Effects of Interface Morphology on the Shear Mechanical Properties of Sand–Concrete Interfaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
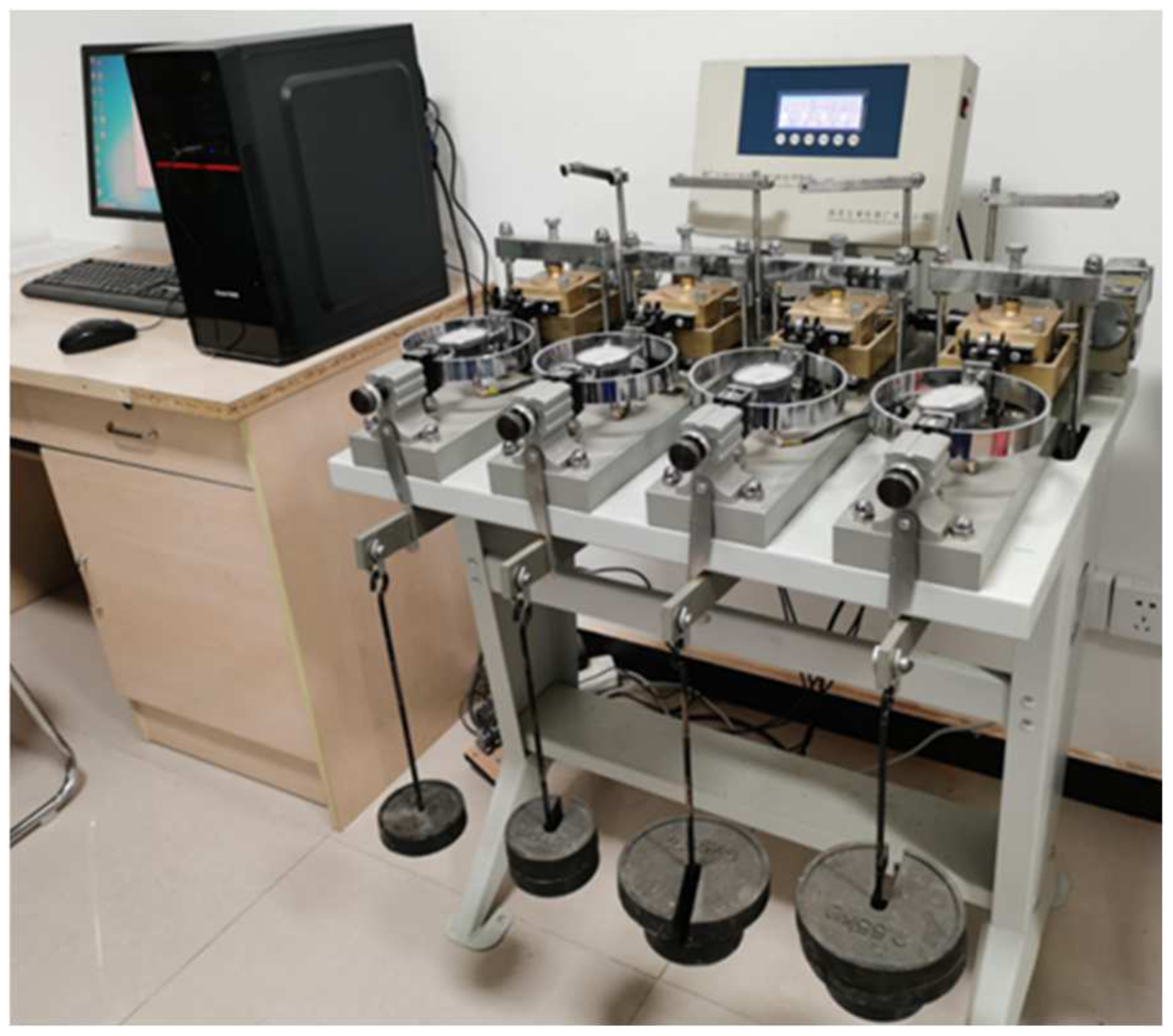
2.1. Testing Equipment and Materials
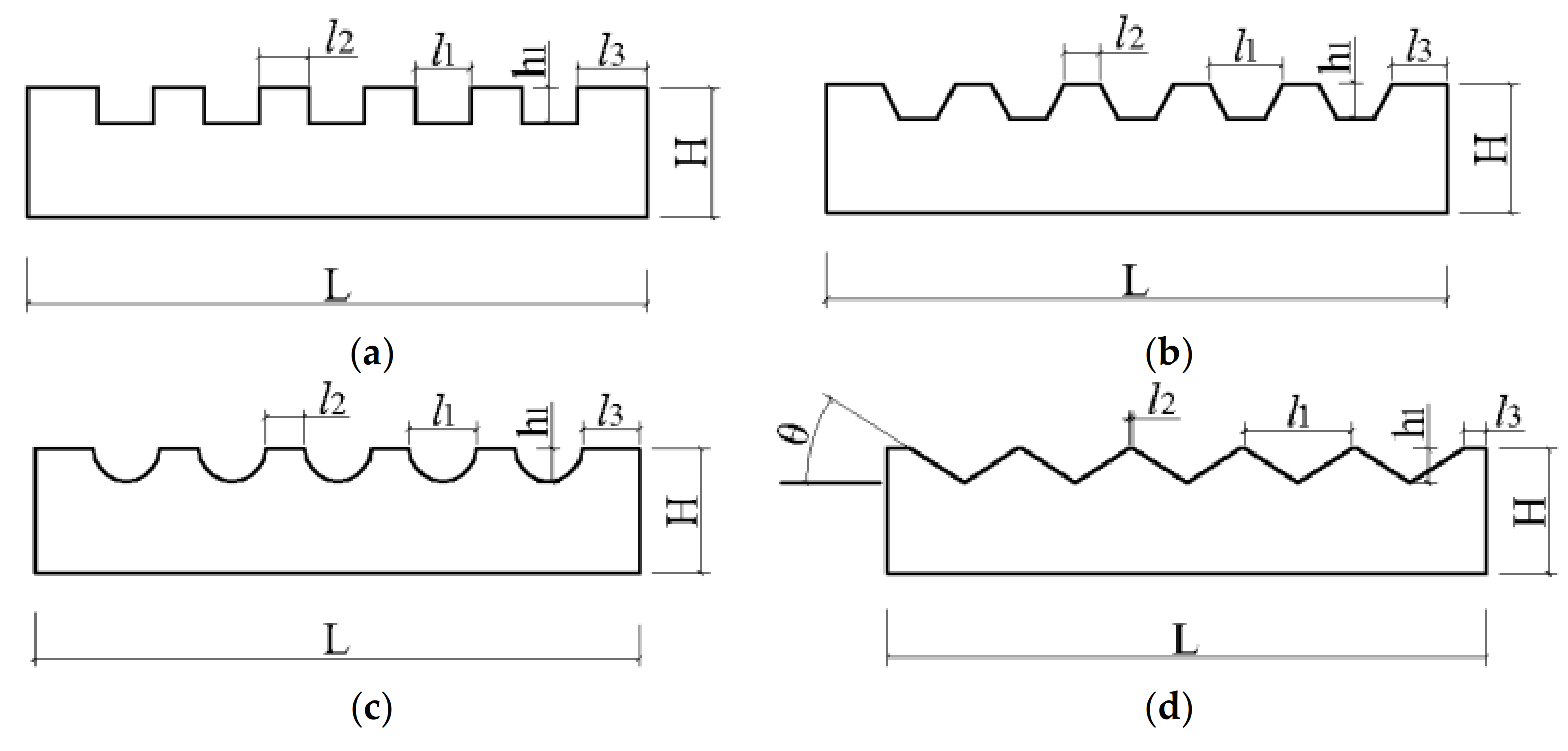
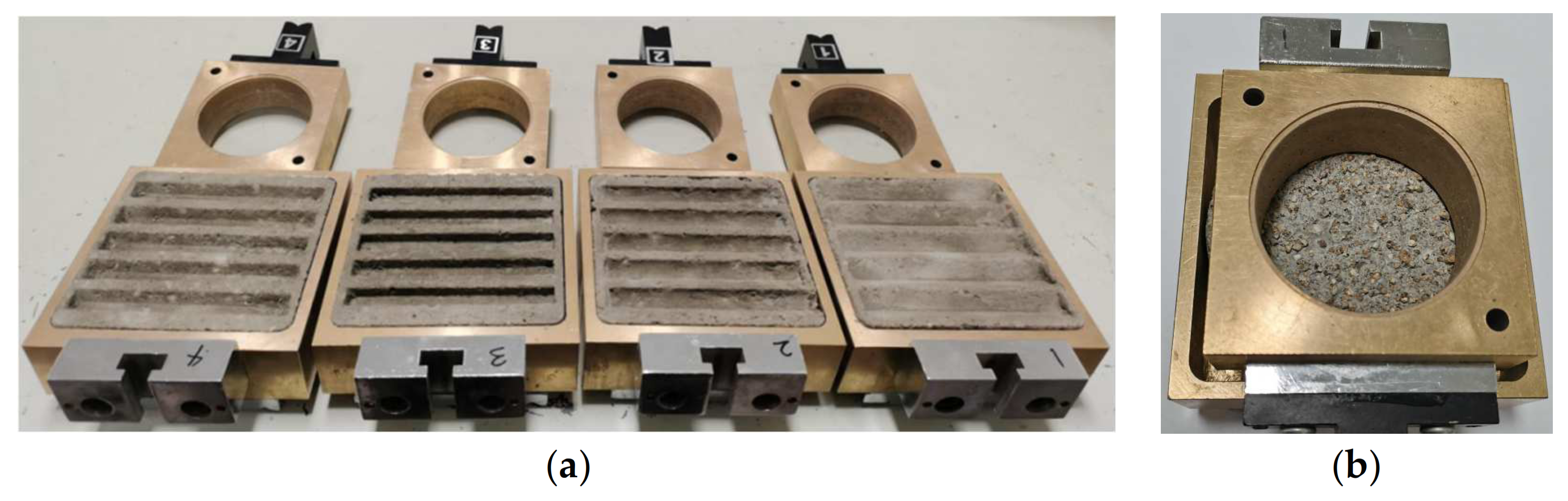
2.2. Specimen Preparation
2.3. Test Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
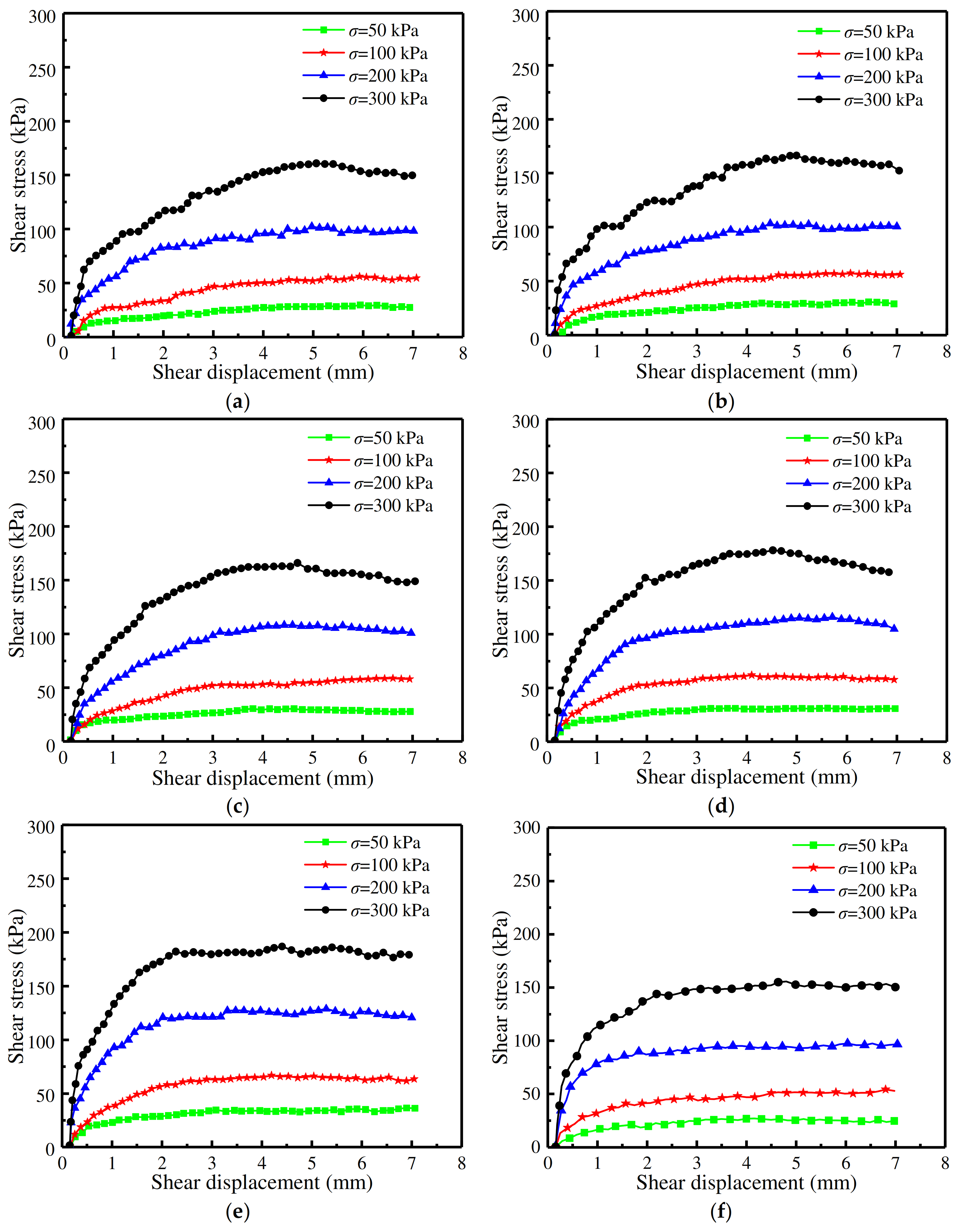
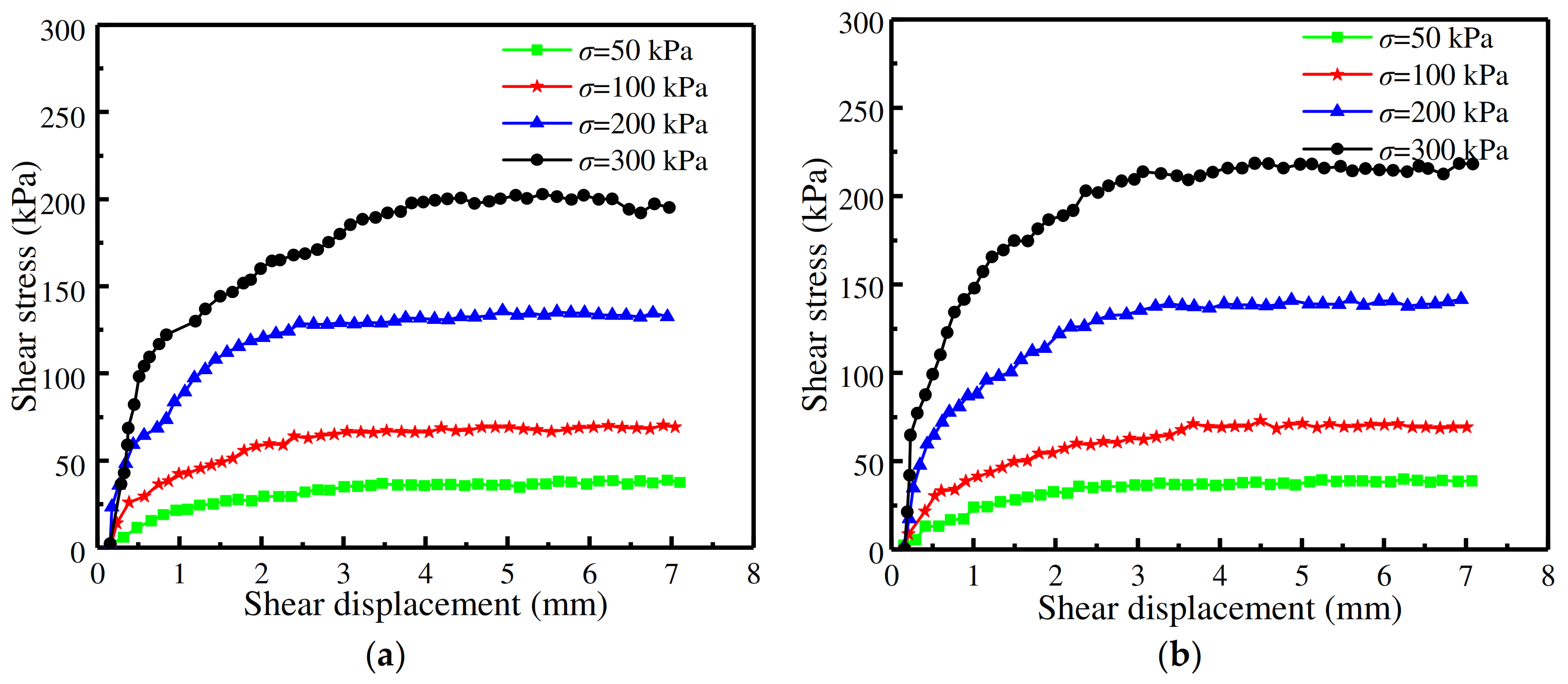
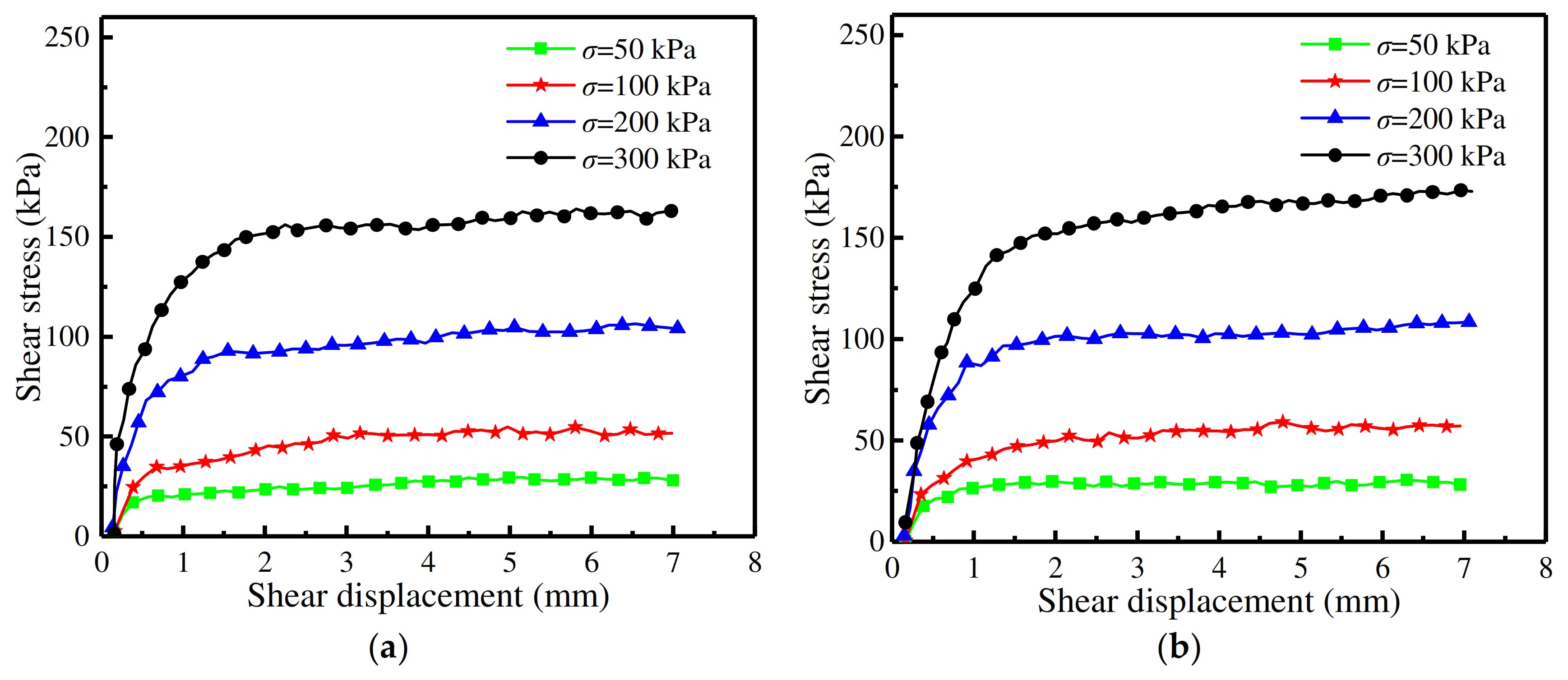
3.1. Shear Stress–Displacement Relationship
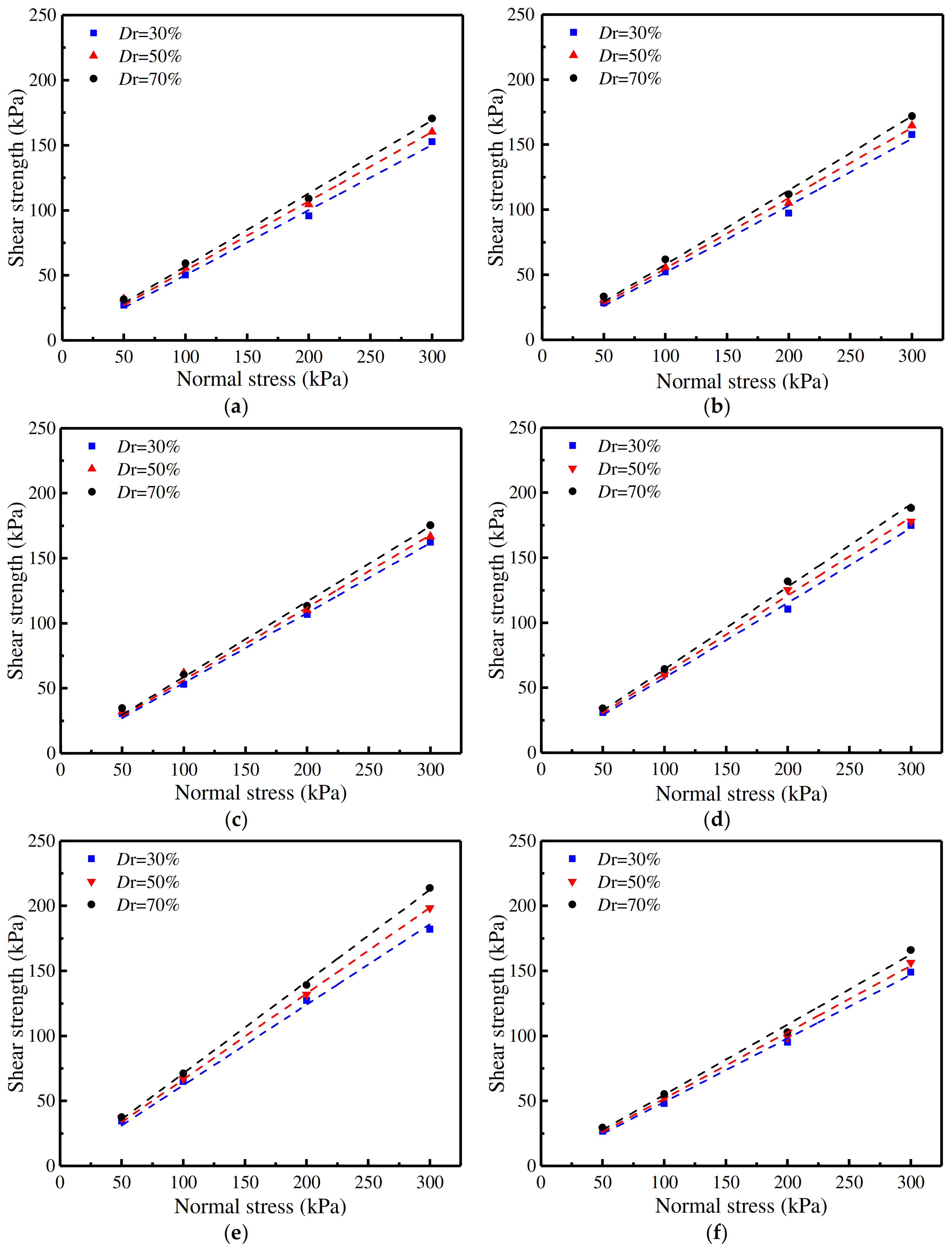
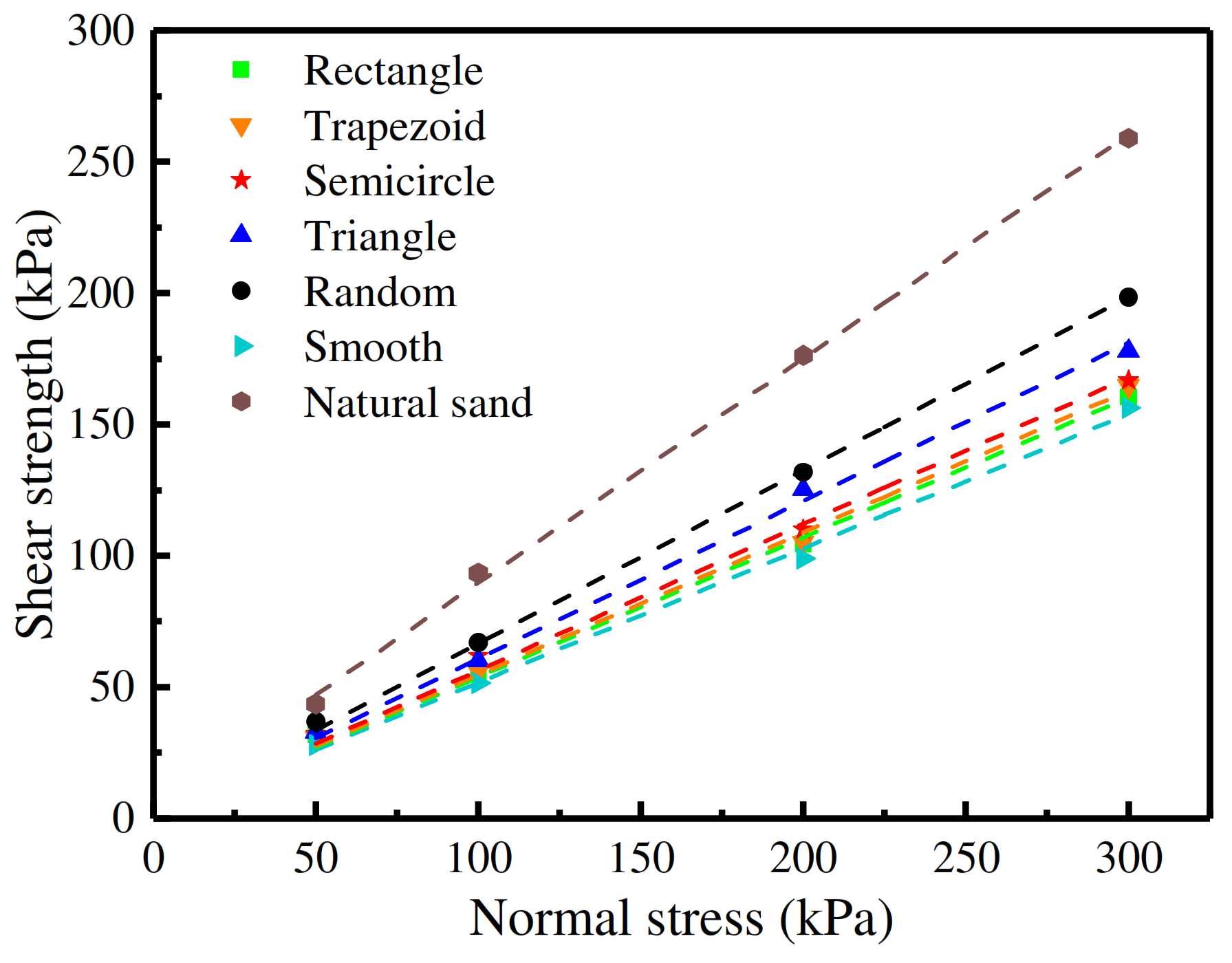
3.2. Shear Strength
3.3. Shear Failure Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, L.M.; Pu, J.L. Testing and Modeling of Soil-Structure Interface. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2004, 30, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaev, O.N.; Sharafutdinov, R.F. Soil Shear Strength at the Structure Interface. Soil Mech. Found. Eng. 2020, 57, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beren, M.; Çobanoglu, I.; Çelik, S.; Ündül, Ö. Shear Rate Effect on Strength Characteristics of Sandy Soils. Soil Mech. Found. Eng. 2020, 57, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uesugi, M.; Kishida, H. Influential Factors of Friction Between Steel and Dry Sands. Soils Found. 