Processing, Mechanical and Morphological Properties of GTR Modified by SBS Copolymers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.2.1. GTR Thermo-Mechanically Treated in the Presence of SBS Copolymers
2.2.2. GTR Modified by SBS and Curing System
2.3. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
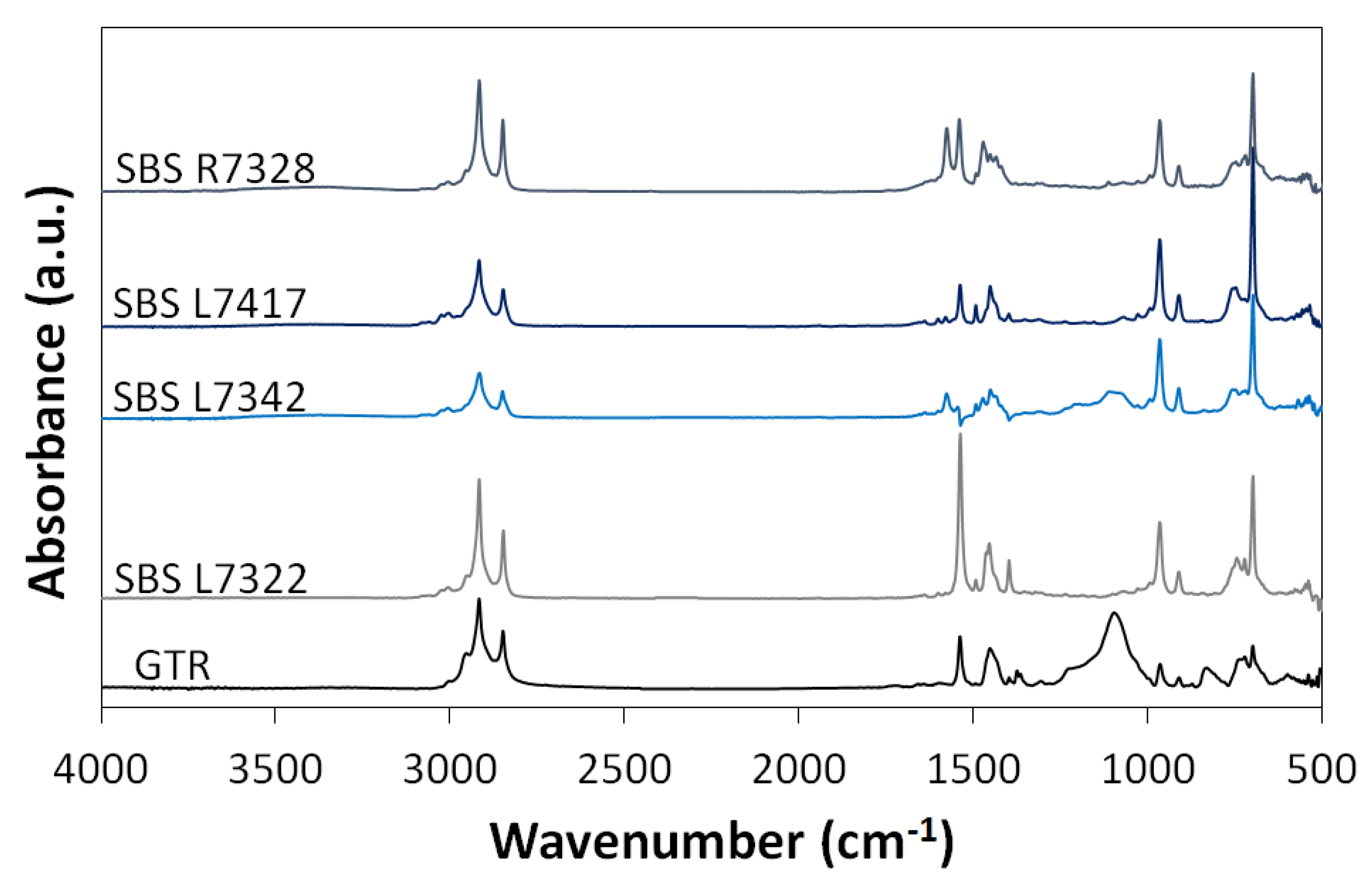
3.1. Chemical Structure of GTR and SBS Copolymers
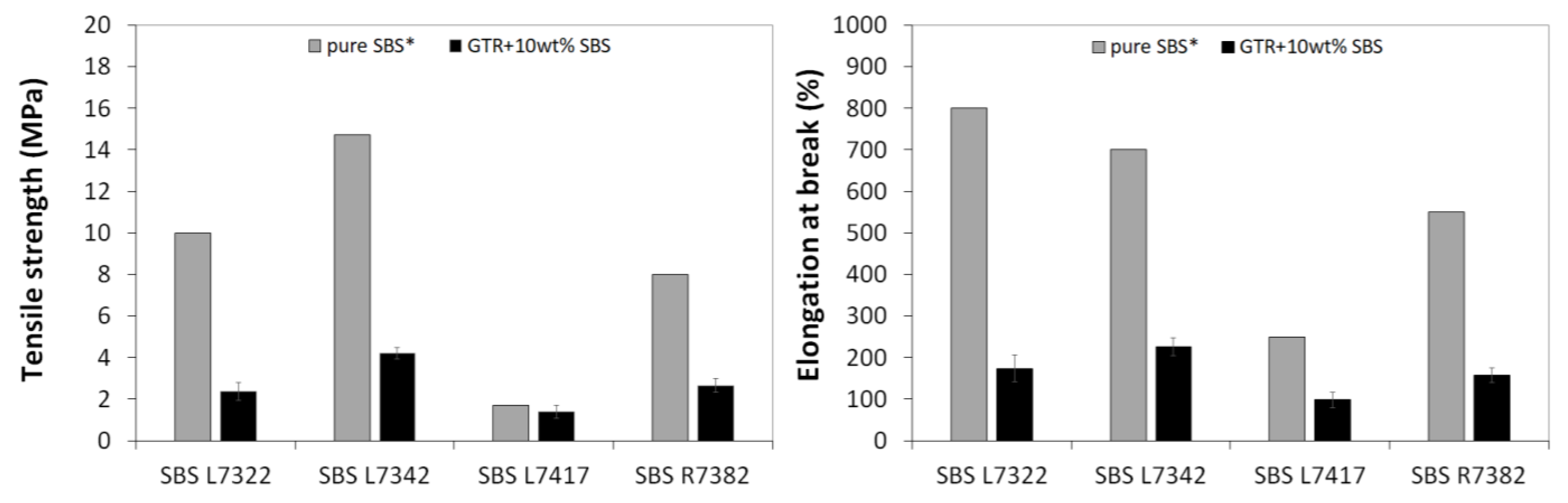
3.2. MFR of SBS Copolymers and GTR Modified by SBS Copolymers
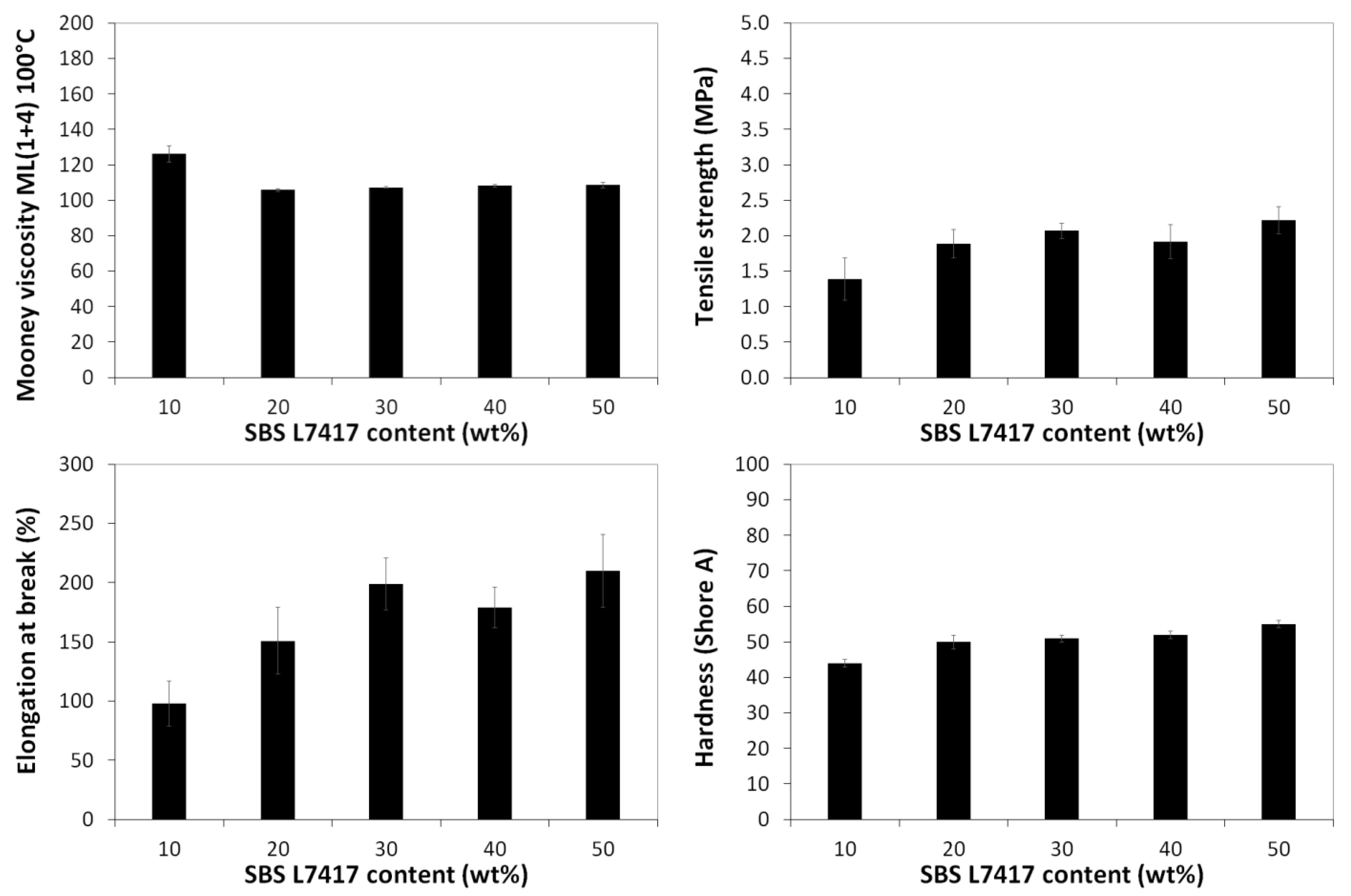
3.3. Mooney Viscosity and Physico-Mechanical Properties of GTR Modified by SBS Copolymers
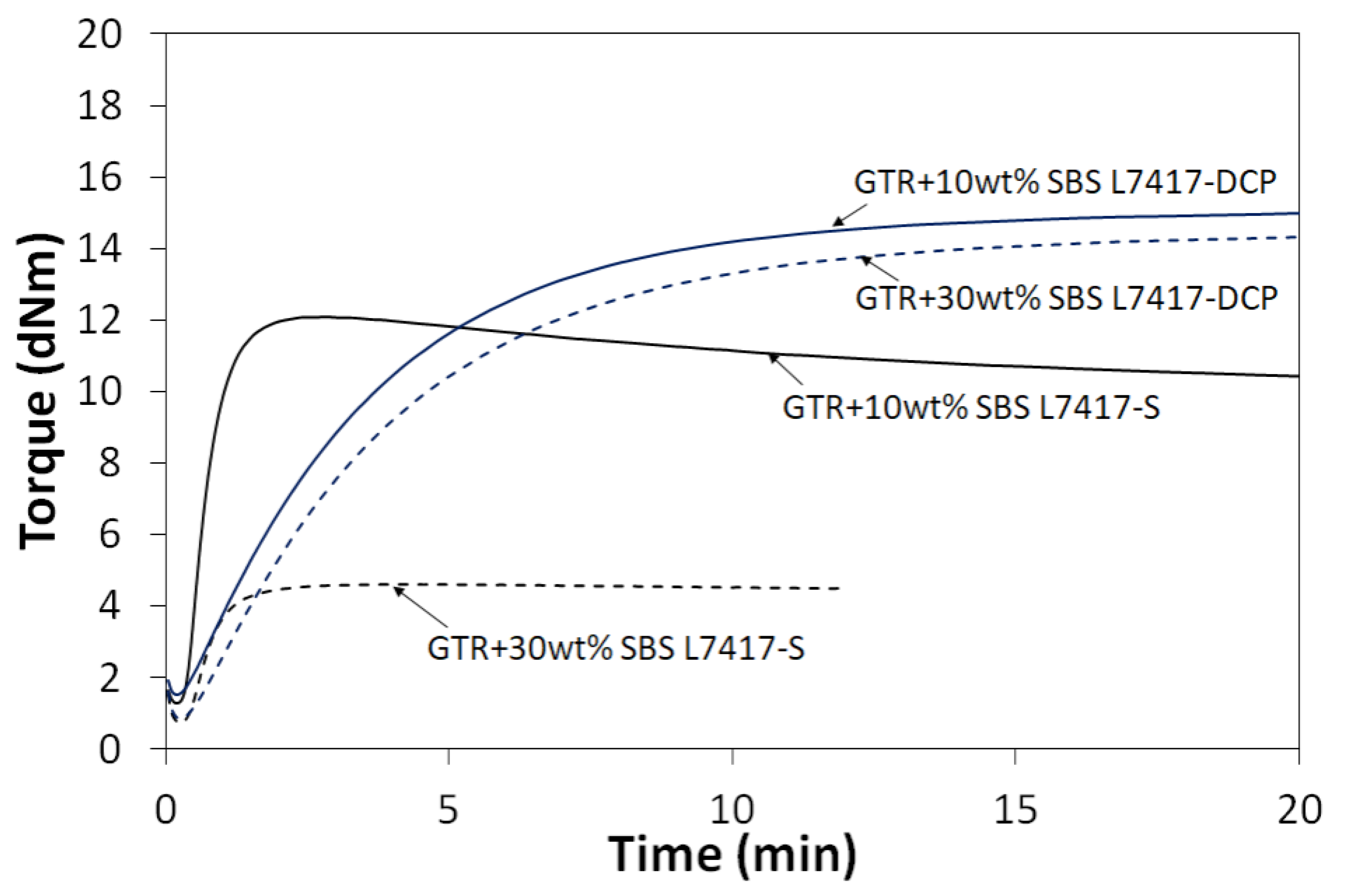
3.4. Mooney Viscosity and Curing Characteristics of GTR Modified by SBS and Curing System
3.5. Physico-Mechanical Properties of GTR Modified by SBS and Curing System
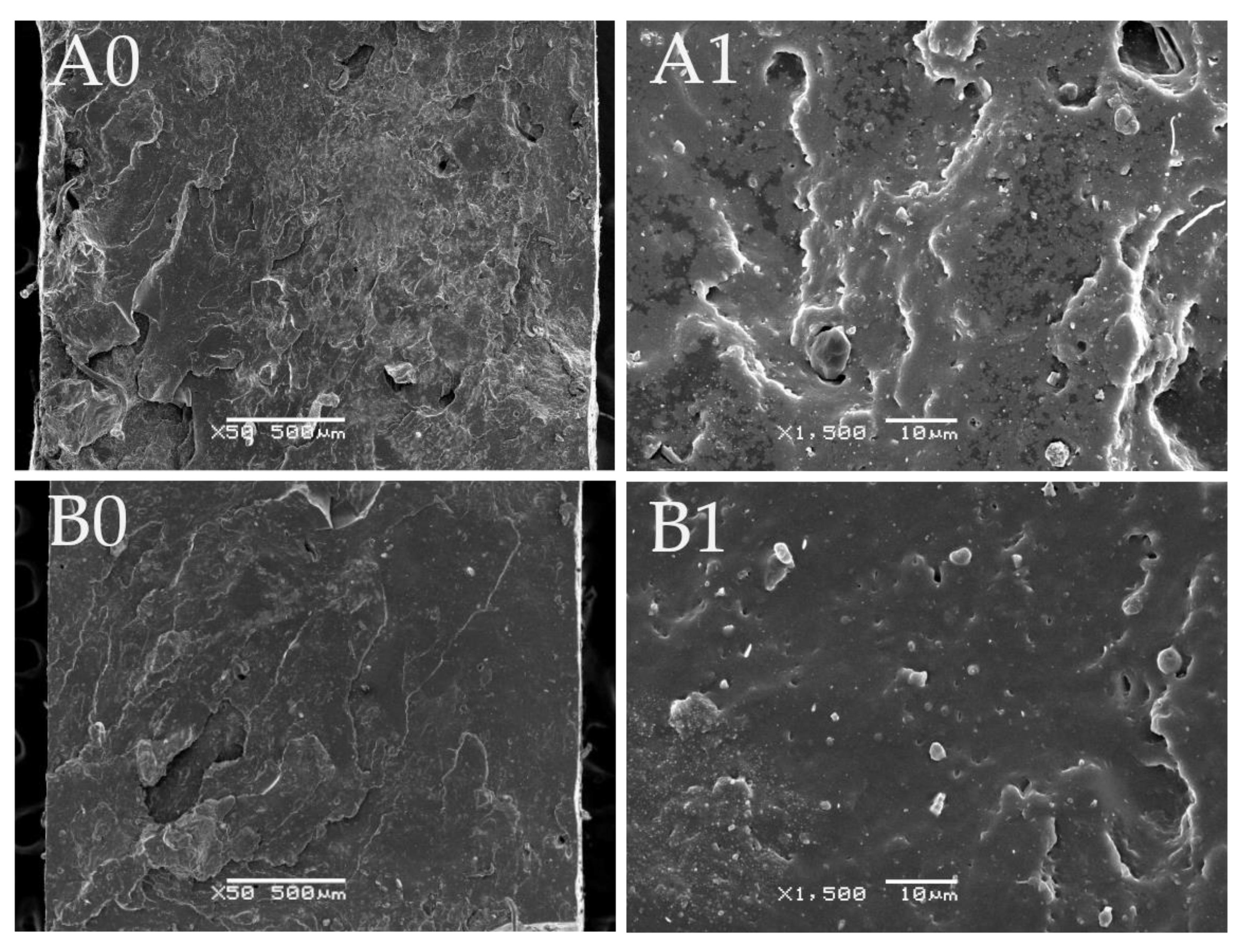
3.6. Microstructure of GTR Modified by SBS and Curing System
3.7. Thermal Stability of GTR Modified by SBS and Curing System
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://www.etrma.org/rubber-goods/ (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Fukumori, K.; Matsushita, M. Material recycling technology of crosslinked rubber waste. RD Rev. Toyota CRDL 2003, 38, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Valentini, F.; Pegoretti, A. End-of-life options of tyres. A review. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2022, 5, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Ding, Y.N.; Jalali, S. Properties and durability of concrete containing polymeric wastes (type rubber and polyethylene terephthalate bottles): An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Jiang, W.; Guo, R.; Huang, Y.; Pan, W. Thermogravimetric and kinetic analysis of co-combustion of waste tires and coal blends. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 5479–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Pramanik, A.; Basak, A.K.; Prakash, C.; Shankar, S. Material recovery and recycling of waste tyres-A review. Clean. Mater. 2022, 5, 100115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, M.; Rovira, J.; Díaz-Ferrero, J.; Schuhmacher, M.; Domingo, J.L. Human exposure to environmental pollutants after a tire landfill fire in Spain: Health risks. Environ. Int. 2016, 97, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudonytė-Svirbutavičienė, E.; Stakėnienė, R.; Jokšas, K.; Valiulis, D.; Byčenkienė, S.; Žarkov, A. