Corrosion Behavior of CrFeCoNiV0.5 and CrFeCoNiV Alloys in 0.5 M and 1 M Sodium Chloride Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murty, B.S.; Yeh, J.W.; Ranganathan, S.; Bhattacharjee, P.P. High-Entropy Alloys, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 13–30. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, J.W. Alloy Design Strategies and Future Trends in High-Entropy Alloys. JOM 2013, 65, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, P.; Sun, H.; Li, T.; Qin, C. Effects of Elements on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AlCoCrFeNiTi High-Entropy Alloys. Metals 2023, 13, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Chauhan, A.; Tirunilai, A.S.; Freudenberger, J.; Kauffmann, A.; Heilmaier, M.; Aktaa, J. Deformation Mechanisms of CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy Under Low-Cycle-Fatigue Loading. Acta Mater. 2021, 215, 117089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, M.; Gariapati, M.M.; Murty, B.S. High-Entropy Alloys by Mechanical Alloying: A Review. J. Mater. Res. 2019, 34, 664–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkodich, N.; Sedegov, A.; Kuskov, K.; Busurin, S.; Scheck, Y.; Vadchenko, S.; Moskovskikh, D. Refractory High-Entropy HfTaTiNbZr-Based Alloys by Combined Use of Ball Milling and Spark Plasma Sintering: Effect of Milling Intensity. Metals 2020, 10, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ma, Z.L.; Xu, Z.Q.; Cheng, X.W. Designing VNbMoTa Refractory High-Entropy Alloys with Improved Properties for High-Temperature Applications. Scr. Mater. 2021, 191, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Su, K.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Peng, H.; Li, X. Enhanced Strength of a Mechanical Alloyed NbMoTaWVTi Refractory High Entropy Alloy. Materials 2018, 11, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsau, C.H.; Tsai, M.C.; Wang, W.L. Microstructures of FeCoNiMo and CrFeCoNiMo Alloys, and the Corrosion Properties in 1 M Nitric Acid and 1 M Sodium Chloride Solutions. Materials 2022, 15, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geantă, V.; Voiculescu, I.; Cotrut, M.C.; Vrânceanu, M.D.; Vasile, I.M.; Rosca, J.C.M. Effect of Al on Corrosion Behavior in 3.5% NaCl Solution of AlxCoCrFeNi High Entropy Alloys. Int. J. Eng. Res. Afr. 2021, 53, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Yi, H.; Qi, W.; Peng, Q. Effect of Molybdenum Additives on Corrosion Behavior of (CoCrFeNi)100−x Mo x High-Entropy Alloys. Entropy 2018, 20, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, X.R.; Wang, Z.Q.; He, P. Microstructure and Corrosion Properties of AlCrxNiCu0.5Mo (x = 0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0) High Entropy Alloy Coatings on Q235 Steel by Electrospark—Computer Numerical Control Deposition. Mater. Lett. 2021, 292, 129642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito-Garcia, S.; Mirza-Rosca, J.; Geanta, V.; Voiculescu, I. Mechanical and Corrosion Behavior of Zr-Doped High-Entropy Alloy from CoCrFeMoNi System. Materials 2023, 16, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, R.; Jin, P.; Zhang, Y. Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of NbTiAlSiZrNx High-Entropy Films Prepared by RF Magnetron Sputtering. Entropy 2019, 21, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muangtong, P.; Rodchanarowan, A.; Chaysuwan, D.; Chanlek, N.; Goodall, R. The Corrosion Behaviour of CoCrFeNi-x (x = Cu, Al, Sn) High Entropy Alloy Systems in Chloride Solution. Corros. Sci. 2020, 172, 108740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Yuasa, M.; Miyamoto, H.; Edalati, K. Corrosion Behavior of Ultrafine-Grained CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloys Fabricated by High-Pressure Torsion. Materials 2022, 15, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsau, C.H.; Yeh, C.Y.; Tsai, M.C. The Effect of Nb-Content on the Microstructures and Corrosion Properties of CrFeCoNiNbx High-Entropy Alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsau, C.H.; Chen, J.Y.; Chien, T.Y. Corrosion Behavior of CrFeCoNiVx (x = 0.5 and 1) High-Entropy Alloys in 1M Sulfuric Acid and 1M Hydrochloric Acid Solutions. Materials 2022, 15, 3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 808–810. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM G150-99; Standard Test Method for Electrochemical Critical Pitting Temperature Testing of Stainless Steels. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010.