1986, 26, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sang, S.; Wang, Y.; Bai, X. Factors Influencing the Mechanical Characteristics of a Pile–Soil Interface in Clay Soil. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 7, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.; Palumbo, S.; Todd, B.D. Bioinspiration for Anisotropic Load Transfer at Soil–Structure Interfaces. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2019, 145, 04019074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.Z.; Zhu, C.Q.; Meng, Q.S. Large-scale Direct Shear Tests of Interfaces Between Different Soils and Concrete Considering Roughness Effect. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2019, 51, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Islam, M.R. Effects of water content and interface roughness on the shear strength of silt–cement mortar interface. Soils Found. 2021, 61, 1615–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafaei, N.; Fakharian, K.; Sadrekarimi, A. Sand-sand and sand-steel interface grain-scale behavior under shearing. Transp. Geotech. 2021, 30, 100636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Lv, M.F.; Guo, Y.C.; Huang, M.S. Effects of the soil water content and relative roughness on the shear strength of silt and steel plate interface—ScienceDirect. Measurement 2021, 174, 109003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koval, G.; Chevoir, F.; Roux, J.-N.; Sulem, J.; Corfdir, A. Interface roughness effect on slow cyclic annular shear of granular materials. Granul. Matter 2011, 13, 525–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoodi, S.; Cuisinier, O.; Masrouri, F. Thermal effects on mechanical behaviour of soil–structure interface. Can. Geotech. J. 2020, 57, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeri, H.; Sarfarazi, V.; Zhu, Z.; Marji, M.F.; Masoumi, A. Investigation of shear behavior of soil-concrete interface. Smart Struct. Syst. 2019, 23, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.B.; Zhao, C.; Wu, Y. Study on the Effects of Grouting and Roughness on the Shear Behavior of Cohesive Soil-Concrete Interfaces. Materials 2020, 13, 3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, A.; Frost, J.D. The influence of surface roughness form on the strength of sand–structure interfaces. Géotechnique Lett. 2017, 7, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Yan, P.