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and heavy metals in soil following a large tire fire incident: A case study. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentes, D.; Tóth, C.E.; Nagy, G.; Muránszky, G.; Póliska, C. Investigation of gaseous and solid pollutants emitted from waste tire combustion at different temperatures. Waste Manag. 2022, 149, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.etrma.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/20210520_ETRMA_PRESS-RELEASE_ELT-2019.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Przydatek, G.; Budzik, G.; Janik, M. Effectiveness of selected issues related to used tyre management in Poland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 31467–31475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Koh, T.Y.; Ang, D.T.C. 4R of rubber waste management: Current and outlook. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo-Morera, J.; Verdejo, R.; López-Manchado, M.A.; Hernández Santana, M. Sustainable mobility: The route of tires through the circular economy model. Waste Manag. 2021, 126, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-M.; An, J.-Y.; Bang, D.; Kim, B.-S.; Oh, M.-H. Characteristics studies of waste tire rubber powders using the different grinding methods. J. Korean Inst. Resour. Recycl. 2014, 23, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, S.; Kroll, L.; Sykutera, D. Technology comparison for the production of fine rubber powder from end of life tyres. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 43, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formela, K. Sustainable development of waste tires recycling technologies—Recent advances, challenges and future trends. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2021, 4, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, M.M.; Phiri, M.J.; Formela, K.; Hlangothi, S.P. Chemical surface etching methods for ground tire rubber as sustainable approach for environmentally-friendly composites development—A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 204, 108429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.Q.; Thomas, B.S.; Zhang, W.; Ji, B.; Li, S.; Brand, A.S. A comprehensive review on treatment methods for end-of-life tire rubber used for rubberized cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 359, 129365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Internal de-crosslinking of scrap tire crumb rubber to improve compatibility of rubberized asphalt. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 32, e00417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archibong, F.N.; Sanusi, O.M.; Médéric, P.; Hocine, N.A. An overview on the recycling of waste ground tyre rubbers in thermoplastic matrices: Effect of added fillers. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 175, 105894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniewska, P.; Wang, S.; Formela, K. Waste tire rubber devulcanization technologies: State-of-the-art, limitations and future perspectives. Waste Manag. 2022, 150, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, D.A.; Bárány, T. Effective thermomechanical devulcanization of ground tire rubber with a co-rotating twin-screw extruder. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 190, 109626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunella, V.; Aresti, V.; Romagnolli, U.; Muscato, B.; Girotto, M.; Rizzi, P.; Luda, M.P. Recycling of EPDM via continuous thermo-mechanical devulcanization with co-rotating twin-Sscrew extruder. Polymers 2022, 14, 4853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innes, J.R.; Shriky, B.; Allan, S.; Wang, X.; Hebda, M.; Coates, P.; Whiteside, B.; Benkreira, H.; Caton-Rose, P.; Lu, C.H.; et al. Effect of solid-state shear milled natural rubber particle size on the processing and dynamic vulcanization of recycled waste into thermoplastic vulcanizates. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 32, e00424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrotă, D.; Dobrotă, G. An innovative method in the regeneration of waste rubber and the sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 3591–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.T.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, M. Process for Devulcanization of Rubber. U.S. Patent Application 2009/0082475A1, 26 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zedler, Ł.; Kowalkowska-Zedler, D.; Colom, X.; Cañavate, J.; Saeb, M.R.; Formela, K. Reactive sintering of ground tire rubber (GTR) modified by a trans-polyoctenamer rubber and curing additives. Polymers 2020, 12, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-K.; Rodrigue, D. Production