Abstract
The traditional roasting technique using sodium salts in vanadium production has been disadvantageous due to the large consumption of energy and the emission of harmful gases. A modified process using molten salt roasting and water leaching to extract vanadium and titanium from domestic titanomagnetite concentrate was investigated. The roasting process was performed under optimal conditions: the weight ratio between the sample and NaOH of 1:1, the temperature of 400 °C, and the experiment time 90 min, and the conversion of vanadium could be maximized to 90%. The optimization of water leaching (at 60 °C for 90 min with a pulp density of 0.05 g/mL) could extract 98% of the vanadium from the roasted products into the solution, leaving titanium and iron remaining in the residue. Further purification of vanadium and titanium using the precipitation/hydrolysis process followed by calcination obtained the final products V2O5 and TiO2 with high purities of 90% and 96%, respectively. A potential approach with modification of the roasting stage using NaOH was proposed, which was not only efficient to selectively extract the value metals from the titanomagnetite but also eco-friendly based on the reduction in energy consumption and emission of harmful gases.
1. Introduction
Vanadium and its compounds have been used widely in a variety of important fields, mainly in: steelmaking, petrochemical industry, non-ferrous alloys, chemical production, and batteries [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Recently, the increasing global consumption of vanadium is not only derived from the necessity of strength improvement in stainless steel and vanadium-titanium alloys but also from the rise in the use of vanadium in lithium batteries for energy storage at a large scale [7,8,9]. Therefore, consideration should be given to maintain adequate supplies of vanadium and develop a more sustainable production. Generally, vanadium exists in the form of oxides, sulfides, or phosphates associated with other metals (iron, titanium, lead, aluminum, zinc, chromium…) in natural ores such as titanomagnetite, patronite, vanadinite, descloizite, and carnotite [10]. Although titanomagnetite has been the major resource for vanadium metallurgical processes, the initial contents of vanadium are critically low (less than 1%) to supply for direct production [11]. It is necessary to enrich the content of vanadium using physical separations or to exploit the slags bearing vanadium generated during the smelting of titanomagnetite in the iron/steelmaking process by using a blast furnace or the direct reduction technique [4,5,6]. The vanadium contents in the collected slags can be enhanced by 5–20% after the smelting and converting stage depending on the feed resources, process efficiency, and the utilized techniques [4,5]. However, the mineralogical compositions of vanadium are normally present in the stable spinel phases (Fe, Mn)2(V, Ti)O4 or (Fe, Mg, Mn)(V, Cr)2O4, which leads to the inefficiency of direct leaching from titanomagnetite concentrates or vanadium-bearing slags without the assistance of pressure, microwave, or ultrasound [5]. The conventional approach is the conversion of vanadium in the spinel phases to more leachable phases by using pre-roasting with or without additives for further dissolution in water, acidic or alkaline media.
The traditional roasting technique involving the presence of sodium salts at high temperatures (NaCl 750–850 °C, Na2CO3 800–1000 °C or Na2SO4 1200–1250 °C) has been assigned as the most popular process with the longest history of development in vanadium production [5]. However, the emission of harmful gases (CO2, SO2 or Cl2) and the large consumption of energy are the disadvantageous problems of sodium salt roasting, which leads to the investigation of alternative roasting techniques such as molten salt roasting, calcia roasting, magnesia roasting, or microwave-assisted roasting. Molten roasting using NaOH with a mass ratio of 1:1, at 500 °C for 60 min followed by water leaching at 50 °C, for 20 min with a pulp density of 20% could effectively leach out 96.6% of vanadium from titanomagnetite concentrates [12]. Furthermore, modification of the NaOH roasting technique by using a concentrated solution of NaOH, KOH, or a combination of NaOH and NaNO3, namely liquid oxidation technology, was demonstrated to obtain an excellent extraction efficiency of 95% while the operated temperature was significantly reduced to 200–400 °C [13,14]. Binary sodium salts (NaOH-NaNO3) roasting with microwave assistance not only performed efficient recovery of vanadium 94.1%, but also reduced the roasting duration since the microwave power could improve the heating speed and accelerate the oxidation reactions [15]. Calcification roasting (at 850 °C for 120 min) followed by sulfuric acid leaching was found to reach the maximum vanadium leachability of 93% [16]. MgO-based roasting was employed to effectively extract ~95% of vanadium under optimal conditions: a temperature of 900 °C, a duration of 90 min, and a Mg/V ratio of 0.6 [17]. Recently, direct reduction roasting with carbon sources such as graphite powder, calcium carbonate, or a mixture of (H2 + CO) has been investigated to develop a cleaner and more productive process for vanadium extraction [18,19,20,21]. Although there are a variety of alternative approaches to modify roasting techniques for vanadium production, molten salt roasting with the presence of sodium hydroxide or binary salts has been evaluated as the most promising technique. It is evidently more advantageous than other roasting techniques with regard to significantly reducing the impact on the environment based on the exclusion of harmful gases while maintaining the sufficient efficiency of vanadium recovery. Moreover, the avoidance of using carbon-sources and lower roasting temperatures can reduce the release of CO2 gas and the high consumption of energy, which has been a long-term concern due to global warming. Therefore, it is worth developing such a “greener process” to produce vanadium and other valuable metals to solve the issue of balance and direct efforts to more sustainable metallurgy.
In the present work, roasting using sodium hydroxide followed by the water leaching of domestic titanomagnetite concentrate was investigated to maximize the recovery efficiency of vanadium. The vanadium in leaching liquor was precipitated as ammonium polyvanadate by the addition of ammonium chloride, and further calcined to generate the product V2O5. Meanwhile, the collected residue after water leaching was consequently dissolved in sulfuric acid H2SO4 solution and then hydrolyzed to form the precipitation of H2TiO3 and converted to the product TiO2 using calcination. The modification of the roasting technique by using NaOH as the substitute for sodium salts and the avoidance of using carbon sources in the roasting stage is an alternative approach to reduce the harmfulness to the environment, the consumption of energy, and the emission of CO2 while still being an effective process to selectively recover value materials (V and Ti) with high purity from titanomagnetite concentrate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The titanomagnetite concentrate in this study was supplied by SAMYANG M. B. T from Gwan-in Mine, Gyeonggi-do, Republic of Korea. The wet digestion method was used to analyze the chemical compositions of the concentrate (listed in Table 1). Sodium hydroxide (NaOH, purity 97%, Junsei Chemical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) was used as the roasting additive, while ammonium chloride (NH4Cl, purity 99%, Oriental Chemical Industries Co., Ltd., Seoul, Republic of Korea) was employed to precipitate vanadium in the solution after water leaching with pH adjustment by hydrochloric acid (HCl, 35%, Junsei Chemical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Sulfuric acid (H2SO4, 95%, Junsei Chemical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) was used to dissolve the titanium-bearing residue before hydrolysis to purify titanium.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of titanomagnetite concentrate.
2.2. Methods
Ten grams of titanomagnetite concentrate was mixed with NaOH powered at a ratio varied from 0.5:1 to 2:1, and then roasted in an electric furnace (KF-S-1001-1000, Korea Furnace Development Co., Seoul, Republic of Korea) to select the optimal conditions at the temperature range of 100–400 °C and the duration of 10–120 min. Water leaching experiments were performed in a glass beaker at a fixed stirring speed of 250 rpm using a magnetic stirrer bar. A specific amount of roasted product was dissolved in a certain volume of water, maintained at the desired conditions of the investigated experiment, and filtrated to obtain the leach liquor for the analysis of metal contents. The vanadium in the solution was precipitated using NH4Cl with pH adjustment by HCl solution. The leach residues were properly washed and further dissolved in H2SO4 solution for the hydrolysis of titanium. The sample, the roasted products, and the leach residues were collected to be analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD, D2 Phaser, Bruker, Republic of Korea).