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Y. The influence of roughness on cyclic and post-cyclic shear behavior of red clay-concrete interface subjected to up to 1000 cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 273, 121718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fu, S.; Zhu, D.; Li, G.; Shen, S. Experimental study on the effects of triangular groove inclination angles on the mechanical behavior of sand–concrete interfaces. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50123-2019; Standard for Geotechnical Testing Method. Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. China Planning Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Lei, S.; Wang, R.; Kou, H.; Wei, D. Effects of Groove Feature on Shear Behavior of Steel-Sand Interface. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 9593187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.Q.; Xia, C.H.; Wang, P.S. Effect of shape scale on characteristics of coarse grained soil-structural interface under medium and high pressures. Rock Soil Mech. 2013, 34, 3491–3499. [Google Scholar]
- Janipour, A.K.; Mousivand, M.; Bayat, M. Study of interface shear strength between sand and concrete. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.F.; Gong, H.; Zhao, C. Elastoplastic analysis of interface between clay and concrete considering effect of normal stress history. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2012, 31, 848–855. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.H.; Zhang, J.S.; Li, J. Experimental research on mechanical characteristics of cohesive soil-structure interface by considering its roughness. J. Cent. South Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2016, 47, 1682–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.J.; Zhou, W.H.; Chen, W.B.; Jie, X. Effects of relative roughness and mean particle size on the shear strength of sand-steel interface. Measurement 2018, 122, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, L.; Guo, Q. Experimental Study on Mechanical Properties of Grout–Soil Interface in Anchor System of Rammed Earthen Sites. Int. J. Géoméch. 2020, 20, 04020064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Li, J. Effect of roughness on shear behavior of red clay—concrete interface in large-scale direct shear tests. Can. Geotech. J. 2015, 52, 1122–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

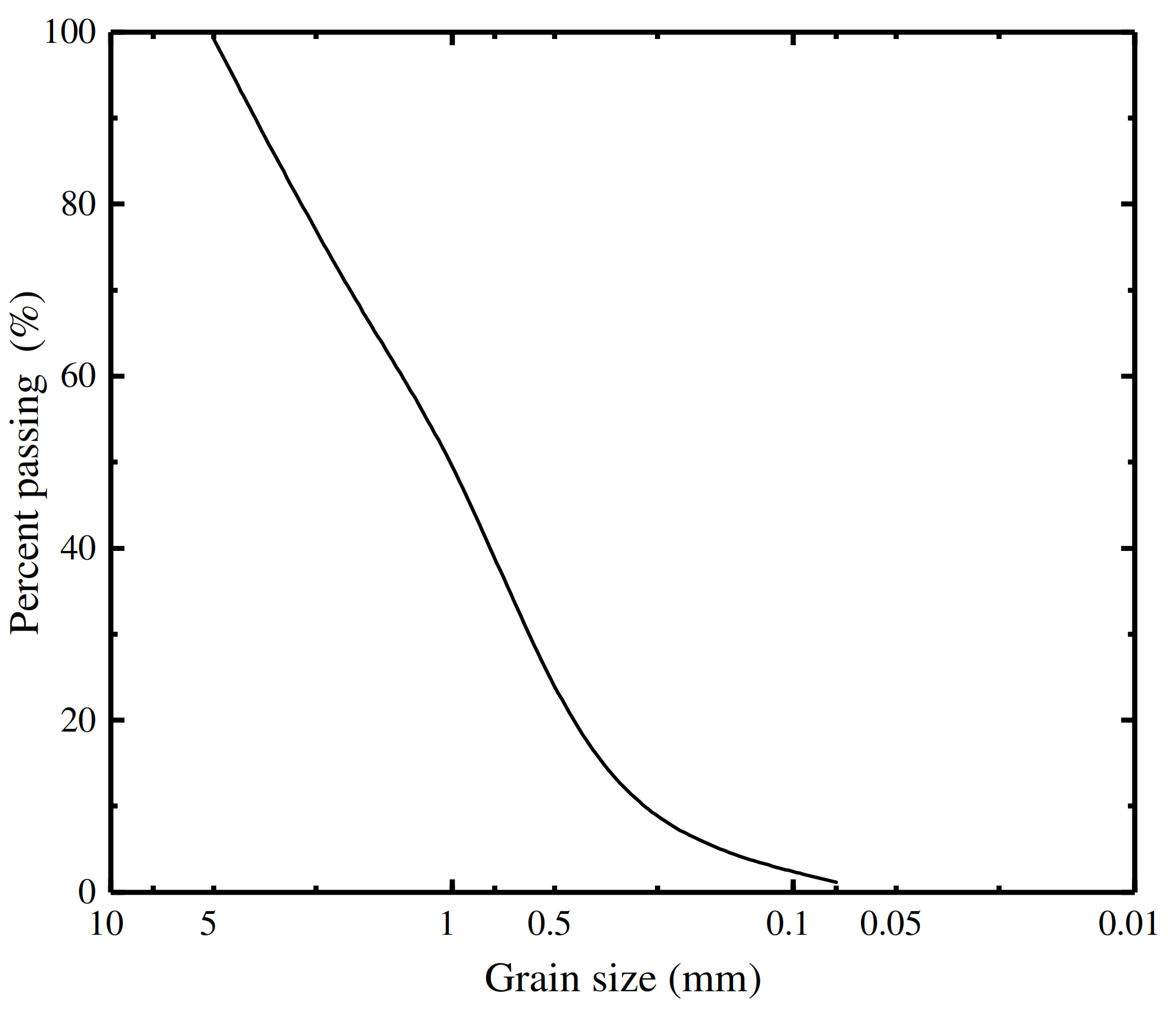
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Specific gravity (Gs) | 2.65 |