of thermoplastic elastomers based on recycled PE and ground tire rubber: Morphology, mechanical properties and effect of compatibilizer addition. Int. Polym. Proc. 2018, 33, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.T.; dos Santos, R.E.; Pereira, J.S.; Barbosa, R.; Ambrósio, J.D. Characterization of waste tire rubber devulcanized in twin-screw extruder with thermoplastics. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2018, 34, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, R.; Ambrósio, J.D. Devulcanization of natural rubber compounds by extrusion using thermoplastics and characterization of revulcanized compounds. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedler, Ł.; Burger, P.; Wang, S.; Formela, K. Ground tire rubber modified by ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer: Processing, physico-mechanical properties, volatile organic compounds emission and recycling possibility. Materials 2020, 13, 4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y. Effects of high shear stress on the devulcanization of ground tire rubber in a twin-screw extruder. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 2307–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeb, M.R.; Wiśniewska, P.; Susik, A.; Zedler, Ł.; Vahabi, H.; Colom, X.; Cañavate, J.; Tercjak, A.; Formela, K. GTR/thermoplastics blends: How do interfacial interactions govern processing and physico-mechanical properties? Materials 2022, 15, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Rodrigue, D.; Wang, S. Compatibilized thermoplastic elastomers based on highly filled polyethylene with ground tire rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelescu, M.D.; Sonmez, M.; Alexandrescu, L.; Nituica, M.; Gurau, D.F.; Georgescu, M. Structure and properties of blends based on vulcanized rubber waste and styrene–butadiene–styrene thermoplastic elastomer. J. Rubber Res. 2022, 25, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y. Asphalt modified by thermoplastic elastomer based on recycled rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cui, C.; Temitope, A.A.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, G.; Guo, P. Effect of SBS and crumb rubber on asphalt modification: A review of the properties and practical application. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2022, 9, 836–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Hložeková, K.; Kvasničáková, A.; Tomanová, K.; Hudec, I. Application of sulfur and peroxide curing systems for cross-linking of rubber composites filled with calcium lignosulfonate. Polymers 2022, 14, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Kvasničáková, A.; Hudec, I. Peroxide curing systems applied for cross-linking of rubber compounds based on SBR. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2020, 3, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Sýkora, R.; Hudec, I. Sulphur and peroxide vulcanisation of rubber compounds—Overview. Chem. Pap. 2016, 70, 1533–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zhao, S.; Li, W.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, C. Microbial desulfurization of SBR ground rubber by Sphingomonas sp. and its utilization as filler in NR compounds. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2011, 22, 2344–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, L.; Mantovani, G.; deAzevedo, E.; Bonagamba, T.J.; Hage, E.; Pessan, L.A. Molecular characterization of styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymers (SBS) by GPC, NMR, and FTIR. Polym. Bull. 2006, 57, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Shao, H.; Yao, W.; Huang, B. Fourier transform infrared spectral analysis of polyisoprene of a different microstructure. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2013, 2013, 937284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, M.; Jayaramudu, J.; Suchismita, S.; Rajkumar, K.; Babul Reddy, A.; Sadiku, E.R.; Priti, R.; Maurya, D.J. A unique application of the second order derivative of FTIR–ATR spectra for compositional analyses of natural rubber and polychloroprene rubber and their blends. Polym. Test. 2017, 62, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.S.; de Sousa, F.D.B.; de Lima, J.A.; Cruz, S.A.; Scuracchio, C.H. Devulcanization of ground tire rubber: Physical and chemical changes after different microwave exposure times. Express Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluppel, M.; Schuster, R.H.; Schaper, J. Carbon black distribution in rubber blends: A dynamic-mechanical analysis. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1999, 72, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa, F.D.B.; Hu, G.