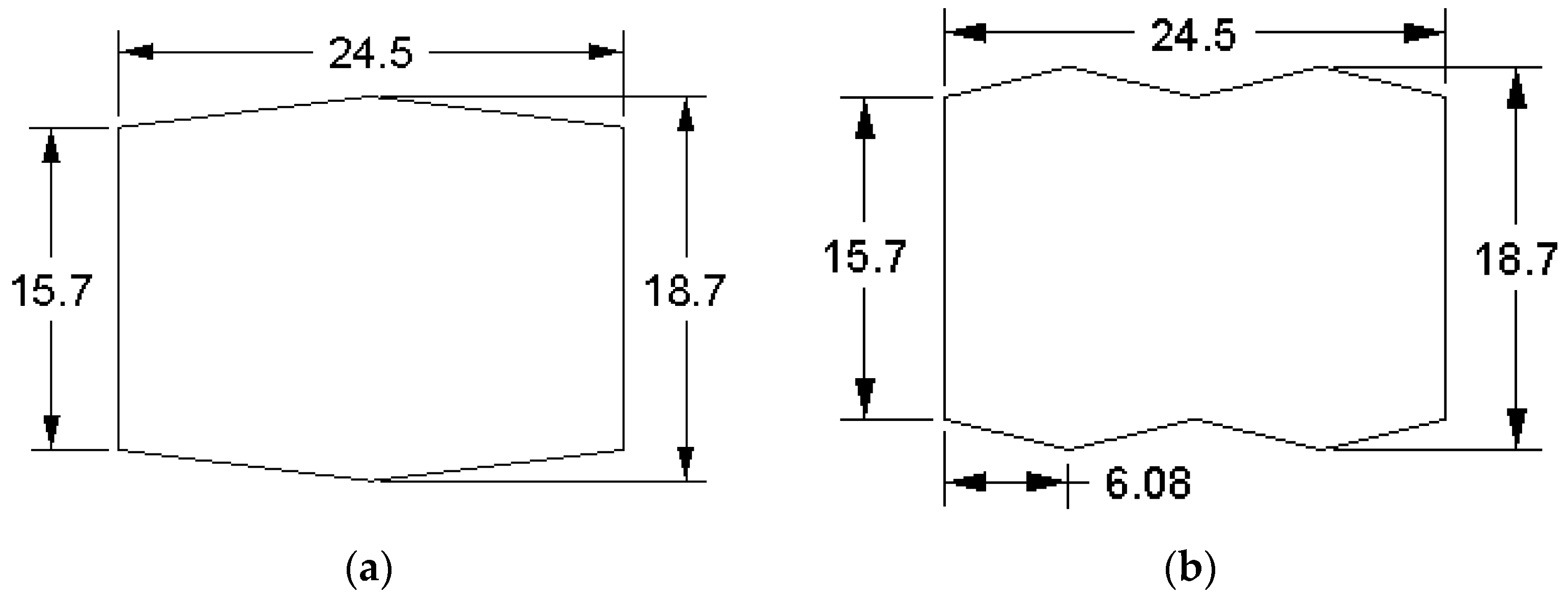
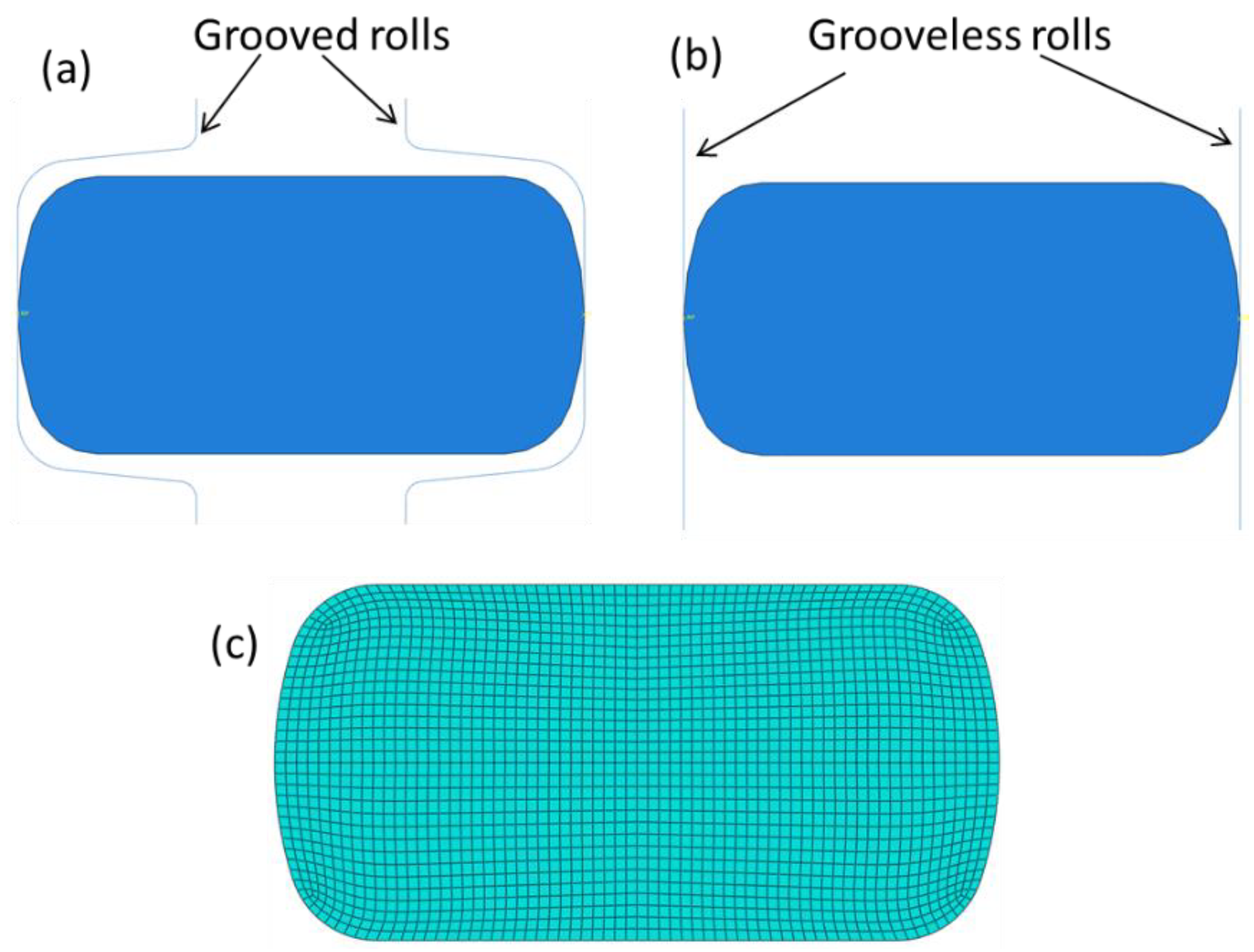
4.1. Strip Edging for Preslitting
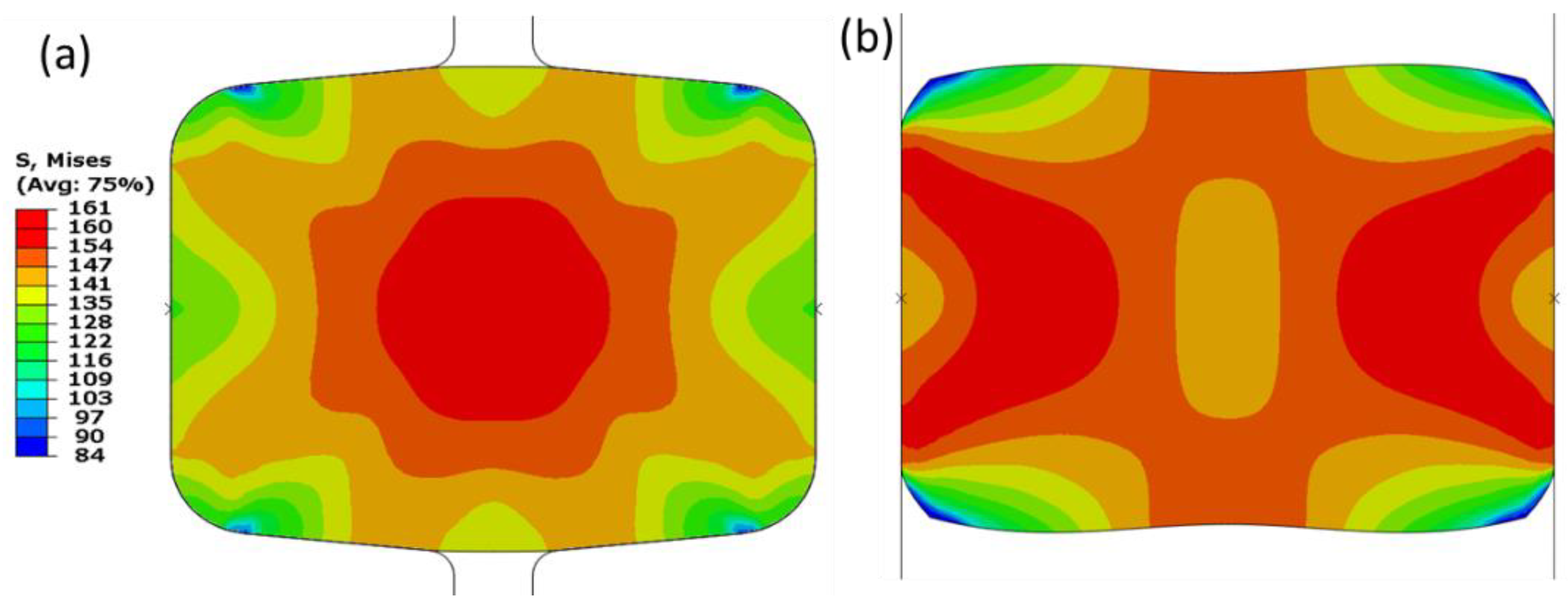
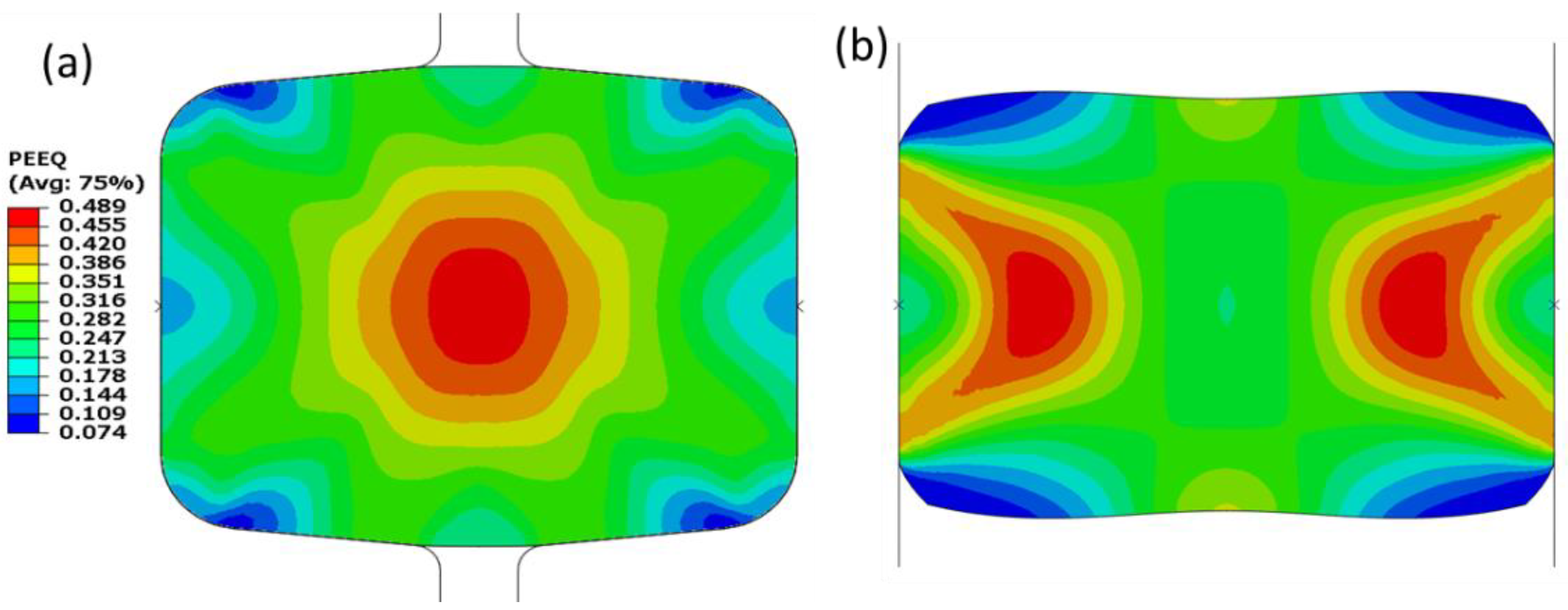
4.2. Finite Element Simulations of Preslitting Stand
4.3. Deformation Behaviour at the Preslitting Stand
5. Conclusions
- The geometry (W/H) of the strip entering the edging pass is numerically tested by compression using grooved and grooveless dies, and verified by comparing it with the images of produced strips.