- Fontana, M.G. Corrosion Engineering, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Book Co.: Singapore, 1987; p. 172. [Google Scholar]







| Alloys (at.%) | Cr | Fe | Co | Ni | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (wt.%) | |||||
| CrFeCoNiV0.5 | |||||
| nominal | 20.72 | 22.25 | 23.48 | 23.39 | 10.16 |
| actual | 21.6 | 22.6 | 22.3 | 22.3 | 11.2 |
| CrFeCoNiV | |||||
| Nominal | 18.81 | 20.20 | 21.32 | 21.24 | 18.43 |
| actual | 19.4 | 20.2 | 20.5 | 20.2 | 19.7 |
| 0.5 M NaCl | 1 M NaCl | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C | 60 °C | 30 °C | 60 °C | |
| Ecorr (VSHE) | −0.79 | −0.67 | −0.55 | −0.49 |
| icorr (μA/cm2) | 1.80 | 4.20 | 2.90 | 5.40 |
| Epp (VSHE) | −0.60 | −0.53 | −0.12 | −0.17 |
| icrit (μA/cm2) | 3.80 | 7.40 | 2.76 | 154 |
| Epp2 (VSHE) * | −0.09 | 0.01 | N/A | N/A |
| icrit2 (μA/cm2) * | 4.10 | 15.3 | N/A | N/A |
| 0.5 M NaCl | 1 M NaCl | |
|---|---|---|
| Rs (Ω) | 26 | 27 |
| Rp (kΩ) | 517 | 164 |
| 0.5 M NaCl | 1 M NaCl | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C | 60 °C | 30 °C | 60 °C | |
| Ecorr (VSHE) | −0.71 | −0.83 | −0.76 | −0.90 |
| icorr (μA/cm2) | 3.50 | 4.00 | 5.00 | 6.00 |
| Epp (VSHE) | −0.55 | N/A | −0.51 | N/A |
| icrit (μA/cm2) | 9.30 | N/A | 17.1 | N/A |
| 0.5 M NaCl | 1 M NaCl | |
|---|---|---|
| Rs (Ω) | 14 | 20 |
| Rp (kΩ) | 591 | 470 |
| Applied Potential | CrFeCoNiV0.5 | CrFeCoNiV | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mVSHE) | 0.5 M NaCl | 1 M NaCl | 0.5 M NaCl | 1 M NaCl |