The metal content was analyzed with an inductively coupled plasma atomic-emission spectrometer (AES-ICP, OPTIMA 7300DV, Perkin Elmer, Seoul, Republic of Korea). The ICP results were used to estimate the metal leaching efficiency as:
where MS and ML are the metal masses in the initial feed sample and the leach liquor, respectively.
3. Results
3.1. NaOH Roasting to Decompose the Vanadium Spinel in the Titanomagnetite Concentrate
3.1.1. Effect of Roasting Temperature and Time
The influence of temperature and time on conversion efficiency during NaOH roasting was investigated by varying in the range of 100–400 °C from 10 to 120 min with the fixed weight ratio of 1:1 between the NaOH and the sample. Subsequently, water leaching of the roasted products was carried out at 60 °C for 120 min and a pulp density (PD) 0.01 g/mL to evaluate the conversion of vanadium by NaOH roasting based on the obtained leachability.
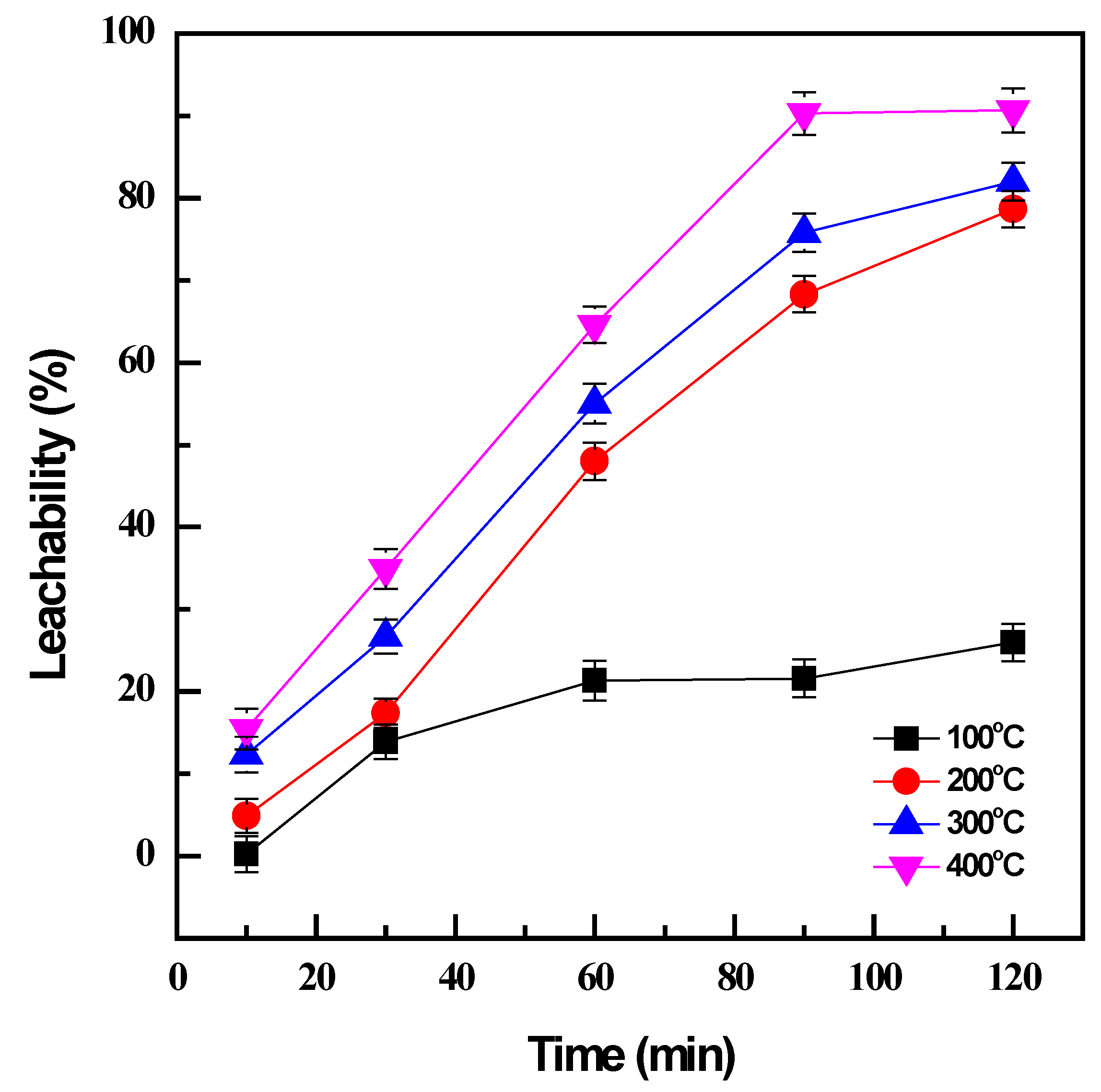
At low temperatures, roasting was not effective to transform the sample to the desired products; only 21% of vanadium was converted at 100 °C after 60 min (Figure 1). A higher temperature is evidently essential since an increase in roasting temperature from 100 °C to 400 °C could significantly enhance the conversion efficiency from 21% to 64% for the same roasting time. The increase in roasting temperature not only accelerated the oxidation reactions but also supported the mass transfer by reducing the viscosity of NaOH molten phases [14]. Although the decomposition of vanadium spinel in the titanomagnetite concentrate was more favorable at higher temperatures, reasonable conditions should be selected to avoid the large consumption of energy while still maintaining productive efficiency. Therefore, the roasting time was considered as well as the roasting temperature. The prolonged roasting duration did not improve the roasting effectiveness at low temperatures; the conversion efficiency was less than 30% after 120 min roasting at 100 °C. However, there was a considerable enhancement from 12% to 68% at a higher roasting temperature of 200 °C when the roasting time increased from 10 min to 90 min, and 90% roasting efficiency could be obtained at 400 °C with the same duration. Further improvement was not observed after the roasting time was extended to 120 min. Consequently, the optimal conditions were managed at 400 °C and 90 min to achieve the effective conversion of vanadium by NaOH roasting.
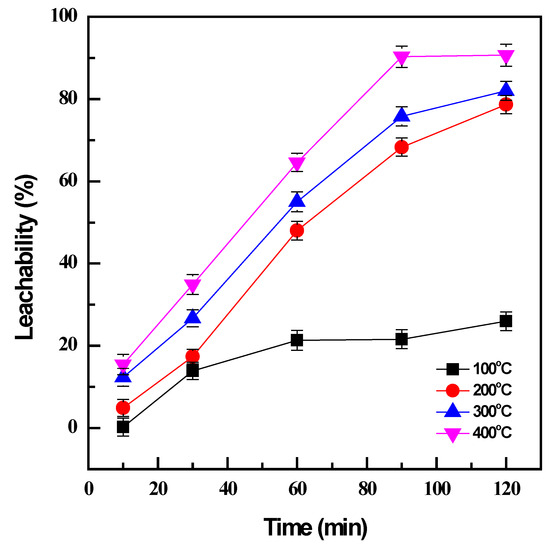
Figure 1.
Effect of roasting temperature and time on vanadium conversion (roasting conditions: 100–400 °C, 10–120 min, and NaOH: sample ratio 1:1; water leaching conditions: 60 °C, 120 min, and PD 0.01 g/mL).
