Thermodynamic Insights into the Oxidation Mechanisms of CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy Using In Situ X-ray Diffraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Materials Characterisation
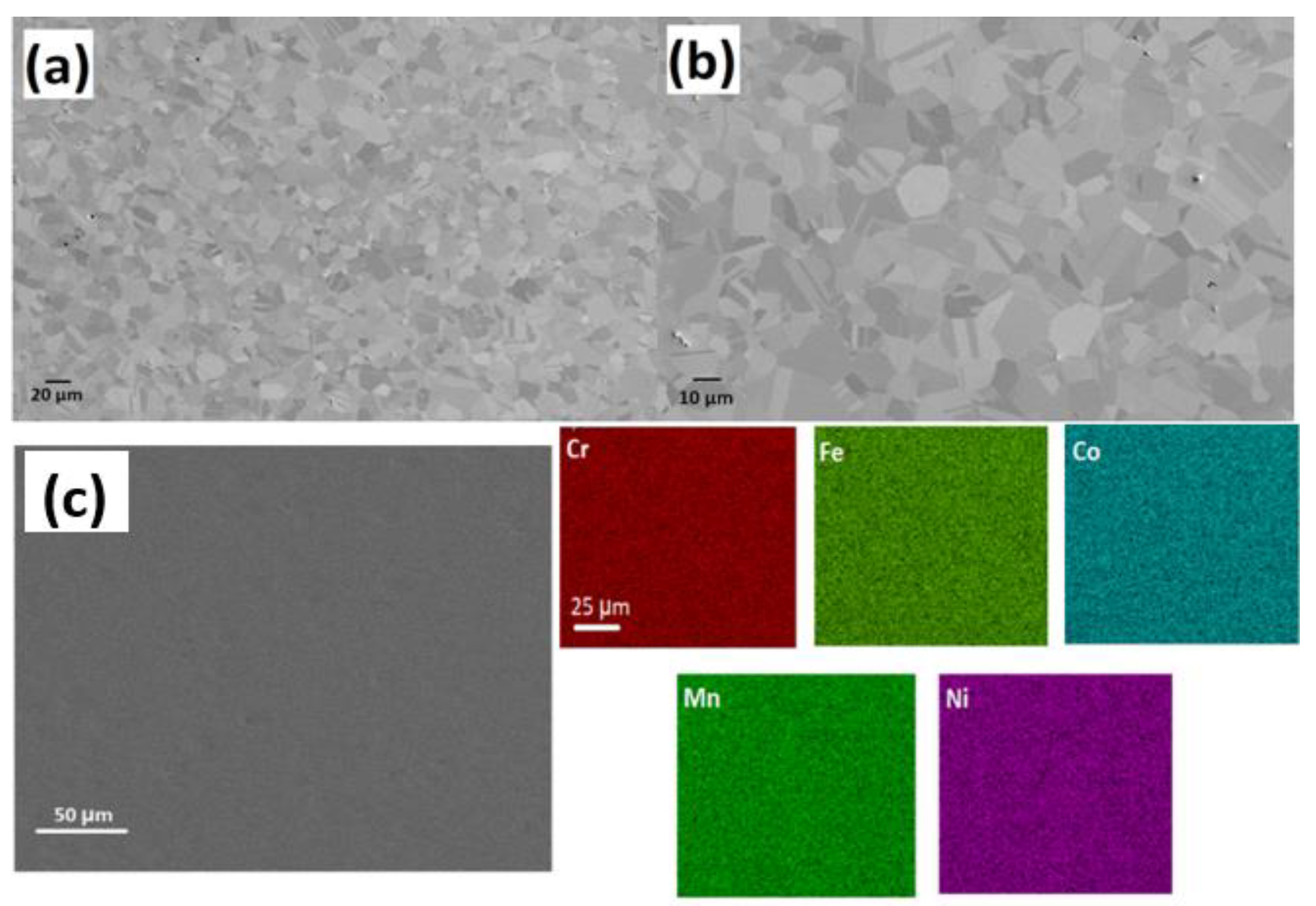
