Analysis on Seismic Performance of Steel-Reinforced Concrete-Filled Circular Steel Tubular (SRCFST) Members Subjected to Post-Fire
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Finite Element Modeling
2.1. Temperature Field Calculation Model
2.1.1. Thermal Parameters
2.1.2. Contact Thermal Resistance
2.2. Calculation Model of Post-Fire Seismic Performance
2.2.1. Material Properties
2.2.2. Geometric Model
2.2.3. Loading Procedure
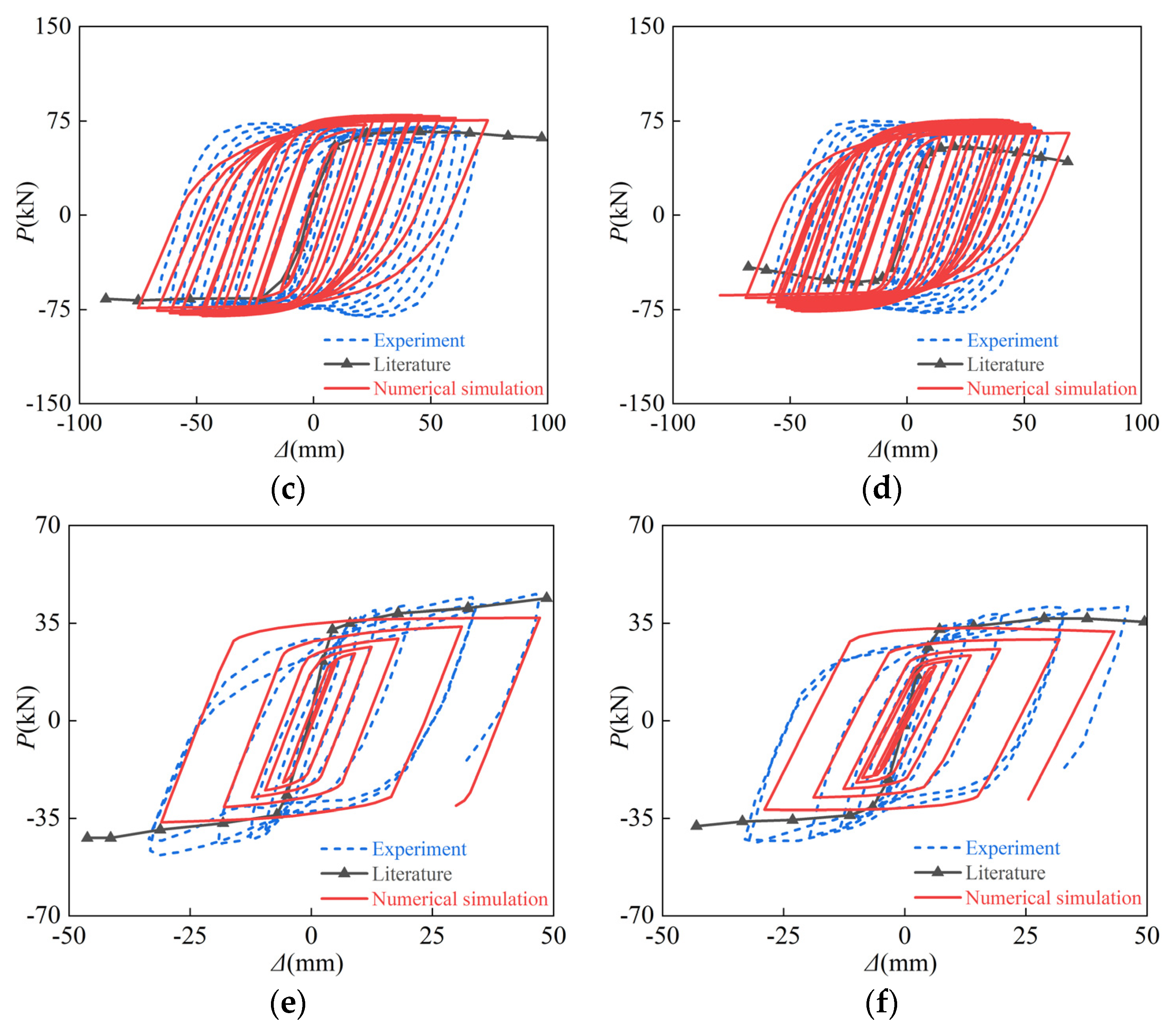
2.3. Verification of Numerical Calculation Model
3. Numerical Calculation Results and Discussion