-H.; Hoppe, S.; Scuracchio, C.H. Influence of devulcanization and revulcanization of ground tire rubber in dynamic mechanical properties of blends ground tire rubber/high density polyethylene. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2139, 090002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo-Morera, J.; Hernández Santana, M.; Verdejo, R.; López-Manchado, M.A. Giving a second opportunity to tire waste: An alternative path for the development of sustainable self-healing styrene–butadiene rubber compounds overcoming the magic triangle of tires. Polymers 2019, 11, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuracchio, C.H.; Waki, D.A.; da Silva, M.L.C.P. Thermal analysis of ground tire rubber devulcanized by microwaves. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 87, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Kandare, E.; Maniam, S.; Zhou, A.; Robert, D.; Buddhacosa, N.; Giustozzi, F. Thermal-based experimental method and kinetic model for predicting the composition of crumb rubber derived from end-of-life vehicle tyres. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 357, 132002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal Gisbert, A.; Crespo Amorós, J.E.; López Martínez, J.; Macias Garcia, A. Study of thermal degradation kinetics of elastomeric powder (ground tire rubber). Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2007, 47, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadrini, F.; Santo, L.; Musacchi, E. A sustainable molding process for new rubber products from tire recycling. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2019, 35, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.X.; Wei, Y.C.; Zhang, H.F.; Zheng, T.T.; Luo, M.C.; Liao, S. Effect of N, N′-m-phenylene bismaleimide on mechanical performance of waste rubber powder sintered by high-pressure high-temperature method. J. Rubber Res. 2020, 23, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedler, Ł.; Kowalkowska-Zedler, D.; Vahabi, H.; Saeb, M.R.; Colom, X.; Cañavate, J.; Wang, S.; Formela, K. Preliminary Investigation on Auto-Thermal Extrusion of Ground Tire Rubber. Materials 2019, 12, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, R.; Wang, Z. Reusing ground tire rubber powder as thermoplastic elastomers with excellent superhydrophobicity and self-cleaning performance. Prog. Rubber Plast. Recycl. Technol. 