2.2.1. Microstructure Analysis
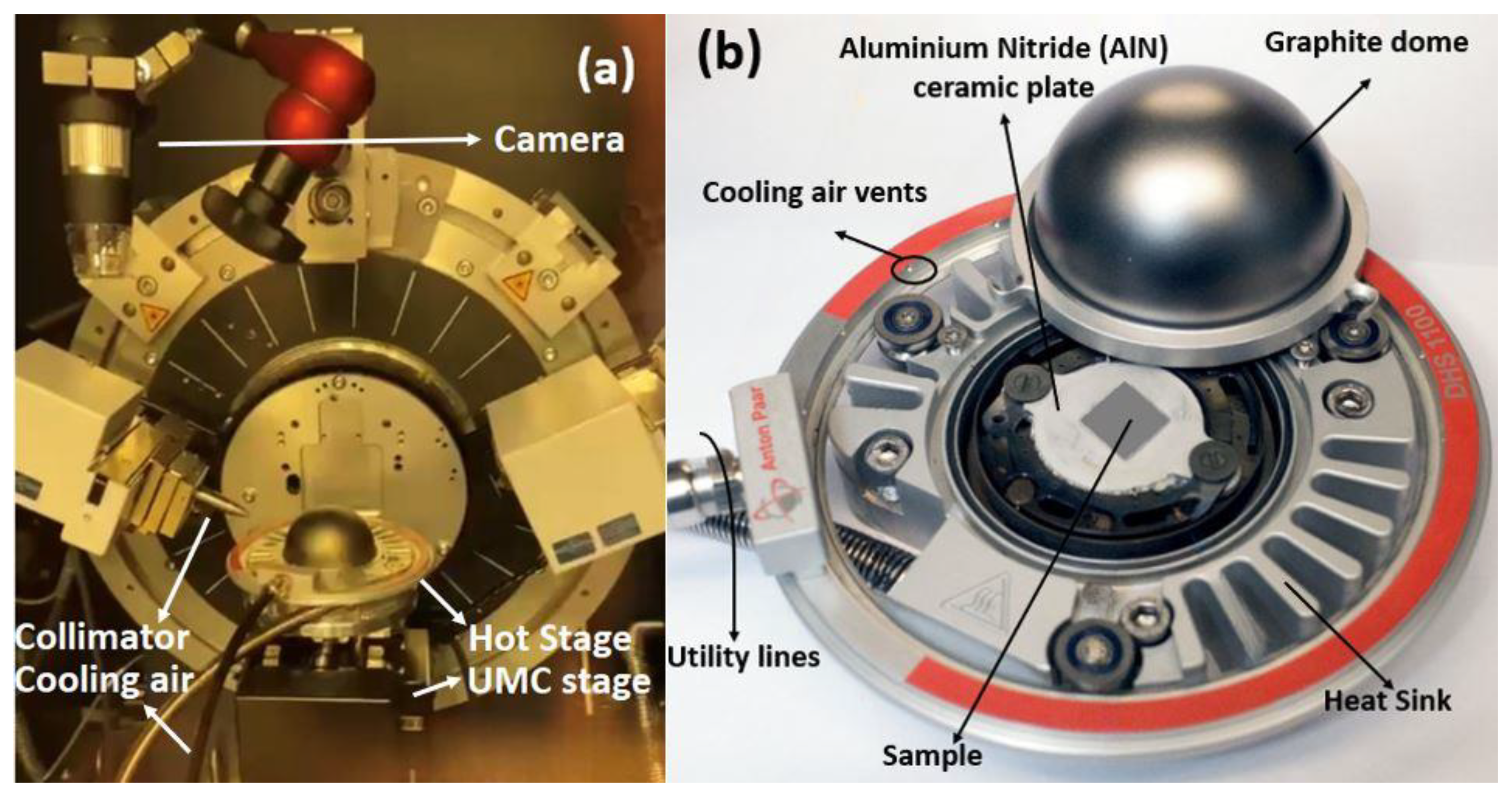
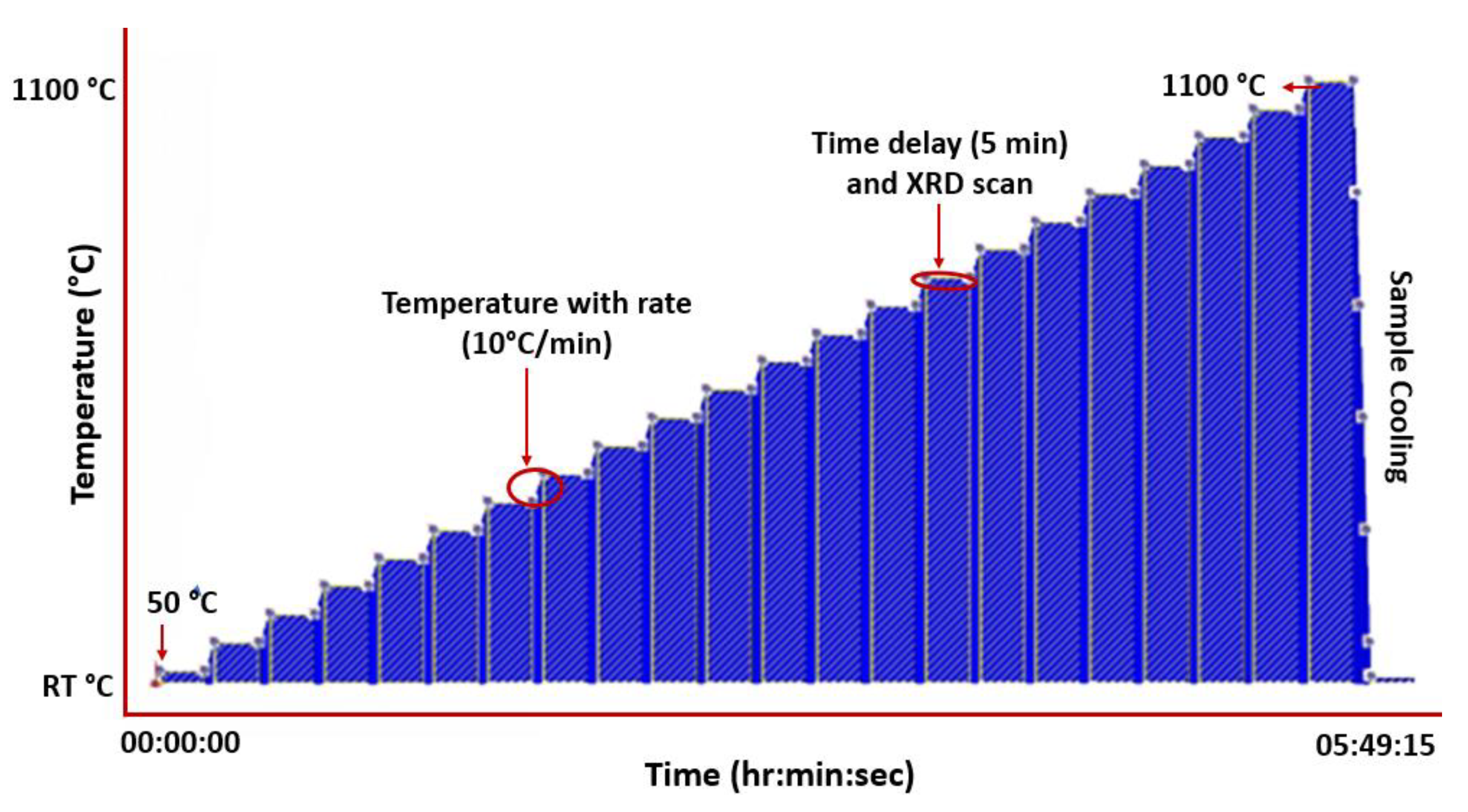
2.2.2. In Situ High Temperature X-ray Diffraction (HTXRD)
2.3. Thermodynamic Calculations for High-Temperature Oxide Formation
3. Results