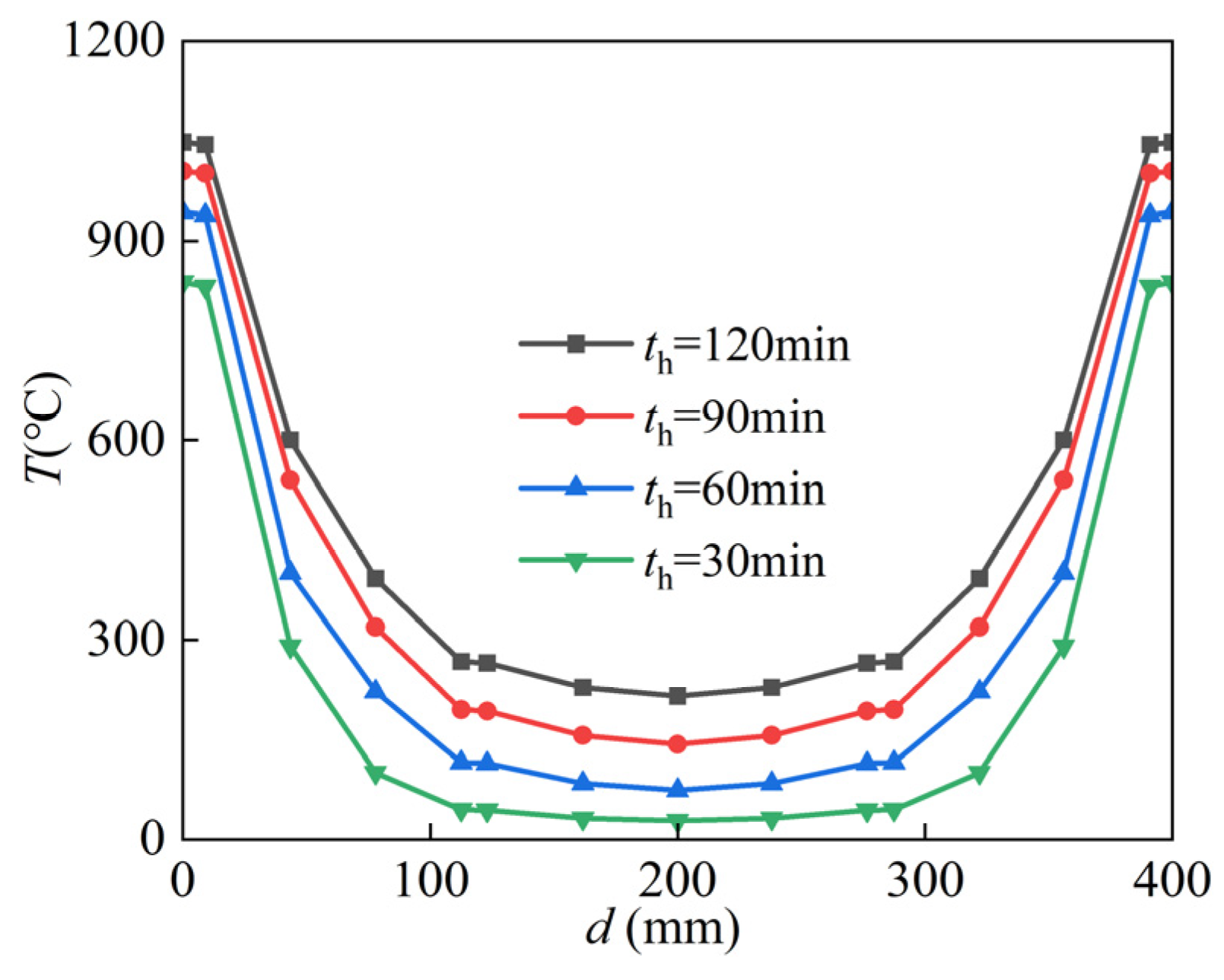
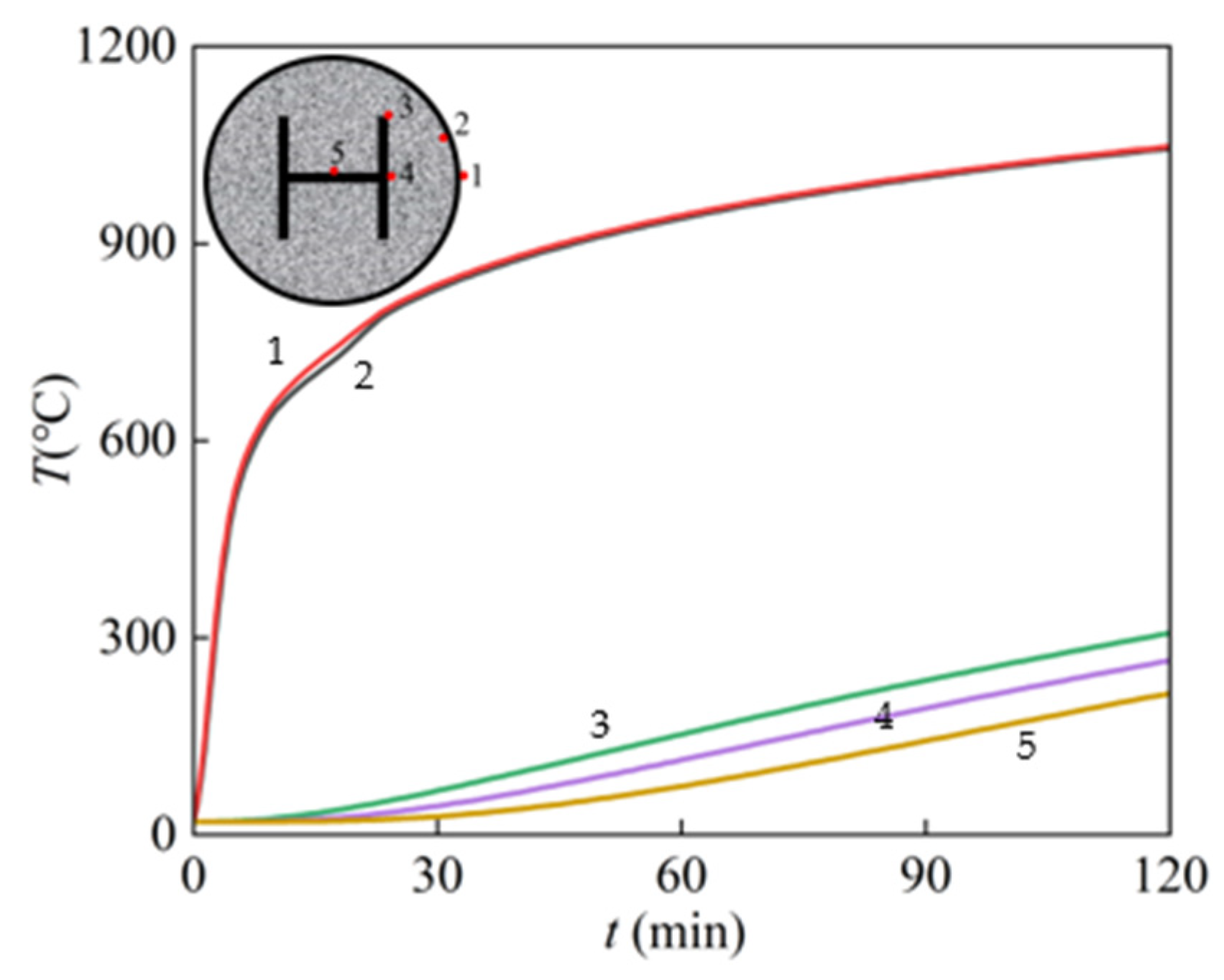
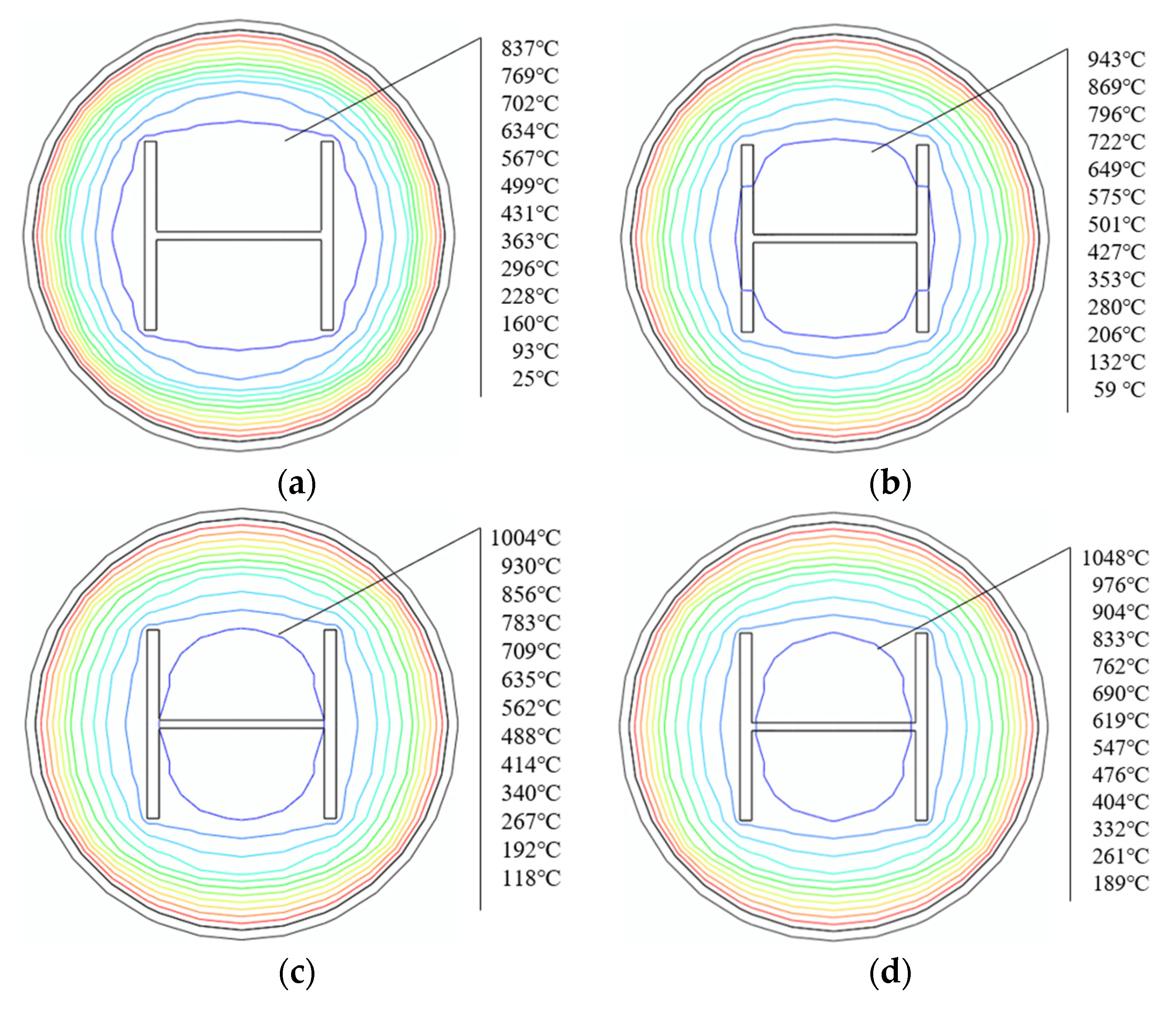
3.1. Temperature Field Analysis
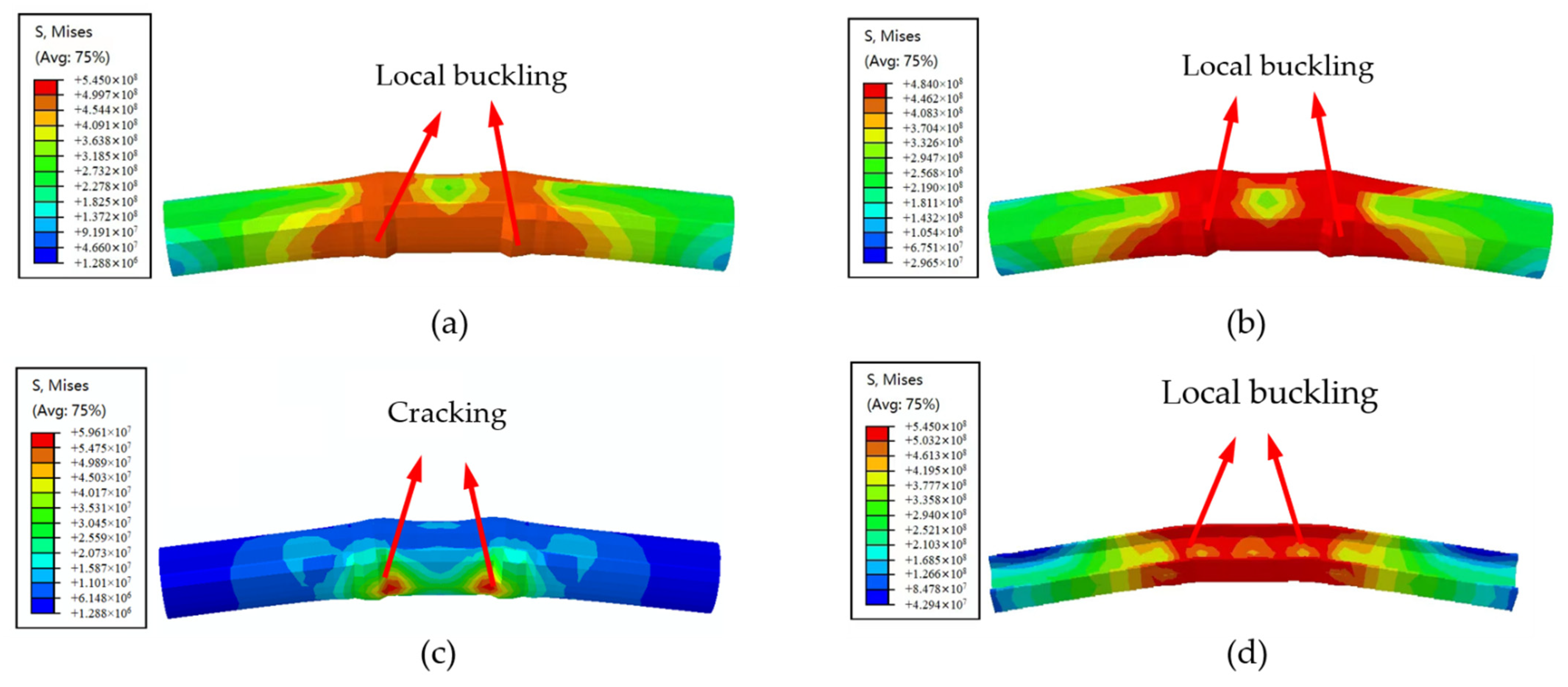
3.2. Failure Mode
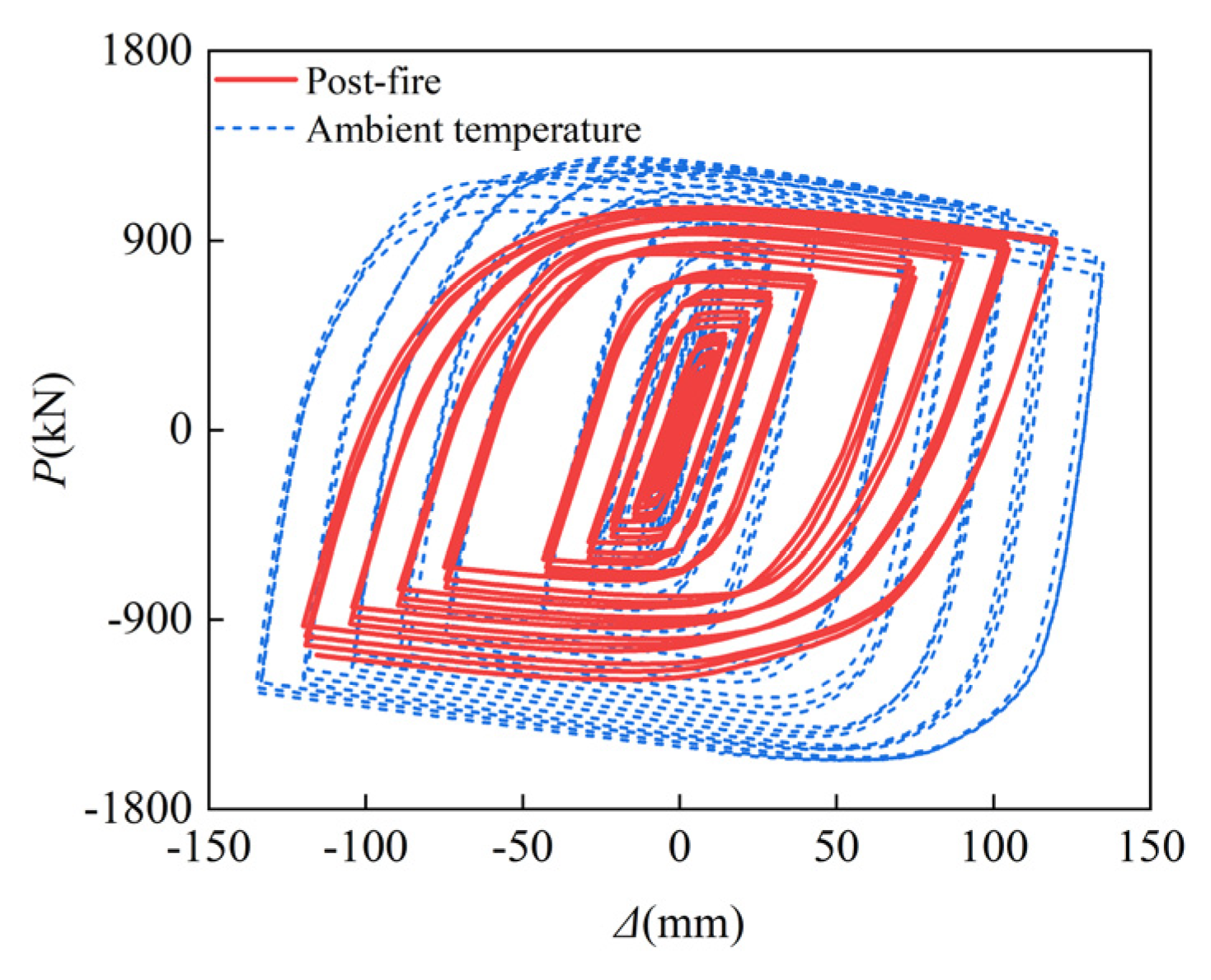
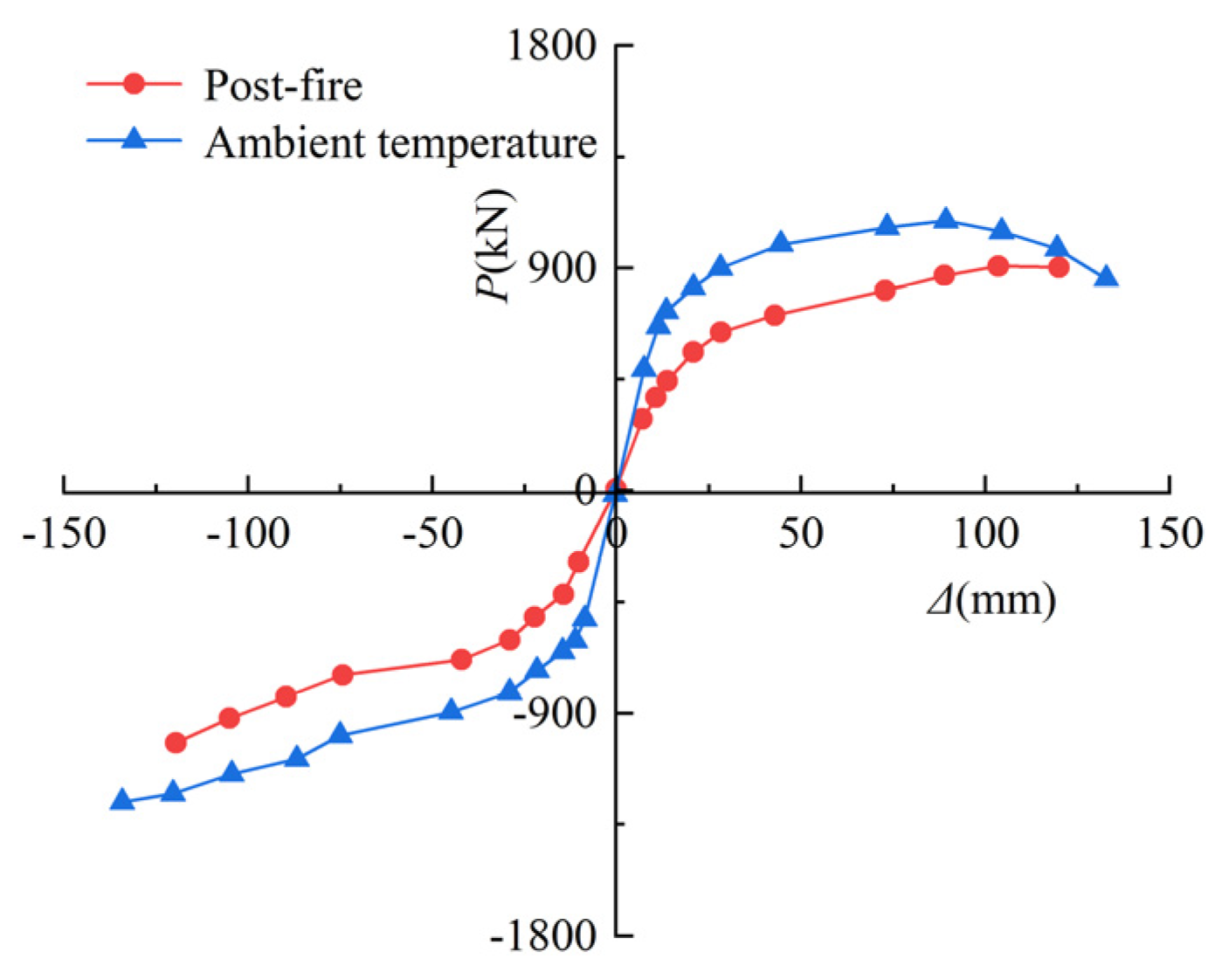
3.3. Hysteresis Curves and Skeleton Curves
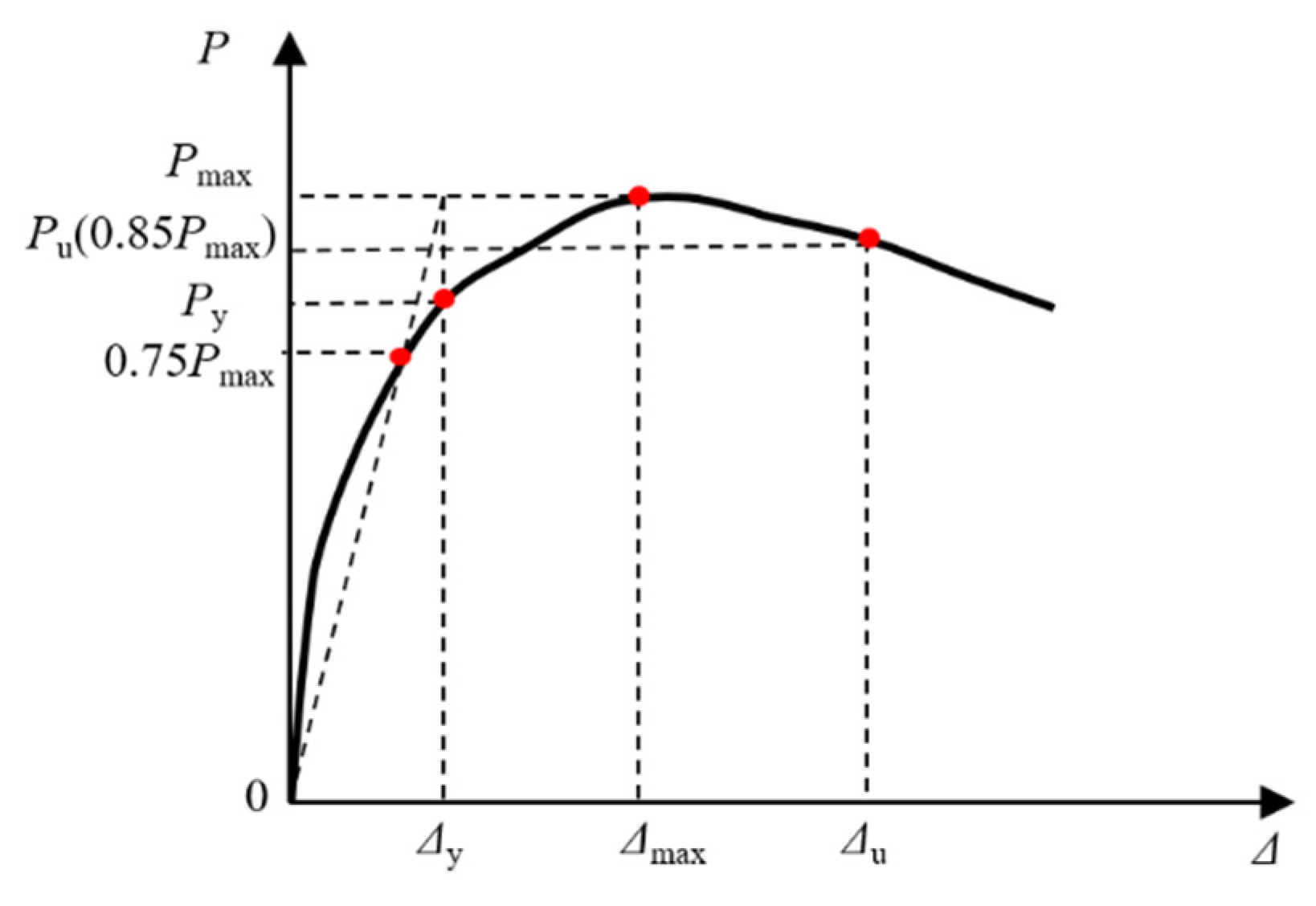
3.4. Ductility
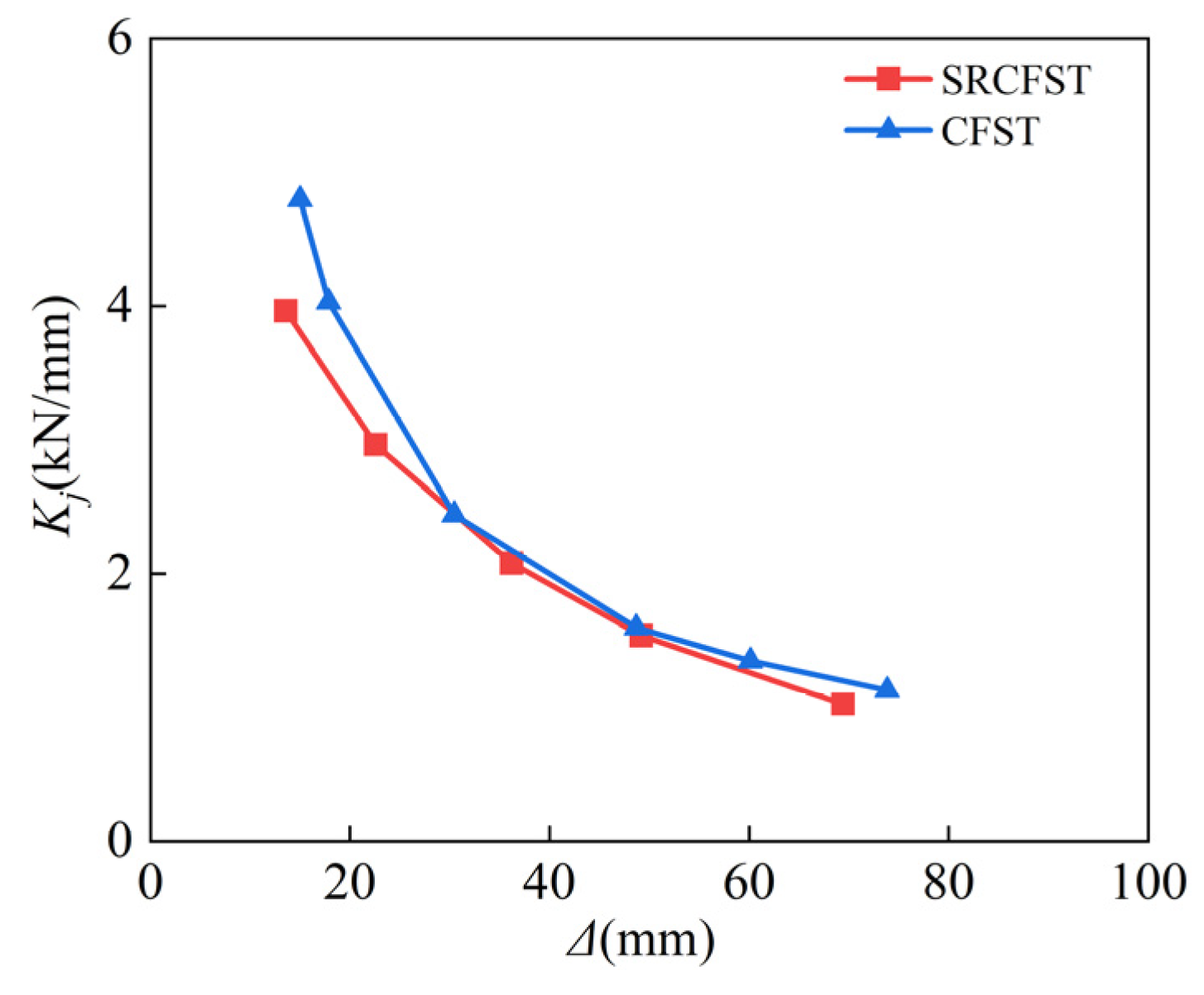
3.5. Stiffness Degradation
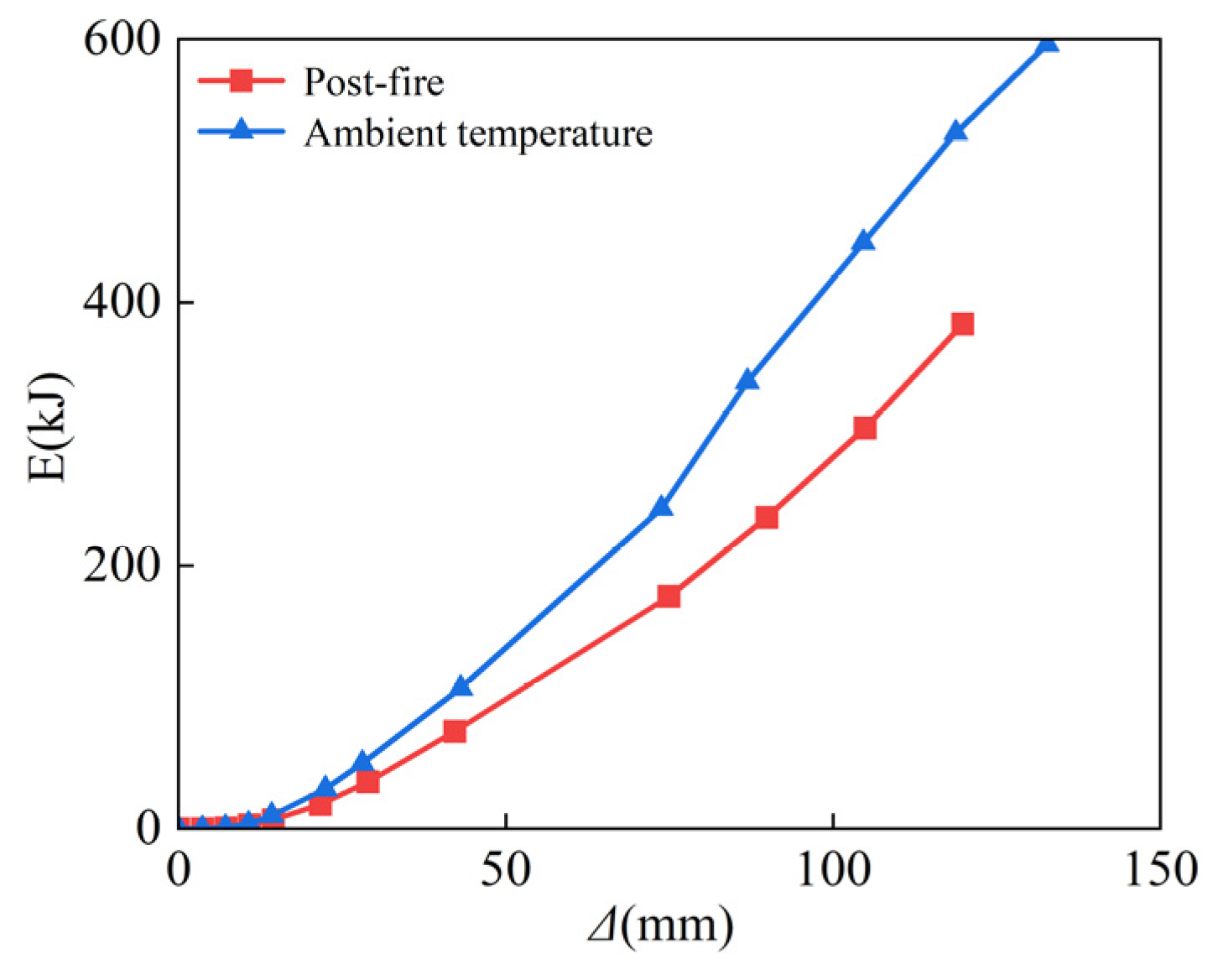
3.6. Energy Dissipation
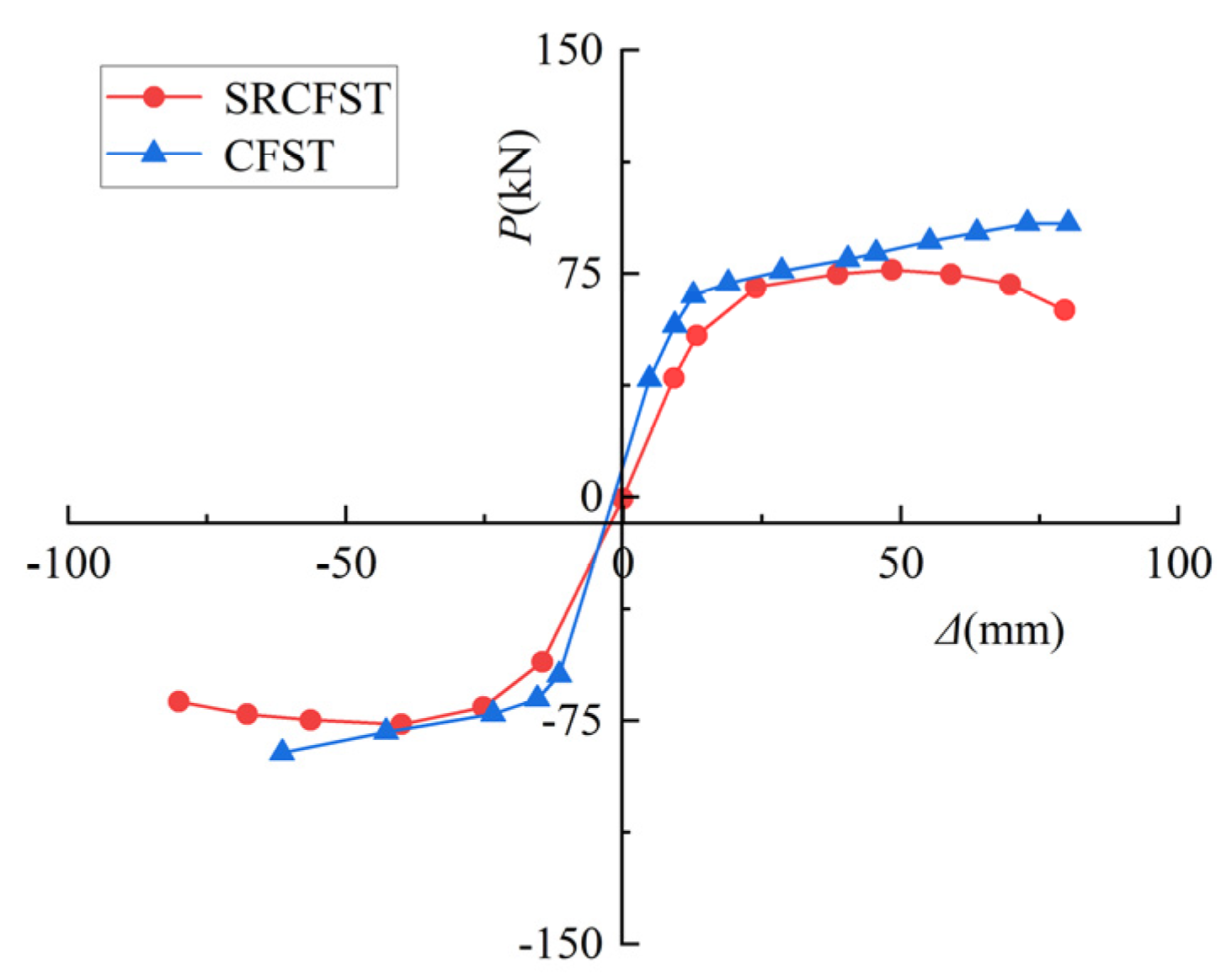