| D10 (mm) | 0.30 |
| D30 (mm) | 0.61 |
| D60 (mm) | 1.39 |
| Uniformity coefficient (Cu) | 4.63 |
| Coefficient of curvature (Cc) | 0.89 |
| Maximum void ratio emax | 1.04 |
| Minimum void ratio emin | 0.57 |
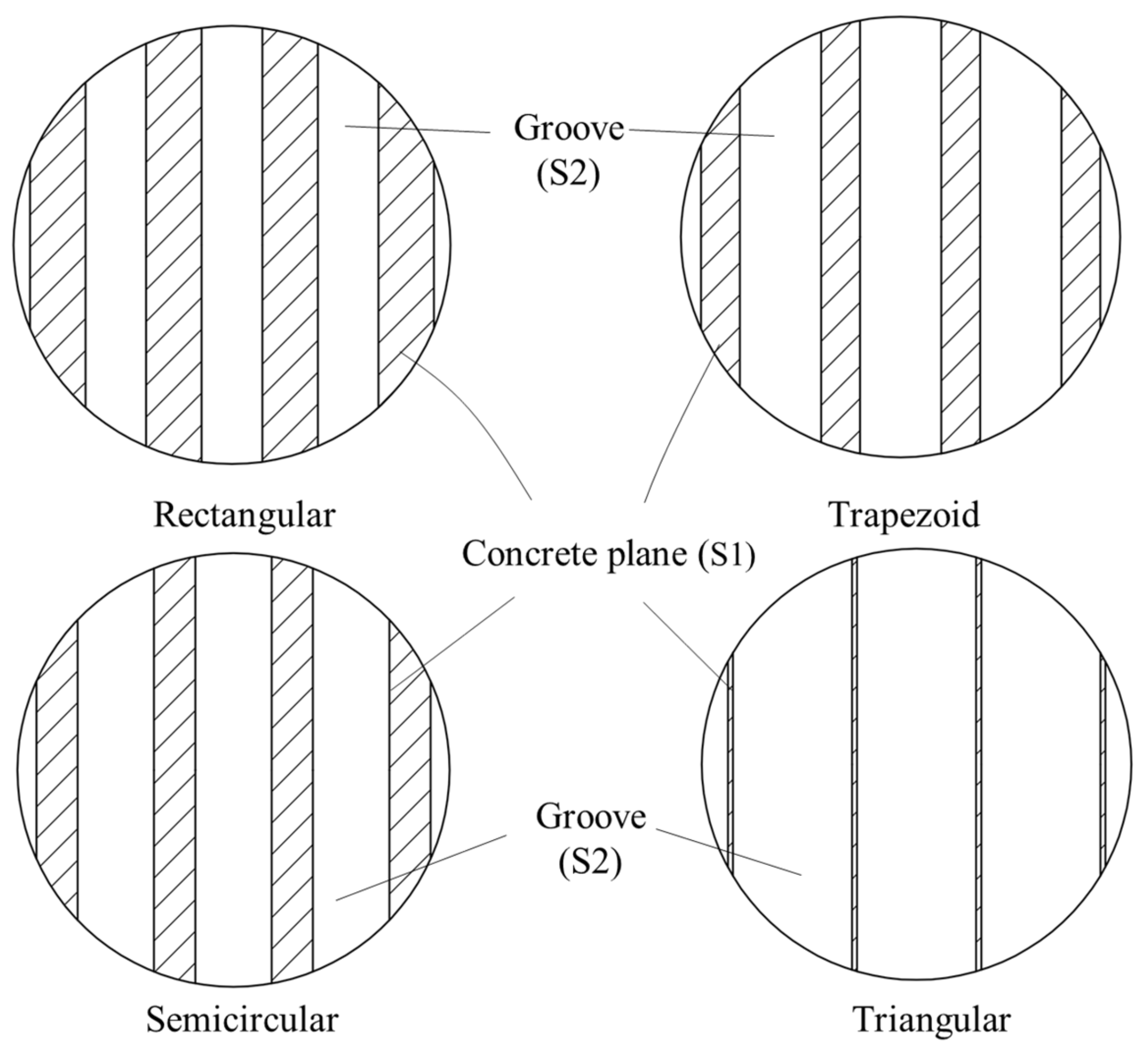
| Groove Type | L (mm) | H (mm) | l1 (mm) | l2 (mm) | l3 (mm) | h1 (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rectangular | 96 | 20 | 8.57 | 7.86 | 10.86 | 5.46 |
| Trapezoid | 96 | 20 | 11.43 | 5.48 | 8.47 | 5.46 |
| Semicircular | 96 | 20 | 10.92 | 5.9 | 8.9 | 5.46 |
| Triangular | 96 | 20 | 17.14 | 0.72 | 3.71 | 5.46 |
| Specimen | S_1 | S_2 | S_3 | S_4 | S_5 | S_6 | S_7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test object | Natural sand | Sand–concrete (smooth surface) | Sand–concrete (random surface) | Sand–concrete (Triangular groove surface) | Sand–concrete (Rectangular groove surface) | Sand–concrete (Trapezoid groove surface) | Sand–concrete (Semicircular groove surface) |
| Normal stress (kPa) | 50, 100, 200, 300 | ||||||
| Dr (%) | Interface Morphology | Shear Strength Formula | c (kPa) | φ (°) | R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | Smooth | τf = 0.1522 + 0.4896σ | 0.1522 | 26.09 | 0.996 |