3.1. Microstructural Analysis of CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy
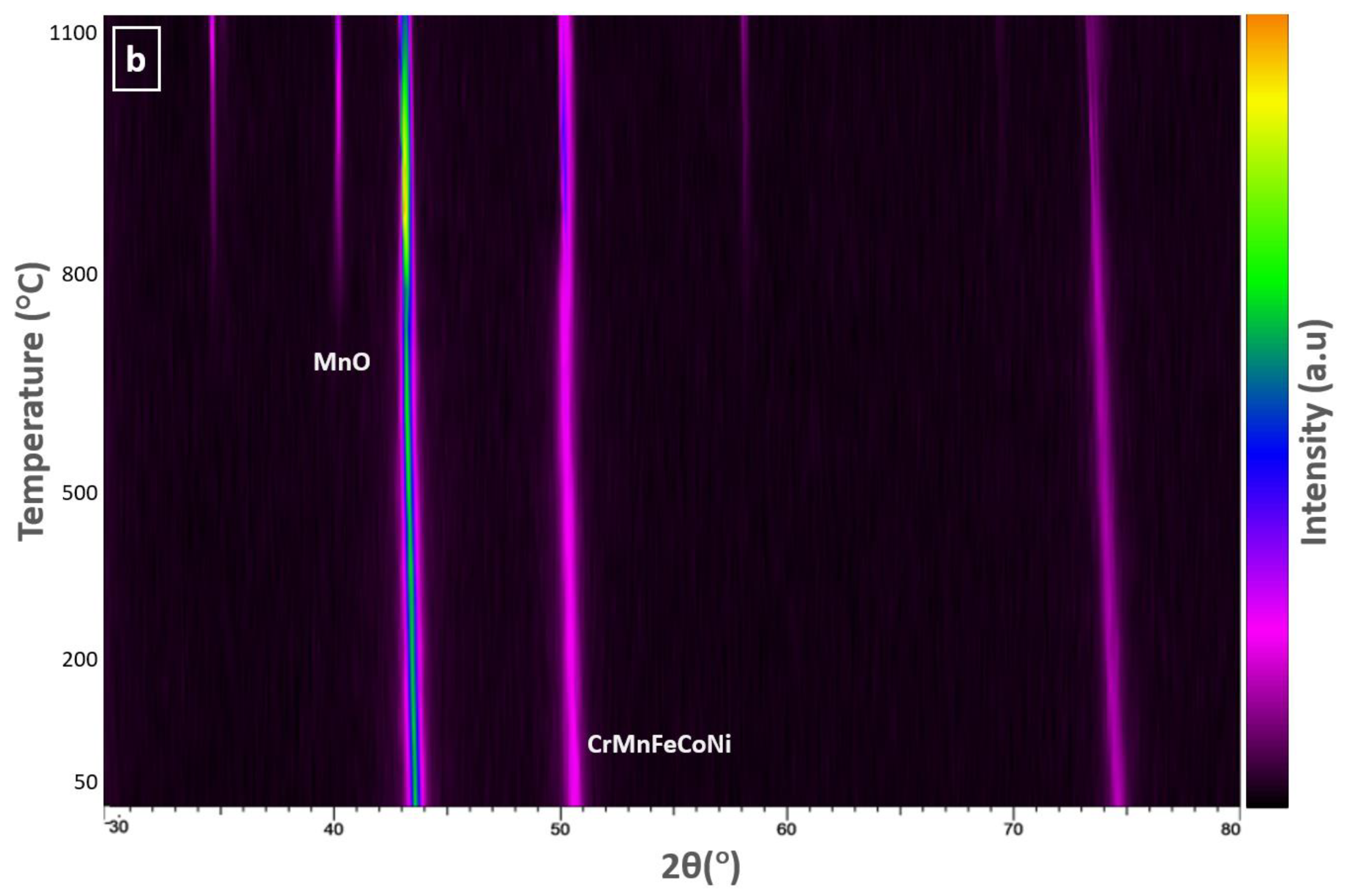
3.2. HTXRD in Vacuum
3.3. HTXRD in Air
4. Discussion
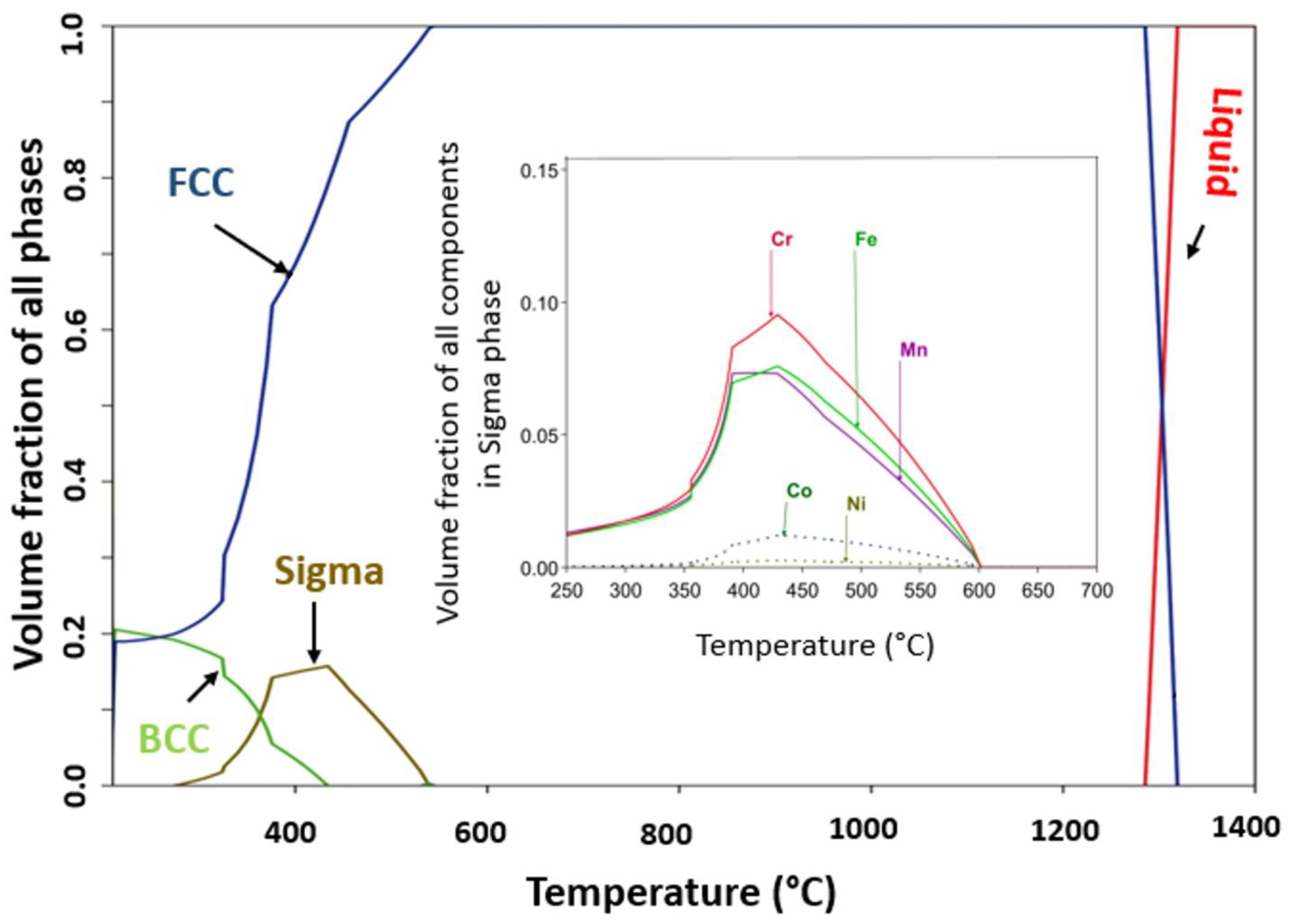
4.1. Phase Stability at High Temperature
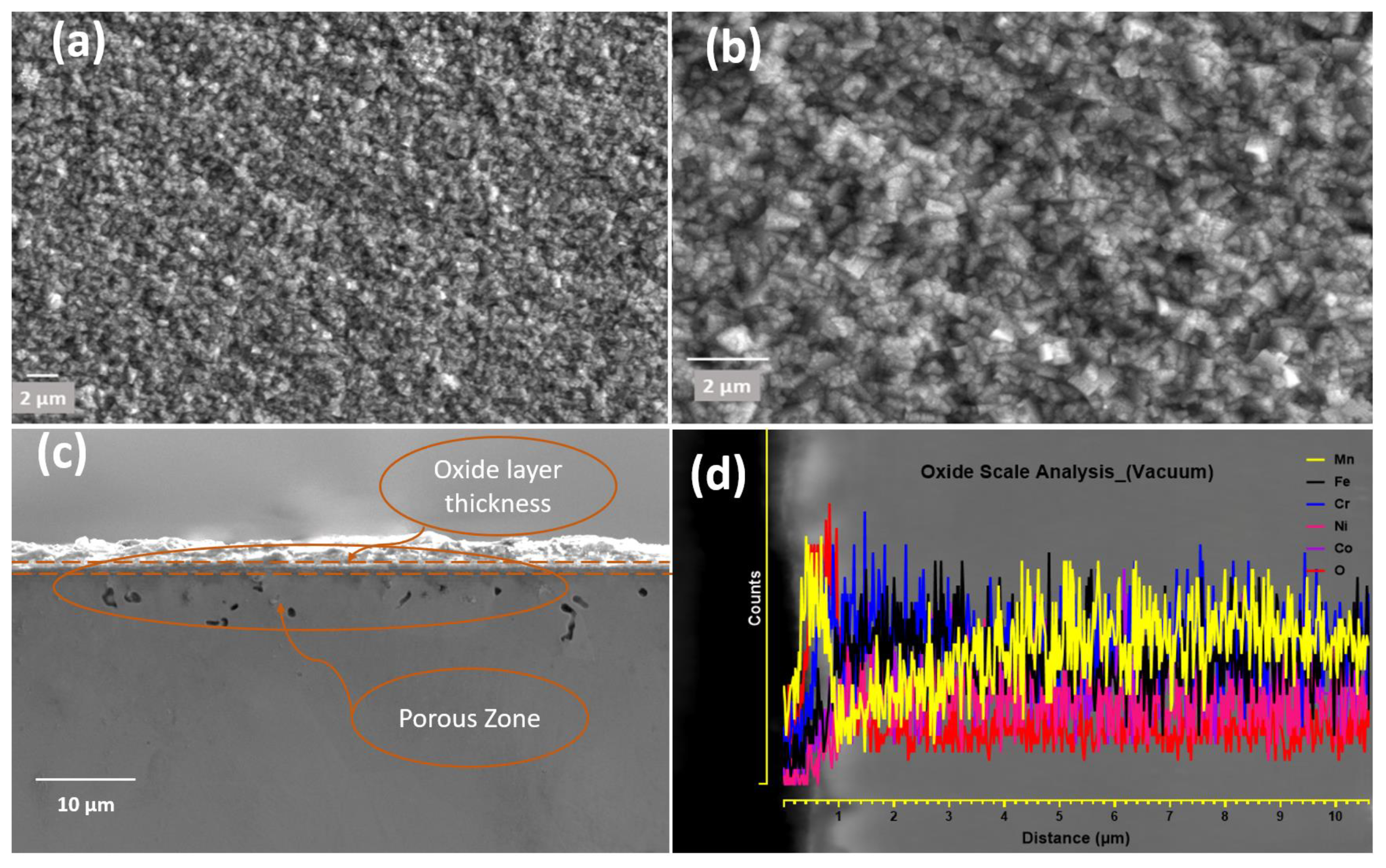