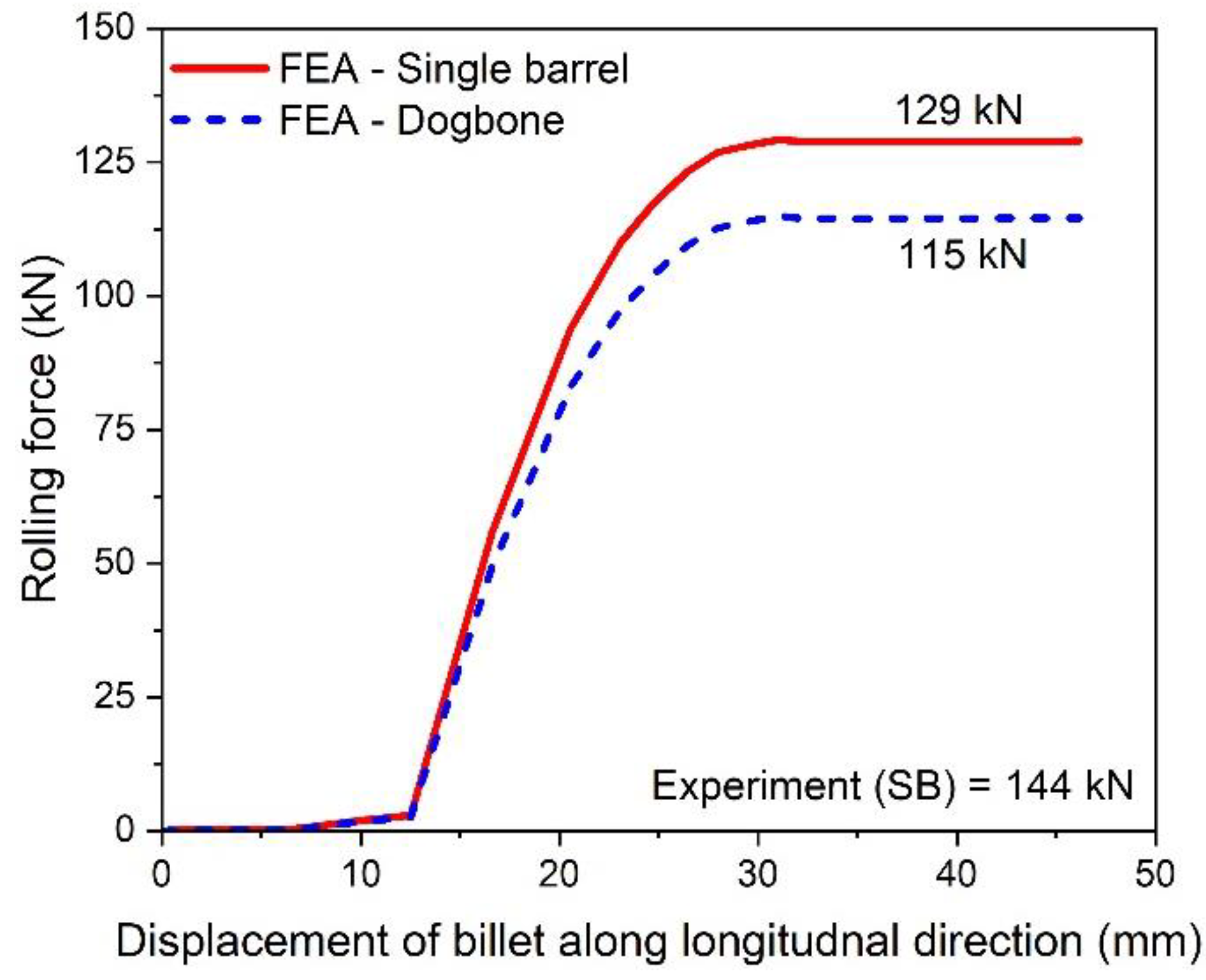
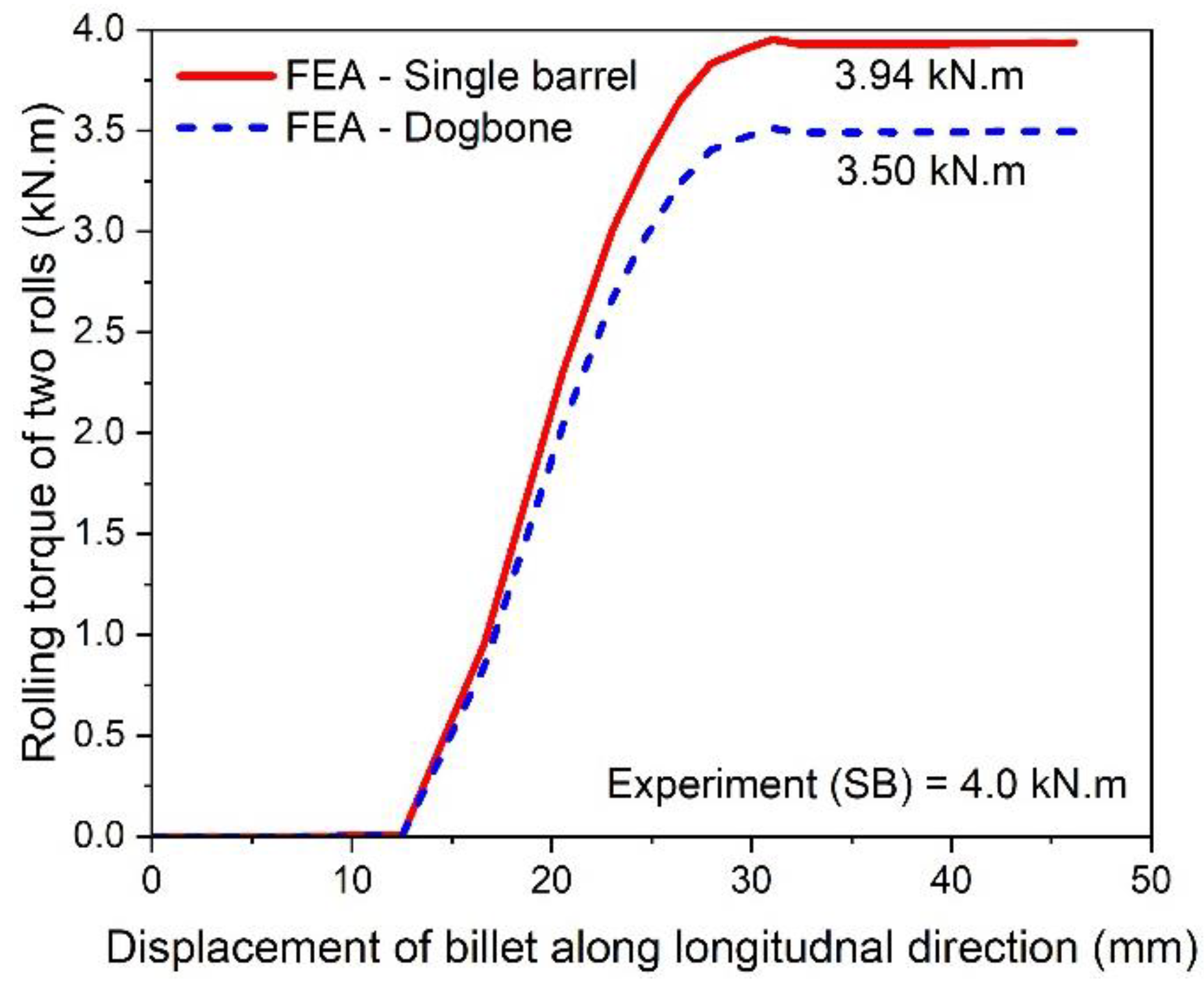
- The FE result of rolling power (185 kW) is found to be in good agreement with the available experimental data (216 kW). This shows the validation of the FE model and boundary conditions.