3.7. Comparison of Post-Fire Seismic Performance of SRCFST and CFST Columns
4. Parameter Analysis of Seismic Performance
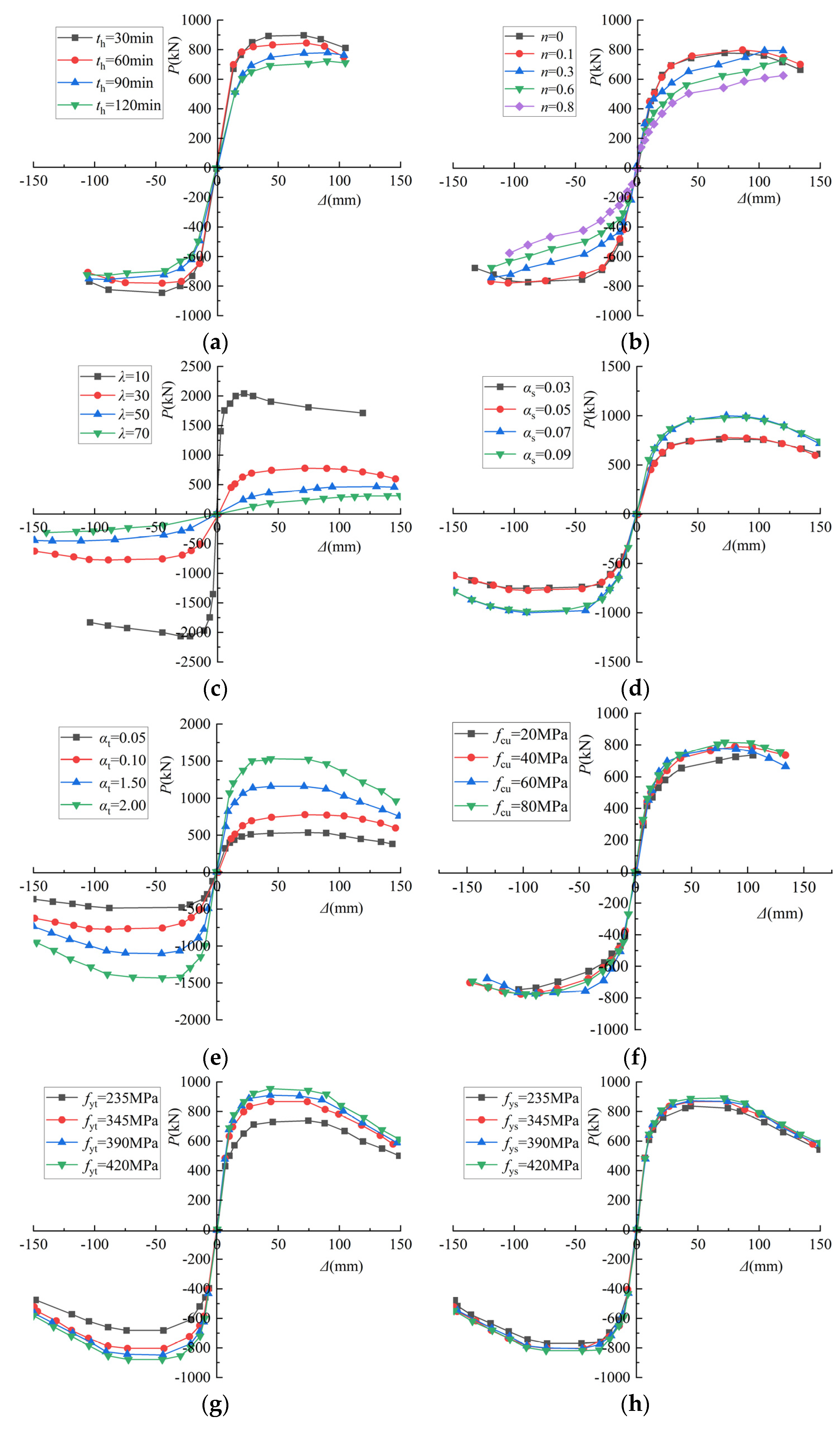
4.1. Parameters Analysis of Skeleton Curve
4.1.1. Heating Time
4.1.2. Axial Compression Ratio
4.1.3. Slenderness Ratio
4.1.4. Profiled Steel Ratio
4.1.5. Steel Tube Ratio
4.1.6. Concrete Cubic Compressive Strength
4.1.7. Yield Strength of Steel Tube
4.1.8. Yield Strength of Profiled Steel
4.1.9. Protective Layer Thickness
4.2. Parameters Analysis of Ductility Coefficient
4.2.1. Heating Time
4.2.2. Axial Compression Ratio
4.2.3. Slenderness Ratio
4.2.4. Profiled Steel Ratio
4.2.5. Steel Tube Ratio
4.2.6. Concrete Cubic Compressive Strength
4.2.7. Yield Strength of Steel Tube
4.2.8. Yield Strength of Profiled Steel
4.2.9. Protective Layer Thickness
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The temperature field of the SRCFST column is symmetrically distributed along the diameter, increasing the closer to the center of the circle. In addition, the concrete is thermally inert and functions as a natural fire protection layer for the profile steel, lowering the temperature of the profiled steel.