4.2. Oxidation in Vacuum
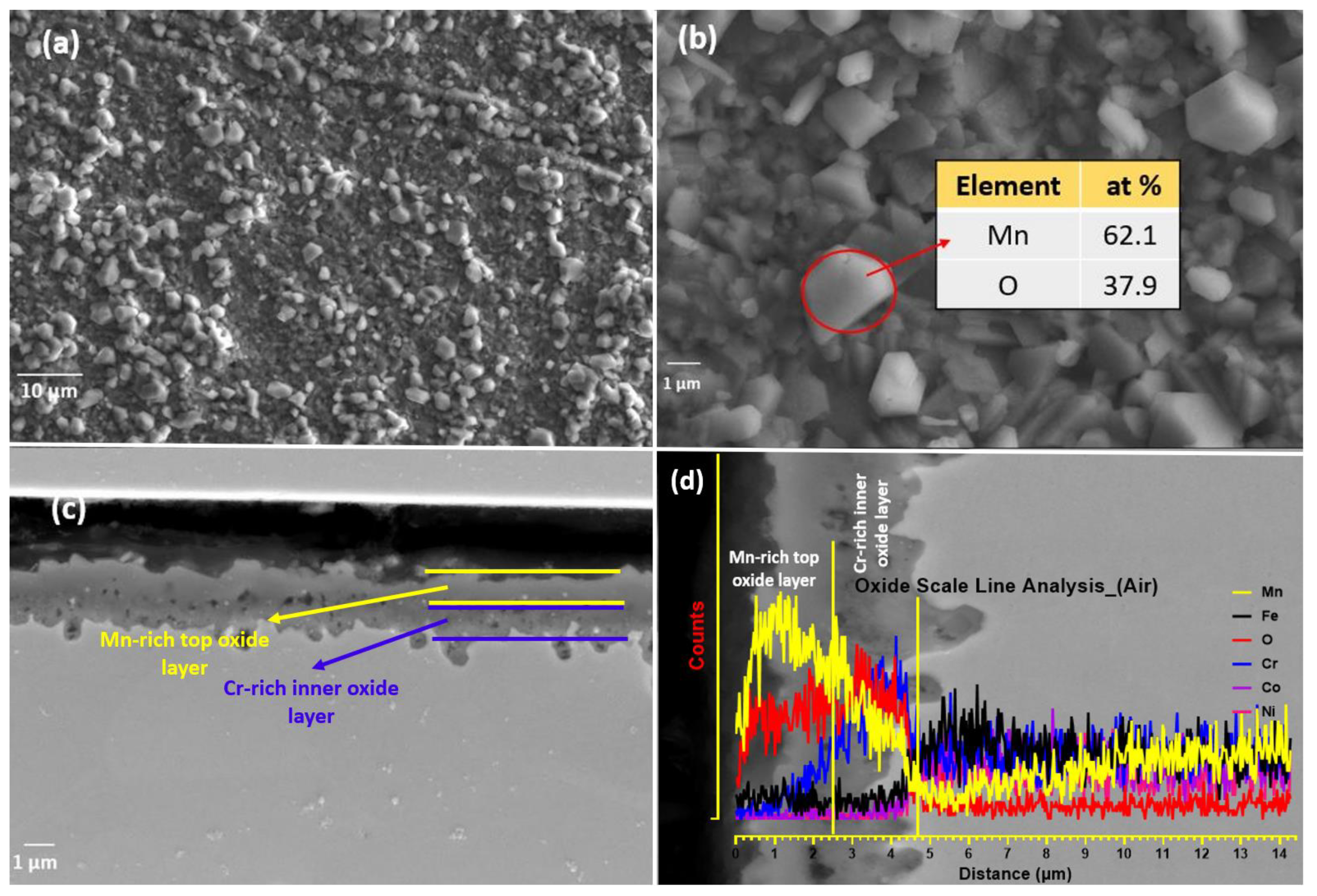
4.3. Oxidation in Air
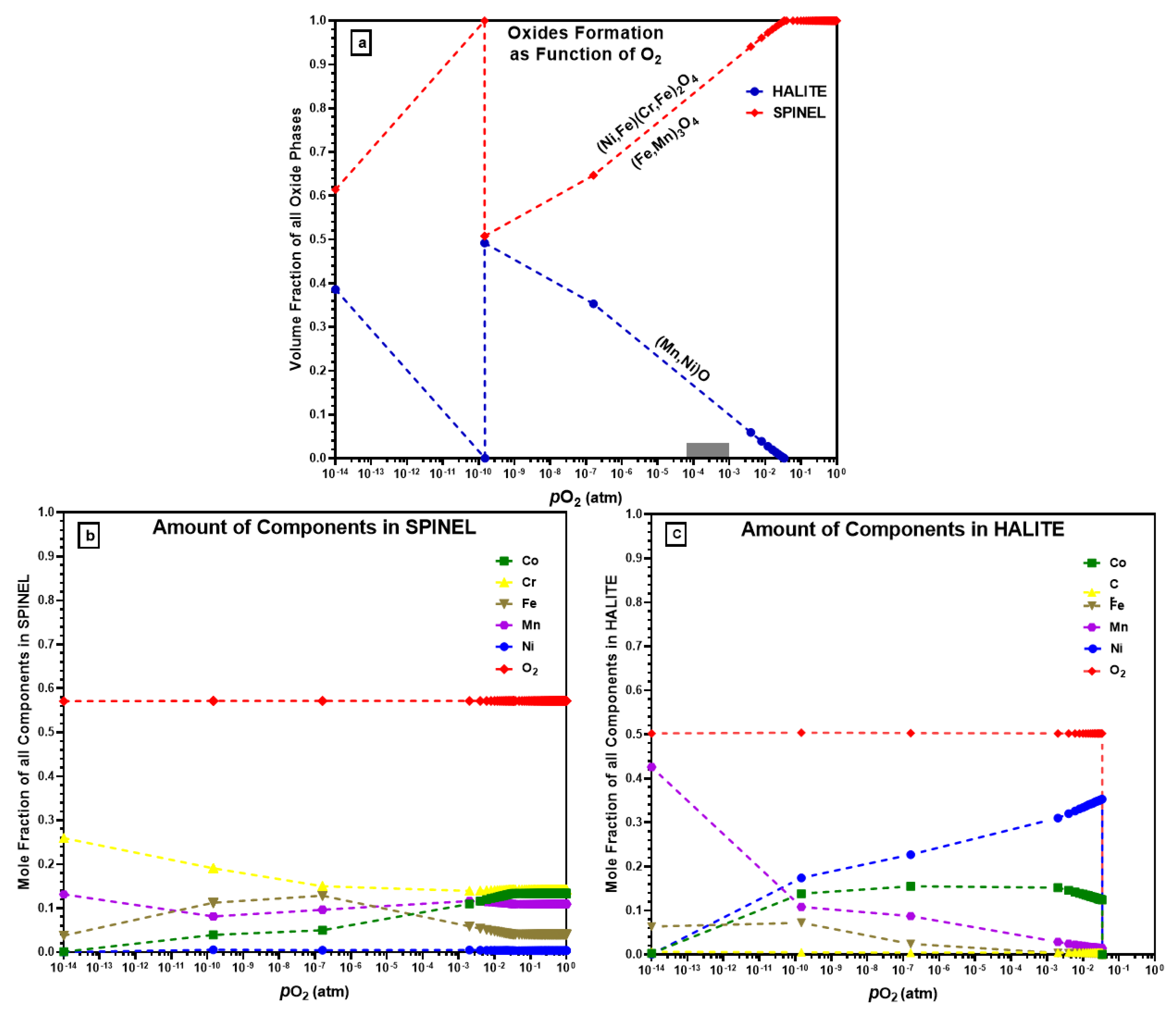
4.4. Oxidation Thermodynamics
5. Conclusions
- In a vacuum (4.2 × 10−6 atm), only MnO, a halite-type oxide, was formed during in situ oxidation, contrary to ThermoCalc’s prediction of both halite and spinel oxides, and Ni/Co forming halite.
- In air (1.0 atm), vigorous oxidation was observed, with most of the oxides formed being spinel. Mn remained important in the formation of spinel oxides, and Co was predicted to form spinel oxides by ThermoCalc but was not found in oxide-forming elements. Oxides like Cr2O3, Fe2O3, and Fe3O4 were not detected during in situ HTXRD in either vacuum or air, which contrasts with previous studies on the isothermal oxidation of CrMnFeCoNi HEA.
