Adsorptive Removal of Rhodamine B Dye Using Carbon Graphite/CNT Composites as Adsorbents: Kinetics, Isotherms and Thermodynamic Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Adsorption Experiments
3. Results
3.1. Kinetics Study
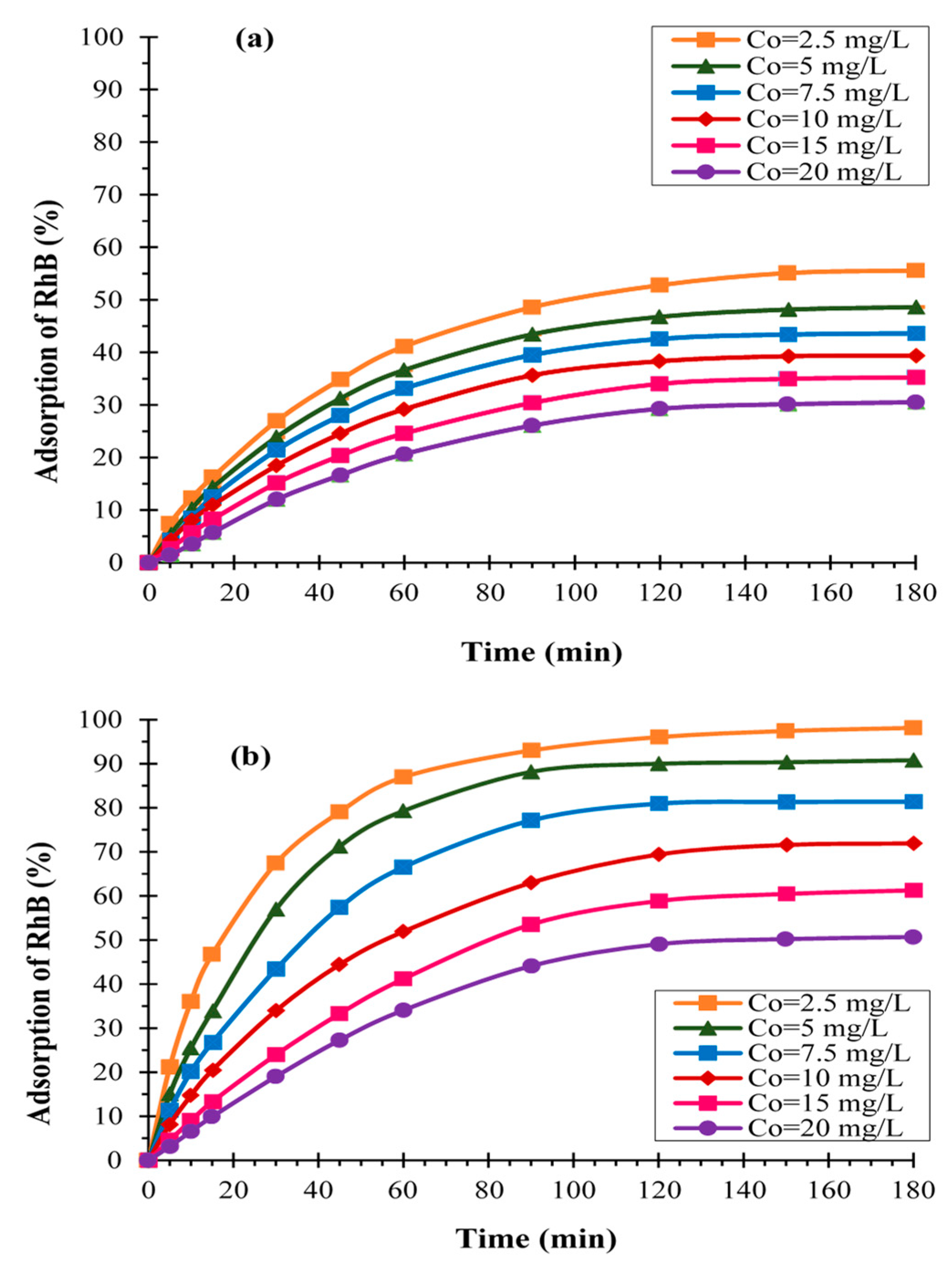
3.1.1. Effect of Initial Dye Concentration
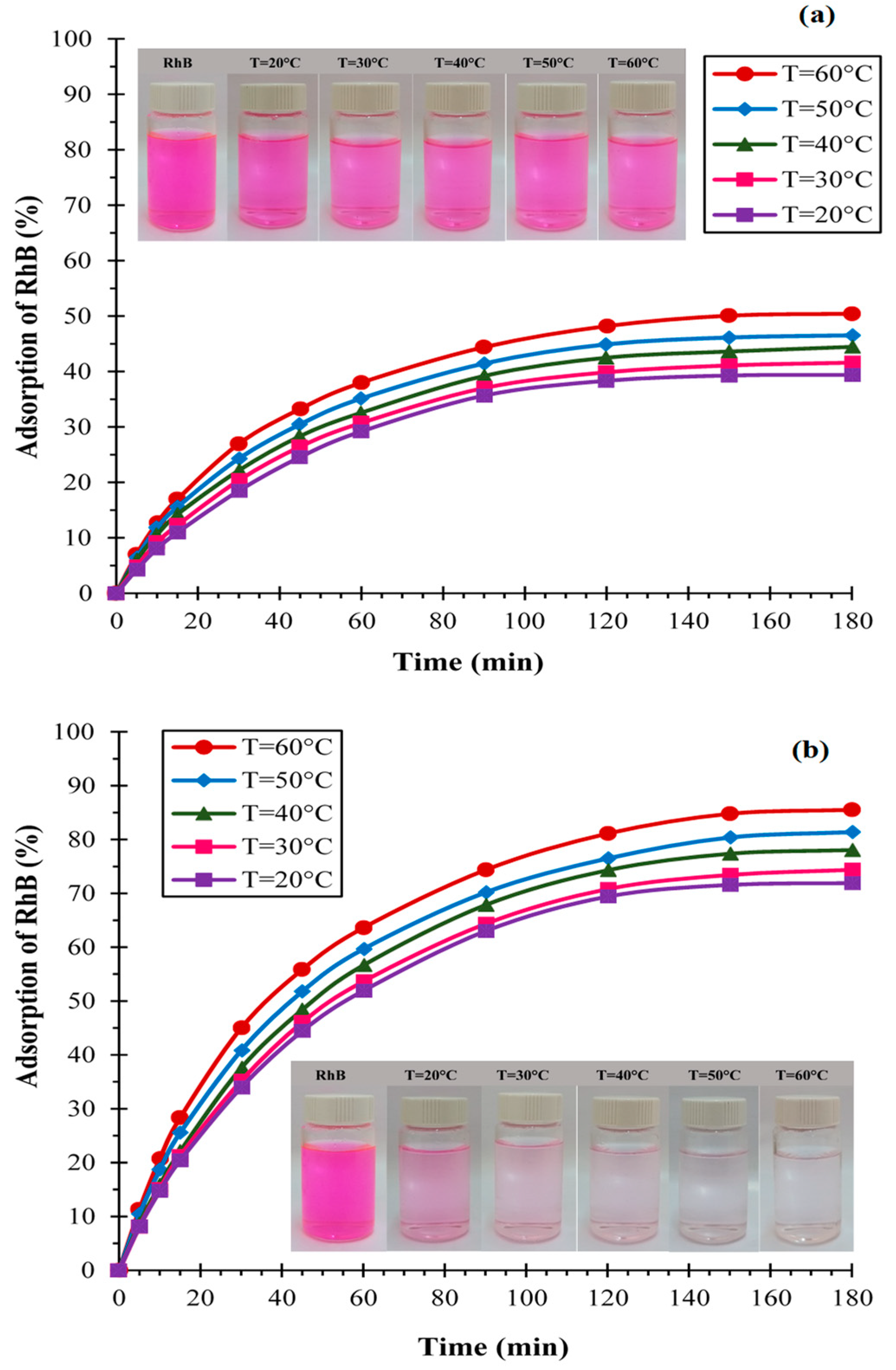
3.1.2. Effect of Temperature
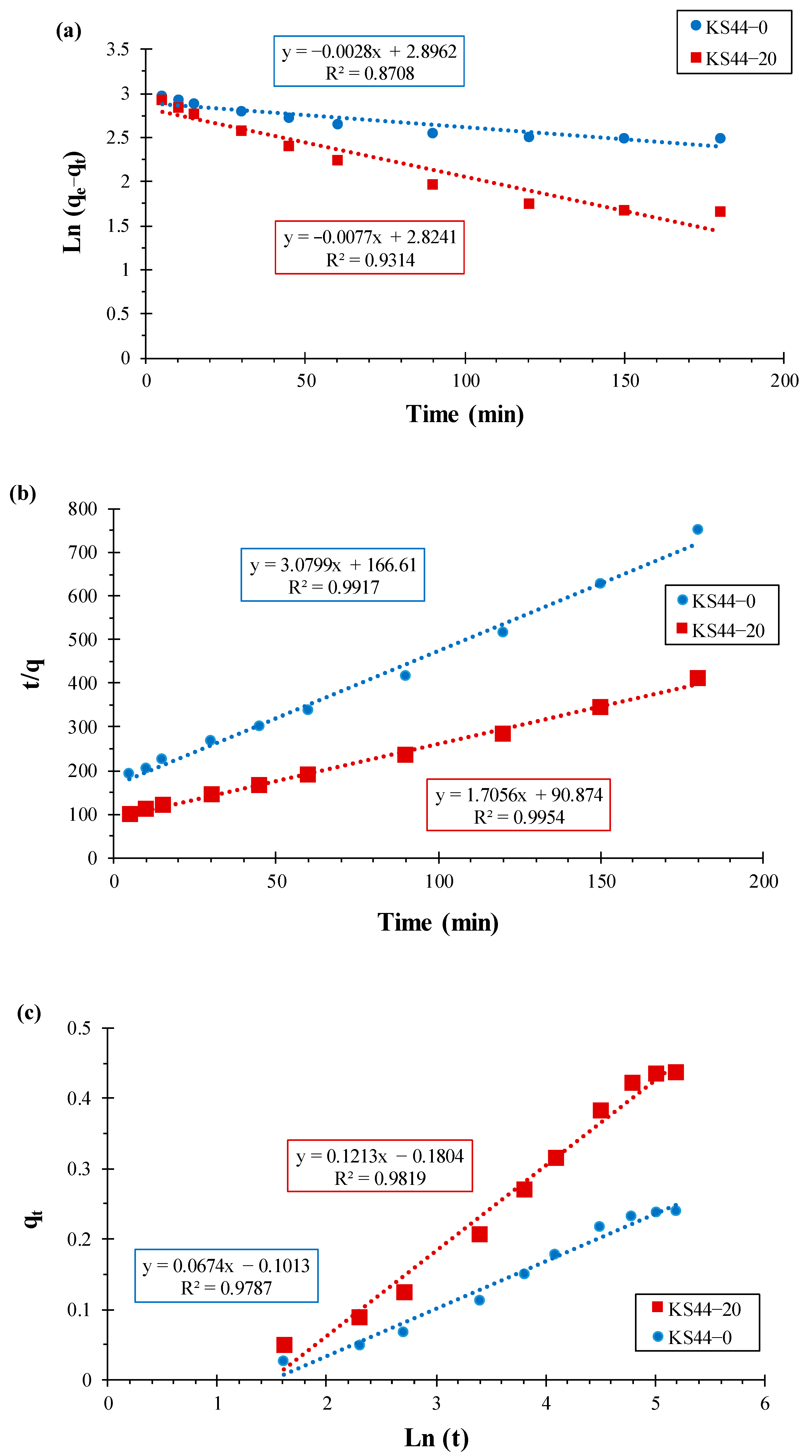
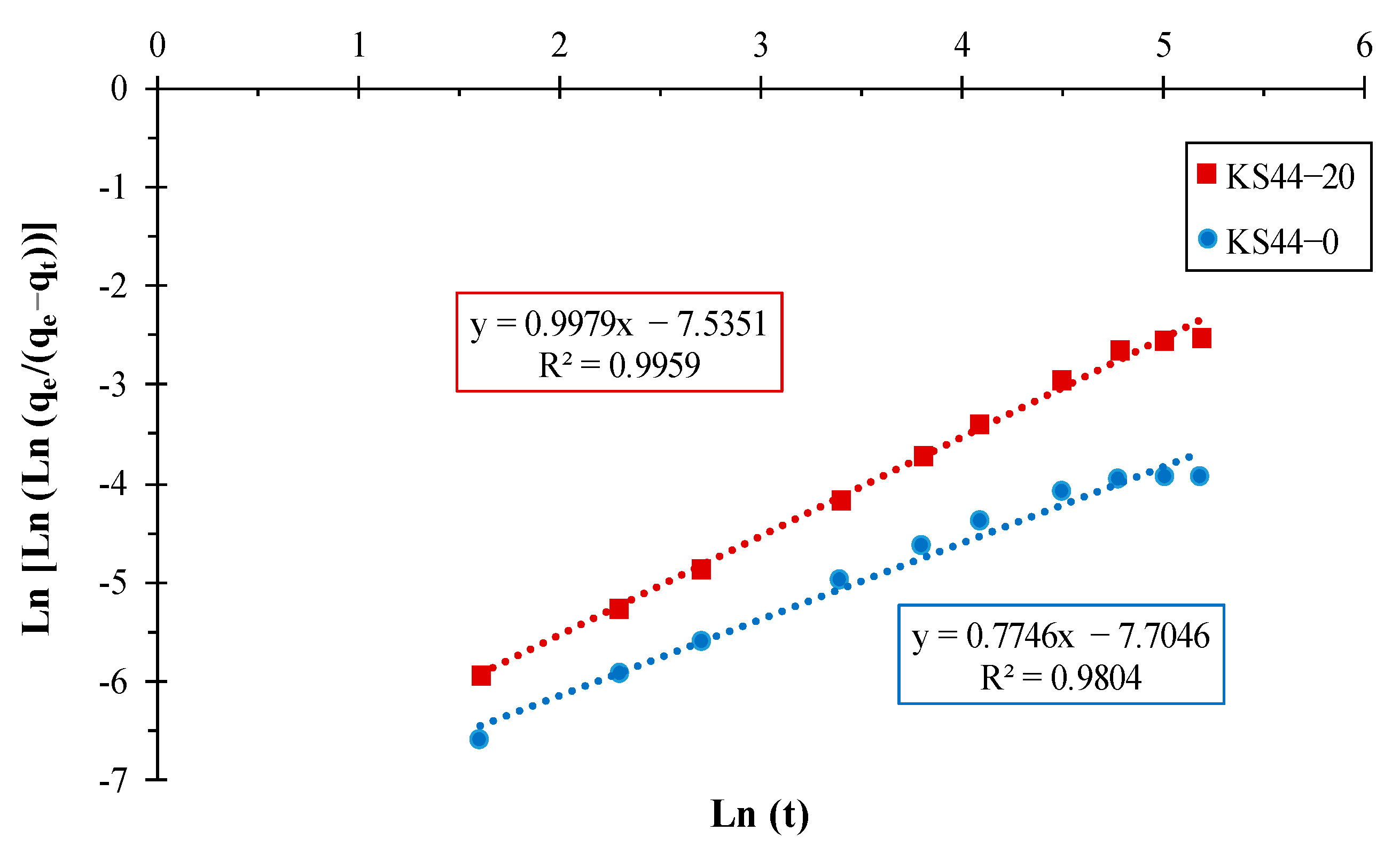
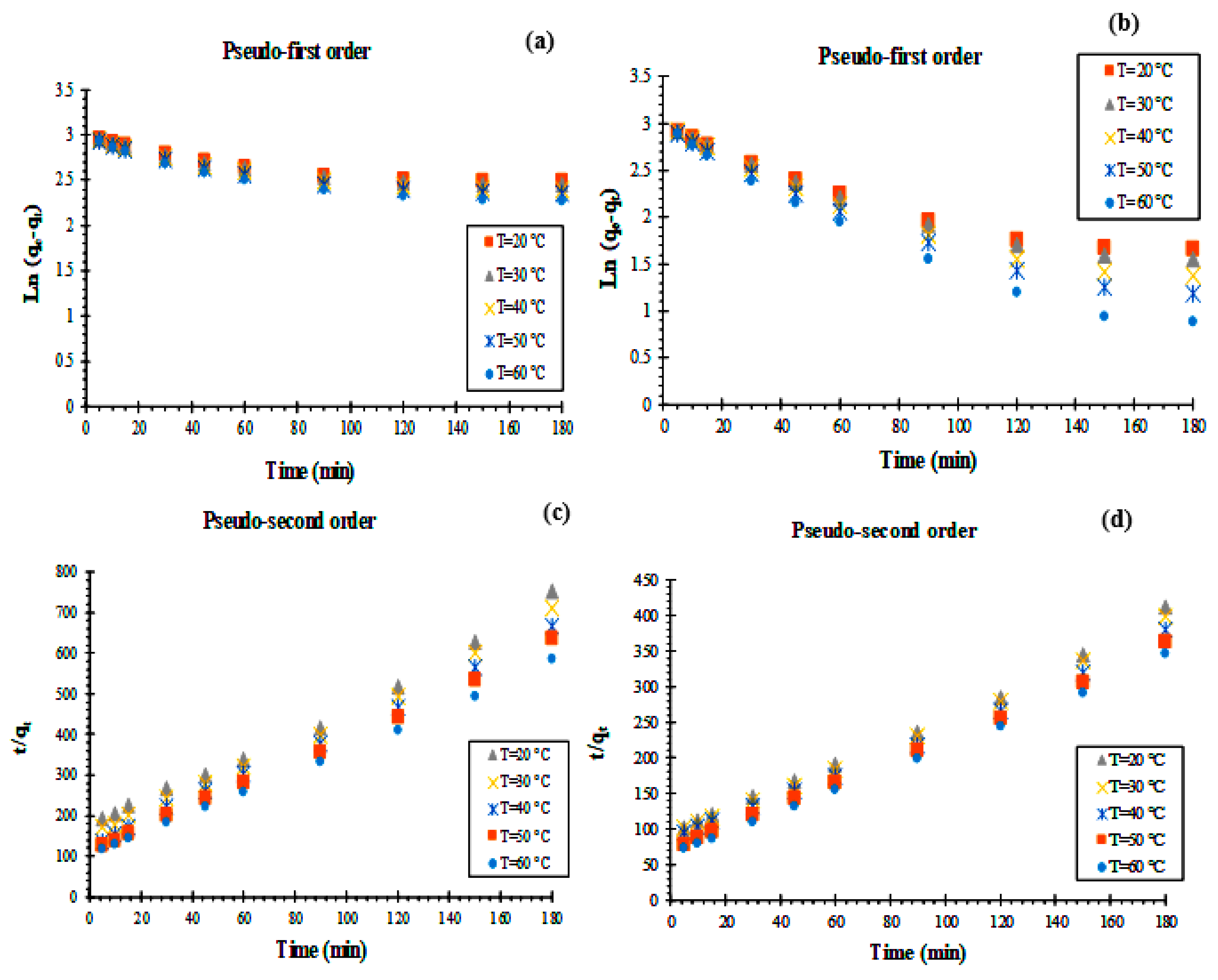
3.1.3. Adsorption Kinetics
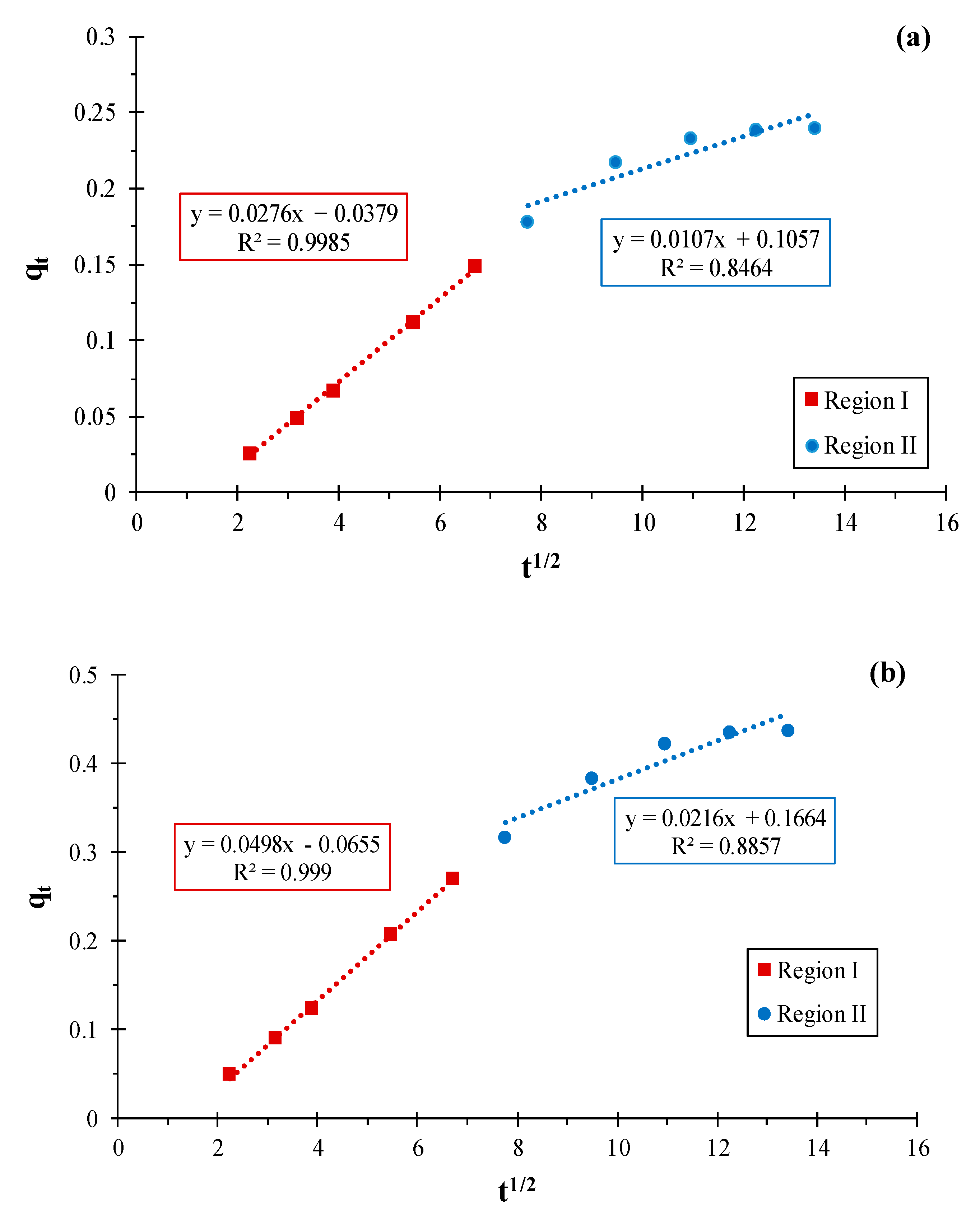
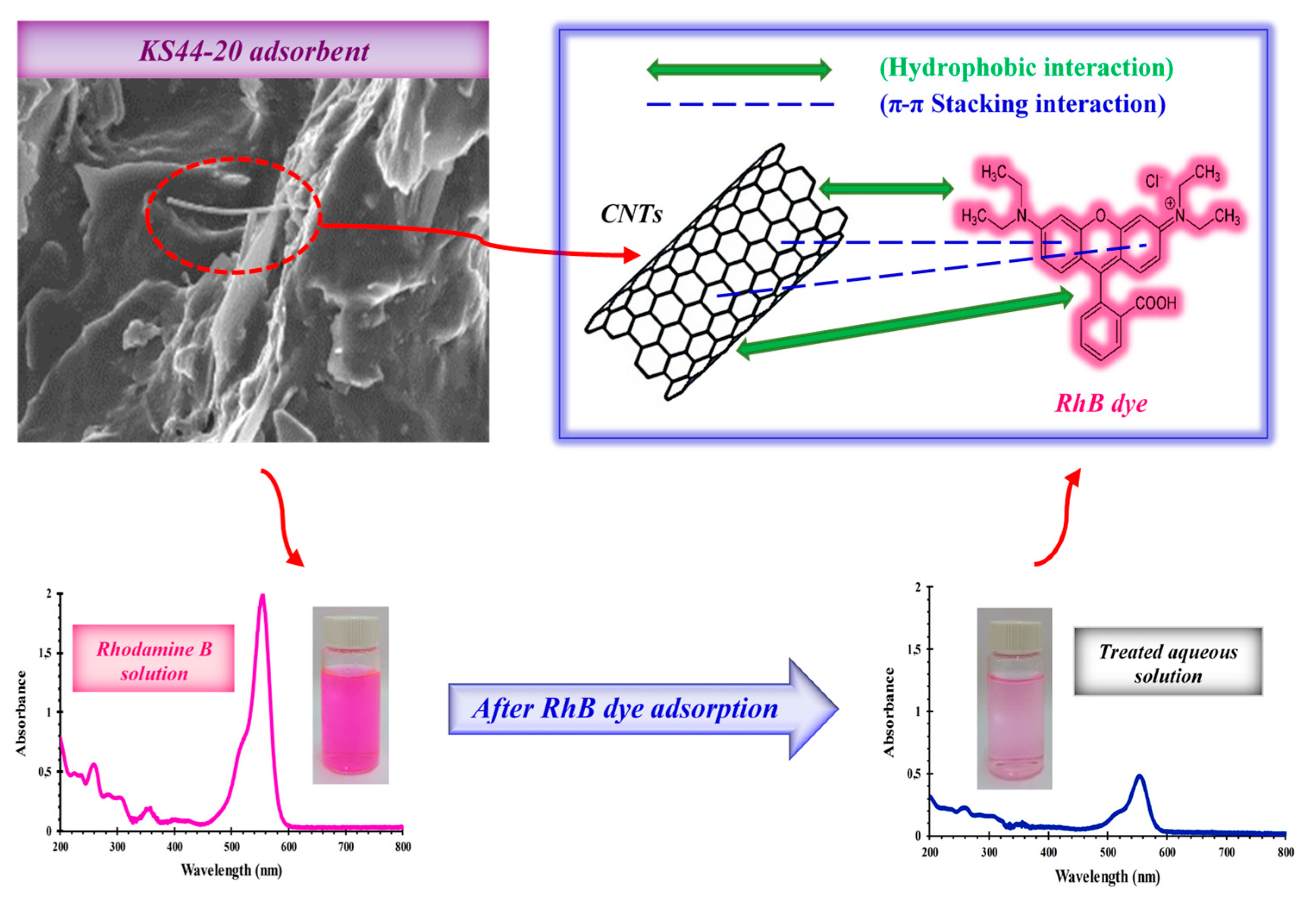
3.1.4. Adsorption Mechanism
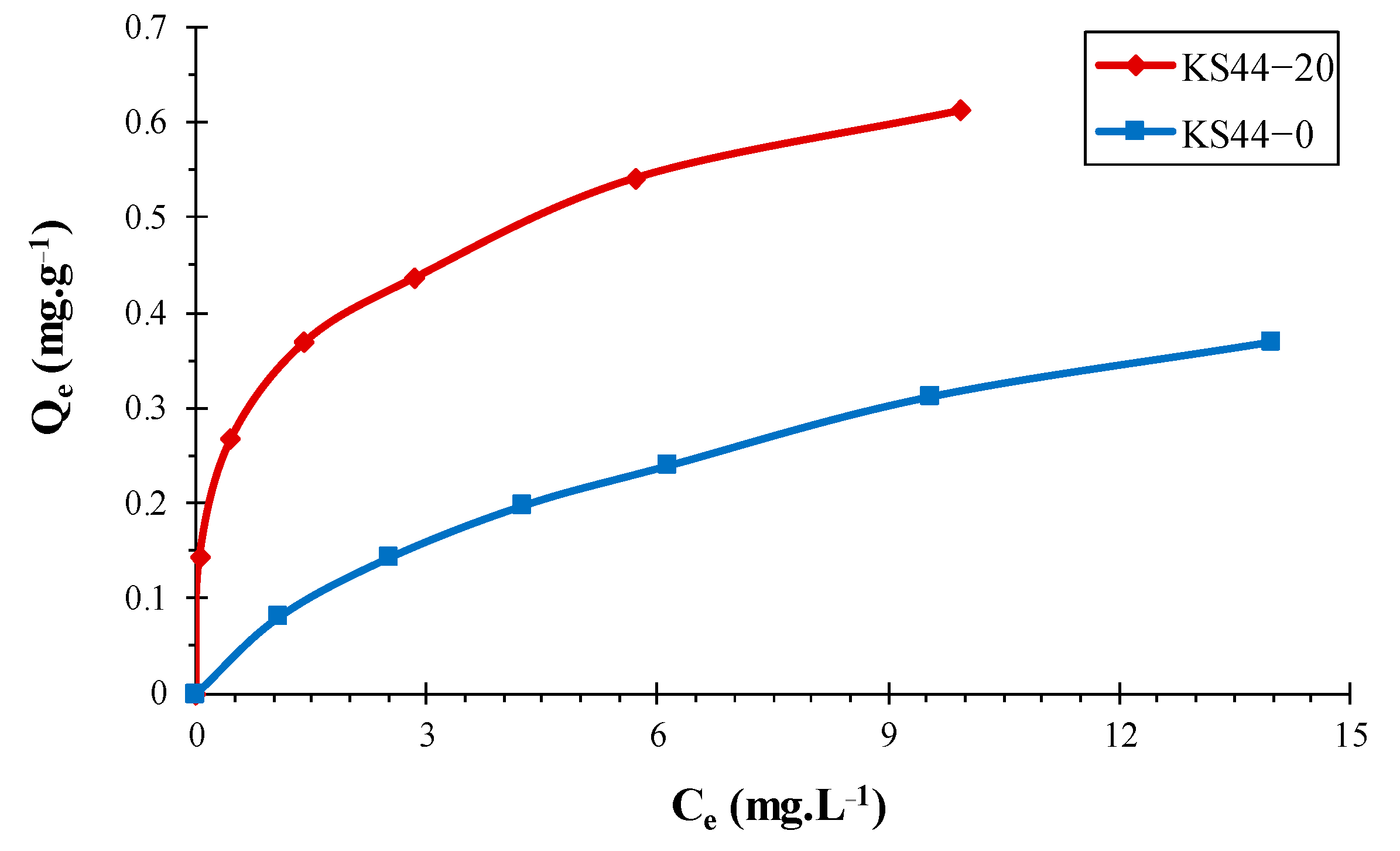
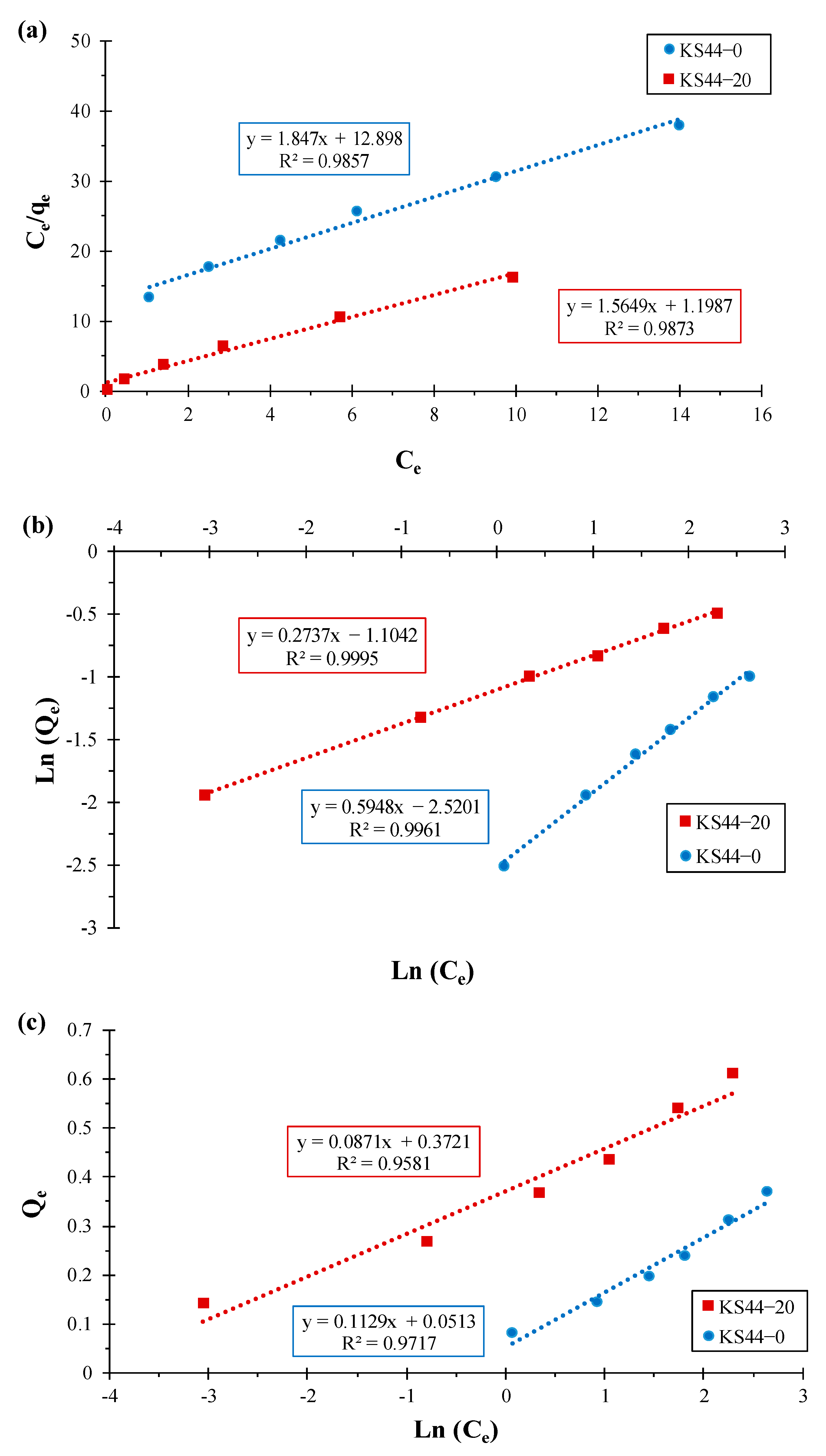
3.2. Adsorption Isotherm Study
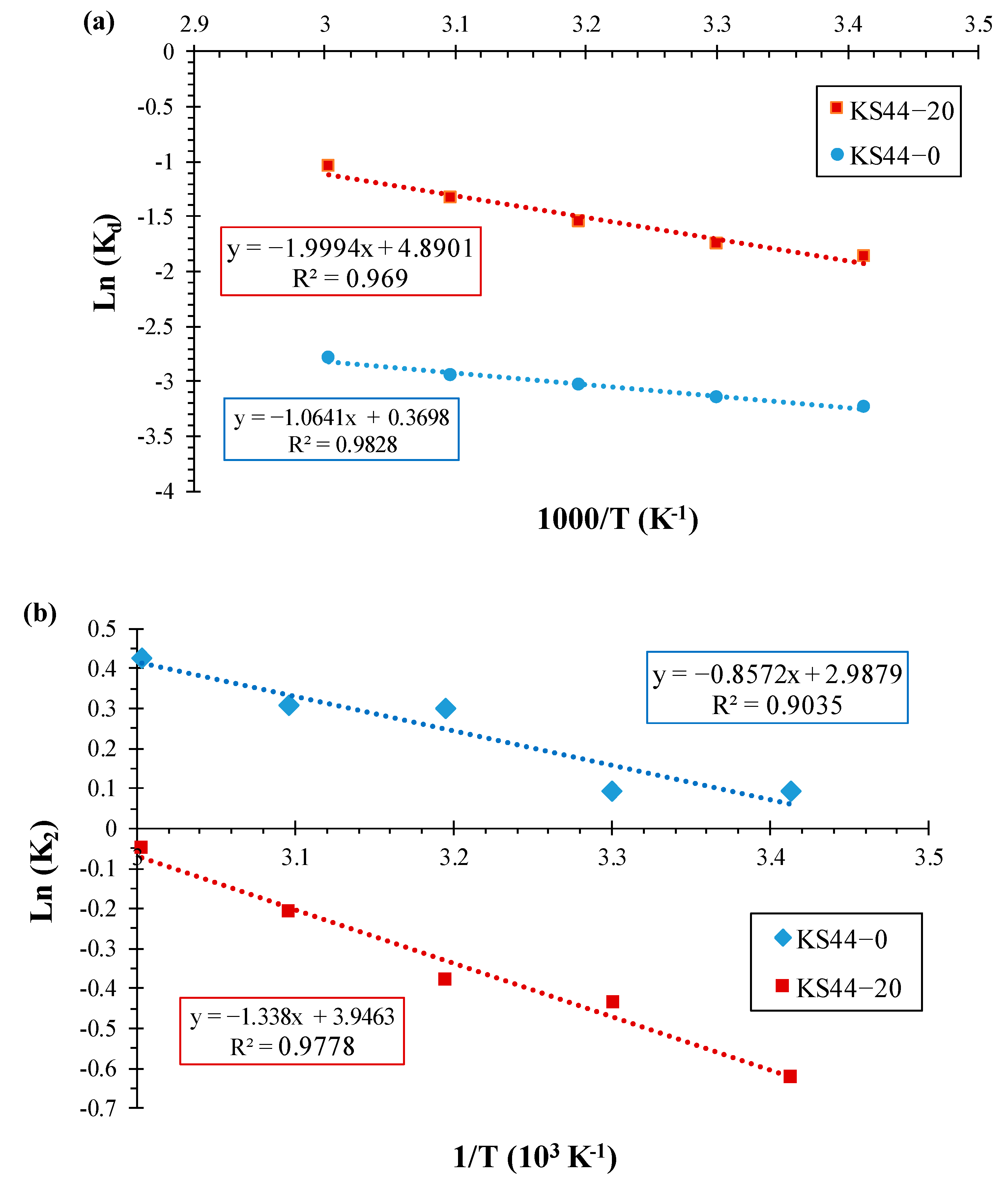
3.3. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.4. Comparison of Performances with Other Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pagga, U.; Brown, D. The degradation of dyestuffs. Part II. Behavior of dyestuffs in aerobic biodegradation tests. Chemosphere 1986, 15, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chequer, F.D.; De Oliveira, G.R.; Ferraz, E.A.; Cardoso, J.C.; Zanoni, M.B.; De Oliveira, D.P. Textile dyes: Dyeing process and environmental impact. Eco-Friendly Text. Dye. Finish. 2013, 6, 151–176. [Google Scholar]
- DEPA (Danish Environmental Protection Agency). Toxicity and Fate of Azo Dyes. In Survey of Azo-Colorants in Denmark; DEPA: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Khadhraoui, M.; Trabelsi, H.; Ksibi, M.; Bouguerra, S.; Elleuch, B. Discoloration and detoxicification of a Congo red dye solution by means of ozone treatment for a possible water reuse. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolrahimi, N.; Tadjarodi, A. Adsorption of rhodamine-B from aqueous solution by activated carbon from almond shell. Proceedings 2019, 41, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, M.; Hassani, A.J.; Mohamed, A.R.; Najafpour, G.D. Removal of rhodamine B from aqueous solution using palm shell-based activated carbon: Adsorption and kinetic studies. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2010, 55, 5777–5785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyinbor, A.A.; Adekola, F.A.; Olatunji, G.A. Adsorption of Rhodamine B dye from aqueous solution on Irvingia gabonensis biomass: Kinetics and thermodynamics studies. S. Afr. J. Chem. 2015, 68, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayeeye, F.; Sattar, M.; Tekasakul, S.; Sirichote, O. Adsorption of Rhodamine B on activated carbon obtained from pericarp of rubber fruit in comparison with the commercial activated carbon. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2014, 36, 177–187. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesan, P.; Kamaraj, R.; Sozhan, G.; Vasudevan, S. Oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes as adsorbent for the removal of manganese from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.R.; Vasudevan, S.; Shibayama, A.; Yamada, M. Graphene and graphene-based composites: A rising star in water purification-a comprehensive overview. Chem. Select. 2016, 1, 4358–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zghal, S.; Jedidi, I.; Cretin, M.; Cerneaux, S.; Abdelmouleh, M. One-step synthesis of highly porous carbon graphite/carbon nanotubes composite by in-situ growth of carbon nanotubes for the removal of humic acid and copper (II) from wastewater. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2020, 101, 107557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zghal, S.; Jedidi, I.; Cretin, M.; Cerneaux, S.; Cot, D.; Lagerge, S.; Deabate, S.; Abdelmouleh, M. Electroactive adsorbent composites of porous graphite carbon/carbon nanotube for highly efficient organic dye removal. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 2239–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, R.; Khan, M.; Rehman, R.U.; Shujah, S.; Khan, M.; Ullah, M.; Zada, A.; Mahmood, N.; Ahmad, I. Adsorption of selected azo dyes from an aqueous solution by activated carbon derived from Monotheca buxifolia waste seeds. Soil Water Res. 2020, 15, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.W.; Lee, E.J.; Yoon, C.S.; Myung, S.T.; Sun, Y.K. Optimization of layered cathode material with full concentration gradient for lithium-ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, J.; Kumar, U.; Meikap, B.C. Thermodynamic characterization of adsorption of lead (II) ions on activated carbon developed from tamarind wood from aqueous solution. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 18, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X. Modeling of experimental adsorption isotherm data. Information 2015, 6, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, S.; Lakshmi, J. Electrochemical removal of boron from water: Adsorption and thermodynamic studies. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 90, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Qu, H.; Shao, R.; Wang, Q.; Xie, H. Mechanism and kinetics of dye desorption from dye-loaded carbon (XC-72) with alcohol-water system as desorbent. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, R.; Vasudevan, S. Facile one-pot electrosynthesis of Al (OH)3– kinetics and equilibrium modeling for adsorption of 2, 4, 5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid from aqueous solution. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 2249–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, R.; Davidson, D.J.; Sozhan, G.; Vasudevan, S. Adsorption of herbicide 2-(2, 4-dichlorophenoxy) propanoic acid by electrochemically generated aluminum hydroxides: An alternative to chemical dosing. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 39799–39809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, R.; Pandiarajan, A.; Gandhi, M.R.; Shibayama, A.; Vasudevan, S. Eco–friendly and easily prepared graphenenanosheets for safe drinking water: Removal of chlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicides. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Tseng, R.L.; Juang, R.S. Initial behavior of intraparticle diffusion model used in the description of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 153, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyinbor, A.A.; Adekola, F.A.; Olatunji, G.A. Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic modeling of liquid phase adsorption of Rhodamine B dye onto Raphia hookerie fruit epicarp. Water Resour. Ind. 2016, 15, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahir, A.; Aslam, Z.; Aslam, U.; Abdullah, A.; Ali, R.; Bello, M.M. Paspalum notatum grass-waste-based adsorbent for rhodamine B removal from polluted water. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2020, 34, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljebori, A.M.K.; Alshirifi, A.N. Effect of different parameters on the adsorption of textile dye maxilon blue GRL from aqueous solution by using white marble. Asian J. Chem. 2012, 24, 5813. [Google Scholar]
- Dridi, C.; Youcef, L. Removal of lead by adsorption on kaolin. Larhyss J. 2016, 27, 7–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, A.; Malviya, A.; Kaur, D.; Mittal, J.; Kurup, L. Studies on the adsorption kinetics and isotherms for the removal and recovery of Methyl Orange from wastewaters using waste materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postai, D.L.; Demarchi, C.A.; Zanatta, F.; Melo, D.C.C.; Rodrigues, C.A. Adsorption of rhodamine B and methylene blue dyes using waste of seeds of Aleurites Moluccana, a low cost adsorbent. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, R.; Saadi, Z.; Fazaeli, R.; Fard, N.E. Monolayer and multilayer adsorption isotherm models for sorption from aqueous media. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanov, L.N. Kinetic equations of non-localized physical adsorption in vacuum for Freundlich adsorption isotherm. Vacuum 2021, 189, 110267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Nazir, R.; Khan, M.; Khan, W.; Shah, M.; Afridi, S.G.; Zada, A. The effective removal of heavy metals from water by activated carbon adsorbents of Albizia lebbeck and Melia azedarach seed shells. Soil Water Res. 2020, 15, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberty, R.A. Standard Gibbs free energy, enthalpy, and entropy changes as a function of pH and pMg for several reactions involving adenosine phosphates. J. Boil. Chem. 1969, 244, 3290–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimaitiniyazi, R.; Zhou, X. Comment on the calculation of equilibrium constant and thermodynamic parameters by the distribution coefficient in Environmental Research 203 2022 111814. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, S.; Sheela, S.M.; Lakshmi, J.; Sozhan, G. Optimization of the process parameters for the removal of boron from drinking water by electrocoagulation-a clean technology. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Gomes, A.A.; Tran, H.N. Comparison of the nonlinear and linear forms of the van’t Hoff equation for calculation of adsorption thermodynamic parameters (∆S° and ∆H°). J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 311, 113315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Lima, E.C.; Juang, R.S.; Bollinger, J.C.; Chao, H.P. Thermodynamic parameters of liquid–phase adsorption process calculated from different equilibrium constants related to adsorption isotherms: A comparison study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, R.; Pandiarajan, A.; Jayakiruba, S.; Naushad, M.; Vasudevan, S. Kinetics, thermodynamics and isotherm modeling for removal of nitrate from liquids by facile one-pot electrosynthesized nano zinc hydroxide. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 215, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidler, K.J. The development of the Arrhenius equation. J. Chem. Educ. 1984, 61, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzas, G.Z.; McKay, G.; Al-Musawi, T.J.; Salehi, S.; Balarak, D. Removal of Benzene and Toluene from Synthetic Wastewater by Adsorption onto Magnetic Zeolitic Imidazole Framework Nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, P.; Chowdhury, S. Insight into adsorption thermodynamics. Thermodynamics 2011, 16, 349–364. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, S.; Mishra, R.; Kushwaha, P.; Saha, P. Removal of safranin from aqueous solutions by NaOH-treated rice husk: Thermodynamics, kinetics and isosteric heat of adsorption. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 7, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoh, B.S.; Christopher, W. Adsorption of metal ions from carwash wastewater by phosphoric acid modified clay: Kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Adsorption 2015, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; El-Halwany, M.M. Adsorption of cadmium onto orange peels: Isotherms, kinetics, and thermodynamics. J. Chromatogr. Sep. Tech. 2014, 5, 1000238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulczycki, A.; Kajdas, C. A new attempt to better understand Arrehnius equation and its activation energy. In Tribology in Engineering; 2013; pp. 47–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kalaivanan, R.; Ganesh, N.V.; Al-Mdallal, Q.M. An investigation on Arrhenius activation energy of second grade nanofluid flow with active and passive control of nanomaterials. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2020, 22, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.A. Kinetics and thermodynamics of aluminum oxide nanopowder as adsorbent for Fe (III) from aqueous solution. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 4, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhayem, M.; Gaith, R.; Otman, O.E.; Frage, M.U. Adsorption, kinetic and thermodynamic study for removal of nickel ions by activated carbon from palm kernel. Iran. J. Energy Environ. 2020, 11, 339–350. [Google Scholar]
- Nnaji, C.C.; Agim, A.E.; Mama, C.N.; Emenike, P.C.; Ogarekpe, N.M. Equilibrium and thermodynamic investigation of biosorption of nickel from water by activated carbon made from palm kernel chaff. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harby, N.F.; Albahly, E.F.; Mohamed, N.A. Kinetics, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Studies for Efficient Adsorption of Congo Red Dye from Aqueous Solution onto Novel Cyanoguanidine-Modified Chitosan Adsorbent. Polymers 2021, 13, 4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, N.; Selimi, T.; Mele, A.; Thaçi, V.; Halili, J.; Berisha, A.; Sadiku, M. Theoretical, Equilibrium, Kinetics and Thermodynamic Investigations of Methylene Blue Adsorption onto Lignite Coal. Molecules 2022, 27, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantu, Y.; Remes, A.; Reyna, A.; Martinez, D.; Villarreal, J.; Ramos, H.; Trevino, S.; Tamez, C.; Martinez, A.; Eubanks, T. Thermodynamics, kinetics, and activation energy studies of the sorption of chromium (III) and chromium (VI) to a Mn3O4 nanomaterial. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.A.; Maschio, L.J.; Evangelista da Silva, R.; Pinto da Silva, M.L.C. Adsorption of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution by hydrous zirconium oxide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musorrafiti, M.J.; Konek, C.T.; Hayes, P.L.; Geiger, F.M. Interaction of Chromium(VI) with the α-Aluminum Oxide-Water Interface. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2008, 112, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boparai, H.K.; Joseph, M.; O’Carroll, D.M. Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nanozerovalent iron particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xue, Z.; Yao, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, F.; Hong, C. Oxidation degradation of rhodamine B in aqueous by treatment system. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rabti, A.; Hannachi, A.; Maghraoui-Meherzi, H.; Raouafi, N. Ferrocene-functionalized carbon nanotubes: An adsorbent for Rhodamine B. Chem. Afr. 2019, 2, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, B.; Kim, G.; Yoon, H.K.; Park, J.B.; Kopelman, R.; Cheng, W. Fluorophore and dye-assisted dispersion of carbon nanotubes in aqueous solution. Langmuir 2012, 28, 11676–11686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournus, F.; Latil, S.; Heggie, M.I.; Charlier, J.C. π-stacking interaction between carbon nanotubes and organic molecules. Phys. Rev. B. 2005, 72, 075431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, K.; Lu, N.; Yuan, X. Simultaneous determination of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol and pentachlorophenol based on poly (Rhodamine B)/graphene oxide/multiwalled carbon nanotubes composite film modified electrode. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 361, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.S.; Ahmad, M.A. Adsorptive removal of a synthetic textile dye using cocoa podhusks. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2011, 93, 1298–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.S.; Alabi, E.O.; Adegoke, K.A.; Adegboyega, S.A.; Inyinbor, A.A.; Dada, A.O. Rhodamine B dye sequestration using Gmelina aborea leaf powder. Heliyon 2020, 6, e02872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, O.S.; Adegoke, K.A.; Inyinbor, A.A.; Dada, A.O. Trapping Rhodamine B dye using functionalized mango (Mangifera indica) pod. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 2308–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojemaye, M.O.; Okoh, A.I. Multiple nitrogen functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as an efficient adsorbent: Synthesis, kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamic studies for the removal of rhodamine B from aqueous solution. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Shahzad, R.; Asim, S.; BiBi, S.; Iqbal, J.; Muhammad, N.; Sillanpaa, M.; Din, I.U. Experimental and theoretical studies of Rhodamine B direct dye sorption onto clay-cellulose composite. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 328, 115165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Ali, I.; Singh, V.V.; Sharma, S. Utilization of fly ash as low-cost adsorbent for the removal of methylene blue, malachite green and rhodamine B dyes from textile wastewater. J. Environ. Prot. Sci. 2009, 3, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sahara, J.; Naeem, A.; Farooq, M.; Zareen, S.; Rahman, A.U. Thermodynamic studies of adsorption of rhodamine B and Congo red on graphene oxide. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 164, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bhanjana, G.; Jangra, K.; Dilbaghi, N.; Umar, A. Utilization of carbon nanotubes for the removal of rhodamine B dye from aqueous solutions. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 4331–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
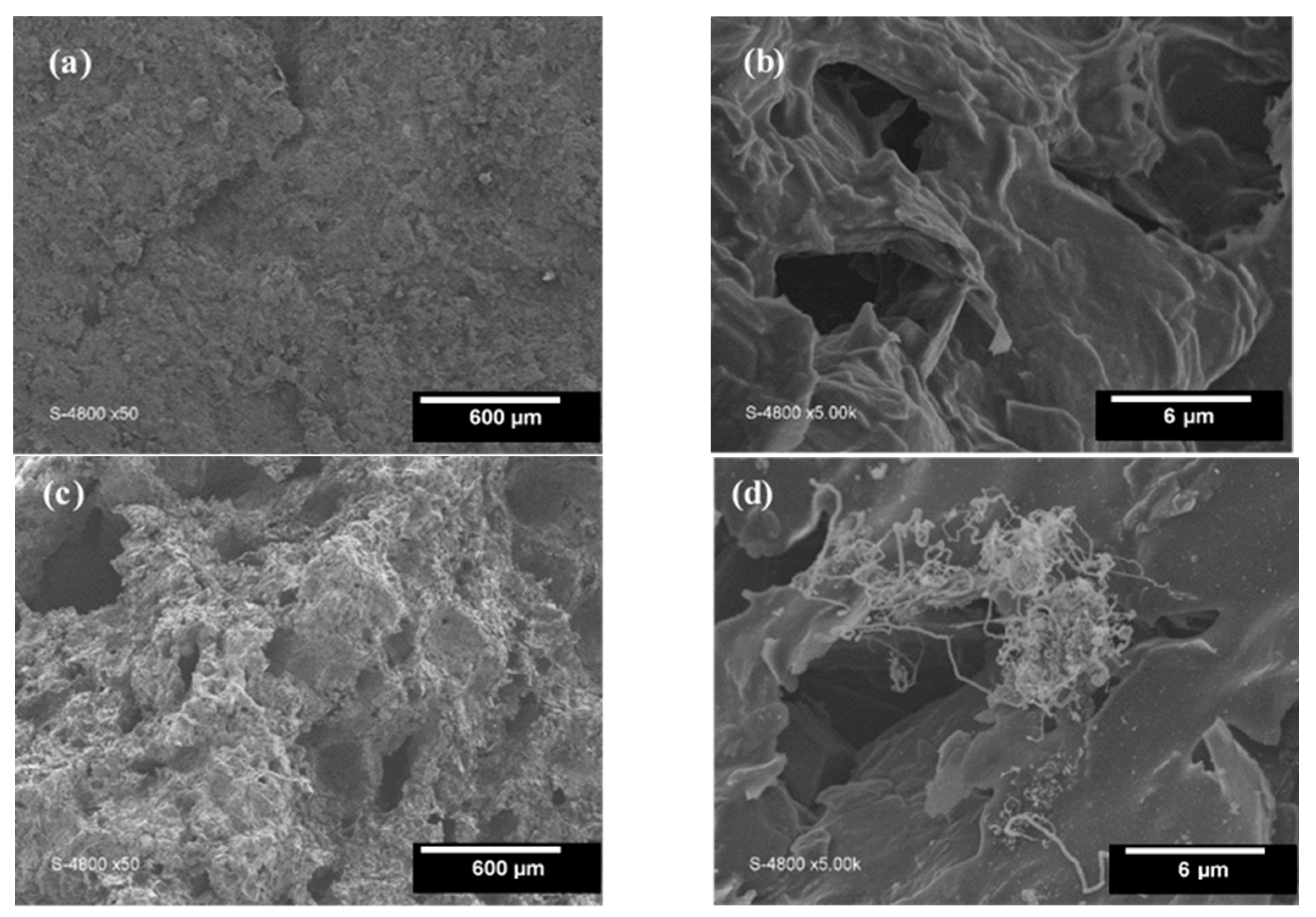
| Composites | Porosity (%) | Average Pore Diameter (4 V/A) (nm) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| KS44-0 | 45.65 | 102.20 | 85.67 |
| KS44-20 | 52.08 | 150.20 | 131.47 |
| Composite | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | Elovich | qe (exp) (mg.g−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (min−1) | qe (cal) (mg.g−1) | R2 | k2 (g.mg−1.min−1) | qe (cal) (mg.g−1) | R2 | β (g.mg−1) | α mg.g−1.min−1) | R2 | ||
| KS44-0 | 0.002 | 18.105 | 0.870 | 1.095 | 0.249 | 0.991 | 0.067 | 0.101 | 0.978 | 0.239 |
| KS44-20 | 0.007 | 16.845 | 0.931 | 0.536 | 0.452 | 0.995 | 0.121 | 0.180 | 0.981 | 0.437 |
| Composites | Intra-Particle Diffusion Model | Bangham Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region I | Region II | ||||||||
| kdif (min−1) | C (mg.L−1) | R2 | kdif (min−1) | C (mg.L−1) | R2 | KB (min−α) | A | R2 | |
| KS44-0 | 0.027 | 0.037 | 0.998 | 0.010 | 0.105 | 0.846 | 0.774 | −7.704 | 0.980 |
| KS44-20 | 0.049 | 0.065 | 0.999 | 0.021 | 0.166 | 0.885 | 0.997 | −7.535 | 0.995 |
| Composites | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | Temkin Isotherm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qmax (mg.g−1) | KL (L.mg−1) | R2 | KF (mg.g−1) | n | R2 | BT (J.mol−1) | KT (L.mg−1) | R2 | |
| KS44-0 | 0.541 | 6.983 | 0.985 | 0.080 | 1.681 | 0.996 | 0.112 | 1.575 | 0.971 |
| KS44-20 | 0.639 | 0.765 | 0.987 | 0.331 | 3.653 | 0.999 | 0.087 | 71.671 | 0.958 |
| Composites | ΔH° (kJ·mol–1) | ΔS° (J.mol–1) | ΔG° (kJ·mol–1) | R2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T = 20 °C | T = 30 °C | T = 40 °C | T = 50 °C | T = 60 °C | ||||
| KS44-0 | 9.079 | 4.010 | −1.165 | −1.206 | −1.246 | −1.286 | −1.326 | 0.982 |
| KS44-20 | 16.747 | 41.583 | −1.158 | −1.198 | −1.238 | −1.278 | −1.318 | 0.969 |
| Composites | Activation Energy (Ea) (kJ·mol–1) | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| KS44-0 | 7.126 | 0.903 |