3.1.2. Effect of NaOH Dosage
The conversion of vanadium by roasting required a certain high dosage of NaOH [6,14]; therefore, the amount of NaOH as the additive was optimized by mixing with the titanomagnetite concentrate at the mass ratio (NaOH: sample) varied from 0.5:1 to 2:1.
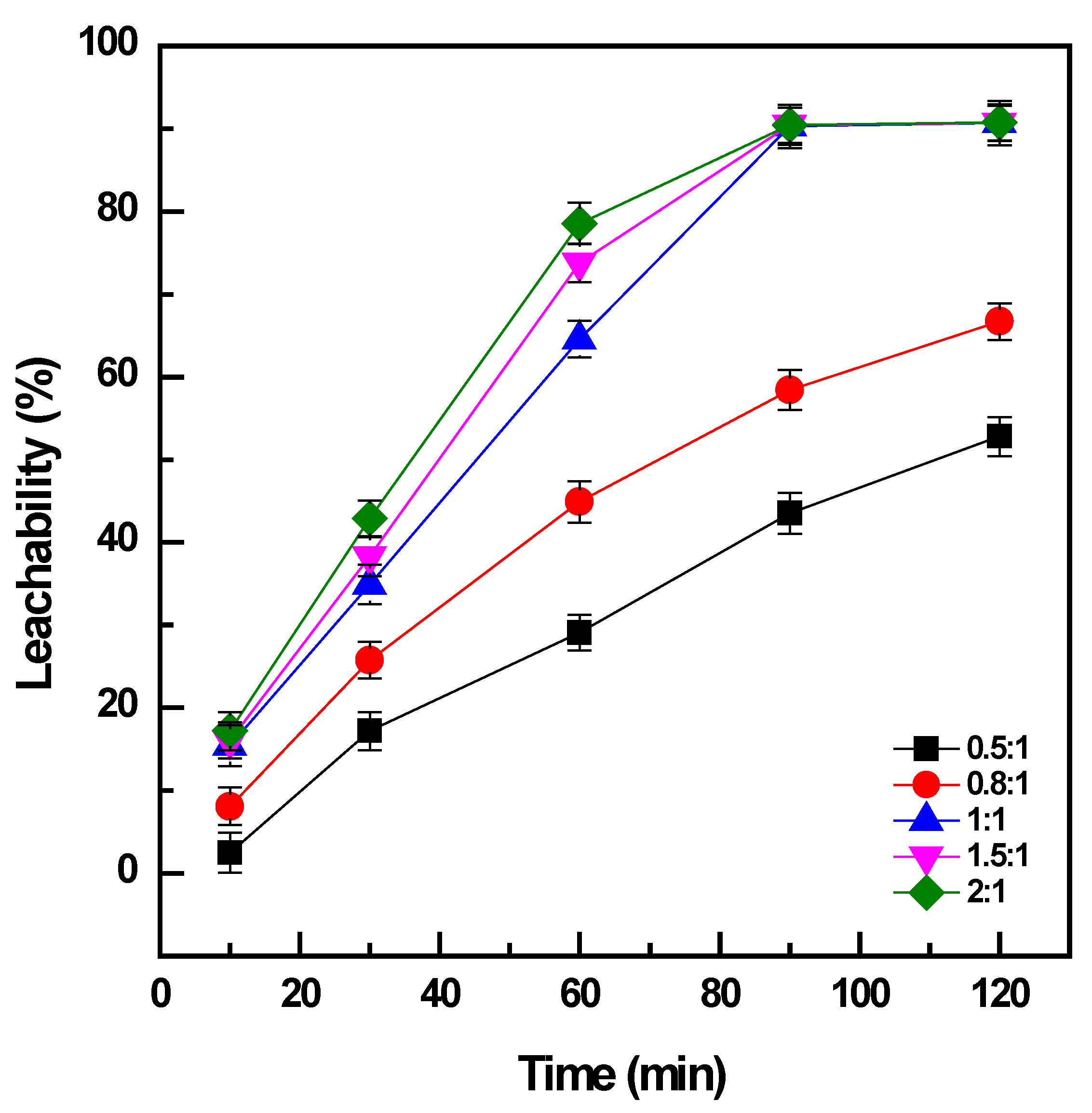
The addition of NaOH to the sample at a ratio of 0.5:1 could convert a minor amount of the vanadium in the concentrate: ~30% for 60 min (Figure 2). Under the same conditions, the increase in NaOH amount to the ratio of 1:1 promoted the conversion of vanadium to 65%, and it reached a maximum efficiency of 90% after 90 min. The addition of NaOH at a ratio of more than 1:1 was effective for a short duration of roasting less than 60 min; however, the enhancement was not significant after roasting for 90 min. When the addition of NaOH was not adequate, it could generate sodium vanadate with an Na:V ratio of less than 1 as the roasted product, which had lower solubility than the other compounds with a high Na:V ratio forming at high doses of NaOH, such as sodium pyrovanadate or orthovanadate [4]. Moreover, the increase in NaOH addition could decrease the viscosity of the molten phase and support the mass transfer of oxygen gas and the sample particles in the media during roasting [14]. Therefore, the amount of NaOH should be sufficiently maintained to form the soluble products of vanadates and accelerate the roasting reactions in the molten phase. Consequently, the weight ratio between NaOH and the sample of 1:1 was selected as the optimal dosage for further investigations. The dissolution of titanium and iron was not observable, which was attributed to the alkaline media of the solution during water leaching (with the pH in the range of 12.5 to 12.6).
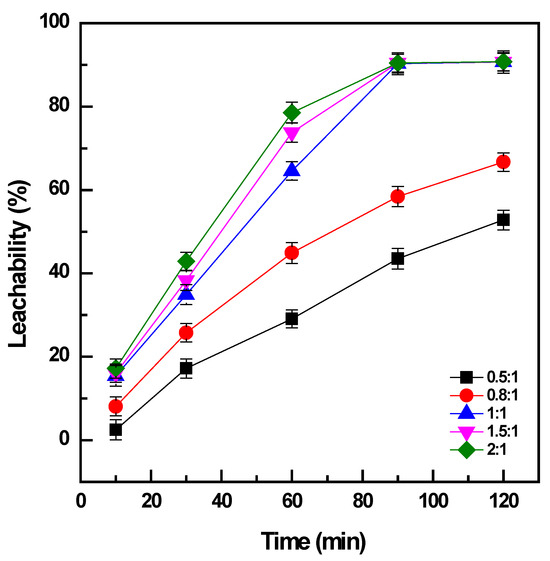
Figure 2.
Effect of NaOH dosage on vanadium conversion (roasting conditions: 400 °C, 10–120 min, and NaOH: sample ratio from 0.5:1 to 2:1; water leaching conditions: 60 °C, 120 min, and PD 0.01 g/mL).