- Mn was found to be a higher oxide-forming element, producing non-protective oxides, and leading to the depletion of Mn in the bulk alloy beneath the oxide layer. Mn depletion creates doubt about the application of HEA for high-temperature applications and due to the higher diffusion rate may affect the sluggish kinetic diffusion effect, one of the four characteristic features of HEAs.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsai, K.Y.; Tsai, M.H.; Yeh, J.W. Sluggish diffusion in Co–Cr–Fe–Mn–Ni high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4887–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heczel, A.; Kawasaki, M.; Lábár, J.L.; Jang, J.-I.; Langdon, T.G.; Gubicza, J. Defect structure and hardness in nanocrystalline CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy processed by High-Pressure Torsion. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 711, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gludovatz, B.; Hohenwarter, A.; Catoor, D.; Chang, E.H.; George, E.P.; Ritchie, R.O. A fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy for cryogenic applications. Science 2014, 345, 1153–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Wanderka, N.; Murty, B.; Glatzel, U.; Banhart, J. Decomposition in multi-component AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yeh, J.; Shih, H. Pitting corrosion of the high-entropy alloy Co1.5CrFeNi1.5Ti0.5Mo0.1 in chloride-containing sulphate solutions. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3481–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, D.; Cheng, Y.-B.; Zhou, C.; Shen, G. Hierarchical silicon nanowires-carbon textiles matrix as a binder-free anode for high-performance advanced lithium-ion batteries. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Tsai, H.-L. Evolution of microstructure, hardness, and corrosion properties of high-entropy Al0.5CoCrFeNi alloy. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varalakshmi, S.; Rao, G.A.; Kamaraj, M.; Murty, B.S. Hot consolidation and mechanical properties of nanocrystalline equiatomic AlFeTiCrZnCu high entropy alloy after mechanical alloying. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 5158–5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Senkova, S.V.; Woodward, C. Effect of aluminum on the microstructure and properties of two refractory high-entropy alloys. Acta Mater. 2014, 68, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, Y.-Z.; Pan, Y.; Guo, S. Thermally stable laser cladded CoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy coating with low stacking fault energy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 600, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-H.; Yeh, J.-W. High-entropy alloys: A critical review. Mater. Res. Lett. 2014, 2, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kauffmann, A.; Gorr, B.; Schliephake, D.; Seemüller, C.; Wagner, J.; Christ, H.-J.; Heilmaier, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties at elevated temperatures of a new Al-containing refractory high-entropy alloy Nb-Mo-Cr-Ti-Al. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 661, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Joo, Y.-A.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, K.-A. High temperature oxidation behavior of Cr-Mn-Fe-Co-Ni high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2018, 98, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Cai, Z.; Guan, Y.; Cui, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Dong, M.; Zhang, D. High temperature wear performance of laser-cladded FeNiCoAlCu high-entropy alloy coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, W.; Cheng, F.; Liao, C.; Li, C.; Huang, R.; Kai, J. The oxidation behavior of the quinary FeCoNiCrSix high-entropy alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, T.M.; Weaver, M.L. Oxidation behavior of arc melted AlCoCrFeNi multi-component high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 674, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Wang, H.M.; Zhang, S.Q.; Tang, H.B.; Zhang, A.L. Microstructure and oxidation behavior of new refractory high entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 583, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miracle, D.B.; Miller, J.D.; Senkov, O.N.; Woodward, C.; Uchic, M.D.; Tiley, J. Exploration and Development of High Entropy Alloys for Structural Applications. Entropy 2014, 16, 494–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Jiao, Z.; Yang, Y. Effect of medium temperature precipitation phase and Mn element diffusion mechanism on high temperature oxidation process of repair and remanufacture CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy cladding. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 056521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplanche, G.; Volkert, U.F.; Eggeler, G.; George, E.P. Oxidation Behavior of the CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy. Oxid. Met. 2016, 85, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, G.R.; Tylczak, J.H.; Carney, C.S. Oxidation of CoCrFeMnNi High Entropy Alloys. JOM 2015, 67, 2326–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomfield, M.E.; Christofidou, K.A.; Jones, N.G. Effect of Co on the phase stability of CrMnFeCoxNi high entropy alloys following long-duration exposures at intermediate temperatures. Intermetallics 2019, 114, 106582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, W.; Cheng, F.; Chien, F.; Lin, Y.; Chen, D.; Kai, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, C. The oxidation behavior of a Ni2FeCoCrAl0.5 high-entropy superalloy in O2-containing environments. Corros. Sci. 2019, 158, 108093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Liu, H.; Jiao, J.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Y.; Ren, X. Laser additive manufacturing of CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy: Microstructural evolution, high-temperature oxidation behavior and mechanism. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 130, 106326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan-Scherb, C.; Schulz, W.; Schneider, M.; Karafiludis, S.; Laplanche, G. High-Temperature Oxidation in Dry and Humid Atmospheres of the Equiatomic CrMnFeCoNi and CrCoNi High- and Medium-Entropy Alloys. Oxid. Met. 2021, 95, 105–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doležal, T.D.; Samin, A.J. Adsorption of Oxygen to High Entropy Alloy Surfaces for up to 2 ML Coverage Using Density Func-tional Theory and Monte Carlo Calculations. Langmuir 2022, 38, 3158–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Ren, Q.; Agbedor, S.