| Rectangular | τf = 0.1522 + 0.5001σ | 0.1522 | 26.57 | 0.998 | |
| Trapezoid | τf = 0.1522 + 0.5147σ | 0.1522 | 27.23 | 0.998 | |
| Semicircular | τf = 0.1522 + 0.5388σ | 0.1522 | 28.32 | 0.999 | |
| Triangular | τf = 0.1522 + 0.5757σ | 0.1522 | 29.93 | 0.998 | |
| Random | τf = 0.1522 + 0.6190σ | 0.1522 | 31.76 | 0.998 | |
| Natural sand | τf = 4.4300 + 0.8188σ | 4.4300 | 39.31 | 0.993 | |
| 50 | Smooth | τf = 0.5724 + 0.5111σ | 0.5724 | 27.07 | 0.996 |
| Rectangular | τf = 0.5724 + 0.5320σ | 0.5724 | 28.01 | 0.998 | |
| Trapezoid | τf = 0.5724 + 0.5414σ | 0.5724 | 28.43 | 0.999 | |
| Semicircular | τf = 0.5724 + 0.5576σ | 0.5724 | 29.14 | 0.998 | |
| Triangular | τf = 0.5724 + 0.6017σ | 0.5724 | 31.04 | 0.999 | |
| Random | τf = 0.5724 + 0.6599σ | 0.5724 | 33.42 | 0.999 | |
| Natural sand | τf = 4.3263 + 0.8535σ | 4.3263 | 40.48 | 0.998 | |
| 70 | Smooth | τf = 0.6425 + 0.5400σ | 0.6425 | 28.37 | 0.993 |
| Rectangular | τf = 0.6425 + 0.5619σ | 0.6425 | 29.33 | 0.999 | |
| Trapezoid | τf = 0.6425 + 0.5709σ | 0.6425 | 29.72 | 0.998 | |
| Semicircular | τf = 0.6425 + 0.5803σ | 0.6425 | 30.13 | 0.998 | |
| Triangular | τf = 0.6425 + 0.6352σ | 0.6425 | 32.42 | 0.999 | |
| Random | τf = 0.6425 + 0.7055σ | 0.6425 | 35.20 | 0.999 | |
| Natural sand | τf = 4.7900 + 0.9084σ | 4.7900 | 42.25 | 0.995 |
| Groove Type | S1/mm2 | S2/mm2 | S1/S2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rectangular | 1473.00 | 3000 | 49.11% |
| Trapezoid | 1019.89 | 3000 | 34.00% |
| Semicircular | 1000.20 | 3000 | 33.34% |
| Triangular | 129.49 | 3000 | 4.32% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Meng, Z.; Shen, S. Effects of Interface Morphology on the Shear Mechanical Properties of Sand–Concrete Interfaces. Materials 2023, 16, 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16186122
Li H, Meng Z, Shen S. Effects of Interface Morphology on the Shear Mechanical Properties of Sand–Concrete Interfaces. Materials. 2023; 16(18):6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16186122
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huanhuan, Zhigang Meng, and Songlin Shen. 2023. "Effects of Interface Morphology on the Shear Mechanical Properties of Sand–Concrete Interfaces" Materials 16, no. 18: 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16186122
APA StyleLi, H., Meng, Z., & Shen, S. (2023). Effects of Interface Morphology on the Shear Mechanical Properties of Sand–Concrete Interfaces. Materials, 16(18), 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16186122