3.2. Water Leaching of Roasted Products
3.2.1. Effect of Leaching Temperature and Time
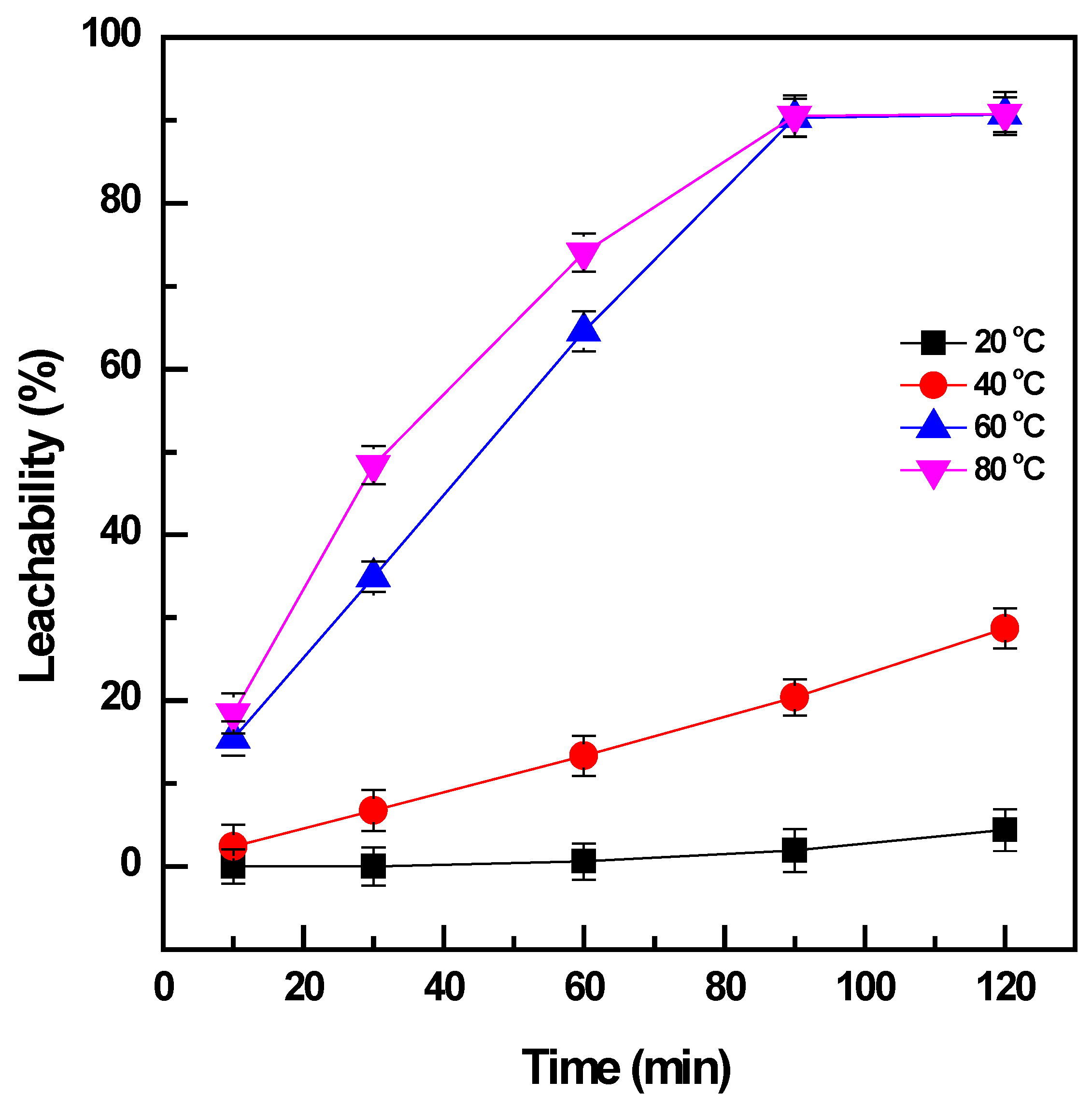
The effect of temperature on the leaching of vanadium from the roasted products was studied in a range of 20 to 80 °C when the pulp density was maintained at 0.01 mg/L and the time was varied from 10 to 120 min. The increase in temperature had a significant influence on the leachability of the vanadium (Figure 3). The roasted products were not effectively dissolved at the low temperature of 20 °C, and vanadium was slightly extracted (~4%) after leaching for 120 min. The higher leaching temperature of 40 °C could enhance the dissolution of vanadium from 4% to 29% for the same duration of leaching; however, it was not sufficient to obtain the total leaching of vanadium. The temperature was continuously increased to 60 °C, and there was a considerable improvement in vanadium extraction to ~91%. Further enhancement of vanadium leachability was not observed when the temperature reached 80 °C and the leaching time increased to more than 90 min. Therefore, the temperature of 60 °C was selected to obtain the effective extraction of vanadium from the roasted products.
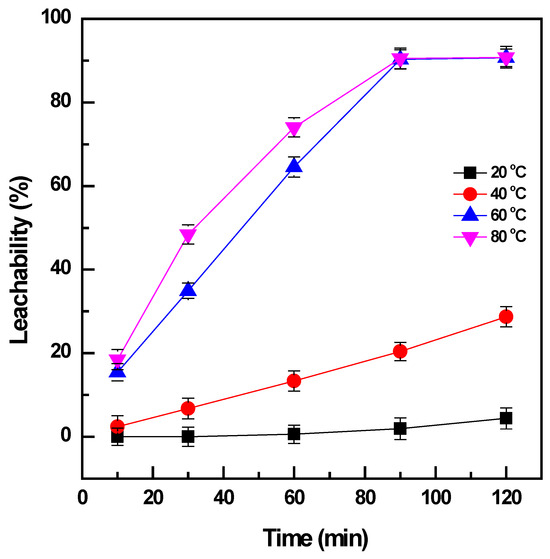
Figure 3.
Effect of temperature and time on vanadium leachability (roasting conditions: 400 °C, 90 min, and NaOH: sample ratio 1:1; water leaching conditions: 20–80 °C, 10–120 min, and PD 0.01 mg/L).
The leaching of vanadium from the roasted products was assumed to follow several kinetic equations, as listed in Table 2 [22]. The leachability with variation in temperature and time was used to evaluate the most suitable kinetic model. The fitting results presented a good linear relationship regarding the kinetic equations, with the average value of the regression coefficient R2 being more than 0.9 in all cases of the kinetic models. However, the significant influence of temperature on the dissolution of vanadium and the high value of the activation energy Ea(leaching) > 40 kJ/mol indicated that the leaching of vanadium followed the chemical-controlled model [23]. Therefore, the equation 1 − (1 − x)1/3 = kc × t was selected to interpret the vanadium leaching mechanism. The chemical control model with a high value of activation energy explained the dependence of vanadium leaching on temperature, which is expressed by the significant enhancement of efficiency with the increase in temperature.

Table 2.
Fitting the leaching data to kinetic model equations [22].
3.2.2. Effect of Pulp Density
The ratio between the roasted products and the volume of the leaching solution can have a certain influence on the leaching of vanadium; hence, it was investigated by varying the pulp density (PD, solid/liquid ratio of roasted products and water volume, g/mL) from 0.01 to 0.1 while the leaching time was varied in a range of 10 to 120 min and the leaching temperature was fixed at 60 °C.
