In-Situ Growth of ZnO Whiskers on Ti2ZnC MAX Phases
Abstract
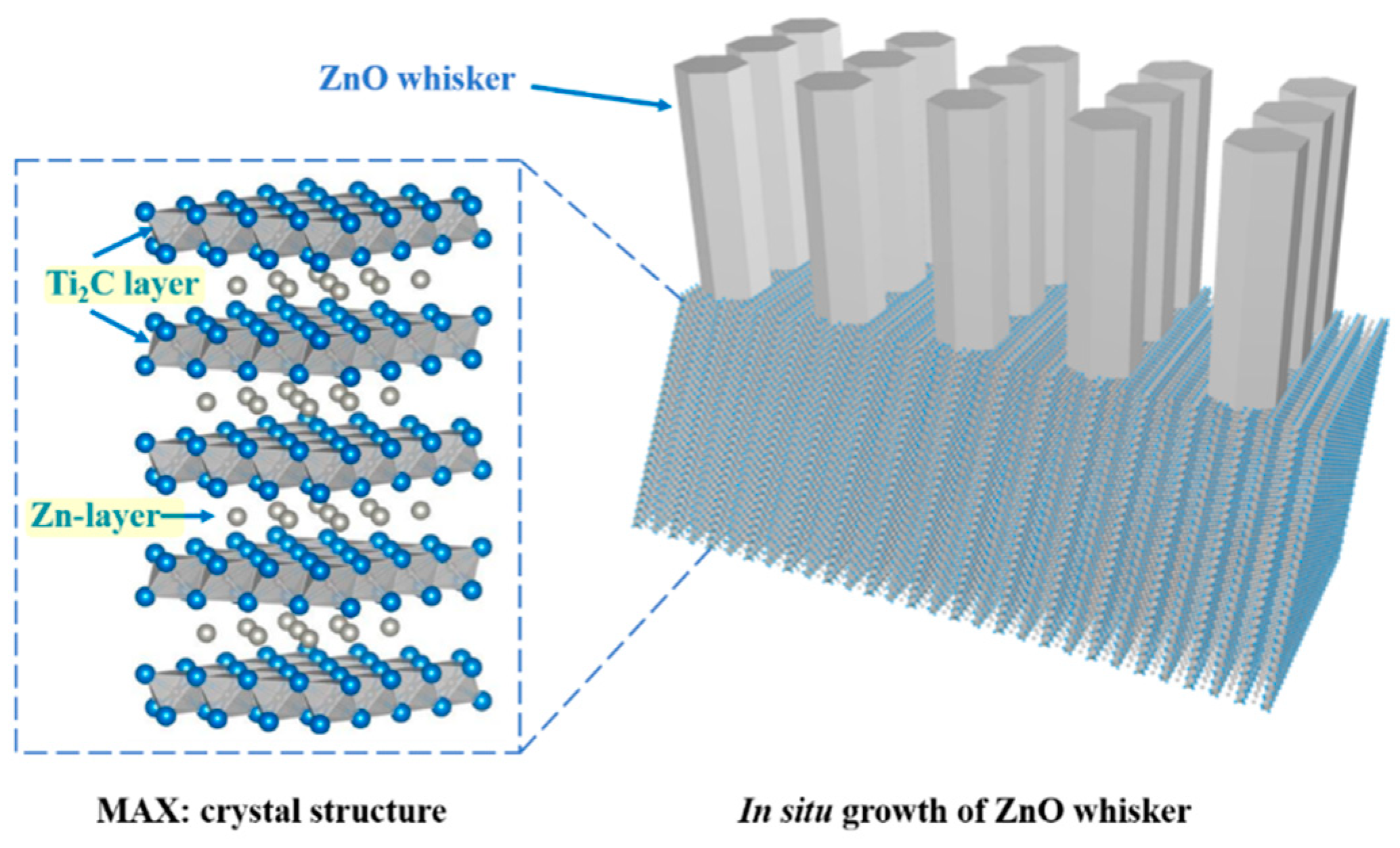
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wlazlo, M.; Haras, M.; Kolodziej, G.; Szawcow, O.; Ostapko, J.; Andrysiewicz, W.; Kharytonau, D.S.; Skotnicki, T. Piezoelectric Response and Substrate Effect of ZnO Nanowires for Mechanical Energy Harvesting in Internet-of-Things Applications. Materials 2022, 15, 6767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peksu, E.; Karaagac, H. Doping and annealing effects on structural, electrical and optical properties of tin-doped zinc-oxide thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 764, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Mawignon, F.J.; Hussain, M.; Ange, N.K.; Lu, S.; Hafezi, M.; Dong, G. Economic Friendly ZnO-Based UV Sensors Using Hydrothermal Growth: A Review. Materials 2021, 14, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Yu, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Li, Y. Review of ZnO-based nanomaterials in gas sensors. Solid State Ionics 2021, 360, 115544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, M.T.; Amor, N.; Petru, M.; Mahmood, A.; Kejzlar, P. Photocatalytic Behaviour of Zinc Oxide Nanostructures on Surface Activation of Polymeric Fibres. Polymers 2021, 13, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhong, K.; Fang, X.; Fang, D.; Zhao, H.; Wang, D.; Li, B.; Zhai, Y.; Chu, X.; Li, J.; et al. Brief Review of Photocatalysis and Photoresponse Properties of ZnO–Graphene Nanocomposites. Energies 2021, 14, 6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ding, J.; Cai, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, C.; Foss, M.; Yang, R. Plasmon-enhanced photocatalytic properties of Au/ZnO nanowires. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 583, 152539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Xu, L.; Tian, Z.; Zang, A. Changes in photocatalytic activity and optical properties of ZnO whiskers induced by UV irradiation. J. Lumin. 2022, 249, 119015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekofteh-Gohari, M.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Abitorabi, M.; Rouhi, A. Magnetically separable nanocomposites based on ZnO and their applications in photocatalytic processes: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 806–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Casas, B.; Galdámez-Martínez, A.; Gutiérrez-Flores, J.; Baca Ibañez, A.; Kumar Panda, P.; Santana, G.; de la Vega, H.A.; Suar, M.; Gutiérrez Rodelo, C.; Kaushik, A.; et al. Bio-acceptable 0D and 1D ZnO nanostructures for cancer diagnostics and treatment. Mater. Today 2021, 50, 533–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Song, J.J.S. Piezoelectric nanogenerators based on zinc oxide nanowire arrays. Science 2006, 312, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.T.; Le, T.D.H.; Cheong, K.-Y.; Pung, S.-Y. Immobilization of zinc oxide-based photocatalysts for organic pollutant degradation: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, N.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Zhuge, F.; Li, J.; Gao, X.P.A.; Du, J. Control of ZnO nanowire growth and optical properties in a vapor deposition process. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guniat, L.; Caroff, P.; Fontcuberta, I.M.A. Vapor Phase Growth of Semiconductor Nanowires: Key Developments and Open Questions. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 8958–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- McIntyre, P.C.; Fontcuberta i Morral, A. Semiconductor nanowires: To grow or not to grow? Mater. Today Nano 2020, 9, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Li, Q.; Guang, H.; An, M. Electrodeposited Zn: A promising alternative to ZnO seed layer for hydrothermal growth of ZnO nanowire array. Mater. Lett. 2022, 314, 131848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almamari, M.R.; Ahmed, N.M.; Holi, A.M.; Yam, F.K.; Kyaw, H.H.; Almessiere, M.A.; Al-Abri, M.Z. Some Distinct Attributes of ZnO Nanorods Arrays: Effects of Varying Hydrothermal Growth Time. Materials 2022, 15, 5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podrezova, L.V.; Porro, S.; Cauda, V.; Fontana, M.; Cicero, G. Comparison between ZnO nanowires grown by chemical vapor deposition and hydrothermal synthesis. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 113, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J. Zinc oxide nanowires. Mater. Charact. 2012, 64, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. The use of nanoparticles in polymeric and ceramic membrane structures: Review of manufacturing procedures and performance improvement for water treatment. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2335–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.; Zhang, D.; Mo, Y.; Song, L.; Brewer, E.; Huang, X.; Xiong, Y. Photocatalytic activity of polymer-modified ZnO under visible light irradiation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, R.; Dutta, J. Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes with manganese-doped ZnO nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleye, A.S.; Conway, J.R.; Garner, K.; Huang, Y.; Su, Y.; Keller, A.A. Engineered nanomaterials for water treatment and remediation: Costs, benefits, and applicability. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 286, 640–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, W.; Pan, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z. Rapid and massive growth of tin whisker on mechanochemically decomposed Ti2SnC. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Xu, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, F.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z. Large-scale preparation of nano-sized carbides and metal whiskers via mechanochemical decomposition of MAX phases. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2022, 20, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, J.; Shi, J.; Sun, Z.J.M.L. Spontaneous growth of Sn whiskers and a new formation mechanism. Mater. Lett. 2016, 178, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Tang, J.; Tang, H.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.M. Method for inhibiting Sn whisker growth on Ti2SnC. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 20462–20471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.G.; Ding, J.X.; Liu, Y.S.; Yang, L.; Tian, W.B.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, Z.M. Mechanism and mitigation of spontaneous Ga whisker growth on Cr2GaC. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2020, 63, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, M.; Natu, V.; Kota, S.; Barsoum, M.W. On the Chemical Diversity of the MAX Phases. Trends Chem. 2019, 1, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Wu, F.; Hu, P.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Z. Synthesis of Ti3(SnxAl1−x)C2 solid solutions over the whole composition range. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 894, 162429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Xia, W. MAX Phases as Nanolaminate Materials: Chemical Composition, Microstructure, Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2021, 23, 2001191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Z. MXenes with applications in supercapacitors and secondary batteries: A comprehensive review. Mater. Rep. Energy 2022, 2, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Duan, X.