2021, 37, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zedler, Ł.; Colom, X.; Cañavate, J.; Saeb, M.R.; Haponiuk, J.T.; Formela, K. Investigating the impact of curing system on structure-property relationship of natural rubber modified with brewery by-product and ground tire rubber. Polymers 2020, 12, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, E.W.B. Processes of reclaiming rubber and their relative merits. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1944, 17, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahed, S.O.; Ansarifar, A.; Zohuri, G.; Ghaneie, N.; Kermany, Y. Devulcanization of ethylene-propylene-diene waste rubber by microwaves and chemical agents. J. Elastom. Plast. 2016, 48, 122–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, R.T.; Song, P.; Wang, S. Thermal analysis on the interactions among asphalt modified with SBS and different degraded tire rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 182, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Sýkora, R.; Hudec, I. Peroxide vulcanization of natural rubber. Part I: Effect of temperature and peroxide concentration. J. Polym. Eng. 2014, 34, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, A.; Zhou, T.; Cao, X.; Xie, Z. A study on thermal oxidation mechanism of styrene–butadiene–styrene block copolymer (SBS). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1682–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Reinforcement of styrene–butadiene–styrene tri-block copolymer by multi-walled carbon nanotubes via melt mixing. Carbon 2007, 45, 2621–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-C.; McCoy, B.J. Degradation kinetics enhancement of polystyrene by peroxide addition. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 2811–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item | SBS L7322 | SBS L7342 | SBS L7417 | SBS R 7382 | GTR +10 wt% SBS L7322 | GTR +10 wt% SBS L7417 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFR200 °C/5 kg (g/10 min) | 4.2 ± 0.1 | -* | 23.9 ± 0.1 | -* | -** | -** |
| Appearance of the sample after test |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Observations | good flowability, transparent | poor flowability, yellowish, partial degradation | good flowability, transparent | poor flowability, yellowish, partial degradation | poor flowability | poor flowability |