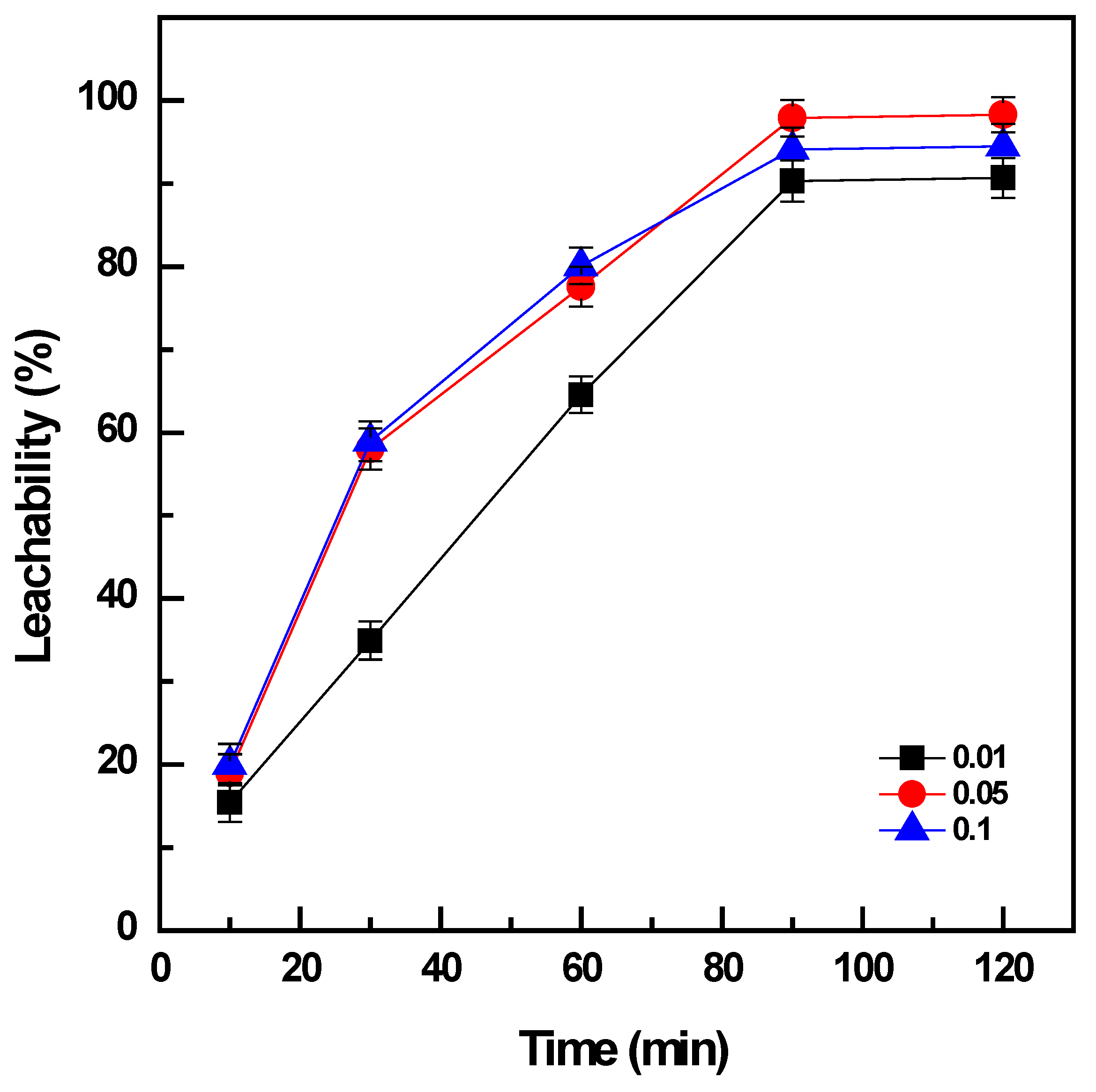
The results indicated that the increase in PD from 0.01 to 0.1 promoted the leachability of vanadium from 91% to ~98% after leaching for 90 min (Figure 4). However, the double amount of the solid phase, PD = 0.1 g/mL, produced a slight decrease on the vanadium dissolution to 94% for the same duration of leaching. The increase in the duration of leaching from 10 to 90 min could enhance the extraction efficiency of vanadium under the condition of PD = 0.05 g/mL from 20% to ~98%, and the same tendency was observed for PD = 0.01 or 0.1 mg/L. There was no further improvement in the leachability of vanadium when the leaching time was extended to more than 90 min. Consequently, water leaching was optimized under the conditions: 60 °C, PD = 0.05 g/mL, and 90 min to obtain the maximum extraction of 98% vanadium from the roasted products.
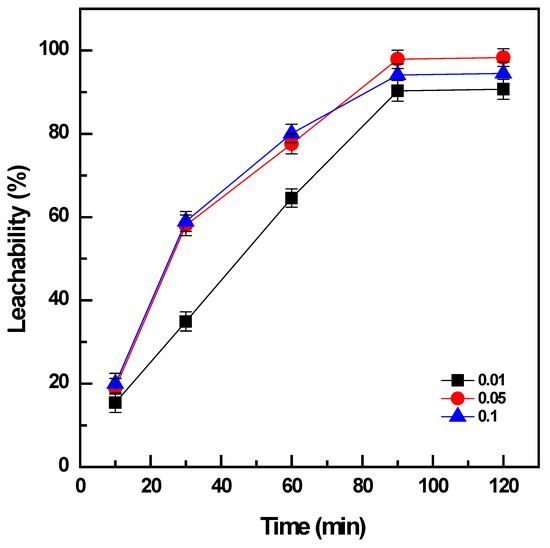
Figure 4.
Effect of pulp density on vanadium leachability (roasting conditions: 400 °C, 90 min, and NaOH: sample ratio 1:1; water leaching conditions: 60 °C, 10–120 min, and PD 0.01 to 0.1 g/mL).
3.3. Preparation and Characterization of the Final Products (V2O5 and TiO2)
NaOH roasting and water leaching under optimal conditions could extract 98% of the vanadium into the solution (final pH = 12.5). In contrast, the dissolution of titanium and iron were critically low and remained in the residue. Purification of vanadium was necessary to separate it from other impurities, and precipitation using ammonium salts was the suitable method for the solution obtained from NaOH roasting and water leaching [5]. Although vanadium could be directly precipitated in alkaline media, the acidic media was preferred due to the higher purity of the final product and the less significant effect of Na on the precipitation efficiency of vanadium [24]. Therefore, the solution was initially adjusted from pH = 12.5 to acidic media pH = 2 using HCl solution, and vanadium was precipitated under the following conditions: NH4Cl as the precipitant, a temperature of 90 °C, and a duration of 120 min.