- (2)
- Although the peak load, ductility coefficient, energy dissipation capacity, and stiffness of the skeleton line of this column were slightly reduced after fire compared to the SRCFST members at ambient temperature, the hysteresis curves did not pinch significantly and still exhibited better seismic performance.
- (3)
- After exposure to fire, the effects of heating time (th), axial compression ratio (n), slenderness ratio (λ), and steel tube ratio (αt) on the skeleton line of SRCFST columns are more significant. Moreover, the axial compression ratio (n), slenderness ratio (λ), and steel tube ratio (αt) have a negative influence on the ductility of SRCFST columns after fire.
- (4)
- The hysteresis curve and stiffness of the SRCFST column after fire are similar to that of the CFST column when the total steel ratio is kept constant, while the ductility is better. To fully exploit post-fire the seismic performance of SRCFST members, the appropriate percentage of steel tube and profiled steel needs to be researched further.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Ac | section area of concrete |
| As | section area of profiled steel |
| At | section area of steel tube |
| B | width of concrete-filled square steel tube column |
| D | diameter of circular SRCFST column |
| E | energy dissipation |
| Kj | secant stiffness |
| λ | slenderness ratio of column |
| αt | steel tube ratio |
| αs | profiled steel ratio |
| th | heating time |
| ts | thickness of the steel tube |
| tw | width of profile web |
| tf | width of profile flange |
| fyt | yield strength of steel tube |
| fcu | concrete cubic compressive strength |
| L | length of the specimen |
| n | axial compression ratio of column |
| a | protective layer thickness |
| μ | ductility coefficient of column |
| Δu | failure displacement |
| Δy | yield displacement |
| Δmax | ultimate displacement |
| Δj | displacement corresponding to Pj under the first cycle of level j |
| Py | yield load |
| Pmax | ultimate strength |
| Pu | failure load |
| Pj | peak load under the first cycle of level j |
References
- Zhu, M.C. Research on Mechanical Behavior of Square Steel Tube Column Filled with Steel-Reinforced Self-Consolidating High-Strength Concrete. Ph.D. Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- EN 1994-1-1: 2004; Design of Composite Steel and Concrete Structures-Part 1-1, General Rules and Rules for Building. European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2004.
- Wang, Q.X.; Zhao, D.Z.; Guan, P. Study on the Mechanical Properties of Axially Loaded Steel Tube Columns Filled with Steel-Reinforced High-Strength Concrete. J. Build. Struct. 2003, 24, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.B.; Xiao, A.L.; Guo, J.; Zhou, H.B. Bearing Capacity of Stub Columns Composed of Structural Steel and Self-Compacting High-Strength Concrete-Filled Steel Tube: Experimental Research. J. Nat. Dis. 2010, 19, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.Z.; Wang, Q.X. Study on Load-Carrying Capacity of Steel-Concrete-Filled Steel Tube Column. Inde. Constr. 2005, 35, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, S.R. Mechanical Property and Bearing Capacity of Steel Tube Filled with Steel-reinforced Concrete. J. Chongqing Univ. Sci. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2009, 11, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; Xiang, C.Y.; Li, D.; Hao, F. The Simulate Analysis on Circular Steel Tube Composite Short Column Filled in Steel Reinforced Concrete Under Axial Compression. J. Shenyang Jianzhu Univ. Nat. Sci. 2007, 23, 747–750. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, F.X.; Li, G.; Gong, Y.Z.; Yu, Z.W. Behavior of Tubular Stub Columns of Axially Loaded Steel-Reinforced Concrete-Filled Circular Steel. J. Cent. South Univ. 2012, 43, 3625–3630. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.C.; Wang, Q.X.; Liu, S.R.; Zhu, Y.G. Experimental Study of Centrally Loaded Square Steel Tubular Slender Columns Filled with Steel-Reinforced Self-Consolidating High-Strength Concrete. J. Dalian. Univ. Technol. 2006, 46, 875–879. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, A.L.; He, Y.B.; Huang, P.; Guo, J. Analysis of Stability Bearing Capacity of Steel Tubular Slender Columns Filled with Steel-reinforced-concrete. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Urban Sci. Ed. 2008, 25, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.G.; Zhao, T.F.; Li, H.N. Experimental Research and Theoretical Analysis of Square Steel Tube Columns Filled with Steel Reinforced High Strength Concrete Subject to Eccentric Loading. J. Build. Struct. 2010, 31, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.B.; Xiao, A.L.; Guo, J.; Zhou, H.B.; Huang, P. Experimental Study on Behavior of Eccentrically Loaded Steel-Reinforced Self-Compacting High-Strength Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Columns. J. Build. Struct. 2010, 31, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Pan, J.; Wu, Y.-F. Mechanical behavior of steel-reinforced concrete-filled steel tubular (SRCFST) columns under uniaxial compressive loading. Thin-Walled Struct. 2015, 97, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cheng, X.; Yan, L.; Wu, C. Numerical study on I-section steel-reinforced concrete-filled steel tubes (SRCFST) under bending. Eng. Struct. 2020, 225, 111276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.F.; Wang, L.G. Calculation on Compression-Bending of Square Tube Filled with Steel-Reinforced High-Strength Concrete. Eng. Mech. 2008, 25, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-L.; Xian, W.; Wang, W.-D.; Li, H.-W. Experimental performance of circular concrete-filled steel tubular members with inner profiled steel under lateral shear load. Eng. Struct. 2019, 201, 109746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-L.; Jia, Z.-L.; Wang, W.-D.; Xian, W.; Tan, E.L. Experimental and numerical study on torsional behaviour of steel-reinforced concrete-filled square steel tubular members. Structures 2021, 32, 713–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-D.; Jia, Z.-L.; Shi, Y.-L.; Tan, E.L. Performance of steel-reinforced circular concrete-filled steel tubular members under combined compression and torsion. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 173, 106271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.-L.; Shi, Y.-L.; Xian, W.; Wang, W.-D. Torsional behaviour of concrete-filled circular steel tubular members under coupled compression and torsion. Structures 2021, 34, 931–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.D.; Sun, J.H.; Shi, Y.L.; Zhang, C. Mechanical Behavior of Square Steel-Reinforced Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular (SRCFST) Members under Compression-Bending-Shear Loads. Chin. Civil. Eng. J. 2021, 54, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wei, Y.-Y.; Yun, Y.-C. Analysis of steel-reinforced concrete-filled-steel tubular (SRCFST) columns under cyclic loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Zhu, X.; Wang, R.; An, G.Q. Study on Impact Resistance of Circular Steel Tube Columns Filled with Steel-Reinforced Concrete under Lateral Impact. J. Build. Struct. 2020, S01, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, W.; Wang, W.-D.; Wang, R.; Chen, W.; Hao, H. Dynamic response of steel-reinforced concrete-filled circular steel tubular members under lateral impact loads. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 151, 106736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, W.D. Fire Performance of Concrete-filled Steel Tubular Column with Encased Profile Steel under Axial Compression. J. Nat. Dis. 2015, 24, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Wang, W.D. Numerical Simulation Analysis on Concrete-filled Square Steel Tubular Columns with Internal Profiled Steel under Eccentric Compression Exposure to Full-Range Fire. Eng. Mech. 2015, 32, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Mao, W.J.; Wang, W.D. Fire Behavior of Concrete-filled Square Steel Tubular Column with Encased Profiled Steel Subjected to Non-Uniform Fires. J. Nat. Dis. 2016, 25, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zhu, M.-C.; Mou, B.; He, B.-J. Residual Strength of Steel-Reinforced Concrete-Filled Square Steel Tubular (SRCFST) Stub Columns After Exposure to ISO-834 Standard Fire. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2018, 19, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.-J.; Wang, W.-D.; Zhou, K.; Du, E.-F. Experimental study on steel-reinforced concrete-filled steel tubular columns under the fire. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 185, 106867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.-Q.; Zhu, M.-C.; Clifton, G.C.; Ukanwa, K.U.; Lim, J.B. Performance of square steel-reinforced concrete-filled steel tubular columns subject to non-uniform fire. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 166, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Xie, F.D.; Zhang, F.D.; Zhang, D.M.; Zheng, C.C. Test and Parametric Analysis on Post-Fire Seismic Performance of Steel Reinforced Concrete Columns. Chin. Civil Eng. J. 2015, 48, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Cao, W.; Bian, J.; Zhang, J. The Fire Resistance Performance of Recycled Aggregate Concrete Columns with Different Concrete Compressive Strengths. Materials 2014, 7, 7843–7860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Bao, Y.; Yang, L.; Yu, Y. Analysis of Fire Resistance of Square-Cased Square Steel Tube Reinforced Concrete (ST-RC) Columns. Materials 2021, 14, 5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.-H.; Huo, J.-S.; Wang, Y.-C. Behavior of Steel Beam to Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Column Connections after Exposure to Fire. J. Struct. Eng. 2007, 133, 800–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.-S.; Han, L.-H.; Wang, Y.-C. Behaviour of Repaired Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Column to Steel Beam Joints after Exposure to Fire. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2010, 13, 53–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.-Y.; Han, L.-H.; Uy, B. Performance of CFST column to steel beam joints subjected to simulated fire including the cooling phase. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2010, 66, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-R.; Song, Y.-P.; Qu, F.-L. Post-fire cyclic behavior of reinforced concrete shear walls. J. Central South Univ. Technol. 2010, 17, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqub, M.; Bailey, C. Repair of fire damaged circular reinforced concrete columns with FRP composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Y.; Lin, Y.Q.; Yang, Q.W.; Lin, B.L. Experimental Study on Seismic Performance of Concrete Short Columns after Fire and Strengthened with CFRP. Eng. Mech. 2014, 31, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, E.-F.; Shu, G.-P.; Mao, X.-Y. Analytical behavior of eccentrically loaded concrete encased steel columns subjected to standard fire including cooling phase. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2013, 13, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodur, V.K.R.; Raut, N.; Mao, X.Y.; Khaliq, W. Simplified approach for evaluating residual strength of fire-exposed reinforced concrete columns. Mater. Struct. 2013, 46, 2059–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, D.M.; Zhang, C. A Finite Element Model for Post-Fire Seismic Performance of Steel Reinforced Concrete Columns. Eng. Mech. 2016, 33, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Zhang, Z.H.; Chi, Y.Y. Experimental Study on Seismic Performance of Steel Reinforced Concrete Beam-Column Joints after Exposure to Fire. Eng. Mech. 2017, 34, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, D.-M. Post-fire seismic performance of SRC beam to SRC column frames. Structures 2020, 25, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.H. Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Structures-Theory and Practice, 3rd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lie, T.T. Fire Resistance of Circular Steel Columns Filled with Bar-Reinforced Concrete. J. Struct. Eng. 1994, 120, 1489–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.K. Cyclic Performance of Concrete-Filled Steel Tubular Columns after Exposure to Fire. Ph.D. Thesis, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- JGJ/T 101-2015; Specification for Test Methods of Seismic Buildings. Architecture Industrial Press: Beijing, China, 1997.