- The established FE model is used further to simulate the rolling of a double barreled strip to evaluate its performance in terms of rolling power.
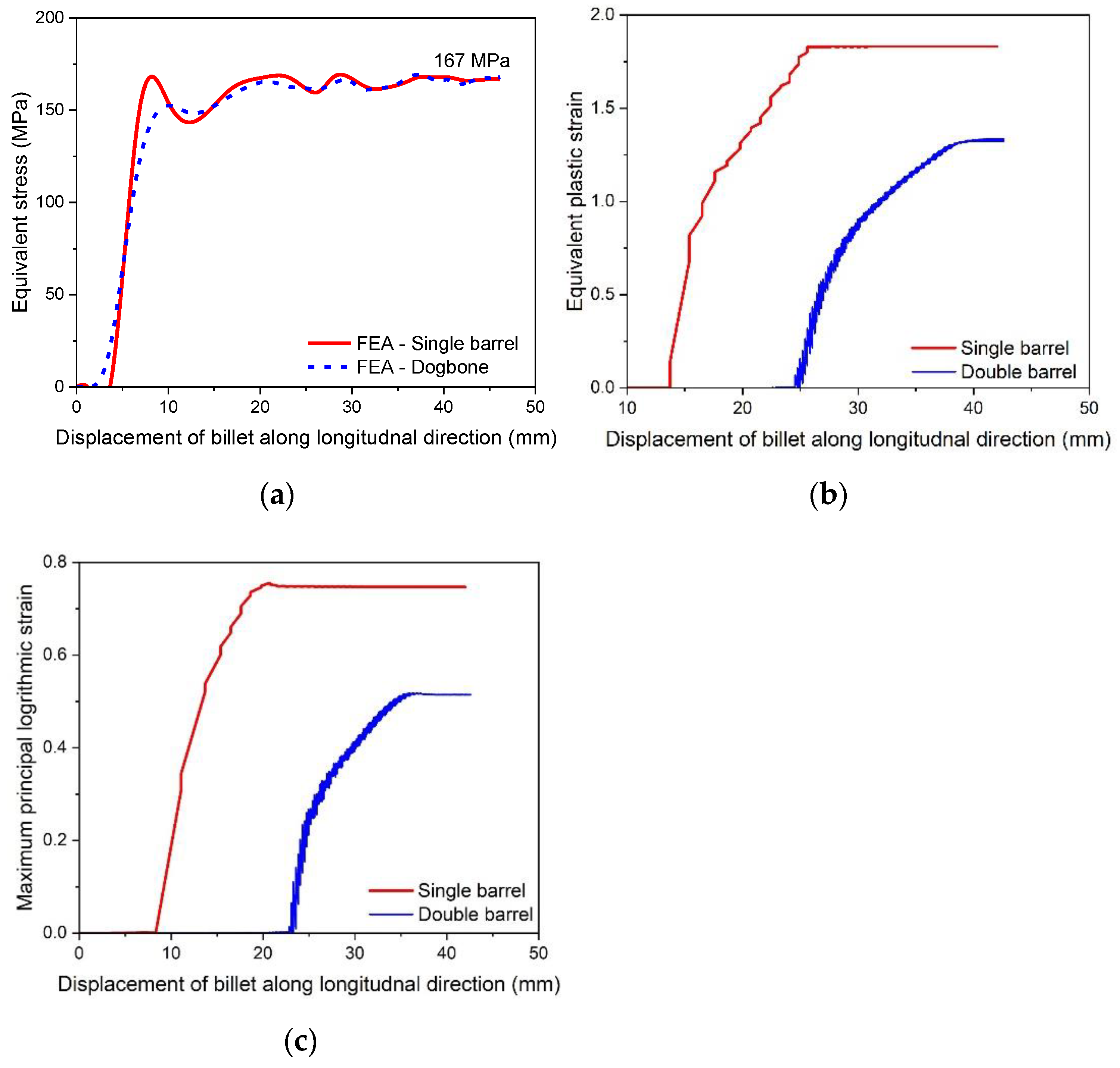
- The FE results revealed that pre slit rolling of single barrel strip is associated with a power reduction of approximately 12.12%.