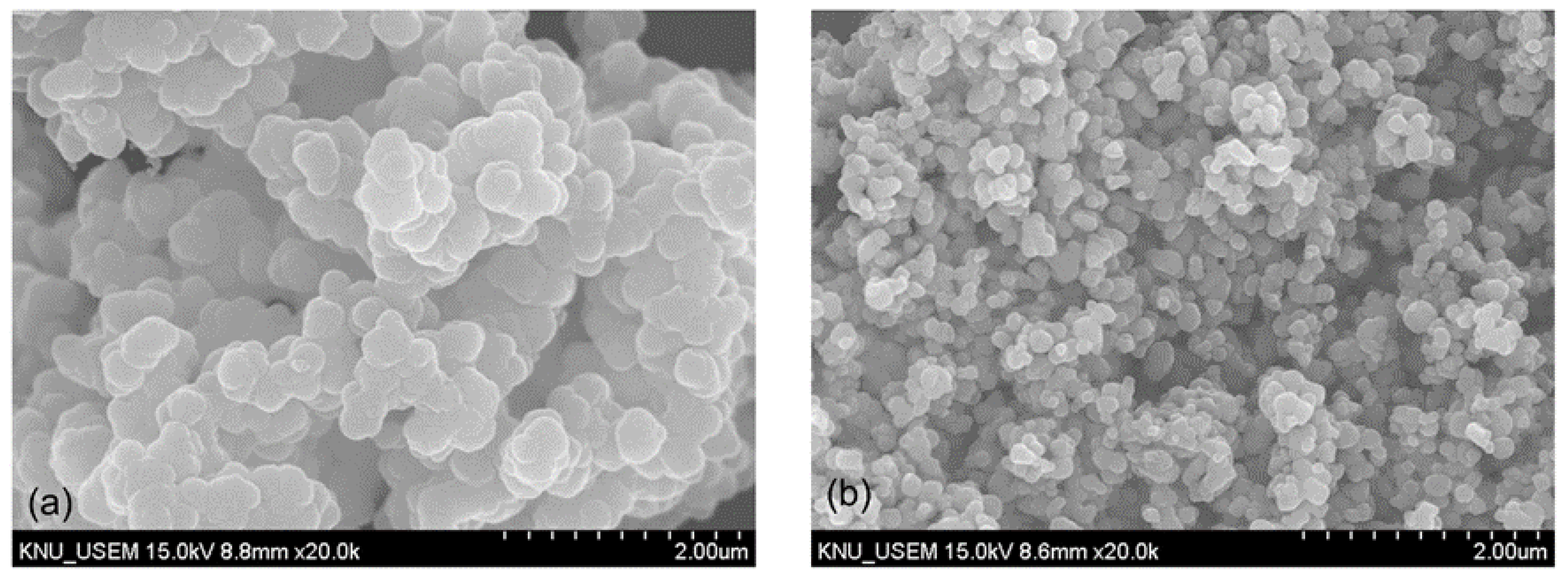
The precipitation of vanadium was characterized using a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Hitachi S–4800, Tokyo, Japan), which showed the spherical structure with irregular edges of the precipitated product (Figure 5a). The solid product was collected and properly washed with NH4Cl solution before calcination at 550 °C for 120 min to produce the vanadium pentoxide V2O5. The residue after water leaching was further dissolved in H2SO4 solution of 2.0 M to selectively extract titanium from iron by using the hydrolysis process (1 g seed TiO2, 100 °C, 120 min) [25]. The SEM image presented the relatively uniform spherical shape and radius of the product particles (Figure 5b). The H2TiO3 precipitate was filtrated, washed, and calcinated at 800 °C to produce the titanium dioxide TiO2. The chemical composition analysis demonstrated that the purity of V2O5 was relatively low at 90%, and the other impurities were Al2O3 5.7% and SiO2 3.5%. However, TiO2 could be obtained with 96% purity and a low level of other impurities (Fe2O3 3.8%).

Figure 5.
SEM images of precipitated products; (a) morphology of the vanadium precipitate using NH4Cl and (b) morphology of the titanium precipitate using hydrolysis.
3.4. Phase Transformation during the Recovery Process
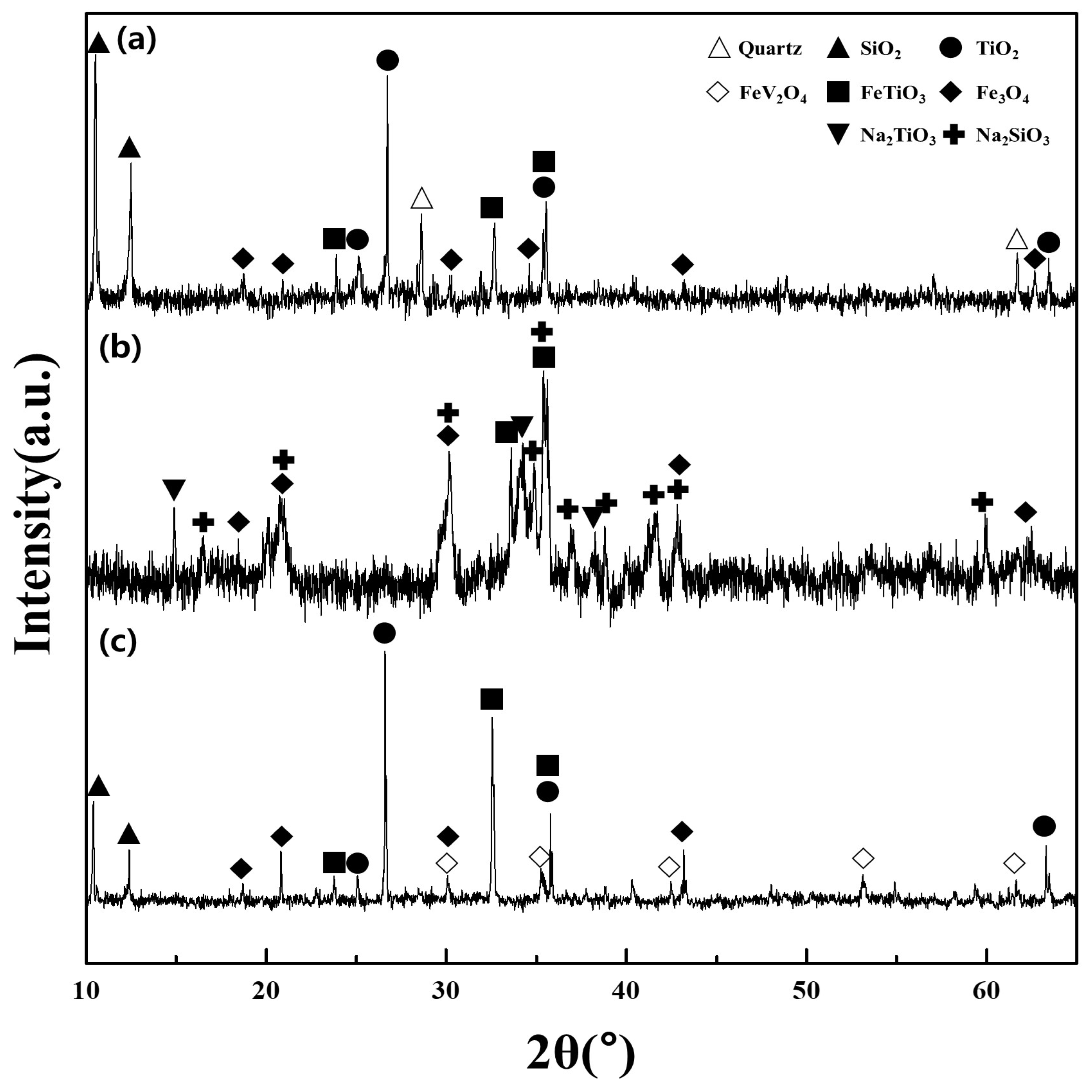
The major components of the titanomagnetite concentrate included Ilmenite FeTiO3, Fe3O4, TiO2, and SiO2 (Figure 6a). The vanadium was not detected in the XRD pattern of the concentrate sample due to the minor content present (4.18%). However, the peaks of the spinel phase FeV2O4 were observed in the patterns of the residue after water leaching. This provided indirect evidence for the phase of V in the initial concentrate since the spinel phase FeV2O4 was not completely converted and therefore appeared in the residue. After roasting using NaOH under optimal conditions, the vanadium in the spinel phase FeV2O4 could be converted into several vanadate products (NaVO3 or Na4V2O7) since the amount of additive NaOH exceeded the amount of vanadium in the sample (Equations (2) and (3) in Table 3) [4]. The other roasted products were Na2SiO3 and Na2TiO3 produced by reactions between NaOH and TiO2, SiO2, while the phases of Fe3O4 and FeTiO3 were maintained in the residue (Figure 6b and Equations (4) and (5)). In the water leaching stage, the vanadate compounds were dissolved to form a stable phase of HVO42− with regard to the redox potential 377 mV and the pH 12.5 of the leaching solution [4] (Equations (6) and (7)). The titanium and iron were observed as the phases of FeTiO3, Fe3O4, and TiO2 in the residue (Figure 6c and Equation (8)). Generally, the vanadium in the solution after the water leaching was transferred to the polymer ions such as V10O286−, HV10O285−, H2V10O284− in the acidic media and precipitated using NH4Cl [6]. In the present study, the redox potential (1105 mV) and the pH = 2 of the solution after the pH adjustment indicated that the vanadium existed as H2V10O284− and could be converted to (NH4)2V6O16 (Equation (9)). The titanium-bearing residue was dissolved into TiOSO4 using H2SO4 solution of 2.0 M (redox potential 980 mV and pH < 0), and titanium was separated from the solution by hydrolysis as H2TiO3 (Equations (10)–(12)). Finally, the vanadium pentoxide and titanium dioxide were prepared by calcination of the solid products obtained from the precipitation stage (Equations (13) and (14)).