- GB 50936-2014; Technical Code for Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Structures. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2014.
- JGJ 138-2001; Technical Specification for Steel Reinforced Concrete Composite Structures. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2001.
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.X. Finite Element Analysis of Residual Strength of Concrete-filled Rectangular Steel Tubular Column with Encased H Shaped Profiled Steel after Exposure to Fire. Fire Saf. Sci. 2019, 28, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R. Ductility evaluation from laboratory and analytical testing. In Proceedings of the 9th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering, Tokyo, Japan, 2–9 August 1988; pp. 605–616. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, C.X. Post-Fire Performance of Structural Steels. Master’s Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Wang, T.; Han, L.-H. Seismic performance of concrete-filled double-skin steel tubes after exposure to fire: Experiments. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2019, 154, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
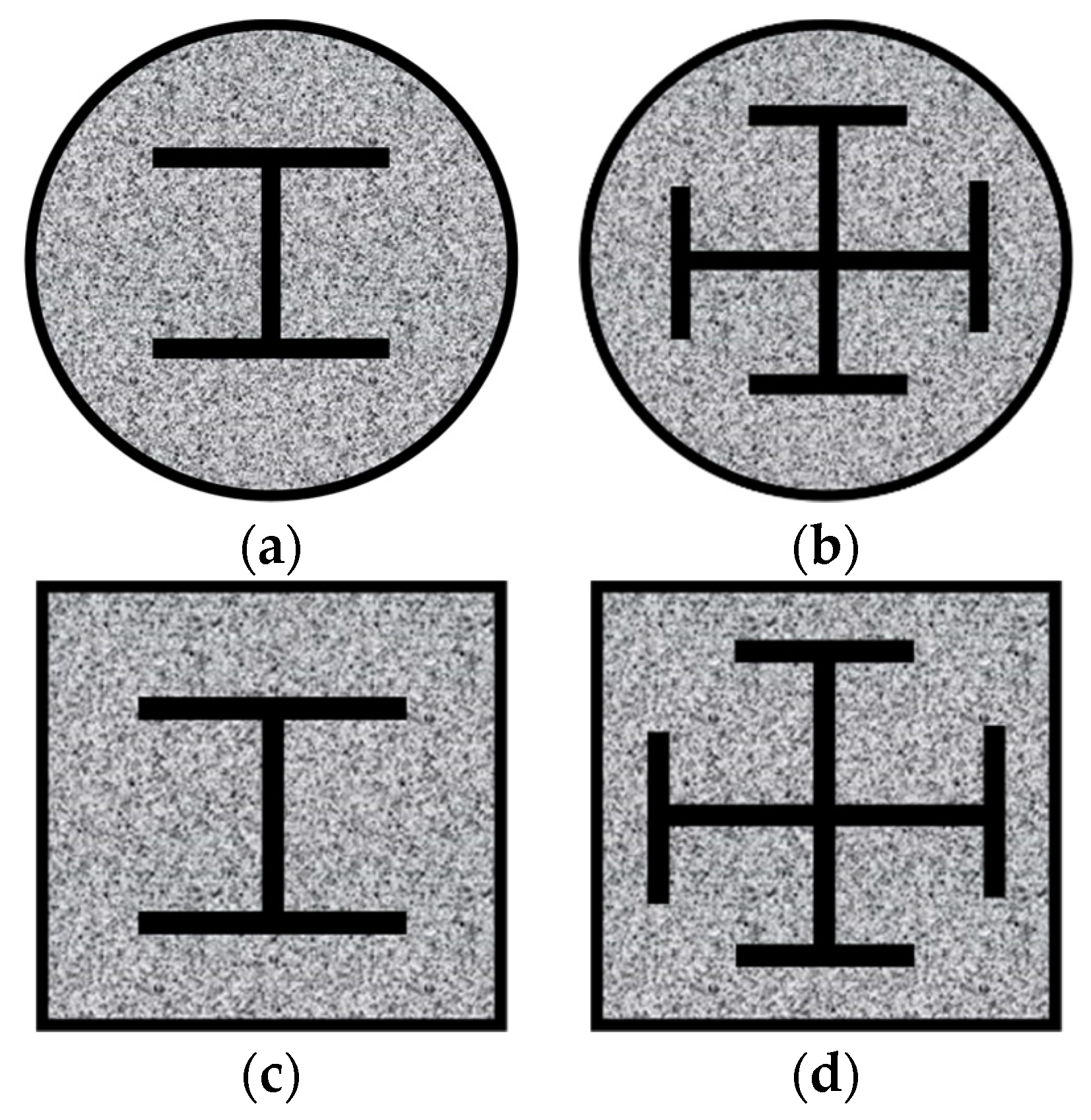

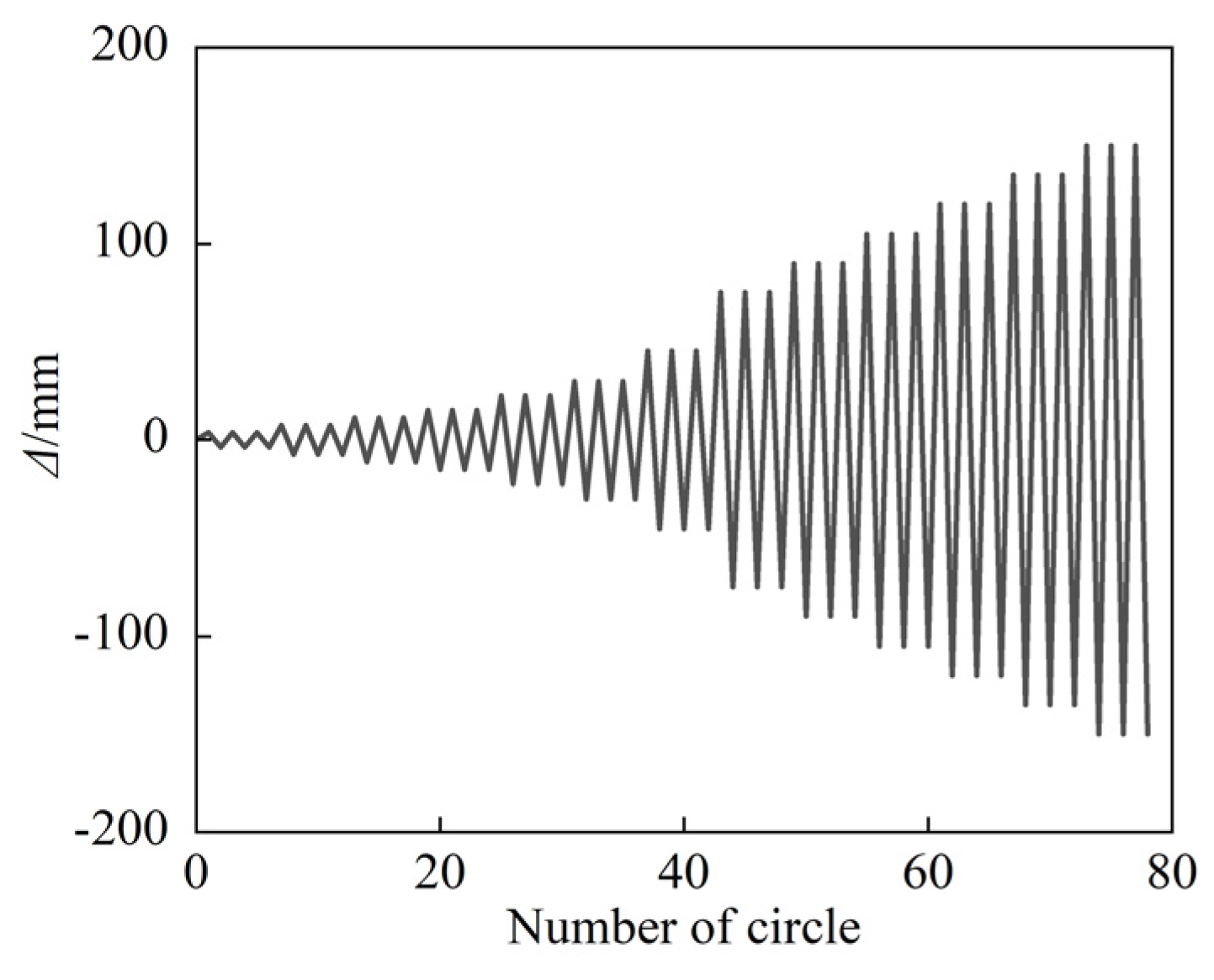
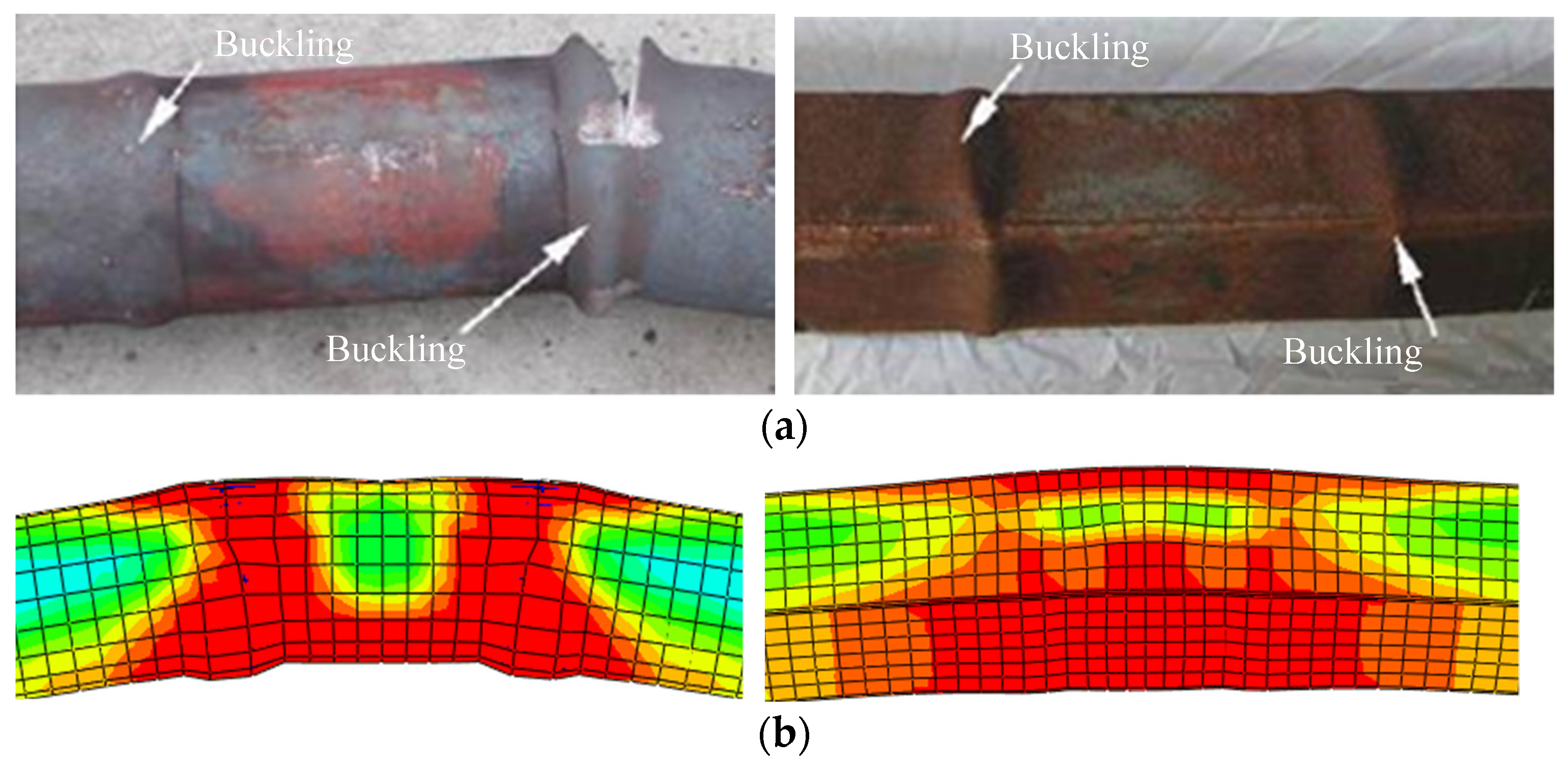
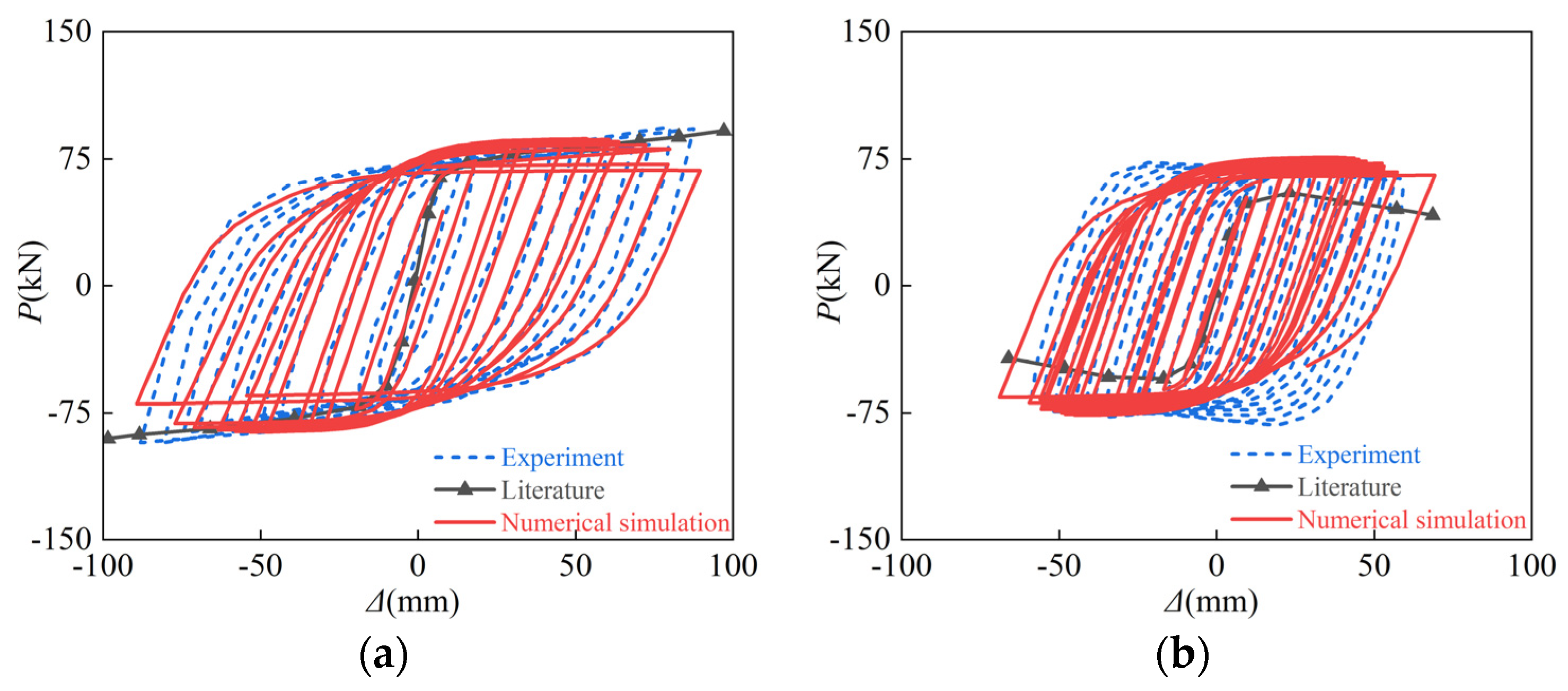


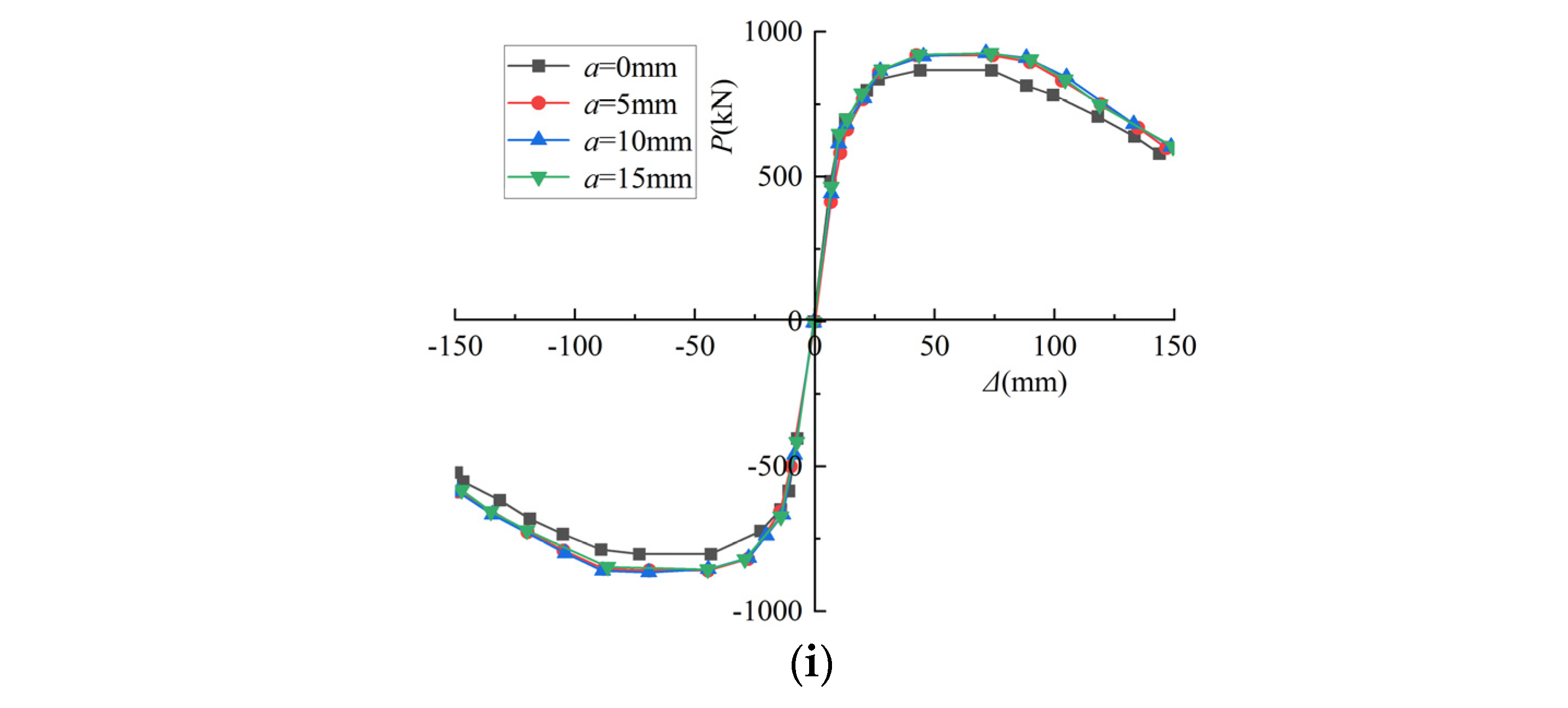
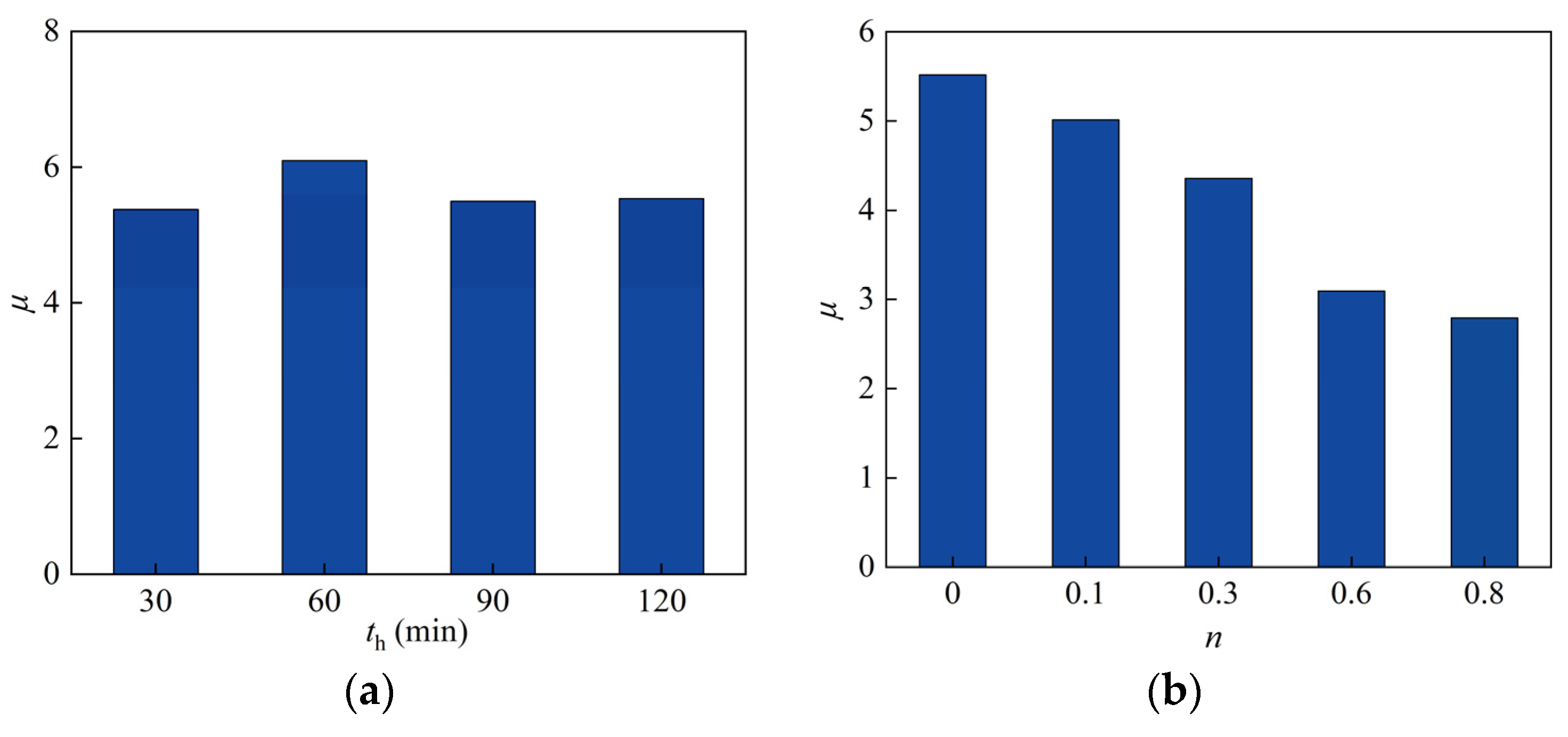
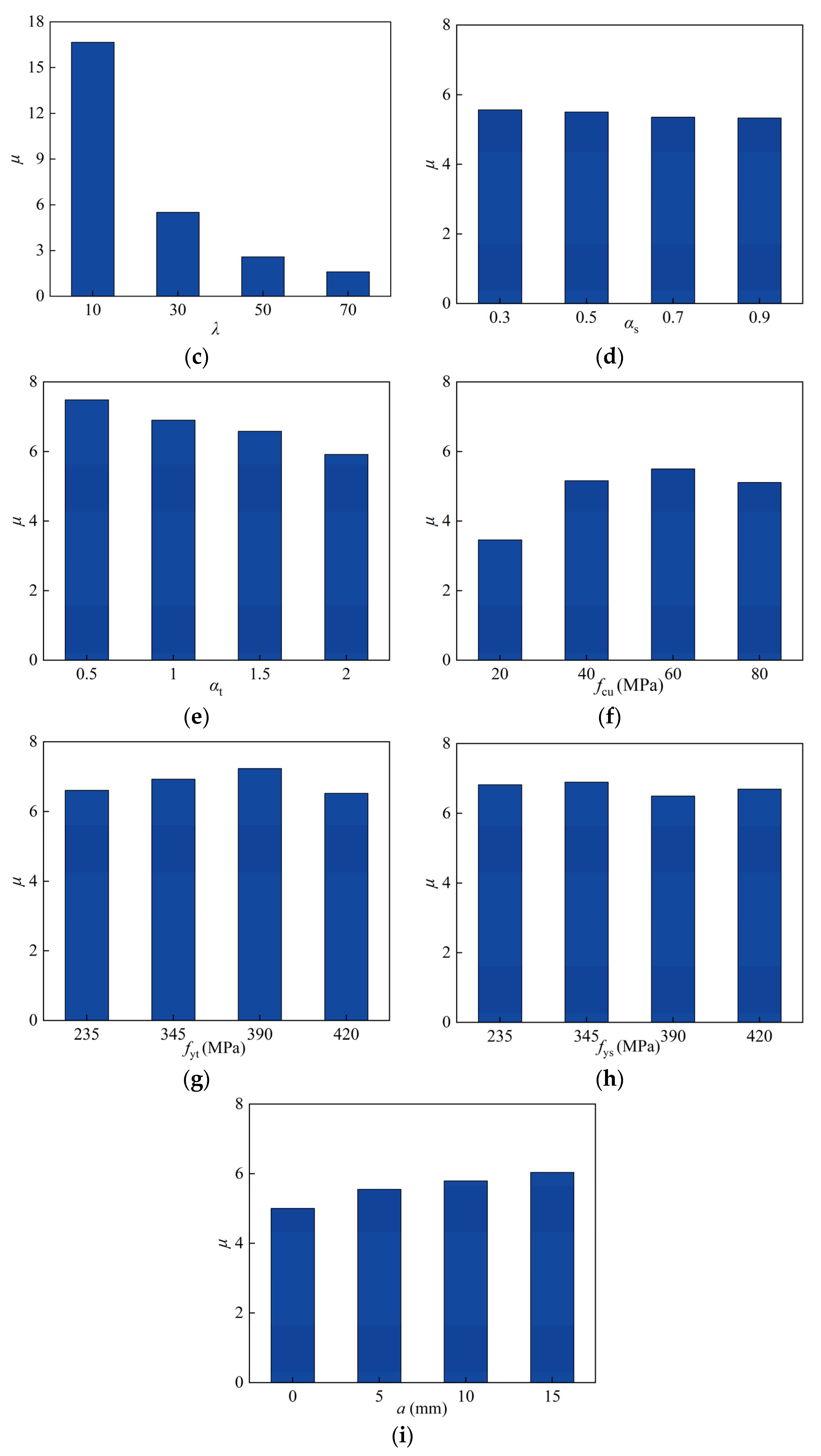
| Section Type | Specimen | D (B) × ts (mm) | t (min) | L (mm) | N0 (kN) | n0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circular | CF1 | 133 × 4.7 | 90 | 1500 | 0 | 0 |