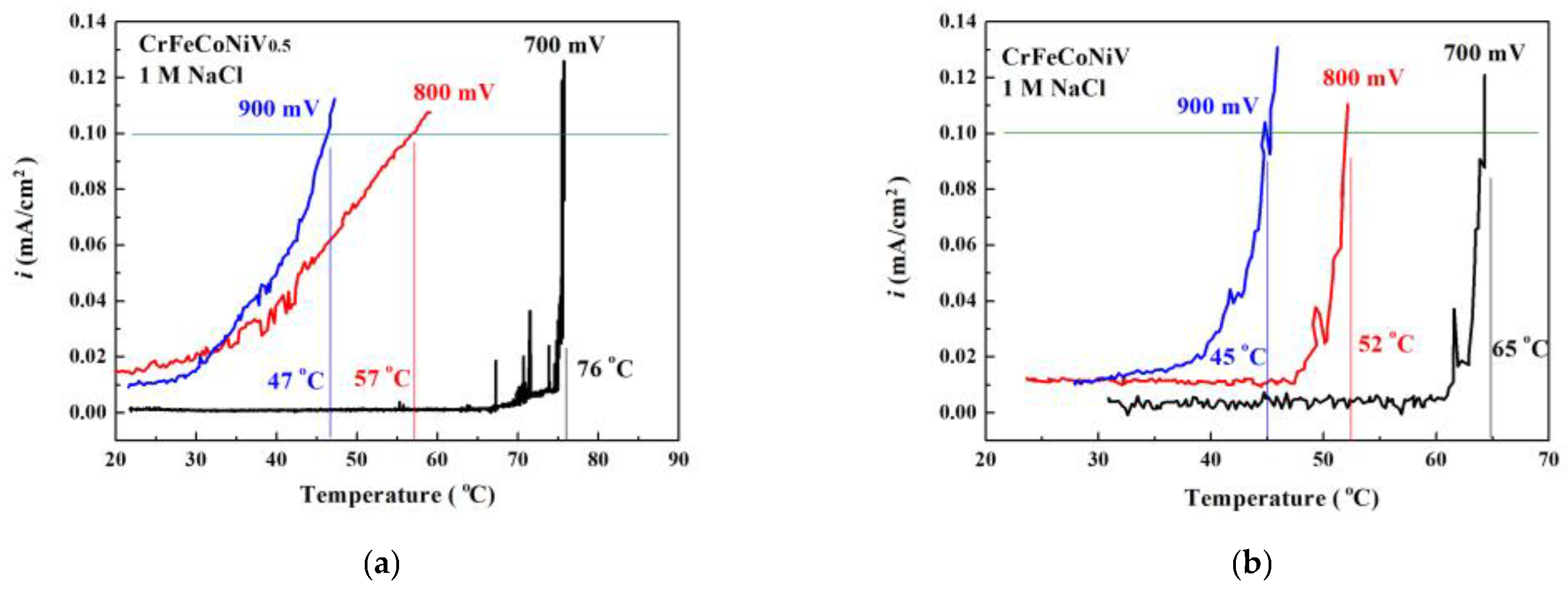
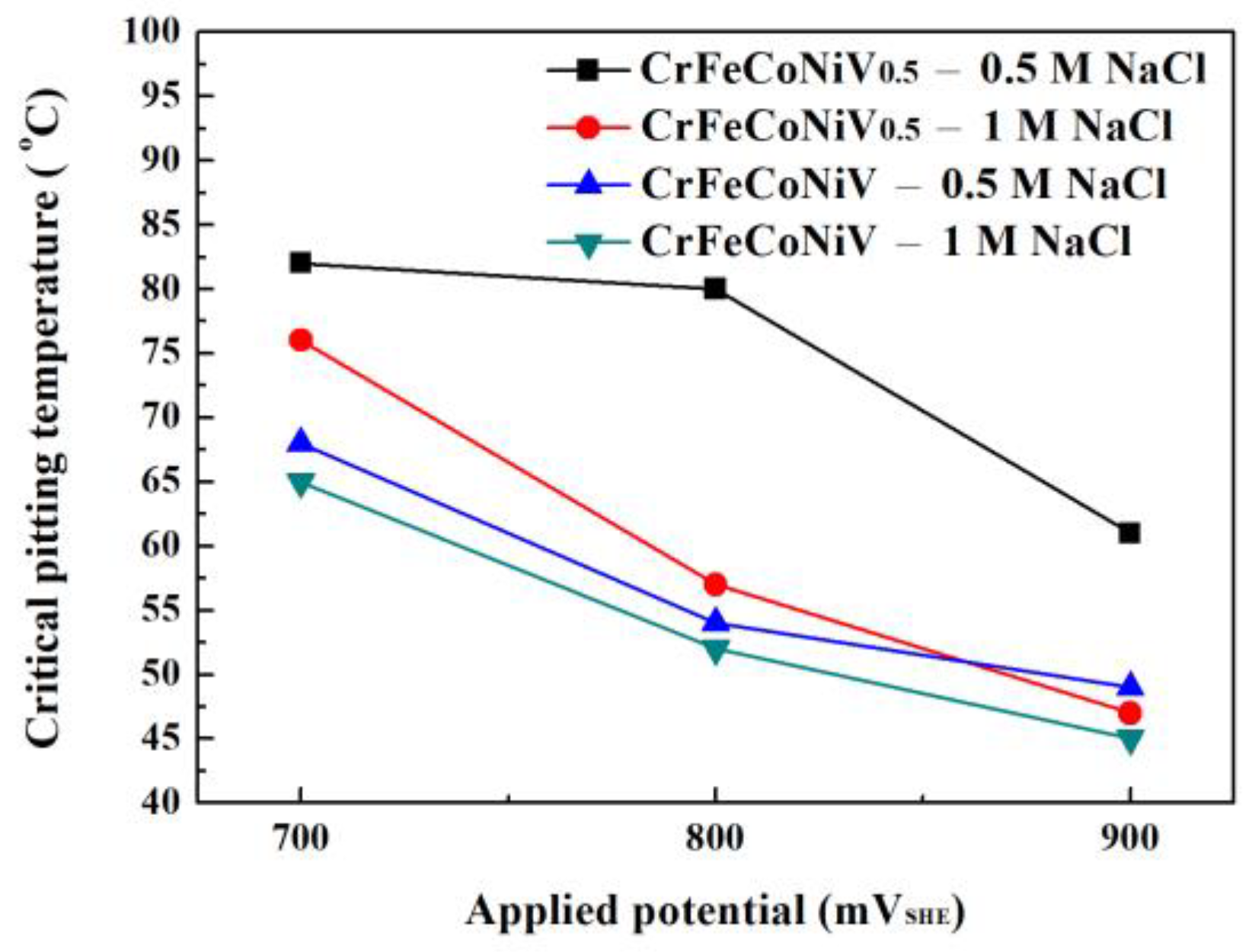
| 700 | 82 | 76 | 68 | 65 |
| 800 | 80 | 57 | 54 | 52 |
| 900 | 61 | 47 | 49 | 45 |
| Alloys | 0.5 M NaCl (mm/y) | 1 M NaCl (mm/y) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 30 °C | 60 °C | 30 °C | 60 °C | |
| CrFeCoNiV0.5 | 0.016 | 0.026 | 0.038 | 0.048 |
| CrFeCoNiV | 0.029 | 0.033 | 0.041 | 0.050 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsau, C.-H.; Hsiao, H.-P.; Chien, T.-Y. Corrosion Behavior of CrFeCoNiV0.5 and CrFeCoNiV Alloys in 0.5 M and 1 M Sodium Chloride Solutions. Materials 2023, 16, 4900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16144900
Tsau C-H, Hsiao H-P, Chien T-Y. Corrosion Behavior of CrFeCoNiV0.5 and CrFeCoNiV Alloys in 0.5 M and 1 M Sodium Chloride Solutions. Materials. 2023; 16(14):4900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16144900
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsau, Chun-Huei, Hui-Ping Hsiao, and Tien-Yu Chien. 2023. "Corrosion Behavior of CrFeCoNiV0.5 and CrFeCoNiV Alloys in 0.5 M and 1 M Sodium Chloride Solutions" Materials 16, no. 14: 4900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16144900
APA StyleTsau, C.-H., Hsiao, H.-P., & Chien, T.-Y. (2023). Corrosion Behavior of CrFeCoNiV0.5 and CrFeCoNiV Alloys in 0.5 M and 1 M Sodium Chloride Solutions. Materials, 16(14), 4900. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16144900