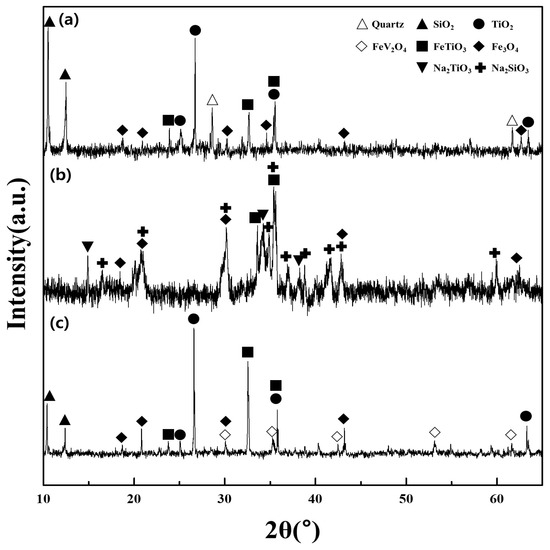
Figure 6.
XRD patterns of samples and products during the recovery process; (a) titanomagnetite concentrate sample; (b) roasted products with NaOH; and (c) titanium-bearing residue after water leaching.

Table 3.
The chemical reactions during the recovery process.
3.5. Comparison between Modified and Conventional Roasting Processes
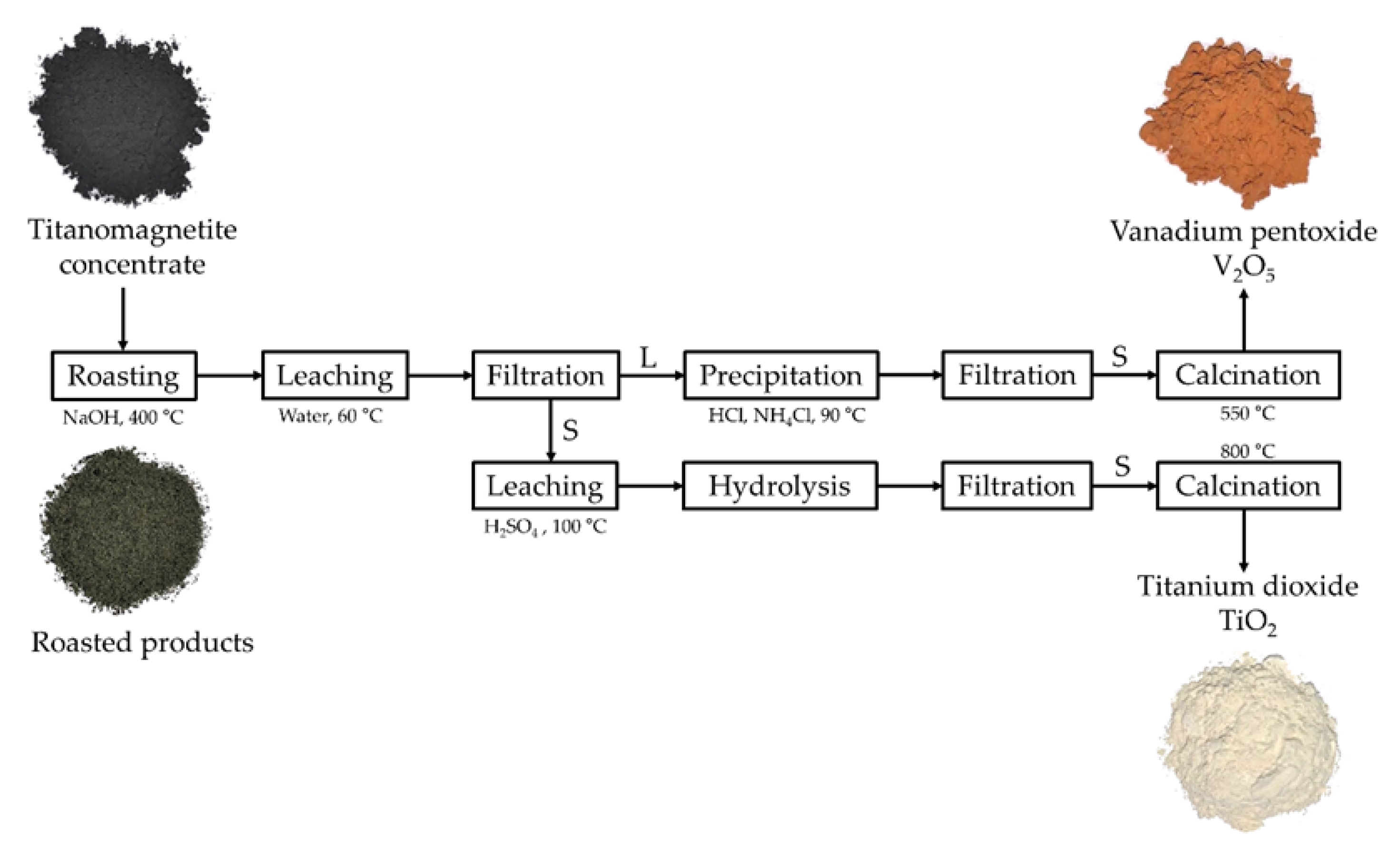
An efficient process to recover the value metals vanadium and titanium from domestic titanomagnetite is presented (Figure 7). The conventional roasting technique using sodium salts as additives required high-temperature NaCl at 750–850 °C, Na2CO3 at 800–1000 °C, or Na2SO4 at 1200–1250 °C. In this study, the roasting stage was modified by using NaOH and avoiding the addition of sodium salts; hence, the operating temperature was significantly reduced to 400 °C as the melting point of NaOH was less than NaCl, Na2CO3, and Na2SO4. The amount of required energy for roasting was simply evaluated based on the heat for the increasing temperature of 1 kg of additives (Equation (15)) [26] and the heat for the transformation from the solid to the molten phase. The volumes of emitted gases were calculated with the assumption of the completed decomposition of sodium salts at the operating temperature.
where Q: the heat kJ, m: the weight of the additive kg, c: specific heat kJ/kg.K, and ΔT: the change in temperature K.
Q = m × c × ΔT
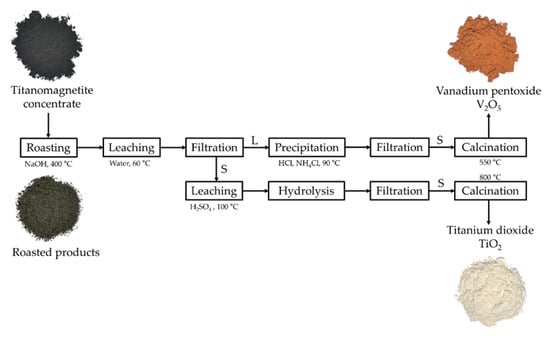
Figure 7.
Flowsheet of the NaOH roasting and water leaching process to recover vanadium and titanium from the titanomagnetite concentrate (S: solid phase; L: liquid phase in the filtration stage).