| Sample Coding | Mooney Viscosity ML(1 + 4) 100 °C | ML (dNm) | MH (dNm) | ΔM (dNm) | ts2 (min) | t90 (min) | CRI (min−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTR + 10 wt% SBS L7417-S | 94.6 | 1.3 | 12.1 | 10.8 | 0.6 | 1.7 | 93.5 |
| GTR + 10 wt% SBS L7417-DCP | 87.1 | 1.5 | 15.0 | 13.5 | 0.9 | 9.7 | 11.4 |
| GTR + 30 wt% SBS L7417-S | 93.8 | 0.7 | 4.6 | 3.9 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 125.0 |
| GTR + 30 wt% SBS L7417-DCP | 77.5 | 0.9 | 14.3 | 13.5 | 0.8 | 8.7 | 12.7 |
| Sample Coding | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Hardness (Shore A) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTR + 10 wt% SBS L7417-S | 7.3 ± 0.6 | 171 ± 15 | 61 ± 2 | 1.169 ± 0.004 |
| GTR + 10 wt% SBS L7417-DCP | 7.8 ± 0.2 | 190 ± 8 | 59 ± 1 | 1.133 ± 0.001 |
| GTR + 30 wt% SBS L7417-S | 7.6 ± 0.8 | 217 ± 23 | 67 ± 1 | 1.126 ± 0.005 |
| GTR + 30 wt% SBS L7417-DCP | 8.1 ± 0.3 | 202 ± 10 | 65 ± 2 | 1.077 ± 0.002 |
| Sample Coding | Thermal Decomposition Temperature (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T−2% | T−5% | T−10% | T−50% | |
| SBS L7417 | 350.6 | 379.2 | 398.4 | 454.9 |
| GTR | 244.1 | 264.8 | 293.9 | 482.7 |
| GTR + 10 wt% SBS L7417-S | 255.9 | 314.4 | 365.5 | 458.2 |
| GTR + 10 wt% SBS L7417-DCP | 184.4 | 277.6 | 344.4 | 458.7 |
| GTR + 30 wt% SBS L7417-S | 253.3 | 317.0 | 365.7 | 457.9 |
| GTR + 30 wt% SBS L7417-DCP | 240.0 | 312.1 | 363.5 | 459.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Susik, A.; Rodak, A.; Cañavate, J.; Colom, X.; Wang, S.; Formela, K. Processing, Mechanical and Morphological Properties of GTR Modified by SBS Copolymers. Materials 2023, 16, 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051788
Susik A, Rodak A, Cañavate J, Colom X, Wang S, Formela K. Processing, Mechanical and Morphological Properties of GTR Modified by SBS Copolymers. Materials. 2023; 16(5):1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051788
Chicago/Turabian StyleSusik, Agnieszka, Agata Rodak, Javier Cañavate, Xavier Colom, Shifeng Wang, and Krzysztof Formela. 2023. "Processing, Mechanical and Morphological Properties of GTR Modified by SBS Copolymers" Materials 16, no. 5: 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051788
APA StyleSusik, A., Rodak, A., Cañavate, J., Colom, X., Wang, S., & Formela, K. (2023). Processing, Mechanical and Morphological Properties of GTR Modified by SBS Copolymers. Materials, 16(5), 1788. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051788