| CF2 | 133 × 4.7 | 90 | 1500 | 80 | 0.15 | |
| CF3 | 133 × 4.7 | 90 | 1500 | 160 | 0.3 | |
| CF5-1 | 133 × 4.7 | 90 | 1500 | 240 | 0.45 | |
| square | SF1 | 120 × 2.9 | 90 | 1500 | 0 | 0 |
| SF2-1 | 120 × 2.9 | 90 | 1500 | 60 | 0.15 |
| Section Type | Specimen | D × ts (mm) | th (min) | αt | αs | λ | fys (MPa) | fyt (MPa) | fcu (MPa) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circular | SRCFST | 400 × 9 | 90 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 30 | 345 | 345 | 60 | 0.6 |
| Specimen | Direction | Yield Load Py/kN | Yield Displacement Δy/mm | Maximum Load Pmax/kN | Maximum Displacement Δmax/mm | Failure Displacement Δu/mm | Ductility μ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-fire | + | 729.9 | 49.2 | 907.9 | 120.0 | 120.0 | 2.4 1.8 |
| − | 910.2 | 103.3 | 1019.2 | 119.7 | 119.7 | 1.2 | |
| Ambient temperature | + | 891.8 | 27.4 | 1090.8 | 125.0 | 132.8 | 4.5 3.1 |
| − | 1040.1 | 81.2 | 1259.9 | 134.2 | 134.2 | 1.6 |
| Specimen | Direction | Yield Load Py/kN | Yield Displacement Δy/mm | Ultimate Load Pmax/kN | Ultimate Displacement Δmax/mm | Failure Displacement Δu/mm | Ductility μ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SRCFST | + | 64.8 | 20.2 | 76.1 | 79.5 | 77.4 | 3.8 3.7 |
| − | 64.7 | 21.2 | 76.1 | 80.1 | 80.1 | 3.5 | |
| CFST | + | 71.8 | 19.2 | 91.8 | 80.2 | 80.2 | 4 3.4 |
| − | 69.6 | 18.4 | 85.8 | 61.5 | 61.5 | 2.8 |
| Parameter | Values | Default Values |
|---|---|---|
| Heating time th/(min) | 30, 60, 90, 120, | 90 |