The results in Table 4 show that roasting using NaOH requires the lowest amount of energy, and roasting using other additives consumes a greater amount of heat (1.5 to 3.3 times). This is mostly attributed to the value of the gradient temperature between the initial and operating temperature and the moderate heat capacity and heat of fusion of NaOH, although the mole of NaOH is the largest one. The decomposition of sodium salts induces large volumes of gas emissions: Cl2/191.5 L, CO2/210.5 L, and SO2/156.8 L, while using NaOH only releases H2O. Therefore, this method could minimize the adverse impacts on the environment caused by the emission of harmful gases and reduce the consumption of energy during roasting. Moreover, the combination of NaOH roasting and water leaching could selectively extract vanadium into the solution while titanium and iron remained in the leach residue based on the differences in the stabilities of their species in the alkaline media, which was necessary for the further purification stage. The recovery efficiency of vanadium was optimized to 98%, and the final products V2O5 and TiO2 could be simply obtained by using precipitation and hydrolysis processes with high purity ≥90%. It is worth investigating such a “greener process” at a larger scale and applying it to other available resources for the sustainable development of vanadium production.

Table 4.
Comparison between modified roasting using NaOH and conventional roasting techniques using sodium salts.
4. Conclusions
The extraction of the value metals vanadium and titanium from domestic titanomagnetite with modification in roasting technique to reduce the consumption of energy and emission of harmful gases was investigated in the present study. NaOH roasting could effectively convert 90% of vanadium in the spinel phase to more soluble phases under the conditions: sample and NaOH weight ratio of 1:1, a temperature of 400 °C, a duration of 90 min. The roasted products were dissolved at 60 °C for 90 min and PD = 0.05 g/mL to selectively extract 98% of the vanadium from titanium and iron. The increase in temperature had a significant effect on the leaching of vanadium, and the kinetic study demonstrated that the leaching mechanism was controlled by the chemical reaction with high activation energy Ea(leaching) 69 kJ/mol. The vanadium in the leach liquor was further purified using NH4Cl in acidic media to produce the vanadium precipitate, which was calcinated at 550 °C to obtain vanadium pentoxide V2O5. Titanium in the residue after water leaching was dissolved in H2SO4 solution for the hydrolysis process, and the H2TiO3 was collected to prepare the titanium dioxide TiO2 by calcination at 800 °C. Both of the final products V2O5 and TiO2 presented high purities of 90% and 96%, respectively. The extraction process with modification in the roasting stage using NaOH is not only advantageous to reduce the roasting temperature but also to avoid the emission of harmful gases, which is suitable for the necessity of a cleaner approach for vanadium production.
Author Contributions
Data analysis, Visualization, Writing-original draft, and Editing, H.B.T.; Investigations and Data analysis, S.K.; Conceptualization, Methodology, and Supervision, J.L.; Review, Editing, and Supervision, S.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea Institute of Energy Technology evaluation and Planning (KETEP) grant funded by the Korea government (MOTIE) (20216110100040). This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2019R1A6A1A03033167).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Muroga, T.; Nagasaka, T.; Abe, K.; Chernov, V.M.; Matsui, H.; Smith, D.L.; Xu, Z.Y.; Zinkle, S.J. Vanadium alloys—Overview and recent results. J. Nucl. Mater. 2002, 307, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalyk, R.R.; Alfantazi, A.M. Processing of vanadium: A review. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langeslay, R.R.; Kaphan, D.M.; Marshall, C.L.; Stair, P.C.; Sattelberger, A.P.; Delferro, M. Catalytic applications of vanadium: A mechanistic perspective. Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 2128–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilligan, R.; Nikoloski, A.N. The extraction of vanadium from titanomagnetites and other sources. Miner. Eng. 2020, 146, 106106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Kim, E.Y.; Chung, K.W.; Kim, R.; Jeon, H.S. A review on the metallurgical recycling of vanadium from slags: Towards a sustainable vanadium production. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H. A literature review on leaching and recovery of vanadium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barote, L.; Weissbach, R.; Teodorescu, R.; Marinescu, C.; Cirstea, M. Stand-alone wind system with vanadium redox battery energy storage. In Proceedings of the 2008 11th International Conference on Optimization of Electrical and Electronic Equipment, Brasov, Romania, 22–24 May 2008; pp. 407–412. [Google Scholar]
- Skyllas-Kazacos, M.; Kazacos, G.; Poon, G.; Verseema, H. Recent advances with UNSW vanadium-based redox flow batteries. Int. J. Energy Res. 2010, 34, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Kim, S.; Kim, R.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.; Jung, H.Y.; Kim, H.T. A review of vanadium electrolytes for vanadium redox flow batteries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, M.; Hawthorne, F.C.; Baur, W.H. A crystal-chemical approach to the composition and occurrence of vanadium minerals. Can. Mineral. 2000, 38, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Du, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.L.; Zhang, Y. A new metallurgical process for the clean utilization of chromite ore. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 131, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Qi, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. A novel process for recovery of iron, titanium, and vanadium from titanomagnetite concentrates: NaOH molten salt roasting and water leaching processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 244, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.B.; Hao, D.U.; Wang, D.W.; Wang, S.N.; Zheng, S.L.; Zhang, Y. Kinetics analysis of decomposition of vanadium slag by KOH sub-molten salt method. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 1489–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Zheng, S.L.; Wang, S.N.; Biao, L.I.U.; Wang, D.W.; Hao, D.U.; Zhang, Y. Research and prospect on extraction of vanadium from vanadium slag by liquid oxidation technologies. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 1273–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, A.; Xue, X. A novel roasting process to extract vanadium and chromium from high chromium vanadium slag using a NaOH-NaNO3 binary system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 379, 120805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Li, H.Y.; Yin, X.C.; Yan, Z.M.; Yan, X.M.; Xie, B. Leaching kinetics of calcification roasted vanadium slag with high CaO content by sulfuric acid. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 133, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Wang, C.J.; Yuan, Y.H.; Guo, Y.; Diao, J.; Xie, B. Magnesiation roasting-acid leaching: A zero-discharge method for vanadium extraction from vanadium slag. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.M.; Yi, L.Y.; Wang, L.N.; Chen, D.S.; Wang, W.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Qi, T. A novel process for the recovery of iron, titanium, and vanadium from vanadium-bearing titanomagnetite: Sodium modification–direct reduction coupled process. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2017, 24, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Kou, J.; Sun, T.C.; Wu, S.C.; Zhao, Y.Q. Effects of calcium compounds on the carbothermic reduction of vanadium titanomagnetite concentrate. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2020, 27, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fu, G.; Chu, M.; Zhu, M. An effective and cleaner process to recovery iron, titanium, vanadium, and chromium from Hongge vanadium titanomagnetite with hydrogen-rich gases. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2021, 48, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; He, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Cleaner and effective extraction and separation of iron from vanadium slag by carbothermic reduction-chlorination-molten salt electrolysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Habashi, F. Principles of Extractive Metallurgy; Gordon and Breach Science Publishers: London, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, P.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, S.; Huang, J. Precipitation of vanadium using ammonium salt in alkaline and acidic media and the effect of sodium and phosphorus. Hydrometallurgy 2018, 180, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Trinh, H.B.; Lee, J. Titanium Dioxide Recovery from Soda-roasted Spent SCR Catalysts through Sulphuric Acid Leaching and Hydrolysis Precipitation. Resour. Recycl. 2020, 29, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, S.B. Thermodynamics Made Simple for Energy Engineers; River Publishers: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2021. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).