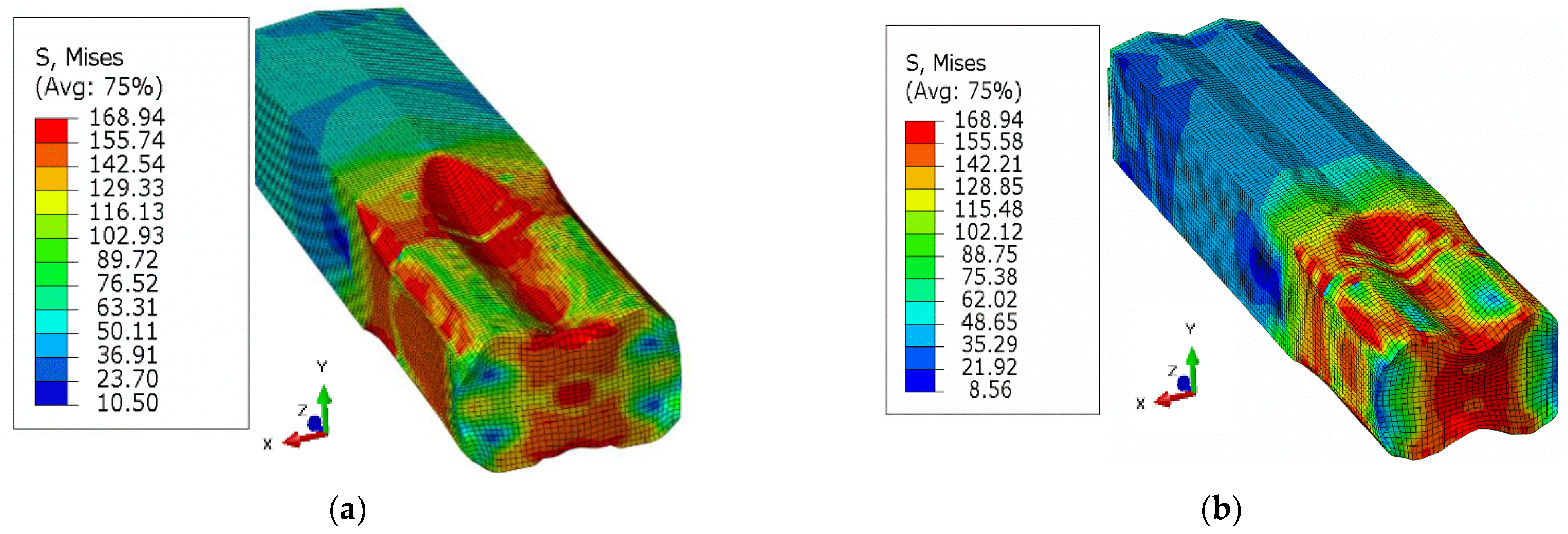
- Higher localized stresses in a preslitting pass at the roll knife of a single barrel strip could cause severe wear of the roll knife apex.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yanazawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Noda, A.; Takeda, R.; Inoue, M. Method of Rolling Steel Rods and Wires with Grooveless Rolls and Grooveless Rolling Entry Guide. U.S. Patent 4,685,320, 11 August 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Singh, P.K. Effect of Process Parameters on Roll Separating Force, Driving Torque and End Crop Length during Grooved Hot Rolling of SAE 1020 Steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 79, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmotte, R. Rolling of long products: Development and trends. In Proceedings of the Commission of the European Communities; (Report). EUR, European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 1982; pp. 145–174. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, S.-E. Grooveless Finish-Rolling of Square Edge Flats in a Small Section Mill. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1996, 59, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starkov, N.V.; Bobarikin, Y.L. Choosing a System for the Slit-Rolling of Rebars. Metallurgist 2016, 60, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turczyn, S.; Nowakowski, A.; Michalowski, M. Roll Pass Design For Ribbed Bars; METAL 2004: Hradec nad Moravicí, Czech Republic, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn, H.A. Uniaxial Compression Testing. In ASM Handbook; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2000; pp. 339–341. [Google Scholar]
- Na, D.H.; Cho, S.H.; Lee, Y. Experimental and Numerical Studies for the Forming Groove and Separating Groove Design in Slit Rolling Process. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2011, 25, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, M.A.; Goldschmit, M.B.; Dvorkin, E.N. Finite Element Analysis of Steel Rolling Processes. Comput. Struct. 2001, 79, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, M.; Main, J.; Weigand, J.; Sadek, F.; Choe, L.; Zhang, C.; Gross, J.; Luecke, W.; McColskey, D. Temperature-Dependent Material Modeling for Structural Steels: Formulation and Application; US Department of Commerce, National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2016.