-O.; Lei, Q. High-temperature oxidation behaviors of an equiatomic CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 32, 104185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, W.; Li, C.C.; Cheng, F.P.; Chu, K.P.; Huang, R.T.; Tsay, L.W.; Kai, J.J. The oxidation behavior of an equimolar FeCoNiCrMn high-entropy alloy at 950 °C in various oxygen-containing atmospheres. Corros. Sci. 2016, 108, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, M.; Amer, M.; Hayat, Q.; Janik, V.; Zhang, X.; Moradi, M.; Bai, M. High-Entropy Coatings (HEC) for High-Temperature Applications: Materials, Processing, and Properties. Coatings 2022, 12, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolique, V.; Thomann, A.-L.; Brault, P.; Tessier, Y.; Gillon, P. Thermal stability of AlCoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy thin films studied by in-situ XRD analysis. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 1989–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Engström, A.; Sundman, B. Thermodynamic investigations on materials corrosion in some industrial and environmental processes. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratberg, J.; Mao, H.; Kjellqvist, L.; Engström, A.; Mason, P.; Chen, Q. The development and validation of a new thermodynamic database for Ni-based alloys. Superalloys 2012, 12, 803–812. [Google Scholar]
- Pala, Z.; Bai, M.; Lukac, F.; Hussain, T. Laser Clad and HVOF-Sprayed Stellite 6 Coating in Chlorine-Rich Environment with KCl at 700 °C. Oxid. Met. 2017, 88, 749–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, O. Influence of oxygen partial pressure in sintering atmosphere on properties of Cr–Mo prealloyed powder metallurgy steel. Powder Met. 2007, 50, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gali, A.; George, E.P. Tensile properties of high- and medium-entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2013, 39, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-L.; Mao, H.; Chen, Q. Database development and Calphad calculations for high entropy alloys: Challenges, strategies, and tips. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 210, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, Y. The CALPHAD approach for HEAs: Challenges and opportunities. MRS Bull. 2022, 47, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Hanold, N.L.; George, E.P. Microstructural evolution after thermomechanical processing in an equiatomic, single-phase CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy with special focus on twin boundaries. Intermetallics 2014, 54, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.J.; Muñoz-Moreno, R.; Stone, H.J.; Jones, N.G. Precipitation in the equiatomic high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi. Scr. Mater. 2016, 113, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, B.; Douglass, D.L.; Gesmundo, F. A comprehensive investigation of the sulfidation behavior of binary Co-Mo alloys. Oxid. Met. 1990, 33, 425–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, F.; Dlouhý, A.; Pradeep, K.; Kuběnová, M.; Raabe, D.; Eggeler, G.; George, E. Decomposition of the single-phase high-entropy alloy CrMnFeCoNi after prolonged anneals at intermediate temperatures. Acta Mater. 2016, 112, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, C. Phase separation of metastable CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy at intermediate temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2017, 126, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saal, J.E.; Berglund, I.S.; Sebastian, J.T.; Liaw, P.K.; Olson, G.B. Equilibrium high entropy alloy phase stability from experiments and thermodynamic modeling. Scr. Mater. 2018, 146, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speidel, D.H.; Muan, A. The system manganese oxide–Cr2O3 in air. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1963, 46, 577–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opeka, M.M.; Talmy, I.G.; Zaykoski, J.A. Oxidation-based materials selection for 2000 °C+ hypersonic aerosurfaces: Theoretical considerations and historical experience. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 5887–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, R.K. High temperature oxidation of austenitic stainless steel in low oxygen pressure. Corros. Sci. 1977, 17, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.C.; Kumar, B.A.; Reddappa, H.N.; Ramesh, M.R.; Koppad, P.G.; Kord, S. HVOF sprayed Ni3Ti and Ni3Ti+ (Cr3C2+ 20NiCr) coatings: Microstructure, microhardness and oxidation behaviour. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 736, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Alloy Composition (at.%) | Co | Cr | Mn | Fe | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Experimental (EDS) | 21.04 | 18.22 | 20.34 | 20.37 | 20.38 |
| Temperature (°C) | 1100 | |
| Pressure (Pa) | 101,325 | |
| System Size (mol) | 1.0 | |
| Composition | Cr | 15 |
| Mn | 15 | |
| Fe | 15 | |
| Co | 15 | |
| Ni | 35 | |
| O | 05 | |
| Activity of O2 | Min | 1.0 × 10−14 |
| Max | 1.0 | |
| No of Steps | 100 | |
| Composition | Homogenisation Conditions | Ageing Conditions | Observed Phases | CALPHAD Phases | Solvus | Equili Solidus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otto et al. [38] | CrCoFeMnNi | 1200 °C 48 h | 500 °C 12,000 h | L10, BCC, B2 | FCC, Sigma | 798 | 1286 |
| CrCoFeMnNi | 1200 °C 48 h | 700 °C 12,000 h | FCC, Sigma | FCC, Sigma | 798 | 1286 | |
| CrCoFeMnNi | 1200 °C 48 h | 900 °C 12,000 h | FCC | FCC | 798 | 1286 | |
| Pickring et al. [36] | CrCoFeMnNi | 1240 °C 1000 h | 700 °C 1000 h | FCC, Sigma, M23C6 | FCC, Sigma | 798 | 1286 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arshad, M.; Bano, S.; Amer, M.; Janik, V.; Hayat, Q.; Huang, Y.; Guan, D.; Bai, M. Thermodynamic Insights into the Oxidation Mechanisms of CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy Using In Situ X-ray Diffraction. Materials 2023, 16, 5042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145042
Arshad M, Bano S, Amer M, Janik V, Hayat Q, Huang Y, Guan D, Bai M. Thermodynamic Insights into the Oxidation Mechanisms of CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy Using In Situ X-ray Diffraction. Materials. 2023; 16(14):5042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145042
Chicago/Turabian StyleArshad, Muhammad, Saira Bano, Mohamed Amer, Vit Janik, Qamar Hayat, Yuze Huang, Dikai Guan, and Mingwen Bai. 2023. "Thermodynamic Insights into the Oxidation Mechanisms of CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy Using In Situ X-ray Diffraction" Materials 16, no. 14: 5042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145042
APA StyleArshad, M., Bano, S., Amer, M., Janik, V., Hayat, Q., Huang, Y., Guan, D., & Bai, M. (2023). Thermodynamic Insights into the Oxidation Mechanisms of CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy Using In Situ X-ray Diffraction. Materials, 16(14), 5042. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16145042