| KS44-20 | 11.124 | 0.977 |
| Carbon-Based Materials | Conditions | Qe (mg.g−1) | Kinetic Model | Isotherm Model | ΔH°ads (kJ·mol−1) | ΔG°ads (kJ·mol−1) | ΔS°ads (kJ·mol−1) | Ea (kJ·mol−1) | Ref | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (RhB) (mg.L−1) | pH | T (°C) | Time (h) | |||||||||
| MNP-Tppy | 10 | 6 | 20 | 4 | 4.742 | Pseudo-second-order | Langmuir | 0.937 | −1.220 | 3.69 | - | [63] |
| Cellulose–clay | 10 | 2 | 30 | 2 | 2.789 | Pseudo-second-order | Redlich–Peterson | 0.911 | −3055.14 | 10.086 | - | [64] |
| Fly ash | 10 | 7 | 30 | 3 | 0.334 | Pseudo-first-order | Langmuir and Freundlich | −24.97 | −9.49 | 51.05 | - | [65] |
| CAC | 150 | 4 | 30 | 12 | 0.428 | Pseudo-second-order | Langmuir | 4.01 | - | - | - | [8] |
| PrAC | 300 | 4 | 30 | 36 | 0.110 | Pseudo-second-order | Langmuir | 14.81 | - | - | - | [8] |
| GO | 67 | 7 | 25 | 24 | 0.043 | - | Freundlich | 4.18 | −1.77 | 5.95 | - | [66] |
| MWCNTs | 10 | 1 | 25 | 0.5 | 0.148 | Pseudo-second-order | Langmuir and Freundlich | - | - | - | - | [67] |
| 10 | 7 | 25 | 0.5 | 0.109 | ||||||||
| 10 | 10 | 25 | 0.5 | 0.127 | ||||||||
| KS44-0 | 10 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 0.239 | Pseudo-second-order | Freundlich | 9.079 | −1.165 | 4.010 | 7.126 | This work |
| KS44-20 | 10 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 0.437 | Pseudo-second-order | Freundlich | 16.747 | −1.158 | 41.583 | 11.124 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zghal, S.; Jedidi, I.; Cretin, M.; Cerneaux, S.; Abdelmouleh, M. Adsorptive Removal of Rhodamine B Dye Using Carbon Graphite/CNT Composites as Adsorbents: Kinetics, Isotherms and Thermodynamic Study. Materials 2023, 16, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031015
Zghal S, Jedidi I, Cretin M, Cerneaux S, Abdelmouleh M. Adsorptive Removal of Rhodamine B Dye Using Carbon Graphite/CNT Composites as Adsorbents: Kinetics, Isotherms and Thermodynamic Study. Materials. 2023; 16(3):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031015
Chicago/Turabian StyleZghal, Sabrine, Ilyes Jedidi, Marc Cretin, Sophie Cerneaux, and Makki Abdelmouleh. 2023. "Adsorptive Removal of Rhodamine B Dye Using Carbon Graphite/CNT Composites as Adsorbents: Kinetics, Isotherms and Thermodynamic Study" Materials 16, no. 3: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031015
APA StyleZghal, S., Jedidi, I., Cretin, M., Cerneaux, S., & Abdelmouleh, M. (2023). Adsorptive Removal of Rhodamine B Dye Using Carbon Graphite/CNT Composites as Adsorbents: Kinetics, Isotherms and Thermodynamic Study. Materials, 16(3), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16031015