- Mecking, H.; Kocks, U.F. Kinetics of flow and strain-hardening. Acta Metal. 1981, 29, 1865–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Magd, E.; Treppman, C.; Korthäuer, M. Description of Flow Curves over Wide Ranges of Strain Rate and Temperature. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2006, 97, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Magd, E. Modelling and Simulation of Mechanical Behaviour. In Modelling and Simulation for Material Selection and Mechanical Design; Totten, G.E., Xie, L., Funatani, K., Eds.; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 207–213. ISBN 9781351254502. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, J.U.; Na, D.H.; Lee, Y. A Study on Design Equation of Separating and Oval Roll Grooves in Rebar Manufacturing Process. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turczyn, S.; Dziedzic, M.; Kuźmiński, Z. A study on design of slitting passes used for rebar rolling. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Metallurgy and Materials, Cracow, Poland, 21–23 May 2014; pp. 303–308, ISBN 978-80-87294-52-9. [Google Scholar]
- Lambiase, F. Prediction of Geometrical Profile in Slit Rolling Pass. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2014, 71, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM A615/A615M-18e1; ASTM Standard Specification for Deformed and Plain Billet-Steel Bars for Concrete. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999.
- Byon, S.; Na, D.; Lee, Y. Flow Stress Equation in Range of Intermediate Strain Rates and High Temperatures to Predict Roll Force in Four-Pass Continuous Rod Rolling. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, B.; Kodur, V. Effect of Temperature on Strength and Elastic Modulus of High-Strength Steel. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essam El-Magd, M.A. Influence of Strain Rate and Temperature on the Compressive Ductility of AI, Mg and Ti Alloys. J. Phys. IV Fr. 2003, 110, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groover, M.P. Principles of Modern Manufacturing: S1 Version; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lapovok, R.; Thomson, P.F. An Approach to the Optimal Design of Rolling Passes. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1997, 37, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wusatowski, Z. Principles of roll pass design. In Fundamentals of Rolling; Wusatowski, Z., Ed.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1969; Chapter 7; pp. 494–657. ISBN 978-0-08-012276-2. [Google Scholar]
- Szota, P.; Strycharska, D.; Mróz, S.; Stefanik, A. Analysis of rolls wear during the ribbed bars multi-slit rolling process. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2015, 60, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