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y.; van der Zwaag, S. On the formation mechanisms and properties of MAX phases: A review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 3851–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.G.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.B.; Wang, X.H.; Ying, G.B.; Xia, Q.X.; Zhang, P.G. From structural ceramics to 2D materials with multi-applications: A review on the development from MAX phases to MXenes. J. Adv. Ceram. 2021, 10, 1194–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Shen, L.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Sun, Z.J. Room temperature mushrooming of gallium wires and its growth mechanism. J. Alloy Compd. 2015, 619, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhang, P.G.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, C.J.; Pan, L.; Ding, J.X.; Sun, Z.M. Interface energy-driven indium whisker growth on ceramic substrates. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 16881–16888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, J.; Luo, K.; Li, Y.; Chang, K.; Chen, K.; Zhou, J.; Rosen, J.; Hultman, L.; Eklund, P.; et al. Element Replacement Approach by Reaction with Lewis Acidic Molten Salts to Synthesize Nanolaminated MAX Phases and MXenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4730–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hashimoto, S.; Takeuchi, M.; Inoue, K.; Honda, S.; Awaji, H.; Fukuda, K.; Zhang, S. Pressureless sintering and mechanical properties of titanium aluminum carbide. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 1480–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng-Ming, S.U.N.; Wu-Bian, T.; Pei-Gen, Z.; Dan-Dan, W.; Yu-Hui, Z.H.A.; Pei-Yan, H.; Jian-Xiang, D. High-purity Ti2AlC Powder: Preparation and Application in Ag-based Electrical Contact Materials. J. Inorg. Mater. 2019, 35, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.C. Low-temperature instability of Ti2SnC: A combined transmission electron microscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, and X-ray diffraction investigations. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 24, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajalakshmi, M.; Arora, A.K.; Bendre, B.S.; Mahamuni, S. Optical phonon confinement in zinc oxide nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 2445–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthik, K.V.; Raghu, A.V.; Reddy, K.R.; Ravishankar, R.; Sangeeta, M.; Shetti, N.P.; Reddy, C.V. Green synthesis of Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles and its application for the photocatalytic degradation of hazardous organic pollutants. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, Y.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, F.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Z. In-Situ Growth of ZnO Whiskers on Ti2ZnC MAX Phases. Materials 2023, 16, 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103610
Ren Y, Tian Z, Zhang Y, Wu F, Xie H, Zhang Q, Zhang P, Sun Z. In-Situ Growth of ZnO Whiskers on Ti2ZnC MAX Phases. Materials. 2023; 16(10):3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103610
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Yinan, Zhihua Tian, Yan Zhang, Fushuo Wu, Hao Xie, Qianqian Zhang, Peigen Zhang, and Zhengming Sun. 2023. "In-Situ Growth of ZnO Whiskers on Ti2ZnC MAX Phases" Materials 16, no. 10: 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103610
APA StyleRen, Y., Tian, Z., Zhang, Y., Wu, F., Xie, H., Zhang, Q., Zhang, P., & Sun, Z. (2023). In-Situ Growth of ZnO Whiskers on Ti2ZnC MAX Phases. Materials, 16(10), 3610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16103610