| Axial compression ratio n | 0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.6, 0.8 | 0 |
| Slenderness ratio λ | 10, 30, 50, 70 | 30 |
| profiled steel ratio αs | 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, 0.09 | 0.05 |
| Steel tube ratio αt | 0.05, 0.10, 0.15, 0.20 | 0.1 |
| Concrete cubic compressive strength fcu/(N/mm2) | 20, 40, 60, 80 | 60 |
| Yield strength of steel tube fyt/(N/mm2) | 235, 345, 390, 420 | 345 |
| Yield strength of profiled steel fys/(N/mm2) | 235, 345, 390, 420 | 345 |
| Protective layer thickness a/(mm) | 0, 5, 10, 15 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Y.; Bao, Y. Analysis on Seismic Performance of Steel-Reinforced Concrete-Filled Circular Steel Tubular (SRCFST) Members Subjected to Post-Fire. Materials 2022, 15, 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062294
Han Y, Bao Y. Analysis on Seismic Performance of Steel-Reinforced Concrete-Filled Circular Steel Tubular (SRCFST) Members Subjected to Post-Fire. Materials. 2022; 15(6):2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062294
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Yi, and Yanhong Bao. 2022. "Analysis on Seismic Performance of Steel-Reinforced Concrete-Filled Circular Steel Tubular (SRCFST) Members Subjected to Post-Fire" Materials 15, no. 6: 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062294
APA StyleHan, Y., & Bao, Y. (2022). Analysis on Seismic Performance of Steel-Reinforced Concrete-Filled Circular Steel Tubular (SRCFST) Members Subjected to Post-Fire. Materials, 15(6), 2294. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15062294