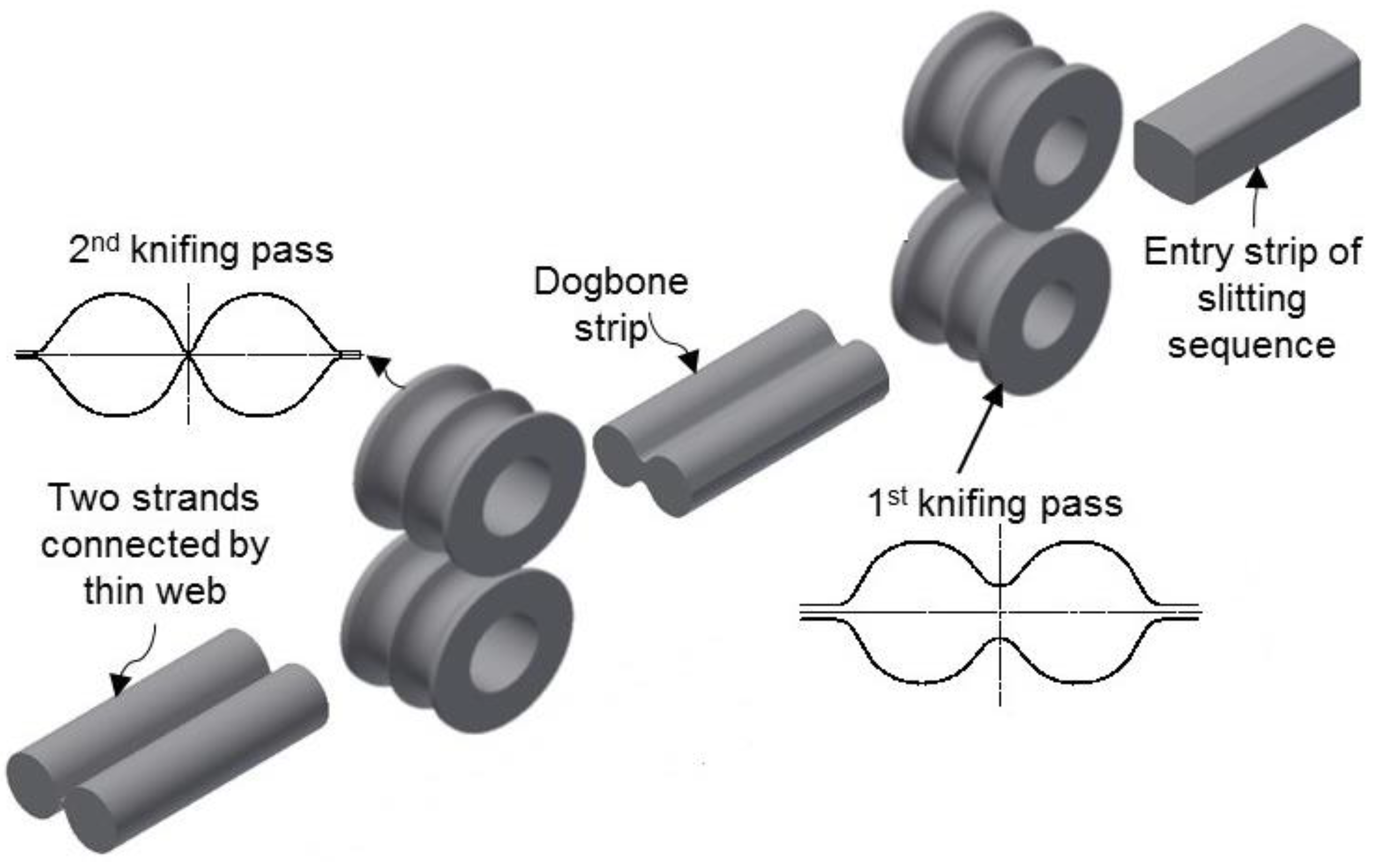

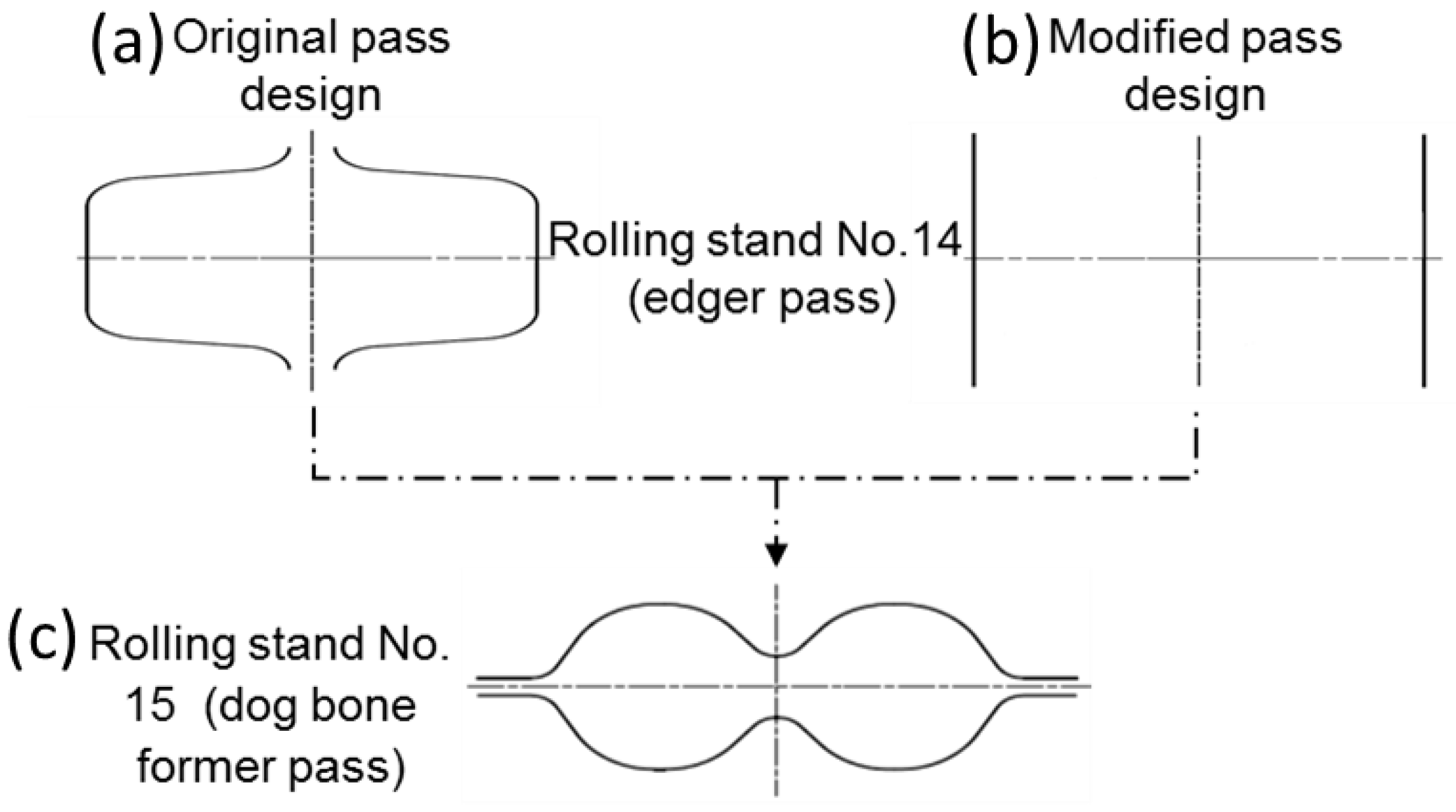
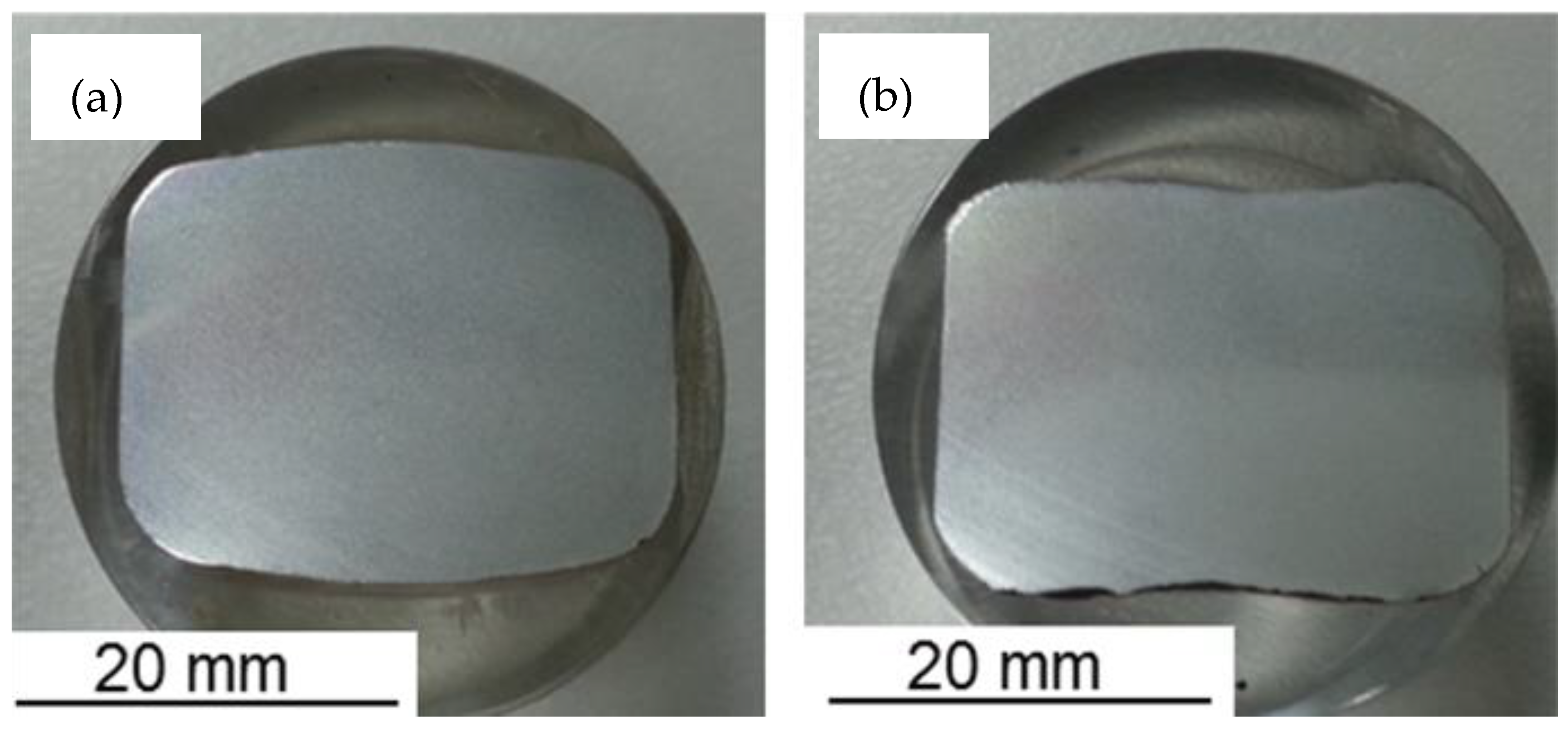
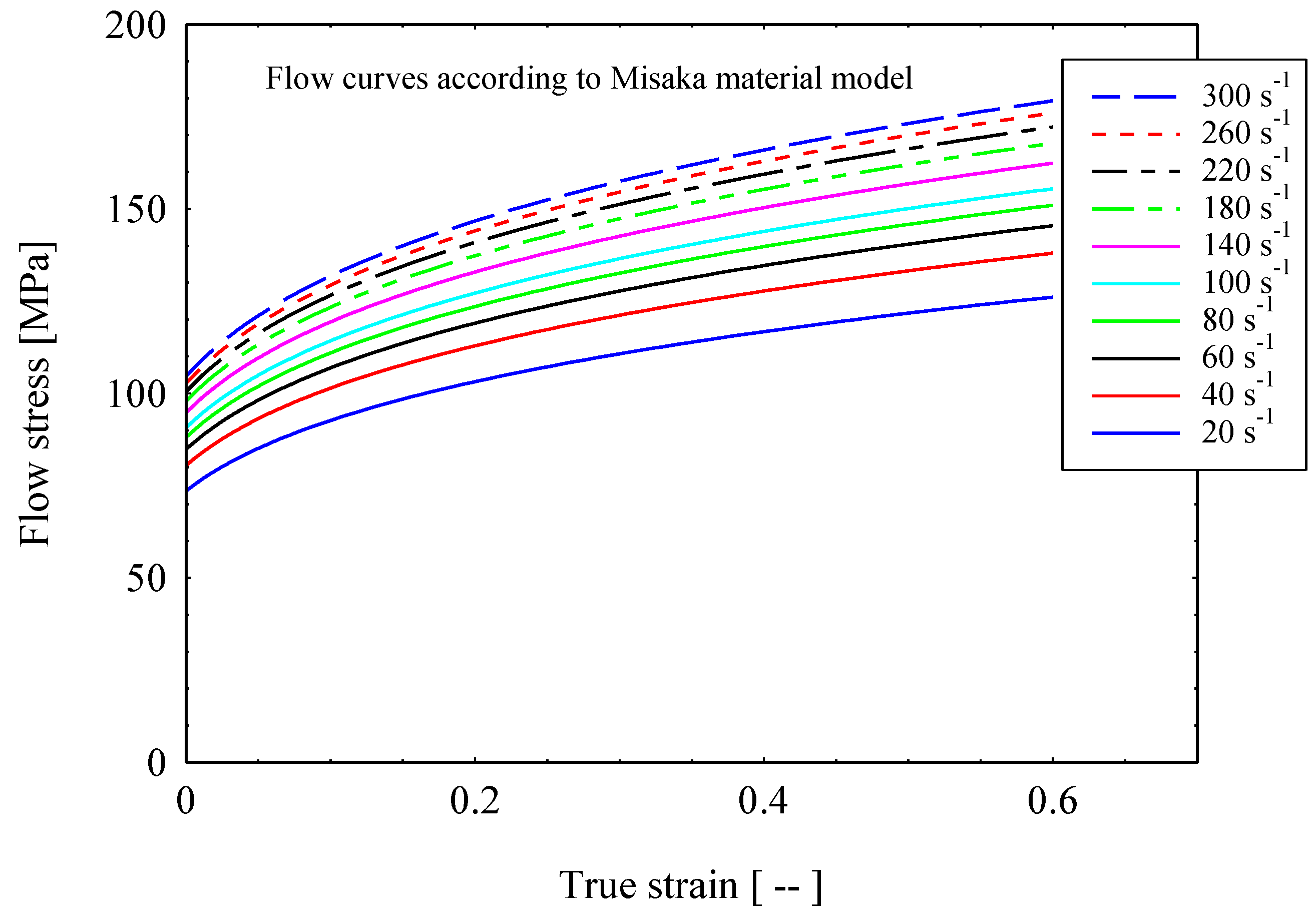




| Element | C | Mn | Si | Cr | Ni | S | P | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt. % | 0.25 | 0.55 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0.04 | Bal. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, R.; Ataya, S.; Elgammal, I.; Essa, K. Reduced Slit Rolling Power in Rebar Steel Production. Materials 2023, 16, 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16052104
Khan R, Ataya S, Elgammal I, Essa K. Reduced Slit Rolling Power in Rebar Steel Production. Materials. 2023; 16(5):2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16052104
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Rashid, Sabbah Ataya, Islam Elgammal, and Khamis Essa. 2023. "Reduced Slit Rolling Power in Rebar Steel Production" Materials 16, no. 5: 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16052104
APA StyleKhan, R., Ataya, S., Elgammal, I., & Essa, K. (2023). Reduced Slit Rolling Power in Rebar Steel Production. Materials, 16(5), 2104. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16052104









